A New Synthetic Methodology in the Preparation of Bimetallic Chalcogenide Clusters via Cluster-to-Cluster Transformations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthetic Strategy
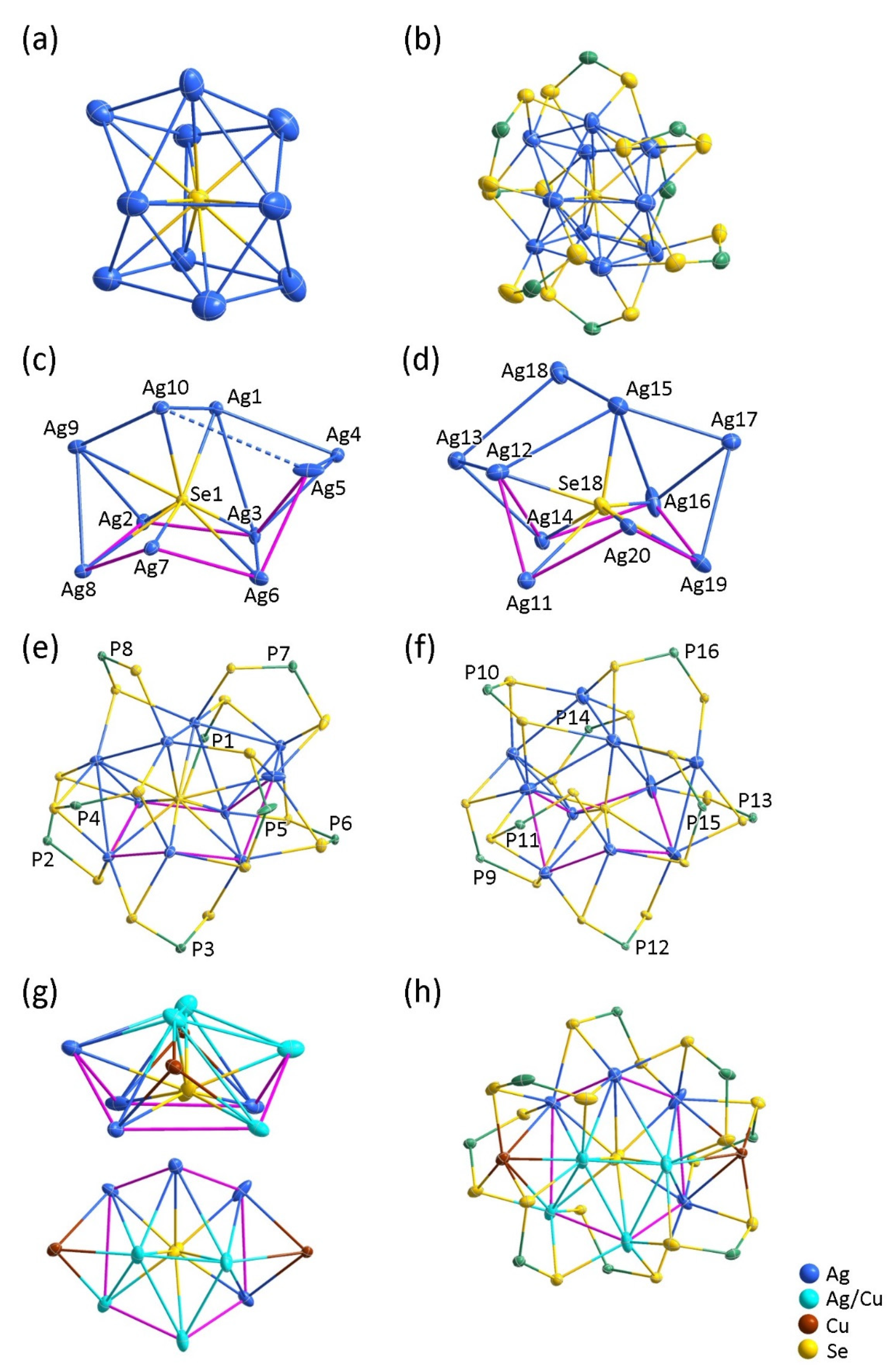
2.2. Structural Analyses
2.3. ESI Mass Spectroscopy
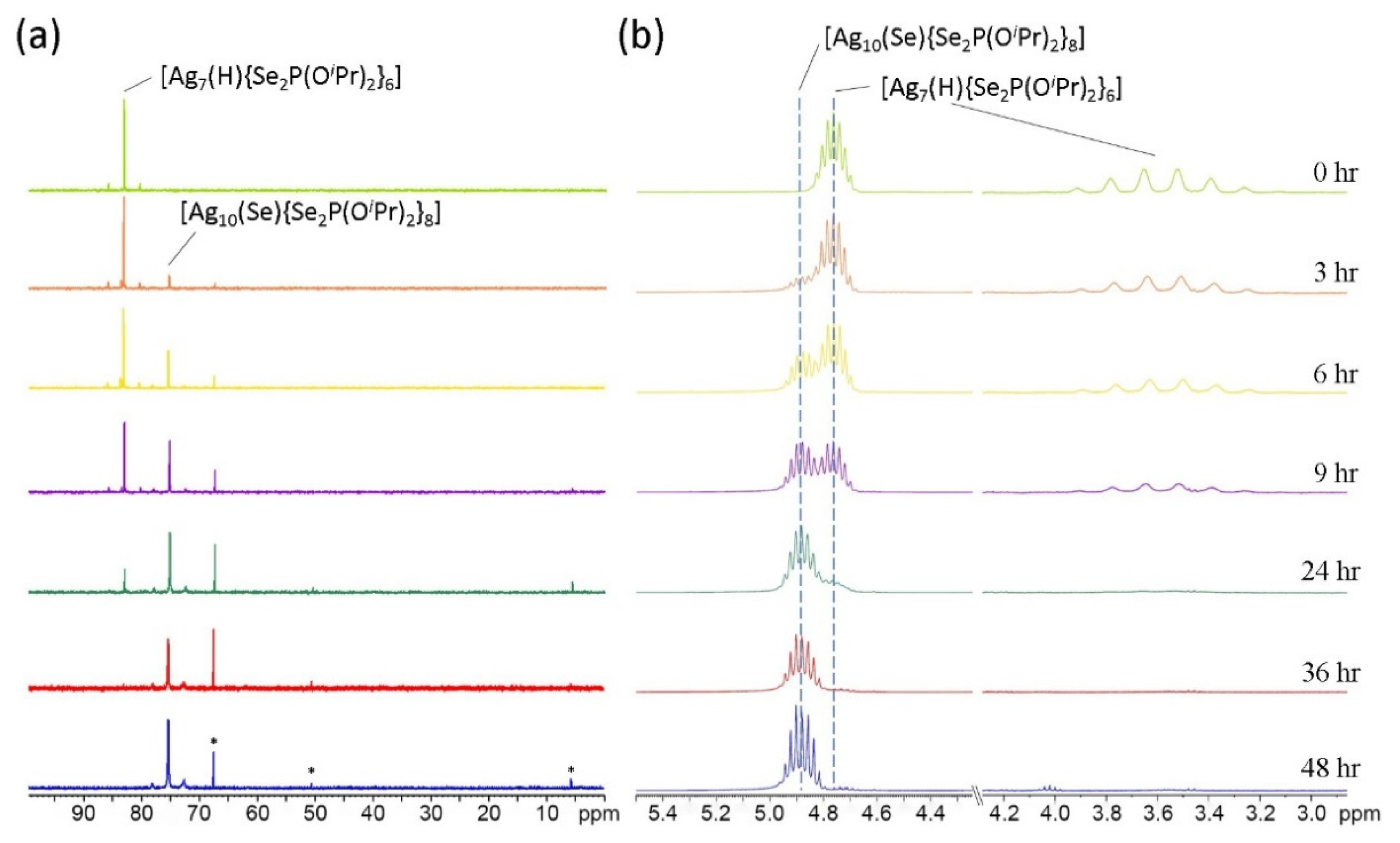
2.4. NMR Spectroscopy
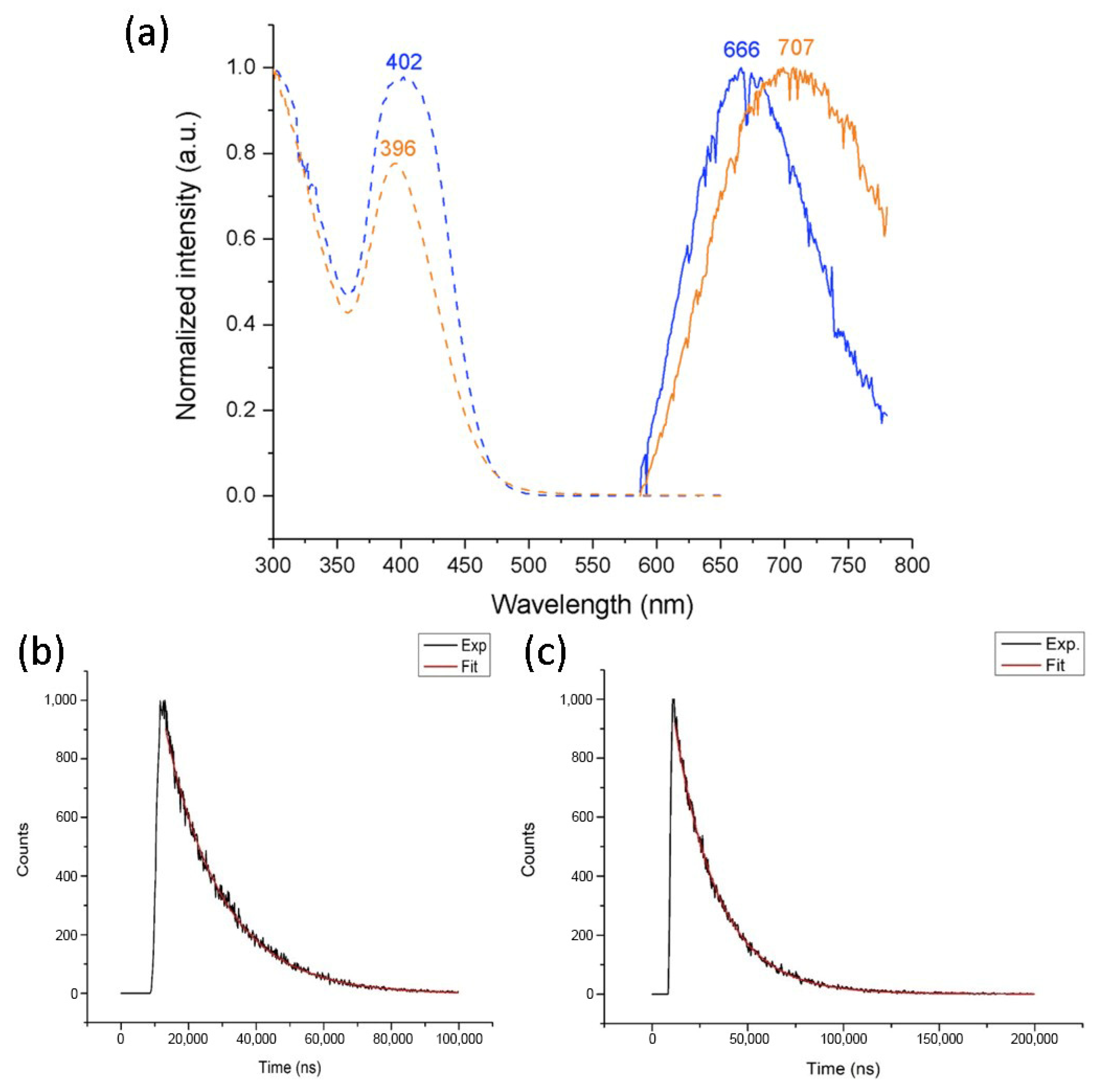
2.5. Photophysical Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Remarks
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Compounds 2–3
3.2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of [Ag10(Se){Se2P(OiPr)2}8] (2)
3.2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of [CuxAg10-x(Se){Se2P(OiPr)2}8], x = 0–7 (3)
3.3. X-ray Crystallography
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Fuhr, O.; Dehnen, S.; Fenske, D. Chalcogenide clusters of copper and silver from silylated chalcogenide sources. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-P.; Jin, J.-L.; Duan, G.-X.; Lu, X.; Mak, T.C.W. High-nuclearity silver(I) chalcogenide clusters: A novel class of supramolecular assembly. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 331, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, M.C.; Laguna, A. Chalcogenide centred gold complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, M.N.; Van Zyl, W.E.; Liu, C.W. A construction guide for high-nuclearity (≥50 metal atoms) coinage metal clusters at the nanoscale: Bridging molecular precise constructs with the bulk material phase. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 24331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.G.; Corrigan, J.F. Metal chalcogenide nanoclusters with ‘tailored’ surfaces via ‘designer’ silylated chalcogen reagents. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A. 2010, 368, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenske, D.; Zhu, N.; Langetepe, T. Synthesis and structure of new Ag-Se clusters: [Ag30Se8(SetBu)14(PnPr3)8], [Ag90Se38(SetBu)14(PEt3)22], [Ag114Se34(SenBu)46(PtBu3)14], [Ag112Se32(SenBu)48(PtBu3)12], and [Ag172Se40(SenBu)92(dppp)4]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anson, C.E.; Eichhöfer, A.; Issac, I.; Fenske, D.; Fuhr, O.; Sevillano, P.; Persau, C.; Stalke, D.; Zhang, J. Synthesis and crystal structures of the ligand-stabilized silver chalcogenide clusters [Ag154Se77(dppxy)18], [Ag320(StBu)60S130(dppp)12], [Ag352S128(StC5H11)96], and [Ag490S188(StC5H11)114]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Tam, D.Y.S.; Mak, T.C.W. Chloride assisted supramolecular assembly of a luminescent gigantic cluster: [Ag216S56Cl7(CuCPh)98(H2O)12]− with pseudo-Th skeleton and five-shell arrangement. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 8930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.-W.; Su, H.-F.; Zhao, Q.-Q.; Kurmoo, M.; Wang, X.-P.; Tung, C.-H.; Sun, D.; Zheng, L.-S. Chalcogens-induced Ag6Z4@Ag36 (Z = S or Se) core—shell nanoclusters: Enlarged tetrahedral core and homochiral crystallization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Tam, D.Y.S.; Mak, T.C.W. Ethynide-stabilized high-nuclearity silver(I) sulfido molecular clusters assembled using organic sulfide precursors. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, J.-L.; Xie, Y.-P.; Cui, H.; Duan, G.-X.; Lu, X.; Mak, T.C.W. Structure-directing role of phosphonate in the synthesis of high-nuclearity silver(I) sulfide-ethynide-thiolate clusters. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 10412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, R.; Breitung, B.; Wünsche, L.; Fenske, D.; Fuhr, O. Functionalised silver chalcogenide clusters. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2011, 637, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayek, H.P.; Massa, W.; Dehnen, S. Presence or absence of a central Se atom in silver selenide/selenolate clusters with halite topology: Syntheses and properties of [(Ph3PAg)8Ag6(μ6-Se)1-x/2(SePh)12]x+ (x = 0, 1). Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, R.; Hong, M.; Su, W.; Liu, H. Polynuclear silver compound formed from aggregation of Se and Ag(1)-thiolate complex. Synthesis, structure and spectroscopic characterization of Ag11(μ5-Se)(μ4-Et2NCS2)3(μ3-Et2NCS2)6. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1998, 277, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.W.; Shang, I.-J.; Wang, J.-C.; Keng, T.-C. Metal dialkyl diselenophosphates: A rare example of co-crystallization with clusters, Ag8(μ8-Se)[Se2P(OPri)2]6 and Ag6[Se2P(OPri)2]6, superimposing in a trigonal lattice. Chem. Commun. 1999, 995–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latouche, C.; Kahlal, S.; Furet, E.; Liao, P.-K.; Lin, Y.-R.; Fang, C.-S.; Cuny, J.; Liu, C.W.; Saillard, J.-Y. Shape modulation of octanuclear Cu(I) or Ag(I) dichalcogeno template clusters with respect to the nature of their encapsulated anions: A combined theoretical and experimental investigation. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.W.; Shang, I.-J.; Fu, R.-J.; Liaw, B.-J.; Wang, J.-C.; Chang, I.-J. Selenium-centered, undecanuclear silver cages surrounded by iodo and dialkyldiselenophosphato ligands. Syntheses, structures, and photophysical properties. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.W.; Feng, C.-S.; Fu, R.-J.; Chang, H.-W.; Saillard, J.-Y.; Kahlal, S.; Wang, J.-C.; Chang, I.-J. Structure, photophysical properties, and DFT calculations of selenide-centered pentacapped trigonal prismatic silver(I) clusters. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.W.; Shang, I.-J.; Hung, C.-M.; Wang, J.-C.; Keng, T.-C. Novel silver diselenophosphate clusters: Structures of Ag10(μ10-Se)[Se2P(OEt)2]8 and {Ag[Se2P(OPri)2]}6. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2002, 1974–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-W.; Shiu, R.-Y.; Fang, C.-S.; Liao, J.-H.; Kishore, P.V.V.N.; Kahlal, S.; Saillard, J.-Y.; Liu, C.W. A sulfide (selenide)-centered nonanuclear silver cluster: A distorted and flexible tricapped trigonal prismatic Ag9 framework. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.W.; Chang, H.-W.; Liao, P.-K.; Fang, C.-S.; Saillard, J.-Y.; Kahlal, S. Crystal structure, photophysical properties, and theoretical investigation of extremely distorted pentacapped trigonal-prismatic undecasilver clusters. J. Clust. Sci. 2011, 22, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrahari, K.K.; Silalahi, R.P.B.; Liao, J.-H.; Kahlal, S.; Liu, Y.-C.; Lee, J.-F.; Chiang, M.-H.; Saillard, J.-Y.; Liu, C.W. Synthesis and structural characterization of inverse-coordination clusters from a two-electron superatomic copper nanocluster. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haiduic, I. Inverse coordination—An emerging new chemical concept. Oxygen and other chalcogens as coordination centers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 338, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiduic, I. Inverse coordination—An emerging new chemical concept. II. Halogens as coordination centers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 348, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.-J.; Liao, J.-H.; Chiu, T.-H.; Kahlal, S.; Lin, C.-J.; Saillard, J.-Y.; Liu, C.W. A two-electron silver superatom isolated from thermally induced internal redox reaction of a silver(I) hydride. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.-J.; Liao, J.-H.; Chiu, T.-H.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Kahlal, S.; McGlinchey, M.J.; Saillard, J.-Y.; Liu, C.W. Intercluster exchanges leading to hydride-centered bimetallic clusters: A multi-NMR, X-ray crystallographic, and DFT study. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.-J.; Liao, J.-H.; Chiu, T.-H.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Kahlal, S.; Saillard, J.-Y.; Liu, C.W. Hydride-encapsulated bimetallic clusters supported by 1,1-dithiolates. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 9300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.-J.; Liao, J.-H.; Chiu, T.-H.; Gam, F.; Kahlal, S.; Saillard, J.-Y.; Liu, C.W. Doping effect on the structure and properties of eight-electron silver nanoclusters. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 155, 034304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.-H.; Kahlal, S.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chiang, M.-H.; Saillard, J.-Y.; Liu, C.W. Identification of an eight-electron superatomic cluster and its alloy in one co-crystal structure. J. Clust. Sci. 2018, 29, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodiuzzaman, M.; Dar, W.A.; Pradeep, T. Cocrystals of Atomically Precise Noble Metal Nanoclusters. Small 2020, 17, 2003981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Malola, S.; Hu, C.; Peng, J.; Dittrich, B.; Teo, B.K.; Häkkinen, H.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, N. Co-crystallization of atomically precise metal nanoparticles driven by magic atomic and electronic shells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.W. Phosphor-1,1-diselenolato metal complexes of group 11 and 12. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2005, 180, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glidewell, C.; Leslie, E.J. Ambidentate nucleophiles. Part 3. Reactions of phosphoroselenoates with molecular halides: The use of lJ(PSe) as a structural diagnostic. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1977, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobana, T.S.; Wang, J.-C.; Liu, C.W. Recent advances in the coordination chemistry of diselenophosphates and allied ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, D.D.; Armarego, W.L.F. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 3rd ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- SADABS, version 2014-11.0; Bruker Area Detector Absorption Corrections; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2014.
- SAINT, version 8.30A; Software for the CCD detector system; Bruker Analytical: Madison, WI, USA, 2012.
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta. Cryst. 2008, A64, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SHELXTL, version 6.14; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2003.
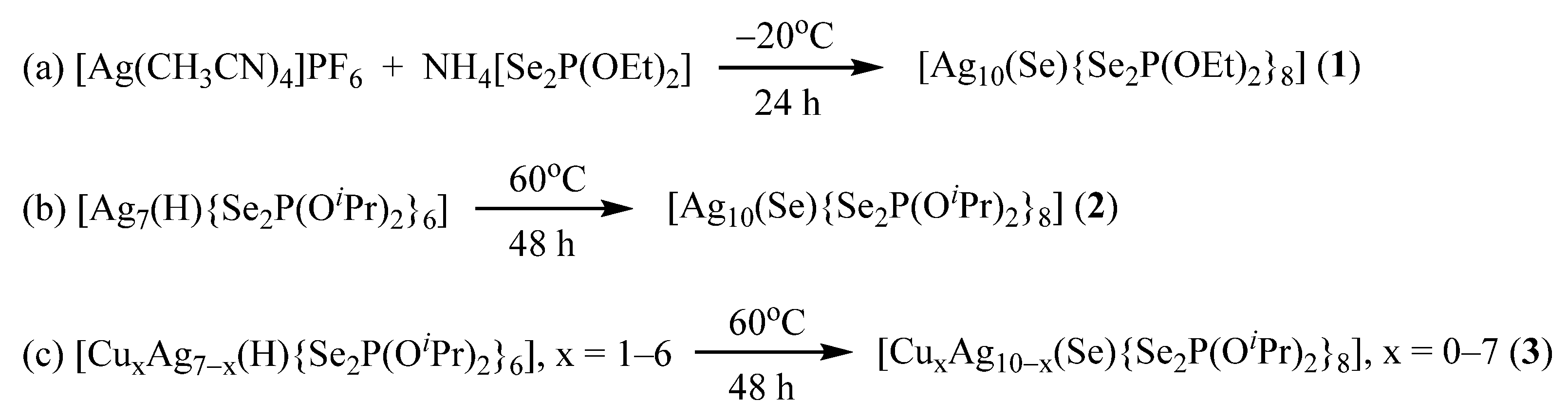

| Comp. | 1 | 2 | [3a]0.6[3b]0.4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag-Ag/M-M (Å) | 2.957(3)–3.378(2), avg. 3.083(3) | Clust. A | 2.8786(12)–3.3004(11), avg. 3.0786(13) | 2.8625(15)–2.7856(18), avg. 3.036(2) |
| Clust. B | 2.9186(11)–3.3321(11), avg. 3.0780(12) | |||
| Seencap-Ag/Seencap-M (Å) | 2.6312(19)–3.187(3), avg. 2.939(2) | Clust. A | 2.5279(12)–3.0496(12), avg. 2.8271(12) | 2.425(2)–3.127(2), avg. 2.778(2) |
| Clust. B | 2.5113(13)–3.0596(12), avg. 2.7586(13) | |||
| Se-Ag/Se-M (Å) | 2.557(3)–3.127(3), avg. 2.685(3) | Clust. A | 2.5496(13)–3.0811(12), avg. 2.693(2) | 2.351(2)–2.8797(19), acg. 2.593 (2) |
| Clust. B | 2.5368(13)–3.0478(14), avg. 2.6672(13) | |||
| Comp. | λabs/nm (ε/cm −1 M−1) | λex/nm (at 77K) | λem/nm (at 77K) | Stoke Shift/cm−1 | Lifetime/ μs (at 77K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 402 (14,600) | 384 | 666 | 9900 | 16 |
| 3 | 396 (11,500) | 387 | 707 | 11,100 | 22 |
| Compound | 2 | [3a]0.6[3b]0.4 |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C48H112Ag10O16P8Se17 | C48H112Ag6.6Cu3.4O16P8Se17 |
| Formula weight | 3614.15 | 3463.43 |
| Crystal System | Triclinic | Triclinic |
| Space group | P(-)1 | P(-)1 |
| a, Å | 14.7908(9) | 14.8584(4) |
| b, Å | 24.8040(16) | 14.8871(5) |
| c, Å | 27.5596(17) | 25.6577(7) |
| α, deg. | 83.563(2) | 100.1735(13) |
| β, deg. | 85.402(2) | 96.5137(13) |
| γ, deg. | 82.033(2) | 115.4953(15) |
| V, Å3 | 9928.6(11) | 4926.2(3) |
| Z | 4 | 2 |
| Temperature, K | 100(2) | 100(2) |
| ρcalcd, g/cm3 | 2.418 | 2.335 |
| μ, mm−1 | 8.335 | 8.458 |
| θmax, deg. | 25.000 | 24.999 |
| Completeness, % | 97.5 | 100 |
| Reflection collected/unique | 53,934/34,122 [Rint = 0.0383] | 167,862/17,346 [Rint = 0.2349] |
| Restraints/parameters | 876/1888 | 382/937 |
| a R1, b wR2 [I > 2σ(I)] | 0.0490, 0.1010 | 0.0555, 0.1029 |
| a R1, b wR2 (all data) | 0.0714, 0.1082 | 0.1139, 0.1290 |
| GOF | 1.006 | 1.023 |
| Largest diff. peak and hole, e/Å3 | 2.269 and −2.512 | 2.287 and −2.157 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.-J.; Liao, J.-H.; Chiu, T.-H.; Wen, Y.-S.; Liu, C.W. A New Synthetic Methodology in the Preparation of Bimetallic Chalcogenide Clusters via Cluster-to-Cluster Transformations. Molecules 2021, 26, 5391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175391
Zhong Y-J, Liao J-H, Chiu T-H, Wen Y-S, Liu CW. A New Synthetic Methodology in the Preparation of Bimetallic Chalcogenide Clusters via Cluster-to-Cluster Transformations. Molecules. 2021; 26(17):5391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175391
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yu-Jie, Jian-Hong Liao, Tzu-Hao Chiu, Yuh-Sheng Wen, and C. W. Liu. 2021. "A New Synthetic Methodology in the Preparation of Bimetallic Chalcogenide Clusters via Cluster-to-Cluster Transformations" Molecules 26, no. 17: 5391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175391
APA StyleZhong, Y.-J., Liao, J.-H., Chiu, T.-H., Wen, Y.-S., & Liu, C. W. (2021). A New Synthetic Methodology in the Preparation of Bimetallic Chalcogenide Clusters via Cluster-to-Cluster Transformations. Molecules, 26(17), 5391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175391







