Role of Indole Scaffolds as Pharmacophores in the Development of Anti-Lung Cancer Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
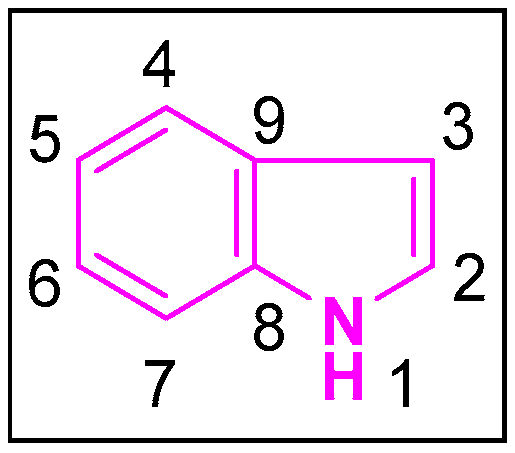
1.1. Indole and its Pharmacological Significance
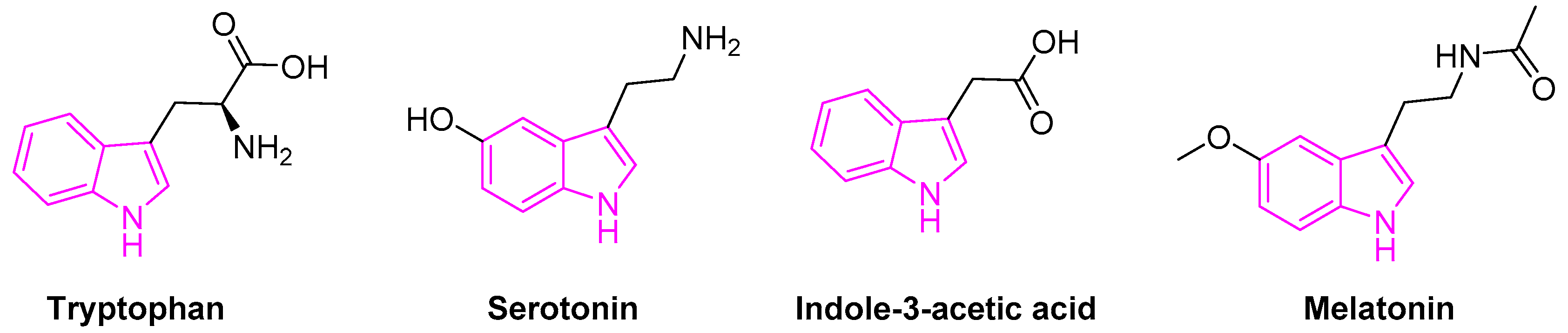
1.2. Natural Abundance of Indoles
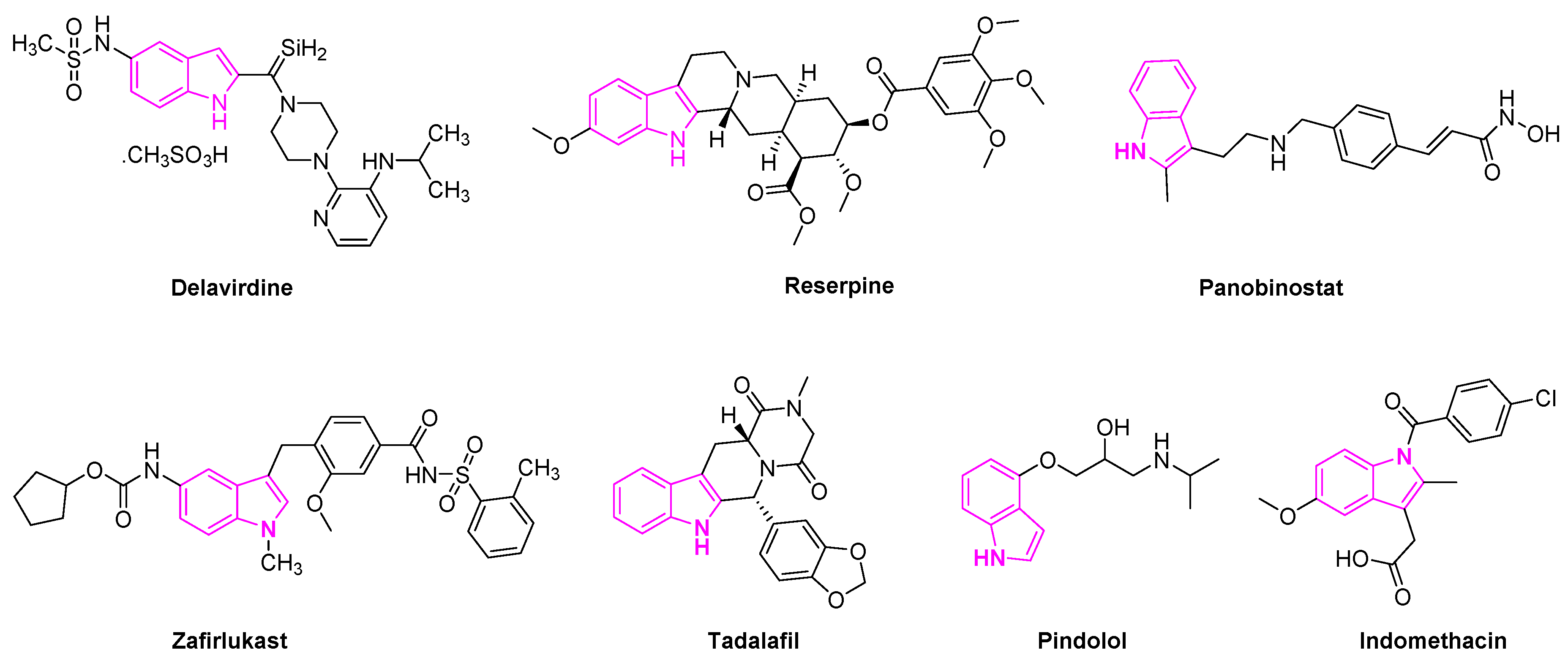
1.3. Significance of Indole Based Drugs
1.4. Methodology for Bibliographic Search
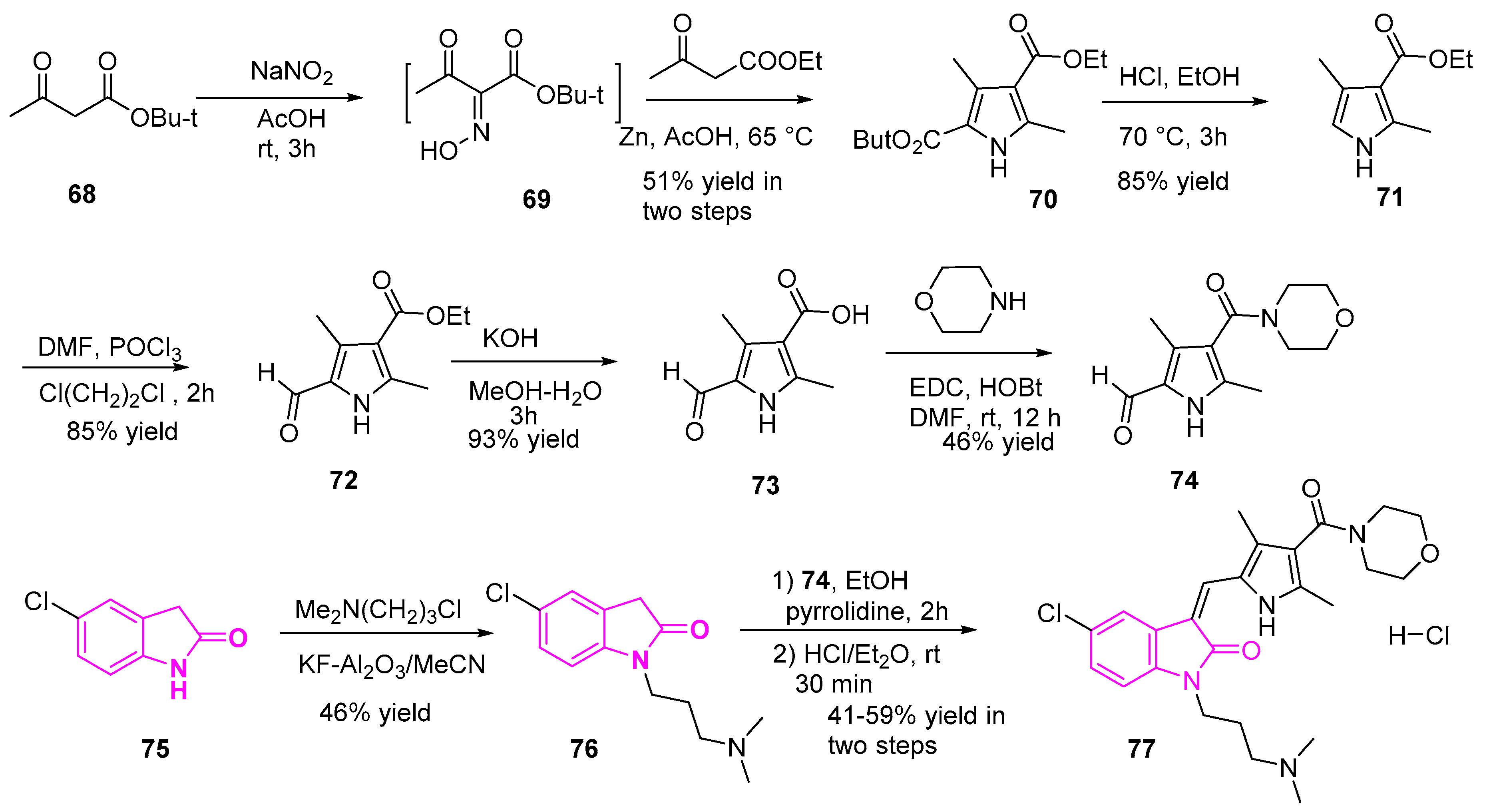
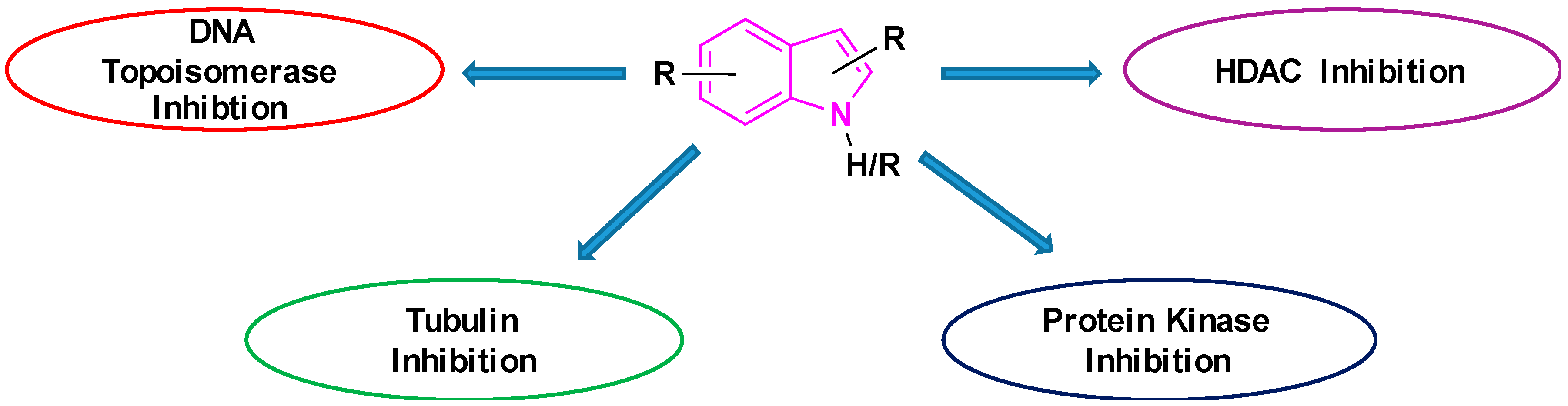
2. Indole Derivatives as Anti-Lung Cancer Agents
2.1. Indole Derivatives as Kinase Inhibitors
2.2. Targeting Akt Signaling Pathway
2.3. Epidermal Growth Factor (EGFR) Inhibition
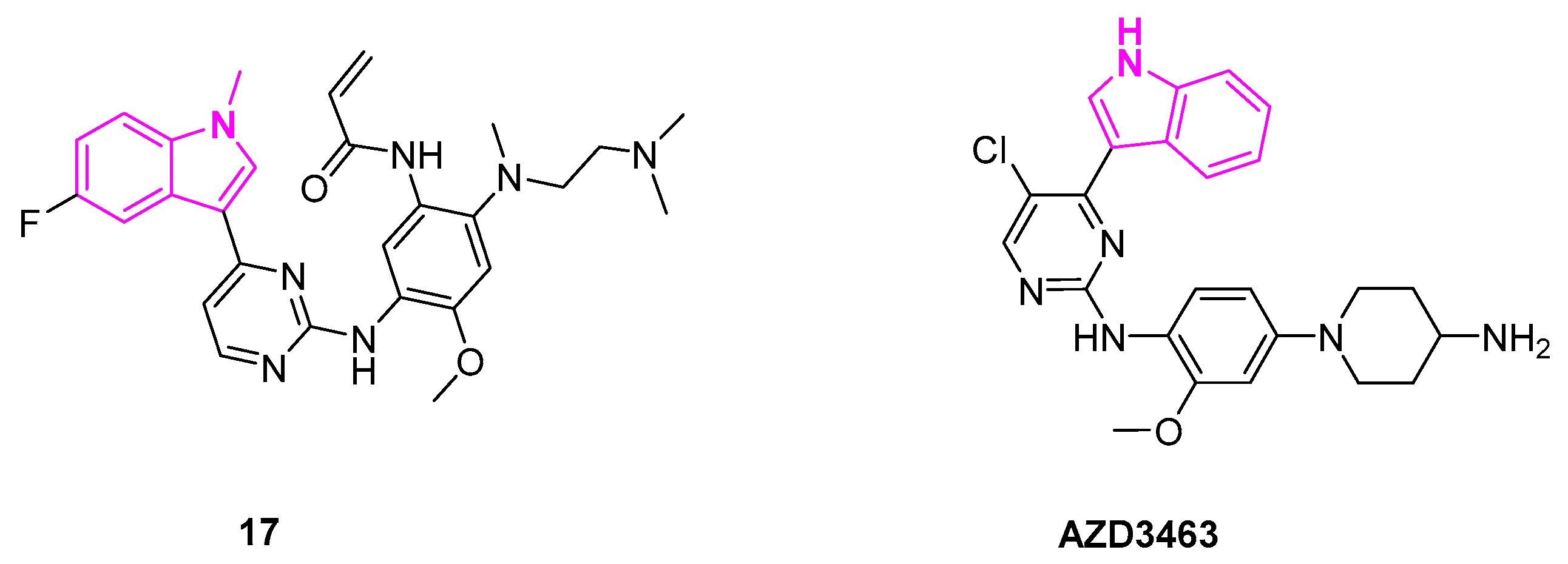
2.4. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibition
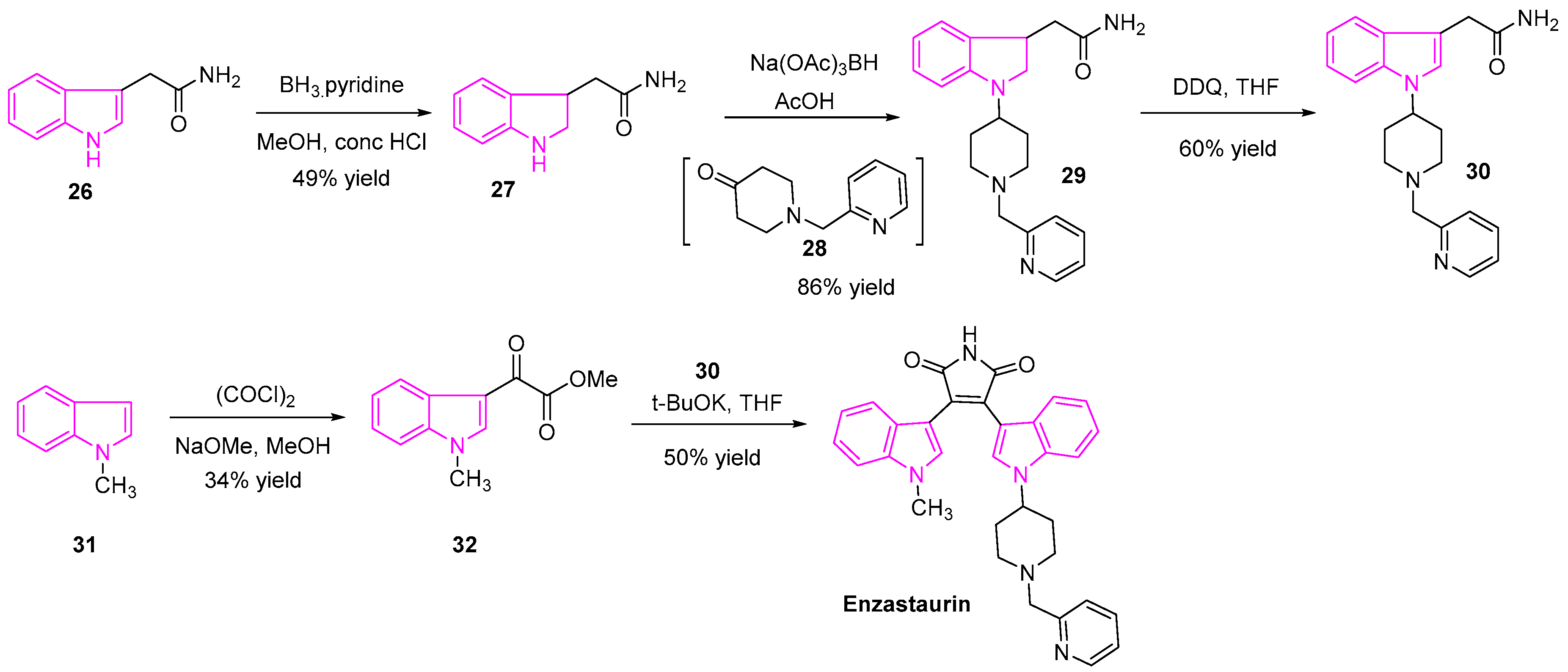
2.5. Protein Kinase C Inhibition
2.6. GSK Inhibition
2.7. Inhibition of Multiple Receptor Kinases
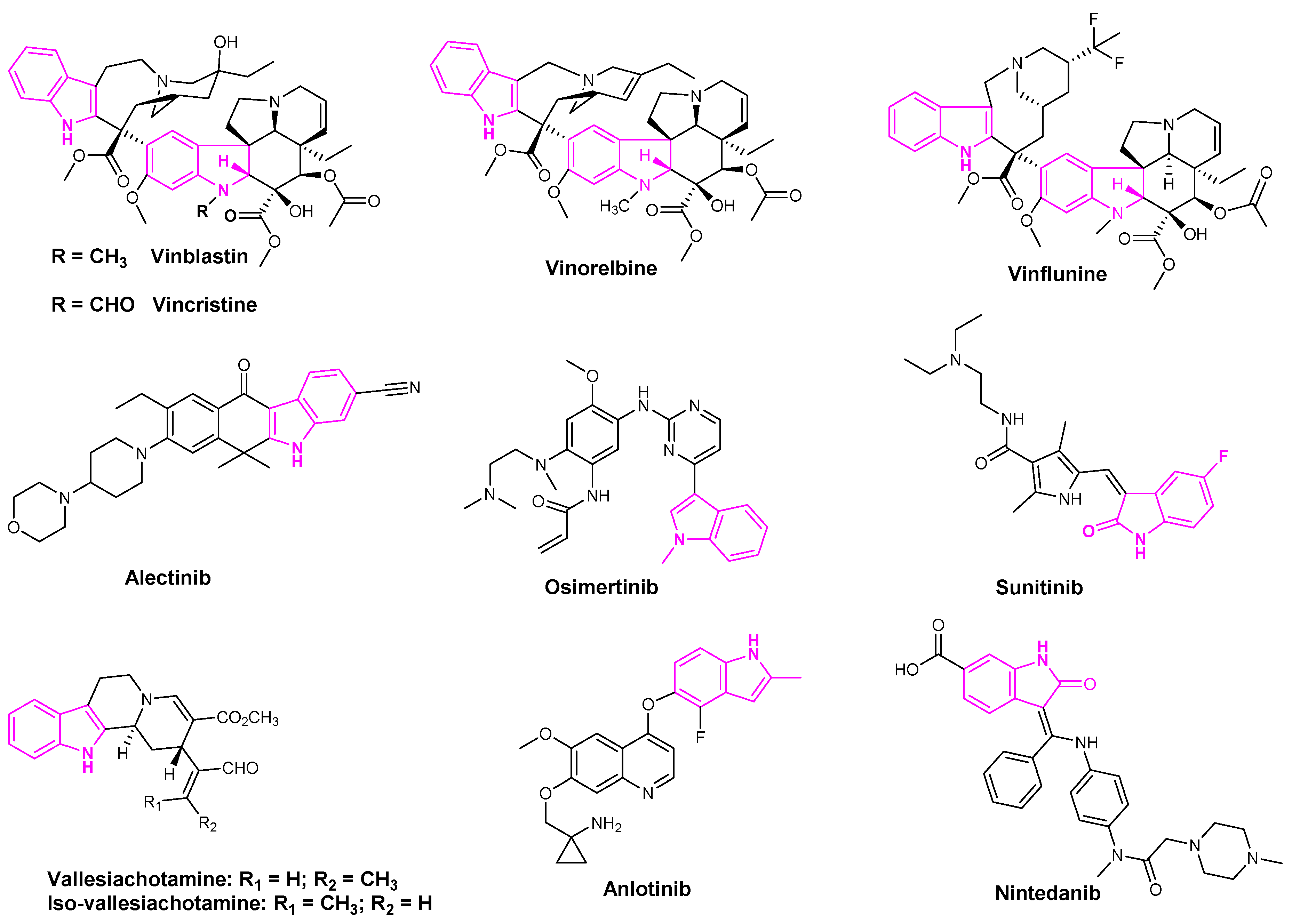
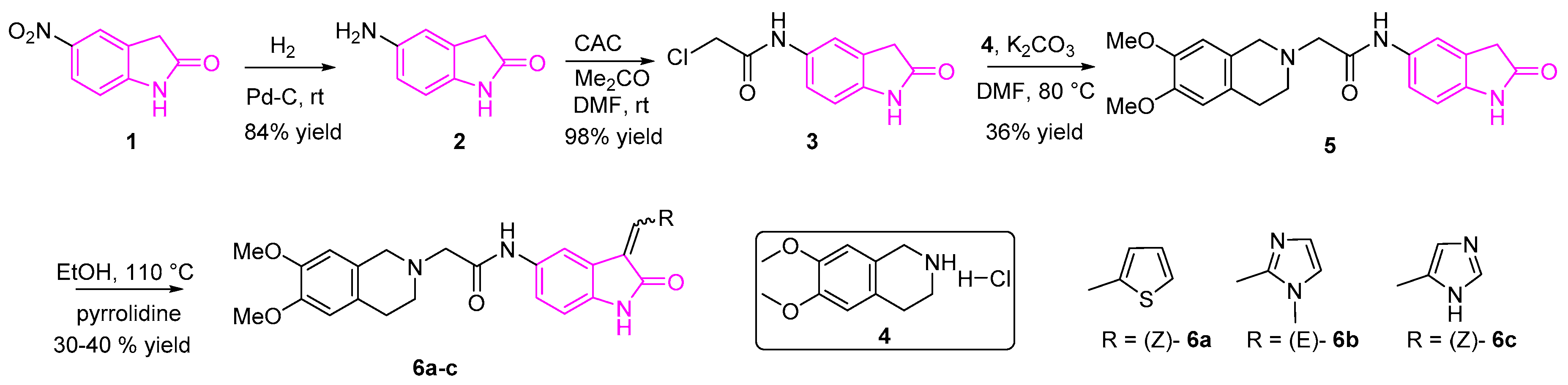
2.8. Tubulin Inhibition
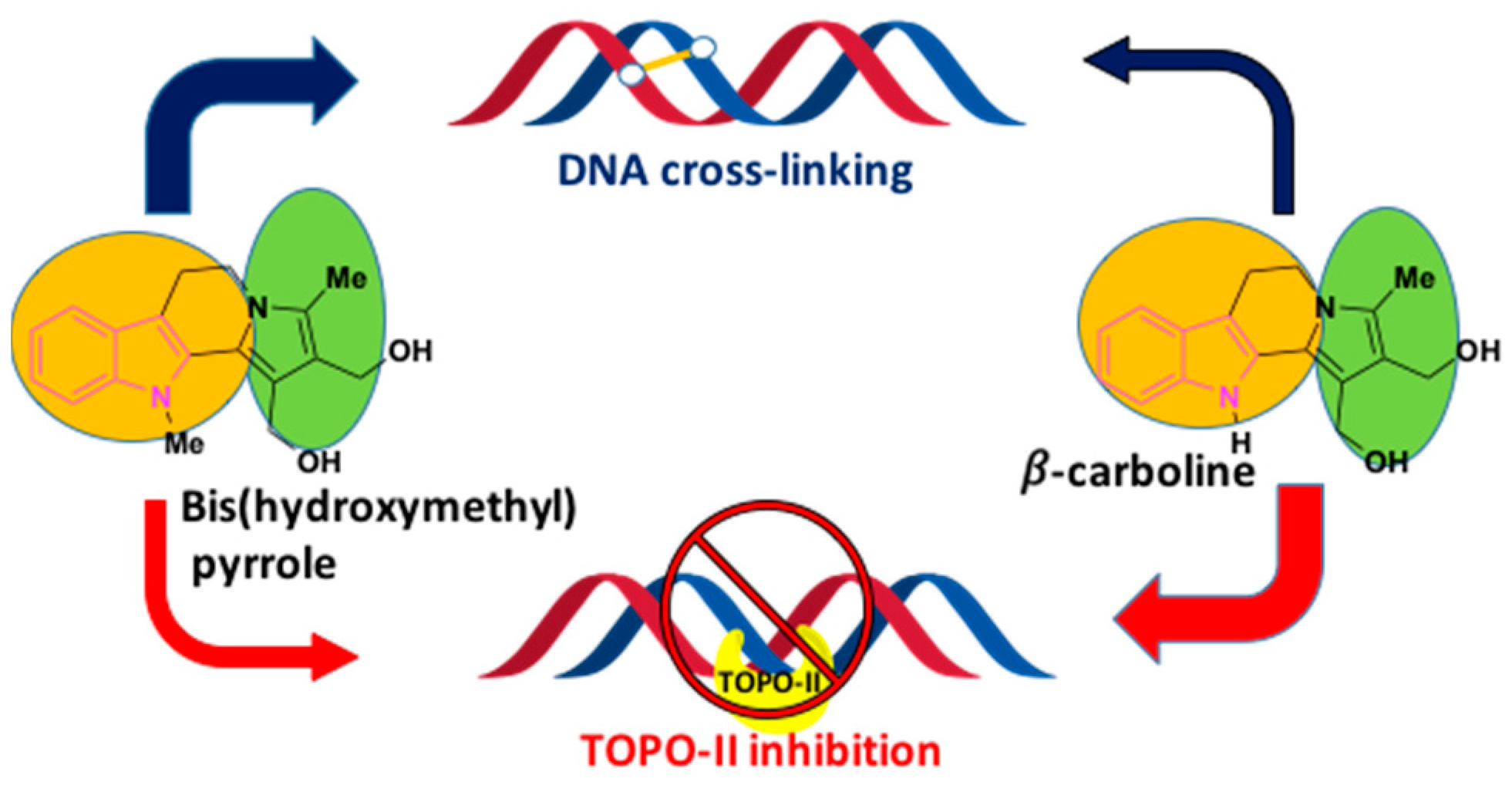
2.9. Inhibition of DNA-Topoisomerases
2.10. Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors
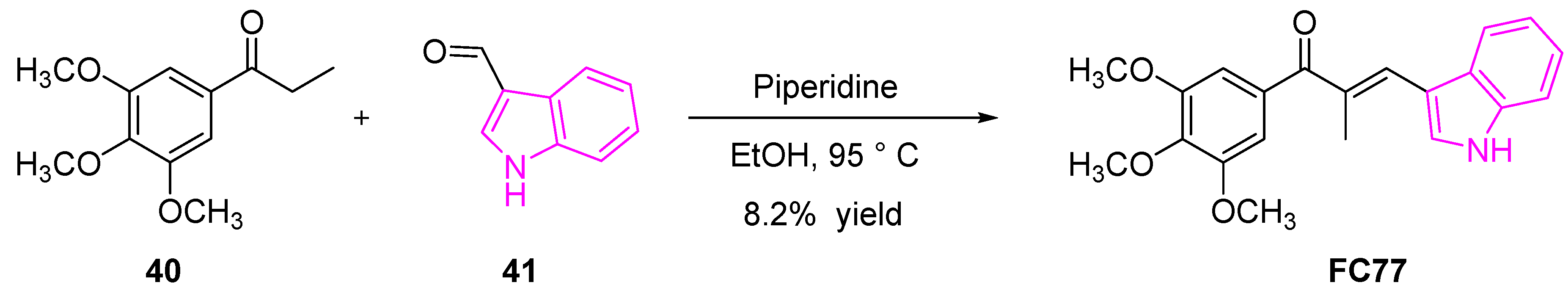
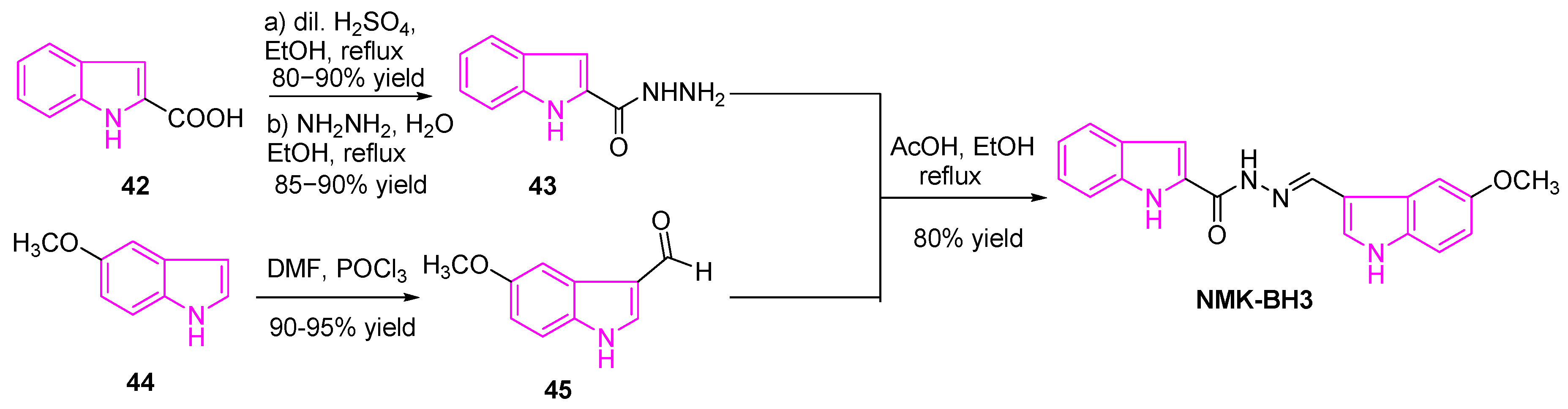
2.11. Miscellaneous Indole Derivatives in Anti-Lung Cancer Treatment
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I. Global. GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries, CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V.; et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.S.; Baldwin, D.R. Recent Advances in the Management of Lung Cancer. Clin. Med. Lond. Engl. 2018, 18, s41–s46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.; Broza, Y.Y.; Barash, O.; Peled, N.; Phillips, M.; Amann, A.; Haick, H. Volatile Organic Compounds of Lung Cancer and Possible Biochemical Pathways. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5949–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi Ziarani, G.; Moradi, R.; Ahmadi, T.; Lashgari, N. Recent Advances in the Application of Indoles in Multicomponent Reactions. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 12069–12103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, R.J. Electrophilic Substitution Reactions of Indoles. In Heterocyclic Scaffolds II: Reactions and Applications of Indoles; Gribble, G.W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 47–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeyer, A.; Emmerling, A. Synthese des Indols. Berichte Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1869, 2, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.; Hess, O. Synthese von Indolderivaten. Berichte Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1884, 17, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischler, A.; Napieralski, B. Zur Kenntniss einer neuen Isochinolinsynthese. Berichte Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1893, 26, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemetsberger, H.; Knittel, D. Synthese und Thermolyse von α-Azidoacrylestern. Mon. Fur Chem. 1972, 103, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenitzescu, C.D. Derivatives of 2-Methyl-5-Hydroxyindole. Bull. Soc. Chim. Rom. 1929, 11, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Bartoli, G.; Palmieri, G.; Bosco, M.; Dalpozzo, R. The Reaction of Vinyl Grignard Reagents with 2-Substituted Nitroarenes: A New Approach to the Synthesis of 7-Substituted Indoles. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 2129–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, M.; Nishigai, K.; Ishii, A.; Hata, T.; Urabe, H. Facile Preparation of Indoles and 1,2-Benzothiazine 1,1-Dioxides: Nucleophilic Addition of Sulfonamides to Bromoacetylenes and Subsequent Palladium-Catalyzed Cyclization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6471–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Hartwig, J.F. Palladium-Catalyzed Amination of Aromatic C−H Bonds with Oxime Esters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 3676–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li Petri, G.; Cascioferro, S.; El Hassouni, B.; Carbone, D.; Parrino, B.; Cirrincione, G.; Peters, G.J.; Diana, P.; Giovannetti, E. Biological Evaluation of the Antiproliferative and Anti-Migratory Activity of a Series of 3-(6-Phenylimidazo[2,1-b][1,3,4]Thiadiazol-2-Yl)-1 H -Indole Derivatives Against Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 3615–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascioferro, S.; Attanzio, A.; Di Sarno, V.; Musella, S.; Tesoriere, L.; Cirrincione, G.; Diana, P.; Parrino, B. New 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Nortopsentin Derivatives with Cytotoxic Activity. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Parrino, B.; Cusimano, M.; Spanò, V.; Montalbano, A.; Barraja, P.; Schillaci, D.; Cirrincione, G.; Diana, P.; Cascioferro, S. New Thiazole Nortopsentin Analogues Inhibit Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higdon, J.; Delage, B.; Williams, D.; Dashwood, R. Cruciferous Vegetables and Human Cancer Risk: Epidemiologic Evidence and Mechanistic Basis. Pharmacol. Res. 2007, 55, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Da Costa, G.; Cerezo, A.B.; Troncoso, A.M.; Richard, T.; Garcia-Parrilla, M.C. In Vitro Effects of Serotonin, Melatonin, and Other Related Indole Compounds on Amyloid-β Kinetics and Neuroprotection. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, A.; Petrini, M. Tryptophol and Derivatives: Natural Occurrence and Applications to the Synthesis of Bioactive Compounds. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 490–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-F.; Wei, J.-Y.; Chen, H.-W.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Lu, H.-Y.; Chou, J.-Y. Indole-3-Acetic Acid: A Widespread Physiological Code in Interactions of Fungi with Other Organisms. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 10, e1048052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Sun, W.; Zhang, A.; Wang, X. Metabolite Profiling and Biomarkers Analysis of Jaundice Syndrome-Related Animal Models. In Chinmedomics; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 109–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavirdine Gets FDA Approval. Food and Drug Administration. AIDS Alert 1997, 12, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Lobay, D. Rauwolfia in the Treatment of Hypertension. Integr. Med. Encinitas Calif. 2015, 14, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Yee, A.J.; Raje, N.S. Panobinostat and Multiple Myeloma in 2018. Oncologist 2018, 23, 516–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, T.A.; Tolstrup, M.; Brinkmann, C.R.; Olesen, R.; Erikstrup, C.; Solomon, A.; Winckelmann, A.; Palmer, S.; Dinarello, C.; Buzon, M.; et al. Panobinostat, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, for Latent-Virus Reactivation in HIV-Infected Patients on Suppressive Antiretroviral Therapy: A Phase 1/2, Single Group, Clinical Trial. Lancet HIV 2014, 1, e13–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelloway, J.S. Zafirlukast: The First Leukotreene-Receptor Antagonist Approved for the Treatment of Asthma. Ann. Pharmacother. 1997, 31, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frajese, G.V.; Pozzi, F.; Frajese, G. Tadalafil in the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction; an Overview of the Clinical Evidence. Clin. Interv. Aging 2006, 1, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, D.; Chen, J.; Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, D.; Meng, H.; Luo, Q.; et al. Is Pindolol Augmentation Effective in Depressed Patients Resistant to Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: PINDOLOL IN SSRI-RESISTANT DEPRESSION. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2015, 30, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blier, P.; Bergeron, R. The Use of Pindolol to Potentiate Antidepressant Medication. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1998, 59, 16–23, discussion 24-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, S.H.; Moncada, S.; Vane, J.R. Indomethacin and Aspirin Abolish Prostaglandin Release from the Spleen. Nat. New Biol. 1971, 231, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijden, R.; Jacobs, D.; Snoeijer, W.; Hallard, D.; Verpoorte, R. The Catharanthus Alkaloids:Pharmacognosy and Biotechnology. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 607–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.-H.; Guo, X.-L. New Insights into Vinca Alkaloids Resistance Mechanism and Circumvention in Lung Cancer. Biomed. Pharm. Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 96, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
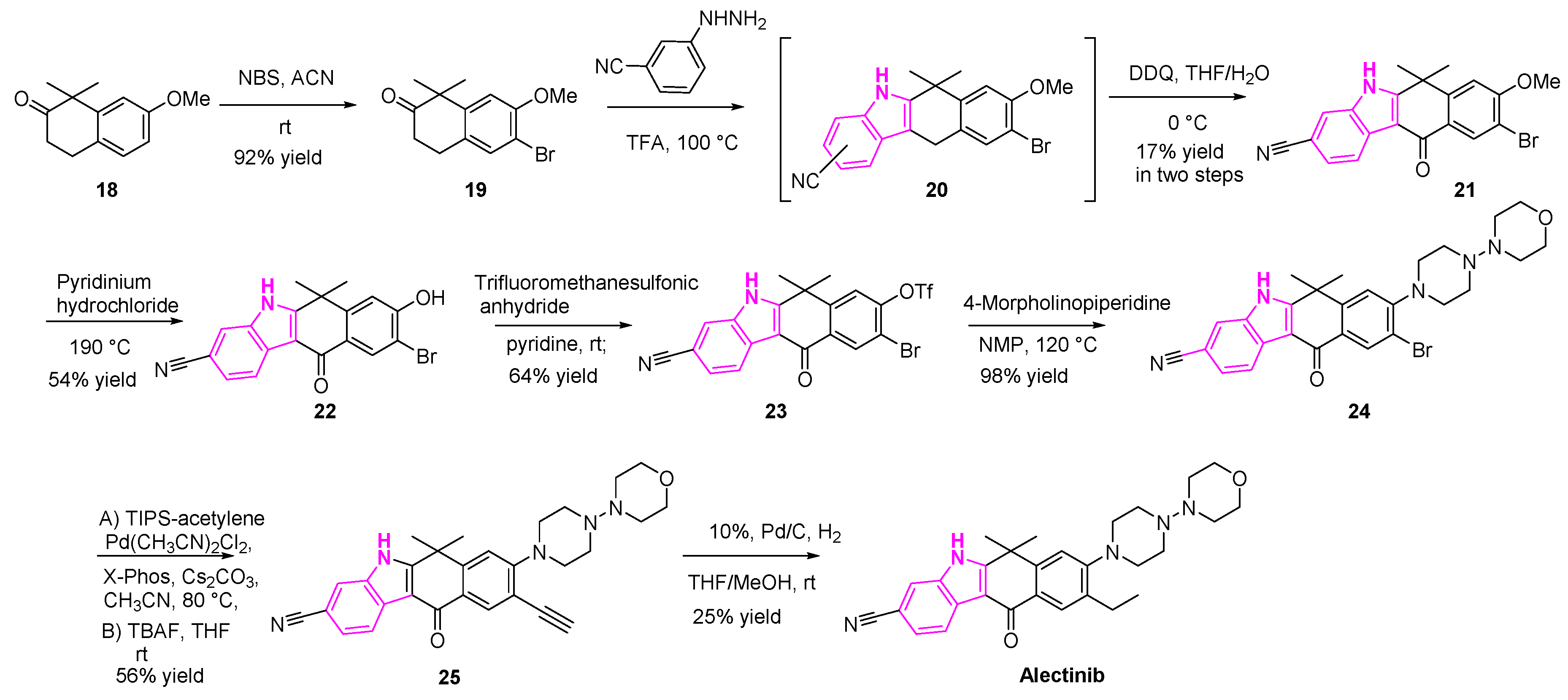
- Tomasini, P.; Egea, J.; Souquet-Bressand, M.; Greillier, L.; Barlesi, F. Alectinib in the Treatment of ALK-Positive Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Clinical Trial Evidence and Experience with a Focus on Brain Metastases. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Tourneau, C.; Raymond, E.; Faivre, S. Sunitinib: A Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. A Brief Review of Its Therapeutic Potential in the Treatment of Renal Carcinoma and Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST). Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2007, 3, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greig, S.L. Osimertinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2016, 76, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, D.P.; Khan, M.A.; Yadav, D.K.; Rawat, A.K.; Singh, R.K.; Ahamad, T.; Hussain, M.K.; Saquib, M.; Khan, M.F. Monoterpene Indole Alkaloids from Anthocephalus Cadamba Fruits Exhibiting Anticancer Activity in Human Lung Cancer Cell Line H1299. Chem. Sel. 2018, 3, 8468–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Y. The Efficacy and Safety of Anlotinib Treatment for Advanced Lung Cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 6549–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashpour, S.; Emami, S. Indole in the Target-Based Design of Anticancer Agents: A Versatile Scaffold with Diverse Mechanisms. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 150, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, A.; Locatelli, A.; Morigi, R.; Rambaldi, M. 2-Indolinone a Versatile Scaffold for Treatment of Cancer: A Patent Review (2008–2014). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.M.; Kumar, D. Recent Developments on Synthetic Indoles as Potent Anticancer Agents. Chem. Biol. Interface 2013, 3, 276–303. [Google Scholar]
- De Sa Alves, F.; Barreiro, E.; Manssour Fraga, C. From nature to drug discovery: The indole scaffold as a ‘privileged structure. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sravanthi, T.V.; Manju, S.L. Indoles—A Promising Scaffold for Drug Development. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 91, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, N.; Kaushik, N.; Attri, P.; Kumar, N.; Kim, C.; Verma, A.; Choi, E. Biomedical Importance of Indoles. Molecules 2013, 18, 6620–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunil, D.; Kamath, P. Multi-Target Directed Indole Based Hybrid Molecules in Cancer Therapy: An Up-To-Date Evidence-Based Review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 959–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadha, N.; Silakari, O. Indoles as Therapeutics of Interest in Medicinal Chemistry: Bird’s Eye View. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 134, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-sayed, M.T.; Hamdy, N.A.; Osman, D.A.; Ahmed, K.M. Indoles as Anticancer Agents. Adv. Mod. Oncol. Res. 2015, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.I.; Gee, J.M.W.; Harper, M.E. EGFR and Cancer Prognosis. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A. The Role of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Pathway Inhibitors in the Treatment of Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4637s–4640s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brognard, J.; Clark, A.S.; Ni, Y.; Dennis, P.A. Akt/Protein Kinase B Is Constitutively Active in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells and Promotes Cellular Survival and Resistance to Chemotherapy and Radiation. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3986–3997. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings, B.A.; Restuccia, D.F. PI3K-PKB/Akt Pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, D.A.; Testa, J.R. Perturbations of the AKT Signaling Pathway in Human Cancer. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7455–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Shcherba, M.; Pendurti, G.; Liang, Y.; Piperdi, B.; Perez-Soler, R. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/MTOR Pathway: Potential for Lung Cancer Treatment. Lung Cancer Manag. 2014, 3, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Du, J.; Kwiatkowski, D.J. Molecular Dissection of AKT Activation in Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesi, G.; Sestito, S.; Mey, V.; Ricciardi, S.; Falasca, M.; Danesi, R.; Lapucci, A.; Breschi, M.C.; Fogli, S.; Rapposelli, S. Synthesis of Novel 3,5-Disubstituted-2-Oxindole Derivatives As Antitumor Agents against Human Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
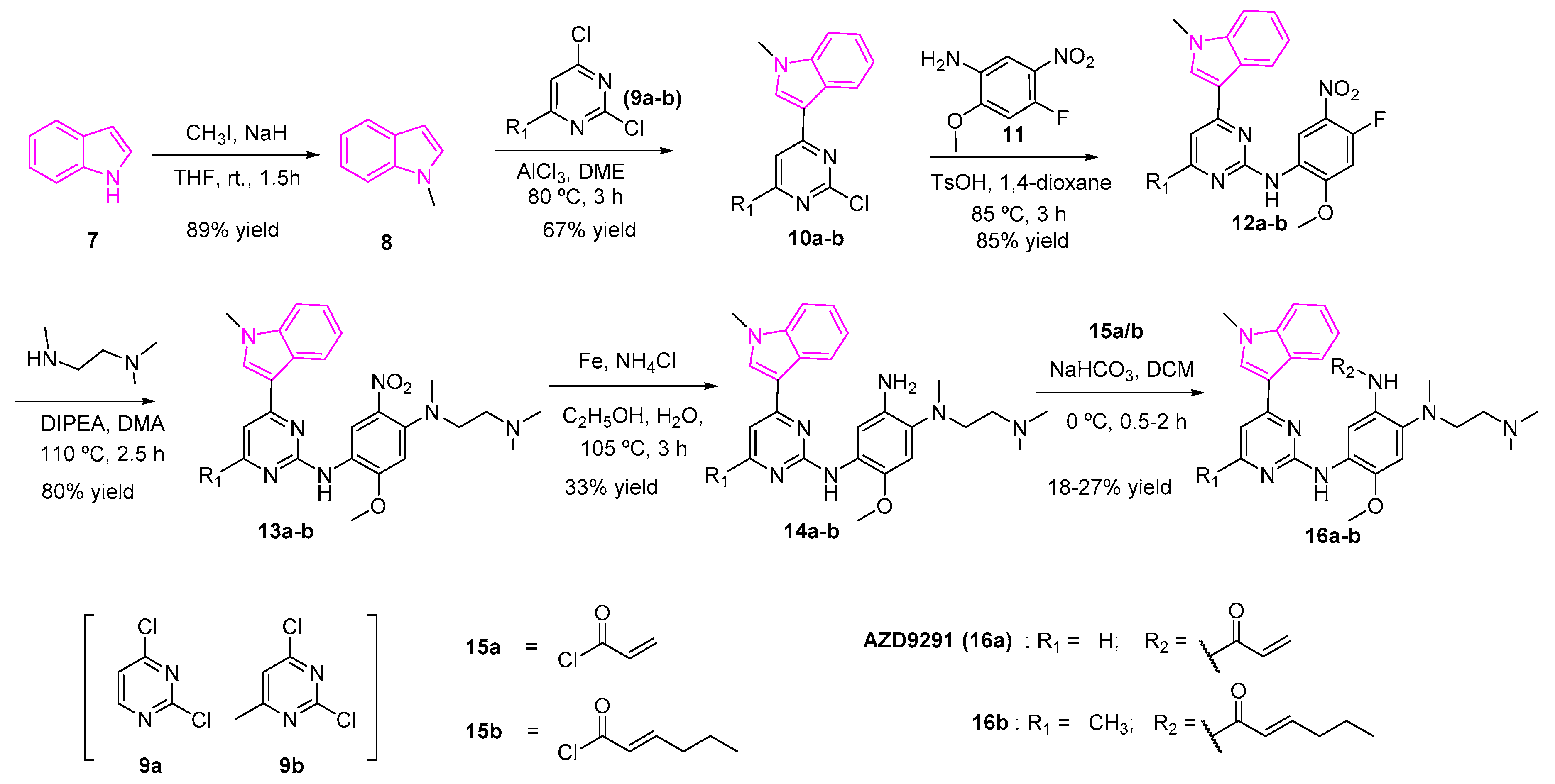
- Zhao, B.; Xiao, Z.; Qi, J.; Luo, R.; Lan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Tang, Q.; Zheng, P.; Xu, S.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of AZD9291 Derivatives as Selective and Potent EGFRL858R/T790M Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, B.; Maurice, R.V.F.; Richard, A.W.; Vasantha, K.K.; Reddy, C.C.; Andiappan, M.; Heather, M.R. 2-(2,4,5-Substituted Anilino)Pyrimidine Derivatives as EGFR Modulators Useful for Treating Cancer. WO2013014448A1, 31 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Guan, S.; Cao, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Pang, J.C.; et al. Novel ALK Inhibitor AZD3463 Inhibits Neuroblastoma Growth by Overcoming Crizotinib Resistance and Inducing Apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the Transforming EML4–ALK Fusion Gene in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, K.; Asoh, K.; Furuichi, N.; Ito, T.; Kawada, H.; Hara, S.; Ohwada, J.; Miyagi, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Takanashi, K.; et al. Design and Synthesis of a Highly Selective, Orally Active and Potent Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitor (CH5424802). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Asoh, K.; Furuichi, N.; Ito, T.; Kawada, H.; Hara, S.; Ohwada, J.; Hattori, K.; Miyagi, T.; et al. 9-Substituted 6,6-Dimethyl-11-Oxo-6,11-Dihydro-5 H -Benzo[ b ]Carbazoles as Highly Selective and Potent Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6286–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.C. Protein Kinase C: Structure, Function, and Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 28495–28498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Oh, Y.; Wagle, A.; Lahn, M. Enzastaurin, a Protein Kinase C Selective Inhibitor, and Its Potential Application as an Anticancer Agent in Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4641s–4646s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, M.M.; Bruce, W.K.; Rebecca, L.L.; Donald, T.; Larry, D.; Bruce, C.; Julia, H.C.; Jeremy, R.G. Enzastaurin (LY317615.HCl) Suppresses Signaling through the PKC and AKT Pathways, Inducing Apoptosis, Suppressing Tumor-Induced Angiogenesis and Reducing Growth of Human Cancer Xenografts. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 314–315. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, E.; Helfrich, B.; Chan, D.; Zhang, Z.; Hirsch, F.R.; Chen, V.; Ma, D.; Bunn, P.A. Enzastaurin a Protein Kinase Cbeta-Selective Inhibitor, Inhibits the Growth of SCLC and NSCLC Cell Lines. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 13138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, M.; Leppä, S.; Fayad, L.; Lee, J.J.; Di Rocco, A.; Ogura, M.; Hagberg, H.; Schnell, F.; Rifkin, R.; Mackensen, A.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial of Enzastaurin Versus Placebo in Patients Achieving Remission After First-Line Therapy for High-Risk Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2484–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xu, L.; Gao, M.; Miller, K.D.; Sledge, G.W.; Zheng, Q.-H. [11C]Enzastaurin, the First Design and Radiosynthesis of a New Potential PET Agent for Imaging of Protein Kinase, C. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1649–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
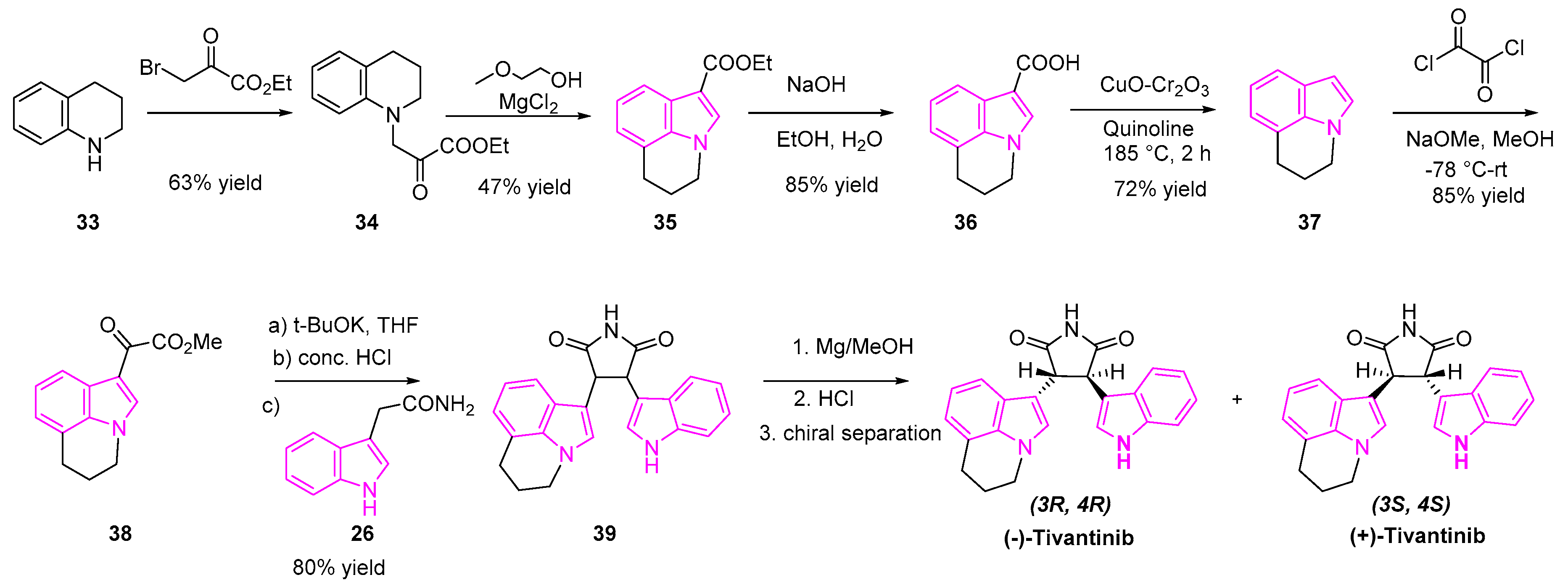
- Remsing Rix, L.L.; Kuenzi, B.M.; Luo, Y.; Remily-Wood, E.; Kinose, F.; Wright, G.; Li, J.; Koomen, J.M.; Haura, E.B.; Lawrence, H.R.; et al. GSK3 Alpha and Beta Are New Functionally Relevant Targets of Tivantinib in Lung Cancer Cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scagliotti, G.V.; Shuster, D.; Orlov, S.; von Pawel, J.; Shepherd, F.A.; Ross, J.S.; Wang, Q.; Schwartz, B.; Akerley, W. Tivantinib in Combination with Erlotinib versus Erlotinib Alone for EGFR-Mutant NSCLC: An Exploratory Analysis of the Phase 3 MARQUEE Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Ashwell, M.A.; Hill, J.; Moussa, M.M.; Munshi, N. Maleimide Derivatives, Pharmaceutical Compositions and Methods for Treatment of Cancer. EP1846406B9, 11 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.; Song, X.; Yang, D.; Bai, D.; Yao, Y.; Lu, N. Anlotinib Inhibits Angiogenesis via Suppressing the Activation of VEGFR2, PDGFRβ and FGFR1. Gene 2018, 654, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, K.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Han, B.; Chen, G.; He, J.; Wang, J.; et al. 1738OOverall Survival (OS) Update in ALTER 1202: Anlotinib as Third-Line or Further-Line Treatment in Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Mellemgaard, A.; Novello, S.; Postmus, P.E.; Gaschler-Markefski, B.; Kaiser, R.; Buchner, H. Change in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Tumor Size in Patients Treated with Nintedanib plus Docetaxel: Analyses from the Phase III LUME-Lung 1 Study. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 4573–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, L.; Nogueira, A.; Passiglia, F.; Listi, A.; Caglevic, C.; Giallombardo, M.; Raez, L.; Santos, E.; Rolfo, C. Second-Line Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Clinical, Pathological, and Molecular Aspects of Nintedanib. Front. Med. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, D.A.; Mullins, R.D. Cell Mechanics and the Cytoskeleton. Nature 2010, 463, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaz, F.; Haider, M.R.; Shafi, S.; Yar, M.S. Anti-Tubulin Agents of Natural Origin: Targeting Taxol, Vinca, and Colchicine Binding Domains. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 171, 310–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, Z.; Coupková, H.; Kolek, V.; Kucera, M.; Loffelmann, L.; Martinez, A.; Nováková, M.; Průsa, P.; Reiterer, P.; Skalová, B. Vinorelbine and Cisplatin in the Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results of a Multicenter Czech Study. Acta Med. Austriaca 1995, 22, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Genova, C.; Alama, A.; Coco, S.; Rijavec, E.; Dal Bello, M.G.; Vanni, I.; Biello, F.; Barletta, G.; Rossi, G.; Grossi, F. Vinflunine for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2016, 25, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, H.; Zhao, X.; Castle, B.T.; Pomeroy, E.J.; Zhou, B.; Lee, J.; Wang, Y.; Bian, T.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, W.; et al. An Indole–Chalcone Inhibits Multidrug-Resistant Cancer Cell Growth by Targeting Microtubules. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 3892–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das Mukherjee, D.; Kumar, N.M.; Tantak, M.P.; Das, A.; Ganguli, A.; Datta, S.; Kumar, D.; Chakrabarti, G. Development of Novel Bis(Indolyl)-Hydrazide–Hydrazone Derivatives as Potent Microtubule-Targeting Cytotoxic Agents against A549 Lung Cancer Cells. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 3020–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
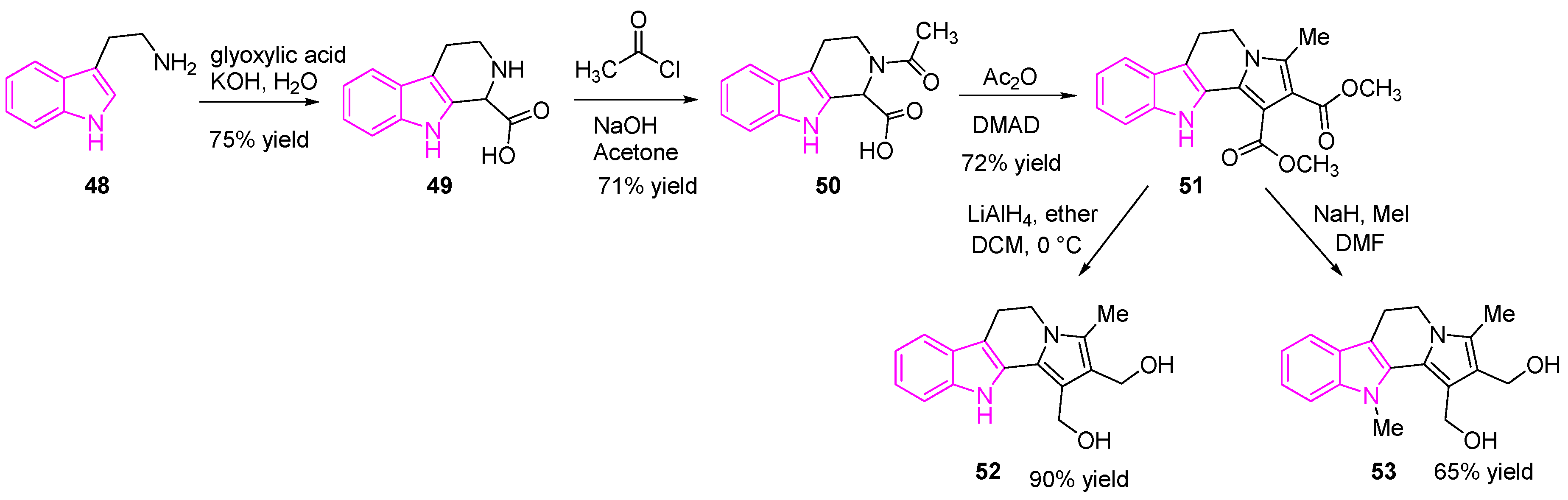
- Chaniyara, R.; Tala, S.; Chen, C.-W.; Zang, X.; Kakadiya, R.; Lin, L.-F.; Chen, C.-H.; Chien, S.-I.; Chou, T.-C.; Tsai, T.-H.; et al. Novel Antitumor Indolizino[6,7- b ]Indoles with Multiple Modes of Action: DNA Cross-Linking and Topoisomerase I and II Inhibition. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1544–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-W.; Wu, M.-H.; Chen, Y.-F.; Yen, T.-Y.; Lin, Y.-W.; Chao, S.-H.; Tala, S.; Tsai, T.-H.; Su, T.-L.; Lee, T.-C. A Potent Derivative of Indolizino[6,7-b]Indole for Treatment of Human Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Neoplasia 2016, 18, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
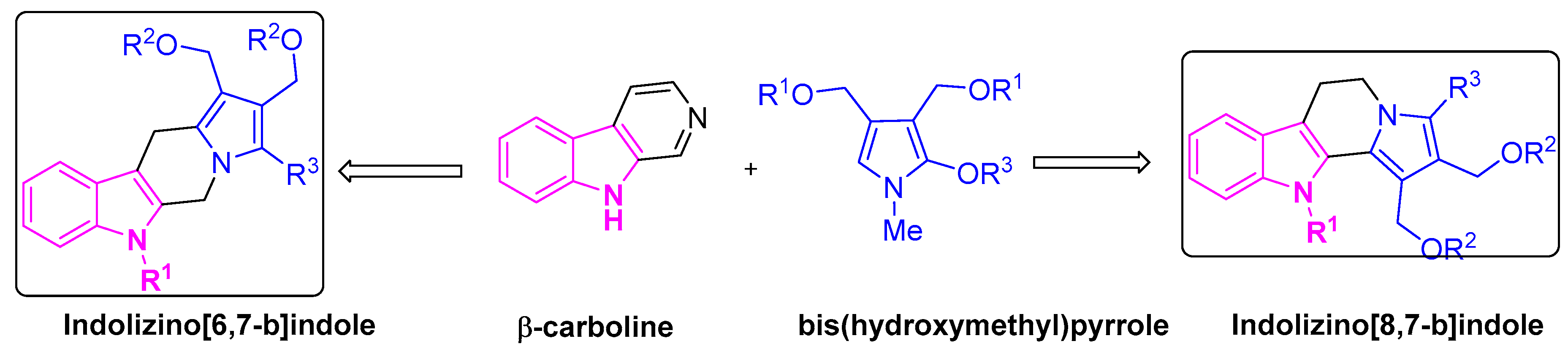
- Chang, S.-M.; Christian, W.; Wu, M.-H.; Chen, T.-L.; Lin, Y.-W.; Suen, C.-S.; Pidugu, H.B.; Detroja, D.; Shah, A.; Hwang, M.-J.; et al. Novel Indolizino[8,7-b]Indole Hybrids as Anti-Small Cell Lung Cancer Agents: Regioselective Modulation of Topoisomerase II Inhibitory and DNA Crosslinking Activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-L.; Dong, Y.-F.; Yang, T.; Zhang, C.-C.; Su, L.-M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, D.-N.; Yang, G.-L.; Liu, Y.-X. Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Novel Bisindolylalkanes Analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 7624–7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrows, L.R.; Radisky, D.C.; Copp, B.R.; Swaffar, D.S.; Kramer, R.A.; Warters, R.L.; Ireland, C.M. Makaluvamines, Marine Natural Products, Are Active Anti-Cancer Agents and DNA Topo II Inhibitors. Anticancer Drug Des. 1993, 8, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nadkarni, D.; Wang, F.; Wang, W.; Rayburn, E.; Ezell, S.; Murugesan, S.; Velu, S.; Zhang, R. Synthesis and In Vitro Anti-Lung Cancer Activity of Novel 1, 3, 4, 8- Tetrahydropyrrolo [4, 3, 2-de]Quinolin-8(1H)-o Ne Alkaloid Analogs. Med. Chem. 2009, 5, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, A.A.; Chabner, B.A. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5459–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richon, V.M.; O’Brien, J.P. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: A New Class of Potential Therapeutic Agents for Cancer Treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 662–664. [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone, R.W. Histone-Deacetylase Inhibitors: Novel Drugs for the Treatment of Cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinji, C.; Maeda, S.; Imai, K.; Yoshida, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Miyachi, H. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Cyclic Amide/Imide-Bearing Hydroxamic Acid Derivatives as Class-Selective Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 7625–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
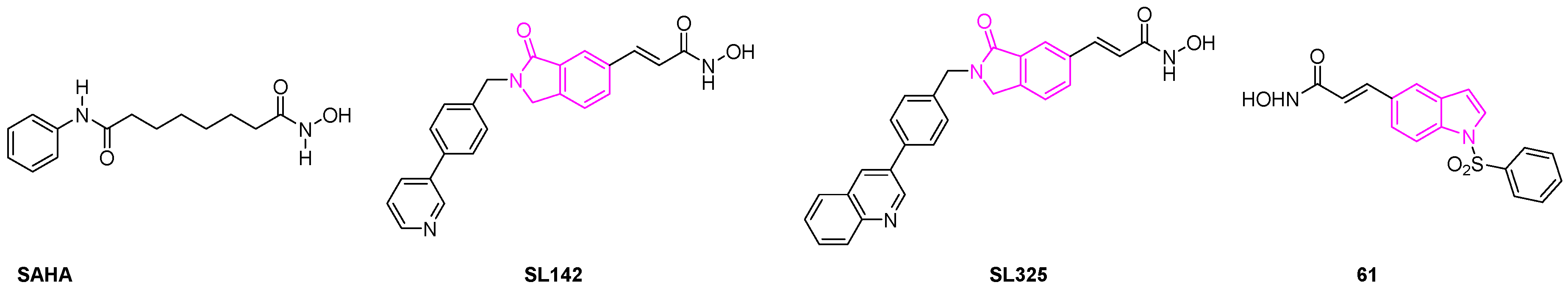
- Han, S.; Fukazawa, T.; Yamatsuji, T.; Matsuoka, J.; Miyachi, H.; Maeda, Y.; Durbin, M.; Naomoto, Y. Anti-Tumor Effect in Human Lung Cancer by a Combination Treatment of Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: SL142 or SL325 and Retinoic Acids. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.-J.; Huang, H.-L.; Pan, S.-L.; Liu, Y.-M.; Peng, C.-Y.; Lee, H.-Y.; Yeh, T.-K.; Huang, P.-H.; Teng, C.-M.; Chen, C.-S.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 1-Arylsulfonyl-5-(N-Hydroxyacrylamide)Indoles as Potent Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors with Antitumor Activity in Vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3777–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
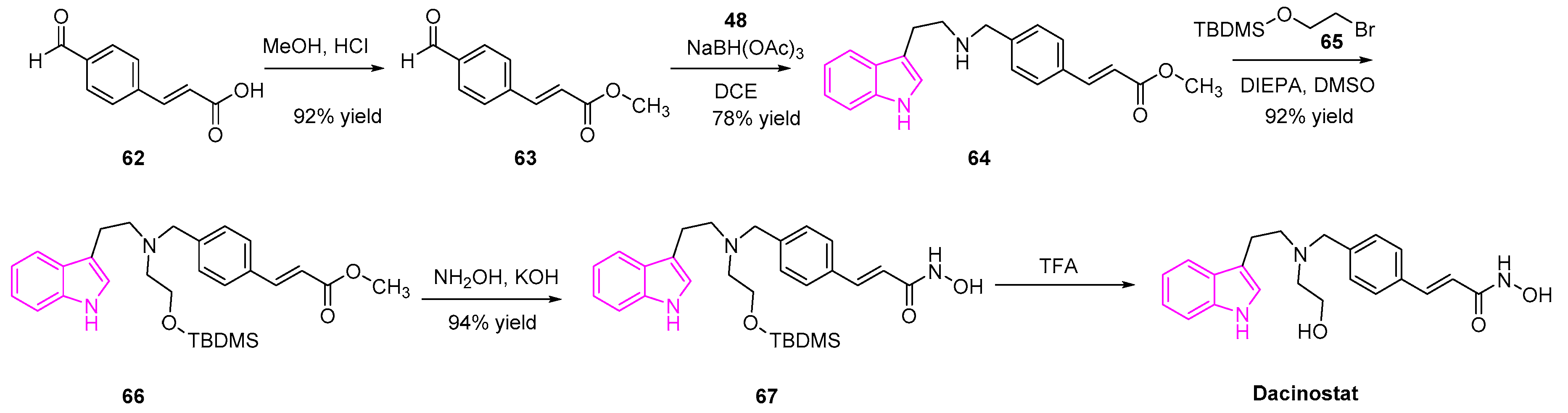
- Remiszewski, S.W.; Sambucetti, L.C.; Bair, K.W.; Bontempo, J.; Cesarz, D.; Chandramouli, N.; Chen, R.; Cheung, M.; Cornell-Kennon, S.; Dean, K.; et al. N -Hydroxy-3-Phenyl-2-Propenamides as Novel Inhibitors of Human Histone Deacetylase with in Vivo Antitumor Activity: Discovery of (2 E)- N -Hydroxy-3-[4-[[(2-Hydroxyethyl)[2-(1 H -Indol-3-Yl)Ethyl]Amino]Methyl]Phenyl]-2-Propenamide (NVP-LAQ824). J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 4609–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catley, L.; Weisberg, E.; Tai, Y.-T.; Atadja, P.; Remiszewski, S.; Hideshima, T.; Mitsiades, N.; Shringarpure, R.; LeBlanc, R.; Chauhan, D.; et al. NVP-LAQ824 Is a Potent Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor with Significant Activity against Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2003, 102, 2615–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atadja, P.; Gao, L.; Kwon, P.; Trogani, N.; Walker, H.; Hsu, M.; Yeleswarapu, L.; Chandramouli, N.; Perez, L.; Versace, R.; et al. Selective Growth Inhibition of Tumor Cells by a Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, NVP-LAQ824. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuneo, K.C.; Fu, A.; Osusky, K.; Huamani, J.; Hallahan, D.E.; Geng, L. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor NVP-LAQ824 Sensitizes Human Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer to the Cytotoxic Effects of Ionizing Radiation: Anticancer. Drugs 2007, 18, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, L.; Bots, M.; Lindemann, R.K.; Bolden, J.E.; Newbold, A.; Cluse, L.A.; Scott, C.L.; Strasser, A.; Atadja, P.; Lowe, S.W.; et al. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors LAQ824 and LBH589 Do Not Require Death Receptor Signaling or a Functional Apoptosome to Mediate Tumor Cell Death or Therapeutic Efficacy. Blood 2009, 114, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remiszewski, S.W. The Discovery of NVP-LAQ824: From Concept to Clinic. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 2393–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, K.; Wang, L.-L.; Zhou, X.-B.; Liu, M.-L.; Liu, H.-Y.; Zheng, Z.-B.; Li, S. Synthesis and in Vitro Antitumor Activity of 1-(3-Dimethylamino)Propyl Indolin-2-One Derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Wang, L.-L.; Liu, M.-L.; Zhou, X.-B.; Fan, S.-Y.; Liu, H.-Y.; Zheng, Z.-B.; Li, S. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of 5-[1-(3-(Dimethylamino)Propyl)-5-Halogenated-2-Oxoindolin-(3Z)-Ylidenemethyl]-2,4-Dimethyl-1H-Pyrrole-3-Carboxamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 3062–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
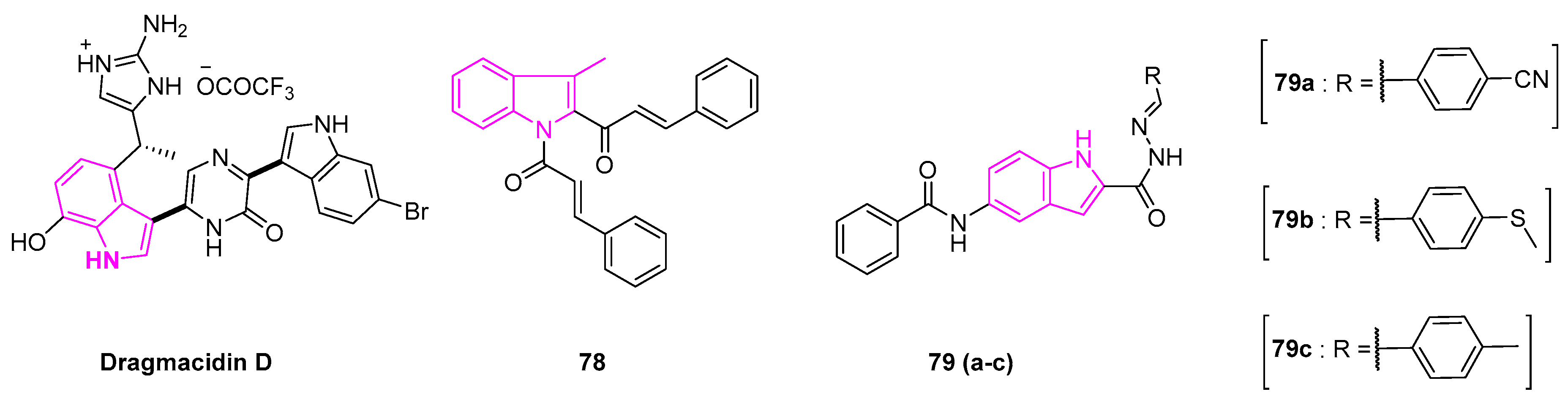
- Kohmoto, S.; Kashman, Y.; McConnell, O.J.; Rinehart, K.L.; Wright, A.; Koehn, F. Dragmacidin, a New Cytotoxic Bis(Indole) Alkaloid from a Deep Water Marine Sponge, Dragmacidon sp. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 3116–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Dong, W.; Gao, Y.; Shin, D.-S.; Ye, Q.; Su, L.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, B.; Miao, J. Novel Indolyl-Chalcone Derivatives Inhibit A549 Lung Cancer Cell Growth through Activating Nrf-2/HO-1 and Inducing Apoptosis in Vitro and in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wu, J.; Ao, M.; Wang, H.; Zhou, T.; Xue, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Fang, M.; Wu, Z. Synthesis, Structure-Activity Relationship Studies and Biological Evaluation of Novel 2,5-Disubstituted Indole Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016, 88, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
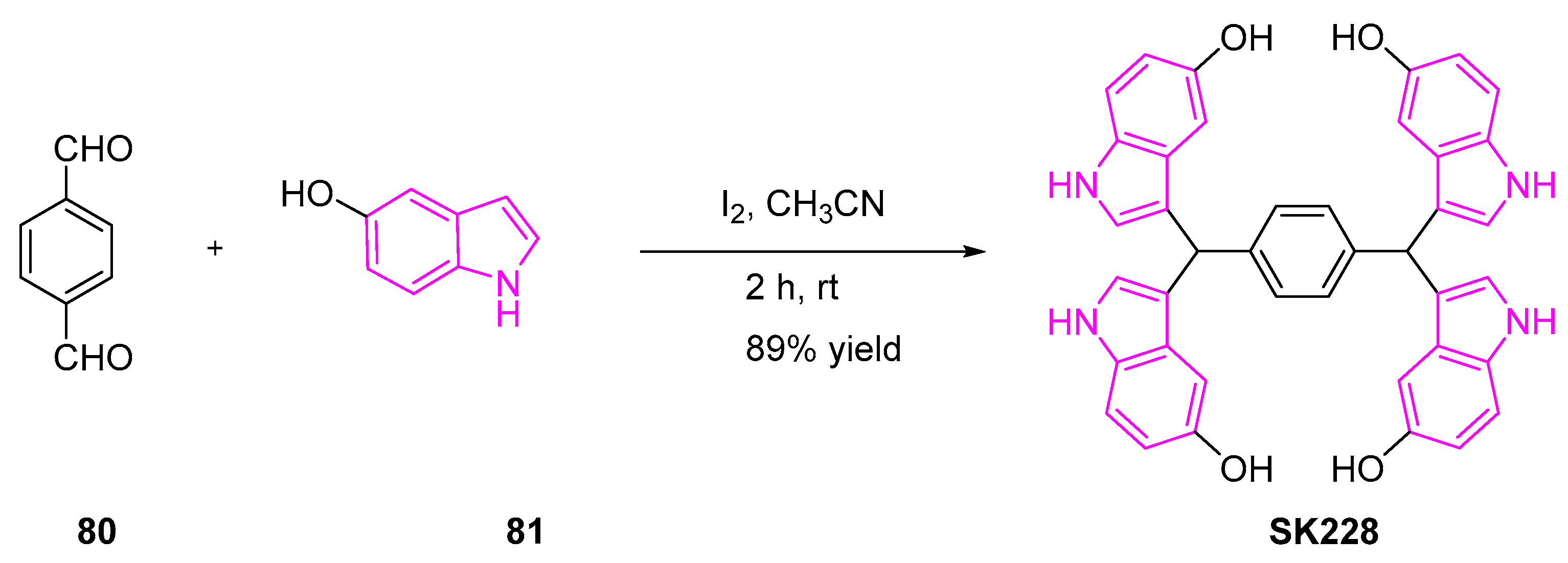
- Huang, S.-M.; Hsu, P.-C.; Chen, M.-Y.; Li, W.-S.; More, S.V.; Lu, K.-T.; Wang, Y.-C. The Novel Indole Compound SK228 Induces Apoptosis and FAK/Paxillin Disruption in Tumor Cell Lines and Inhibits Growth of Tumor Graft in the Nude Mouse. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-S.; Wang, C.-H.; Ko, S.; Chang, T.T.; Jen, Y.C.; Yao, C.-F.; More, S.V.; Jao, S.-C. Synthesis and Evaluation of the Cytotoxicities of Tetraindoles: Observation That the 5-Hydroxy Tetraindole (SK228) Induces G 2 Arrest and Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
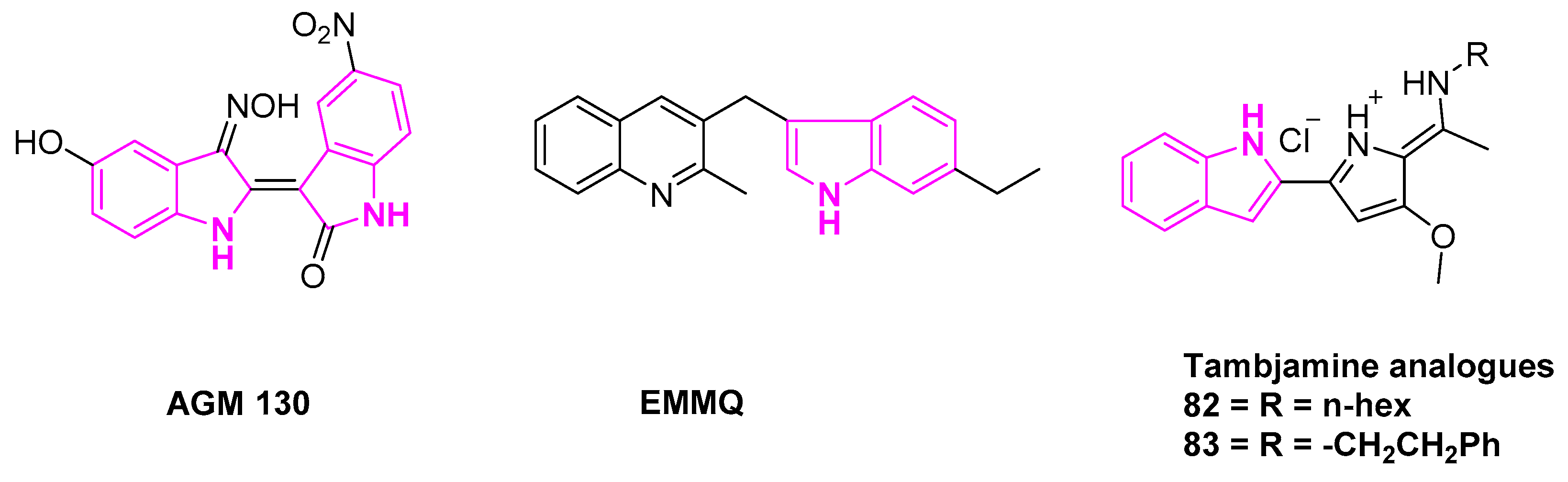
- Ahn, M.-Y.; Kim, T.-H.; Kwon, S.-M.; Yoon, H.-E.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, J.-I.; Kim, Y.-C.; Kang, K.-W.; Ahn, S.-G.; Yoon, J.-H. 5-Nitro-5′-Hydroxy-Indirubin-3′-Oxime (AGM130), an Indirubin-3′-Oxime Derivative, Inhibits Tumor Growth by Inducing Apoptosis against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Vitro and in Vivo. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 79, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Wu, P.-T.; Wang, J.-P.; Fan, P.-W.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Su, C.-L.; Chiu, C.-C.; Yao, C.-F.; Fang, K. An Indolylquinoline Derivative Promotes Apoptosis in Human Lung Cancer Cells by Impairing Mitochondrial Functions. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuel-Manresa, P.; Korrodi-Gregório, L.; Hernando, E.; Villanueva, A.; Martínez-García, D.; Rodilla, A.M.; Ramos, R.; Fardilha, M.; Moya, J.; Quesada, R.; et al. Novel Indole-Based Tambjamine-Analogues Induce Apoptotic Lung Cancer Cell Death through P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, E.; Soto-Cerrato, V.; Cortés-Arroyo, S.; Pérez-Tomás, R.; Quesada, R. Transmembrane Anion Transport and Cytotoxicity of Synthetic Tambjamine Analogs. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Liu, Y.; Qin, Z. Metadherin Contributes to Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Paclitaxel Resistance Induced by Acidic Extracellular PH in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 3, 3858–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
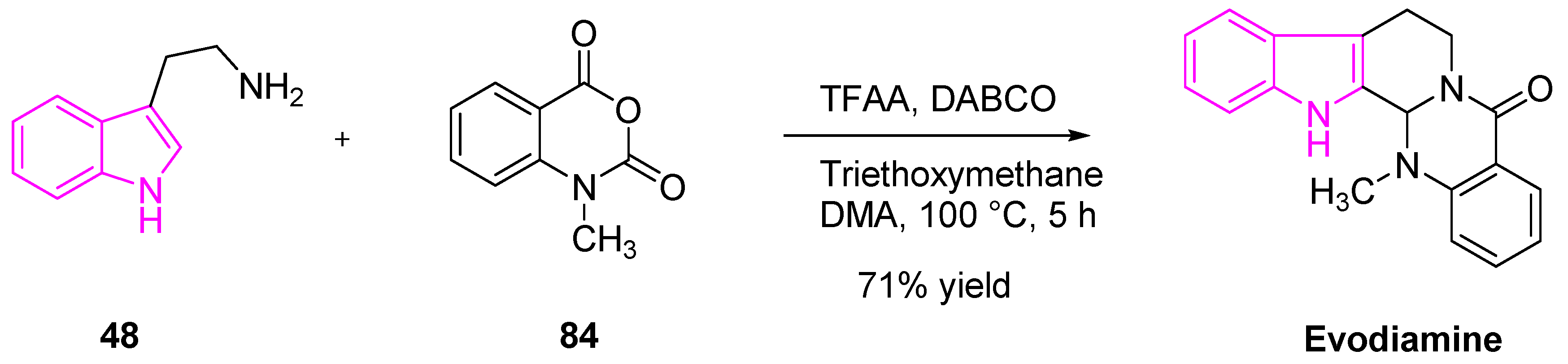
- Zou, Y.; Qin, X.; Xiong, H.; Zhu, F.; Chen, T.; Wu, H. Apoptosis of Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer A549 Cells Triggered by Evodiamine through MTDH-Dependent Signaling Pathway. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 5187–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, S.-F.; Yu, C.-H.; Pu, H.-F.; Hsu, J.-M.; Chen, M.-J.; Wang, P.S. Anti-Proliferative Effects of Evodiamine on Human Prostate Cancer Cell Lines DU145 and PC3. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 101, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Hu, C. Evodiamine: A Novel Anti-Cancer Alkaloid from Evodia Rutaecarpa. Molecules 2009, 14, 1852–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-X.; Xiang, J.-C.; Wang, M.; Ma, J.-T.; Wu, Y.-D.; Wu, A.-X. One-Pot Total Synthesis of Evodiamine and Its Analogues through a Continuous Biscyclization Reaction. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 6380–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
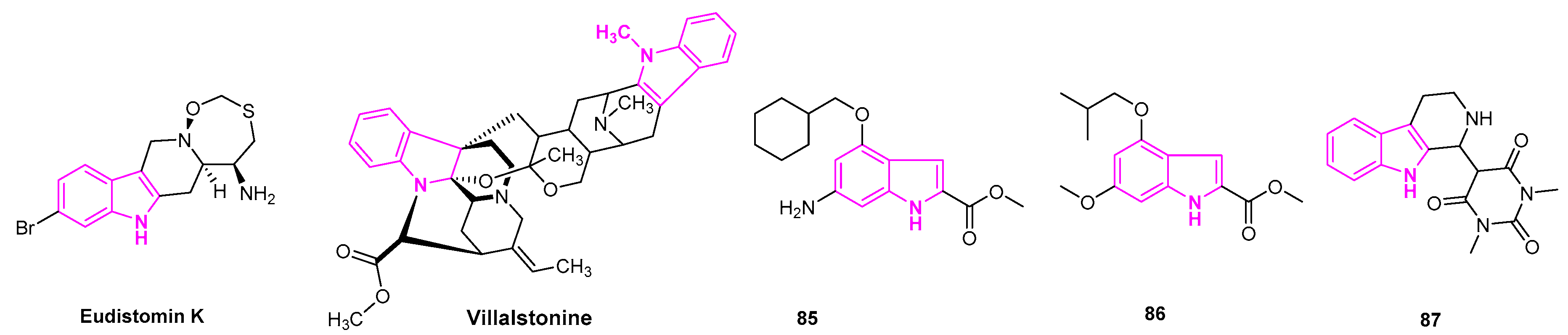
- Menna, M.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C. Alkaloids from Marine Ascidians. Molecules 2011, 16, 8694–8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keawprdub, N.; Houghton, P.; Eno-Amooquaye, E.; Burke, P. Activity of Extracts and Alkaloids of Thai Alstonia Species Against Human Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Planta Med. 1997, 63, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Xue, S.; Zhan, Y.; Shen, J.; Wu, L.; Jin, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z. Design, Synthesis and Antiproliferative Activity of a Novel Class of Indole-2-Carboxylate Derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 83, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
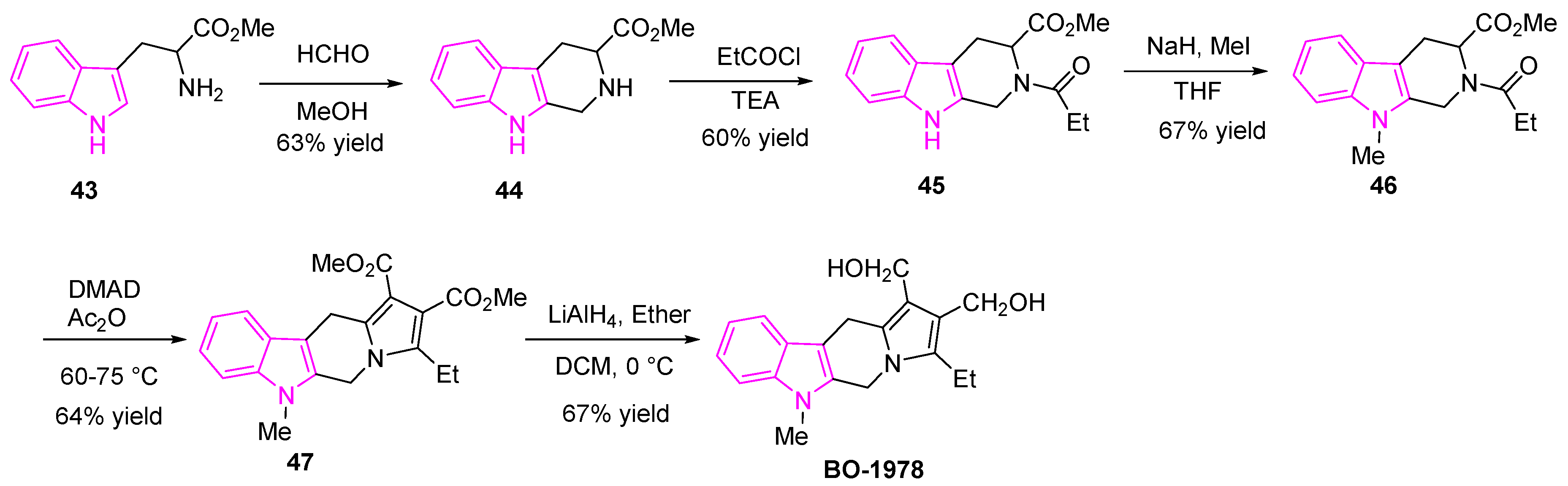
- Skouta, R.; Hayano, M.; Shimada, K.; Stockwell, B.R. Design and Synthesis of Pictet–Spengler Condensation Products That Exhibit Oncogenic-RAS Synthetic Lethality and Induce Non-Apoptotic Cell Death. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 5707–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhuguru, J.; Skouta, R. Role of Indole Scaffolds as Pharmacophores in the Development of Anti-Lung Cancer Agents. Molecules 2020, 25, 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071615
Dhuguru J, Skouta R. Role of Indole Scaffolds as Pharmacophores in the Development of Anti-Lung Cancer Agents. Molecules. 2020; 25(7):1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071615
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhuguru, Jyothi, and Rachid Skouta. 2020. "Role of Indole Scaffolds as Pharmacophores in the Development of Anti-Lung Cancer Agents" Molecules 25, no. 7: 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071615
APA StyleDhuguru, J., & Skouta, R. (2020). Role of Indole Scaffolds as Pharmacophores in the Development of Anti-Lung Cancer Agents. Molecules, 25(7), 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071615