The Biological Activities and Therapeutic Potentials of Baicalein Extracted from Oroxylum indicum: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
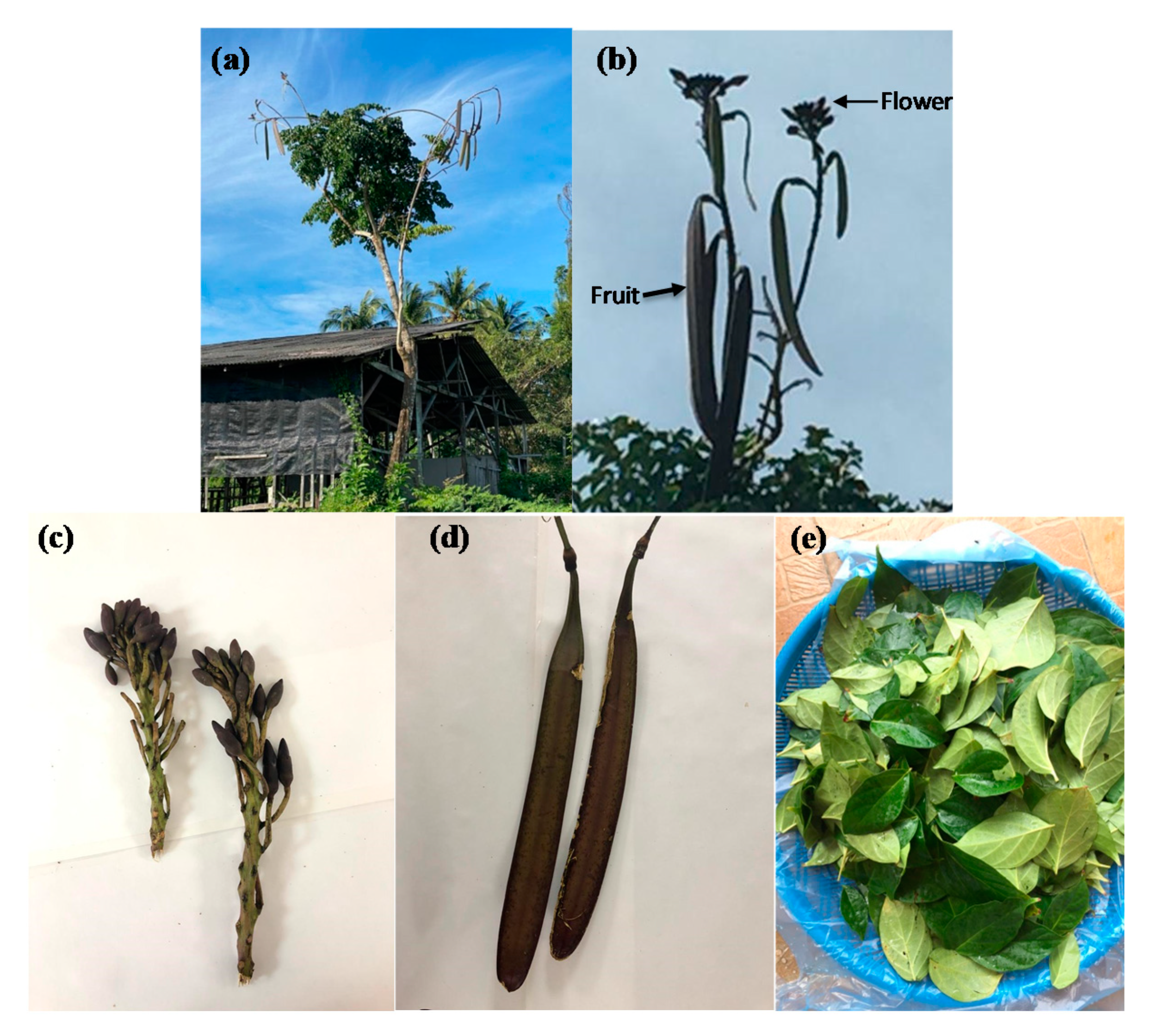
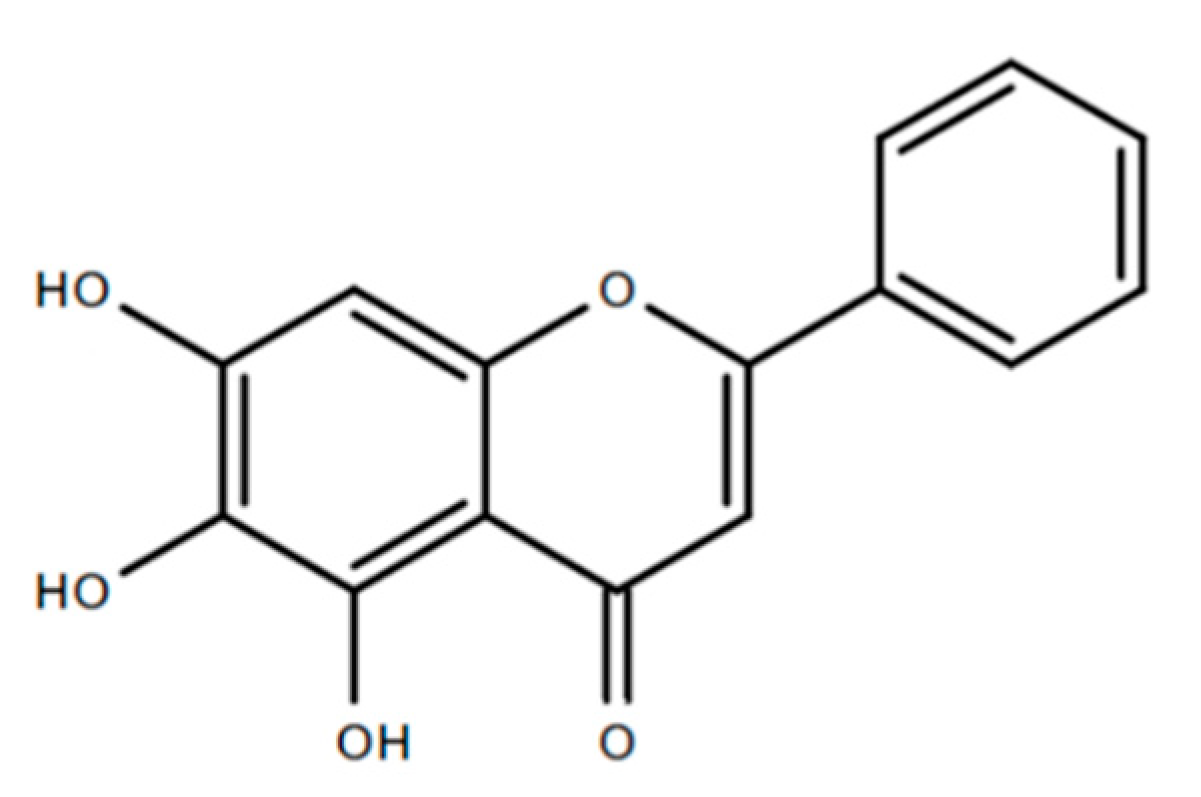
Baicalein—The Major Chemical Compound Found in O. indicum
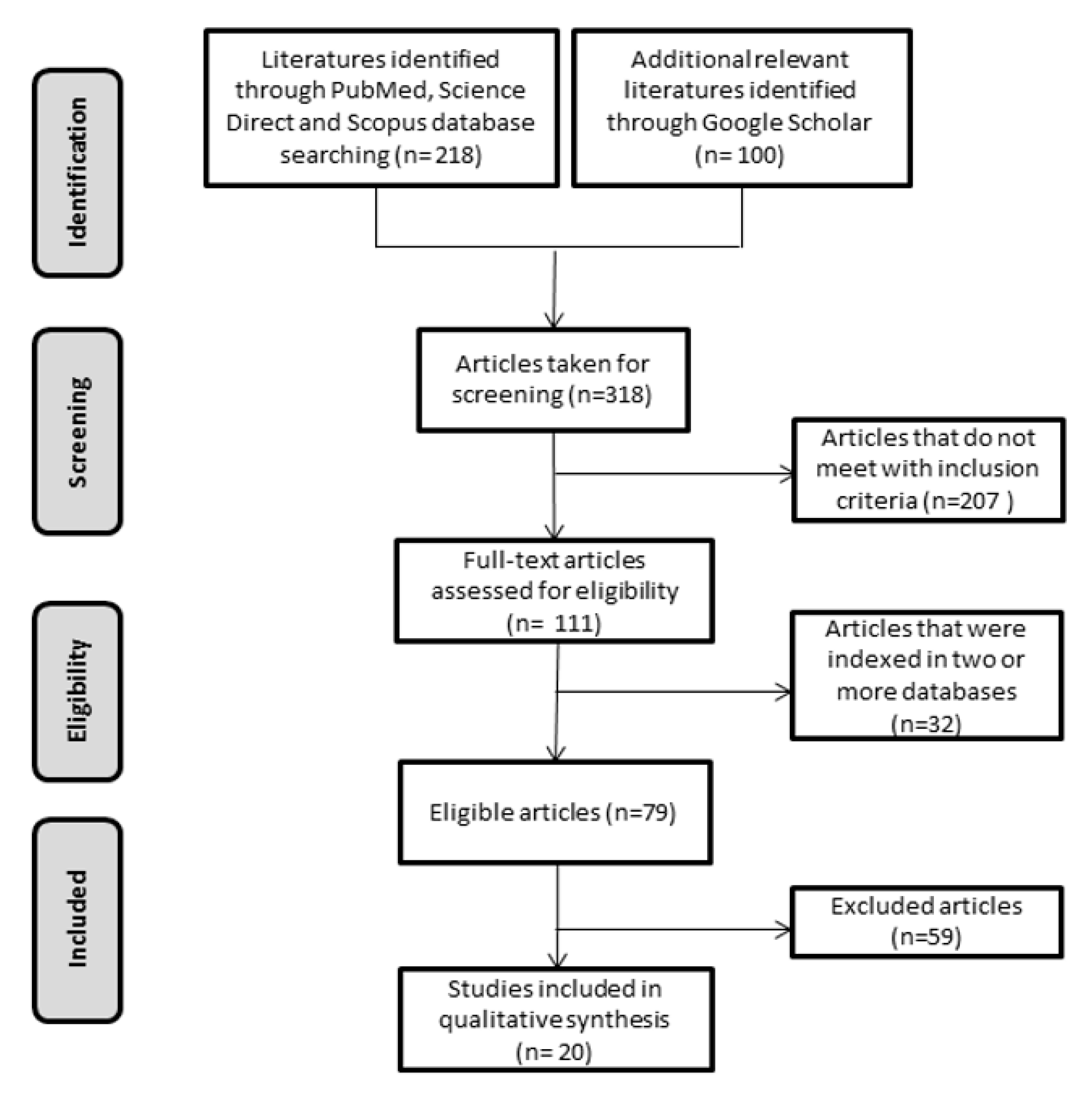
2. Methodology
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Research Article Selection and Evaluation
- In vitro studies related to baicalein extracted from Oroxylum indicum
- In vivo studies related to baicalein extracted from Oroxylum indicum
- Intervention clinical study with baicalein extracted from Oroxylum indicum
- Full-text articles
- Irrelevant titles and abstracts
- Duplicated studies
- Review articles/meta-analyses
- News/editorials/letters
- Case reports
- Baicalein extracted from other medicinal plant
- Synthetic/commercialized baicalein
- Non-English language
3. Results
4. Discussion
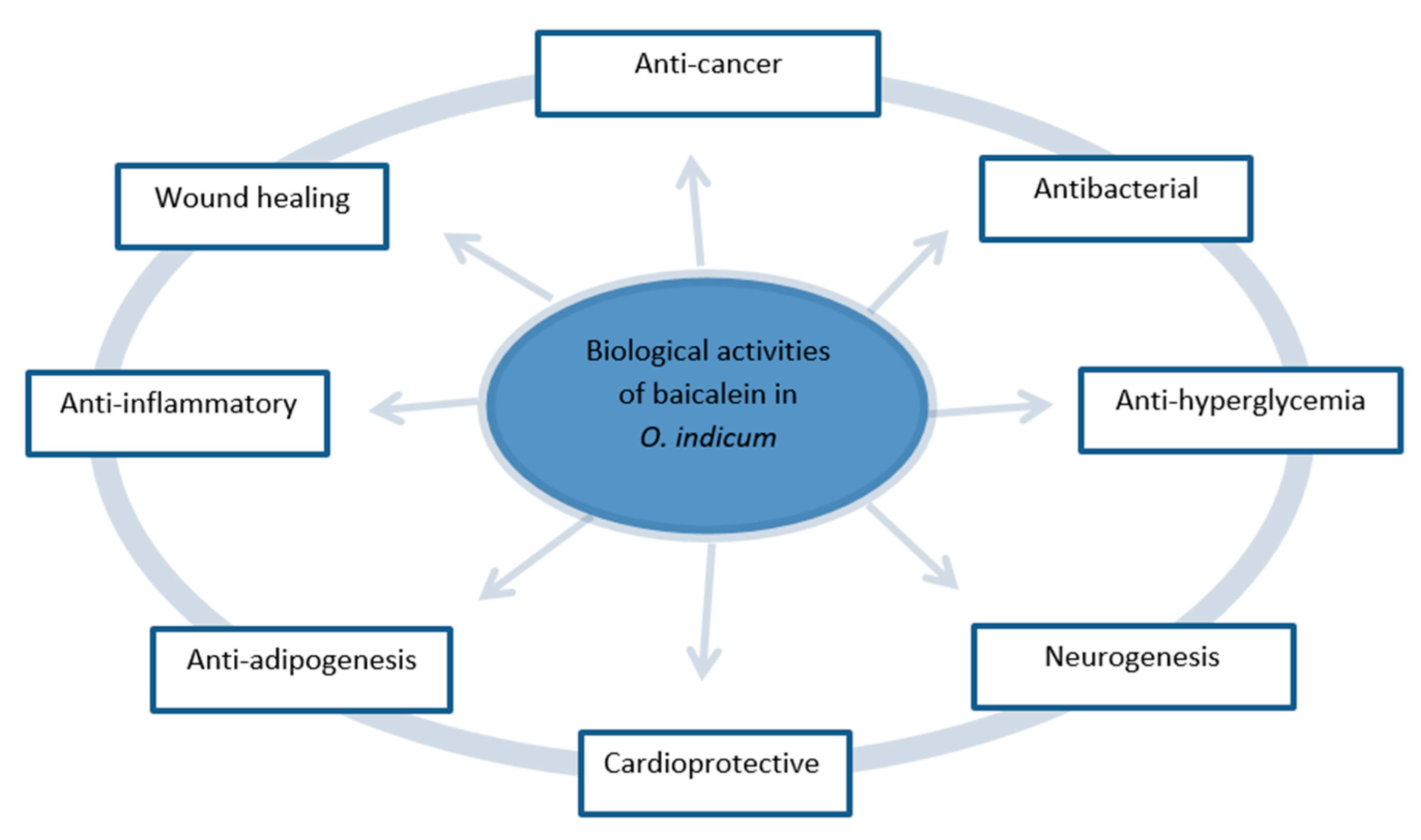
4.1. Biological Activities of Baicalein Extracted from O. indicum
4.1.1. Anti-Cancer
4.1.2. Antibacterial
4.1.3. Anti-Hyperglycemia
4.1.4. Neurogenesis
4.1.5. Cardioprotective
4.1.6. Anti-Adipogenesis
4.1.7. Anti-Inflammatory
4.1.8. Wound Healing
4.2. Strength and Limitations
4.3. Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dev, L.R.; Anurag, M.; Rajiv, G. Oroxylum indicum: A review. Pharmacog. J. 2010, 2, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, D.C.; Kumar, V.; Prasad, C.; Kumar, K.; Gogoi, B.J.; Singh, L.; Srivastava, R.B. Oroxylum indicum—A medicinal plant of North East India: An overview of its nutritional, remedial, and prophylactic properties. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, S104–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, A.M.Z.; Norazianand, M.H.; Rashidi, O. Identification of carotenoid composition in selected “ulam” or traditional vegetables in Malaysia. Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 19, 527–530. [Google Scholar]
- Lalrinzuali, K.; Vabeiryureilai, M.; Jagetia, G.C. Topical application of stem bark ethanol extract of Sonapatha, Oroxylum indicum (L.) Kurz accelerates healing of deep dermal excision wound in Swiss albino mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 227, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaveri, M.; Khandhar, A.; Jain, S. Quantification of baicalein, chrysin, biochanin-A and ellagic acid in root bark of Oroxylum indicum by RP-HPLC with UV detection. Eurasian J. Anal. 2008, 3, 245–257. [Google Scholar]
- Rojsanga, P.; Bunsupa, S.; Brantner, A.H.; Sithisarn, P. Comparative Phytochemical Profiling and in Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Extracts from Raw Materials, Tissue-Cultured Plants, and Callus of Oroxylum indicum (L.) Vent. Evid.-Based Complemen. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 6853212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sithisarn, P.; Nantateerapong, P.; Rojsanga, P.; Sithisarn, P. Screening for Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities and Phytochemical Analysis of Oroxylum indicum Fruit Extracts. Molecules 2016, 21, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.J.; Games, D.E.; Jones, J. Isolation and identification of four flavonoid constituents from the seeds of Oroxylum indicum by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 988, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, A.; Ganzera, M. Oroxylum indicum seeds—Analysis of flavonoids by HPLC-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 70, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, A.; Zaman, K.; Singh, M.; Gupta, R.; Singh, V. Pharmacognostical studies on Oroxylum indicum (Linn.)Vent. stem bark. Indian J. Natur. Prod. Resour. 2011, 2, 472–478. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, I.N.; Salleh, N.N.H.N.; Chung, W.J.; Lee, C.Y.; Tan, S.C. Baicalein-enriched fraction extracted from Oroxylum indicum (L.) Benth. ex kurz leaves exerts antioxidant and inhibitory effects against glioblastoma multiforme. Processes 2019, 7, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithisarn, P.; Rojsanga, P.; Sithisarn, P. Inhibitory Effects on Clinical Isolated Bacteria and Simultaneous HPLC Quantitative Analysis of Flavone Contents in Extracts from Oroxylum indicum. Molecules 2019, 24, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.-Y.; Cao, Y.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Dai, H.-Q.; Yu, S.-X.; Wei, J.-L.; Li, H.; Yang, B. Antioxidant flavonoids from the seed of Oroxylum indicum. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.K.; Manika, N.; Bagchi, G.D.; Gupta, M.M. Simultaneous determination of flavonoids in Oroxylum indicum by RP-HPLC. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 2222–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.V.A.; Malainer, C.; Schwaiger, S.; Hung, T.; Atanasov, A.G.; Heiss, E.H.; Dirsch, V.M.; Stuppner, H. Screening of Vietnamese medicinal plants for NF-κB signaling inhibitors: Assessing the activity of flavonoids from the stem bark of Oroxylum indicum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 159, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassagne, F.; Haddad, M.; Amiel, A.; Phakeovilay, C.; Manithip, C.; Bourdy, G.; Deharo, E.; Marti, G. A metabolomic approach to identify anti-hepatocarcinogenic compounds from plants used traditionally in the treatment of liver diseases. Fitoterapia 2018, 127, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, K.; Yang, L.; Zhang, G. Bladder cancer cell viability inhibition and apoptosis induction by baicalein through targeting the expression of anti-apoptotic genes. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenzel, A.; Grespi, F.; Chmelewskij, W.; Villunger, A. Bcl2 family proteins in carcinogenesis and the treatment of cancer. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizdar, L.; Tomczak, M.; Werner, T.A.; Safi, S.A.; Riemer, J.C.; Verde, P.E.; Stoecklein, N.H.; Knoefel, W.T.; Krieg, A. Survivin and XIAP expression in distinct tumor compartments of surgically resected gastric cancer: XIAP as a prognostic marker in diffuse and mixed type adenocarcinomas. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 6847–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H. Baicalein induces the apoptosis of U251 glioblastoma cell lines via the NF-kB-p65-mediated mechanism. Anim. Cells Syst. 2016, 20, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, A.Y.; Ye, X.; Luo, H.; Rankin, G.O.; Chen, Y.C. Inhibitory Effect of Baicalin and Baicalein on Ovarian Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6012–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.-R.; Zuon, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Chen, S.-T.; Wang, M.-Y.; Jeng, Y.-M.; Lee, P.-H.; Kuo, M.-L. Cyr61 Induces Gastric Cancer Cell Motility/Invasion via Activation of the Integrin/Nuclear Factor- B/Cyclooxygenase-2 Signaling Pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5809–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Li, Z.; Dai, C.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.; Ma, C.; Liu, C. Chrysophanol inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis through NF-κB/cyclin D1 and NF-κB/Bcl-2 signaling cascade in breast cancer cell lines. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4376–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, C.; Han, M.-H.; Hong, S.-H.; Kim, G.-Y.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, N.D.; Choi, Y.H. Baicalein Induces Caspase-dependent Apoptosis Associated with the Generation of ROS and the Activation of AMPK in Human Lung Carcinoma A549 Cells. Drug Dev. Res. 2016, 77, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, S.Y.K.; Wong, Y.C.; Zuo, Z. Development of a SPE-LC/MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of baicalein, wogonin, oroxylin A and their glucuronides baicalin, wogonoside and oroxyloside in rats and its application to brain uptake and plasma pharmacokinetic studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 97, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahab, N.H.; Mat, N.F.C. Baicalein-rich fraction of Oroxylum indicum leaves induces apoptosis by repressing E6 and E7 expression in HPV-associated cervical cancer cell lines. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 9, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Kundu, R. Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7: The Cervical Cancer Hallmarks and Targets for Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazali, K.E.; Abdullah, H.; Izani, N.; Jamil, N. Methanol extract of Oroxylum indicum leaves induces G 1/S cell cycle arrest in HeLa cells via p53-mediated pathway. Int. J. Med. Plant Res. 2013, 2, 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, K.D.; Galbraith, M.D.; Andrysik, Z.; Espinosa, J.M. Mechanisms of transcriptional regulation by p53. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalou, C.; Basak, A.; Mishra, P.; Mohanta, B.; Banik, R.; Dinda, B.; Khatib, A. Inhibition of Tumor Cells Proliferation and Migration by the Flavonoid Furin Inhibitor Isolated From Oroxylum indicum. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, D.E.; Zhang, J.; Cenna, J.; Litwin, S.; Cukierman, E.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.P. Proprotein convertase inhibition results in decreased skin cell proliferation, tumorigenesis, and metastasis. Neoplasia 2010, 12, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Nik, M.E.; Jaafari, M.R.; Banach, M.; Sahebkar, A. Potential anti-tumor effect of a nanoliposomal antiPCSK9 vaccine in mice bearing colorectal cancer. Arch. Med. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Nik, M.E.; Jaafari, M.R.; Banach, M.; Sahebkar, A. Effects of immunization against PCSK9 in an experimental model of breast cancer. Arch. Med. Sci. 2019, 15, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Kakkar, P. Modulation of liver function, antioxidant responses, insulin resistance and glucose transport by Oroxylum indicum stem bark in STZ induced diabetic rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, A.S.; Hidayathulla, S.; Rehman, T.; El Gamal, A.; Al-Massarani, S.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Alqahtani, M.S.; El-Dib, R.; Alajmi, M.F. Alpha-Amylase and Alpha-Glucosidase Enzyme Inhibition and Antioxidant Potential of 3-Oxolupenal and Katononic Acid Isolated from Nuxia oppositifolia. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Sang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yu, X.; Xu, Q.; Xiu, Z.; Dong, Y. Synergistic effects of acarbose and an Oroxylum indicum seed extract in streptozotocin and high-fat-diet induced prediabetic mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zand, A.; Ibrahim, K.; Patham, B. Prediabetes: Why Should We Care? Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc. J. 2019, 14, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.H.; Liao, L.H.; Cheng, P.N.; Wu, T.J. Hepatoxixicty associated with acarbose therapy. Ann. Pharmacother. 2006, 40, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-W.; Sang, Y.-B.; Sun, W.-L.; Yu, H.-S.; Ma, B.; Xiu, Z.-L.; Dong, Y. Combination of flavonoids from Oroxylum indicum seed extracts and acarbose improves the inhibition of postprandial blood glucose: In vivo and in vitro study. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassara, H.; Uribarri, J. Advanced glycation end products (AGE) and diabetes: Cause, effect, or both? Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowotny, K.; Jung, T.; Höhn, A.; Weber, D.; Grune, T. Advanced glycation end products and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 194–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmat, U.; Abad, K.; Ismail, K. Diabetes mellitus and oxidative stress—A concise review. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimojo, H.; Ohtsuka, T.; Kageyama, R. Dynamic expression of Notch signaling genes in neural stem/progenitor cells. Front. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, R.G.; Arai, M.A.; Sadhu, S.K.; Ahmed, F.; Ishibashi, M. Phenolic compounds from the bark of Oroxylum indicum activate the Ngn2 promoter. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 69, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, S.; Lawrence, L.; Sivaram, V.P.; Padikkala, J. Oroxylum indicum root bark extract prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiac damage by restoring redox balance. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2019, 10, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengpratom, T.; Lowe, G.M.; Thumanu, K.; Suknasang, S.; Tiamyom, K.; Eumkeb, G. Oroxylum indicum (L.) Kurz extract inhibits adipogenesis and lipase activity in vitro. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.E. Structure and function of pancreatic lipase and colipase. Ann. Rev. Nutr. 1997, 17, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangal, P.; Khare, P.; Jagtap, S.; Bishnoi, M.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Bhutani, K.K. Screening of six Ayurvedic medicinal plants for anti-obesity potential: An investigation on bioactive constituents from Oroxylum indicum (L.) Kurz bark. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 197, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwatanametanon, N.; Fiebich, B.L.; Efferth, T.; Prieto, J.M.; Heinrich Michael, M. Traditionally used Thai medicinal plants: In vitro anti-inflammatory, anticancer and antioxidant activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; West, A.P.; Ghosh, S. NF-κB and the immune response. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6758–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.; Kodra, A.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Golinko, M.S.; Ehrlich, H.P.; Brem, H. The Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Wound Healing. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 153, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracy, L.E.; Minasian, R.A.; Caterson, E.J. Extracellular Matrix and Dermal Fibroblast Function in the Healing Wound. Adv. Wound Care 2016, 5, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKay, D.; Miller, A.L. Nutritional Support for Wound Healing. Altern. Med. Rev. 2003, 8, 359–377. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.; Singh, V.; Kumar, D.; KChaudhary, A. Wound Healing and Antimicrobial Potential of Oroxylum indicum Vent. in Albino Mice. Nat. Prod. J. 2011, 1, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengpratom, T.; Ngernsoungnern, A.; Ngernsoungnern, P.; Lowe, G.M.; Eumkeb, G. Antiadipogenesis of Oroxylum indicum (L.) Kurz Extract via PPAR γ 2 in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 6720205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | No. of Publication |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 1 |
| 2011 | 1 |
| 2013 | 3 |
| 2015 | 2 |
| 2016 | 1 |
| 2017 | 3 |
| 2018 | 5 |
| 2019 | 3 |
| 2020 (up to 31 March 2020) | 1 |
| TOTAL | 20 |
| Author, Year | Reference | Biological Activities | Part and Solvent Used | Summary of Key Findings in Vitro Tests | Summary of Key Findings in Vivo Tests |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chassagne, 2018 | [16] | Anti-cancer | Stem bark (ethanol extract) |
|
|
| Yang, 2018 | [17] | Anti-cancer | Not mentioned (the baicalein from O. indicum was given as a gift by other research group) |
|
|
| Kang, 2019 | [11] | Anti-cancer | Leaves (petroleum ether-methanol extract) |
|
|
| Wahab, 2018 | [26] | Anti-cancer | Leaves (methanol extract) |
|
|
| Zazali et al., 2013 | [28] | Anti-cancer | Leaves (methanol extract) |
|
|
| Lalou, 2013 | [30] | Anti-cancer | Stem bark (methanol extract) |
|
|
| Sithisarn, 2016 | [7] | Antibacterial, antioxidant | Fruits (ethanol and water extract) |
|
|
| Sithisarn, 2019 | [12] | Antibacterial | Fruits (ethanol and water extract) |
|
|
| Singh & Kakkar, 2013 | [34] | Anti-hyperglycemia, antioxidant | Stem bark (50% aqueous ethanol) |
|
|
| Zhang, 2017 | [39] | Anti-hyperglycemia | Seeds (90% aqueous ethanol) |
|
|
| Sun, 2017 | [36] | Anti-hyperglycemia | Seeds (90% ethanol-water) |
|
|
| Fuentes, 2015 | [44] | Neurogenesis | Bark (methanol) |
|
|
| Menon, 2019 | [45] | Cardioprotective | Root bark (70% methanol) |
|
|
| Tanaporn, 2018 | [46] | Anti-adipogenesis | Fruit pods (ethanol extract) |
|
|
| Tanaporn, 2020 | [55] | Anti-adipogenesis | Fruit pods (ethanol extract) |
|
|
| Mangal et al., 2017 | [48] | Anti-adipogenesis | Bark (ethyl acetate extract) |
|
|
| Siriwatanametanon et al., 2010 | [49] | Anti-inflammatory | Stem bark (methanol extract) |
|
|
| Tran et al., 2015 | [15] | Anti-inflammatory | Stem bark (petroleum ether, ethyl acetate and methanol extract) |
|
|
| Singh, 2011 | [54] | Wound healing, antimicrobial | Root bark (methanol extract) |
|
|
| Lalrinzuali, 2018 | [4] | Wound healing | Stem bark (ethanol) |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nik Salleh, N.N.H.; Othman, F.A.; Kamarudin, N.A.; Tan, S.C. The Biological Activities and Therapeutic Potentials of Baicalein Extracted from Oroxylum indicum: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 5677. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235677
Nik Salleh NNH, Othman FA, Kamarudin NA, Tan SC. The Biological Activities and Therapeutic Potentials of Baicalein Extracted from Oroxylum indicum: A Systematic Review. Molecules. 2020; 25(23):5677. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235677
Chicago/Turabian StyleNik Salleh, Nik Nur Hakimah, Farah Amna Othman, Nur Alisa Kamarudin, and Suat Cheng Tan. 2020. "The Biological Activities and Therapeutic Potentials of Baicalein Extracted from Oroxylum indicum: A Systematic Review" Molecules 25, no. 23: 5677. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235677
APA StyleNik Salleh, N. N. H., Othman, F. A., Kamarudin, N. A., & Tan, S. C. (2020). The Biological Activities and Therapeutic Potentials of Baicalein Extracted from Oroxylum indicum: A Systematic Review. Molecules, 25(23), 5677. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235677






