Photoautotrophic and Mixotrophic Cultivation of Polyhydroxyalkanoate-Accumulating Microalgae Consortia Selected under Nitrogen and Phosphate Limitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
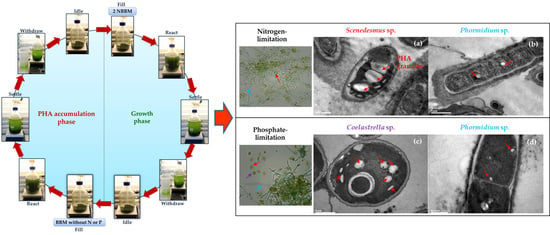
2.1. Enrichment and Selection of PHA-Accumulating Microalgae Consortia
2.2. Batch Cultivation of the Selected Microalgae Consortia
2.2.1. Biomass Production and Sugar Utilization
2.2.2. PHA Accumulation
2.2.3. Protein, Lipid, and Carbohydrate Production
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Media Preparation
3.2. Enrichment and Selection of PHA-Accumulating Microalgae Consortia
3.3. Batch Accumulation Test with Photoautotrophic and Mixotrophic Cultivation
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sharma, V.; Sehgal, R.; Gupta, R. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Properties and Modifications. Polymer 2021, 212, 123161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, P.; Ray, S.; Kalia, V.C. Challenges and Opportunities for Customizing Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Indian J. Microbiol. 2015, 55, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dwivedi, R.; Pandey, R.; Kumar, S.; Mehrotra, D. Poly hydroxyalkanoates (PHA): Role in bone scaffolds. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 10, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Villalba-Rodríguez, A.M.; Romero-Castillo, K.D.; Zavala-Yoe, R.; Bilal, M.; Ramirez-Mendoza, R.A.; Parra-Saldivar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate-based constructs with novel characteristics for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications—A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 1760–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cicek, N.; Levin, D.B.; Logsetty, S.; Liu, S. Bacteria-triggered release of a potent biocide from core-shell polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)-based nanofibers for wound dressing applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmowafy, E.; Abdal-Hay, A.; Skouras, A.; Tiboni, M.; Casettari, L.; Guarino, V. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2019, 16, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, G.; Sosa-Hernandez, J.E.; Rodas-Zuluaga, L.I.; Castillo-Zacarias, C.; Iqbal, H.; Parra-Saldivar, R. Accumulation of PHA in the Microalgae Scenedesmus sp. under Nutrient-Deficient Conditions. Polymers 2021, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabapathy, P.C.; Devaraj, S.; Meixner, K.; Anburajan, P.; Kathirvel, P.; Ravikumar, Y.; Zabed, H.M.; Qi, X. Recent developments in Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) production—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, Z.A.; Abid, S.; Banat, I.M. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Characteristics, production, recent developments and applications. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 126, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilian, N.; Najafpour, G.D.; Khajouei, M. Macro and Micro Algae in Pollution Control and Biofuel Production—A Review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2020, 7, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, R.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Hashem, A.; Allah, E.F.A. Microalgae metabolites: A rich source for food and medicine. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raheem, A.; Prinsen, P.; Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Zhao, M.; Luque, R. A review on sustainable microalgae based biofuel and bioenergy production: Recent developments. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afreen, R.; Tyagi, S.; Singh, G.P.; Singh, M. Challenges and Perspectives of Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production From Microalgae/Cyanobacteria and Bacteria as Microbial Factories: An Assessment of Hybrid Biological System. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 624885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Fatma, T. Cyanobacterial Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB): Screening, Optimization and Characterization. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, C.S.S.; Silva, C.E.; Carvalho, G.; Reis, M.A. Strategies for efficiently selecting PHA producing mixed microbial cultures using complex feedstocks: Feast and famine regime and uncoupled carbon and nitrogen availabilities. New Biotechnol. 2017, 37 Pt A, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyenhuynh, T.; Yoon, L.W.; Chow, Y.H.; Chua, A.S.M. An insight into enrichment strategies for mixed culture in polyhydroxyalkanoate production: Feedstocks, operating conditions and inherent challenges. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 130488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amulya, K.; Jukuri, S.; Mohan, S.V. Sustainable multistage process for enhanced productivity of bioplastics from waste remediation through aerobic dynamic feeding strategy: Process integration for up-scaling. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 188, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad Fauzi, A.H.; Chua, A.S.M.; Yoon, L.W.; Nittami, T.; Yeoh, H.K. Enrichment of PHA-accumulators for sustainable PHA production from crude glycerol. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 122, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monshupanee, T.; Incharoensakdi, A. Enhanced accumulation of glycogen, lipids and polyhydroxybutyrate under optimal nutrients and light intensities in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendhulkar, V.D.; Shetye, L.A. Synthesis of Biodegradable Polymer Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) in Cyanobacteria Synechococcus elongates Under Mixotrophic Nitrogen- and Phosphate-Mediated Stress Conditions. Ind. Biotechnol. 2017, 13, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, D.J. Microalgae for biofuel production. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 109, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, J.; Rong, J.; Wang, Q. Mixotrophic cultivation, a preferable microalgae cultivation mode for biomass/bioenergy production, and bioremediation, advances and prospect. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 8505–8517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Pohnert, G.; Wei, D. Extracellular Metabolites from Industrial Microalgae and Their Biotechnological Potential. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, Y. Polyhydroxyalknoate synthesis in plants as a tool for biotechnology and basic studies of lipid metabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 2002, 41, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, G.; Hossain, A.K.; Sharma, V.; Duraisamy, G. Key Targets for Improving Algal Biofuel Production. Clean Technol. 2021, 3, 711–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębowski, M.; Zieliński, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Kujawska, N.; Talbierz, S. Microalgae Cultivation Technologies as an Opportunity for Bioenergetic System Development—Advantages and Limitations. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiano di Visconte, G.; Spicer, A.; Chuck, C.J.; Allen, M.J. The Microalgae Biorefinery: A Perspective on the Current Status and Future Opportunities Using Genetic Modification. App. Sci. 2019, 9, 4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, Z.; Song, X.; Cao, X. Biochemical compositions of two dominant bloom- forming species isolated from the Yangtze River Estuary in response to different nutrient conditions. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 368, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, W.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Yuan, Z. Metabolic changes of starch and lipid triggered by nitrogen starvation in the microalga Chlorella zofingiensis. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutt, V.; Srivastava, S. Novel quantitative insights into carbon sources for synthesis of poly hydroxybutyrate in Synechocystis PCC 6803. Photosynth. Res. 2018, 136, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Doello, S.; Gutekunst, K.; Forchhammer, K. PHB is Produced from Glycogen Turn-over during Nitrogen Starvation in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goecke, F.; Noda, J.; Paliocha, M.; Gislerod, H.R. Revision of Coelastrella (Scenedesmaceae, Chlorophyta) and first register of this green coccoid microalga for continental Norway. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegewald, H.E. Taxonomy and phylogeny of Scenedesmus. Algae 1997, 12, 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Hašler, P.; Dvořák, P.; Johansen, J.R.; Kitner, M.; Ondřej, V.; Poulíčková, A. Morphological and molecular study of epipelic filamentous genera Phormidium, Microcoleus and Geitlerinema (Oscillatoriales, Cyanophyta/Cyanobacteria). Fottea 2012, 12, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hahn, S.K.; Chang, Y.K.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, K.M.; Chang, H.N. The recovery of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) by using dispersions of sodium hypochlorite solution and chloroform. Biotechnol. Tech. 1993, 7, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruvost, J.; Van Vooren, G.; Le Gouic, B.; Couzinet-Mossion, A.; Legrand, J. Systematic investigation of biomass and lipid productivity by microalgae in photobioreactors for biodiesel application. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, S.K.; Suh, W.I.; Farooq, W.; Moon, M.; Shrivastav, A.; Park, M.S.; Yang, J.W. Rapid quantification of microalgal lipids in aqueous medium by a simple colorimetric method. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 155, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Components | Concentration of Stock Solution (g·L−1) | Volume of Stock Solution (mL/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2NBBM | N-Limited BBM | P-Limited BBM | ||
| (1) NaNO3 | 25 | 20 | None | 20 |
| (2) CaCl2·2H2O | 2.5 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| (3) MgSO4·7H2O | 7.5 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| (4) K2HPO4 | 7.5 | 8 | 8 | None |
| (5) KH2PO4 | 17.5 | 8 | 8 | None |
| (6) NaCl | 2.5 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| (7) FeSO4·7H2O | 4.98 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| (8) H3B3 | 11.42 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| (9) Alkaline EDTA solution | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| (9.1) EDTANa2 | 50 | |||
| (9.2) KOH | 31 | |||
| (10) Trace elements solution | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| (10.1) ZnSO4·7H2O | 8.82 | |||
| (10.2) MnCl2·4H2O | 1.44 | |||
| (10.3) MoO3 | 0.71 | |||
| (10.4) CuSO4·5H2O | 1.57 | |||
| (10.5) Co(NO3)2·6H2O | 0.49 | |||
| Treatment | Source of Inoculum * | Growth Phase | PHA Accumulation Phase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium | C-Source | Medium | C-Source | ||
| Auto-N | Reactor A | 2NBBM | CO2 | N-limited BBM | CO2 |
| Mixo-N-Glu | Reactor A | 2NBBM | CO2 | N-limited BBM | Glucose/CO2 |
| Mixo-N-Flu | Reactor A | 2NBBM | CO2 | N-limited BBM | Fructose/CO2 |
| Mixo-N-Suc | Reactor A | 2NBBM | CO2 | N-limited BBM | Sucrose/CO2 |
| Mixo-N-SCJ | Reactor A | 2NBBM | CO2 | N-limited BBM | Sugarcane juice/CO2 |
| Auto-P | Reactor B | 2NBBM | CO2 | P-limited BBM | CO2 |
| Mixo-P-Glu | Reactor B | 2NBBM | CO2 | P-limited BBM | Glucose/CO2 |
| Mixo-P-Flu | Reactor B | 2NBBM | CO2 | P-limited BBM | Fructose/CO2 |
| Mixo-P-Suc | Reactor B | 2NBBM | CO2 | P-limited BBM | Sucrose/CO2 |
| Mixo-P-SCJ | Reactor B | 2NBBM | CO2 | P-limited BBM | Sugarcane juice/CO2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phalanisong, P.; Plangklang, P.; Reungsang, A. Photoautotrophic and Mixotrophic Cultivation of Polyhydroxyalkanoate-Accumulating Microalgae Consortia Selected under Nitrogen and Phosphate Limitation. Molecules 2021, 26, 7613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247613
Phalanisong P, Plangklang P, Reungsang A. Photoautotrophic and Mixotrophic Cultivation of Polyhydroxyalkanoate-Accumulating Microalgae Consortia Selected under Nitrogen and Phosphate Limitation. Molecules. 2021; 26(24):7613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247613
Chicago/Turabian StylePhalanisong, Parichat, Pensri Plangklang, and Alissara Reungsang. 2021. "Photoautotrophic and Mixotrophic Cultivation of Polyhydroxyalkanoate-Accumulating Microalgae Consortia Selected under Nitrogen and Phosphate Limitation" Molecules 26, no. 24: 7613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247613
APA StylePhalanisong, P., Plangklang, P., & Reungsang, A. (2021). Photoautotrophic and Mixotrophic Cultivation of Polyhydroxyalkanoate-Accumulating Microalgae Consortia Selected under Nitrogen and Phosphate Limitation. Molecules, 26(24), 7613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247613