Rapid Structure Determination of Bioactive 4″-Tetrahydrofurfuryl Macrozone Reaction Mixture Components by LC-SPE/Cryo NMR and MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of Chromatographic Separation
2.2. SPE Preconcentration
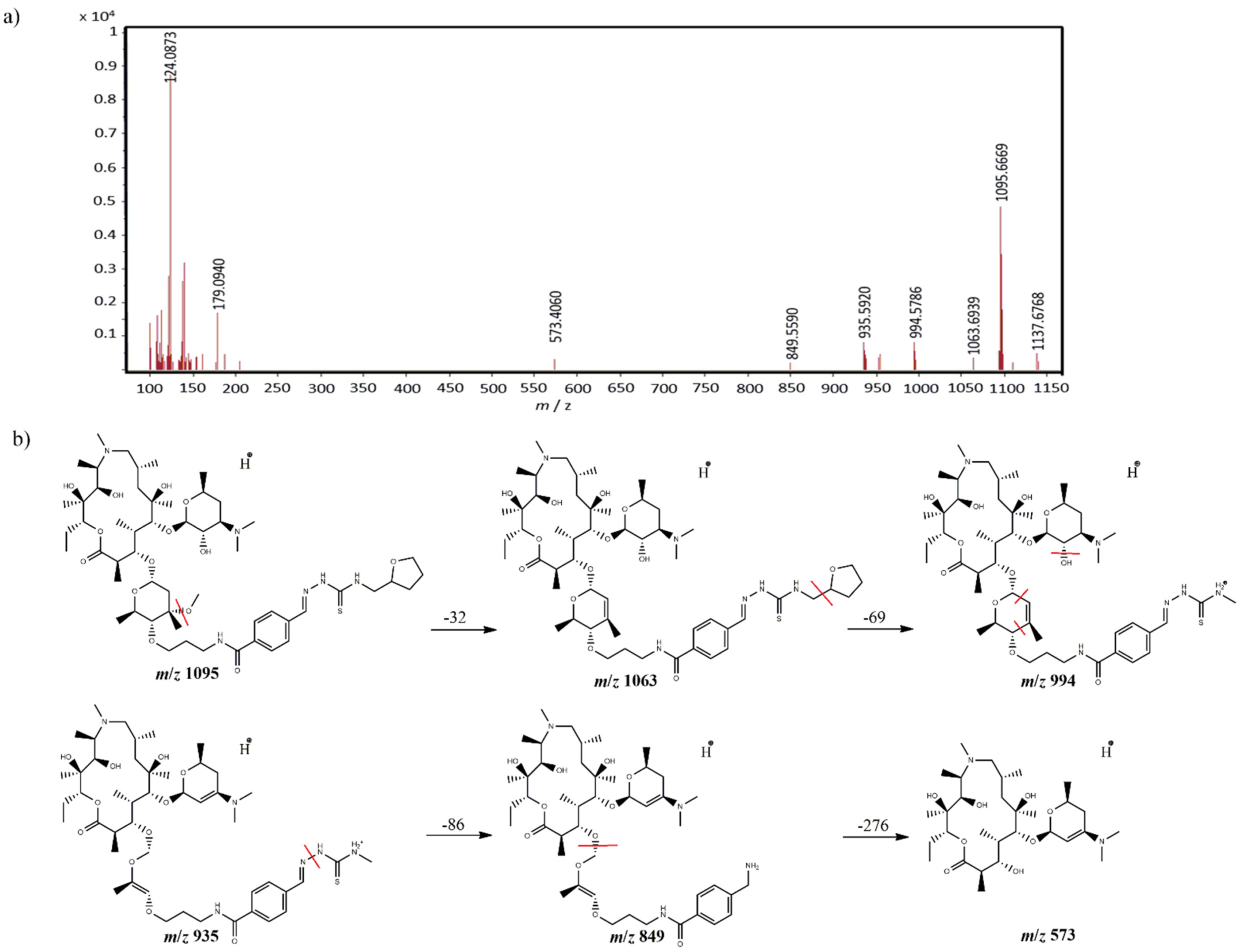
2.3. Identification of Components by Cryo NMR and MS
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Liquid Chromatography
3.4. On-line HPLC-SPE
3.5. NMR Spectroscopy
3.6. MS Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Arsić, B.; Novak, P.; Rimoli, M.G.; Barber, J.; Kragol, G.; Sodano, F. Macrolides. Properties, Synthesys and Applications. In CHEMMEDCHEM, 1st ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–100. [Google Scholar]
- Parnham, M.J.; Eraković Faber, V.; Gimarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Perletti, G.; Verleden, G.M.; Vos, R. Azithromycin: Mechanism of action and their relevance for clinical applications. Pharm. Therap. 2014, 143, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsić, B.; Barber, J.; Čikoš, A.; Mladenović, M.; Stanković, N.; Novak, P. 16-Membered Macrolide Antibiotics: A Review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlünzen, F.; Zarivach, R.; Harm, J.; Bashan, A.; Tocilj, A.; Albrecht, R.; Yonath, A.; Franceschi, F. Structural basis for the interaction of antibiotics with the peptidyl transferase centre in eubacteria. Nature 2001, 413, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.L.; Ippolito, J.A.; Ban, N.; Nissen, P.; Moore, P.B.; Steitz, T.A. The structures of four macrolide antibiotics bound to the large ribosomal subunit. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkle, J.A.; Xiong, L.; Mankin, A.S.; Cate, J.H.D. Structures of the Escherichia coli ribosome with antibiotics bound near the peptidyl transferase center explain spectra of drug action. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17152–17157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, P.; Tatić, I.; Tepeš, P.; Koštrun, S.; Barber, J. A Systematic Approach to Understanding Ribosome-Macrolide Interactions: NMR and Modeling Studies of Oleandomycin and its Derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, P.; Barber, J.; Čikoš, A.; Arsić, B.; Plavec, J.; Lazarevski, G.; Tepeš, P.; Košutić-Hulita, N. Free and bound state structures of 6-O-methyl homoerithromycins and epitope mapping of their interactions with ribosomes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5857–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosol, S.; Schrank, E.; Bukvić Krajačić, M.; Wagner, G.E.; Meyer, H.; Göbl, C.; Rechberger, G.N.; Zangger, K.; Novak, P. Probing the Interactions of Macrolide Antibiotics with Membrane-Mimetics by NMR Spectroscopy. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 5632–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanzer, S.; Pulido, S.A.; Tutz, S.; Wagner, G.E.; Kriechbaum, M.; Gubensäk, N.; Trifunovic, J.; Dorn, M.; Fabian, W.M.F.; Novak, P.; et al. Structural and functional implications of the interaction between macrolide antibiotics and bile acids. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 4350–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.N. Ribosome-targeting antibiotics and mechanisms of bacterial resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgičević, I.; Mikulandra, I.; Bukvić, M.; Banjanac, M.; Habinovec, I.; Bertoša, B.; Novak, P. Discovery of Macrozones, new antimicrobial thiosemicarbazone-based azithromycin conjugates: Design, synthesis and in vitro biological evaluation. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukvić Krajačić, M.; Novak, P.; Cindrić, M.; Brajša, K.; Dumić, M.; Kujundžić, N. Azithromycin-sulfonamide conjugates as inhibitors of resistant Streptococcus pyogenes strains. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 42, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukvić Krajačić, M.; Novak, P.; Dumić, M.; Cindrić, M.; Čipčić Paljetak, H.; Kujundžić, N. Novel Ureas and Thioureas of 15-membered Azalides with Antibacterial Activities Against Key Respiratory Pathogens. Eur. J. Med. Chem 2009, 44, 3459–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukvić Krajačić, M.; Dumić, M.; Novak, P.; Cindrić, M.; Koštrun, S.; Fajdetić, A.; Alihodžić, S.; Brajša, K.; Kujundžić, N. Discovery of Novel Ureas and Thioureas of 3-Decladinosyl-3-hydroxy 15-Membered Azalides Active Against Efflux-mediated Resistant Streptococcus Pneumoniae. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.-Z.; Hiasa, H.; Lv, W.; Brody, S.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Aldrich, C.; Cushman, M.; Liang, J.-H. Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel 15-membered macrolides: Quinolone/quinoline-containing sidechains tethered to the C-6 position of azithromycin acylides. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 193, 112222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajdetić, A.; Vinter, A.; Čipčić Paljetak, H.; Padovan, J.; Jakopović, I.P.; Kapić, S.; Alihodžić, S.; Filić, D.; Modrić, M.; Košutić-Hulita, N.; et al. Synthesis, activity and pharmacokinetics of novel antibacterial 15-membered ring macrolones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 3388–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlović, D.; Mutak, S. Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of novel 4″-glycyl linked quinolyl-azithromycins with potent activity against macrolide-resistant pathogens. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Jiao, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Xian, R.; Zheng, M.; Lou, H. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of 4″,11-di-O-arylalkylcarbamoyl azithromycin derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Cao, J.; Liu, C.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, S. Novel C-4″ modified azithromycin analogs with remarkably enhanced activity against erythromycin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae: The synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 5196–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cong, C.; Chai, W.C.; Dong, R.; Jia, L.; Song, D.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, S. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel 400-O-(1-aralkyl-1,2,3-triazol-4-methylcarbamoyl) azithromycin analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3872–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tevyashova, A.N.; Korolev, A.M.; Mirchink, E.P.; Isakova, E.B.; Osterman, I.A. Synthesis and evaluation of biological activity of benzoxaborole derivatives of azithromycin. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tevyashova, A.N.; Bychkova, E.N.; Korolev, A.M.; Isakova, E.B.; Mirchink, E.P.; Osterman, I.A.; Erdei, R.; Szücs, Z.; Batta, G. Synthesis and evaluation of biological activity for dual-acting antibiotics on the basis of azithromycin and glycopeptides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janas, A.; Przybylski, P. 14- and 15-membered lactone macrolides and their analogues and hybrids: Structure, molecular mechanism of action and biological activity. Eur J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Handa, T.; Narayanam, M.; Sahu, A.; Junwal, M.; Shah, R.P. A critical review on the use of modern sophisticated hyphenated tools in the characterization of impurities and degradation products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 69, 148–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görög, S. Critical review of reports on impurity and degradation product profiling in the last decade. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 101, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godejohan, M. Characterization of a paracetamol metabolite using on-line LC-SPE-NMR-MS and a cryogenic NMR probe. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1058, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, C.; Jäger, A.K.; Staerk, D. Coupling of a high-resolution monoamine oxidase-A inhibitor assay and HPLC-SPE-NMR for advanced bioactivity profiling of plant extracts. Phytochem. Anal. 2013, 2, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, F.; Fan, J.; Pathirana, C.; Palaniswamy, V. Semi-preparative LC-SPE-cryoflow NMR for impurity identifications: Use of mother liquor as a better source of impurities. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2013, 51, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, S.; Seger, C. Liquid chromatography–nuclear magnetic resonance coupling as alternative to liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry hyphenations: Curious option or powerful and complementary routine tool? J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1259, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, P.; Tepeš, P.; Cindrić, M.; Ilijaš, M.; Dragojević, S.; Mihaljević, K. Combined use of liquid chromatography-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for the characterisation of an acarbose degradation product. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1033, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, P.; Tepeš, P.; Ilijaš, M.; Fistrić, I.; Bratoš, I.; Avdagić, A.; Gabelica Marković, V.; Dumić, M. LC-NMR and LC-MS identification of an impurity in a novel antifungal drug icofungipen. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, P.; Tepeš, P.; Fistrić, I.; Bratoš, I.; Gabelica, V. The Application of LC-NMR and LC-MS for the Separation and Rapid Structure elucidation of an Unknown Impurity in drug 5-Aminosalicylic Acid. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfender, J.L.; Querioz, E.F.; Hostettmann, K. Phytochemistry in the microgram domain—A LC-NMR perspective. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2005, 43, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnle, M.; Holtin, K.; Albert, K. Capillary NMR detection in separation science. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandvoss, M.; Bardsley, B.; Beck, T.L.; Lee-Smith, E.; North, S.E.; Moore, P.J.; Edwards, A.J.; Smith, R.J. HPLC-SPE-NMR in pharmaceutical developments: Capabilities and applications. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2005, 43, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harča, M.; Habinovec, I.; Meštrović, E.; Biljan, I.; Novak, P. Rapid Identification of Unknown Impurities in 3-Bromo-5-(trifluoromethyl)aniline by LC-SPE/NMR. Croat. Chem. Acta 2016, 89, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, M.; Wolfender, J.L.; Staerk, D.; Christensen, S.B.; Hostettmann, K.; Jaroszewski, J.W. Identification of Natural Products Using HPLC-SPE Combined with CapNMR. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seger, C.; Godejohann, M.; Spraul, M.; Stuppner, H.; Hadacek, F. Reaction product analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography-solid-phase extraction-nuclear magnetic resonance Application to the absolute configuration determination of naturally occurring polyyne alcohols. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1136, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.; Staerk, D.; Cornett, C.; Hansen, H.S.; Jaroszewski, J.W. Identification of reaction products between drug substances and excipients by HPLC–SPE–NMR: Ester and amide formation between citric acid and 5-aminosalicylic acid. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Habinovec, I.; Jednačak, T.; Novak, P. Rapid identification of bioactive carbohydrazide reaction products by an LC-DAD-SPE-NMR approach. ADMET DMPK 2015, 3, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, U.C. Detection and identification of hydrolysis products of sulfur mustards at trace levels in environmental samples using liquid chromatography solid phase extraction combined with off-line nuclear magnetic resonance analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1286, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Balhara, A.; Raju, N.; Kumar, B.K.; Sharma, P.; Singh, D.K.; Singh, S. Characterization of degradation products of celiprolol hydrochloride using hyphenated mass and NMR techniques. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 197, 113953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
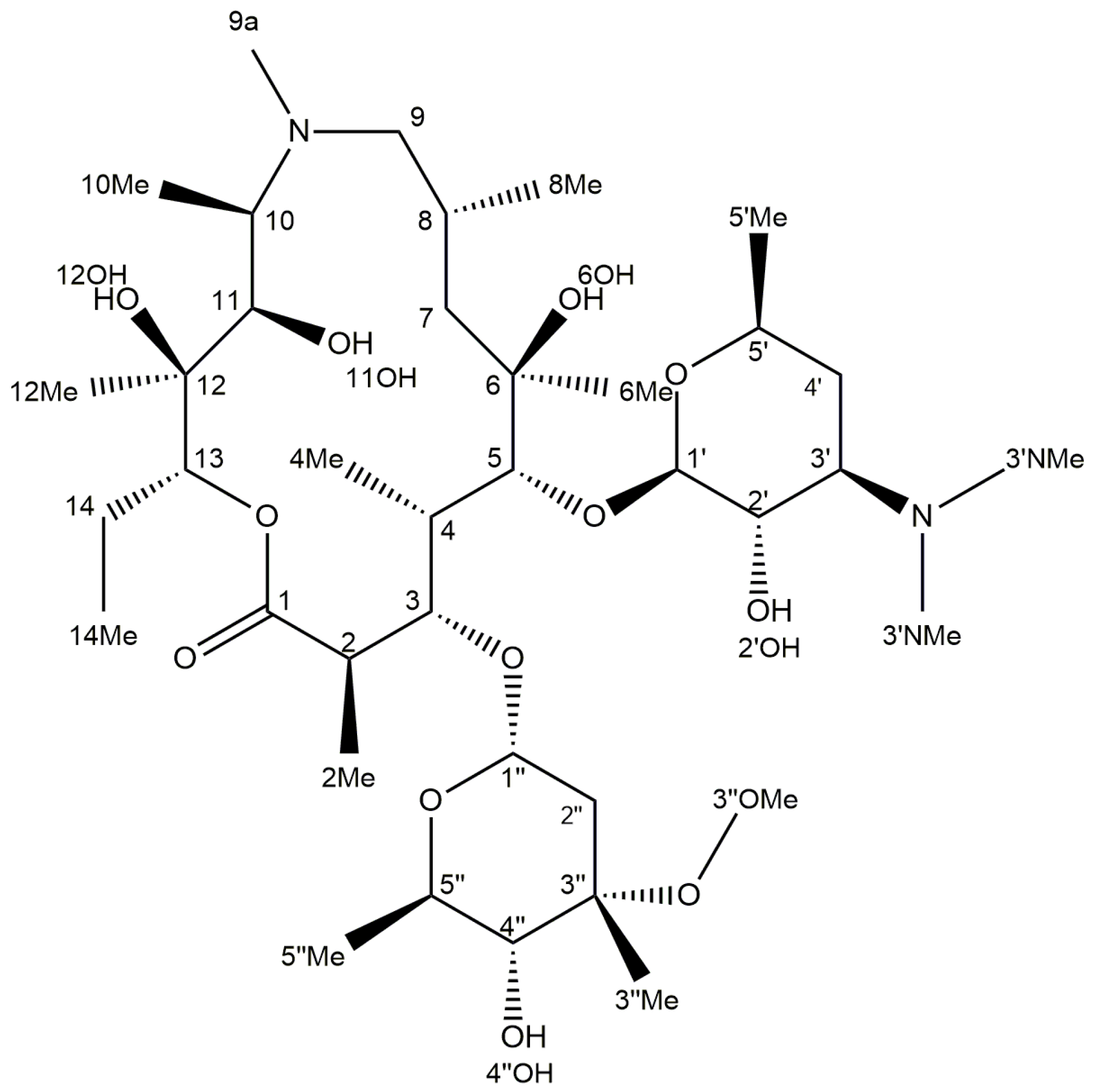
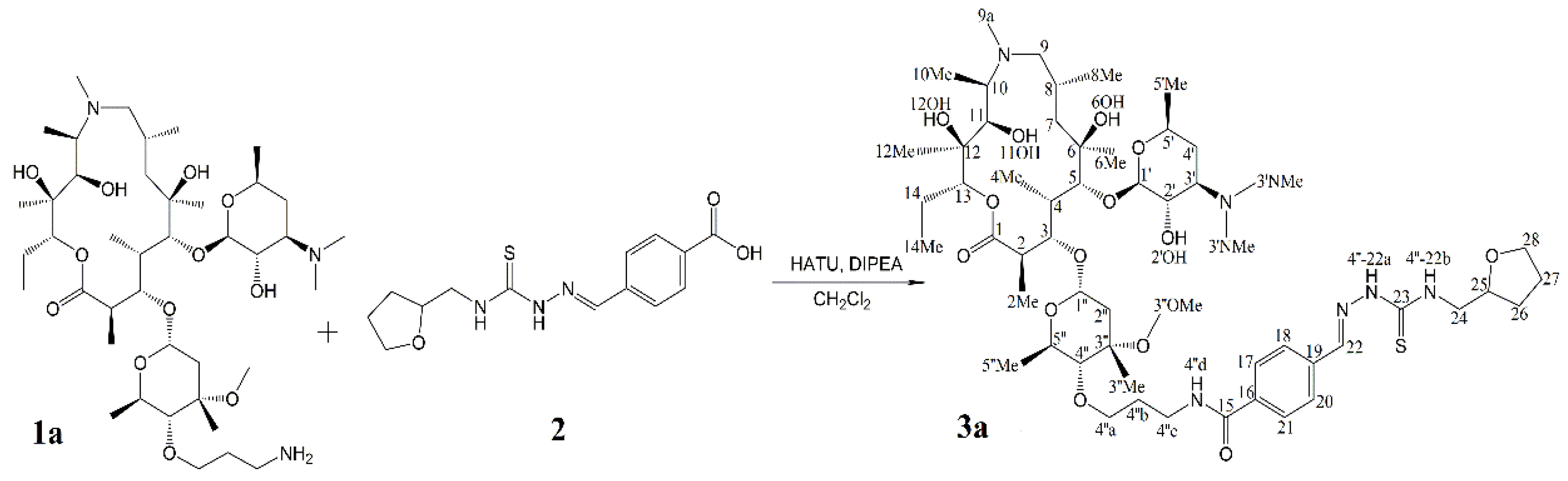
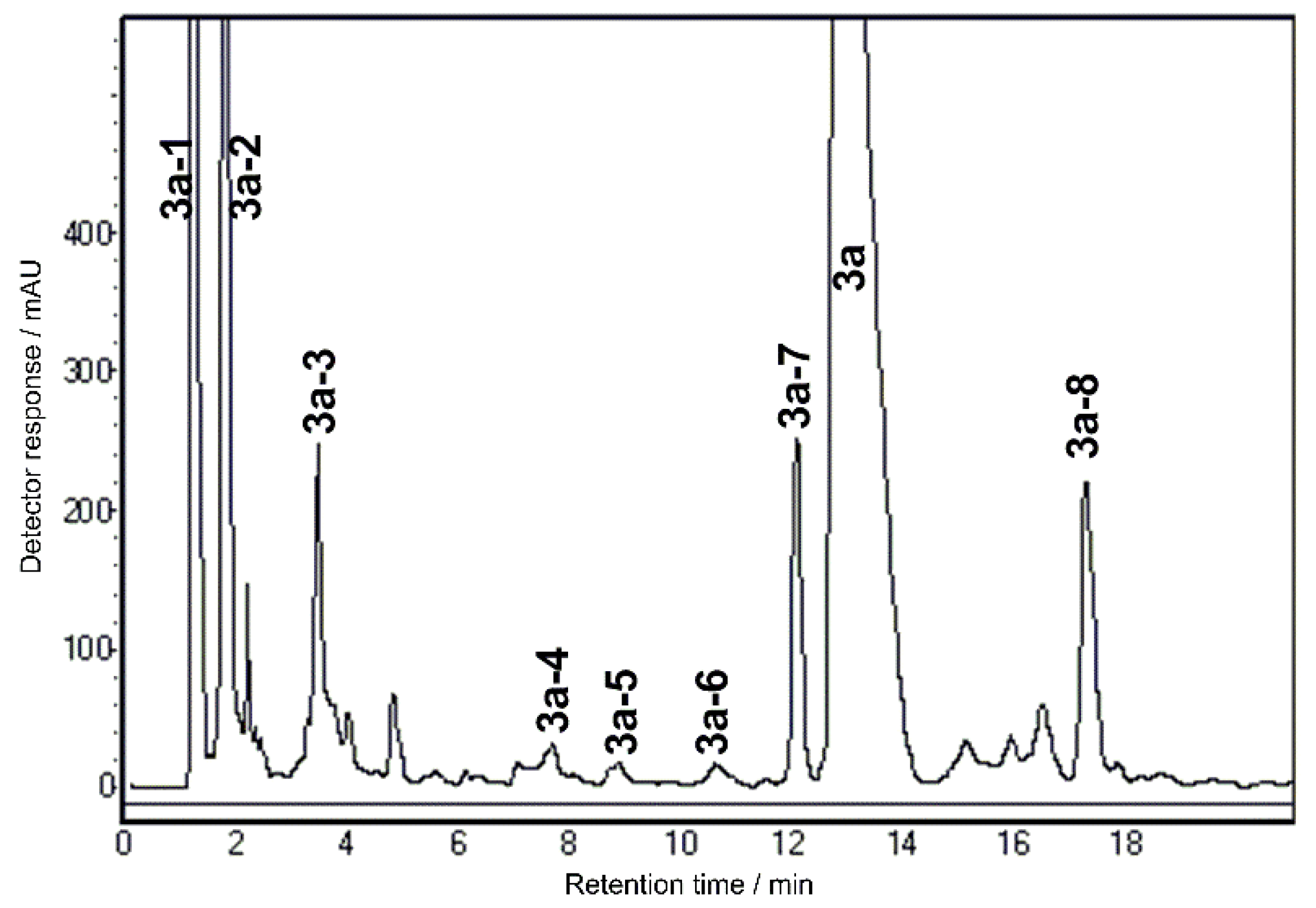
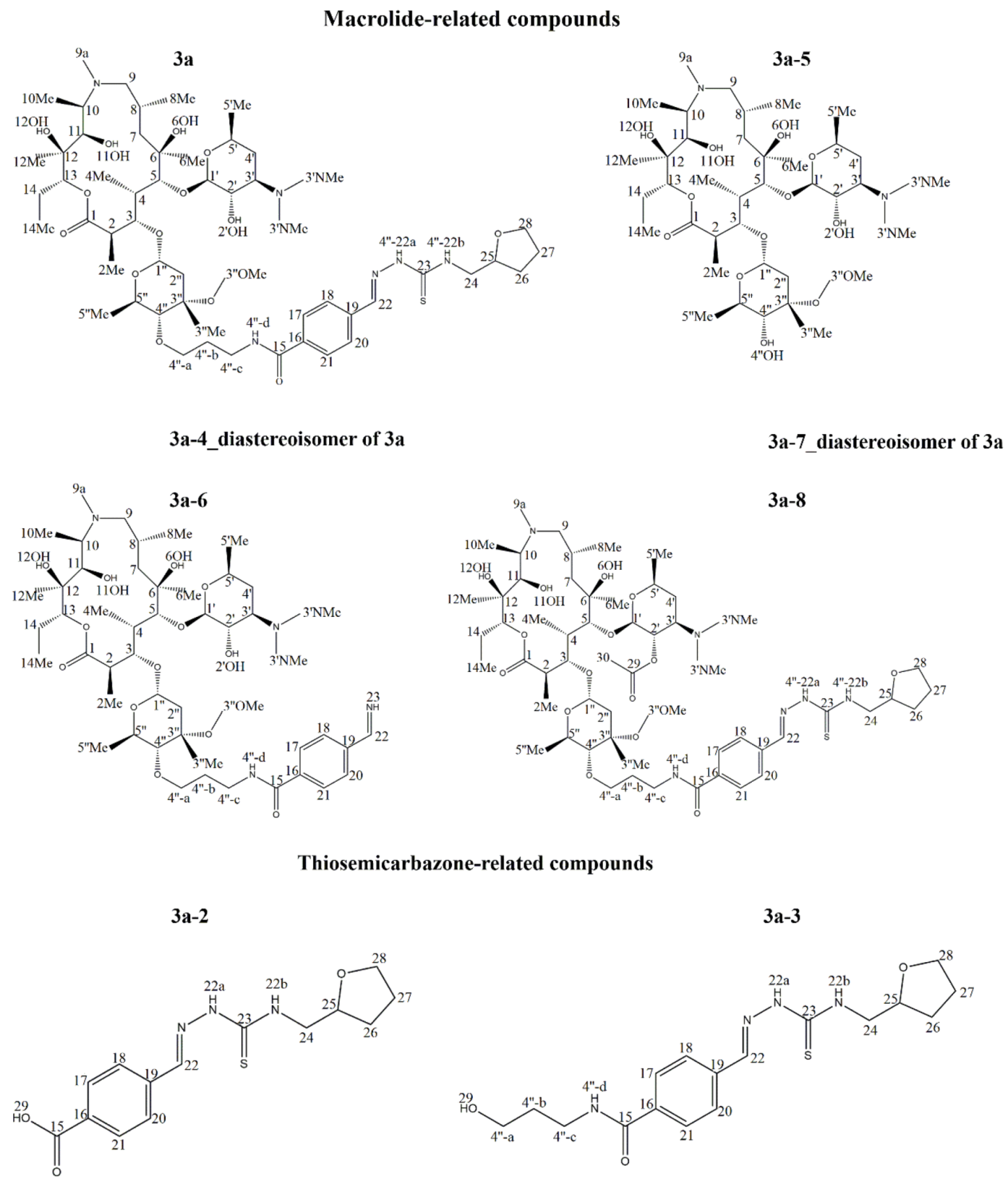
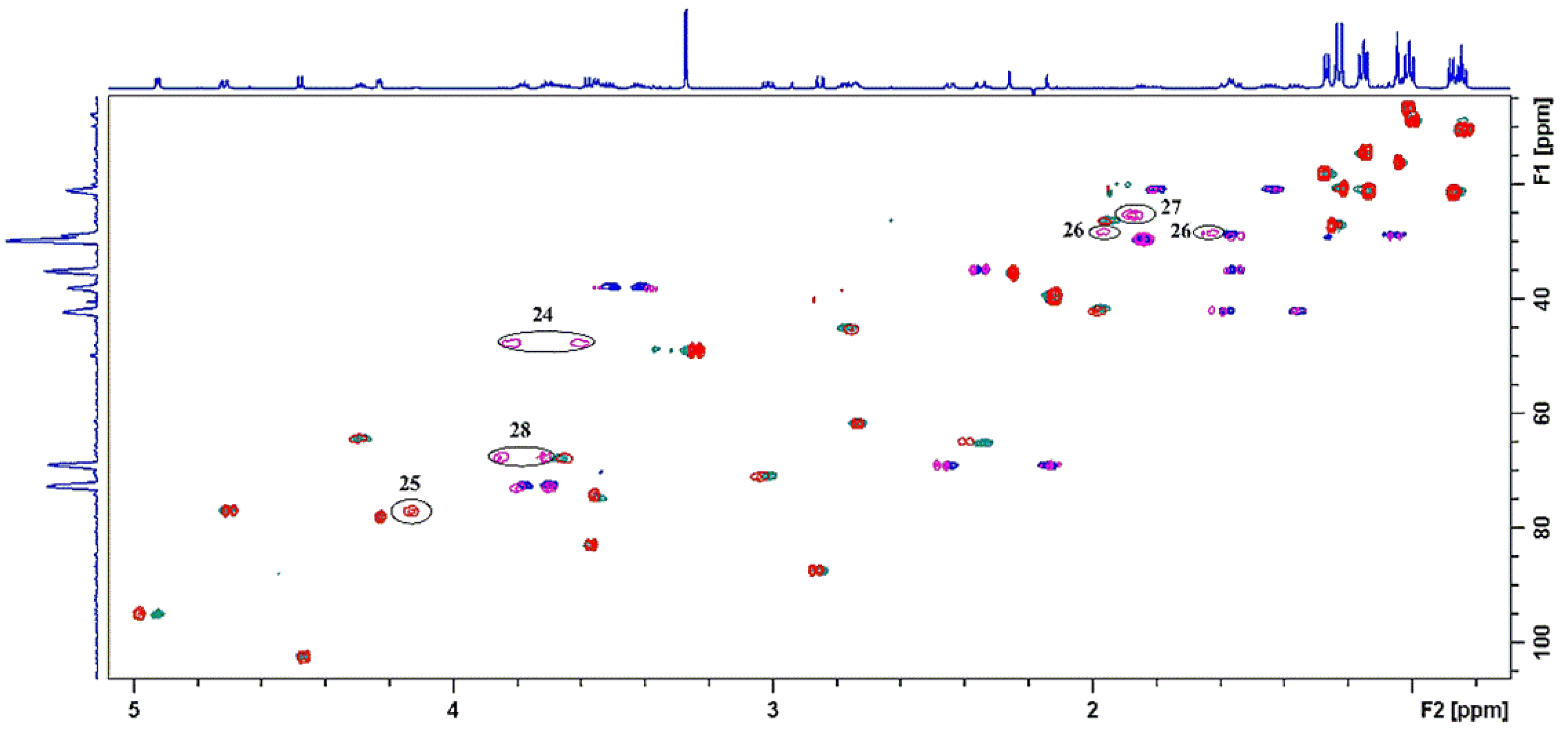
| Compound | 3a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atom | δ(1H)/ppm | δ(13C)/ppm | Atom | δ(1H)/ppm | δ(13C)/ppm |
| 1 | - | 178.98 | 22 | 7.97 | 141.6 |
| 2 | 2.76 | 45.3 | 4″-22a | -a | - |
| 2Me | 1.15 | 14.66 | 4″-22b | 8.00 | - |
| 3 | 4.23 | 78.15 | 23 | - | 178.03 |
| 4 | 1.99 | 42.1 | 24 | 3.83; 3.60 | 47.8 |
| 4Me | 1.00 | 8.99 | 25 | 4.14 | 77.1 |
| 5 | 3.57 | 83.1 | 26 | 1.97; 1.63 | 28.44 |
| 6 | - | 74.0 | 27 | 1.91 | 25.34 |
| 6Me | 1.26 | 27.27 | 28 | 3.86; 3.72 | 67.6 |
| 6OH | -a | - | 1′ | 4.47 | 102.6 |
| 7eq; 7ax | 1.61; 1.37 | 42.1 | 2′ | 3.05 | 71.1 |
| 8 | 1.98 | 26.4 | 2′OH | -a | - |
| 8Me | 0.87 | 21.51 | 3′ | 2.40 | 65.14 |
| 9eq; 9ax | 2.48; 2.14 | 69.12 | 3′NMe2 | 2.12 | 39.7 |
| 9a-N | 2.25 | 35.6 | 4′eq; 4′ax | 1.55; 1.07 | 29.13 |
| 10 | 2.76 | 62.1 | 5′ | 3.66 | 67.9 |
| 10Me | 1.02 | 6.55 | 5′Me | 1.14 | 21.24 |
| 11 | 3.66 | 67.9 | 1″ | 4.98 | 95.1 |
| 11OH | -a | - | 2″eq; 2″ax | 2.34; 1.56 | 34.9 |
| 12 | - | 74.4 | 3″ | - | 73.3 |
| 12Me | 1.05 | 16.13 | 3″Me | 1.21 | 20.92 |
| 12OH | -a | - | 3″OMe | 3.26 | 49.2 |
| 13 | 4.70 | 77.2 | 4″ | 2.87 | 87.5 |
| 14eq; 14ax | 1.82; 1.44 | 21.0 | 4″-a | 3.85; 3.73 | 73.5 |
| 14Me | 0.84 | 10.65 | 4″-b | 1.84 | 29.6 |
| 15 | - | 166.02 | 4″-c | 3.55; 3.41 | 38.2 |
| 16 | - | 135.74 | 4″-d | 7.50 | - |
| 17; 21 | 7.85 | 127.53 | 5″ | 4.30 | 64.4 |
| 18; 20 | 7.81 | 127.24 | 5″Me | 1.28 | 18.18 |
| 19 | - | 136.75 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habinovec, I.; Mikulandra, I.; Sekula, L.E.; Gašperov, J.; Kazazić, S.; Novak, P. Rapid Structure Determination of Bioactive 4″-Tetrahydrofurfuryl Macrozone Reaction Mixture Components by LC-SPE/Cryo NMR and MS. Molecules 2021, 26, 6316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26206316
Habinovec I, Mikulandra I, Sekula LE, Gašperov J, Kazazić S, Novak P. Rapid Structure Determination of Bioactive 4″-Tetrahydrofurfuryl Macrozone Reaction Mixture Components by LC-SPE/Cryo NMR and MS. Molecules. 2021; 26(20):6316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26206316
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabinovec, Iva, Ivana Mikulandra, Lucia Ema Sekula, Jana Gašperov, Saša Kazazić, and Predrag Novak. 2021. "Rapid Structure Determination of Bioactive 4″-Tetrahydrofurfuryl Macrozone Reaction Mixture Components by LC-SPE/Cryo NMR and MS" Molecules 26, no. 20: 6316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26206316
APA StyleHabinovec, I., Mikulandra, I., Sekula, L. E., Gašperov, J., Kazazić, S., & Novak, P. (2021). Rapid Structure Determination of Bioactive 4″-Tetrahydrofurfuryl Macrozone Reaction Mixture Components by LC-SPE/Cryo NMR and MS. Molecules, 26(20), 6316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26206316






