Efficient Low-Cost Procedure for Microextraction of Estrogen from Environmental Water Using Magnetic Ionic Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ramos, L. Critical overview of selected contemporary sample preparation techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1221, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeannot, M.A. Extraction—Liquid phase microextraction. Encycl. Sep. Sci. 2007, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokosa, J.M. Advances in solvent-microextraction techniques. TrAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2013, 43, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.L.; Brennecke, J.A.; Holbrey, J.D.; Maginn, E.J.; Mantz, R.A.; Rogers, R.D.; Trulove, P.C.; Visser, A.E.; Welton, T. Physicochemical properties of ionic liquids. In Ionic Liquids in Synthesis, 1st ed.; Wasserscheid, P., Welton, T., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; pp. 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo-Rodriguez, M.J.; Nan, H.; Varona, M.; Emaus, M.N.; Souza, I.D.; Anderson, J.L. Advances of ionic liquids in analytical chemistry. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 505–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, K.J.; MacFarlane, D.R. Phosphonium-based ionic liquids: An overview. Aust. J. Chem. 2009, 62, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, A.; Morgenbesser, C.; Kogelnig, D.; Krachler, R.; Keppler, B.K. Quaternary ammonium and phosphonium ionic liquids. In Chemical and Environmental Engineering, Ionic Liquids: Theory, Properties, New Approaches, 1st ed.; Kokorin, A., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2011; pp. 657–680. [Google Scholar]
- Berton, P.; Wuilloud, R.G. An online ionic liquid-based microextraction system coupled to electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry for cobalt determination in environmental samples and pharmaceutical formulations. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, E.M.; Berton, P.; Altamirano, J.C.; Hakala, U.; Wuilloud, R.G. Tetradecyl(trihexyl)phosphonium chloride ionic liquid single-drop microextraction for electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometric determination of lead in water samples. Talanta 2010, 80, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, E.M.; Escudero, L.B.; Berton, P.; Monasterio, R.P.; Filippini, M.F.; Wuilloud, R.G. Determination of inorganic selenium species in water and garlic samples with on-line ionic liquid dispersive microextraction and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2011, 30, 2182–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Lu, C.; de Rooy, S.L.; Warner, I.M. Highly efficient extraction of phenolic compounds by use of magnetic room temperature ionic liquids for environmental remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.M.; Borges, R.P.; Godinho, M.; Marques, C.S.; Langa, E.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Lourenço, M.J.V.; Santos, F.J.V.; de Castro, C.A.N.; Macatrão, M.; et al. Thermophysical and magnetic studies of two paramagnetic liquid salts: [C4mim][FeCl4] and [P66614][FeCl4]. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2013, 350, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.D.; Nacham, O.; Purslow, J.A.; Pierson, S.A.; Anderson, J.L. Magnetic ionic liquids in analytical chemistry: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 934, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M. Magnetic ionic liquids in analytical sample preparation: A literature review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Merib, J.; Anderson, J.L. Faster dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction methods using magnetic ionic liquids as solvents. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1463, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzimitakos, T.G.; Pierson, S.A.; Anderson, J.L.; Stalikas, C.D. Enhanced magnetic ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of triazines and sulfonamides through a one-pot, pH-modulated approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1571, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benede, J.L.; Anderson, J.L.; Chisvert, A. Trace determination of volatile polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in natural waters by magnetic ionic liquid-based stir bar dispersive liquid microextraction. Talanta 2018, 176, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisvert, A.; Benede, J.L.; Anderson, J.L.; Pierson, S.A.; Salvador, A. Introducing a new and rapid microextraction approach based on magnetic ionic liquids: Stir bar dispersive liquid microextraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 983, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, E.F.; Escudero, L.B.; Wuilloud, R.G. Magnetic ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction technique for preconcentration and ultra-trace determination of Cd in honey. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4715–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, E.F.; Canizo, B.V.; Wuilloud, R.G. Determination of as in honey samples by magnetic ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2019, 198, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merib, J.; Spudeit, D.A.; Corazza, G.; Carasek, E.; Anderson, J.L. Magnetic ionic liquids as versatile extraction phases for the rapid determination of estrogens in human urine by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4689–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Xue, S.; Zhang, L. Novel functionalized magnetic ionic liquid green separation technology coupled with high performance liquid chromatography: A rapid approach for determination of estrogens in milk and cosmetics. Talanta 2020, 209, 120542–120550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimitakos, T.G.; Anderson, J.L.; Stalikas, C.D. Matrix solid-phase dispersion based on magnetic ionic liquids: An alternative sample preparation approach for the extraction of pesticides from vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1581–1582, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo-Rodriguez, M.J.; Pino, V.; Anderson, J.L. Magnetic ionic liquids as extraction solvents in vacuum headspace single-drop microextraction. Talanta 2017, 172, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racz, L.; Goel, R.K. Fate and removal of estrogens in municipal wastewater. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, Y.F.; Praveena, S.M. Sources, mechanisms, and fate of steroid estrogens in wastewater treatment plants: A mini review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briciu, R.D.; Kot-Wasik, A.; Namiesnik, J. Analytical challenges and recent advances in the determination of estrogens in water environments. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2009, 47, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, B.; Balke, B.; Felser, C.; Mudring, A.-V. Dysprosium room-temperature ionic liquids with strong luminescence and response to magnetic fields. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 7635–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Basheer, C.; Lee, H.K. Solvent-bar microextraction of herbicides combined with non-aqueous field-amplified sample injection capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 6036–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghoff, B.; Goetheer, E.L.V.; de Haan, A.B. COSMO-RS-based extractant screening for phenol extraction as model system. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 4263–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.H.; Montgomery, D.C. Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Derringer, G.C.; Suich, R. Simultaneous optimization of several response variables. J. Qual. Technol. 1980, 12, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Q.; Chen, D.-Y.; Feng, Y.-S.; Deng, H.-M.; Liu, Y.-H.; Zhou, A.-J. Determination of estrogens in water samples by ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Lett. 2012, 45, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melwanki, M.B.; Huang, S.-D. Three-phase system in solvent bar microextraction: An approach for the sample preparation of ionizable organic compounds prior to liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 555, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, H.; Zou, D.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y. Ultrasound-assisted surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction combined with HPLC for the determination of estrogens in water. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Almeida, C.; Nogueira, J.M.F. Determination of steroid sex hormones in water and urine matrices by stir bar sorptive extraction and liquid chromatography with diode array detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2006, 41, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Huang, Y.; He, M.; Hu, B. Hollow fiber liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection for the determination of various environmental estrogens in environmental and biological samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1305, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y. Enrichment and determination of trace estradiol in environmental water samples by hollow-fiber liquid-phase microextraction prior to HPLC. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2011, 49, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjmohammadi, M.R.; Ghoreishi, S.S. Determination of estrogens in water samples using dispersive liquid liquid microextraction and high performance liquid chromatography. Acta Chim. Slov. 2011, 58, 765–771. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, É.M.L.; Dias, R.A.S.; Sousa, E.R.; Brito, N.M.; Freitas, A.S.; Silva, G.S.; Silva, L.K.; Lima, D.L.; Esteves, V.I.; Silva, G.S. Determination of three estrogens in environmental water samples using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction by high-performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detector. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Hernández-Borges, J.; Asensio-Ramos, M.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Palenzuela, J.A.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.A. Determination of estrogens in environmental water samples using 1,3-dipentylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid as extraction solvent in dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 2479–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
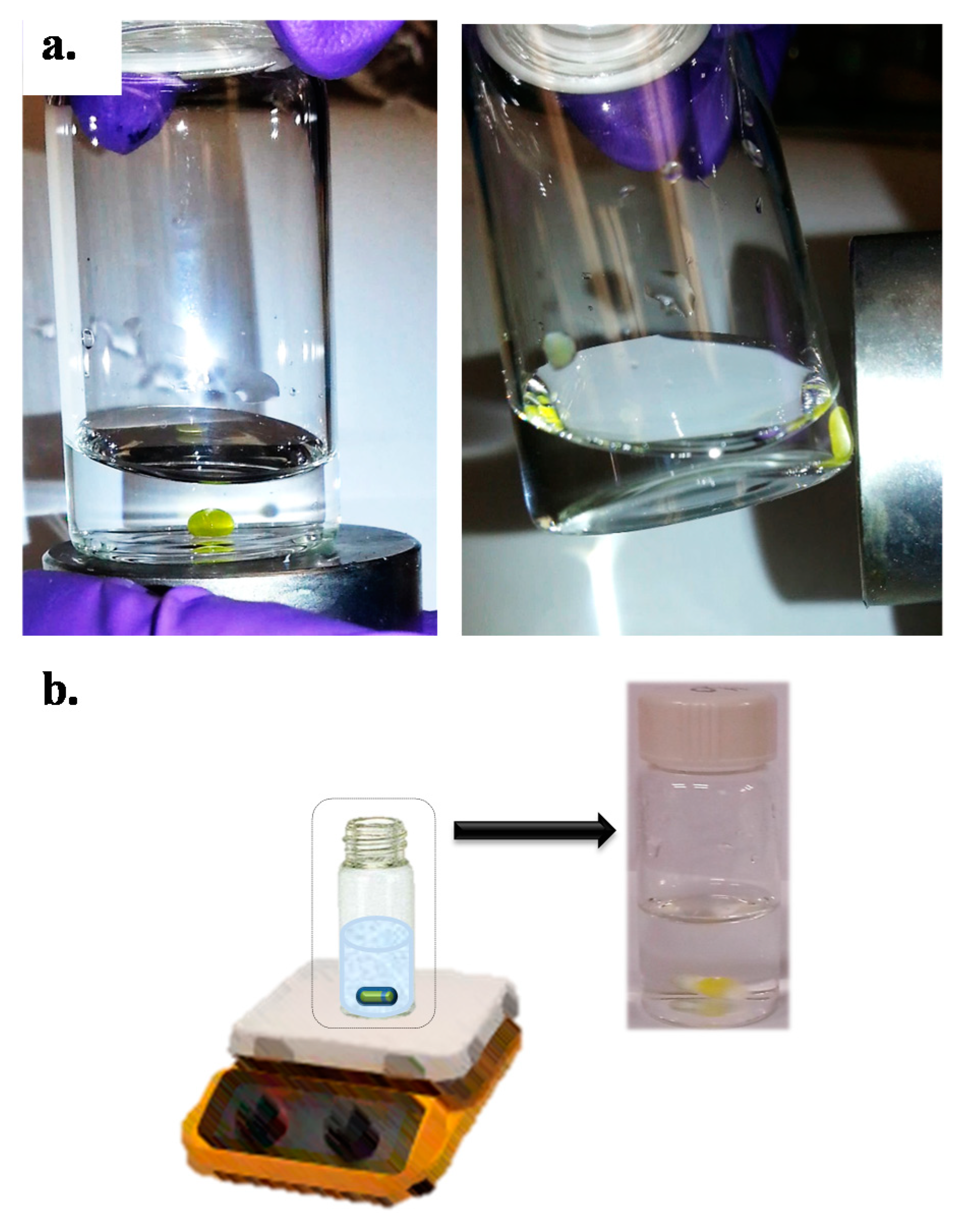
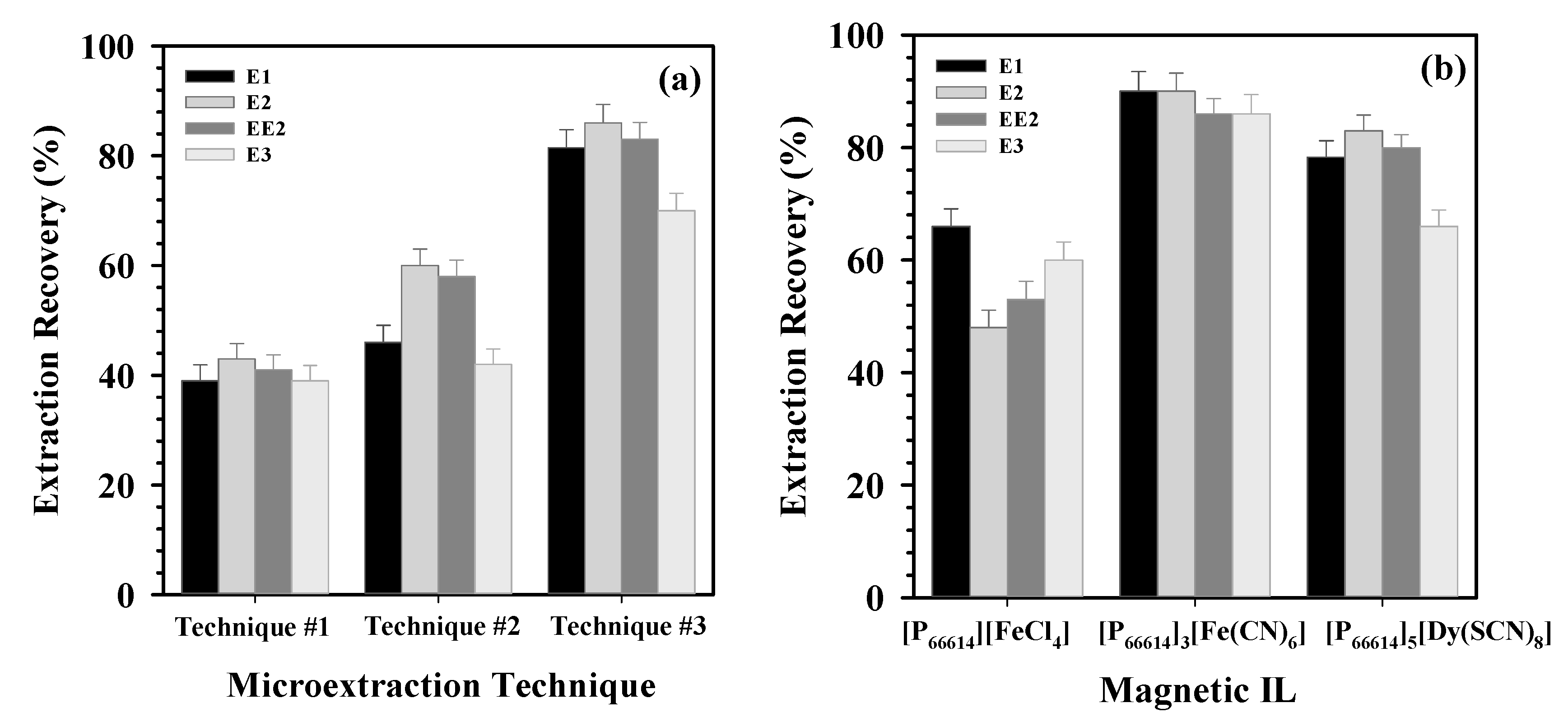
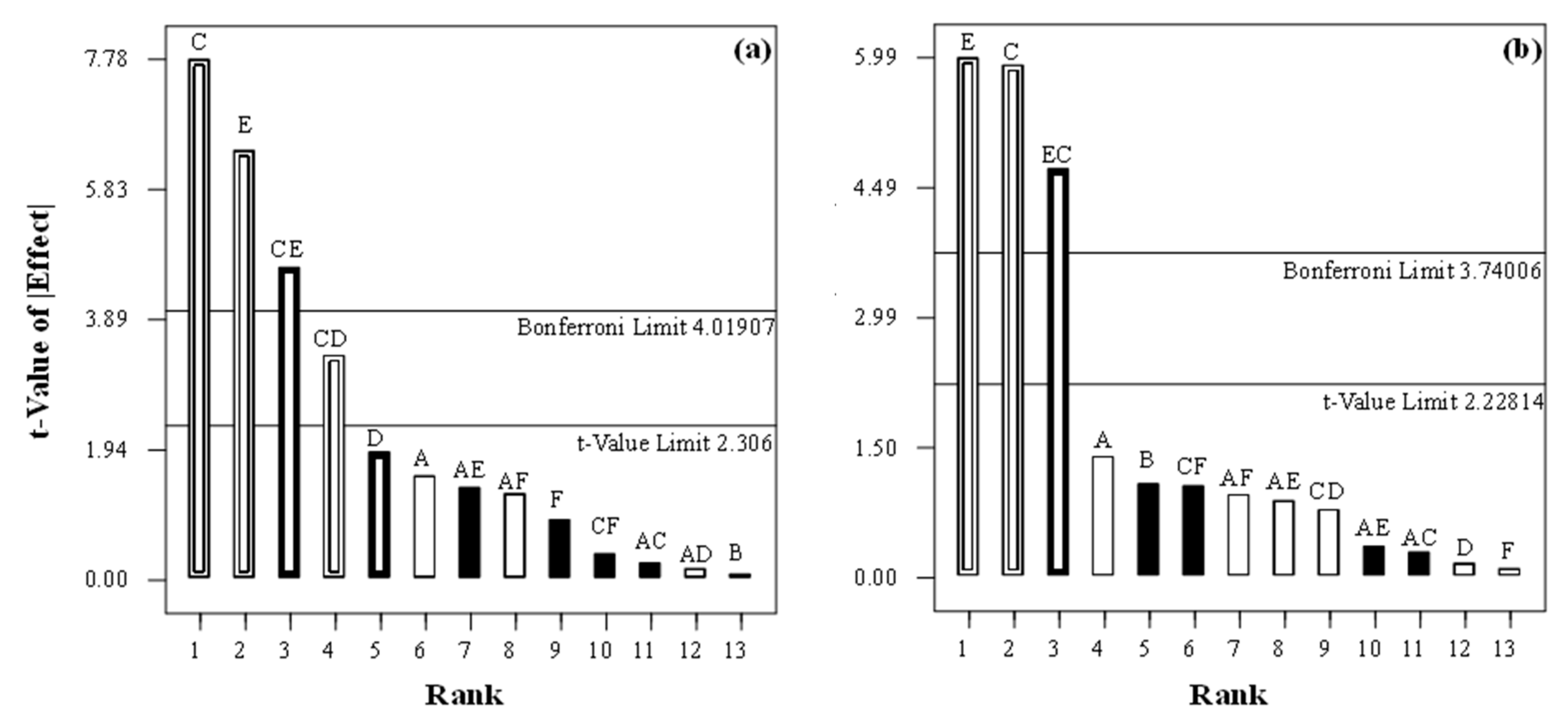
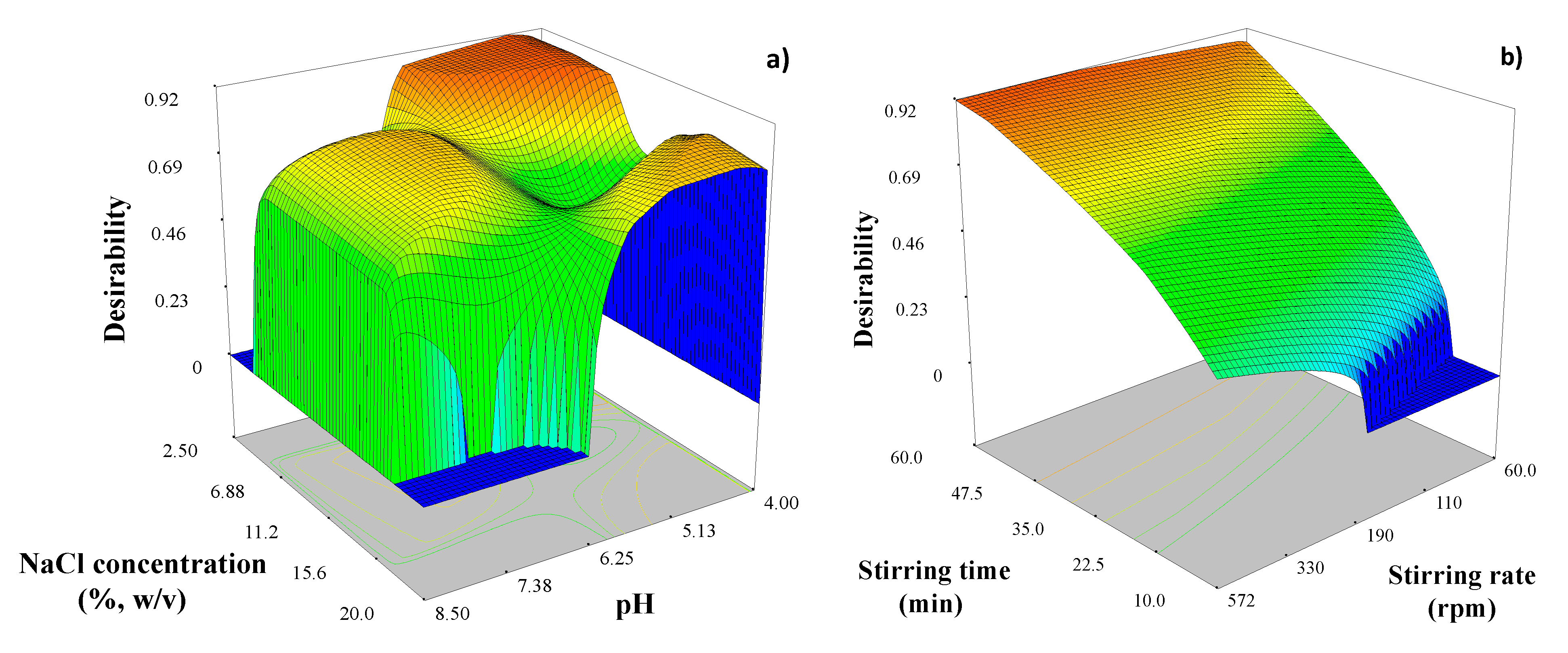
| Parameter | E3 | E2 | EE2 | E1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration range (µg L−1) | 0.5–1000 | 0.5–1000 | 1–1000 | 1–1000 | |||
| Correlation coefficients (r) | 0.9986 | 0.9988 | 0.9990 | 0.9983 | |||
| LOD (µg L−1) | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | |||
| RSD (%) | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.9 | 5.0 | |||
| Retention time (min) | 14.9 | 26.5 | 28.2 | 29.4 | |||
| Capacity factor (k’) | 2.69 | 5.55 | 5.98 | 6.27 | |||
| Efficiency factor (N) | 5929 | 17,838 | 9864 | 28,873 | |||
| Separation factor (α) | 2.06 | 1.08 | 1.05 | ||||
| Resolution (R) | 14.8 | 1.76 | 1.40 | ||||
| Analyte | Tap Water | Lake Water | Wastewater | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added (µg L−1) | Found (µg L−1) | Recovery (%) | Found (µg L−1) | Recovery (%) | Found (µg L−1) | Recovery (%) | |
| E1 | 5.00 | 4.98 ± 0.25 | 99.6 | 4.89 ± 0.24 | 97.8 | 4.53 ± 0.23 | 90.6 |
| 20.0 | 19.6 ± 0.88 | 98.1 | 19.3 ± 0.87 | 96.5 | 17.9 ± 0.72 | 89.5 | |
| E2 | 5.00 | 4.92 ± 0.24 | 98.3 | 4.83 ± 0.22 | 96.6 | 4.43 ± 0.21 | 88.5 |
| 20.0 | 19.7 ± 0.85 | 98.6 | 19.6 ± 0.95 | 97.9 | 17.8 ± 0.86 | 89.2 | |
| EE2 | 5.00 | 4.93 ± 0.20 | 98.5 | 4.91 ± 0.20 | 98.1 | 4.45 ± 0.25 | 88.9 |
| 20.0 | 20.0 ± 0.81 | 99.9 | 19.5 ± 0.82 | 97.8 | 17.7 ± 0.74 | 88.4 | |
| E3 | 5.00 | 4.93 ± 0.21 | 98.6 | 4.90 ± 0.19 | 98.0 | 4.50 ± 0.19 | 89.9 |
| 20.0 | 19.8 ± 0.82 | 98.9 | 19.6 ± 0.81 | 98.2 | 18.1 ± 0.75 | 90.3 | |
| Technique | Estrogens | Extraction Time (min) | LOD (µg L−1) | RSD (%) | Sample Consumption (mL) | Calibration Range (µg L−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UASEME | E1, E2, diethylstilbestrol (DES) | <15 | 0.1–0.2 | <1.28 | 10 | 10–1000 | [35] |
| SBSE-LD | E1, E2, EE2, DES, mestranol, progesterone, norethisterone, norgestrel | 120 | 0.3–1.0 | <17.1 | 30 | 1.25–50.0 | [36] |
| HF-LLLME | E1, E2, E3, EE2, DES, dienestrol (DIS), bisphenol-A, 4-t-octylphenol | 50 | 0.11–0.66 | <8.4 | 6 | 0.5–500 2–1000 | [37] |
| HF-LPME | E2 | 60 | 0.1 | 5.5 | 140 | 1–1000 | [38] |
| DLLME | E1, E2, DES | <11 | 0.008–0.010 | <4.9 | 5 | 0.020–500.0 | [39] |
| DLLME | E1, E2, EE2 | 0.5 | 0.003–0.020 | ---a | 8 | 0.01–0.5 (E2, EE2) 0.04–4 (E1) | [40] |
| IL-DLLME | E1, E2, E3, EE2, DES | <21 | 0.08–0.5 | <5.7 | 5 | 0.2–100 1.0–100 | [33] |
| IL-DLLME | E1, E2, EE2, DES, DIS, hexestrol | 1 | 13.8–37.1 | <8.3 | ---a | 1.5–1732 | [41] |
| IL-on SBME | E1, E2, E3, EE2 | 60 | 0.2–0.5 | < 5.1 | 15 | 1.0–1000 | Present work |
| Extraction Conditions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-treated sample volume (mL) | 15 | ||
| MIL mass (mg) | 26 | ||
| pH | 4.5 | ||
| NaCl concentration (% (w/v)) | 6 | ||
| Extraction time (min) | 60 | ||
| Stirring rate (rpm) | 300 | ||
| HPLC Instrumental Conditions | |||
| Selected absorption wavelength | 200 nm | ||
| Injection volume | 20 µL | ||
| LC column | Luna C18 (4 µm × 4.6 mm i.d. × 250 mm) | ||
| Flow rate | 0.5 mL min−1 | ||
| Column temperature | 25 °C | ||
| Mobile phases | A: water B: acetonitrile | ||
| HPLC Gradient Program | |||
| Step | Initial Time (min) | Final Time (min) | Final Composition of Mobile Phase |
| 0 | 0.0 | 5.0 | 70% A; 30% B (isocratic) |
| 1 | 5.0 | 35 | 20% A; 80% B (linear gradient) |
| 2 | 35 | 40 | 100% B (isocratic) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berton, P.; Siraj, N.; Das, S.; de Rooy, S.; Wuilloud, R.G.; Warner, I.M. Efficient Low-Cost Procedure for Microextraction of Estrogen from Environmental Water Using Magnetic Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2021, 26, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010032
Berton P, Siraj N, Das S, de Rooy S, Wuilloud RG, Warner IM. Efficient Low-Cost Procedure for Microextraction of Estrogen from Environmental Water Using Magnetic Ionic Liquids. Molecules. 2021; 26(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerton, Paula, Noureen Siraj, Susmita Das, Sergio de Rooy, Rodolfo G. Wuilloud, and Isiah M. Warner. 2021. "Efficient Low-Cost Procedure for Microextraction of Estrogen from Environmental Water Using Magnetic Ionic Liquids" Molecules 26, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010032
APA StyleBerton, P., Siraj, N., Das, S., de Rooy, S., Wuilloud, R. G., & Warner, I. M. (2021). Efficient Low-Cost Procedure for Microextraction of Estrogen from Environmental Water Using Magnetic Ionic Liquids. Molecules, 26(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010032








