Davidones F and G, Two Novel Flavonoids from Sophora davidii (Franch.) Skeels
Abstract
1. Introduction
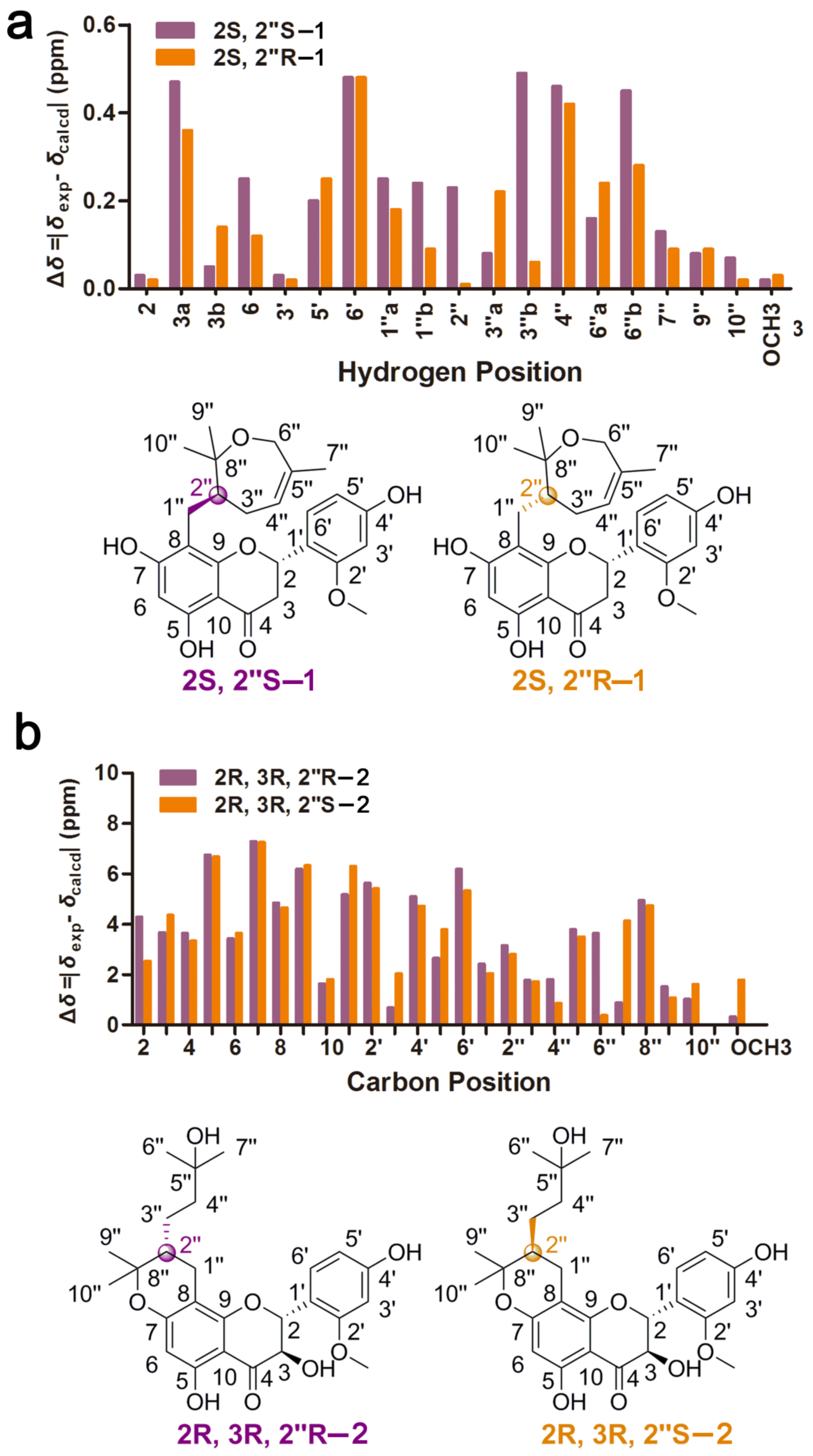
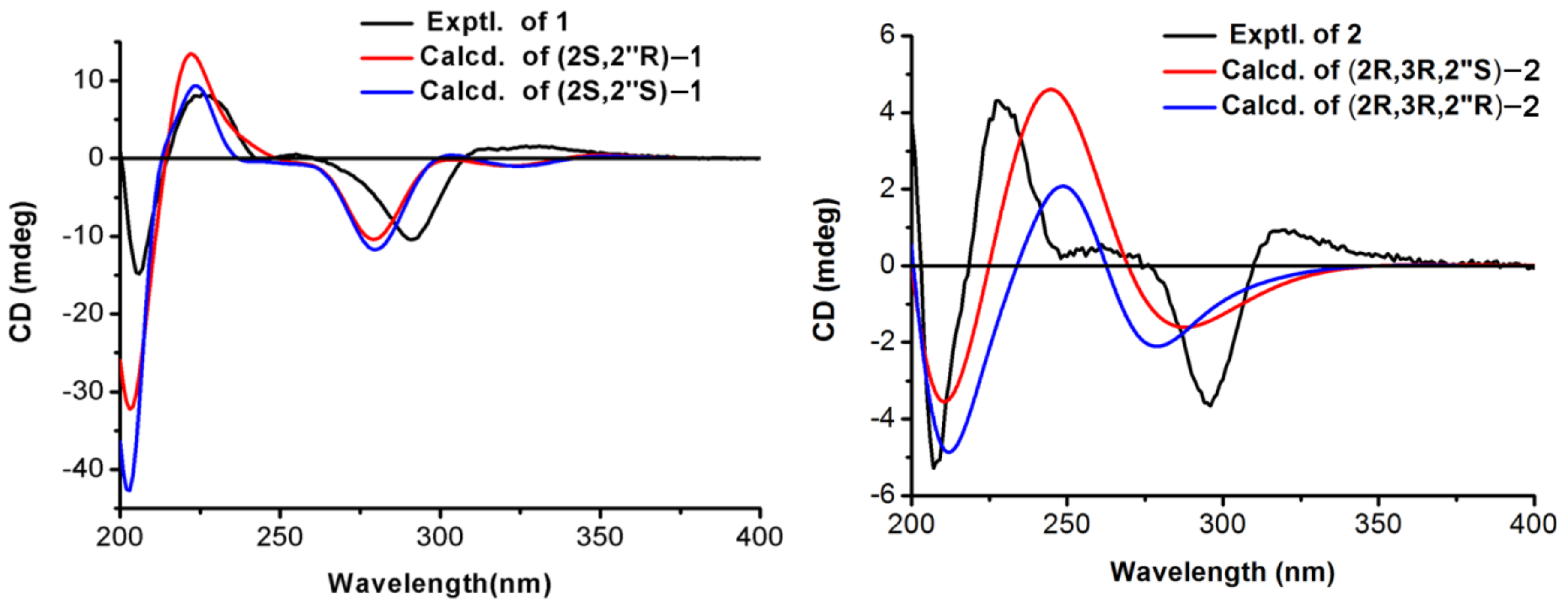
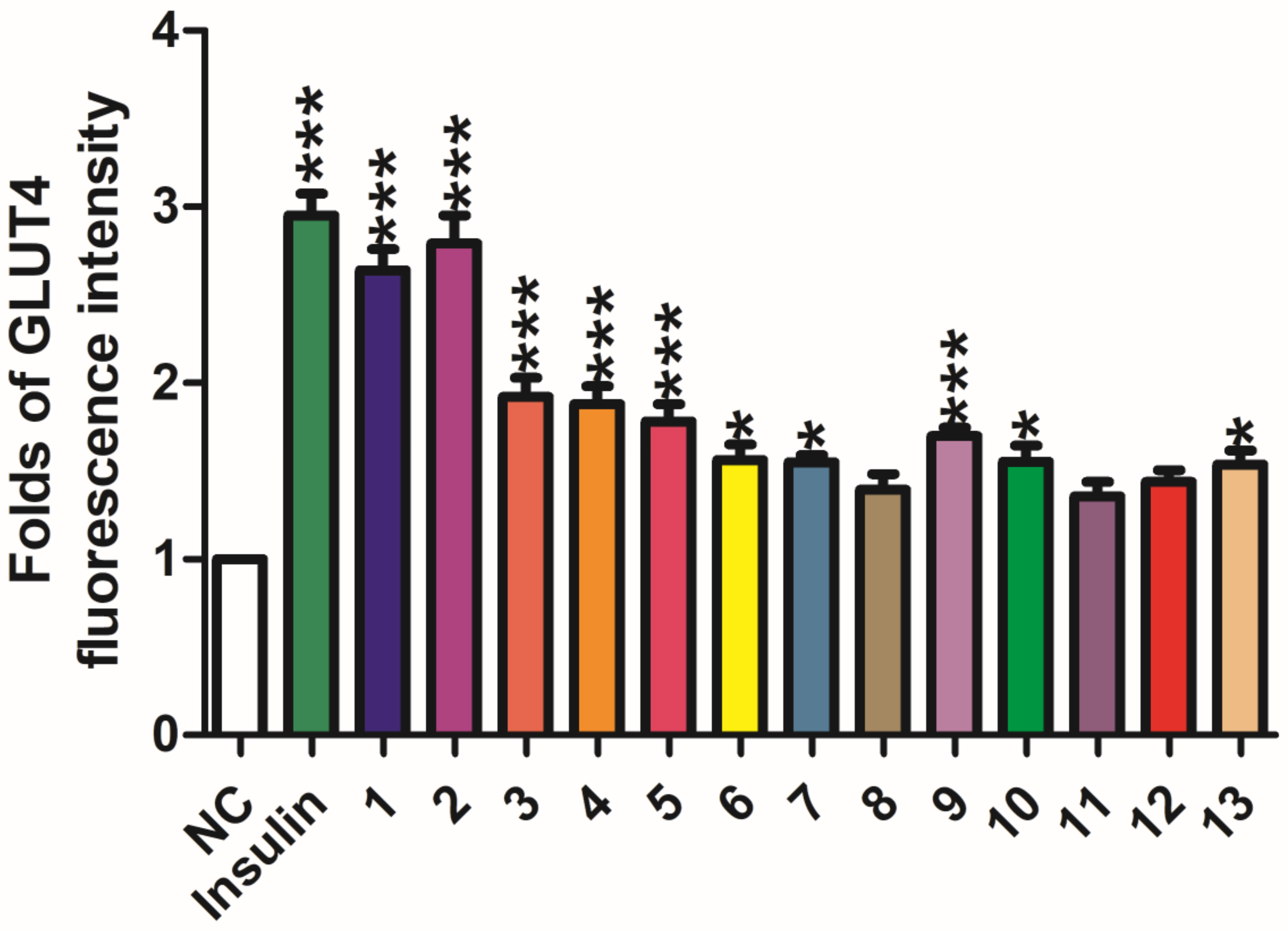
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Materials
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.3.1. Davidone F (1)
3.3.2. Davidone G (2)
3.4. Computation Details
3.5. GLUT-4 Translocation Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Editorial Committee of Chinese of Flora China of Academy of Sciences. Flora China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994; Volume 40, pp. 77–78. [Google Scholar]
- Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Dictionary of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 2006; p. 1774. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Fei, J.; Su, H.; Tian, H.; Huang, S.; Yang, P.; Mao, D.; Hu, S. Flavonoids From the Flowers of Sophora davidii and their Anti-Tobacco Mosaic Virus Activities. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X1985678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Yang, J.; Huang, S.; Wei, T.; Mao, D. Chemical Constituents of the Flowers of Sophora davidii. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2020, 56, 948–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wei, L.; Omiya, S. The alkaloid constituents in the seeds of Sophoar viciifolia. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 20, 168–169. [Google Scholar]
- Boozari, M.; Soltani, S.; Iranshahi, M. Biologically active prenylated flavonoids from the genus Sophora and their structure-activity relationship—A review. Phytother. Res. PTR 2019, 33, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, M.; Yokoe, I.; Shirataki, Y. Studies on the constituents of Sophora species. XII. Constituents of the aerial parts of Sophora tomentosa L. 1. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1978, 26, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimblat, N.; Zanardi, M.M.; Sarotti, A.M. Beyond DP4: An Improved Probability for the Stereochemical Assignment of Isomeric Compounds using Quantum Chemical Calculations of NMR Shifts. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12526–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutateladze, A.G.; Mukhina, O.A. Minimalist Relativistic Force Field: Prediction of Proton-Proton Coupling Constants in (1)H NMR Spectra Is Perfected with NBO Hybridization Parameters. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 5218–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Yang, Y.N.; Feng, Z.M.; Jiang, J.S.; Zhang, P.C. Sophoflavanones A and B, two novel prenylated flavanones from the roots of Sophora flavescens. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 79, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffield, W. Circular dichroism, optical rotatory dispersion and absolute configuration of flavanones, 3-hydroxyflavanones and their glycosides. Tetrahedron 1970, 26, 4093–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, P.; Choi, H.Y.; Hao, J.; Huang, H.; Wu, C.; Yang, X.; Pang, K. New flavonoids from the roots of Sophora davidii (Franch.) Skeels and their glucose transporter 4 translocation activities. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 106, 104500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.W.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, S.U.; Lee, S.; Yuk, H.J.; Seo, K.H.; Kim, Y.U.; Hwang, B.Y.; Oh, S.R. Potential Anti-inflammatory Effects of the Fruits of Paulownia tomentosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2659–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-H.; Chiou, J.-L.; Lee, C.-K.; Kuo, Y.-H. Separation and Determination of Chemical Constituents in the Roots of Rhus Javanica L. Var. Roxburghiana. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2005, 52, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahara, S.; Ogata, T.; Saijo, R.; Konishi, R.; Yamahara, J.; Miyahara, K.; Nohara, T. Isoflavan and related compounds from Dalbergia odorifera. I. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugamoto, K.; Matsusita, Y.-I.; Matsui, K.; Kurogi, C.; Matsui, T. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of chalcones bearing prenyl or geranyl groups from Angelica keiskei. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 5346–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, K.; Tawata, M.; Shindo, H.; Onaya, T.; Sasaki, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Chin, M.; Mitsuhashi, H. Isoliquiritigenin: A new aldose reductase inhibitor from glycyrrhizae radix. Planta Med. 1990, 56, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selepe, M.A.; Drewes, S.E.; van Heerden, F.R. Total synthesis of the pyranoisoflavone kraussianone 1 and related isoflavones. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.N.D.; Xia, M.; Huang, S.; Luo, L.; Li, Z.; Pan, Z. Chemical constituents from EtOAc fraction of Sophora dunnii. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2015, 40, 4428–4432. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.C.; Gerhauser, C.; Song, L.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Kinghorn, A.D. Activity-guided isolation of constituents of Tephrosia purpurea with the potential to induce the phase II enzyme, quinone reductase. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Wang, K.; Jia, X.; Tan, L.; Han, B.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; He, C. Isolation and Identification of Antiarthritic Constituents from Glycine tabacina and Network Pharmacology-Based Prediction of Their Protective Mechanisms against Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 10664–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamnaing, P.; Fanso Free, S.N.Y.; Nkengfack, A.E.; Folefoc, G.; Zacharias Tanee Fomum. An isoflavan-quinone and a flavonol from Millettia laurentii. Phytochemistry 1999, 51, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.; Fu, H.Y.; Hong, J.; Wan, X.; Yang, C.S.; Ho, C.T. Comparison of Antioxidant Activities of Isoflavones from Kudzu Root (Pueraria lobata Ohwi). J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 2117–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Ninomiya, M.; Yasuda, M.; Koshikawa, K.; Deyashiki, Y.; Nozawa, Y.; Akao, Y.; Koketsu, M. Inhibitory effects of flavonoids isolated from Fragaria ananassa Duch on IgE-mediated degranulation in rat basophilic leukemia RBL-2H3. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5374–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hao, J.; Tian, D.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Chen, H.; Lv, Y.; Yang, X. Antidiabetic Activity of a Flavonoid-Rich Extract From Sophora davidii (Franch.) Skeels in KK-Ay Mice via Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Deng, S.; Huang, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Xiong, M.; Yang, J.; Zheng, S.; Ma, X.; Zhao, P.; et al. Chemical constituents from Sophora tonkinensis and their glucose transporter 4 translocation activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Deng, S.; Han, Q.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, S.; Ma, X.; Xu, C.; Yang, J.; Yang, X. Hypoglycemic Activity and the Potential Mechanism of the Flavonoid Rich Extract from Sophora tonkinensis Gagnep. in KK-Ay Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sybyl Software, v. X; Tripos Associates Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013.
- Bruhn, T.; Schaumloffel, A.; Hemberger, Y.; Bringmann, G. SpecDis: Quantifying the comparison of calculated and experimental electronic circular dichroism spectra. Chirality 2013, 25, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Tian, D.; Song, G.; Ming, Q.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Liu, Q.H.; Yang, X. Neferine Promotes GLUT4 Expression and Fusion with the Plasma Membrane to Induce Glucose Uptake in L6 Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | |
| 2 | 5.61, dd, (13.1, 3.0) | 75.5 | 5.42, d, (11.6) | 79.8 |
| 3 | 3.13, dd, (17.1, 13.1) | 42.7 | 4.77, d, (11.6) | 72.5 |
| 2.66, dd, (17.1, 3.0) | ||||
| 4 | 198.7 | 199.3 | ||
| 5 | 163.3 | 162.5 | ||
| 6 | 5.94, s | 96.3 | 5.87, s | 97.8 |
| 7 | 166.3 | 164.0 | ||
| 8 | 108.2 | 102.7 | ||
| 9 | 162.5 | 161.6 | ||
| 10 | 103.3 | 102.1 | ||
| 1′ | 119.2 | 116.9 | ||
| 2′ | 159.3 | 160.8 | ||
| 3′ | 6.48, d, (2.2) | 99.8 | 6.50, d, (2.2) | 100.1 |
| 4′ | 160.5 | 161.0 | ||
| 5′ | 6.43, dd, (8.3, 2.2) | 108.0 | 6.46, dd, (8.3, 2.2) | 108.2 |
| 6′ | 7.32, d, (8.3) | 129.1 | 7.32, d, (8.3) | 130.9 |
| 1″ | 2.40, dd, (12.7, 10.7) | 26.0 | 2.74, dd, (16.8, 5.4) | 22.9 |
| 2.20, overlapped | 2.00, dd, (16.8, 11.2) | |||
| 2″ | 2.20, overlapped | 48.9 | 1.58, m | 42.3 |
| 3″ | 2.18, m | 28.5 | 1.71, m | 26.6 |
| 1.75, m | 1.10, m | |||
| 4″ | 5.29, d, (6.6) | 126.6 | 1.64, m | 42.6 |
| 1.36, m | ||||
| 5″ | 136.8 | 71.3 | ||
| 6″ | 4.26, d, (16.7) | 65.7 | 1.16, s | 29.2 |
| 3.68, d, (16.7) | ||||
| 7″ | 1.52, s | 20.9 | 1.16, s | 29.0 |
| 8″ | 80.3 | 81.0 | ||
| 9″ | 1.18, s | 24.3 | 1.42, s | 28.0 |
| 10″ | 1.08, s | 22.5 | 1.16, s | 20.5 |
| 2″-OCH3 | 3.81, s | 55.9 | 3.82, s | 56.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, P.; Li, X.; Zhou, T.; Peng, Y.; Choi, H.-Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, X. Davidones F and G, Two Novel Flavonoids from Sophora davidii (Franch.) Skeels. Molecules 2021, 26, 4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144182
Song P, Li X, Zhou T, Peng Y, Choi H-Y, Ma Y, Yang X. Davidones F and G, Two Novel Flavonoids from Sophora davidii (Franch.) Skeels. Molecules. 2021; 26(14):4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144182
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Ping, Xuecui Li, Tongxi Zhou, Yu Peng, Ho-Young Choi, Yuanren Ma, and Xinzhou Yang. 2021. "Davidones F and G, Two Novel Flavonoids from Sophora davidii (Franch.) Skeels" Molecules 26, no. 14: 4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144182
APA StyleSong, P., Li, X., Zhou, T., Peng, Y., Choi, H.-Y., Ma, Y., & Yang, X. (2021). Davidones F and G, Two Novel Flavonoids from Sophora davidii (Franch.) Skeels. Molecules, 26(14), 4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144182







