Identification, Characterization and Antihypertensive Effect In Vivo of a Novel ACE-Inhibitory Heptapeptide from Defatted Areca Nut Kernel Globulin Hydrolysates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
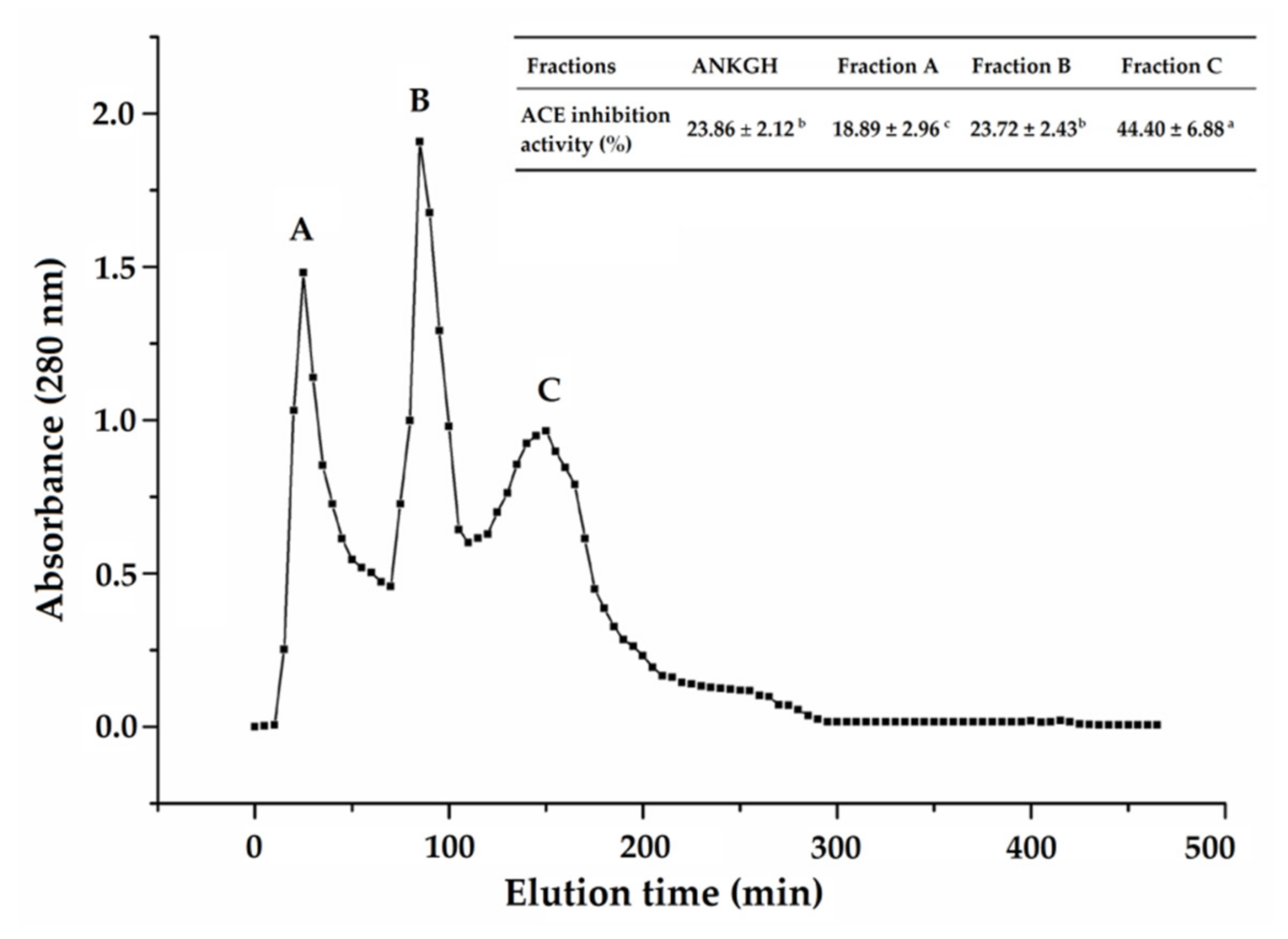
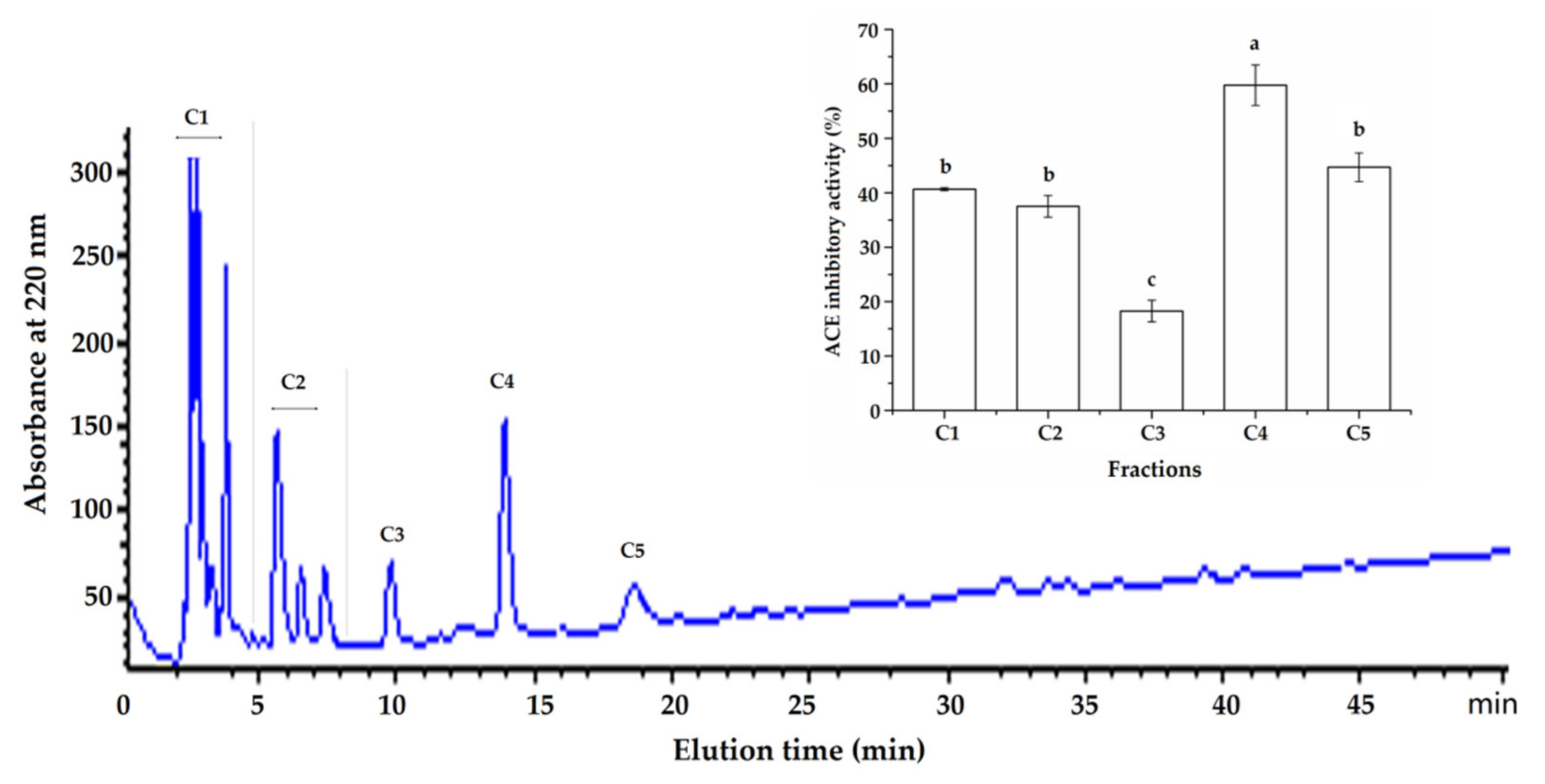
2.1. Purification of ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from ANKGH
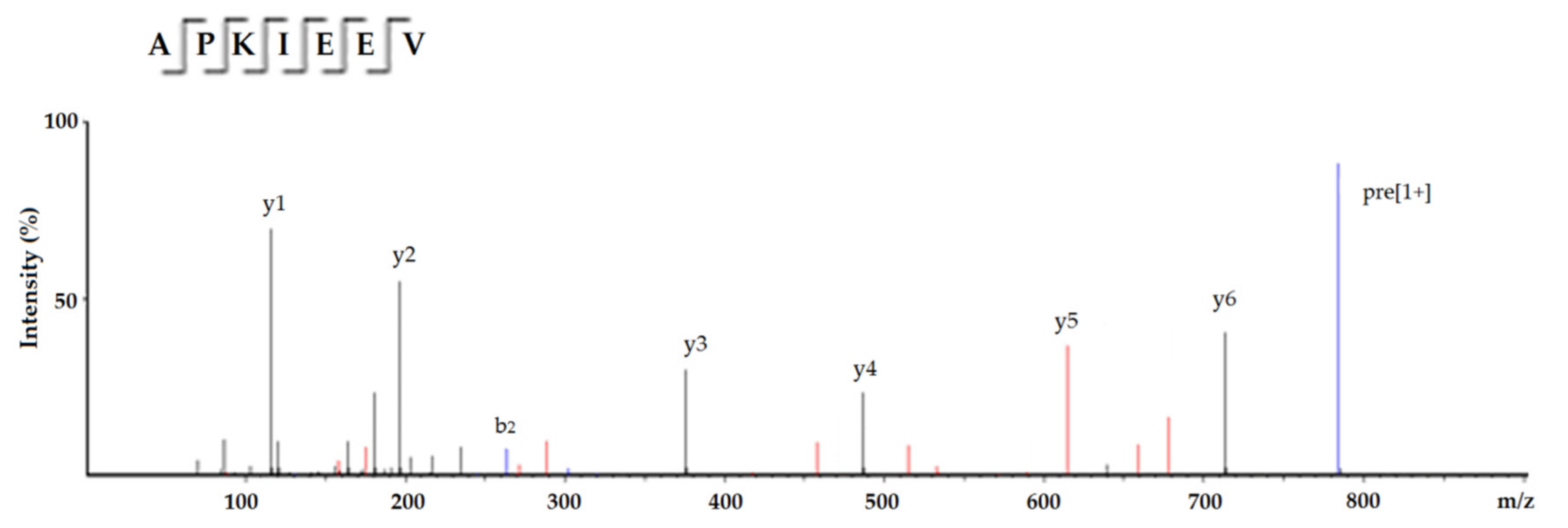
2.2. Identification of Peptides from Subfraction C4 and In Silico Screening
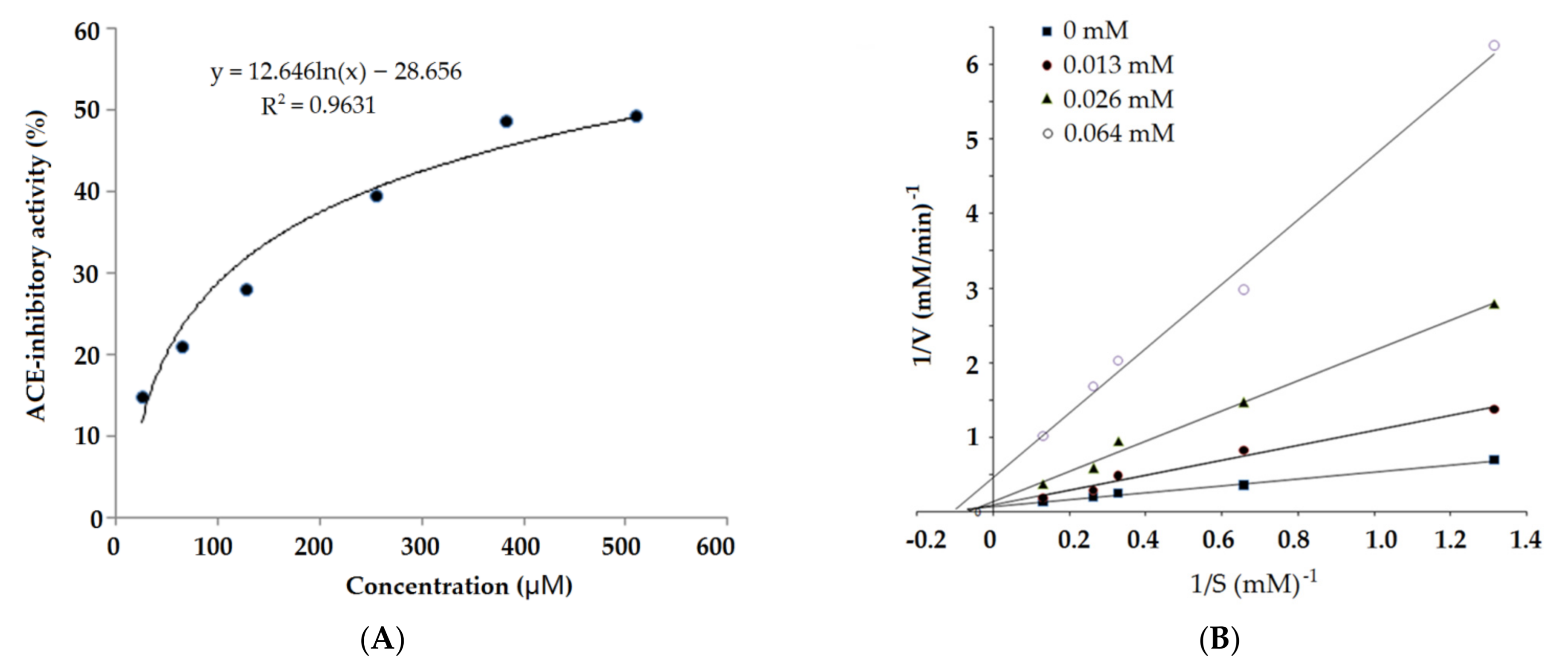
2.3. ACE Inhibition Kinetics of Synthesized Peptides
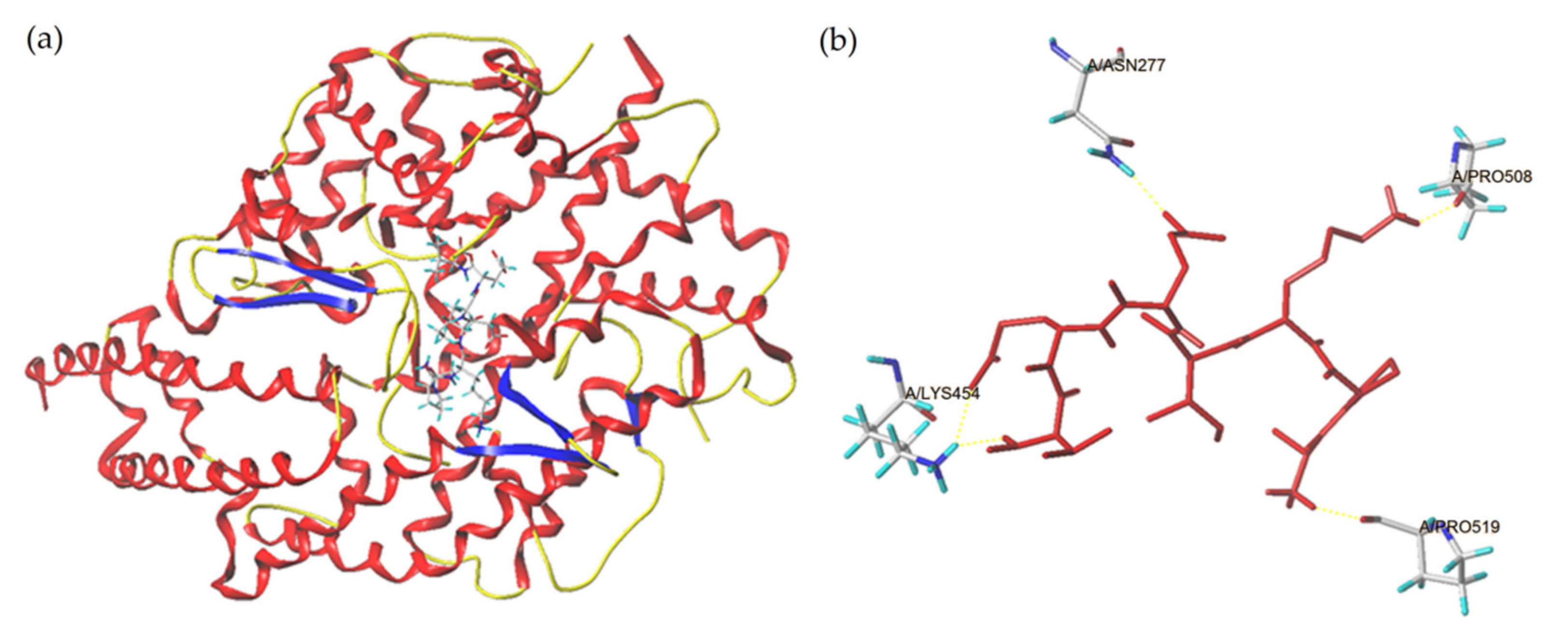
2.4. Combination Pattern between ACE and Peptides
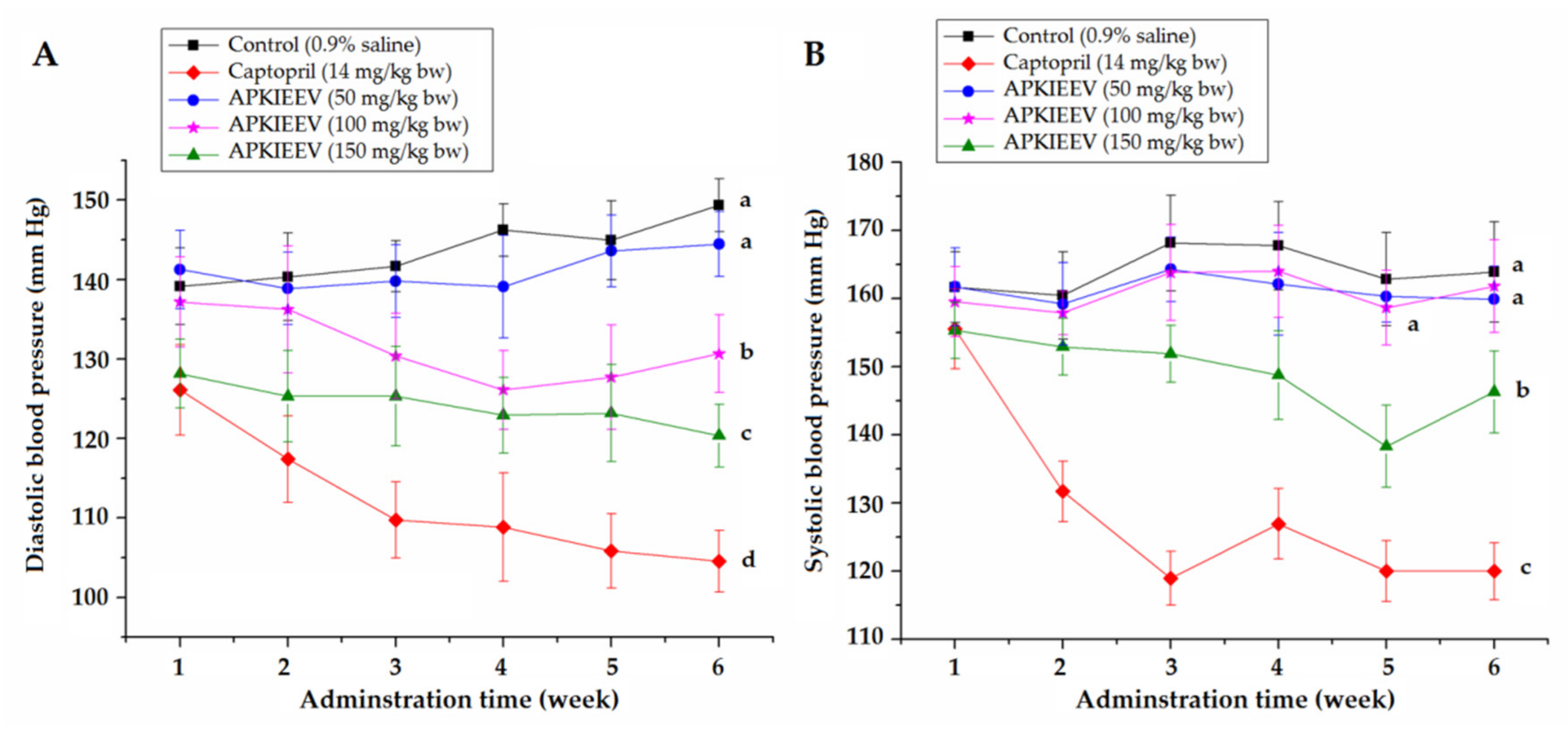
2.5. Antihypertensive Effect of Synthetic Peptides
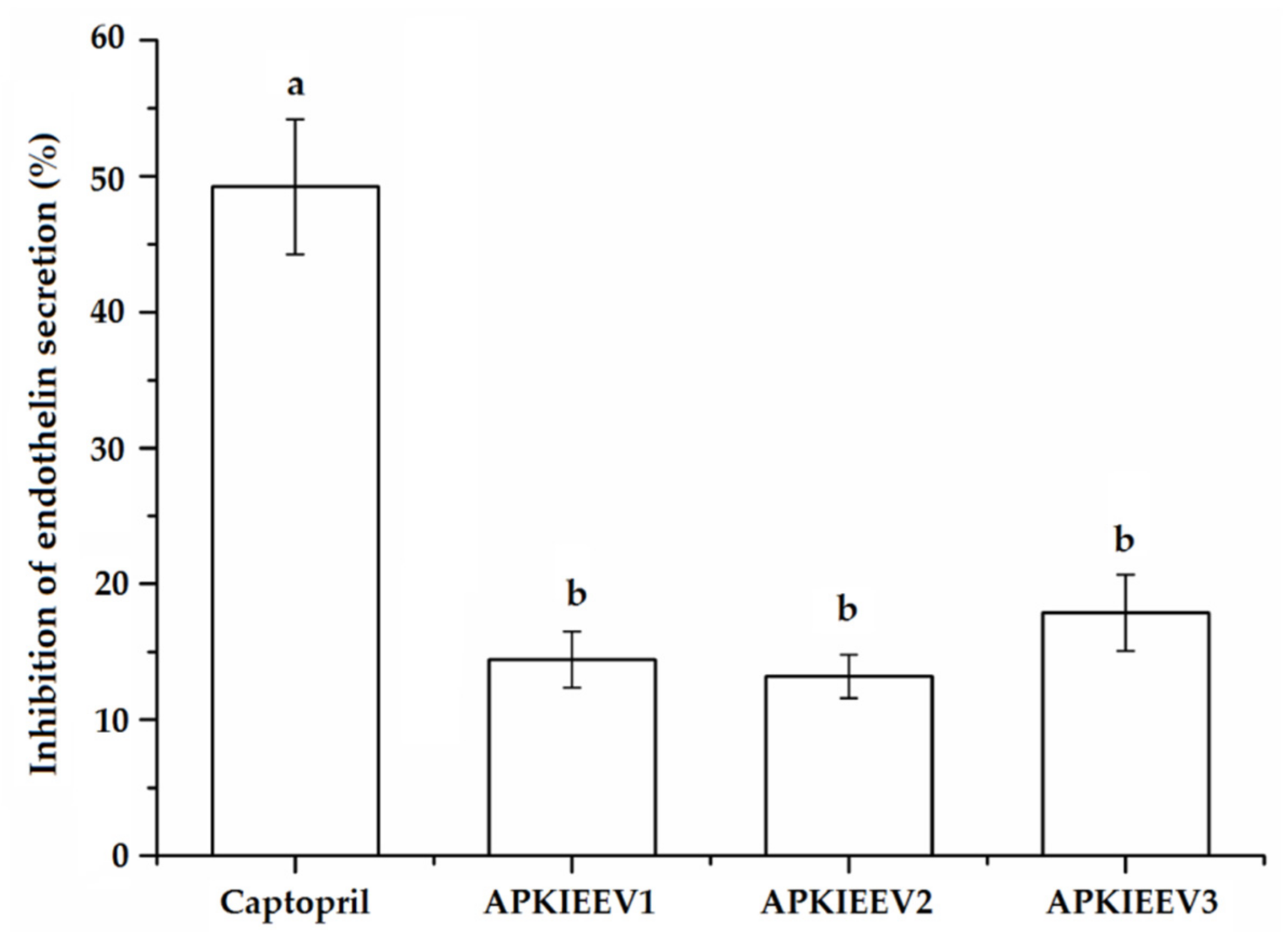
2.6. Effects on Intracellular Endothelin-1 (ET-1)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Areca Nut Kernel Globulin
3.3. Preparation of Areca Nut Kernel Globulin Hydrolysate
3.4. ACE Inhibitory Activity and Inhibition Kinetics
3.5. Purification of ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from ANKGH
3.6. Amino Acid Sequence Identification
3.7. In Silico Screening and Synthesis of Peptides
3.8. Molecular Docking
3.9. Antihypertensive Effect In Vivo
3.10. Effects on Intracellular Endothelin-1
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Fan, H.; Wu, J. Purification and identification of novel ACE inhibitory and ACE2 upregulating peptides from spent hen muscle proteins. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2017 Diet Collaborators. Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 393, 1958–1972.
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Liu, B.; Yuan, L.; Sun, L.; Zhuang, Y. ACE inhibitory activity in vitro and antihypertensive effect in vivo of LSGYGP and its transepithelial transport by Caco-2 cell monolayer. J. Funct. Food 2019, 61, 103488. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ruan, X.H.; Zhang, R.G. Purification, characterization, synthesis, in vivo ACE inhibition and in vitro antihypertensive activity of bioactive peptides derived from palm kernel expeller glutelin-2 hydrolysates. J. Funct. Food 2017, 28, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.F.; San, S. Efficacy of a Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptide from Sargassum maclurei in Hypertension and Reduction of Intracellular Endothelin-1. Nutrients 2020, 12, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovesana, S.; Capriotti, A.L.; Cavaliere, C.; La Barbera, G.; Montone, C.M.; Chiozzi, R.Z.; Laganà, A. Recent trends and analytical challenges in plant bioactive peptide separation, identification and validation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3425–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Contreras, M.M.; Recio, I. Antihypertensive peptides: Production, bioavailability and incorporation into foods. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 165, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, S.; Lunow, D.; Kaiser, S.; Henle, T. Identification and quantification of ACE-inhibiting peptides in enzymatic hydrolysates of plant proteins. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Wang, S.; Zhu, X.; Li, Q.; Fan, Y.; Cheng, D.; Li, B. A novel calcium-binding peptide from Antarctic krill protein hydrolysates and identification of binding sites of calcium-peptide complex. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Garg, A.; Parascandola, M.; Chaturvedi, P.; Khariwala, S.S.; Stepanov, I. Analysis of alkaloids in areca nut-containing products by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, N.; Ali, H.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Ali, A.; Ahmed, A.; Ei-Seedi, H.R.; Musharraf, S.G. Evaluation of cytotoxicity of areca nut and its commercial products on normal human gingival fibroblast and oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusriah, L.; Sapuan, S.M.; Zainudin, E.S.; Mariatti, M. Characterization of physical, mechanical, thermal and morphological properties of agro-waste betel nut (Areca catechu) husk fibre. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 72, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Liu, Y.J.; Wu, N.; Sun, T.; He, X.Y.; Gao, Y.X.; Wu, C.J. Areca catechu L. (Arecaceae): A review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 164, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Tulsyan, S.; Thakur, N.; Sharma, V.; Mehrotra, R. Chemistry, metabolism and pharmacology of carcinogenic alkaloids present in areca nut and factors affecting their concentration. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2019, 110, 104548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, C.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Zhao, T.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Zhao, M.; Su, G. Identification of post-digestion angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from soybean protein Isolate: Their production conditions and in silico molecular docking with ACE. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskar, B.; Ananthanarayana, L.; Jamdar, S. Purification, identification, and characterization of novel angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Alcalase digested horse gram flour. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 103, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.; Zhang, R.; Liu, H.; Lu, W.; Jiang, L.; Du, M. Identification of a novel ACE-inhibitory peptide from casein and evaluation of the inhibitory mechanisms. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Luo, Q.; Hong, H.; Liu, H.; Luo, Y. Novel antioxidant and ACE inhibitory peptide identified from Arthrospira platensis protein and stability against thermal/pH treatments and simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Sun, L.P.; Zhuang, Y.L. Preparation and identification of novel inhibitory angiotensin-I-converting enzyme peptides from tilapia skin gelatin hydrolysates: Inhibition kinetics and molecular docking. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5251–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhedi, O.; Nasri, R.; Mora, L.; Jridi, M.; Toldra, F.; Nasri, M. Peptidomic analysis of antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory peptides obtained from tomato waste proteins fermented using Bacillus subtilis. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Zhao, S.L. Purification, characterization, synthesis, in vivo and in vitro antihypertensive activity of bioactive peptides derived from coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) cake globulin hydrolysates. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 92688–92698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler-Nissen, J. Determination of the degree of hydrolysis of food protein hydrolysates by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1979, 27, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimsheena, V.K.; Gowda, L.R. Colorimetric, high-throughput assay for screening angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9388–9394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Shi, P.Q.; Tian, H.L.; Li, X.T.; Chen, X. Isolation of novel ACE-inhibitory peptide from naked oat globulin hydrolysates in silico approach: Molecular docking, in vivo antihypertension and effects on renin and intracellular endothelin-1. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Chaudhary, K.; Sharma, M.; Nagpal, G.; Chauhan, J.S.; Singh, S.; Gautam, A.; Raghava, P.S. AHTPDB: A comprehensive platform for analysis and presentation of antihypertensive peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D956–D962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaide-Hidalgo, J.M.; Romero, M.; Duarte, J.; López-Huertas, E. Antihypertensive effects of virgin olive oil (unfiltered) low molecular weight peptides with ACE inhibitory activity in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Wang, J.L.; He, G.Q.; Wu, J. Purification, identification, and in vivo activity of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide, from ribbon fish (Trichiurus haumela) backbone. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, C1–C7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Peptide | Mass (Da) | SVMS | Prediction | ALC(%) | Hydrophilicity | Amphiphilicity | Hydrophobicity | Steric Hindrance | Isoelectric Point | IC50 (μmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVDEVLNA | 888.04 | −0.47 | Non-AHT | 80 | −0.09 | 0.32 | 0.49 | 0.74 | 3.58 | ND |
| APKIEEV | 784.99 | 0.77 | AHT | 92 | 0.74 | 0.89 | −0.13 | 0.67 | 4.54 | 550.41 |
| AFSKI | 564.73 | −0.78 | Non-AHT | 79 | −0.30 | 0.73 | 0.05 | 0.69 | 9.11 | ND |
| QFLMQIIRT | 1149.53 | −0.79 | Non-AHT | 75 | −0.69 | 0.05 | −0.09 | 0.78 | 10.11 | ND |
| ALSSAGLQNQIK | 1229.55 | −1.10 | Non-AHT | 71 | −0.18 | 0.51 | −0.10 | 0.66 | 9.11 | ND |
| ASGNSQGT | 720.80 | −0.47 | Non-AHT | 76 | 0.01 | 0.06 | −0.18 | 0.44 | 5.88 | ND |
| ENIDSSR | 819.90 | −2.22 | Non-AHT | 83 | 1.14 | 0.53 | −0.50 | 0.71 | 4.38 | ND |
| Ligand | T-Score | C-Score | Hydrogen Bonds Number | Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| APKIEEV | 11.33 | 400 | 4 | ASN277: 1.43; LYS454: 2.04; PRO508: 1.49, 2.39; PRO519: 2.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Qin, N.; Guo, L.; Wang, X.; Shen, S. Identification, Characterization and Antihypertensive Effect In Vivo of a Novel ACE-Inhibitory Heptapeptide from Defatted Areca Nut Kernel Globulin Hydrolysates. Molecules 2021, 26, 3308. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113308
Liu X, Li G, Wang H, Qin N, Guo L, Wang X, Shen S. Identification, Characterization and Antihypertensive Effect In Vivo of a Novel ACE-Inhibitory Heptapeptide from Defatted Areca Nut Kernel Globulin Hydrolysates. Molecules. 2021; 26(11):3308. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113308
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xing, Guanwen Li, Huimin Wang, Nan Qin, Lili Guo, Xiaomin Wang, and Sang Shen. 2021. "Identification, Characterization and Antihypertensive Effect In Vivo of a Novel ACE-Inhibitory Heptapeptide from Defatted Areca Nut Kernel Globulin Hydrolysates" Molecules 26, no. 11: 3308. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113308
APA StyleLiu, X., Li, G., Wang, H., Qin, N., Guo, L., Wang, X., & Shen, S. (2021). Identification, Characterization and Antihypertensive Effect In Vivo of a Novel ACE-Inhibitory Heptapeptide from Defatted Areca Nut Kernel Globulin Hydrolysates. Molecules, 26(11), 3308. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113308





