Formulation of Cannabidiol in Colloidal Lipid Carriers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Colloidal Lipid Emulsions
2.3. Particle Size Determination
2.4. Lipid Quantification
2.5. Determination of Emulsifier in the Aqueous Phase
2.6. Passive Drug Loading
2.7. Drug Quantification
2.8. Shaking Test
2.9. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.10. Density Measurements
2.11. Computer Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
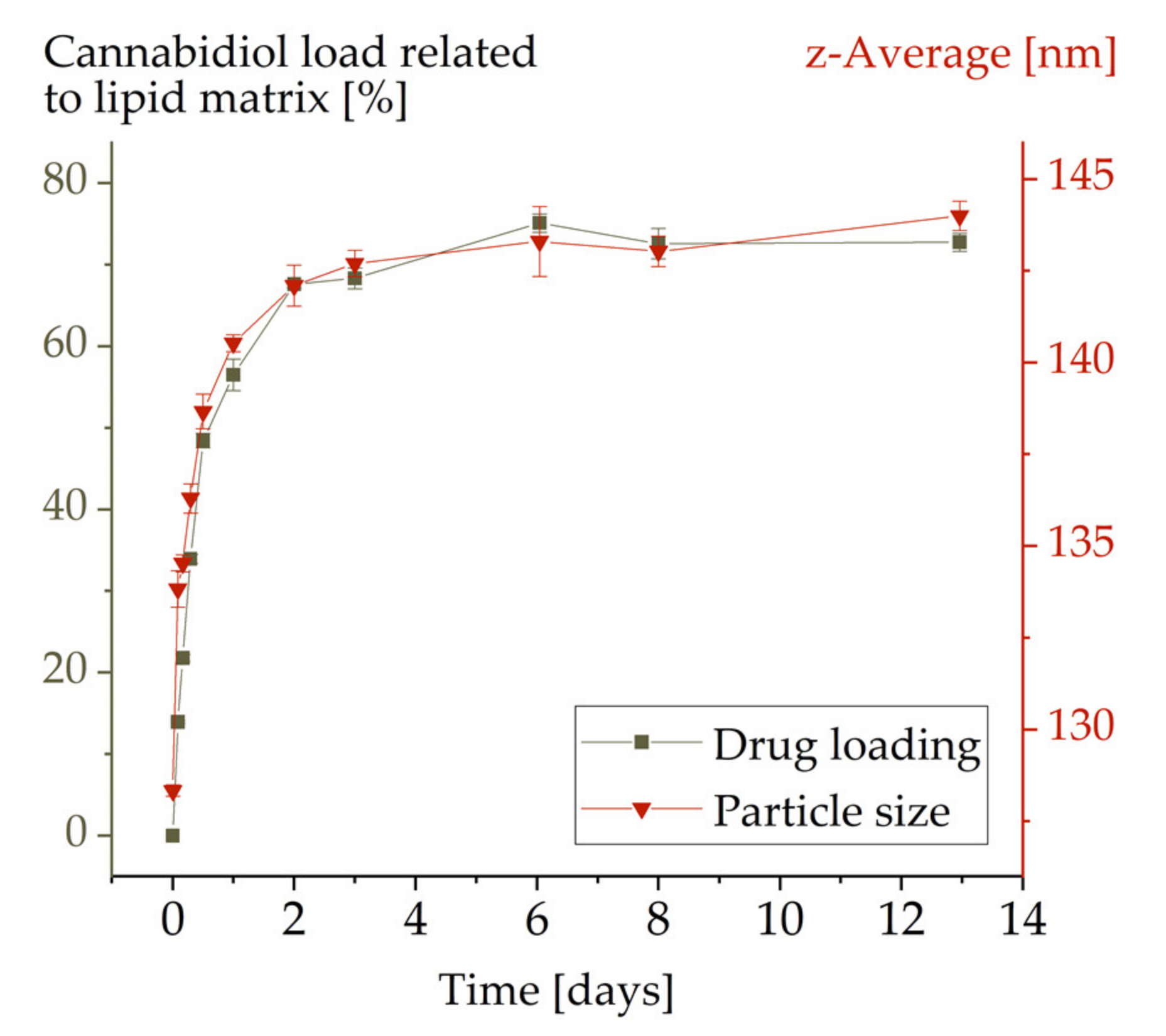
3.1. Kinetics of Drug Loading
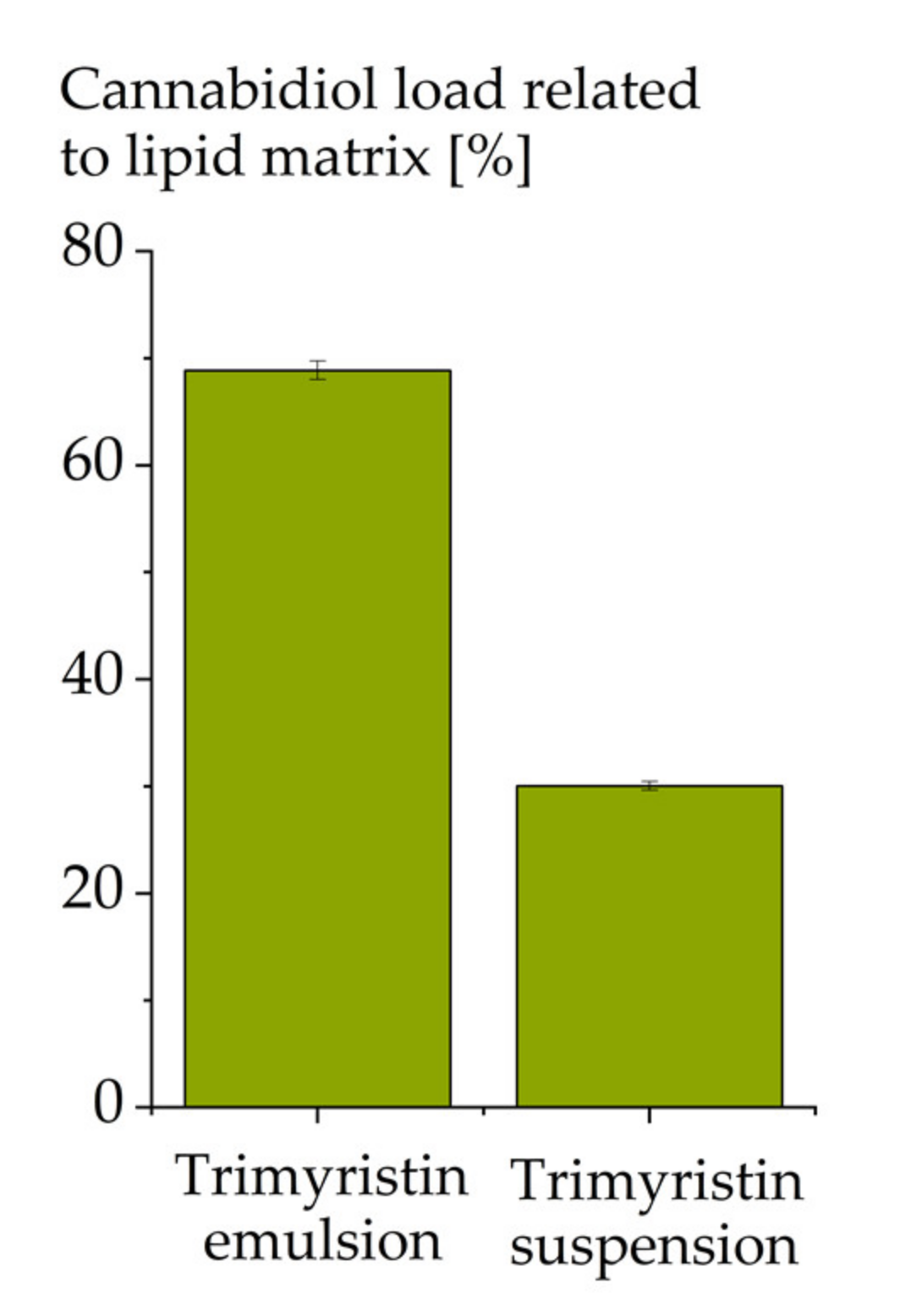
3.2. Influence of the Type of Lipid Matrix
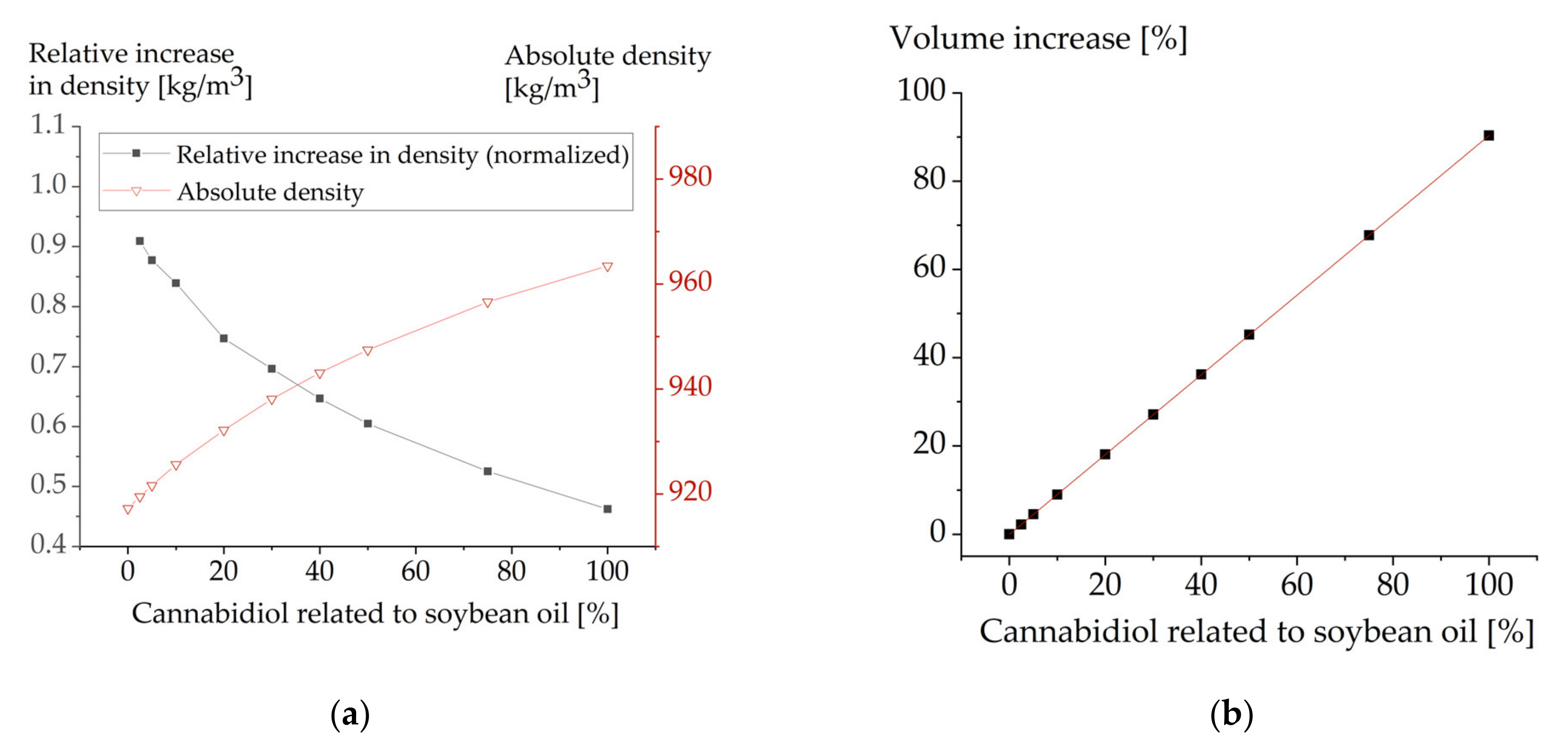
3.3. Effect of Drug Loading on Oil Density
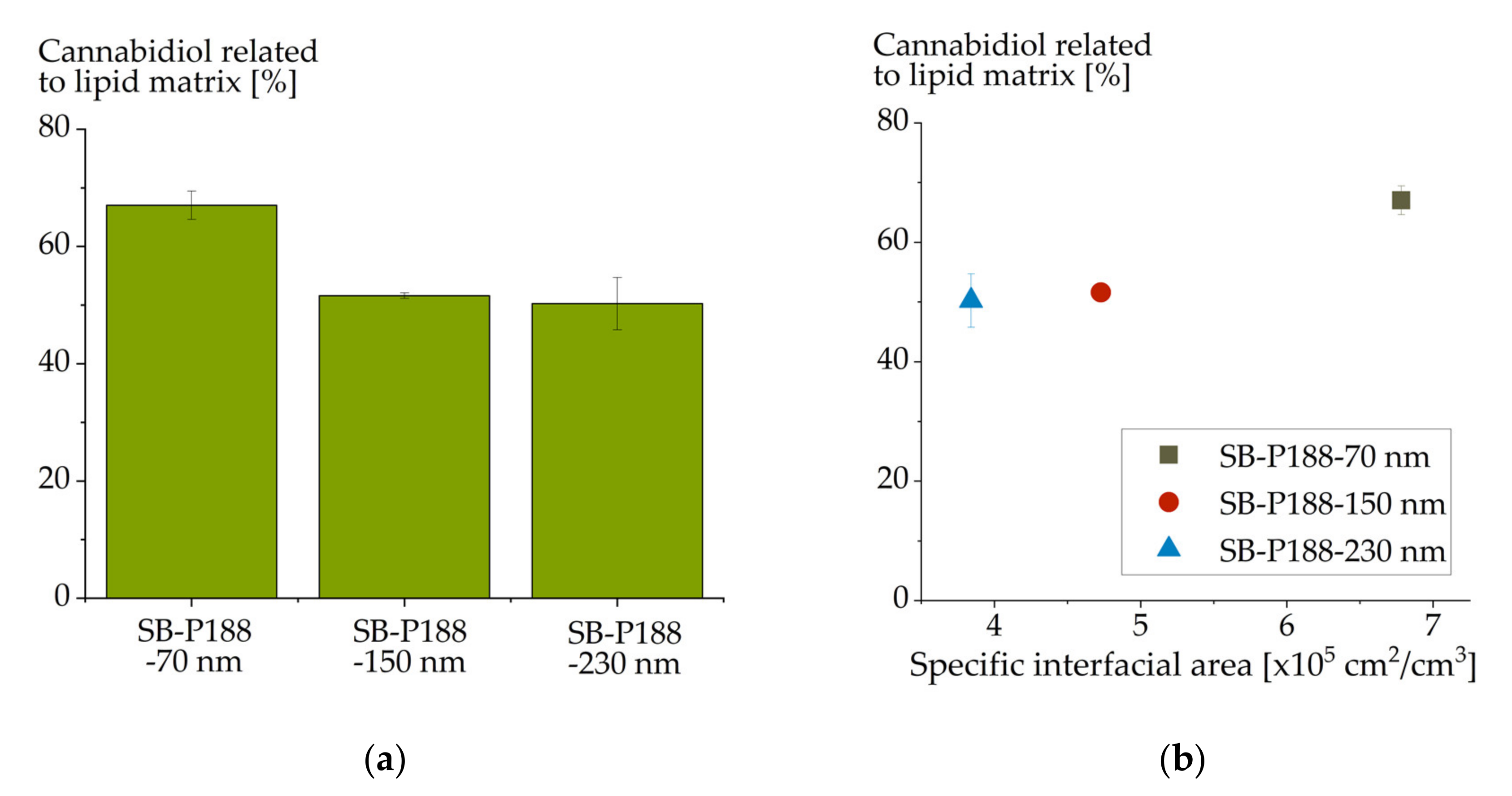
3.4. Drug Localization
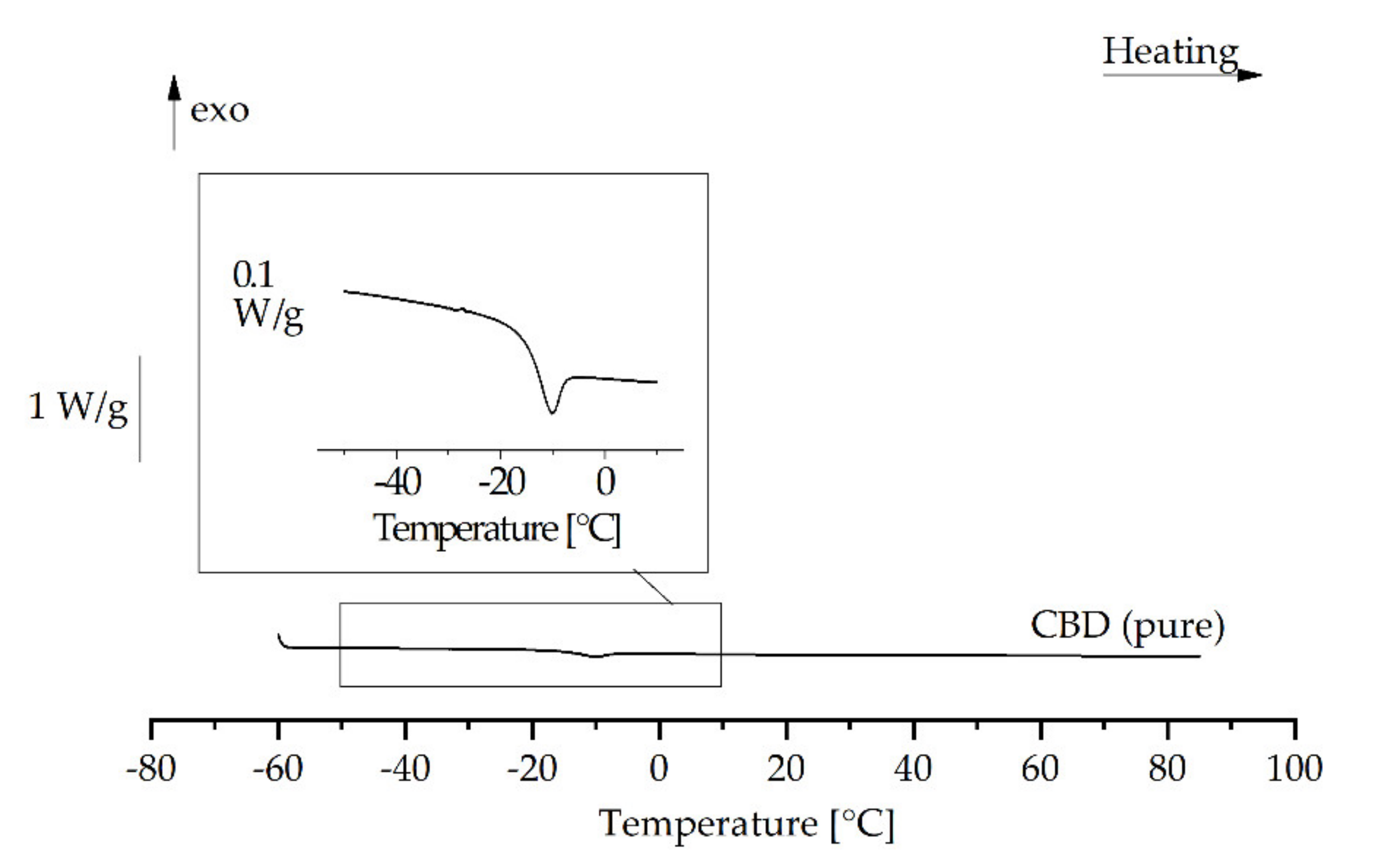
3.5. Influence of the Physical State of the Lipid Matrix
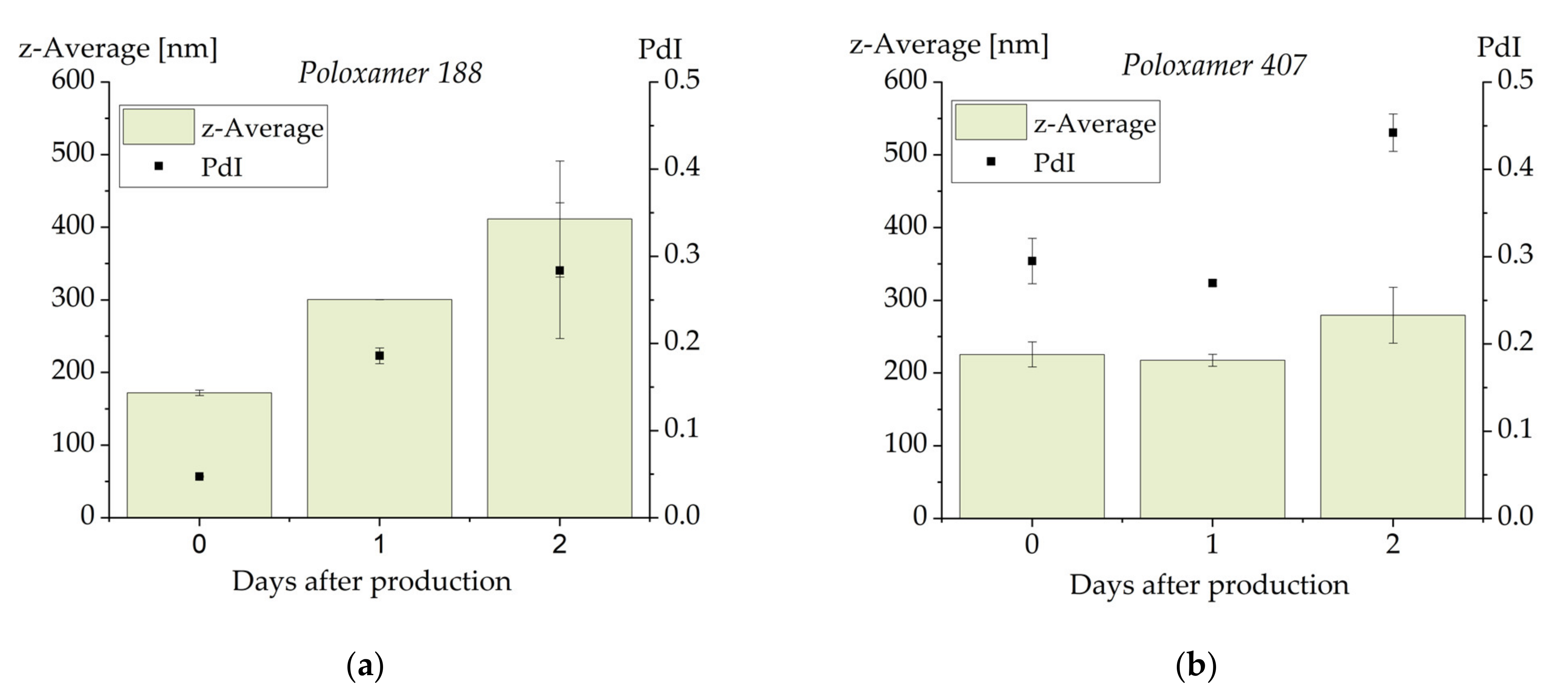
3.6. Influence of Drug Load on Emulsion Stability
3.7. Emulsions of Supercooled Cannabidiol
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Russo, E.B. Cannabidiol claims and misconceptions. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuderi, C.; De Filippis, D.; Iuvone, T.; Blasio, A.; Steardo, A.; Esposito, G. Cannabidiol in medicine: A review of its therapeutic potential in CNS disorders. Phytother. Res. 2008, 23, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA. EPAR Epidyolex. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/epidyolex (accessed on 12 March 2020).
- Thiele, E.A.; Marsh, E.D.; French, J.A.; Mazurkiewicz-Beldzinska, M.; Benbadis, S.R.; Joshi, C.; Lyons, P.D.; Taylor, A.; Roberts, C.; Sommerville, K.; et al. Cannabidiol in patients with seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (GWPCARE4): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devinsky, O.; Cross, J.H.; Laux, L.; Marsh, E.; Miller, I.; Nabbout, R.; Scheffer, I.E.; Thiele, E.A.; Wright, S. Trial of cannabidiol for drug-resistant seizures in the Dravet Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2011–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drugbank. Cannabidiol. Available online: https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09061 (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Nakano, Y.; Tajima, M.; Sugiyama, E.; Sato, V.H.; Sato, H. Development of a novel nanoemulsion formulation to improve intestinal absorption of cannabidiol. Med. Cannabis Cannabinoids 2019, 2, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izgelov, D.; Shmoeli, E.; Domb, A.J.; Hoffman, A. The effect of medium chain and long chain triglycerides incorporated in self-nano emulsifying drug delivery systems on oral absorption of cannabinoids in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 580, 119201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Chang, T.; Du, Y.; Yu, C.; Tan, X.; Li, X. Pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous cannabidiol and its antidepressant-like effects in chronic mild stress mouse model. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 103202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göke, K.; Bunjes, H. Drug solubility in lipid nanocarriers: Influence of lipid matrix and available interfacial area. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 529, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupetz, E.; Bunjes, H. Lipid nanoparticles: Drug localization is substance-specific and achievable load depends on the size and physical state of the particles. J. Control. Release 2014, 189, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, K.M.; Bunjes, H. Evaluation of the drug loading capacity of different lipid nanoparticle dispersions by passive drug loading. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göke, K.; Bunjes, H. Parameters influencing the course of passive drug loading into lipid nanoemulsions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 126, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göke, K.; Bunjes, H. Carrier characteristics influence the kinetics of passive drug loading into lipid nanoemulsions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 126, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francke, N.M.; Bunjes, H. Influence of drug localization on the physical stability of poloxamer 188-stabilized colloidal lipid emulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francke, N.M.; Bunjes, H. Influence of drug loading on the physical stability of phospholipid-stabilised colloidal lipid emulsions. Int. J. Pharm. X 2020, 2, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scifinder. Available online: https://scifinder.cas.org/scifinder/view/scifinder/scifinderExplore.jsf (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Braun, B. Fachinformation (Summary of Product Characteristics) Lipofundin® MCT/LCT 10 %. 2019. Available online: https://www.fachinfo.de/suche/fi/020579 (accessed on 3 March 2021).
- Gelbe Liste. Lipofundin®. Available online: https://www.gelbe-liste.de/produkte/Lipofundin-MCT-10-Emulsion-zur-Infusion-250mLGlasflasche_357386#! (accessed on 21 November 2019).
- Westesen, K.; Bunjes, H. Do nanoparticles prepared from lipids solid at room temperature always possess a solid lipid matrix? Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 115, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrmann, S.; Bunjes, H. Instrumented small scale extruder to investigate the influence of process parameters during premix membrane emulsification. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Product Data Sheet SiLibeads Typ ZY-P Pharma, Sigmund Lindner GmbH. 2019. Available online: https://www.sigmund-lindner.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/PDS-de-SiLibeads-Typ-ZY-P-Pharma.pdf (accessed on 29 January 2020).
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines. European Pharmacopeia, Monography Soybean Oil, 9th ed.; EDQM: Strasbourg, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines. European Pharmacopeia, Monography Medium Chain Triglycerides, 9th ed.; EDQM: Strasbourg, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines. European Pharmacopeia, Monography Rapeseed Oil, 9th ed.; EDQM: Strasbourg, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chemical Book, Glycerintrimyristat. Available online: https://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_DE_cb1222373.htm (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, N.; Eichenberger, A.P.; Choutko, A.; Riniker, S.; Winger, M.; Mark, A.E.; Van Gunsteren, W.F. Definition and testing of the GROMOS force-field versions 54A7 and 54B7. Eur. Biophys. J. 2011, 40, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroet, M.; Caron, B.; Visscher, K.M.; Geerke, D.P.; Malde, A.K.; Mark, A.E. Automated topology builder Version 3.0: Prediction of solvation free enthalpies in water and hexane. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2018, 14, 5834–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.; Andrade, R.; Birgin, E.G.; Martínez, J.M. Software news and update—Packmol: A package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goga, N.; Rzepiela, A.J.; De Vries, A.H.; Marrink, S.J.; Berendsen, H.J.C. Efficient algorithms for Langevin and DPD dynamics. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3637–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; Van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Crystal structure and pair potentials: A molecular-dynamics study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, T.D.; Van Speybroeck, M.; Barillaro, V.; Martens, J.; Annaert, P.; Augustijns, P.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Vermant, J.; Mooter, G.V.D. Formulate-ability of ten compounds with different physicochemical profiles in SMEDDS. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 38, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alskär, L.C.; Porter, C.J.H.; Bergström, C.A.S. Tools for early prediction of Drug loading in lipid-based formulations. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Marra, M.; Anderson, B.D. Predictive relationships for the effects of triglyceride ester concentration and water uptake on solubility and partitioning of small molecules into lipid vehicles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 2768–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, L.C.; Porter, C.J.H.; Charman, W.N.; Bergström, C.A.S. Computational prediction of drug solubility in lipid based formulation excipients. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 3225–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IOI Oleo GmbH. Certificate of Analysis Miglyol 812 N. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- IOI Oleo GmbH. Certificate of Analysis Dynasan 114. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Caelo. Certificate of Analysis Refined Soybean Oil, Batch: 18319902. 2019. Available online: https://www.caelo.de/analysenzertifikate.html?&num=7340 (accessed on 7 March 2021).
- Caelo. Certificate of Analysis Refined Rapeseed Oil, Batch: 18047205. 2018. Available online: https://www.caelo.de/analysenzertifikate.html?&num=7331 (accessed on 7 March 2021).
- Noureddini, H.; Teoh, B.C.; Clements, L.D. Densities of vegetable oils and fatty acids. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1992, 69, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunjes, H.; Steiniger, F.; Richter, W. Visualizing the structure of triglyceride nanoparticles in different crystal modifications. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4005–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, S.; Steiniger, F.; Fischer, D.; Fahr, A.; Bunjes, H. The physical state of lipid nanoparticles influences their effect on in vitro cell viability. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westesen, K.; Bunjes, H.; Koch, M. Physicochemical characterization of lipid nanoparticles and evaluation of their drug loading capacity and sustained release potential. J. Control. Release 1997, 48, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jores, K.; Haberland, A.; Wartewig, S.; Mäder, K.; Mehnert, W. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) and oil-loaded SLN studied by spectrofluorometry and Raman spectroscopy. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braem, C.; Blaschke, T.; Panek-Minkin, G.; Herrmann, W.; Schlupp, P.; Paepenmüller, T.; Müller-Goyman, C.; Mehnert, W.; Bittl, R.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; et al. Interaction of drug molecules with carrier systems as studied by parelectric spectroscopy and electron spin resonance. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washington, C. Stability of lipid emulsions for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1996, 20, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siekmann, B.; Westesen, K. Preparation and physicochemical characterization of aqueous dispersions of coenzyme Q10 nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, W.; Schubert, R.; Massing, U. Small-scale preparation of perfluorocarbon-nanoemulsions utilizing dual centrifugation. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göke, K.; Roese, E.; Bunjes, H. Heat treatment of poloxamer-stabilized triglyceride nanodispersions: Effects and underlying mechanism. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 3111–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


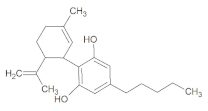
| pKa 1 | Log P 1 | Melting Point [°C] 2 | Molar Mass [g/mol] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9.1 | 6.1 | 67 | 314 |
| Structure | Lipophilicity 3 | ||
 |  | ||
| Lipid | Emulsifier | Preservative | Process Parameters | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinetics of drug loading, influence of the lipid matrix and influence of drug load on emulsion stability | ||||
| SB-P188-120 nm | 10% Soybean oil | 5% Poloxamer 188 | 0.05% Sodium azide | HPH 700 bar |
| TM-P188-120 nm | 5% Trimyristin | 6% Poloxamer 188 | 0.05% Sodium azide | HPH 500 bar |
| RS-P188-120 nm | 10% Rapeseed oil | 5% Poloxamer 188 | 0.05% Sodium azide | HPH 700 bar |
| MCT-P188-120 nm | 10% Miglyol 812 (MCT) | 5% Poloxamer 188 | 0.05% Sodium azide | HPH 700 bar |
| SB-P407-130 nm | 10% Soybean oil | 5% Poloxamer 407 | 0.05% Sodium azide | HPH 700 bar |
| Drug localization | ||||
| SB-P188-70 nm | 10% Soybean oil | 5% Poloxamer 188 | 0.05% Sodium azide | HPH 1500 bar |
| SB-P188-150 nm | 10% Soybean oil | 5% Poloxamer 188 | 0.05% Sodium azide | HPH 300 bar |
| SB-P188-230 nm | 10% Soybean oil | 5% Poloxamer 188 | 0.05% Sodium azide | PME 0.2 mm PE membrane |
| Initially Added CBD Concentration | Sample Volume | Time of Drug Loading |
|---|---|---|
| Kinetics of drug loading | ||
| 30 mg/mL | 1 mL | Equal to sample time |
| Influence of the type of lipid matrix | ||
| 30 mg/mL | 1 mL | 7 days |
| Influence of drug load on emulsion stability | ||
| 60 mg/mL | 6 mL | 7 days |
| Drug localization | ||
| 30 mg/mL | 1 mL | 14 days |
| PCS z-Average Diameter | PCS PdI | Emulsifier Content in the Aqueous Phase | Lipid Content after Production | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinetics of drug loading, influence of the type of lipid matrix and influence of drug load on emulsion stability | ||||
| SB-P188-120 nm | 122 nm | 0.13 | 0.8% | n.d. |
| TM-P188-120 nm | 119 nm | 0.12 | 2.5% | n.d. |
| RS-P188-120 nm | 124 nm | 0.12 | 1.0% | n.d. |
| MCT-P188-120 nm | 117 nm | 0.11 | 2.0% | n.d. |
| SB-P407-130 nm | 128 nm | 0.11 | 0.2% | n.d. |
| Drug localization | ||||
| SB-P188-70 nm | 69 nm | 0.11 | n.d. | 8.9% |
| SB-P188-150 nm | 151 nm | 0.14 | 1.6% | 8.6% |
| SB-P188-230 nm | 233 nm | 0.02 | n.d. | 7.9% |
| Fatty Acids | Miglyol® 812 (MCT) | Dynasan® 114 (Trimyristin) | Soybean Oil | Rapeseed Oil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8:0 | 55.8% | - | - | - |
| C10:0 | 43.3% | - | - | - |
| C12:0 | 0.6% | - | - | - |
| C14:0 | - | 100% | - | - |
| C16:0 | - | - | 10.4% | 4.4% |
| C18:1 | - | - | 23.2% | 64% |
| C18:2 | - | - | 53% | 18.7% |
| C18:3 | - | - | 7.2% | 8.1% |
| Melting points [°C] | Liquid at RT | 57 | Liquid at RT | Liquid at RT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francke, N.M.; Schneider, F.; Baumann, K.; Bunjes, H. Formulation of Cannabidiol in Colloidal Lipid Carriers. Molecules 2021, 26, 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051469
Francke NM, Schneider F, Baumann K, Bunjes H. Formulation of Cannabidiol in Colloidal Lipid Carriers. Molecules. 2021; 26(5):1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051469
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancke, Nadine Monika, Frederic Schneider, Knut Baumann, and Heike Bunjes. 2021. "Formulation of Cannabidiol in Colloidal Lipid Carriers" Molecules 26, no. 5: 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051469
APA StyleFrancke, N. M., Schneider, F., Baumann, K., & Bunjes, H. (2021). Formulation of Cannabidiol in Colloidal Lipid Carriers. Molecules, 26(5), 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051469







