Imaging and SERS Study of the Au Nanoparticles Interaction with HPV and Carcinogenic Cervical Tissues
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles
2.2. Gold Nanoparticles in Cervix Tissue
2.3. Characterization
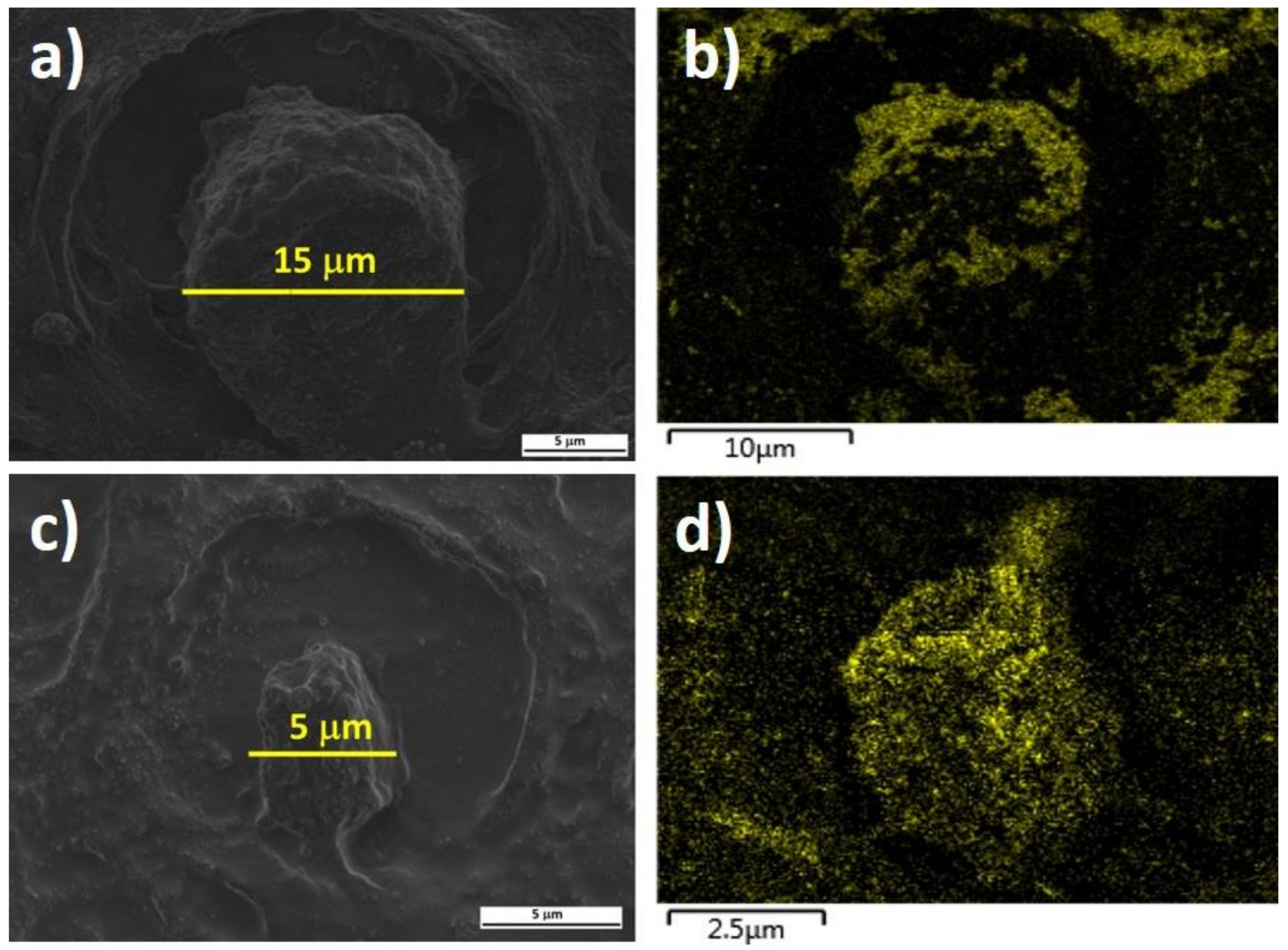
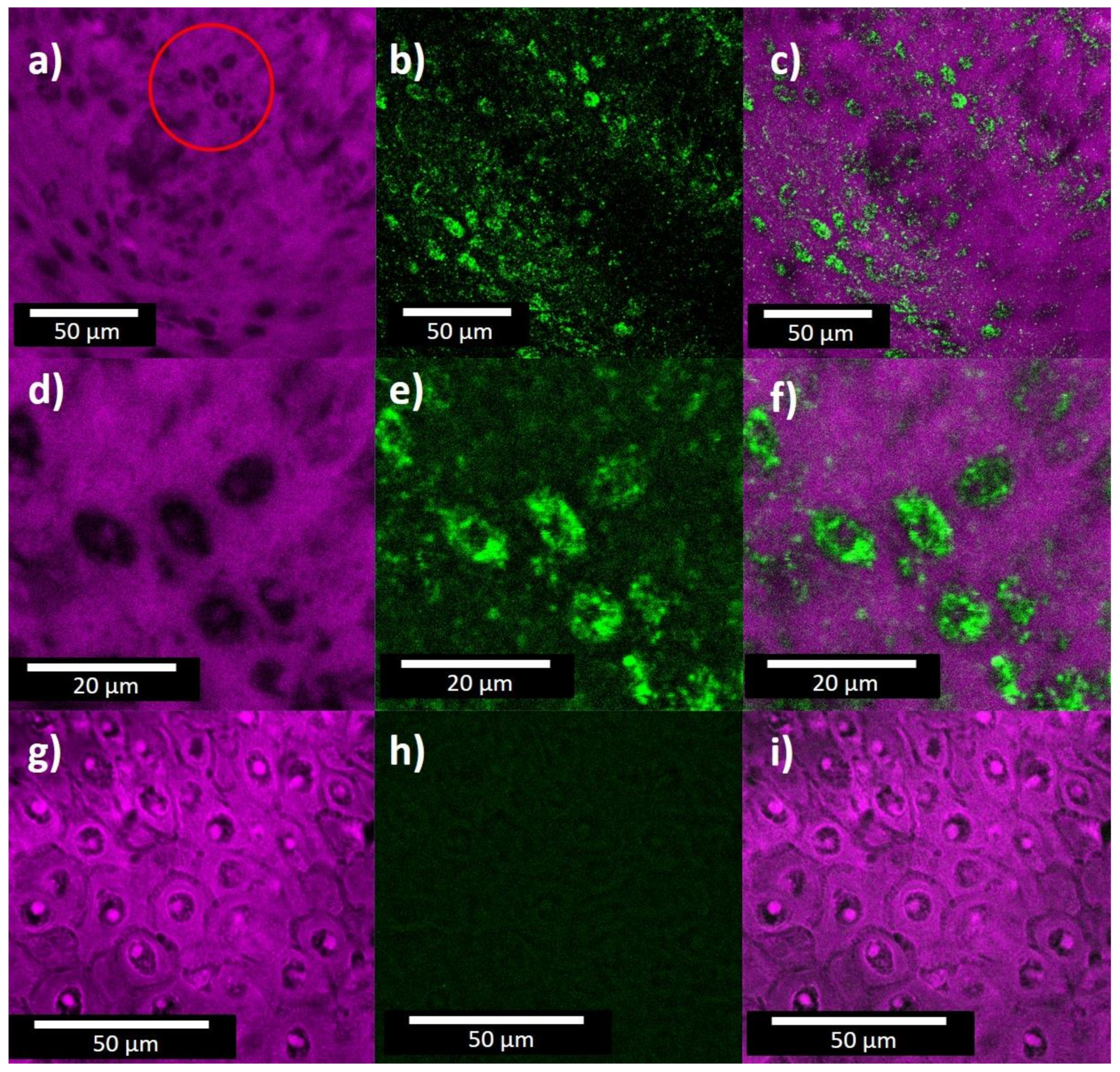
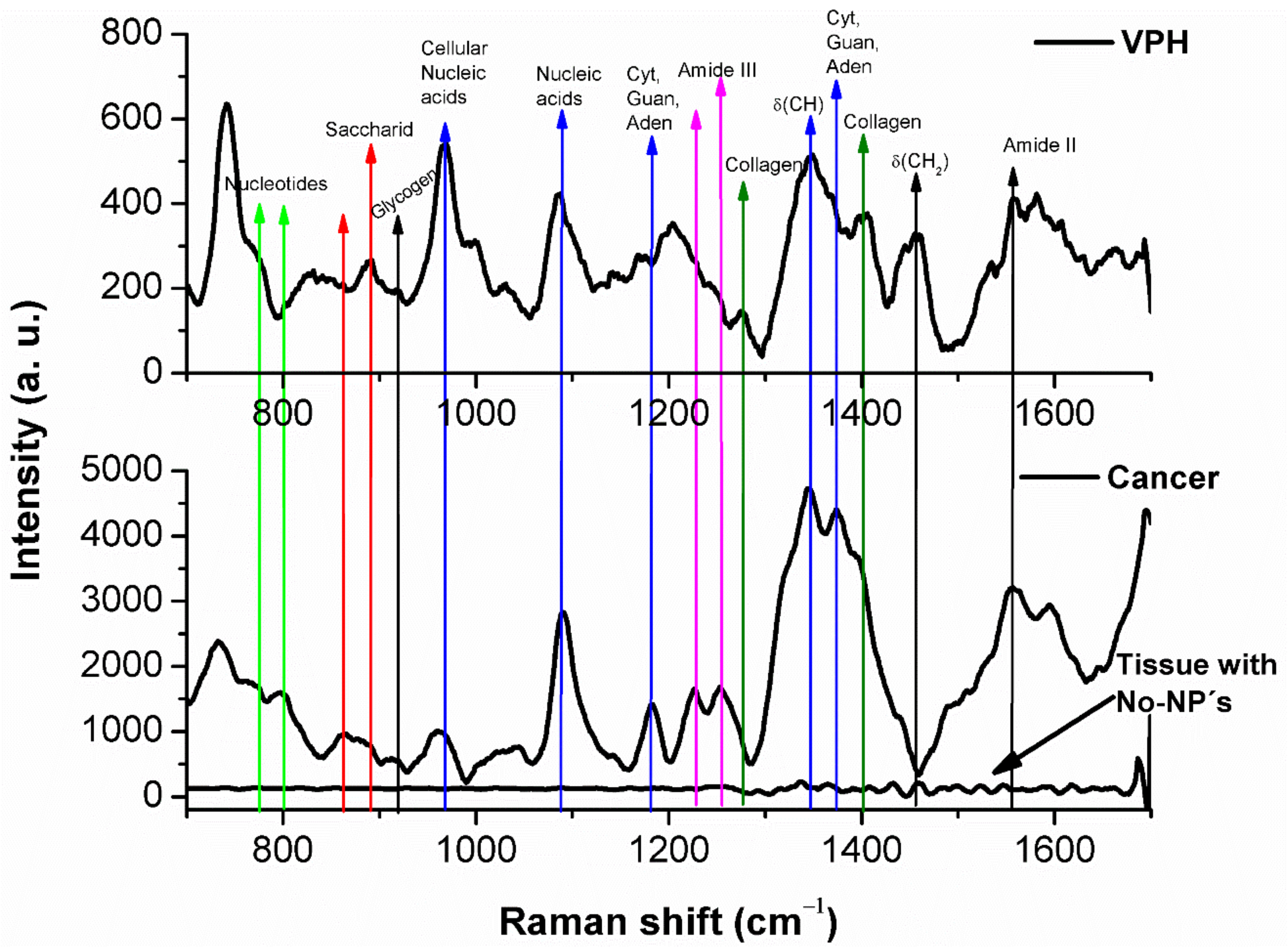
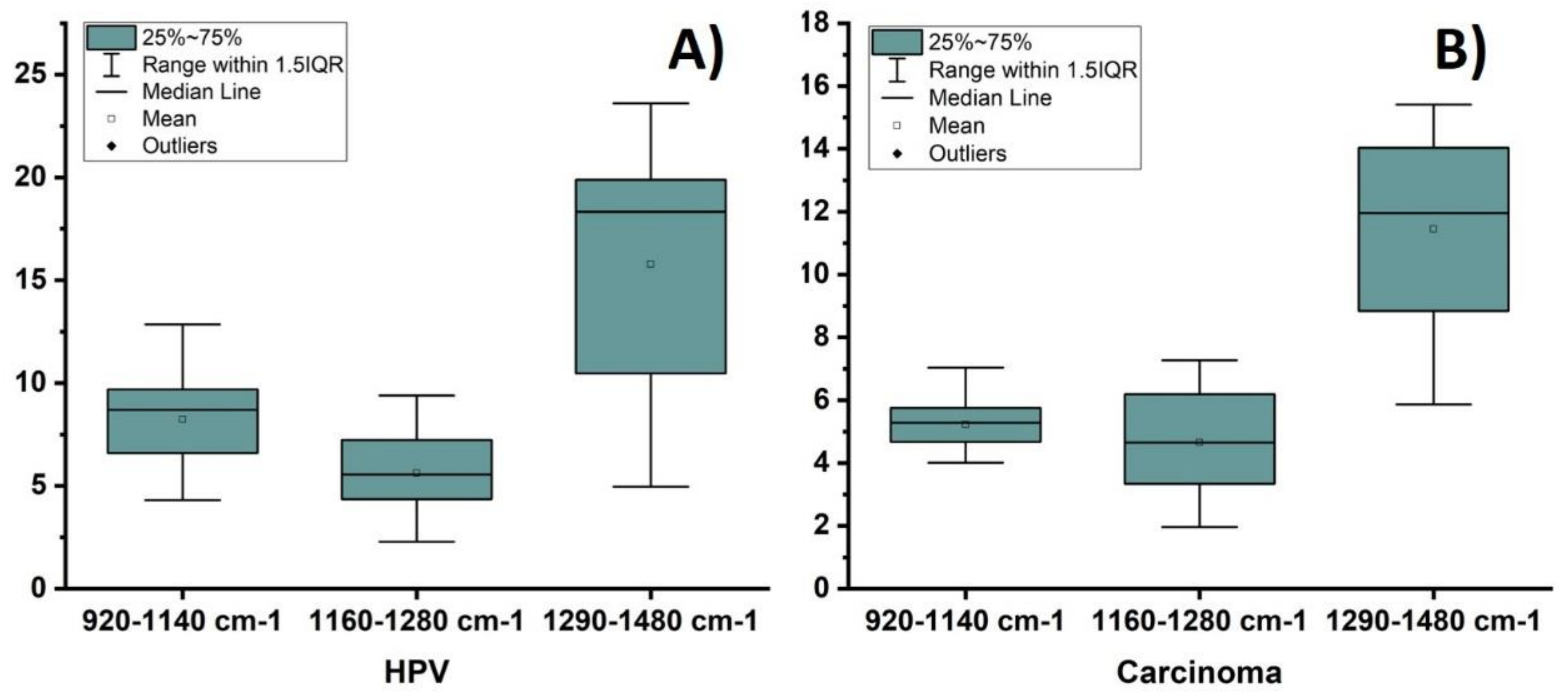
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Buckley, C.H.; Butler, E.B.; Fox, H. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. J. Clin. Pathol. 1982, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, N.; Bosch, F.X.; José, F.X.B.; Herrero, R.; Castellsagué, X.; Shah, K.V.; Snijders, P.J.; Meijer, C.J. Epidemiologic Classification of Human Papillomavirus Types Associated with Cervical Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naucler, P.; Ryd, W.; Törnberg, S.; Strand, A.; Wadell, G.; Elfgren, K.; Rådberg, T.; Strander, B.; Johansson, B.; Forslund, O.; et al. Human Papillomavirus and Papanicolaou Tests to Screen for Cervical Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, K.; McCrory, D.C.; Myers, E.R.; Bastian, L.A.; Hasselblad, V.; Hickey, J.D.; Matchar, D.B. Accuracy of the Papanicolaou Test in Screening for and Follow-up of Cervical Cytologic Abnormalities: A Systematic Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 132, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.; Huang, D.; Strasser, A.; Willis, S.; Chen, L.; Wei, A.; Van Delft, M.; Fletcher, J.; Puthalakath, H.; Kuroda, J.; et al. Subversion of the Bcl-2 Life/Death Switch in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2005, 70, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, N.; Heffron, C.; Regan, I.; Sweeney, M.; Kinsella, S.; McKeown, M.; Creighton, G.; Russell, J.; O’Leary, J. Implementation and evaluation of a new automated interactive image analysis system. Acta Cytol. 2006, 50, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrgiou, M.; Tsoumpou, I.; Vrekoussis, T.; Martin-Hirsch, P.; Arbyn, M.; Prendiville, W.; Mitrou, S.; Koliopoulos, G.; Dalkalitsis, N.; Stamatopoulos, P.; et al. The up-to-date evidence on colposcopy practice and treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: The cochrane colposcopy & cervical cytopathology collaborative group (C5 group) approach. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2006, 32, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D.I.; Cowcher, D.P.; Ashton, L.; O’Hagan, S.; Goodacre, R. Illuminating disease and enlightening biomedicine: Raman spectroscopy as a diagnostic tool. Analyst 2013, 138, 3871–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; Isabelle, M.; Bazant-Hegemark, F.; Hutchings, J.; Orr, L.; Babrah, J.; Baker, R.; Stone, N. Vibrational spectroscopy: A clinical tool for cancer diagnostics. Analyst 2009, 134, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyng, F.M.; Traynor, D.; Ramos, I.; Bonnier, F.; Byrne, H.J. Raman spectroscopy for screening and diagnosis of cervical cancer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8279–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijssen, A.; Schut, T.C.B.; Caspers, P.J.; Puppels, G.J.; Koljenović, S. Towards oncological application of Raman spectroscopy. J. Biophotonics 2009, 2, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceja-Fdez, A.; López-Luke, T.; Oliva, J.; Vivero-Escoto, J.; Gonzalez-Yebra, A.L.; Rojas, R.A.R.; Martínez-Pérez, A.; De La Rosa, E. Labeling of HeLa cells using ZrO2: Yb3+ -Er3+ nanoparticles with upconversion emission. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 046006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda-Pérez, E.; López-Luke, T.; Plascencia-Villa, G.; Mayen, L.P.; Ceja-Fdez, A.; Ponce, A.; Vivero-Escoto, J.; De La Rosa, E. SERS and integrative imaging upon internalization of quantum dots into human oral epithelial cells. J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepeda-Pérez, E.; López-Luke, T.; Salas, P.; Plascencia-Villa, G.; Ponce, A.; Vivero-Escoto, J.; José-Yacamán, M.; De La Rosa, E. SERS-active Au/SiO2 clouds in powder for rapid ex vivo breast adenocarcinoma diagnosis. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 2407–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, I.R.; Meade, A.D.; Ibrahim, O.; Byrne, H.J.; McMenamin, M.; McKenna, M.; Malkin, A.; Lyng, F.M. Raman spectroscopy for cytopathology of exfoliated cervical cells. Faraday Discuss. 2015, 187, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneipp, K.; Haka, A.S.; Kneipp, H.; Badizadegan, K.; Yoshizawa, N.; Boone, C.; Shafer-Peltier, K.E.; Motz, J.T.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy in Single Living Cells Using Gold Nanoparticles. Appl. Spectrosc. 2002, 56, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movasaghi, Z.; Rehman, S.; Rehman, I.U. Raman Spectroscopy of Biological Tissues. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2007, 42, 493–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gelder, J.; De Gussem, K.; Vandenabeele, P.; Moens, L. Reference database of Raman spectra of biological molecules. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2007, 38, 1133–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneipp, K.; Wang, Y.; Kneipp, H.; Perelman, L.T.; Itzkan, I.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S. Single Molecule Detection Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S. Probing Single Molecules and Single Nanoparticles by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Science 1997, 275, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlckova, B.; Pavel, I.; Sladkova, M.; Siskova, K.; Slouf, M. Single molecule SERS: Perspectives of analytical applications. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 834-836, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ru, E.; Etchegoin, P. Rigorous justification of the |E|4 enhancement factor in Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 423, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, A.; Kambhampati, P. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1998, 27, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Aizpurua, J.; Käll, M.; Apell, P. Electromagnetic contributions to single-molecule sensitivity in surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 4318–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.-Y.; Au, L.; Hartland, G.V.; Li, X.; Marquez, M.; Xia, Y. Gold nanostructures: Engineering their plasmonic properties for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebig, F.; Henning, R.; Sarhan, R.M.; Prietzel, C.; Schmitt, C.N.Z.; Bargheer, M.; Koetz, J. A simple one-step procedure to synthesise gold nanostars in concentrated aqueous surfactant solutions. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 23633–23641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebig, F.; Moreno, S.; Thünemann, A.F.; Temme, A.; Appelhans, D.; Koetz, J. Toxicological investigations of “naked” and polymer-entrapped AOT-based gold nanotriangles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 167, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, K.; Riemann, I. High-resolution multiphoton tomography of human skin with subcellular spatial resolution and picosecond time resolution. J. Biomed. Opt. 2003, 8, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, B.R.; So, P.T.C.; Gratton, E. Multiphoton Excitation Microscopy of In Vivo Human Skin: Functional and Morphological Optical Biopsy Based on Three-Dimensional Imaging, Lifetime Measurements and Fluorescence Spectroscopya. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 838, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfel, W.R.; Williams, R.M.; Christie, R.; Nikitin, A.Y.; Hyman, B.T.; Webb, W.W. Live tissue intrinsic emission microscopy using multiphoton-excited native fluorescence and second harmonic generation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7075–7080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, G.T.; Yu, Z.H.; Shen, Y.R. Photoinduced luminescence from the noble metals and its enhancement on roughened surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 33, 7923–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imura, K.; Nagahara, A.T.; Okamoto, H. Near-Field Two-Photon-Induced Photoluminescence from Single Gold Nanorods and Imaging of Plasmon Modes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 13214–13220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albota, M.; Beljonne, D.; Brédas, J.-L.; Ehrlich, J.E.; Fu, J.-Y.; Heikal, A.A.; Hess, S.E.; Kogej, T.; Levin, M.D.; Marder, S.R.; et al. Design of Organic Molecules with Large Two-Photon Absorption Cross Sections. Science 1998, 281, 1653–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, D.; Zipfel, W.; Williams, R.M.; Clark, S.W.; Bruchez, M.P.; Wise, F.W.; Webb, W.W. Water-Soluble Quantum Dots for Multiphoton Fluorescence Imaging in Vivo. Science 2003, 300, 1434–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrer, R.A.; Butterfield, F.L.; Chen, A.V.W.; Fourkas, J.T. Highly Efficient Multiphoton-Absorption-Induced Luminescence from Gold Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M.A. Cancer Cell Imaging and Photothermal Therapy in the Near-Infrared Region by Using Gold Nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönnichsen, C.; Alivisatos, P.A. Gold Nanorods as Novel Nonbleaching Plasmon-Based Orientation Sensors for Polarized Single-Particle Microscopy. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelin, D.; Oron, D.; Thiberge, S.; Moses, E.; Silberberg, Y. Multiphoton plasmon-resonance microscopy. Opt. Express 2003, 11, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.B.; Volkov, V.; Link, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. The ‘lightning’ gold nanorods: Fluorescence enhancement of over a million compared to the gold metal. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 317, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huff, T.B.; Zweifel, D.A.; He, W.; Low, P.S.; Wei, A.; Cheng, J.-X. In vitro and in vivo two-photon luminescence imaging of single gold nanorods. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15752–15756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. The Formation of Colloidal Gold. J. Phys. Chem. 1953, 57, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkevich, J.; Garton, G.; Stevenson, P. The color of colloidal gold. J. Colloid Sci. 1954, 9, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O. On the Origin of Cancer Cells. Science 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.K.; Shin, E.; Kim, B.-S. Cell Nucleus-Targeting Zwitterionic Carbon Dots. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Lin, J.; Cheng, M.; Li, Y.-Z.; Chen, G.; Huang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zeng, H. Gold Nanoparticle Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Spectroscopy of Cancerous and Normal Nasopharyngeal Tissues under Near-Infrared Laser Excitation. Appl. Spectrosc. 2009, 63, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Shi, H.; Feng, S.; Lin, J.; Chen, W.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Lin, D.; Xu, Q.; et al. Silver nanoparticle based surface enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy of diabetic and normal rat pancreatic tissue under near-infrared laser excitation. Laser Phys. Lett. 2013, 10, 045603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyng, F.; Faoláin, E.; Conroy, J.; Meade, A.; Knief, P.; Duffy, B.; Hunter, M.; Byrne, J.; Kelehan, P.; Byrne, H. Vibrational spectroscopy for cervical cancer pathology, from biochemical analysis to diagnostic tool. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2007, 82, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriboga, L.; Xie, P.; Vigorita, V.; Zarou, D.; Zakim, D.; Diem, M. Infrared spectroscopy of human tissue. II. A comparative study of spectra of biopsies of cervical squamous epithelium and of exfoliated cervical cells. Biospectroscopy 1998, 4, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.T.; Wong, R.K.; Caputo, T.A.; Godwin, T.A.; Rigas, B. Infrared spectroscopy of exfoliated human cervical cells: Evidence of extensive structural changes during carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10988–10992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HPV Tissue | Carcinogenic Tissue | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Peak (cm⁻¹) | Assignment | Peak (cm⁻¹) | Assignment |
| 741 774 890 919 967 1002 1030 1087 1167 1203 1277 1345 1400 1456 1554 1665 | DNA DNA Proteins Glycogen Proline, Valine Phenylalanine Phenylalanine DNA Proteins Tryptophan Amide III DNA Collagen Lipids Amide II Amide I | 734 774 864 919 967 1228 1252 1345 1373 1400 1554 1595 1665 | DNA DNA Hidroxiproline Glycogen Proline, Valine Phenylalanine Amide III DNA Thymine Collagen Amide II Lipids Amide I |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceja-Fdez, A.; Carriles, R.; González-Yebra, A.L.; Vivero-Escoto, J.; de la Rosa, E.; López-Luke, T. Imaging and SERS Study of the Au Nanoparticles Interaction with HPV and Carcinogenic Cervical Tissues. Molecules 2021, 26, 3758. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123758
Ceja-Fdez A, Carriles R, González-Yebra AL, Vivero-Escoto J, de la Rosa E, López-Luke T. Imaging and SERS Study of the Au Nanoparticles Interaction with HPV and Carcinogenic Cervical Tissues. Molecules. 2021; 26(12):3758. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123758
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeja-Fdez, Andrea, Ramon Carriles, Ana Lilia González-Yebra, Juan Vivero-Escoto, Elder de la Rosa, and Tzarara López-Luke. 2021. "Imaging and SERS Study of the Au Nanoparticles Interaction with HPV and Carcinogenic Cervical Tissues" Molecules 26, no. 12: 3758. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123758
APA StyleCeja-Fdez, A., Carriles, R., González-Yebra, A. L., Vivero-Escoto, J., de la Rosa, E., & López-Luke, T. (2021). Imaging and SERS Study of the Au Nanoparticles Interaction with HPV and Carcinogenic Cervical Tissues. Molecules, 26(12), 3758. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123758







