Profiling the Effects of Repetitive Morphine Administration on Motor Behavior in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
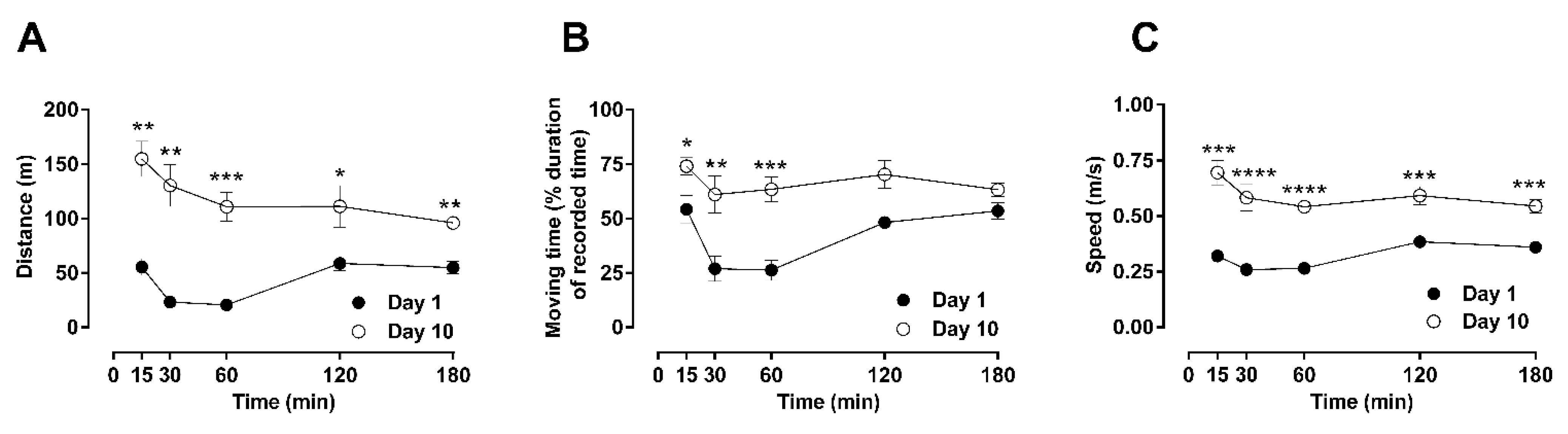
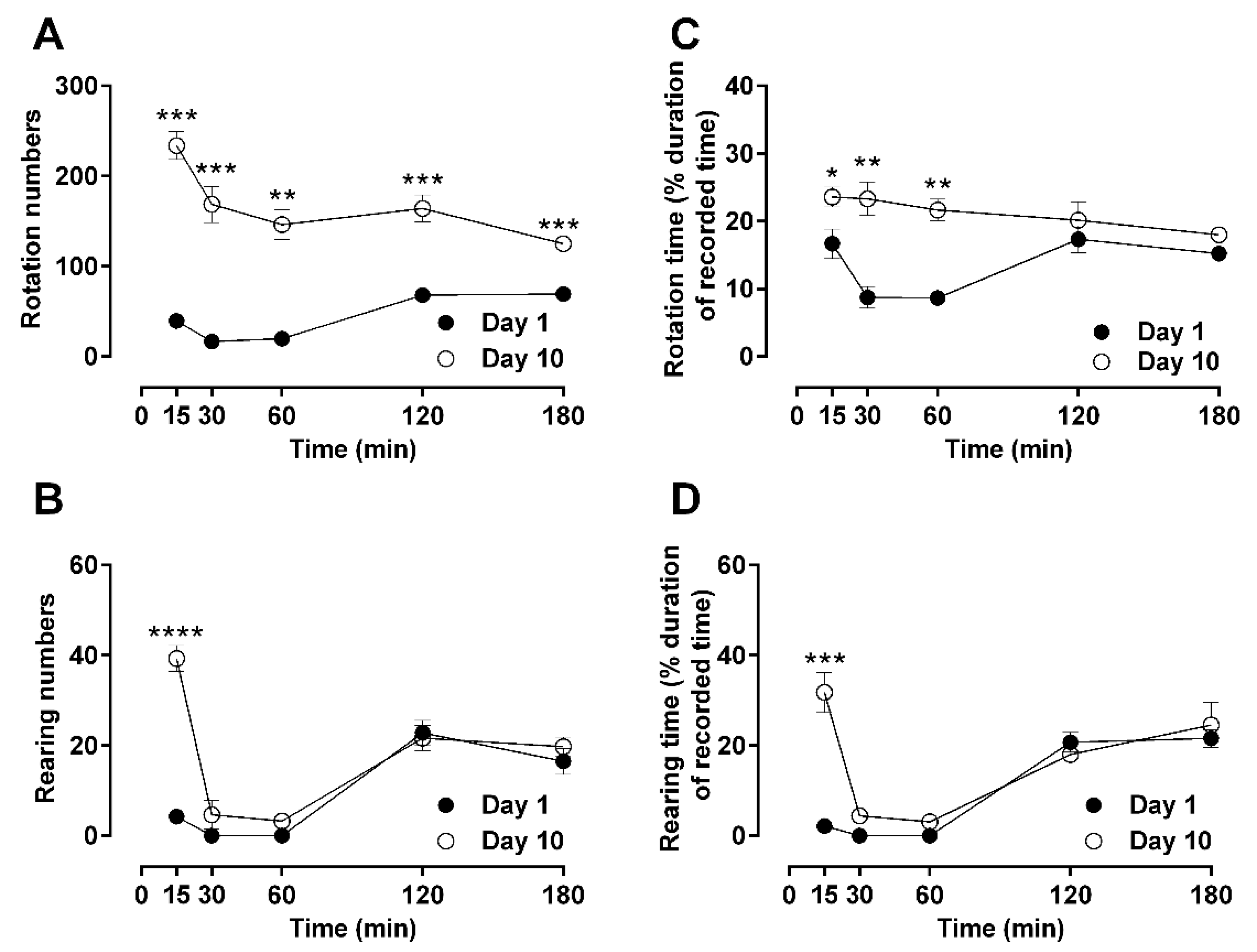
2.1. Time-Dependent Effects of a Single Dose of Morphine to Locomotor Behaviors: Hypoactivity vs. Hyperactivity
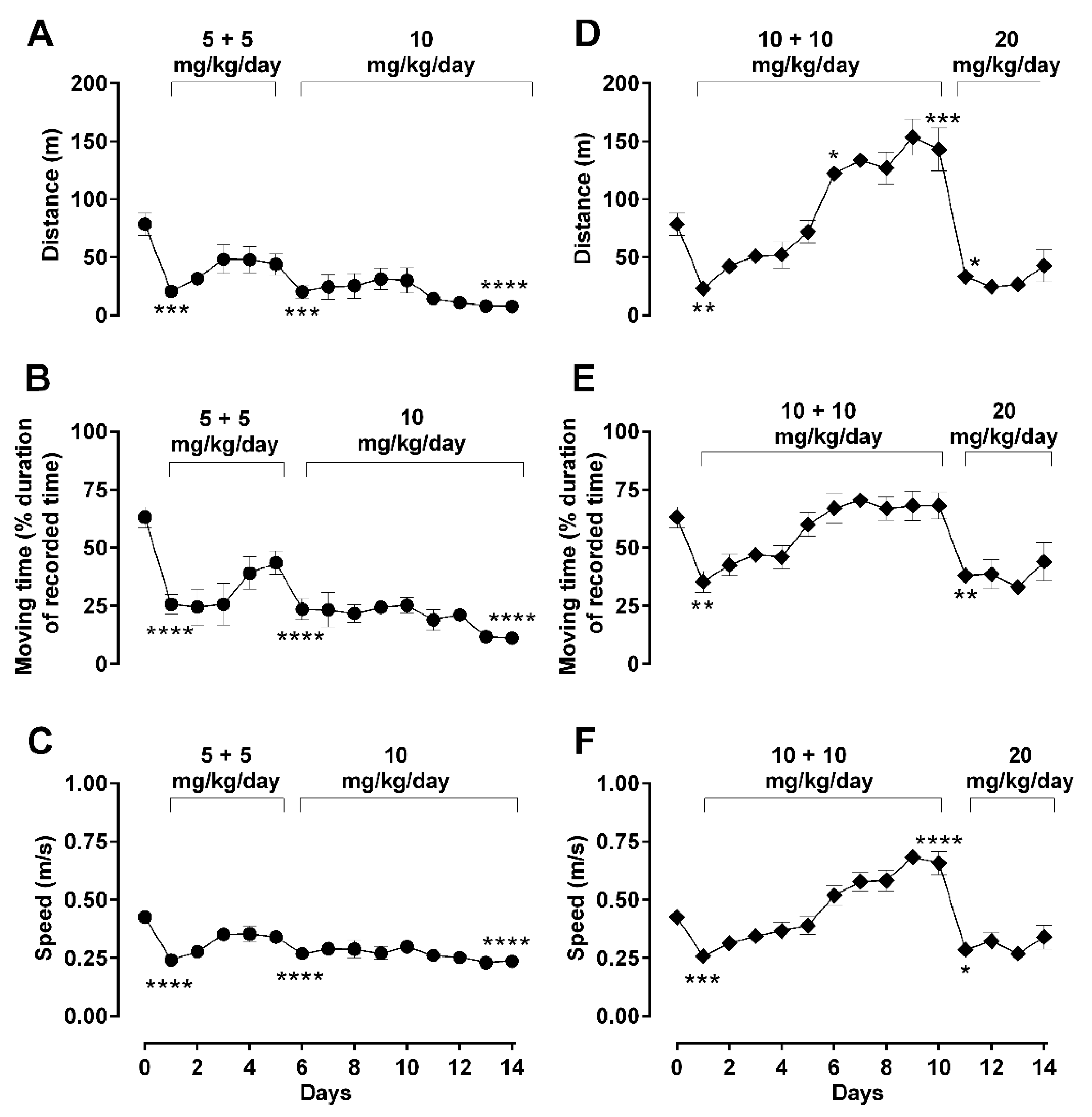
2.2. Dose-Dependent Effects of Repetitive Morphine Administration and Incremental Changes of Dosing on Locomotor Behavior: Hypoactivity vs. Hyperactivity
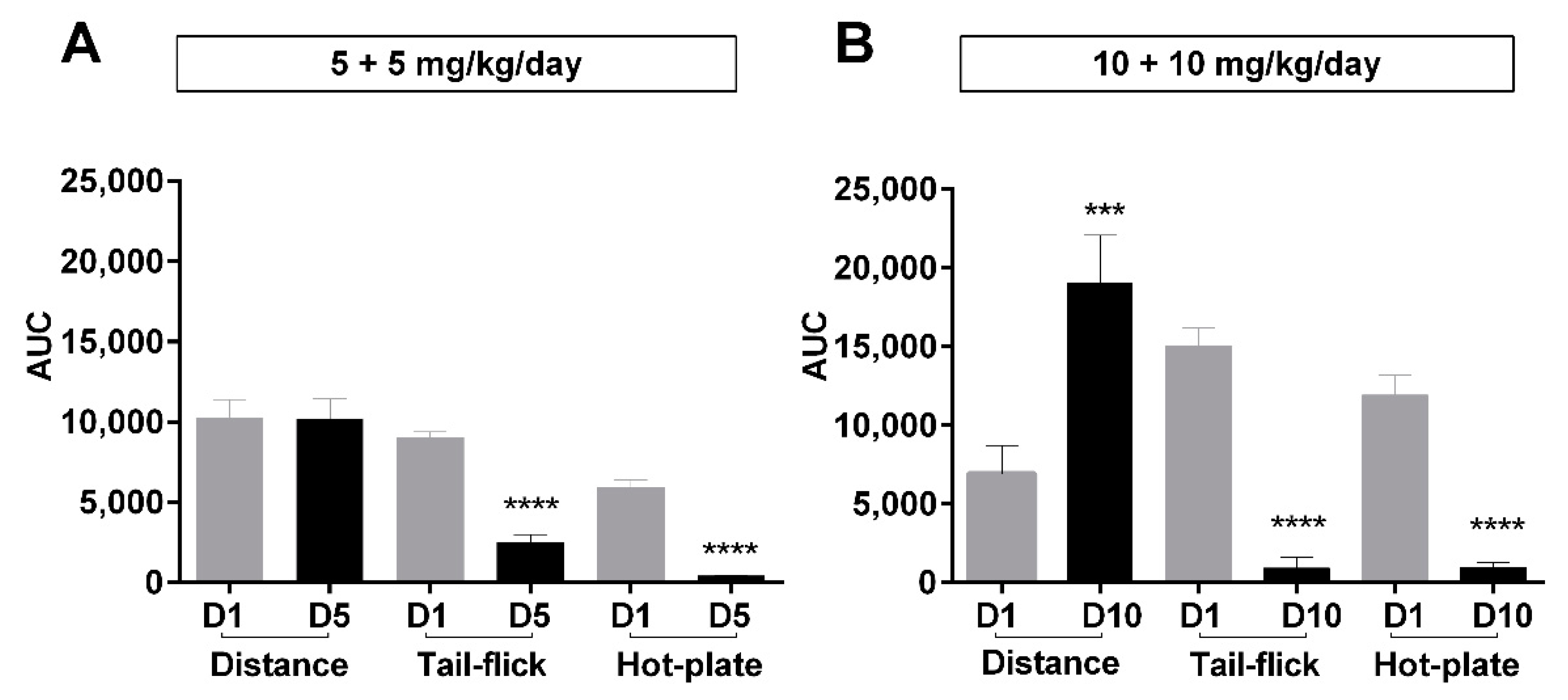
2.3. Relationship between Antinociceptive Tolerance and Locomotor Activities
3. Discussion
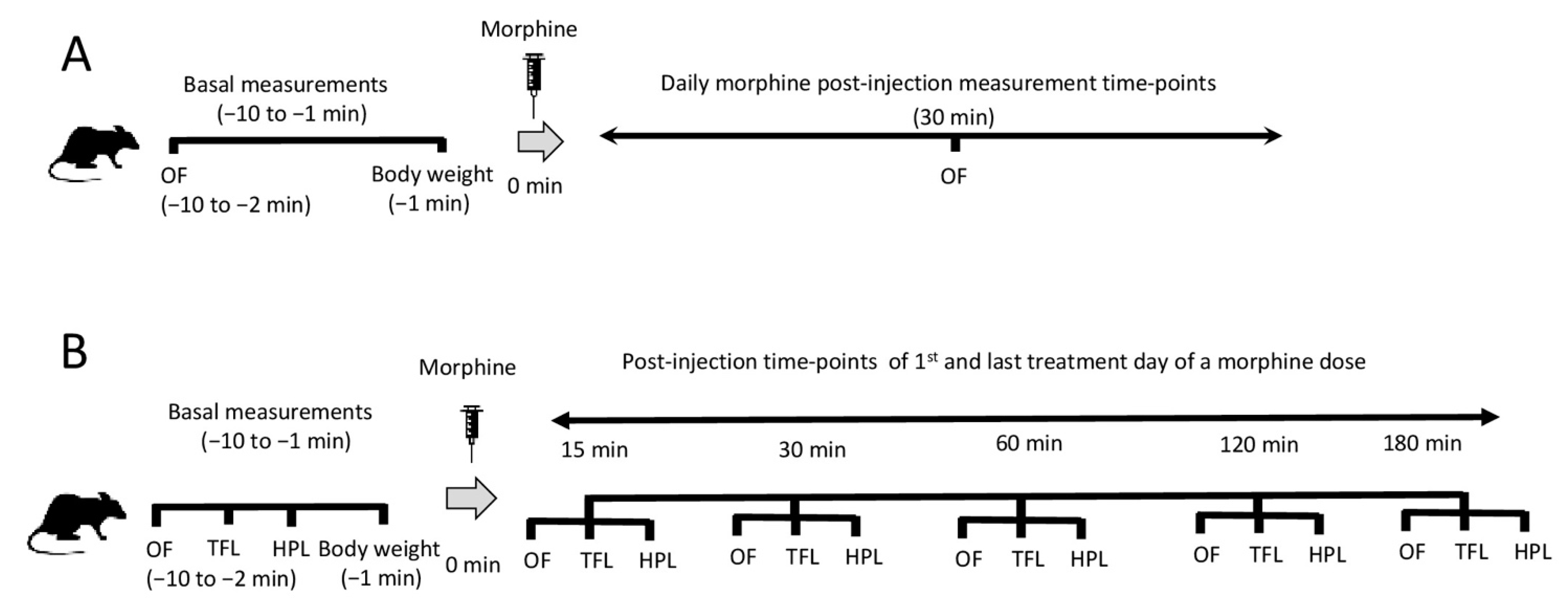
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Maintenance and Care
4.2. Treatment Protocol
4.3. Locomotor Activity Measurements
4.4. Assessment of Antinociception
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CDC. Prescription Opioids: Side Effects. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/opioids/prescribed.html (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- TG. Principles of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Use for Musculoskeletal Conditions in Adults. In eTG Complete Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Limited. Available online: https://tgldcdp.tg.org.au/index (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Azevedo Neto, J.; Costanzini, A.; De Giorgio, R.; Lambert, D.G.; Ruzza, C.; Calò, G. Biased versus Partial Agonism in the Search for Safer Opioid Analgesics. Molecules 2020, 25, 3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droney, J.M.; Gretton, S.K.; Sato, H.; Ross, J.R.; Branford, R.; Welsh, K.I.; Cookson, W.; Riley, J. Analgesia and central side-effects: Two separate dimensions of morphine response. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, J.E.; Habib, A.S. Prophylaxis and treatment of the side-effects of neuraxial morphine analgesia following cesarean delivery. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2013, 26, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girgin, N.K.; Gurbet, A.; Turker, G.; Aksu, H.; Gulhan, N. Intrathecal morphine in anesthesia for cesarean delivery: Dose-response relationship for combinations of low-dose intrathecal morphine and spinal bupivacaine. J. Clin. Anesth. 2008, 20, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffaeli, W.; Marconi, G.; Fanelli, G.; Taddei, S.; Borghi, G.B.; Casati, A. Opioid-related side-effects after intrathecal morphine: A prospective, randomized, double-blind dose-response study. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2006, 23, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.K.; Gueven, N.; Dietis, N. Morphine dosing strategy plays a key role in the generation and duration of the produced antinociceptive tolerance. Neuropharmacology 2017, 121, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollais, A.W.; Patti, C.L.; Zanin, K.A.; Fukushiro, D.F.; Berro, L.F.; Carvalho, R.C.; Kameda, S.R.; Frussa-Filho, R. Effects of acute and long-term typical or atypical neuroleptics on morphine-induced behavioural effects in mice. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. & physiology 2014, 41, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahveci, N.; Gulec, G.; Ozluk, K. Effects of intracerebroventricularly-injected morphine on anxiety, memory retrieval and locomotor activity in rats: Involvement of vasopressinergic system and nitric oxide pathway. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 85, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belknap, J.K.; Riggan, J.; Cross, S.; Young, E.R.; Gallaher, E.J.; Crabbe, J.C. Genetic determinants of morphine activity and thermal responses in 15 inbred mouse strains. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1998, 59, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Arias, M.; Broseta, I.; Aguilar, M.A.; Minarro, J. Lack of specific effects of selective D(1) and D(2) dopamine antagonists vs. risperidone on morphine-induced hyperactivity. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2000, 66, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, C.L.; Frussa-Filho, R.; Silva, R.H.; Carvalho, R.C.; Kameda, S.R.; Takatsu-Coleman, A.L.; Cunha, J.L.; Abilio, V.C. Behavioral characterization of morphine effects on motor activity in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2005, 81, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babbini, M.; Davis, W.M. Time-dose relationships for locomotor activity effects of morphine after acute or repeated treatment. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1972, 46, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.K.; Gueven, N.; Dietis, N. Age-dependent antinociception and behavioral inhibition by morphine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2018, 168, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.K.; Gueven, N.; Dietis, N. Data on prolonged morphine-induced antinociception and behavioral inhibition in older rats. Data Brief. 2018, 19, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtman, J.R., Jr.; Sloan, J.W.; Wala, E.P. Morphine tolerance in male and female rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2004, 77, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, B.; Ma, H.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, C.B. Sex differences in morphine-induced behavioral sensitization and social behaviors in ICR mice. Zool. Res. 2015, 36, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, H.M.; Tannhauser, S.L.; Tannhauser, M.A.; Tannhauser, M. The effects of GABAergic drugs on grooming behaviour in the open field. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1994, 74, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rex, A.; Voigt, J.P.; Voits, M.; Fink, H. Pharmacological evaluation of a modified open-field test sensitive to anxiolytic drugs. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1998, 59, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costall, B.; Fortune, D.H.; Naylor, R.J. Biphasic changes in motor behaviour following morphine injection into the nucleus accumbens [proceedings]. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1976, 57, 423. [Google Scholar]
- Bounes, V.; Charriton-Dadone, B.; Levraut, J.; Delangue, C.; Carpentier, F.; Mary-Chalon, S.; Houze-Cerfon, V.; Sommet, A.; Houze-Cerfon, C.H.; Ganetsky, M. Predicting morphine related side effects in the ED: An international cohort study. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 35, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.L., 3rd; Hastie, B.A.; Glover, T.L.; Fillingim, R.B.; Staud, R.; Campbell, C.M. Cognitive-affective and somatic side effects of morphine and pentazocine: Side-effect profiles in healthy adults. Pain Med. 2010, 11, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, V.E.; Jackson, M.L.; Westlake, J.; Stevens, B.; Barnes, M.; Swann, P.; Rajaratnam, S.M.; Howard, M.E. The accuracy of eyelid movement parameters for drowsiness detection. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2013, 9, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, S.; Kiguchi, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Fukazawa, Y.; Saika, F.; Ueno, K.; Yamamoto, C.; Kishioka, S. Inhibition of morphine tolerance is mediated by painful stimuli via central mechanisms. Drug Discov. Ther. 2012, 6, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Domino, E.F.; Vasko, M.R.; Wilson, A.E. Mixed depressant and stimulant actions of morphine and their relationship to brain acetylcholine. Life Sci. 1976, 18, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brady, L.S.; Holtzman, S.G. Locomotor activity in morphine-dependent and post-dependent rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1981, 14, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulunay, F.C.; Ayhan, I.H.; Sparber, S.B. The effects of morphine and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol on motor activity in rats. Psychopharmacology 1982, 78, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Weele, C.M.; Porter-Stransky, K.A.; Mabrouk, O.S.; Lovic, V.; Singer, B.F.; Kennedy, R.T.; Aragona, B.J. Rapid dopamine transmission within the nucleus accumbens: Dramatic difference between morphine and oxycodone delivery. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 40, 3041–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Chiara, G.; Imperato, A. Opposite effects of mu and kappa opiate agonists on dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and in the dorsal caudate of freely moving rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1988, 244, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, N.P.; Lam, H.A.; Maidment, N.T. A comparison of morphine-induced locomotor activity and mesolimbic dopamine release in C57BL6, 129Sv and DBA2 mice. J. Neurochem. 2001, 79, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D.L.; Blackburn, T.P.; Greenwood, D.T. An automatic apparatus for recording rotational behaviour in rats with brain lesions. Physiol. Behav. 1973, 11, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, J.E.; Crow, T.J. Turning behaviour as an index of the action of amphetamines and ephedrines on central dopamine-containing neurones. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1971, 43, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pycock, C.J. Turning behaviour in animals. Neuroscience 1980, 5, 461–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, C.; Crossman, A.R.; Slater, P. The effect of morphine on turning behaviour in rats and mice with unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesions [proceedings]. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1976, 57, 456p. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet, Y.F.; Carol, M.; Russell, I.S. Morphine-induced rotation in naive, nonlesioned rats. Science 1976, 192, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, C.; Burton, S.; O’Keefe, J. Rearing on hind legs, environmental novelty, and the hippocampal formation. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 17, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguiz, R.M.; Wetsel, W.C. Frontiers in Neuroscience Assessments of Cognitive Deficits in Mutant Mice. In Animal Models of Cognitive Impairment; Levin, E.D., Buccafusco, J.J., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Van Lier, H.; Drinkenburg, W.H.; van Eeten, Y.J.; Coenen, A.M. Effects of diazepam and zolpidem on EEG beta frequencies are behavior-specific in rats. Neuropharmacology 2004, 47, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.; Carvalho, J.G.B.d.; Venditti, M.A.C. High-and Low-Rearing Rats Differ in the Brain Excitability Controlled by the Allosteric Benzodiazepine Site in the GABA A Receptor. J. Behav. Brain Sci. 2012, 2, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, R.N.; Cummins, R.A. The Open-Field Test: A critical review. Psychol. Bull. 1976, 83, 482–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, A.; Sandin, J.; Terenius, L.; Ogren, S.O. Dose- and time-dependent bimodal effects of kappa-opioid agonists on locomotor activity in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 295, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHMRC. Australian Code for the Care and Use of Animals for Scientific Purposes, 8th ed.; National Health and Medical Research Council: Canberra, Australia, 2013.
- Festing, M.F.; Altman, D.G. Guidelines for the design and statistical analysis of experiments using laboratory animals. ILAR J. 2002, 43, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilborn, U.; Rost, B.R.; Arborelius, L.; Brodin, E. Arthritis-induced increase in cholecystokinin release in the rat anterior cingulate cortex is reversed by diclofenac. Brain Res. 2007, 1136, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, B.; Cheng, L.; Bourane, S.; Britz, O.; Padilla, C.; Garcia-Campmany, L.; Krashes, M.; Knowlton, W.; Velasquez, T.; Ren, X.; et al. Identification of spinal circuits transmitting and gating mechanical pain. Cell 2014, 159, 1417–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khroyan, T.V.; Polgar, W.E.; Cami-Kobeci, G.; Husbands, S.M.; Zaveri, N.T.; Toll, L. The first universal opioid ligand, (2S)-2-[(5R,6R,7R,14S)-N-cyclopropylmethyl-4,5-epoxy-6,14-ethano-3-hydroxy-6-meth oxymorphinan-7-yl]-3,3-dimethylpentan-2-ol (BU08028): Characterization of the in vitro profile and in vivo behavioral effects in mouse models of acute pain and cocaine-induced reward. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 336, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, L.S.; Pierson, A.K. Some narcotic antagonists in the benzomorphan series. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1964, 143, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Behavioral Parameter | AUC Units | Day 1 (Dose Group B) | Day 10 (Dose Group B) | Significance (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance | meter × days | 8958 ± 995 | 19,492 ± 1562 | <0.001 |
| Moving time | % of recorded time × days | 8349 ± 643 | 11,715 ± 643 | <0.01 |
| Speed | (meter/sec) × days | 60.22 ± 1.25 | 99.51 ± 3.34 | <0.0001 |
| Rotation numbers | incidences × days | 8374 ± 550 | 25,423 ± 1761 | <0.0001 |
| Rotation time | % of recorded time × days | 2464 ± 240 | 3704 ± 199 | <0.01 |
| Rearing numbers | incidences × days | 3018 ± 308 | 3717 ± 206 | 0.096 |
| Rearing time | % of recorded time × days | 2116 ± 171 | 2803 ± 458 | 0.2269 |
| Behavioral Parameter | AUC Units | Dose Group A | Dose Group B | Significance (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance | meter × days | 369.6 ± 71.6 | 982.3 ± 134.3 | <0.01 |
| Moving time | % of recorded time × days | 305.5 ± 32.6 | 700.2 ± 51.4 | <0.001 |
| Speed | (meter/sec) × days | 3.80 ± 0.23 | 5.69 ± 0.42 | <0.01 |
| Rotation numbers | incidences × days | 255.8 ± 48.4 | 1200 ± 124.2 | <0.001 |
| Rotation time | % of recorded time × days | 103.1 ± 12.6 | 233.4 ± 22.2 | <0.001 |
| Rearing numbers | incidences × days | 48.0 ± 15.5 | 97.4 ± 30.1 | 0.174 |
| Rearing time | % of recorded time × days | 19.4 ± 2.86 | 40.6 ± 9.9 | 0.130 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paul, A.K.; Gueven, N.; Dietis, N. Profiling the Effects of Repetitive Morphine Administration on Motor Behavior in Rats. Molecules 2021, 26, 4355. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144355
Paul AK, Gueven N, Dietis N. Profiling the Effects of Repetitive Morphine Administration on Motor Behavior in Rats. Molecules. 2021; 26(14):4355. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144355
Chicago/Turabian StylePaul, Alok K., Nuri Gueven, and Nikolas Dietis. 2021. "Profiling the Effects of Repetitive Morphine Administration on Motor Behavior in Rats" Molecules 26, no. 14: 4355. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144355
APA StylePaul, A. K., Gueven, N., & Dietis, N. (2021). Profiling the Effects of Repetitive Morphine Administration on Motor Behavior in Rats. Molecules, 26(14), 4355. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144355







