The Two-Way Switch Role of ACE2 in the Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia and Underlying Comorbidities
Abstract
1. Introduction
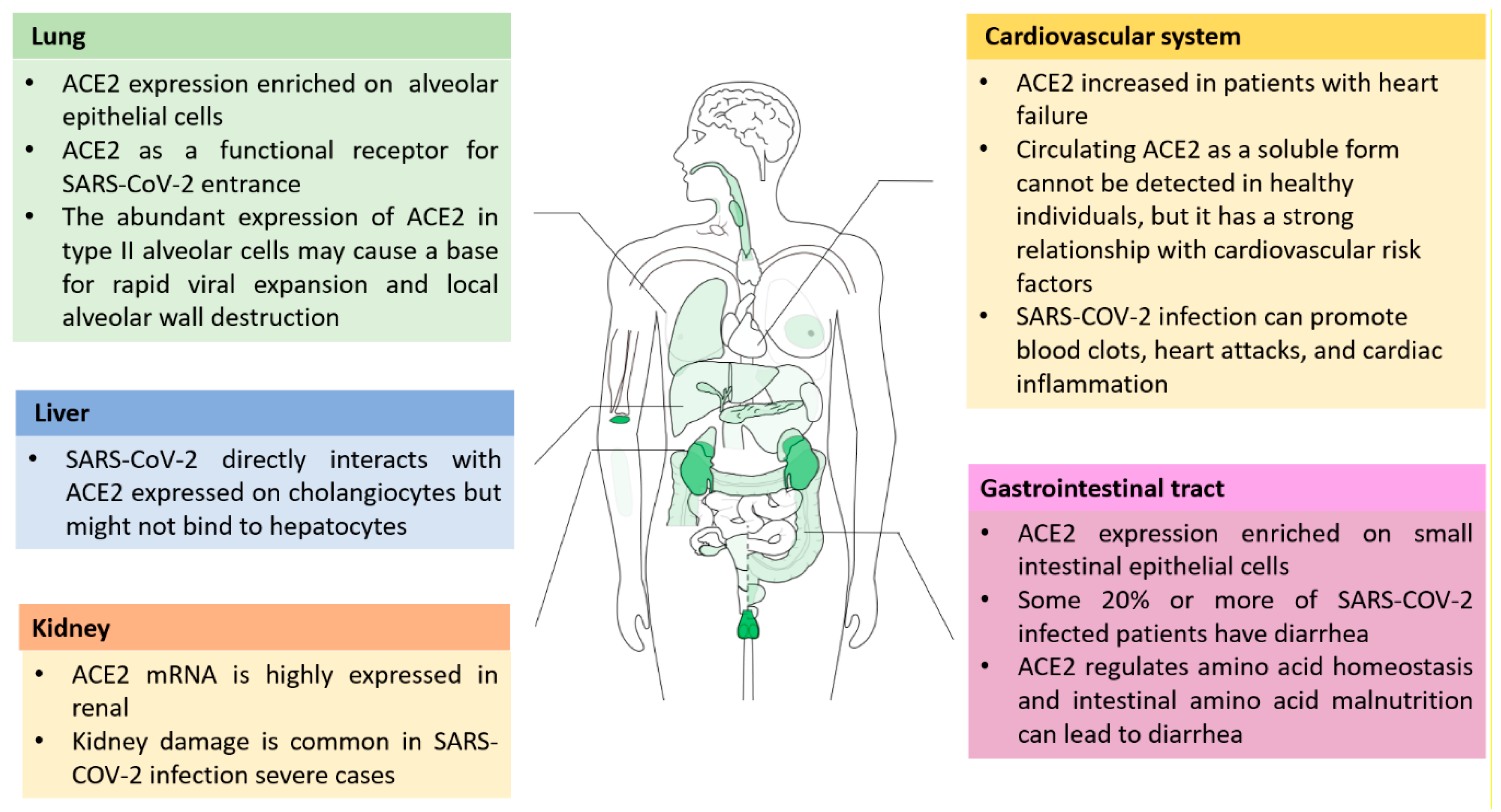
2. Function and Distribution of ACE2
3. Inhibiting ACE2 to Block the Entry of Coronavirus
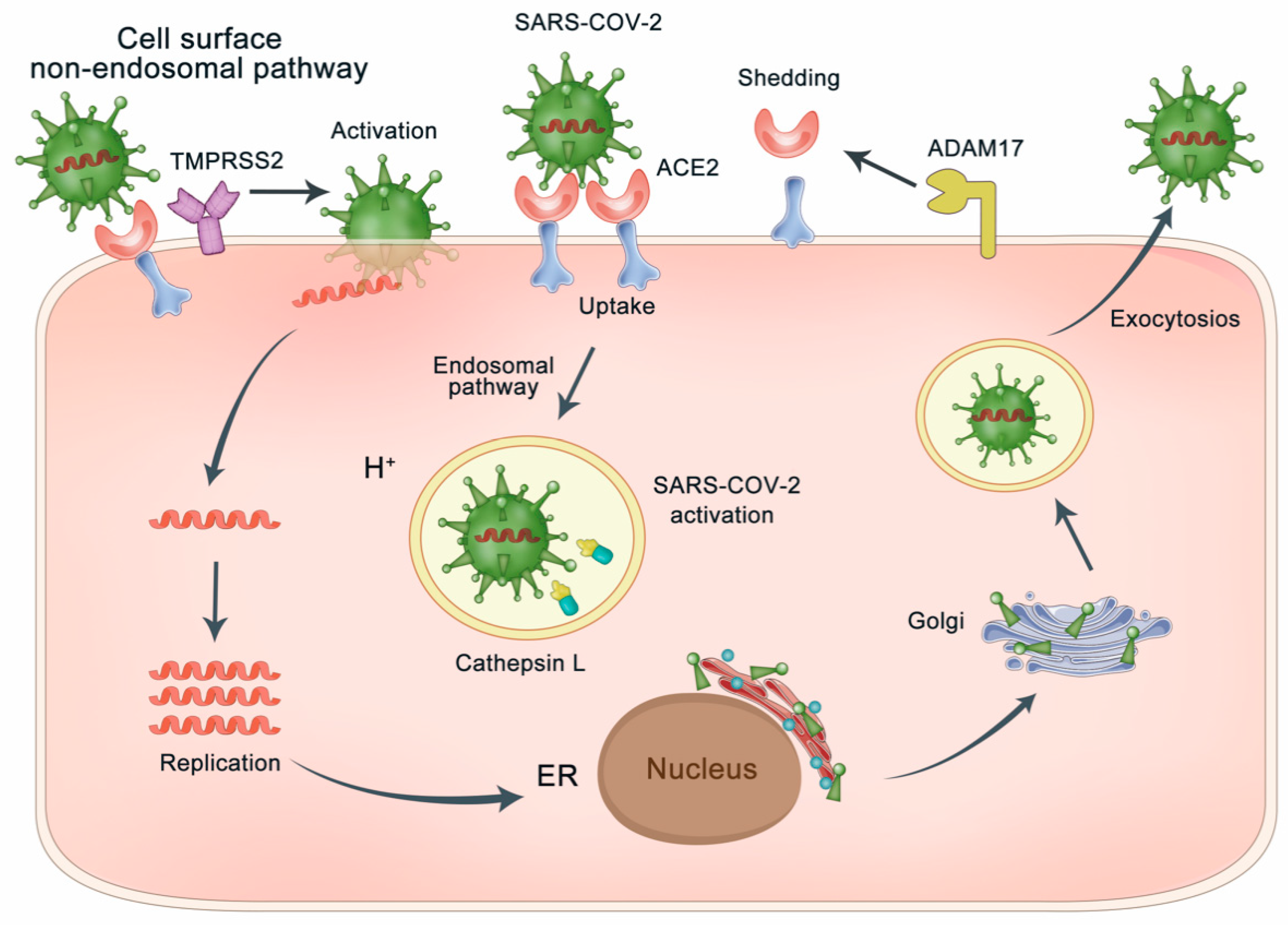
3.1. ACE2 as the Gateway of SARS-CoV-2
3.2. Blocking the Binding of S-Protein Binding Site of ACE2 with SARS-CoV-2
4. Activating the Peptidase Function of ACE2 for Lung Protection
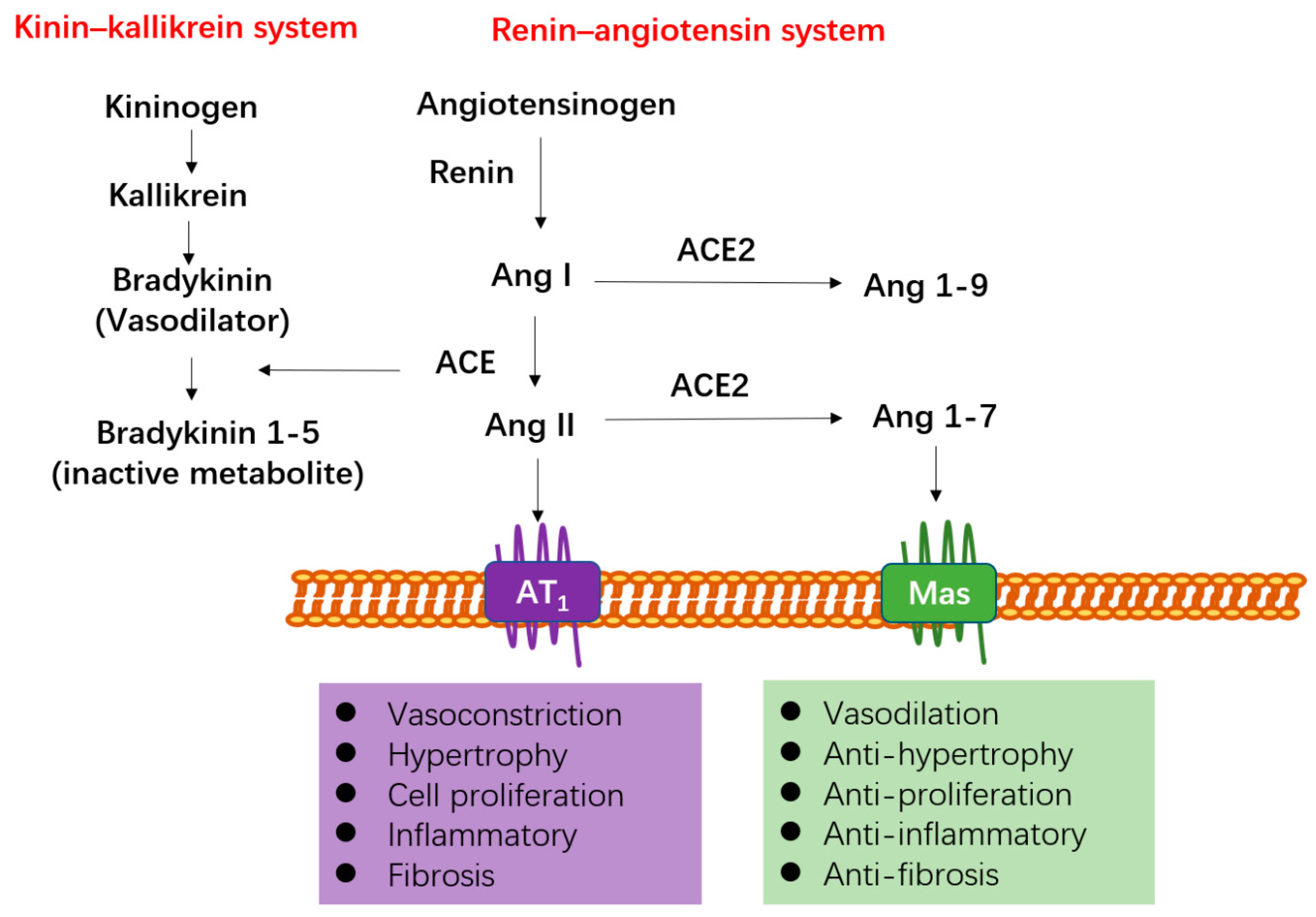
4.1. ACE2 Functions as a Negative Regulator of RAS
4.2. Stimulating the Expression of ACE2
4.3. The Clinical Usage of ACEIs and ARBs for SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patient with Cardiovascular Diseases: Pros and Cons
5. Control of the Two-Way Switch of ACE2 in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Its Underlying Comorbidities
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease 2019 |
| SARS | severe acute respiratory syndrome |
| SARS-CoV-2 | severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 |
| PHEIC | public health emergency of international concern |
| S-protein | spike glycoprotein |
| ACE2 | angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| ACE | angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| RBD | receptor-binding domain |
| cryo-EM | cryo-electron microscopy |
| RAS | renin-angiotensin system |
| Ang I | angiotensin I |
| Ang II | angiotensin II |
| AT1 | angiotensin receptor type 1 |
| AT2 | angiotensin receptor type 2 |
| ACEIs | ACE inhibitors |
| ARBs | AT1 receptor blockers |
| ARDS | acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| ICU | intensive care unit |
| ADAM-17 | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 17 |
| TMPRSS2 | Transmembrane Serine Protease 2 |
| AR | androgen receptor |
| DHT | dihydrotestosterone |
| LNCaP | activin-sensitive prostate cancer cells |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| hESC | human embryonic stem cell |
| PD | peptidase domain |
| NAAE | N-(2-aminoethyl)-1 aziridine-ethanamine |
| IC50 | the half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| KD | the calculated affinity |
| IFN | interferon |
| IL | interleukin |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| IPF | idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| PAH | pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| ALI | acute lung injury |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| TLR4 | toll-like receptor 4 |
| MAP | mitogen-activated protein |
| ERK/MAPK | extracellular-signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| AMPA | alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid |
| APJ | the apelin receptor |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| ISG | interferon stimulated gene |
| fMLP | N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine |
| MAS1 | the G protein-coupled receptor Mas |
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statement on the Meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee Regarding the Outbreak of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Available online: https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/detail/23-01-2020-statement-on-the-meeting-of-the-international-health-regulations-(2005)-emergency-committee-regarding-the-outbreak-of-novel-coronavirus-(2019-ncov) (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.T.; Jia, N.; Zhang, Y.W.; Shum, M.H.; Jiang, J.F.; Zhu, H.C.; Tong, Y.G.; Shi, Y.X.; Ni, X.B.; Liao, Y.S.; et al. Identifying SARS-CoV-2-related coronaviruses in Malayan pangolins. Nature 2020, 583, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosten, C.; Günther, S.; Preiser, W.; van der Werf, S.; Brodt, H.R.; Becker, S.; Rabenau, H.; Panning, M.; Kolesnikova, L.; Fouchier, R.A.; et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Ye, T.; Sun, P.; Gui, S.; Liang, B.; Li, L.; Zheng, D.; Wang, J.; Hesketh, R.L.; Yang, L.; et al. Time Course of Lung Changes at Chest CT during Recovery from Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Radiology 2020, 295, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Lu, Z.; Ke, A.; Zhou, J.; Shi, G.; Fang, N.; Fan, J.; et al. Specific ACE2 Expression in Cholangiocytes May Cause Liver Damage After 2019-nCoV Infection. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.P.; Penn-Nicholson, A.; Cho, M.W. Identification of critical determinants on ACE2 for SARS-CoV entry and development of a potent entry inhibitor. Virology 2006, 350, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, T.; Chung, O.; Csikos, T.; Culman, J.; Gallinat, S.; Gohlke, P.; Höhle, S.; Meffert, S.; Stoll, M.; Stroth, U.; et al. Angiotensin receptors. J. Hypertens. Suppl. 1996, 14, S95–S103. [Google Scholar]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, V.; Qi, Y.; Katovich, M.J.; Raizada, M.K. ACE2, a promising therapeutic target for pulmonary hypertension. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2011, 11, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed-Tabatabaei, F.A.; Oostra, B.A.; Isaacs, A.; van Duijn, C.M.; Witteman, J.C. ACE polymorphisms. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Saku, K.; Karnik, S.S. Molecular analysis of the structure and function of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Hypertens. Res. 2003, 26, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Ye, Y.; Gong, H.; Wu, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, S.; Yin, P.; Ding, Z.; Kang, L.; Jiang, Q.; et al. The effects of different angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers on the regulation of the ACE-AngII-AT1 and ACE2-Ang(1-7)-Mas axes in pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling in male mice. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 97, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, M.; Hsieh, F.; Baronas, E.; Godbout, K.; Gosselin, M.; Stagliano, N.; Donovan, M.; Woolf, B.; Robison, K.; Jeyaseelan, R.; et al. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crackower, M.A.; Sarao, R.; Oudit, G.Y.; Yagil, C.; Kozieradzki, I.; Scanga, S.E.; Oliveira-dos-Santos, A.J.; da Costa, J.; Zhang, L.; Pei, Y.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is an essential regulator of heart function. Nature 2002, 417, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.A.; Simoes e Silva, A.C.; Maric, C.; Silva, D.M.; Machado, R.P.; de Buhr, I.; Heringer-Walther, S.; Pinheiro, S.V.; Lopes, M.T.; Bader, M.; et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) is an endogenous ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor Mas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8258–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Chappell, M.C.; Tallant, E.A.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Diz, D.I. Counterregulatory actions of angiotensin-(1-7). Hypertension 1997, 30, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos-Silva, D.G.; Brandan, E.; Santos, R.A. Angiotensins as therapeutic targets beyond heart disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.L.; Liu, B.C. Role of non-classical renin-angiotensin system axis in renal fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, M.C.; Pirro, N.T.; Sykes, A.; Ferrario, C.M. Metabolism of angiotensin-(1-7) by angiotensin-converting enzyme. Hypertension 1998, 31, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.J.; Hooper, N.M. The angiotensin-converting enzyme gene family: Genomics and pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2002, 23, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, M.J.; Barrios, C.; Oliva, R.; Batlle, D. Pharmacologic modulation of ACE2 expression. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2008, 10, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gembardt, F.; Sterner-Kock, A.; Imboden, H.; Spalteholz, M.; Reibitz, F.; Schultheiss, H.P.; Siems, W.E.; Walther, T. Organ-specific distribution of ACE2 mRNA and correlating peptidase activity in rodents. Peptides 2005, 26, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.L.; Lely, A.T.; Navis, G.; van Goor, H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Rao, S.; Gao, H.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Huan, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; et al. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovac, H. COVID-19: Is the ACE2 just a foe? American journal of physiology. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 318, L1025–L1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vabret, N.; Britton, G.J.; Gruber, C.; Hegde, S.; Kim, J.; Kuksin, M.; Levantovsky, R.; Malle, L.; Moreira, A.; Park, M.D.; et al. Immunology of COVID-19: Current State of the Science. Immunity 2020, 52, 910–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Perlot, T.; Rehman, A.; Trichereau, J.; Ishiguro, H.; Paolino, M.; Sigl, V.; Hanada, T.; Hanada, R.; Lipinski, S.; et al. ACE2 links amino acid malnutrition to microbial ecology and intestinal inflammation. Nature 2012, 487, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, M.; Yao, J.; Guo, J.; Liao, X.; Song, S.; Li, J.; Duan, G.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. Caution on Kidney Dysfunctions of COVID-19 Patients. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, G.I.; Jones, A.L.; Grant, P.J.; Carter, A.M.; Turner, A.J.; Hooper, N.M. Circulating activities of angiotensin-converting enzyme, its homolog, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, and neprilysin in a family study. Hypertension 2006, 48, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguiano, L.; Riera, M.; Pascual, J.; Soler, M.J. Circulating ACE2 in Cardiovascular and Kidney Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 3231–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, L.M.; Burchill, L.; Dean, R.G.; Griggs, K.; Patel, S.K.; Velkoska, E. Chronic kidney disease: Cardiac and renal angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) 2 expression in rats after subtotal nephrectomy and the effect of ACE inhibition. Exp. Physiol. 2012, 97, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, S.; Yusuf, S.; Chong, M.; Ramasundarahettige, C.; Rangarajan, S.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; van Eikels, M.; Leineweber, K.; Wu, A.; Pigeyre, M.; et al. Plasma ACE2 and risk of death or cardiometabolic diseases: A case-cohort analysis. Lancet 2020, 396, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, M.; Silva Enciso, J.E.; Greenberg, B.H. Selective and specific regulation of ectodomain shedding of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 by tumor necrosis factor alpha-converting enzyme. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, C1318–C1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sama, I.E.; Ravera, A.; Santema, B.T.; van Goor, H.; Ter Maaten, J.M.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Rienstra, M.; Friedrich, A.W.; Samani, N.J.; Ng, L.L.; et al. Circulating plasma concentrations of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in men and women with heart failure and effects of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone inhibitors. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1810–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Seddighzadeh, B.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Huang, F.W. Expression of ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor, and TMPRSS2 in Prostate Epithelial Cells. Eur. Urol. 2020, 78, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Miao, L.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, C.; Liu, J.; Zhan, Q.; Guo, B.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; et al. Suppression of Androgen Receptor (AR)-ACE2/TMPRSS2 Axis by AR Antagonists May Be Therapeutically Beneficial for Male COVID-19 Patients. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3580526 (accessed on 18 July 2020).
- Gallagher, T.M.; Buchmeier, M.J. Coronavirus spike proteins in viral entry and pathogenesis. Virology 2001, 279, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, G.; Zmora, P.; Gierer, S.; Heurich, A.; Pöhlmann, S. Proteolytic activation of the SARS-coronavirus spike protein: Cutting enzymes at the cutting edge of antiviral research. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, W.; Farzan, M.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain complexed with receptor. Science 2005, 309, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachery, V.D.; Dinnon, K.H., 3rd; Yount, B.L., Jr.; McAnarney, E.T.; Gralinski, L.E.; Hale, A.; Graham, R.L.; Scobey, T.; Anthony, S.J.; Wang, L.; et al. Trypsin Treatment Unlocks Barrier for Zoonotic Bat Coronavirus Infection. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, G.; Gosalia, D.N.; Rennekamp, A.J.; Reeves, J.D.; Diamond, S.L.; Bates, P. Inhibitors of cathepsin L prevent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11876–11881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata-Yoshikawa, N.; Okamura, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Takeda, M.; Nagata, N. TMPRSS2 Contributes to Virus Spread and Immunopathology in the Airways of Murine Models after Coronavirus Infection. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Krüger, N.; Müller, M.; Drosten, C.; Pöhlmann, S. The novel coronavirus 2019 (2019-nCoV) uses the SARS-coronavirus receptor ACE2 and the cellular protease TMPRSS2 for entry into target cells. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Vedantham, P.; Lu, K.; Agudelo, J.; Carrion, R., Jr.; Nunneley, J.W.; Barnard, D.; Pöhlmann, S.; McKerrow, J.H.; Renslo, A.R.; et al. Protease inhibitors targeting coronavirus and filovirus entry. Antivir. Res. 2015, 116, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheblawi, M.; Wang, K.; Viveiros, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Zhong, J.C.; Turner, A.J.; Raizada, M.K.; Grant, M.B.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the Discovery of ACE2. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1456–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Ye, G.; Shi, K.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Aihara, H.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 581, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, R.M.; Majd, H.; Richter, M.N.; Ghazizadeh, Z.; Zekavat, S.M.; Navickas, A.; Ramirez, J.T.; Asgharian, H.; Simoneau, C.R.; Bonser, L.R.; et al. Androgen Signaling Regulates SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Levels and Is Associated with Severe COVID-19 Symptoms in Men. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 876–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Sui, J.; Kuhn, J.H.; Moore, M.J.; Luo, S.; Wong, S.K.; Huang, I.C.; Xu, K.; Vasilieva, N.; et al. Receptor and viral determinants of SARS-coronavirus adaptation to human ACE2. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Peng, G.; Wilken, M.; Geraghty, R.J.; Li, F. Mechanisms of host receptor adaptation by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 8904–8911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Shang, J.; Graham, R.; Baric, R.S.; Li, F. Receptor Recognition by the Novel Coronavirus from Wuhan: An Analysis Based on Decade-Long Structural Studies of SARS Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Niu, S.; Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Qiao, C.; Hu, Y.; Yuen, K.Y.; et al. Structural and Functional Basis of SARS-CoV-2 Entry by Using Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dales, N.A.; Gould, A.E.; Brown, J.A.; Calderwood, E.F.; Guan, B.; Minor, C.A.; Gavin, J.M.; Hales, P.; Kaushik, V.K.; Stewart, M.; et al. Substrate-based design of the first class of angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 11852–11853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, M.J.; Bergeron, E.; Benjannet, S.; Erickson, B.R.; Rollin, P.E.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Seidah, N.G.; Nichol, S.T. Chloroquine is a potent inhibitor of SARS coronavirus infection and spread. J. Virol. 2005, 2, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huentelman, M.J.; Zubcevic, J.; Hernández Prada, J.A.; Xiao, X.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Raizada, M.K.; Ostrov, D.A. Structure-based discovery of a novel angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inhibitor. Hypertension 2004, 44, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Li, C.; Huang, A.; Xia, S.; Lu, S.; Shi, Z.; Lu, L.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; et al. Potent binding of 2019 novel coronavirus spike protein by a SARS coronavirus-specific human monoclonal antibody. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassiri, Z.; Zhong, J.; Guo, D.; Basu, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, P.P.; Scholey, J.W.; Penninger, J.M.; Oudit, G.Y. Loss of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 accelerates maladaptive left ventricular remodeling in response to myocardial infarction. Circ. Heart Fail. 2009, 2, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, E.S.A.C.; Teixeira, M.M. ACE inhibition, ACE2 and angiotensin-(1-7) axis in kidney and cardiac inflammation and fibrosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 107, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Molina-Molina, M.; Abdul-Hafez, A.; Uhal, V.; Xaubet, A.; Uhal, B.D. Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 is protective but downregulated in human and experimental lung fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 295, L178–L185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Kuba, K.; Rao, S.; Huan, Y.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Yang, P.; Sarao, R.; Wada, T.; Leong-Poi, H.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure. Nature 2005, 436, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaard, H.J.; Abe, K.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Voelkel, N.F. The right ventricle under pressure: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of right-heart failure in pulmonary hypertension. Chest 2009, 135, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Liu, Z. ACE2 exhibits protective effects against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting the LPS-TLR4 pathway. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 113, 104350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Yan, Y.; Shu, Y.; Gao, R.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Ju, X.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from lethal avian influenza A H5N1 infections. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Gu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, W.; Cao, B.; Lai, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) mediates influenza H7N9 virus-induced acute lung injury. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlot, T.; Penninger, J.M. ACE2—From the renin-angiotensin system to gut microbiota and malnutrition. Microbes Infect. 2013, 15, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Jin, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Ye, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Oudit, G.Y.; Ye, J.Y.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 attenuates oxidative stress and VSMC proliferation via the JAK2/STAT3/SOCS3 and profilin-1/MAPK signaling pathways. Regul. Pept. 2013, 185, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koka, V.; Huang, X.R.; Chung, A.C.; Wang, W.; Truong, L.D.; Lan, H.Y. Angiotensin II up-regulates angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE), but down-regulates ACE2 via the AT1-ERK/p38 MAP kinase pathway. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takase, O.; Marumo, T.; Imai, N.; Hirahashi, J.; Takayanagi, A.; Hishikawa, K.; Hayashi, M.; Shimizu, N.; Fujita, T.; Saruta, T. NF-kappaB-dependent increase in intrarenal angiotensin II induced by proteinuria. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oparil, S.; Silfani, T.N.; Walker, J.F. Role of angiotensin receptor blockers as monotherapy in reaching blood pressure goals. Am. J. Hypertens. 2005, 18, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Furuhashi, M.; Moniwa, N.; Mita, T.; Fuseya, T.; Ishimura, S.; Ohno, K.; Shibata, S.; Tanaka, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Akasaka, H.; et al. Urinary angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in hypertensive patients may be increased by olmesartan, an angiotensin II receptor blocker. Am. J. Hypertens. 2015, 28, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocaranza, M.P.; Godoy, I.; Jalil, J.E.; Varas, M.; Collantes, P.; Pinto, M.; Roman, M.; Ramirez, C.; Copaja, M.; Diaz-Araya, G.; et al. Enalapril attenuates downregulation of Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in the late phase of ventricular dysfunction in myocardial infarcted rat. Hypertension 2006, 48, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, J.K.; Ferner, R.E. Drugs and the renin-angiotensin system in covid-19. BMJ 2020, 369, m1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyh, G.I.; Nawarskas, J.J.; Cheng-Lai, A. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: Friend or Foe? Cardiol. Rev. 2020, 28, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Vardeny, O.; Michel, T.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Solomon, S.D. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, S.; Gamliel-Lazarovich, A.; Kaplan, M.; Pavlotzky, E.; Hamoud, S.; Hayek, T.; Karry, R.; Abassi, Z. Mineralocorticoid receptor blocker increases angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activity in congestive heart failure patients. Circ. Res. 2005, 97, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H. Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 7432–7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.; Manansala, J.S.; Abdulrahman, H.A.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Smatti, M.K.; Younes, N.; Althani, A.A.; Yassine, H.M. Immune Modulatory Effects of Vitamin D on Viral Infections. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek Mahdavi, A. A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, e2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Suzuki, T.; Watanabe, H.; Kadowaki, A.; Fukamizu, A.; Liu, P.P.; Kimura, A.; Ito, H.; Penninger, J.M.; Imai, Y.; et al. Apelin is a positive regulator of ACE2 in failing hearts. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 5203–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, M.; Fischer, C.; Basu, R.; Hazra, S.; Couvineau, P.; Paul, M.; Wang, F.; Toth, S.; Mix, D.S.; et al. Apelin protects against abdominal aortic aneurysm and the therapeutic role of neutral endopeptidase resistant apelin analogs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13006–13015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; McKinnie, S.M.; Farhan, M.; Paul, M.; McDonald, T.; McLean, B.; Llorens-Cortes, C.; Hazra, S.; Murray, A.G.; Vederas, J.C.; et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Metabolizes and Partially Inactivates Pyr-Apelin-13 and Apelin-17: Physiological Effects in the Cardiovascular System. Hypertension 2016, 68, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, N.E.; Belyaev, N.D.; Lambert, D.W.; Turner, A.J. Epigenetic regulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) by SIRT1 under conditions of cell energy stress. Clin. Sci. 2014, 126, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Cheng, Y.W.; Jin, H.Y.; Chang, Q.; Shang, Q.H.; Xu, Y.L.; Chen, L.X.; Xu, R.; Song, B.; Zhong, J.C. The sirtuin 6 prevents angiotensin II-mediated myocardial fibrosis and injury by targeting AMPK-ACE2 signaling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 72302–72314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Daiber, A.; Förstermann, U.; Li, H. Antioxidant effects of resveratrol in the cardiovascular system. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1633–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Pan, W.; Huang, H.; Chen, J.; Sun, B.; Yang, L.; Zhu, P. Screening Analysis of Sirtuins Family Expression on Anti-Inflammation of Resveratrol in Endothelial Cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 4137–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lang, A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Haagmans, B.L. Interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 downregulate expression of the SARS coronavirus receptor ACE2 in Vero E6 cells. Virology 2006, 353, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, C.G.K.; Allon, S.J.; Nyquist, S.K.; Mbano, I.M.; Miao, V.N.; Tzouanas, C.N.; Cao, Y.; Yousif, A.S.; Bals, J.; Hauser, B.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 Is an Interferon-Stimulated Gene in Human Airway Epithelial Cells and Is Detected in Specific Cell Subsets across Tissues. Cell 2020, 181, 1016–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhu, Y.C.; Li, J.; Schäfer, H.; Schmidt, W.; Yao, T.; Unger, T. Effects of losartan on haemodynamic parameters and angiotensin receptor mRNA levels in rat heart after myocardial infarction. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2000, 1, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhu, Y.C.; Wang, Z.J.; Lu, Q.; Lee, H.S.; Unger, T. Time-dependent apoptotic development and pro-apoptotic genes expression in rat heart after myocardial infarction. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 86, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, J.L.; Lambert, D.W.; Warner, F.J.; Hooper, N.M.; Turner, A.J. Membrane-associated zinc peptidase families: Comparing ACE and ACE2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1751, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Li, Z.; Geng, J.; Han, H.; Cai, J.; Li, X.; Kang, W.; Weng, D.; et al. The clinical pathology of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS): A report from China. J. Pathol. 2003, 200, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.L.; Al Hosani, F.; Keating, M.K.; Gerber, S.I.; Jones, T.L.; Metcalfe, M.G.; Tong, S.; Tao, Y.; Alami, N.N.; Haynes, L.M.; et al. Clinicopathologic, Immunohistochemical, and Ultrastructural Findings of a Fatal Case of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection in the United Arab Emirates, April 2014. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiden, S.; Nahmod, K.; Nahmod, V.; Semeniuk, G.; Pereira, Y.; Alvarez, C.; Giordano, M.; Geffner, J.R. Nonpeptide antagonists of AT1 receptor for angiotensin II delay the onset of acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Jessup, J.; Chappell, M.C.; Averill, D.B.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Tallant, E.A.; Diz, D.I.; Gallagher, P.E. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockers on cardiac angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Circulation 2005, 111, 2605–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, Y.; Gallagher, P.E.; Averill, D.B.; Tallant, E.A.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Ferrario, C.M. Upregulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 after myocardial infarction by blockade of angiotensin II receptors. Hypertension 2004, 43, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Jessup, J.; Gallagher, P.E.; Averill, D.B.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Ann Tallant, E.; Smith, R.D.; Chappell, M.C. Effects of renin-angiotensin system blockade on renal angiotensin-(1-7) forming enzymes and receptors. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 2189–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, K.; Loomba, R.; Insel, P.A. Targeting the renin-angiotensin signaling pathway in COVID-19: Unanswered questions, opportunities, and challenges. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29274–29282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, P.; Lin, M.; Xu, Y.; Huang, B.; Zuo, X.; et al. ACE2 expression by colonic epithelial cells is associated with viral infection, immunity and energy metabolism. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteil, V.; Kwon, H.; Prado, P.; Hagelkrüys, A.; Wimmer, R.A.; Stahl, M.; Leopoldi, A.; Garreta, E.; Hurtado Del Pozo, C.; Prosper, F.; et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Engineered Human Tissues Using Clinical-Grade Soluble Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendse, L.B.; Danser, A.H.J.; Poglitsch, M.; Touyz, R.M.; Burnett, J.C., Jr.; Llorens-Cortes, C.; Ehlers, M.R.; Sturrock, E.D. Novel Therapeutic Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin System and Associated Peptides in Hypertension and Heart Failure. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 539–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Benthin, C.; Zeno, B.; Albertson, T.E.; Boyd, J.; Christie, J.D.; Hall, R.; Poirier, G.; Ronco, J.J.; Tidswell, M.; et al. A pilot clinical trial of recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minato, T.; Nirasawa, S.; Sato, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hoshizaki, M.; Inagaki, T.; Nakahara, K.; Yoshihashi, T.; Ozawa, R.; Yokota, S.; et al. B38-CAP is a bacteria-derived ACE2-like enzyme that suppresses hypertension and cardiac dysfunction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.K.; Dorosky, D.; Sharma, P.; Abbasi, S.A.; Dye, J.M.; Kranz, D.M.; Herbert, A.S.; Procko, E. Engineering human ACE2 to optimize binding to the spike protein of SARS coronavirus 2. Science 2020, 369, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, Y. Recombinant human ACE2: Potential therapeutics of SARS-CoV-2 infection and its complication. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020, 41, 1255–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mediator | Effect on ACE2 Expression | Pathway | Associated Disease |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT1 receptor blockers, such as olmesartan, losartan, telmisartan, azilsartan | Upregulation | Renin–angiotensin system; extracellular-signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK/MAPK) signaling pathway; nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway | Acute lung injury, hypertensive cardiovascular and renal damage |
| ACE inhibitors, such as Lisinopril, Enalapril | Downregulation | Renin–angiotensin system | Myocardial infarction |
| Vitamin D | Upregulation | Renin–angiotensin system | Acute lung injury (ALI) Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) |
| Spironolactone | Upregulation | NADPH oxidase related pathway | Heart failure |
| Resveratrol | Upregulation | alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) signaling pathway | Diabetes mellitus, cardiac fibrosis and heart disease |
| Apelin-13 | Upregulation | Apelin-the apelin receptor (APJ) activation pathway | Cardiovascular diseases |
| Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) | Upregulation | Cytokine signaling pathway | SARS coronavirus diabetes mellitus |
| Interferon α (IFNα), Interferon γ (IFNγ) | Downregulation | SARS coronavirus | |
| Interleukin-4 (IL-4) | Downregulation | SARS coronavirus |
| Clinical Trials Identifier | Study Title | Interventional Drug | Interventional Study Design |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04351581 | Combination of Recombinant Bacterial ACE2 Receptors -Like Enzyme of B38-CAP and Isotretinoin Could be Promising COVID-19Infection- and Lung Injury Preventing Drug Better Than Recombinant Human ACE2 | rbACE2 plus Aerosolized Isotretinoin | Randomized Parallel Assignment Open Label |
| NCT04355936 | Telmisartan for Treatment of COVID-19 Patients | Telmisartan | Randomized Parallel Assignment Open Label |
| NCT04335786 | Valsartan for Prevention of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Infection Disease | Valsartan | Randomized Parallel Assignment Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor) |
| NCT04312009 | Losartan for Patients with COVID-19 Requiring Hospitalization | Losartan | Randomized Parallel Assignment Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor) |
| NCT04311177 | Losartan for Patients with COVID-19 Not Requiring Hospitalization | Losartan | Randomized Parallel Assignment Quadruple (Participant, Care Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor) |
| NCT04328012 | COVID MED Trial-Comparison of Therapeutics for Hospitalized Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 | Losartan combined with lopinavir/ritonavir | Randomized Parallel Assignment Double blind, placebo controlled |
| NCT04340557 | Do Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Mitigate Progression to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome with SARS-CoV-2 Infection | Losartan | Randomized Parallel Assignment Open Label |
| NCT04332666 | Angiotensin-(1,7) Treatment in COVID-19: the ATCO Trial (ATCO) | Angiotensin 1–7 | Randomized Parallel Assignment Triple (Participant, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, X.C.; Zhang, H.X.; Zhang, Z.; Rinkiko, S.; Cui, Y.M.; Zhu, Y.Z. The Two-Way Switch Role of ACE2 in the Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia and Underlying Comorbidities. Molecules 2021, 26, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010142
Pang XC, Zhang HX, Zhang Z, Rinkiko S, Cui YM, Zhu YZ. The Two-Way Switch Role of ACE2 in the Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia and Underlying Comorbidities. Molecules. 2021; 26(1):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010142
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Xiao Cong, Han Xu Zhang, Zhi Zhang, Suguro Rinkiko, Yi Min Cui, and Yi Zhun Zhu. 2021. "The Two-Way Switch Role of ACE2 in the Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia and Underlying Comorbidities" Molecules 26, no. 1: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010142
APA StylePang, X. C., Zhang, H. X., Zhang, Z., Rinkiko, S., Cui, Y. M., & Zhu, Y. Z. (2021). The Two-Way Switch Role of ACE2 in the Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia and Underlying Comorbidities. Molecules, 26(1), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010142






