Waterborne Polyurethane Dispersions and Thin Films: Biodegradation and Antimicrobial Behaviors
Abstract
1. Introduction
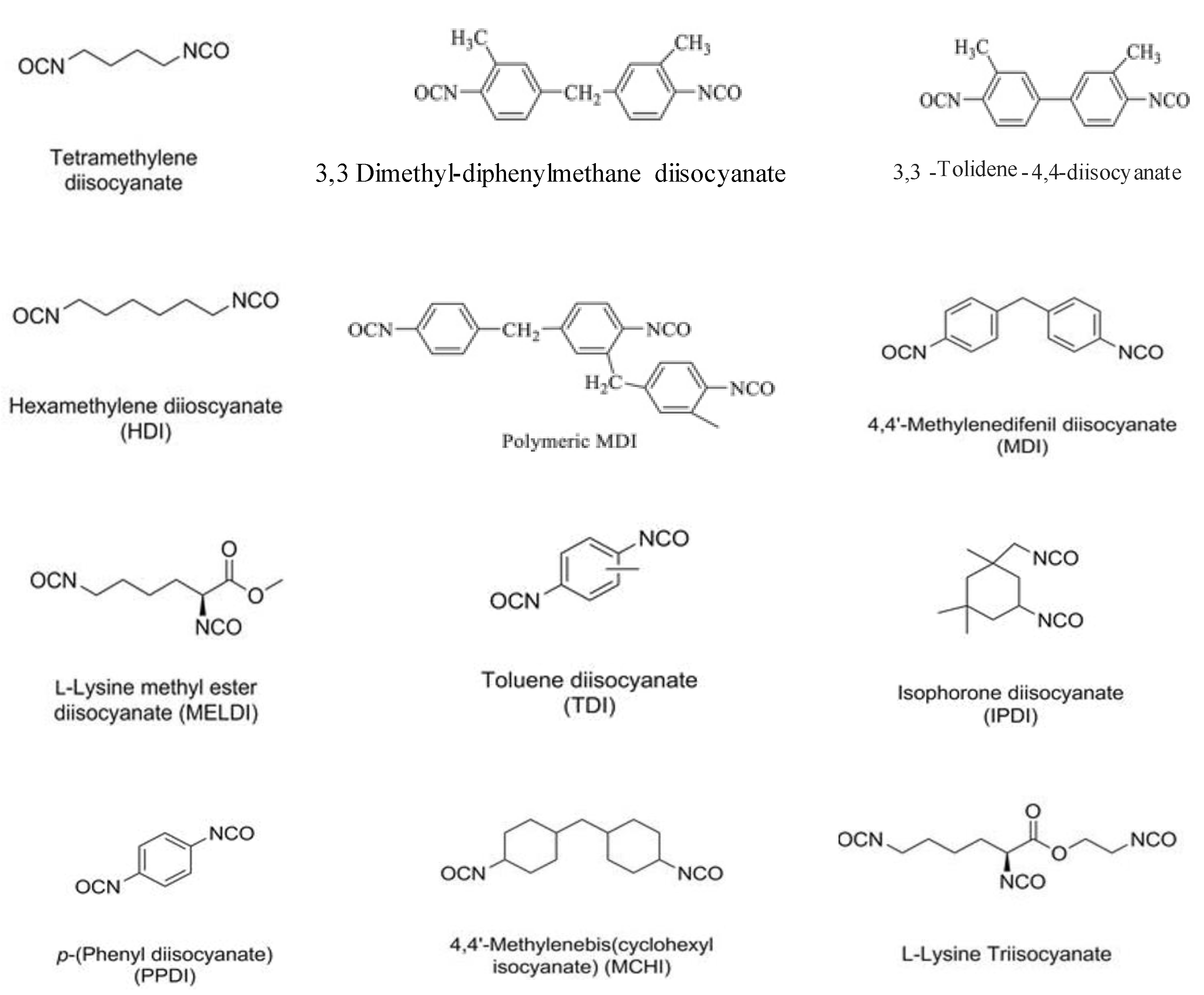
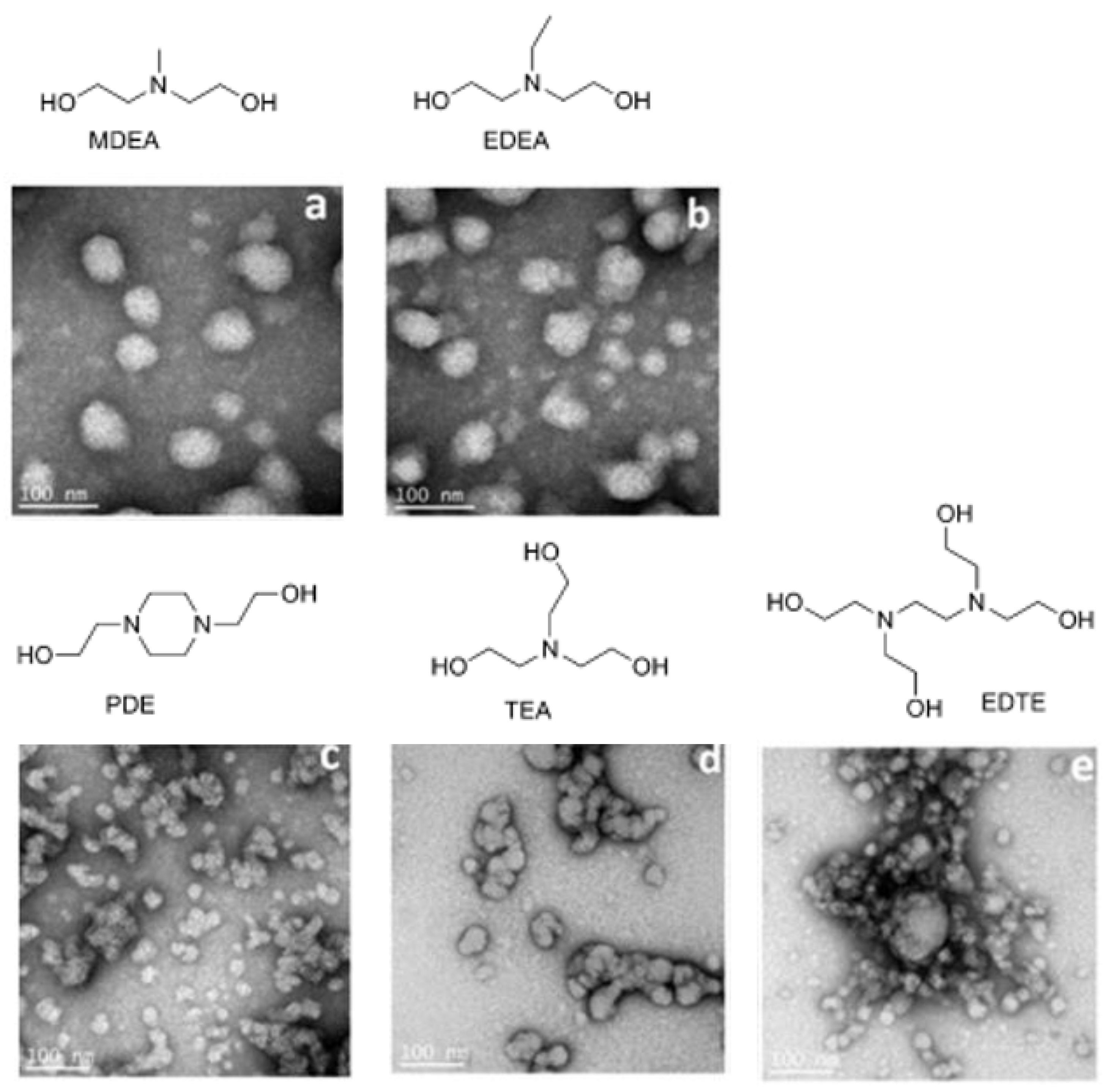
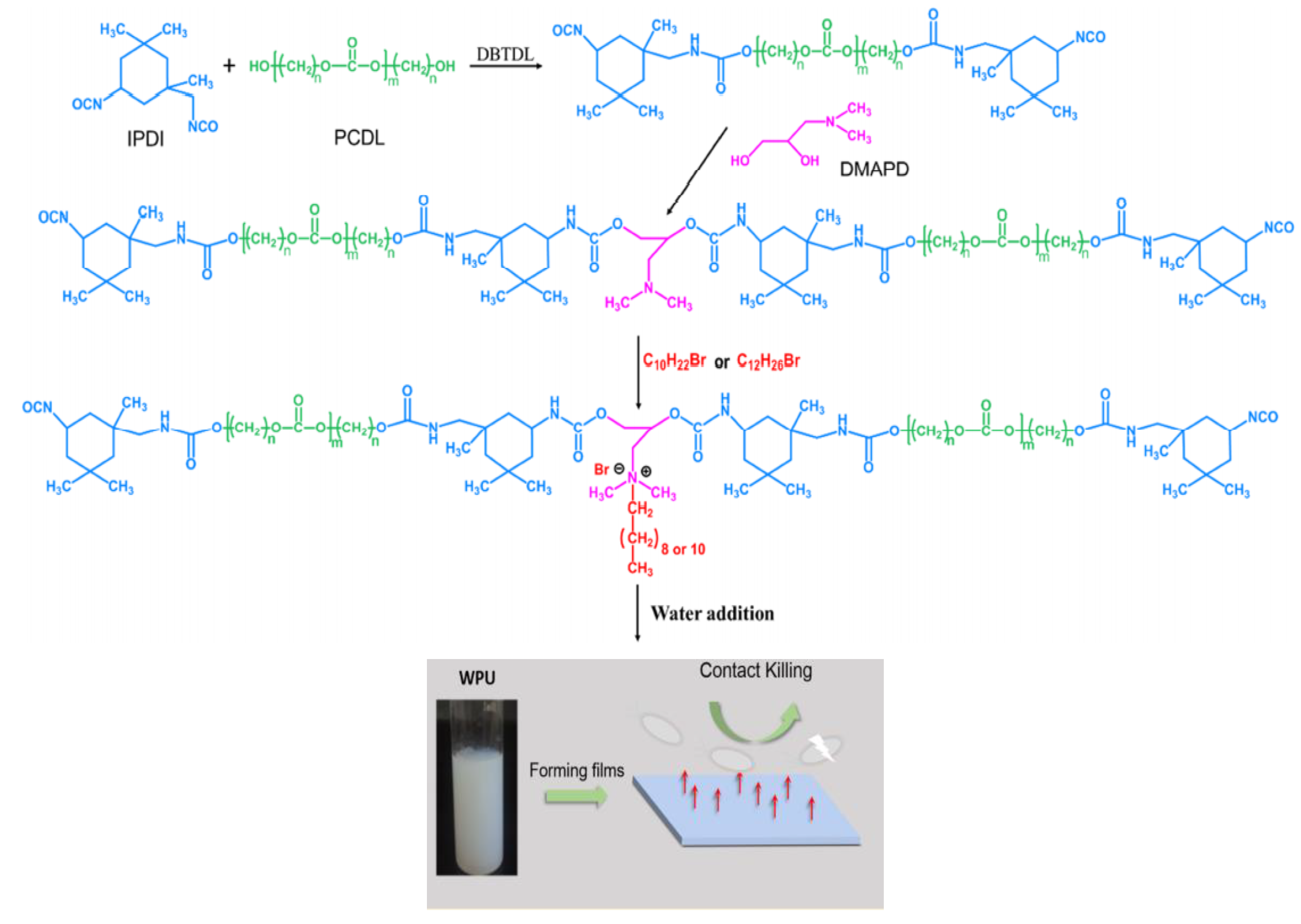
2. PUDs with Antimicrobial Behavior
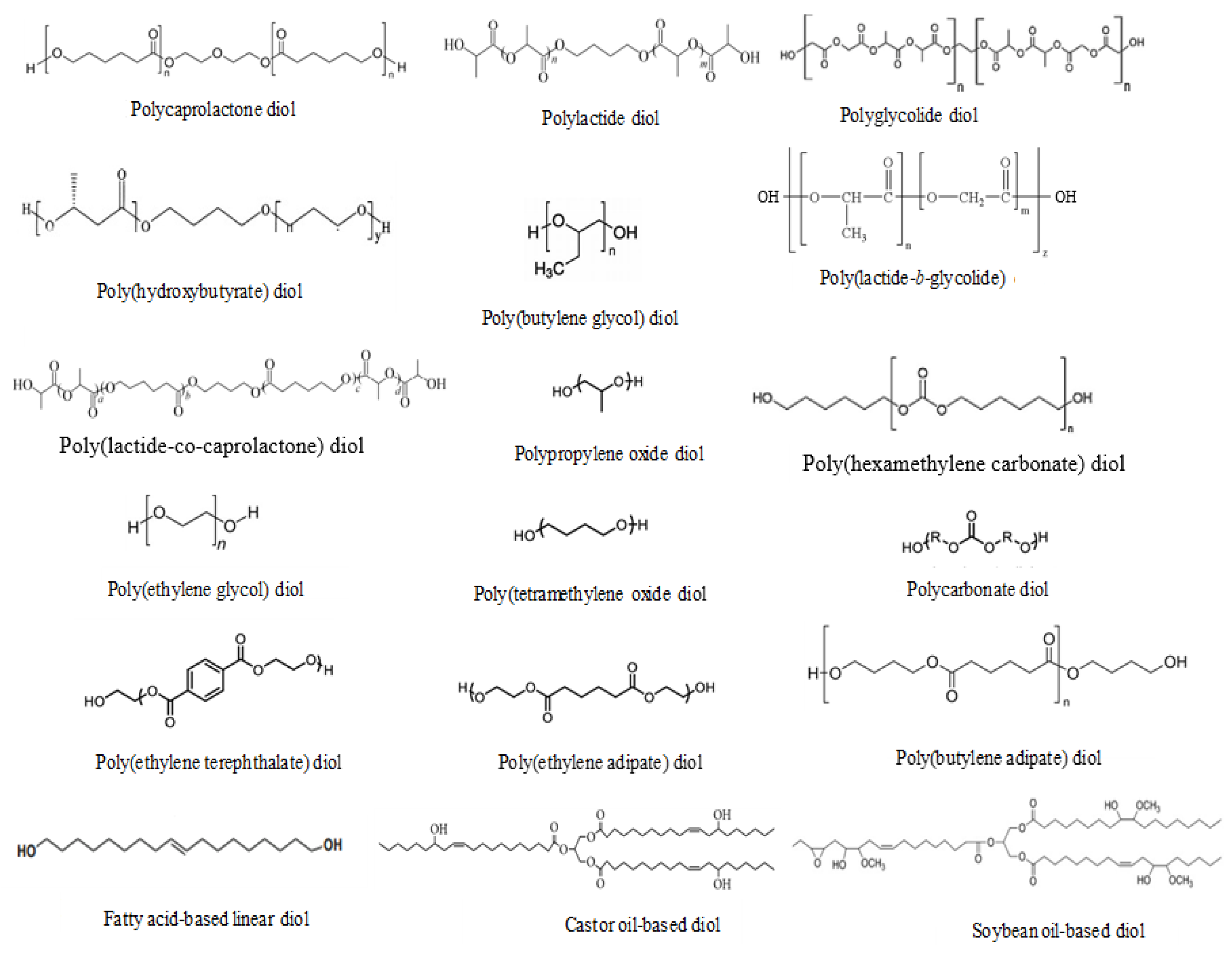
3. Biodegradable PUDs and Their Solid Films
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Mishra, V.; Desai, J.; Patel, K.I. High-performance waterborne UV-curable polyurethane dispersion based on thiol–acrylate/thiol–epoxy hybrid networks. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2017, 14, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehravar, S.; Ballard, N.; Tomovska, R.; Asua, J.M. Polyurethane/Acrylic Hybrid Waterborne Dispersions: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 20902–20922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špírková, M.; Hodan, J.; Kredatusová, J.; Poręba, R.; Uchman, M.; Serkis-Rodzeń, M. Functional properties of films based on novel waterborne polyurethane dispersions prepared without a chain-extension step. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 123, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Fang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Lei, W. Correlation of raw materials and waterborne polyurethane properties by sequence similarity analysis. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.C.; Kim, S.J.; Park, K.K.; Oh, J.G.; Bae, S.G.; Noh, G.H.; Lee, W.K. Synthesis and properties of waterborne UV-curable polyurethane acrylates using functional isocyanate. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 659, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkis, M.; Špírková, M.; Hodan, J.; Kredatusová, J. Nanocomposites made from thermoplastic waterborne polyurethane and colloidal silica. The influence of nanosilica type and amount on the functional properties. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 101, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chen, H.; Xie, A.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, M. Study on associating thickening mechanism and structure–efficiency relationship of hyperbranched waterborne polyurethane. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 92, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Fang, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Xiao, S.; Ding, Y. Waterborne epoxy-modified polyurethane-acrylate dispersions with nano-sized core-shell structure particles: Synthesis, characterization, and their coating film properties. J. Polym. Eng. 2017, 37, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Pu, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, L.; Cheng, J.; Zhong, J. Effect of different carboxylic acid group contents on microstructure and properties of waterborne polyurethane dispersions. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.T.; Lee, J.Y.; Chiu, P.Y.; Hu, C.C.; Chang, F.F.; Hsu, C.H. Waterborne polyurethane molecular structure designed and its acetic acid and ammonia absorption efficiency. Fib. Polym. 2017, 18, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, L.; Dong, D.; Wang, Y. Enhancement of water and organic solvent resistances of a waterborne polyurethane film by incorporating liquid polysulfide. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 17163–17171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Huang, S.; Qu, J. Synthesis and properties of high-functionality hydroxyl-terminated polyurethane dispersions. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 119, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennebroek, R.; van der Hoeven-van Casteren, I.; Swaans, R.; van der Slot, S.; Stals, P.J.; Tuijtelaars, B.; Koning, C. Water-based polyurethane dispersions. Polym. Int. 2019, 68, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzzo, P.J.; Anbinder, P.S.; Pardini, F.M.; Pardini, O.R.; Plivelic, T.S.; Amalvy, J.I. On the strategies for incorporating nanosilica aqueous dispersion in the synthesis of waterborne polyurethane/silica nanocomposites: Effects on morphology and properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2016, 6, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Qu, J. Preparation and assistant-film-forming performance of aqueous polyurethane dispersions. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 105, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, D.; Keberle, W.; Wuest, R. Aqueous dispersions of polyurethane ionomers. J. Oil Colour Chem. Assoc. 1970, 53, 363–379. [Google Scholar]
- Dieterich, D. Aqueous emulsions, dispersions and solutions of polyurethanes; synthesis and properties. Prog. Org. Coat. 1981, 9, 281–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, A.H. Ddp Specialty Electronic Materials US, INC. Formulated Waterborne Polyurethane Dispersion Composition for Stable Ambient-Dried Foams. U.S. Patent Application US2020/0172654A1, 4 June 2020. Appl. 16/695,890. [Google Scholar]
- Hakke, V.S.; Bagale, U.D.; Boufi, S.; Babu, G.U.B.; Sonawane, S.H. Ultrasound Assisted Synthesis of Starch Nanocrystals and It’s Applications with Polyurethane for Packaging Film. J. Renew. Mater. 2020, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, N.; Zia, K.M.; Saeed, M.; Khosa, M.K.; Khan, W.G.; Arain, M.A. Compositional effect on the deformation behavior of polyurethane pressure-sensitive adhesive thin films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Kao, W.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Dai, G.; Li, Z. Preparation and characterization of self-matting waterborne polymer–An overview. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 142, 105569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, P.; Król, B. Structures, properties and applications of the polyurethane ionomers. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.; Atwater, M.N.; Walnut, F.P.; Begin, K.D.; Pankey, T. Illinois Tool Works Inc. Waterborne bonding adhesive formulation for sheet membrane incorporating a solid plasticizer. U.S. Patent Application US 2019/10233684A1, 1 August 2019. Appl. 16/261,135. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, N.; Zia, K.M.; Saeed, M.; Usman, M.; Khan, W.G.; Bashir, M.A. Investigation of non-adhesive behaviour of waterborne polyurethane dispersions. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshandeh, E.; Bastani, S.; Saeb, M.R.; Croutxé-Barghorn, C.; Allonas, X. High-performance water-based UV-curable soft systems with variable chain architecture for advanced coating applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 130, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicks, D.A.; Wicks Jr, Z.W. Blocked isocyanates III: Part A. Mechanisms and chemistry. Prog. Org. Coat. 1999, 36, 148–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourston, D.J.; Williams, G.D.; Satguru, R.; Padget, J.C.; Pears, D. The influence of the degree of neutralization, the ionic moiety, and the counterion on water-dispersible polyurethanes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicks, D.A.; Wicks Jr, Z.W. Multistep chemistry in thin films; the challenges of blocked isocyanates. Prog. Org. Coat. 2001, 43, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayendran, B.R.; Derby, R.; Gruber, B.A. Air Products and Chemicals Inc. Aqueous Polyurethane-Vinyl Polymer Dispersions for Coating Applications. U.S. Patent US005173526A, 22 December 1992. Appl. 5,173,526. [Google Scholar]
- De Gennes, P.G. Polymers at an interface; a simplified view. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1987, 27, 89–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilett, S.M.; Orrock, A.; Poon, W.C.K.; Pusey, P.N. Phase behavior of a model colloid-polymer mixture. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 51, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napper, D.H. Polymeric Stabilization of Colloidal Dispersions; Academic: NewYork, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Yu, X. Synthesis and properties of sulfonated polyurethane ionomers with anions in the polyether soft segments. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1997, 35, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; He, Q.; Yu, X. Synthesis and properties of polyoxyethylated amine polyurethane ionomers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 67, 2179–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, Z.S.; Ferguson, J. Polyurethane elastomers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1991, 16, 695–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.A.; Hwang, K.K.S.; Cooper, S.L. Properties of Polyether–polyurethane anionomers. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 1983, 22, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, S.A.; Cooper, S.L. Comparison of the physical properties of carboxylated and sulfonated model polyurethane ionomers. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.K.; Yang, C.Z.; Cooper, S.L. Properties of polyether-polyurethane zwitterionomers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1981, 21, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.S.; Ding, S.L.; Yang, K.H.; Chwang, C.P.; Chao, D.Y. Study of anionic polyurethane ionomer dispersant. J. Coat. Technol. 1997, 69, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbis, J.A.; de Gracia García-Martín, M.; de Paz, M.V.; Galbis, E. Bio-based polyurethanes from carbohydrate monomers. Aspects Polyur. 2017, 7, 155–192. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, K.C. Recent advances in the chemistry of polyurethanes. Rub. Chem. Technol. 1972, 45, 1442–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepburn, C. Polyurethane Elastomers; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Szycher, M.; Poirier, V.L.; Dempsey, D.J. Development of an aliphatic biomedical-grade polyurethane elastomer. J. Elastom. Plast. 1983, 15, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schollenberger, C.S.; Stewart, F.D. Thermoplastic urethane structure and ultraviolet stability. J. Elastopl. 1972, 4, 294–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauman, S.K.; Mayorga, G.D.; Heller, J. Light stability and discoloration of segmented polyether urethanes. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1981, 9, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schollenberger, C.S.; Scptt, H.; Moore, G.R. Polyurethan VC, a virtually crosslinked elastomer. Rubber Chemistry and Technology 1962, 35, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Kim, B.K. Enhancement of hydrolytic stability and adhesion of waterborne polyurethanes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, D.; Grigat, E.; Hahn, W.; Hespe, H.; Schmelzer, H.G. Principles of polyurethane chemistry and special applications. Polyurethane Handbook: Chemistry, Raw Materials, Processing, Application, Properties; Hanser Publishers, Munich and New York: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 11–31. [Google Scholar]
- Anderle, G.A.; Lenhard, S.L.; Lubnin, A.V.; Snow, G.E.; Tamareselvy, K. Noveon IP Holdings Corp, Plasticized waterborne polyurethane dispersions and manufacturing process. U.S. Patent 6,576,702, 10 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Madbouly, S.A.; Xia, Y.; Kessler, M.R. Rheological behavior of environmentally friendly castor oil-based waterborne polyurethane dispersions. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 4606–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madbouly, S.A.; Otaigbe, J.U. Recent advances in synthesis, characterization and rheological properties of polyurethanes and POSS/polyurethane nanocomposites dispersions and films. Progr. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 1283–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madbouly, S.A.; Otaigbe, J.U. Kinetic analysis of fractal gel formation in waterborne polyurethane dispersions undergoing high deformation flows. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4144–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madbouly, S.A.; Otaigbe, J.U. Rheokinetics of thermal-induced gelation of waterborne polyurethane dispersions. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 10178–10184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madbouly, S.A.; Xia, Y.; Kessler, M.R. Sustainable Polyurethane–Lignin Aqueous Dispersions and Thin Films: Rheological Behavior and Thermomechanical Properties. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 5198–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, A.K.; Wicks, D.A.; Madbouly, S.A.; Otaigbe, J.U. Nanostructured polyurethane/POSS hybrid aqueous dispersions prepared by homogeneous solution polymerization. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 7037–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Y.S.; Kim, E.Y.; Ha Yoo, B.; Kim, H.D. Preparation and properties of waterborne poly (urethane urea) s for adhesives: The effects of the 2, 2-bis (hydroxylmethyl) propionic acid content on the properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cheng, L.; Hu, J. NMR studies of water-borne polyurethanes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, A.K.; Wicks, D.A.; Madbouly, S.A.; Otaigbe, J.U. Effect of ionic content, solid content, degree of neutralization, and chain extension on aqueous polyurethane dispersions prepared by prepolymer method. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 2514–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madbouly, S.A.; Otaigbe, J.U.; Nanda, A.K.; Wicks, D.A. Rheological behavior of aqueous polyurethane dispersions: Effects of solid content, degree of neutralization, chain extension, and temperature. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 4014–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madbouly, S.A.; Otaigbe, J.U.; Nanda, A.K.; Wicks, D.A. Thermal-induced simultaneous liquid–liquid phase separation and liquid–solid transition in aqueous polyurethane dispersions. Polym. 2005, 46, 10897–10907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzaffar, S.; Bhatti, I.A.; Zuber, M.; Bhatti, H.N.; Shahid, M. Study of the UV protective and antibacterial properties of aqueous polyurethane dispersions extended with low molar mass chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, G.P.; Chambhare, S.U.; Jagtap, R.N. Anionic water-based polyurethane dispersions for antimicrobial coating application. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 4781–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestry, S.U.; Patil, D.M.; Mhaske, S.T. Effect of 2-aminobenzothiazole on antimicrobial activity of waterborne polyurethane dispersions (WPUDs). Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, A.K.; Wicks, D.A. The influence of the ionic concentration, concentration of the polymer, degree of neutralization and chain extension on aqueous polyurethane dispersions prepared by the acetone process. Polymer 2006, 47, 1805–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.Y.; Kim, H.J. Effects of Neutralizers and Chain Extenders on the Properties of Cationic Polyurethane Water Dispersions. Polym. Korea 2011, 35, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daemi, H.; Rad, R.R.; Barikani, M.; Adib, M. Catalytic activity of aqueous cationic polyurethane dispersions: A novel feature of polyurethanes. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 468, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubnin, A.V.; Malaba, D. Lubrizol Advanced Materials Inc. Aqueous Cationic Polyurethane Dispersions. U.S. Patent 9,527,328, 27 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Francolini, I.; Ruggeri, V.; Martinelli, A.; D’Ilario, L.; Piozzi, A. Novel Metal-Polyurethane Complexes with Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francolini, I.; D’Ilario, L.; Guaglianone, E.; Donelli, G.; Martinelli, A.; Piozzi, A. Polyurethane anionomers containing metal ions with antimicrobial properties: Thermal, mechanical and biological characterization. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3482–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, T.F.; Zhang, Z.; Kim, H.J.; Mitra, D.; Xia, Y.; Pfister, D.P.; Brehm-Stecher, B.F.; Larock, R.C.; Kessler, M.R. Thermo-mechanical and antibacterial properties of soybean Oil-based cationic polyurethane coatings: Effects of amine ratio and degree of crosslinking. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Kessler, M.R.; Brehm-Stecher, B.; Larock, R.C. Antibacterial soybean-Oil-based cationic polyurethane coatings prepared from different amino polyols. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 2221–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Lu, Q.; Liu, M.; Ou, R.; Wang, Q.; Quirino, R.L.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, C. UV absorption, Anticorrosion, and Long-term Antibacterial Performance of Vegetable Oil based Cationic Waterborne Polyurethanes Enabled by Amino Acids. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 20, 127774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Deng, X.; Luo, X.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y. Self-antibacterial UV-curable waterborne polyurethane with pendant amine and modified by guanidinoacetic acid. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Li, T.; Ma, P.; Zhang, H.; Du, M.; Chen, M.; Dong, W. Antimicrobial Waterborne Polyurethanes Based on Quaternary Ammonium Compounds. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 59, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchet, T.J.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E.M. Hierarchal structure–property relationships of segmented polyurethanes. In Advances in Polyurethane Biomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y.; Han, D.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, S. Oppositely charged polyurethane microspheres with tunable zeta potentials as an injectable dual-loaded system for bone repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 25808–25817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shie, M.Y.; Chang, W.C.; Wei, L.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Chen, C.H.; Shih, C.T.; Chen, Y.W.; Shen, Y.F. 3D printing of cytocompatible water-based light-cured polyurethane with hyaluronic acid for cartilage tissue engineering applications. Materials 2017, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.C.; Tseng, C.S.; Hsu, S.H. Synthesis and 3D printing of biodegradable polyurethane elastomer by a water-based process for cartilage tissue engineering applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmeister, H.; Seyidova, N.; Schreiber, C.; Strobl, M.; Grasl, C.; Walter, I.; Messner, B.; Baudis, S.; Fröhlich, S.; Marchetti-Deschmann, M.; et al. Biodegradable, thermoplastic polyurethane grafts for small diameter vascular replacements. Acta Biomater. 2015, 11, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagi, P.; Ghorpade, R.; Choi, Y.J.; Patil, U.; Kim, I.; Baik, J.H.; Hong, S.C. Carbon dioxide-based polyols as sustainable feedstock of thermoplastic polyurethane for corrosion-resistant metal coating. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3871–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, N.L.; Adhikari, R.; Shanks, R.; Adhikari, B. Flexible starch-polyurethane films: Physiochemical characteristics and hydrophobicity. Carbonhydr. Polym. 2017, 163, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, S.; Hirai, T.; Higaki, Y.; Yoshinaga, K.; Kojio, K.; Takahara, A. Effect of chain architecture of polyol with secondary hydroxyl group on aggregation structure and mechanical properties of polyurethane elastomer. Polymer 2017, 116, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Tang, L.; Hong, Y. Triggerable degradation of polyurethanes for tissue engineering applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 20377–20388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battiston, K.G.; Labow, R.S.; Santerre, J.P. Protein binding mediation of biomaterial-dependent monocyte activation on a degradable polar hydrophobic ionic polyurethane. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8316–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madbouly, S.A.; Lendlein, A. Degradable polyurethane/soy protein shape-memory polymer blends prepared via environmentally-friendly aqueous dispersions. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2012, 297, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viezzer, C.; Feng, Z.; Wang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xu, T.; Guo, Z.; Hussain, M.I.; Zeng, J.; Lou, L.; et al. A novel waterborne polyurethane with biodegradability and high flexibility for 3D printing. Biofabrication 2020, 12, 035015. [Google Scholar]
- Viezzer, C.; Mazzuca, R.; Machado, D.C.; de Camargo Forte, M.M.; Ribelles, J.L.G. A new waterborne chitosan-based polyurethane hydrogel as a vehicle to transplant bone marrow mesenchymal cells improved wound healing of ulcers in a diabetic rat model. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231, 115734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eming, S.A.; Martin, P.; Tomic-Canic, M. Wound repair and regeneration: Mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci. Trans. Med. 2014, 6, 265sr6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.; Tariq, M.; Ali, I.; Asghar, R.; Khanam, P.N.; Augustine, R.; Hasan, A. Novel electrospun chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/zinc oxide nanofibrous mats with antibacterial and antioxidant properties for diabetic wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.H.; Hsieh, C.T.; Sun, Y.M. Synthesis and characterization of waterborne polyurethane containing poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) as new biodegradable elastomers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 9089–9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, M. Biodegradable waterborne polyurethane grafted with gelatin hydrolysate via solvent-free copolymerization for potential porous scaffold material. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 92, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.W.; Su, C.H.; Jeng, U.S.; Hsu, S.H. Characterization of biodegradable polyurethane nanoparticles and thermally induced self-assembly in water dispersion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5685–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.T.; Dai, N.T.; Hsu, S.H. Biodegradable water-based polyurethane scaffolds with a sequential release function for cell-free cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2019, 88, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, H.; Karak, N. Water dispersed bio-derived transparent polyurethane: Synthesis, properties including chemical resistance, UV-aging, and biodegradability. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 146, 105730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.H.; Dai, L.G.; Hung, Y.M.; Dai, N.T. Evaluation and characterization of waterborne biodegradable polyurethane films for the prevention of tendon postoperative adhesion. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbarfar, B.; Ganjali, S.T.; Nikje, M.M.A.; Moradi, S. Synthesis, Characterization and Physicomechanical Properties of Novel Water-based Biodegradable Polyurethane Dispersion. Russian J. Appl. Chem. 2018, 91, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Jiang, P.; Lou, W.; Zhang, P.; Bao, Y.; Gao, X.; Xia, J.; Haryono, A. Preparation of degradable vegetable oil-based waterborne polyurethane with tunable mechanical and thermal properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 139, 109994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, G. Synthetic scheme to improve the solid content of biodegradable waterborne polyurethane by changing the association relationships of hydrophilic fragments. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 28680–28694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, G. Effects of soft segment characteristics on the properties of biodegradable amphiphilic waterborne polyurethane prepared by a green process. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 3139–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

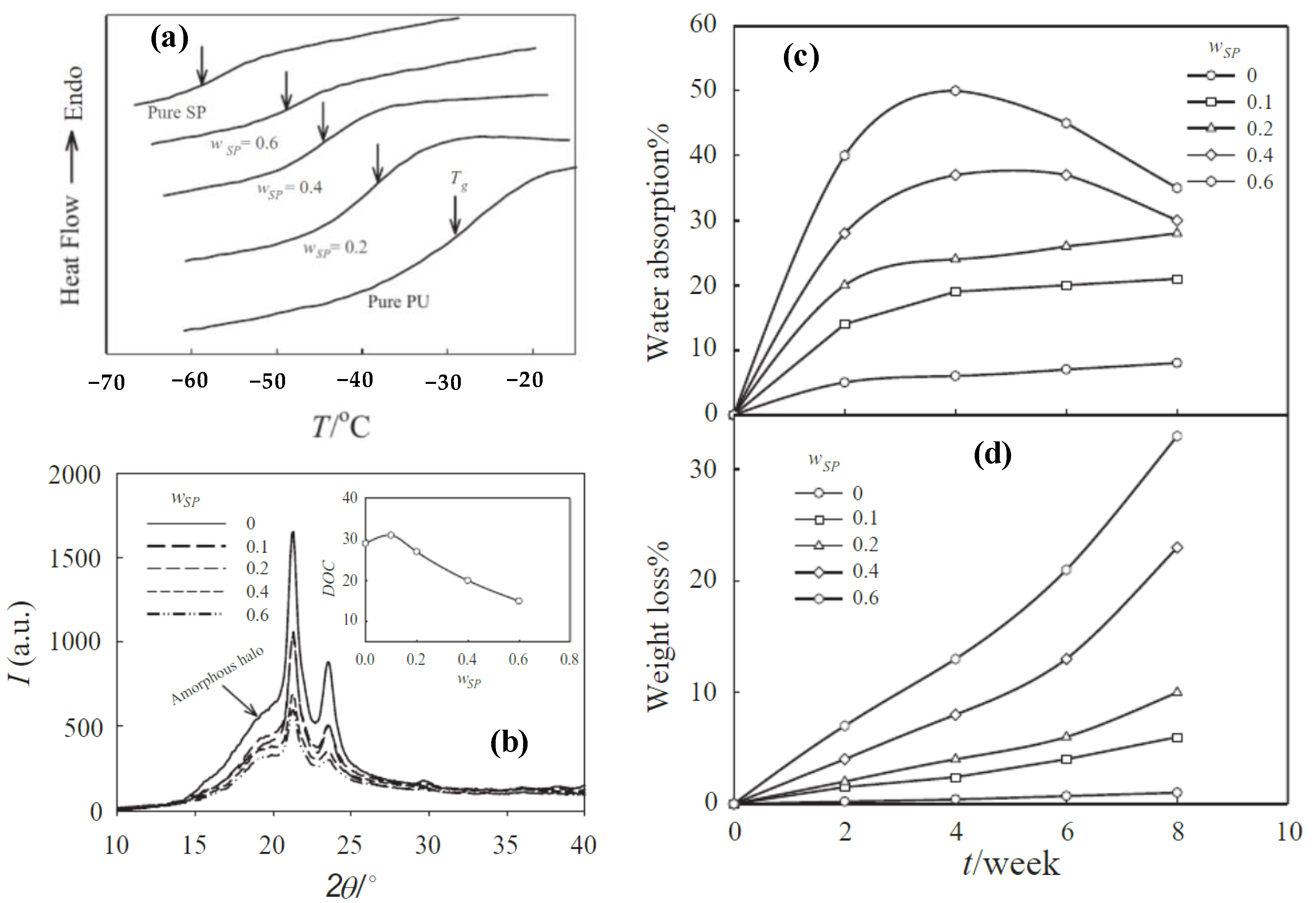


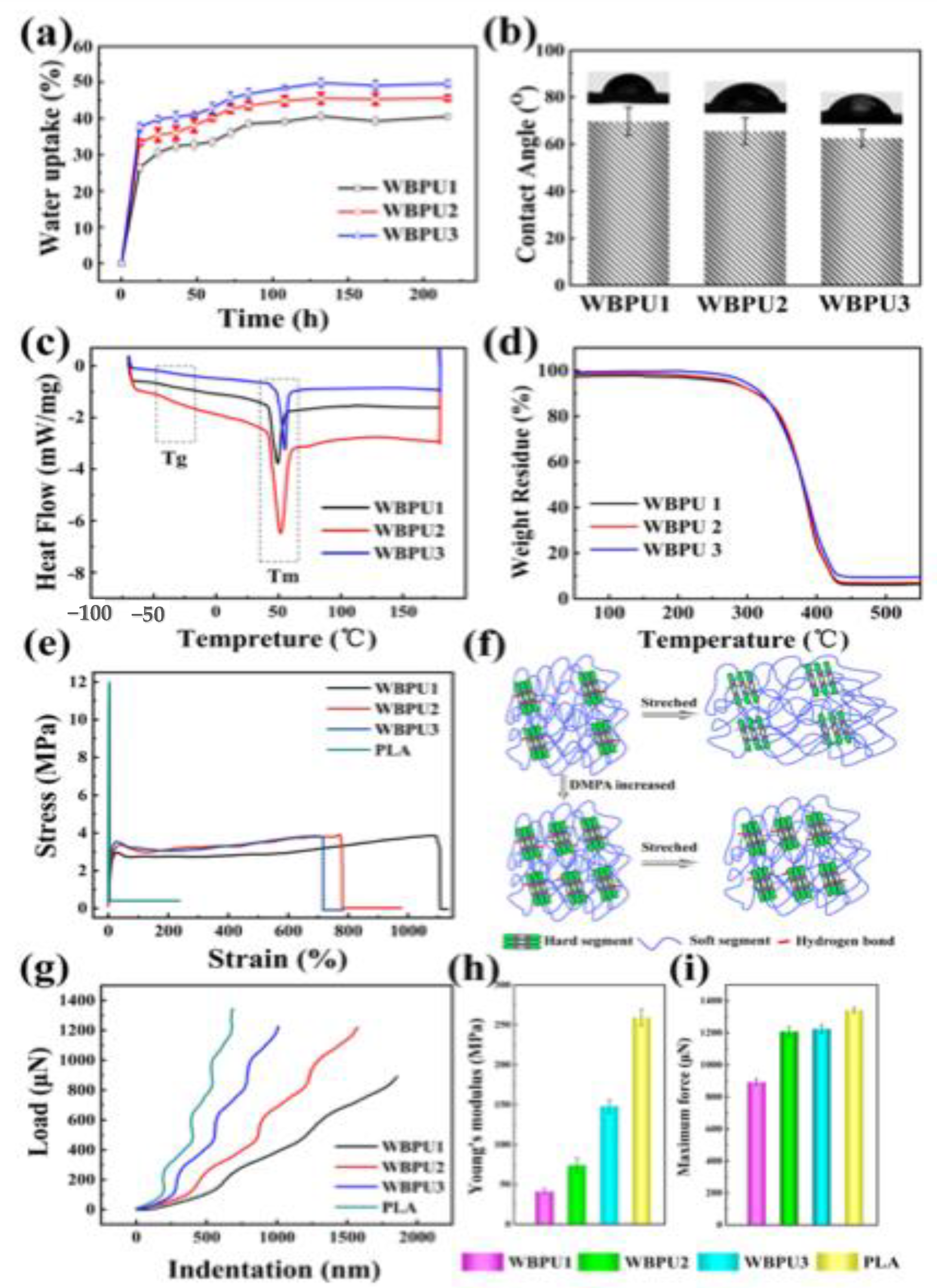




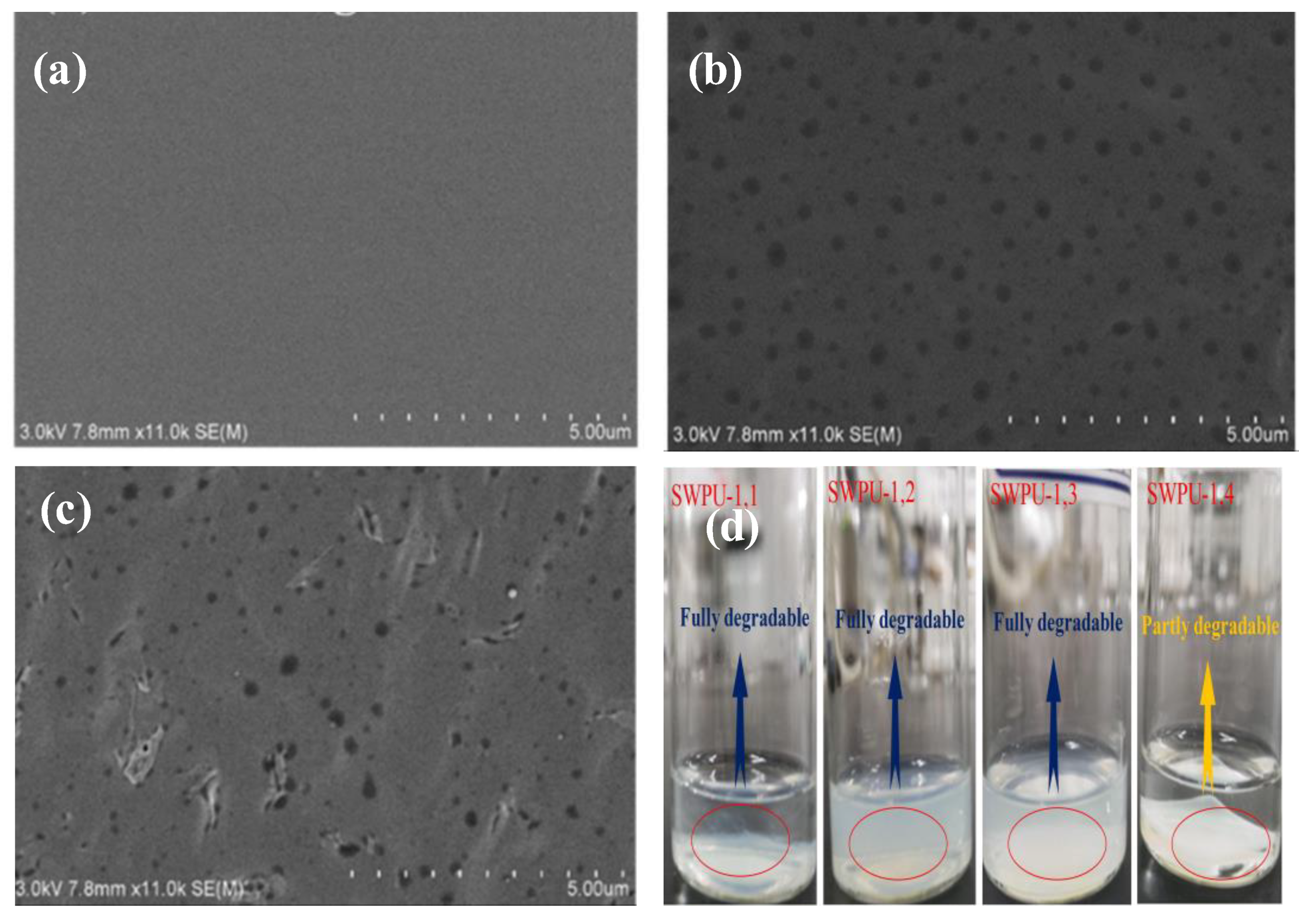
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madbouly, S.A. Waterborne Polyurethane Dispersions and Thin Films: Biodegradation and Antimicrobial Behaviors. Molecules 2021, 26, 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040961
Madbouly SA. Waterborne Polyurethane Dispersions and Thin Films: Biodegradation and Antimicrobial Behaviors. Molecules. 2021; 26(4):961. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040961
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadbouly, Samy A. 2021. "Waterborne Polyurethane Dispersions and Thin Films: Biodegradation and Antimicrobial Behaviors" Molecules 26, no. 4: 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040961
APA StyleMadbouly, S. A. (2021). Waterborne Polyurethane Dispersions and Thin Films: Biodegradation and Antimicrobial Behaviors. Molecules, 26(4), 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040961





