Overexpression of the Gene Encoding Neurosecretory Protein GL Precursor Prevents Excessive Fat Accumulation in the Adipose Tissue of Mice Fed a Long-Term High-Fat Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
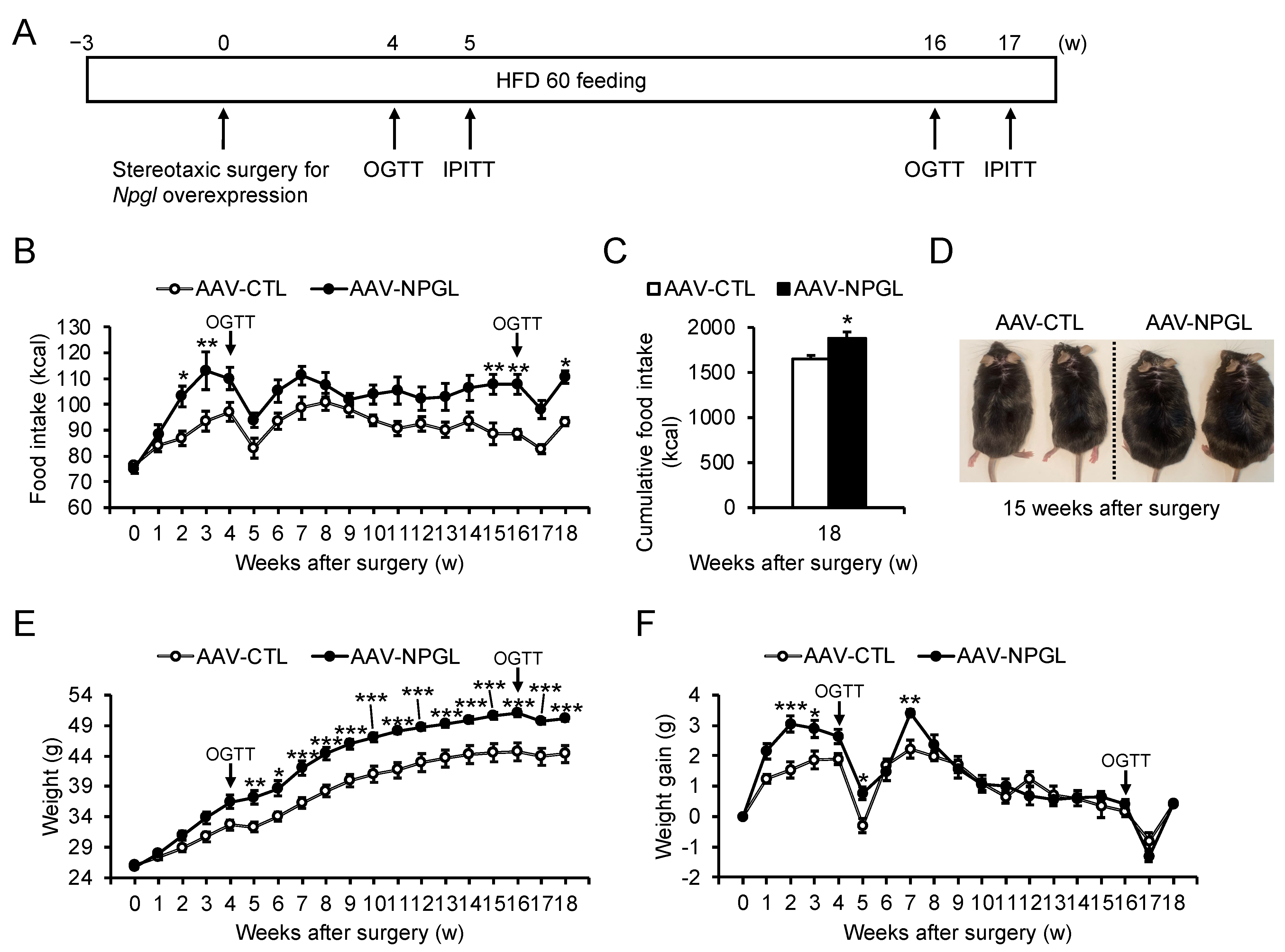
2.1. Food Intake and Weight
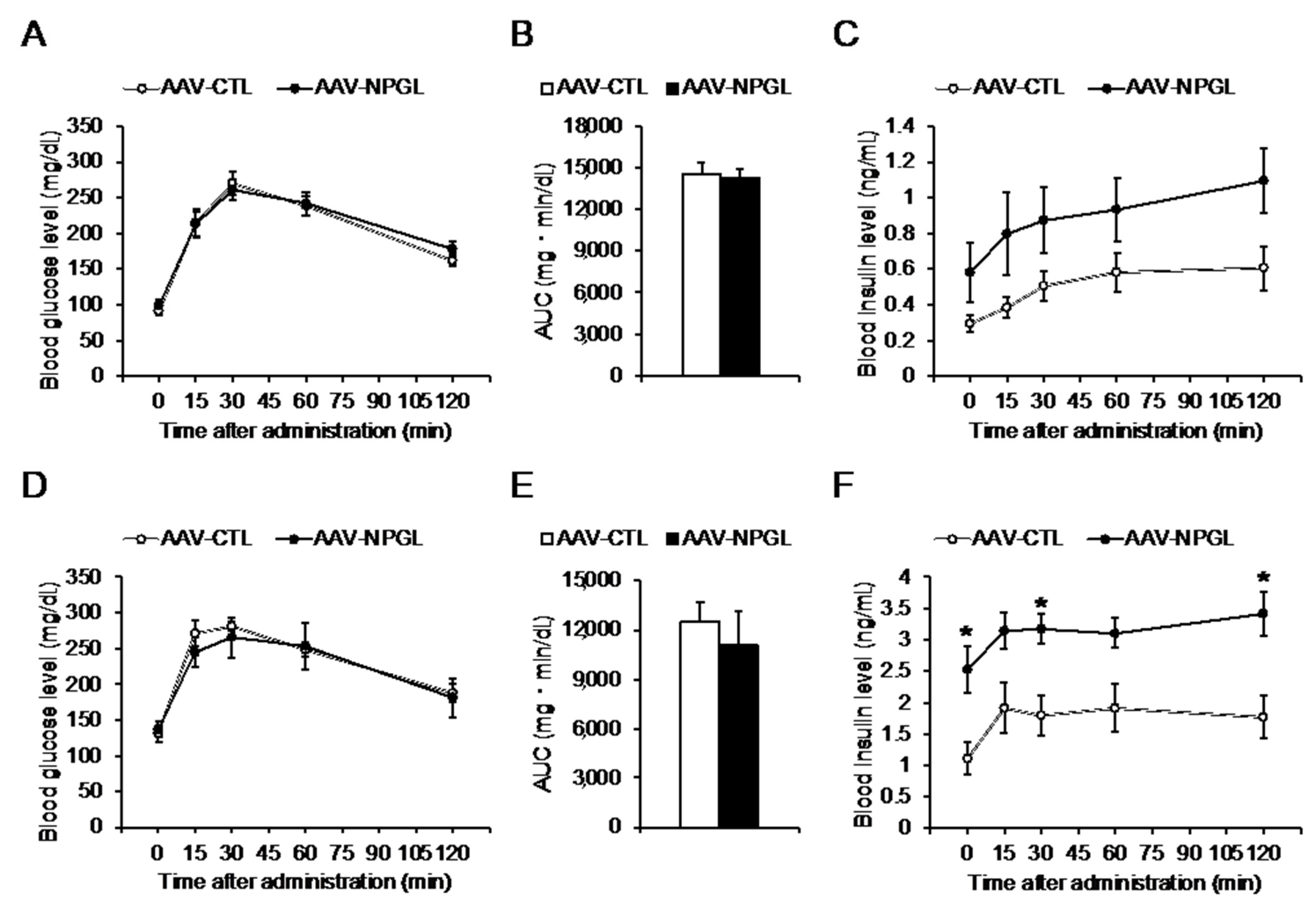
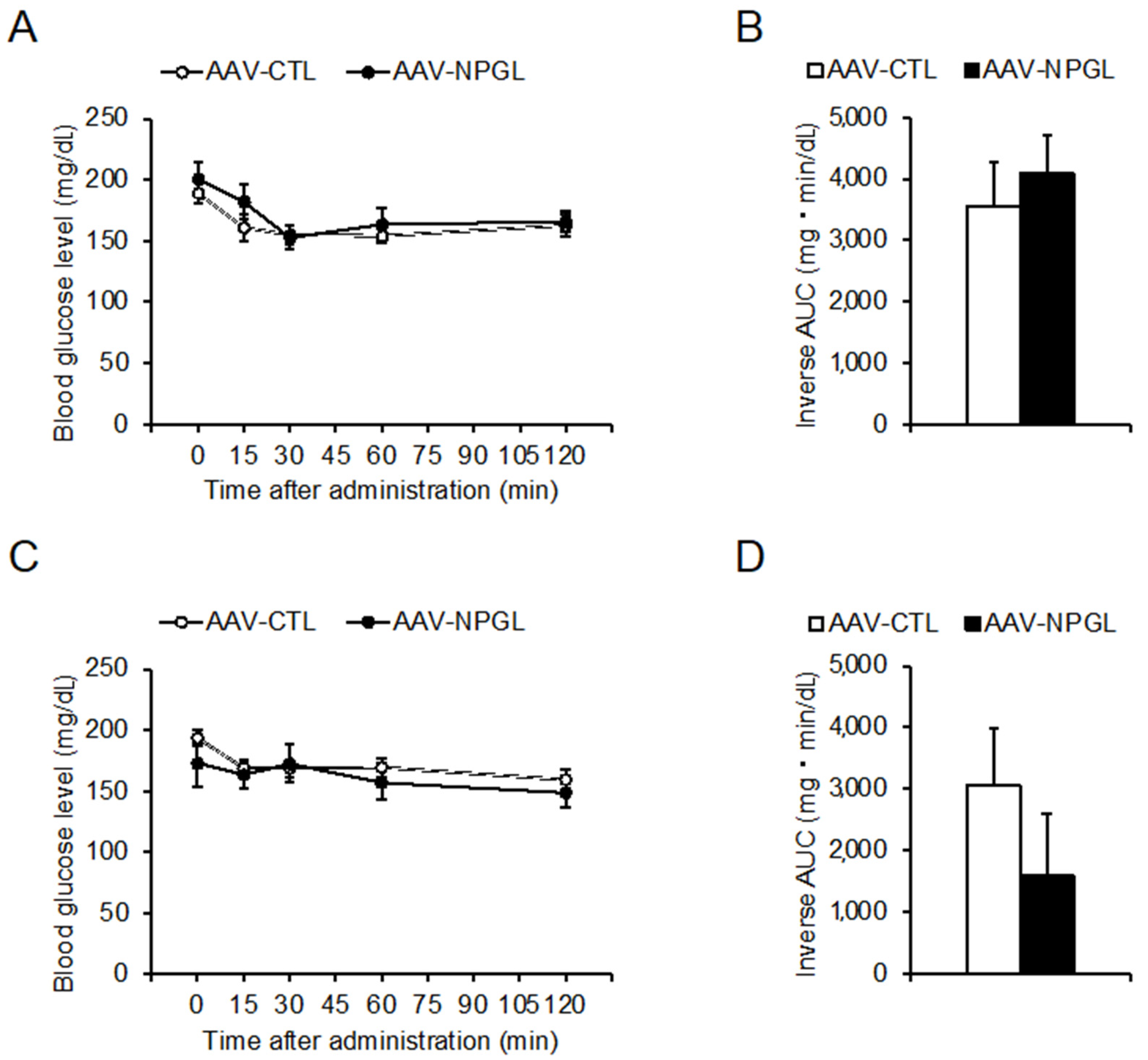
2.2. Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Sensitivity
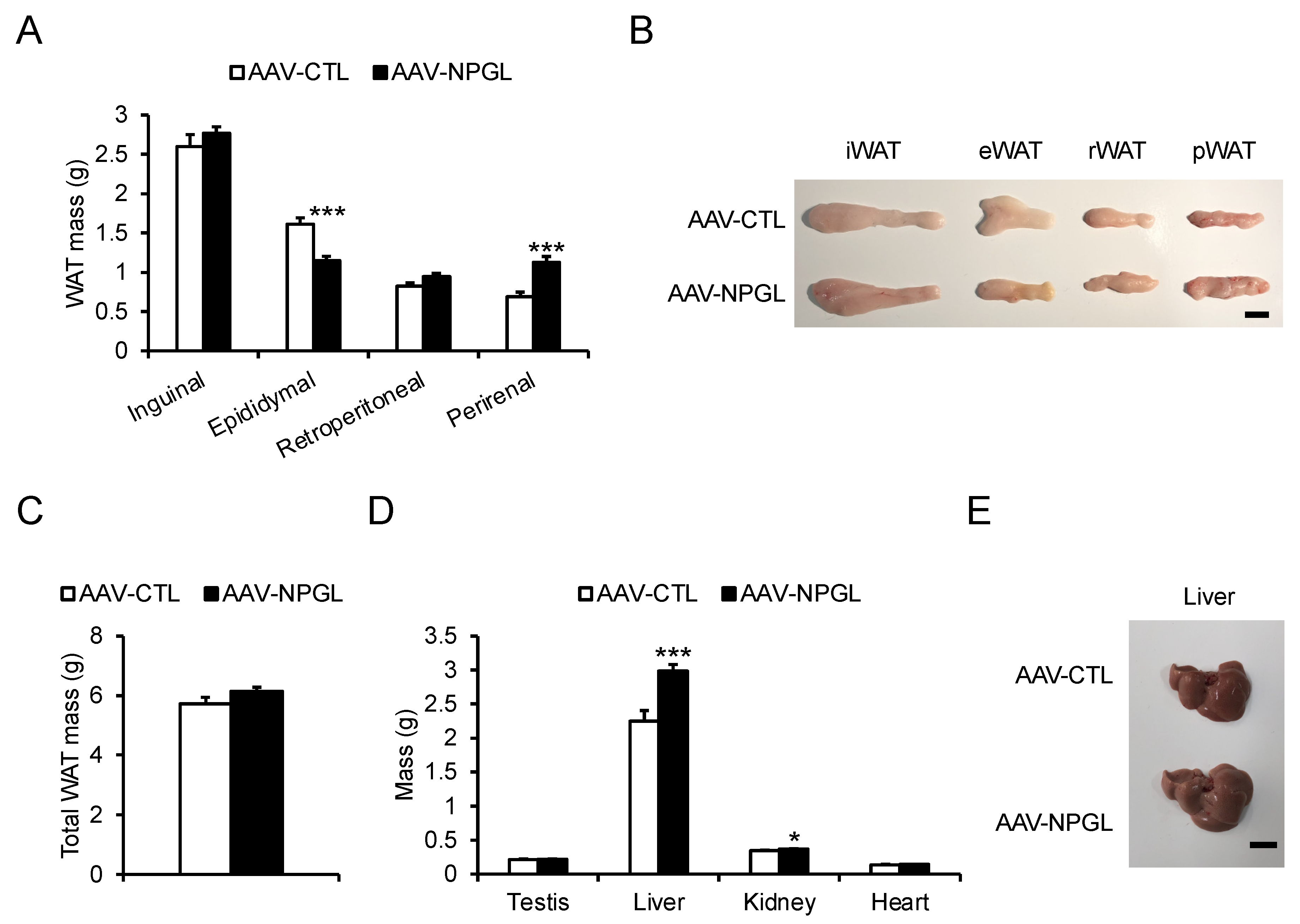
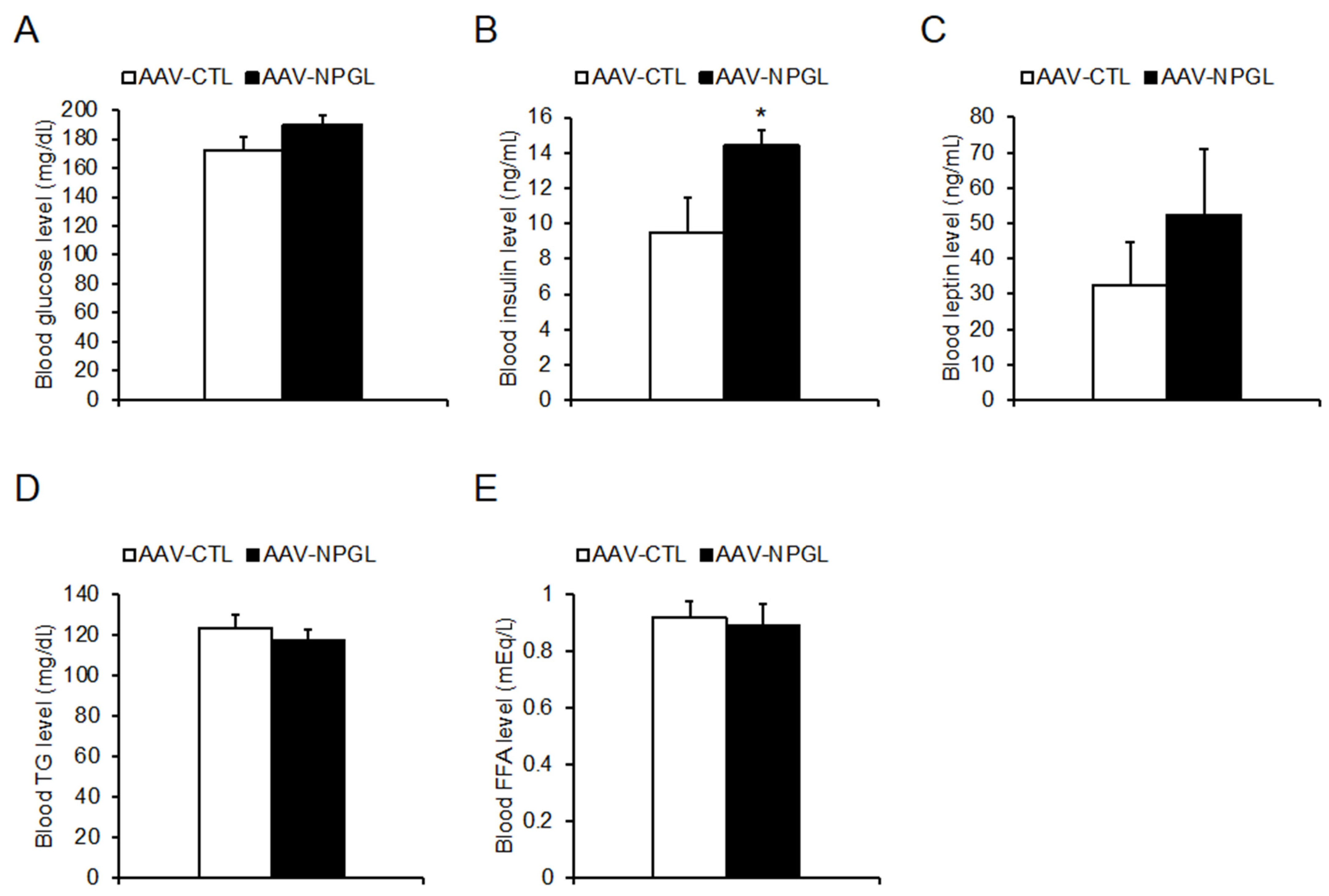
2.3. Tissue and Organ Mass and Blood Biomarkers
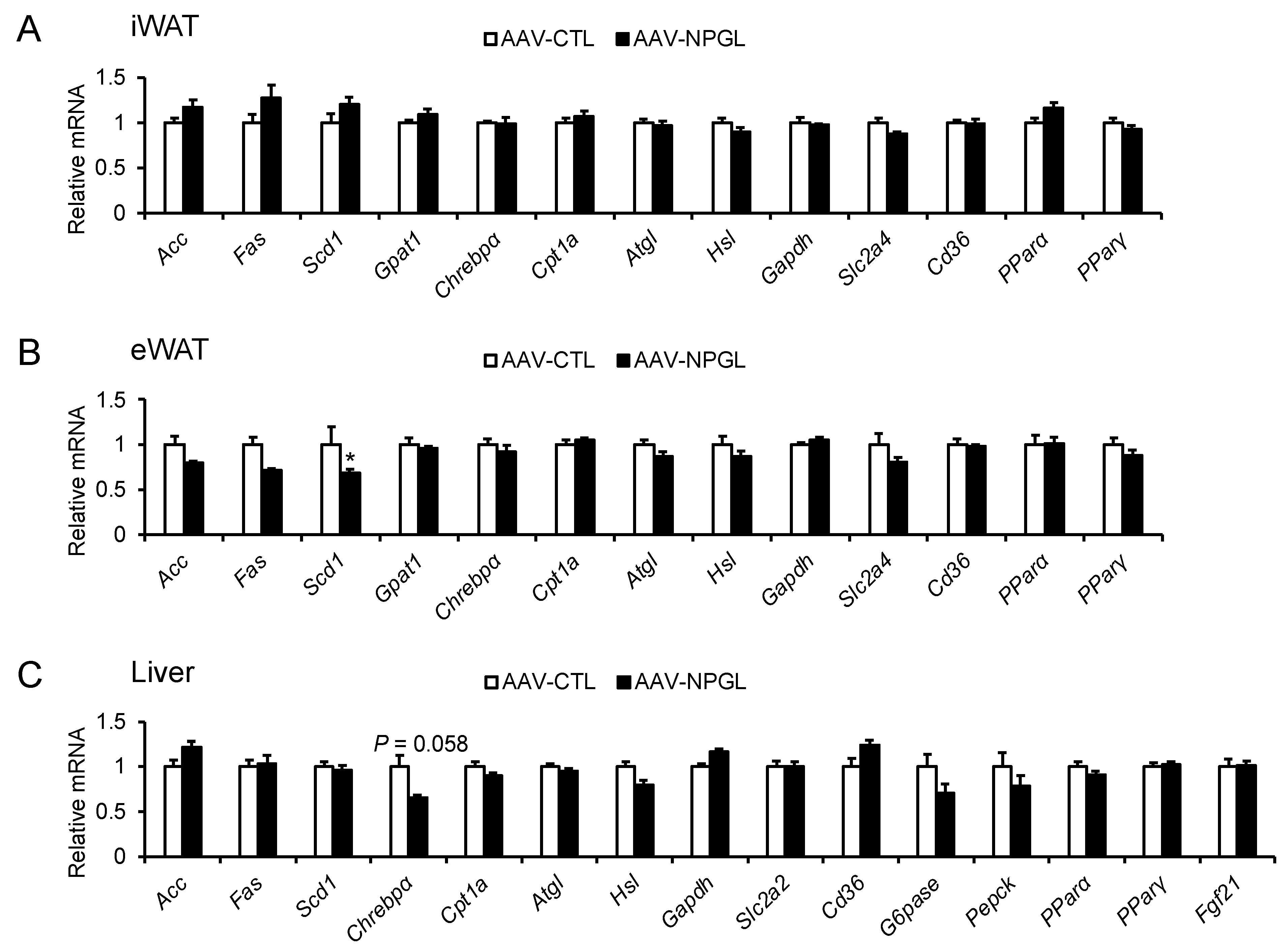
2.4. mRNA Expression of Neuropeptide Genes and Genes Regulating Lipid Metabolism
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Production of AAV-Based Vectors
4.3. Stereotaxic Surgery
4.4. OGTT and IPITT
4.5. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.6. Blood Biomarker Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Haslam, D.W.; James, W.P.T. Obesity. Lancet 2005, 366, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, A.; Hu, F.B. The epidemiology of obesity: A big picture. Pharmacoeconomics 2015, 33, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Bouchard, C. Convergence between biological, behavioural and genetic determinants of obesity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolarczyk, E. Adipose tissue inflammation in obesity: A metabolic or immune response? Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 37, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olefsky, J.M.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.W.; Porte, D. Diabetes, obesity, and the brain. Science 2005, 307, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, G.J.; Cummings, D.E.; Baskin, D.G.; Barsh, G.S.; Schwartz, M.W. Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature 2006, 443, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, G.J.; Meek, T.H.; Schwartz, M.W. Neurobiology of food intake in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macia, L.; Yulyaningsih, E.; Pangon, L.; Nguyen, A.D.; Lin, S.; Shi, Y.C.; Zhang, L.; Bijker, M.; Grey, S.; Mackay, F.; et al. Neuropeptide Y1 receptor in immune cells regulates inflammation and insulin resistance associated with diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 2012, 61, 3228–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamegai, J.; Tamura, H.; Shimizu, T.; Ishii, S.; Sugihara, H.; Wakabayashi, I. Chronic central infusion of ghrelin increases hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and agouti-related protein mRNA levels and body weight in rats. Diabetes 2001, 51, 2438–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakazato, M.; Murakami, N.; Date, Y.; Kojima, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K.; Matsukura, S. A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 2001, 409, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, M.A.; Smith, R.G.; Diano, S.; Tschöp, M.; Pronchuk, N.; Grove, K.L.; Strasburger, C.J.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Esterman, M.; Heiman, M.L.; et al. The distribution and mechanism of action of ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron 2003, 37, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cowley, M.A.; Smart, J.L.; Rubinstein, M.; Cerdán, M.G.; Diano, S.; Horvath, T.L.; Cone, R.D.; Low, M.J. Leptin activates anorexigenic POMC neurons through a neural network in the arcuate nucleus. Nature 2001, 411, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vong, L.; Ye, C.; Yang, Z.; Choi, B.; Chua, S.; Lowell, B.B. Leptin action on GABAergic neurons prevents obesity and reduces inhibitory tone to POMC neurons. Neuron 2011, 71, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitani, M.; Asakawa, A.; Amitani, H.; Inui, A. The role of leptin in the control of insulin-glucose axis. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castañeda, T.R.; Tong, J.; Datta, R.; Culler, M.; Tschöp, M.H. Ghrelin in the regulation of body weight and metabolism. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2010, 31, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, L.; Wunderlich, F.T.; Seibler, J.; Könner, A.C.; Hampel, B.; Irlenbusch, S.; Brabant, G.; Kahn, C.R.; Schwenk, F.; Brüning, J.C. Central insulin action regulates peripheral glucose and fat metabolism in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2132–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of insulin action and insulin resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ukena, K.; Iwakoshi-Ukena, E.; Taniuchi, S.; Bessho, Y.; Maejima, S.; Masuda, K.; Shikano, K.; Kondo, K.; Furumitsu, M.; Tachibana, T. Identification of a cDNA encoding a novel small secretory protein, neurosecretory protein GL, in the chicken hypothalamic infundibulum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 446, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukena, K. Avian and murine neurosecretory protein GL participates in the regulation of feeding and energy metabolism. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 260, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, D.; Shikano, K.; Saito, T.; Iwakoshi-Ukena, E.; Furumitsu, M.; Ochi, Y.; Sato, M.; Bentley, G.E.; Kriegsfeld, L.J.; Ukena, K. Neurosecretory protein GL, a hypothalamic small secretory protein, participates in energy homeostasis in male mice. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakoshi-Ukena, E.; Shikano, K.; Kondo, K.; Taniuchi, S.; Furumitsu, M.; Ochi, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Okamoto, S.; Bentley, G.E.; Kriegsfeld, L.J.; et al. Neurosecretory protein GL stimulates food intake, de novo lipogenesis, and onset of obesity. eLife 2017, 6, e28527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shikano, K.; Kato, M.; Iwakoshi-Ukena, E.; Furumitsu, M.; Matsuura, D.; Masuda, K.; Tachibana, T.; Bentley, G.E.; Kriegsfeld, L.J.; Ukena, K. Effects of chronic intracerebroventricular infusion of neurosecretory protein GL on body mass and food and water intake in chicks. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 256, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikano, K.; Iwakoshi-Ukena, E.; Kato, M.; Furumitsu, M.; Bentley, G.E.; Kriegsfeld, L.J.; Ukena, K. Neurosecretory protein GL induces fat accumulation in chicks. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikano, K.; Iwakoshi-Ukena, E.; Saito, T.; Narimatsu, Y.; Kadota, A.; Furumitsu, M.; Bentley, G.E.; Kriegsfeld, L.J.; Ukena, K. Neurosecretory protein GL induces fat accumulation in mice. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 244, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumura, K.; Shikano, K.; Narimatsu, Y.; Iwakoshi-Ukena, E.; Furumitsu, M.; Naito, M.; Ukena, K. Effects of neurosecretory protein GL on food intake and fat accumulation under different dietary nutrient compositions in rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2021, 85, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumura, K.; Narimatsu, Y.; Moriwaki, S.; Iwakoshi-Ukena, E.; Furumitsu, M.; Ukena, K. Effects of overexpression of neurosecretory protein GL-precursor gene on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthoud, H.R.; Morrison, C. The brain, appetite, and obesity. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2008, 59, 55–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andermann, M.L.; Lowell, B.B. Toward a wiring diagram understanding of appetite control. Neuron 2017, 95, 757–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, T.C.; Pinheiro, D.; Caldeira, M.; Castro, M.M.; Geraldes, C.F.; López-Larrubia, P.; Cerdán, S.; Jones, J.G. Sources of hepatic triglyceride accumulation during high-fat feeding in the healthy rat. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, J.A.; Carvalho, F.; Pearson, M.; Horton, J.D.; Browning, J.D.; Jones, J.G.; Burgess, S.C. A high-fat diet suppresses de novo lipogenesis and desaturation but not elongation and triglyceride synthesis in mice. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2541–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdul-Wahed, A.; Guilmeau, S.; Postic, C. Sweet sixteenth for ChREBP: Established roles and future goals. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 324–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentin, R.; Benhamed, F.; Pégorier, J.P.; Foufelle, F.; Viollet, B.; Vaulont, S.; Girard, J.; Postic, C. Polyunsaturated fatty acids suppress glycolytic and lipogenic genes through the inhibition of ChREBP nuclear protein translocation. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2843–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Youngstrom, T.G.; Bartness, T.J. Catecholaminergic innervation of white adipose tissue in Siberian hamsters. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1995, 268, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamshad, M.; Aoki, V.T.; Adkison, M.G.; Warren, W.S.; Bartness, T.J. Central nervous system origins of the sympathetic nervous system outflow to white adipose tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1998, 275, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartness, T.J.; Song, C.K. Brain-adipose tissue neural crosstalk. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 91, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartness, T.J.; Shrestha, Y.B.; Vaughan, C.H.; Schwartz, G.J.; Song, C.K. Sensory and sympathetic nervous system control of white adipose tissue lipolysis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 318, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bowers, R.R.; Festuccia, W.T.L.; Song, C.K.; Shi, H.; Migliorini, R.H.; Bartness, T.J. Sympathetic innervation of white adipose tissue and its regulation of fat cell number. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 286, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, A.; Richard, D. Neuronal systems and circuits involved in the control of food intake and adaptive thermogenesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1391, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lieu, L.; Chau, D.; Afrin, S.; Dong, Y.; Alhadeff, A.L.; Betley, J.N.; Williams, K.W. Effects of metabolic state on the regulation of melanocortin circuits. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 224, 113039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baver, S.B.; Hope, K.; Guyot, S.; Bjørbaek, C.; Kaczorowski, C.; O’Connell, K.M.S. Leptin modulates the intrinsic excitability of AgRP/NPY neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 5486–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastard, J.P.; Maachi, M.; Lagathu, C.; Kim, M.J.; Caron, M.; Vidal, H.; Capeau, J.; Feve, B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2006, 17, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, D.; Yuan, M.; Frantz, D.F.; Melendez, P.A.; Hansen, L.; Lee, J.; Shoelson, S.E. Local and systemic insulin resistance resulting from hepatic activation of IKK-β and NF-κB. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Okamoto, S.; Shiuchi, T.; Toda, C.; Takagi, K.; Sato, T.; Saito, K.; Yokota, S.; Minokoshi, Y. Sympathetic nerve activity maintains an anti-inflammatory state in adipose tissue in male mice by inhibiting TNF-α gene expression in macrophages. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 3680–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seino, Y.; Fukushima, M.; Yabe, D. GIP and GLP-1, the two incretin hormones: Similarities and differences. J. Diabetes Investig. 2010, 1, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, G.I.; Santerre, R.F.; Mullenbach, G.T. Hamster preproglucagon contains the sequence of glucagon and two related peptides. Nature 1983, 302, 716–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, W.E.; Siegel, E.G.; Creutzfeldt, W. Glucagon-like peptide-1 but not glucagon-like peptide-2 stimulates insulin release from isolated rat pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Nakae, J.; Watanabe, N.; Kikuchi, T.; Tateya, S.; Tamori, Y.; Kaneko, M.; Abe, T.; Onodera, M.; Itoh, H. Colonic pro-inflammatory macrophages cause insulin resistance in an intestinal Ccl2/Ccr2-dependent manner. Cell. Metab. 2016, 24, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salinero, A.E.; Anderson, B.M.; Zuloaga, K.L. Sex differences in the metabolic effects of diet-induced obesity vary by age of onset. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1088–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narimatsu, Y.; Iwakoshi-Ukena, E.; Fukumura, K.; Shikano, K.; Furumitsu, M.; Morishita, M.; Bentley, G.E.; Kriegsfeld, L.J.; Ukena, K. Hypothalamic overexpression of neurosecretory protein GL leads to obesity in male C57BL/6J mice. Neuroendocrinology 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, C.; Einwallner, E. Study of in vivo glucose metabolism in high-fat diet-fed mice using oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and insulin tolerance test (ITT). J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 131, 56672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, K.B.J.; Paxinos, G. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
| Gene | Sense Primer (5′ to 3′) | Antisense Primer (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Npgl | TATGTAGACTGTGTCCTCTC | TCTAAGGAGCTGAGAATATGCA |
| Npy | TATCTCTGCTCGTGTGTTTG | GATTGATGTAGTGTCGCAGA |
| Agrp | TGTTCCCAGAGTTCCCAGGTC | GCATTGAAGAAGCGGCAGTAGCAC |
| Pomc | AGCTGCCTTTCCGCGACA | ATCTATGGAGGTCTGAAGCA |
| Acc | TCCGCACTGACTGTAACCACAT | TGCTCCGCACAGATTCTTCA |
| Fas | AGGGGTCGACCTGGTCCTCA | GCCATGCCCAGAGGGTGGTT |
| Scd1 | CTGTACGGGATCATACTGGTTC | GCCGTGCCTTGTAAGTTCTG |
| Gpat1 | TCATCCAGTATGGCATTCTCACA | GCAAGGCCAGGACTGACATC |
| Chrebpα | CGACACTCACCCACCTCTTC | TTGTTCAGCCGGATCTTGTC |
| Cpt1a | CCTGGGCATGATTGCAAAG | GGACGCCACTCACGATGTT |
| Atgl | AACACCAGCATCCAGTTCAA | GGTTCAGTAGGCCATTCCTC |
| Hsl | GCTGGGCTGTCAAGCACTGT | GTAACTGGGTAGGCTGCCAT |
| Gapdh | AAGGTCATCCCAGAGCTGAA | CTGCTTCACCACCTTCTTGA |
| Slc2a4 | GTAACTTCATTGTCGGCATGG | AGCTGAGATCTGGTCAAACG |
| Cd36 | TCCTCTGACATTTGCAGGTCTATC | AAAGGCATTGGCTGGAAGAA |
| Pparα | TCGAATATGTGGGGACAAGG | GACAGGCACTTGTGAAAACG |
| Pparγ | GCCCTTTGGTGACTTTATGGA | GCAGCAGGTTGTCTTGGATG |
| G6pase | ACTGTGGGCATCAATCTCCTC | CGGGACAGACAGACGTTCAGC |
| Pepck | GTGCTGGAGTGGATGTTCGG | CTGGCTGATTCTCTGTTTCAGG |
| Slc2a2 | GGCTAATTTCAGGACTGGTT | TTTCTTTGCCCTGACTTCCT |
| Fgf21 | CCTCTAGGTTTCTTTGCCAACAG | AAGCTGCAGGCCTCAGGAT |
| Actb | GGCACCACACCTTCTACAAT | AGGTCTCAAACATGATCTGG |
| Rps18 | CCTGAGAAGTTCCAGCACAT | TTCTCCAGCCCTCTTGGTG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukumura, K.; Narimatsu, Y.; Moriwaki, S.; Iwakoshi-Ukena, E.; Furumitsu, M.; Ukena, K. Overexpression of the Gene Encoding Neurosecretory Protein GL Precursor Prevents Excessive Fat Accumulation in the Adipose Tissue of Mice Fed a Long-Term High-Fat Diet. Molecules 2021, 26, 6006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26196006
Fukumura K, Narimatsu Y, Moriwaki S, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Furumitsu M, Ukena K. Overexpression of the Gene Encoding Neurosecretory Protein GL Precursor Prevents Excessive Fat Accumulation in the Adipose Tissue of Mice Fed a Long-Term High-Fat Diet. Molecules. 2021; 26(19):6006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26196006
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukumura, Keisuke, Yuki Narimatsu, Shogo Moriwaki, Eiko Iwakoshi-Ukena, Megumi Furumitsu, and Kazuyoshi Ukena. 2021. "Overexpression of the Gene Encoding Neurosecretory Protein GL Precursor Prevents Excessive Fat Accumulation in the Adipose Tissue of Mice Fed a Long-Term High-Fat Diet" Molecules 26, no. 19: 6006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26196006
APA StyleFukumura, K., Narimatsu, Y., Moriwaki, S., Iwakoshi-Ukena, E., Furumitsu, M., & Ukena, K. (2021). Overexpression of the Gene Encoding Neurosecretory Protein GL Precursor Prevents Excessive Fat Accumulation in the Adipose Tissue of Mice Fed a Long-Term High-Fat Diet. Molecules, 26(19), 6006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26196006






