Synthesis, Modification and Biological Activity of Diosgenyl β-d-Glycosaminosides: An Overview
Abstract
1. Introduction
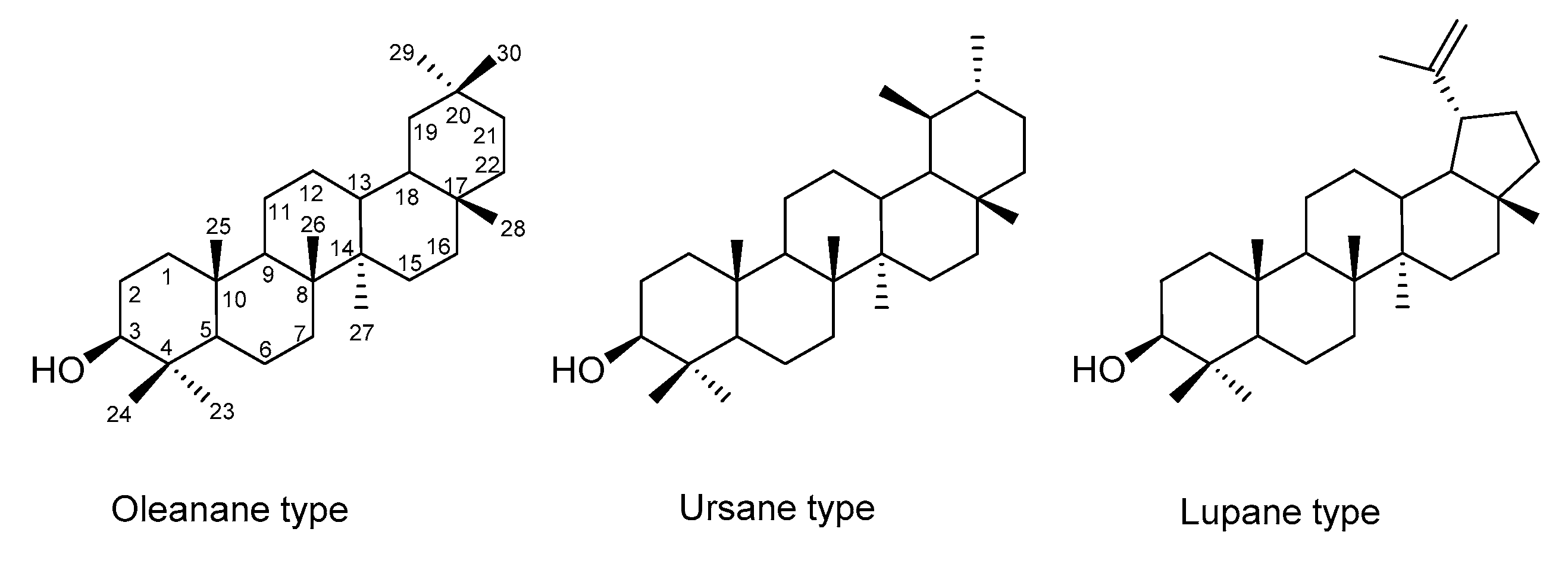
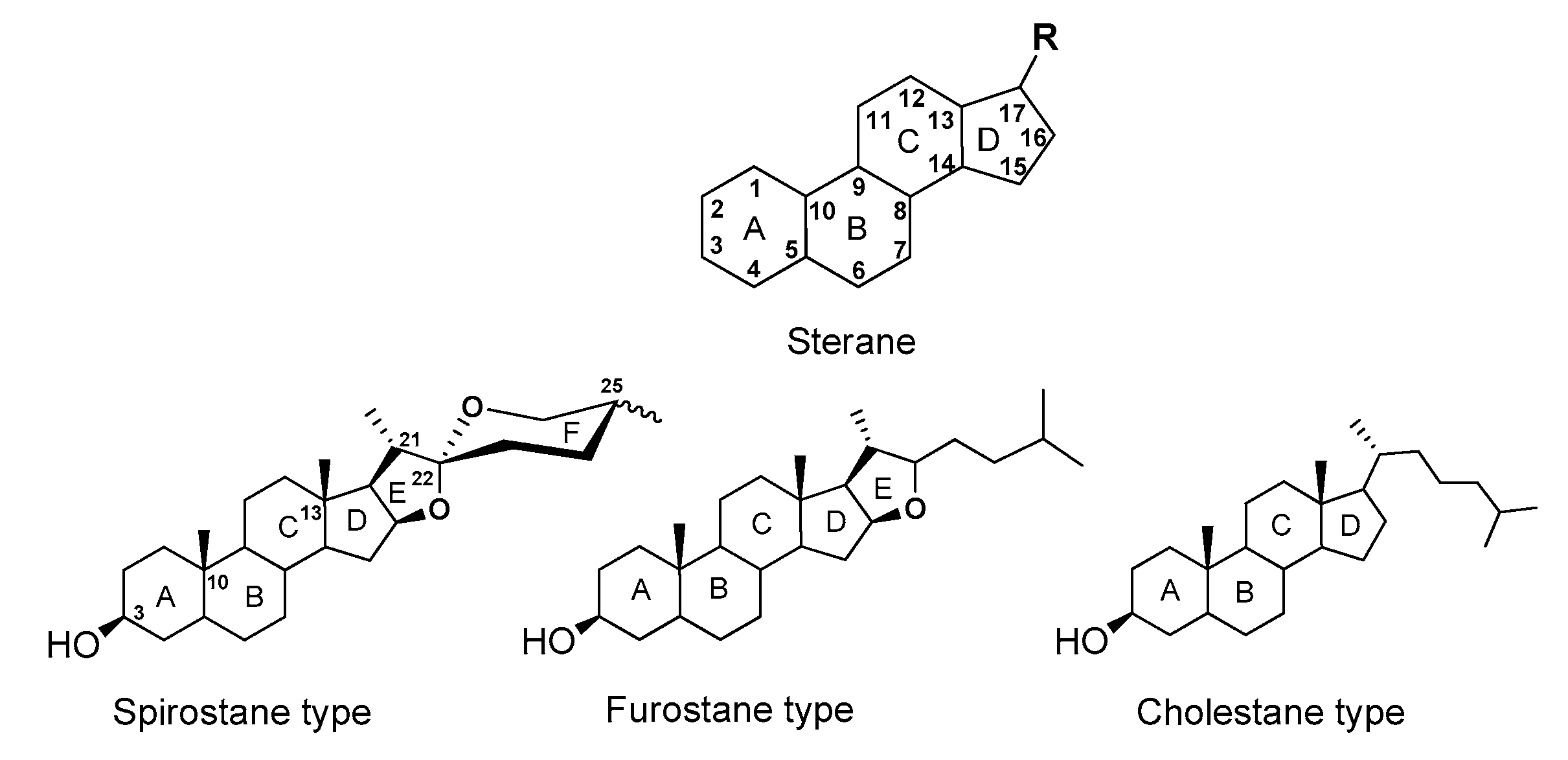
2. Saponins, Their Occurrence, Properties and Structure
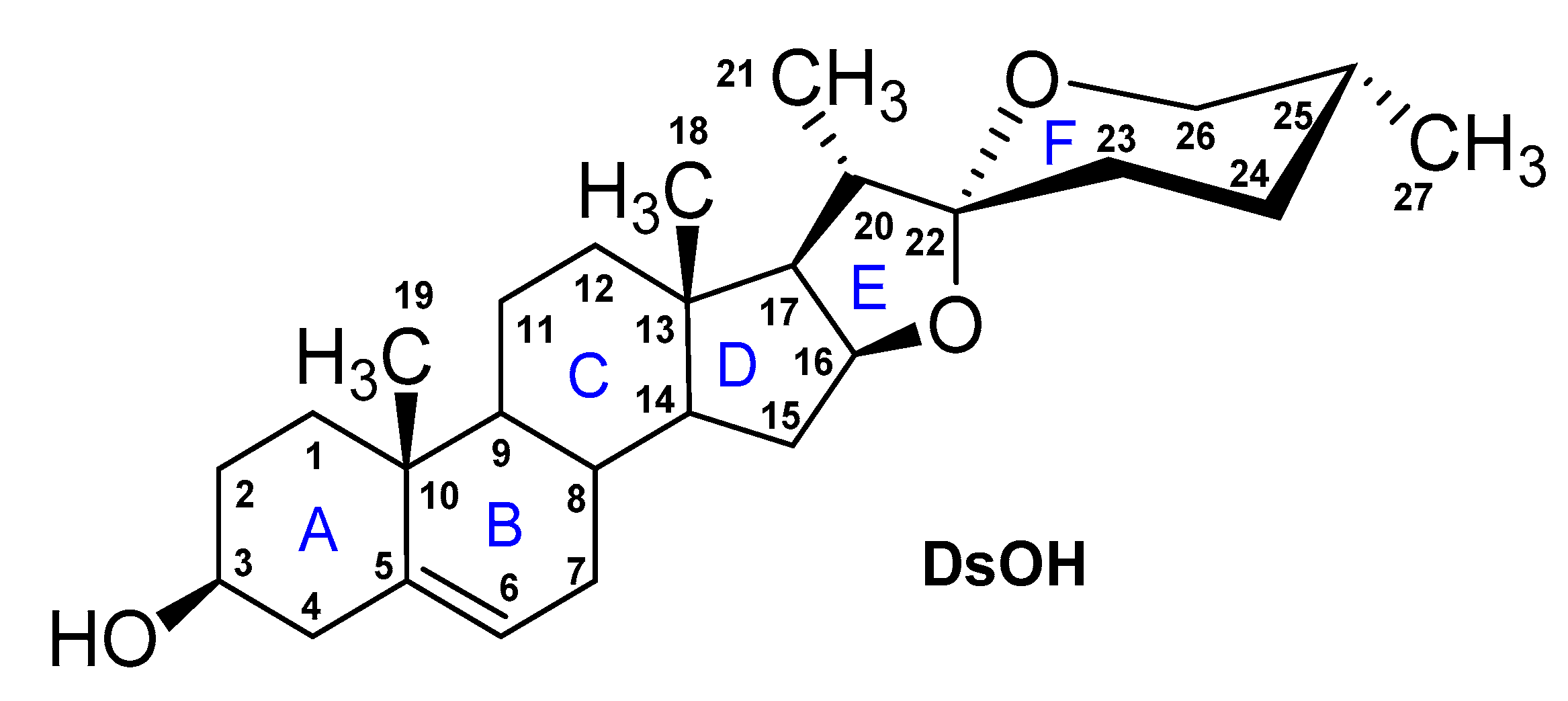
3. Diosgenyl Saponins
4. d-Glycosaminosides of Diosgenin
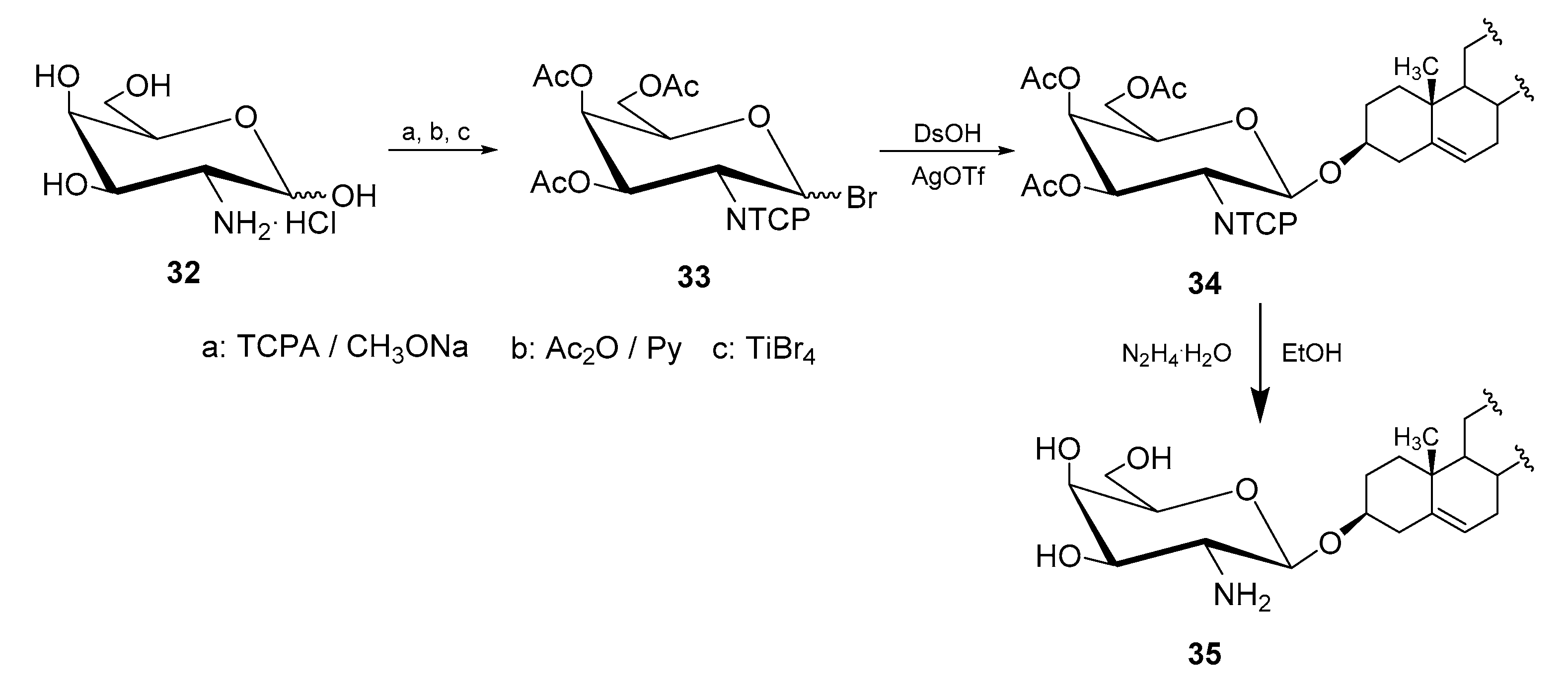
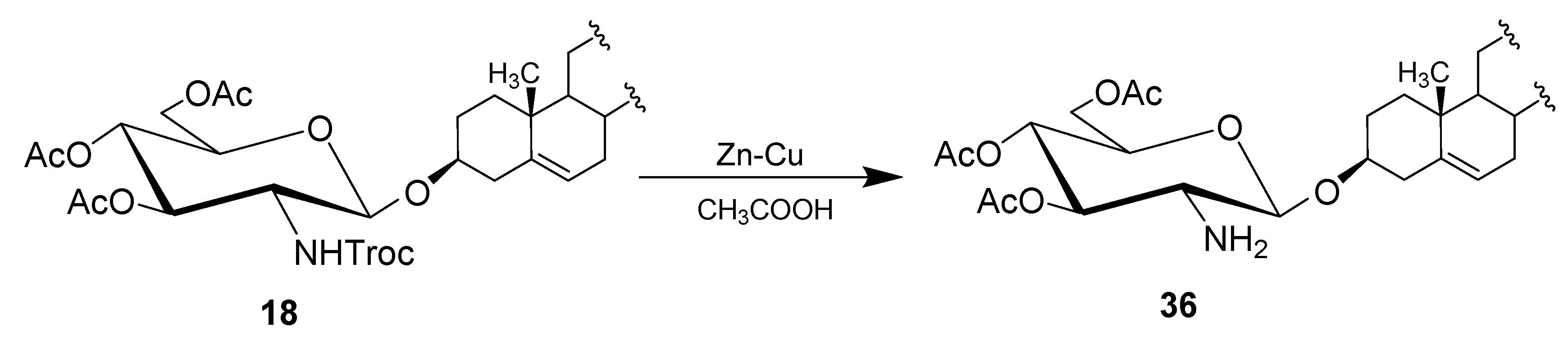
4.1. Methods of Synthesis
4.2. Chemical Modification
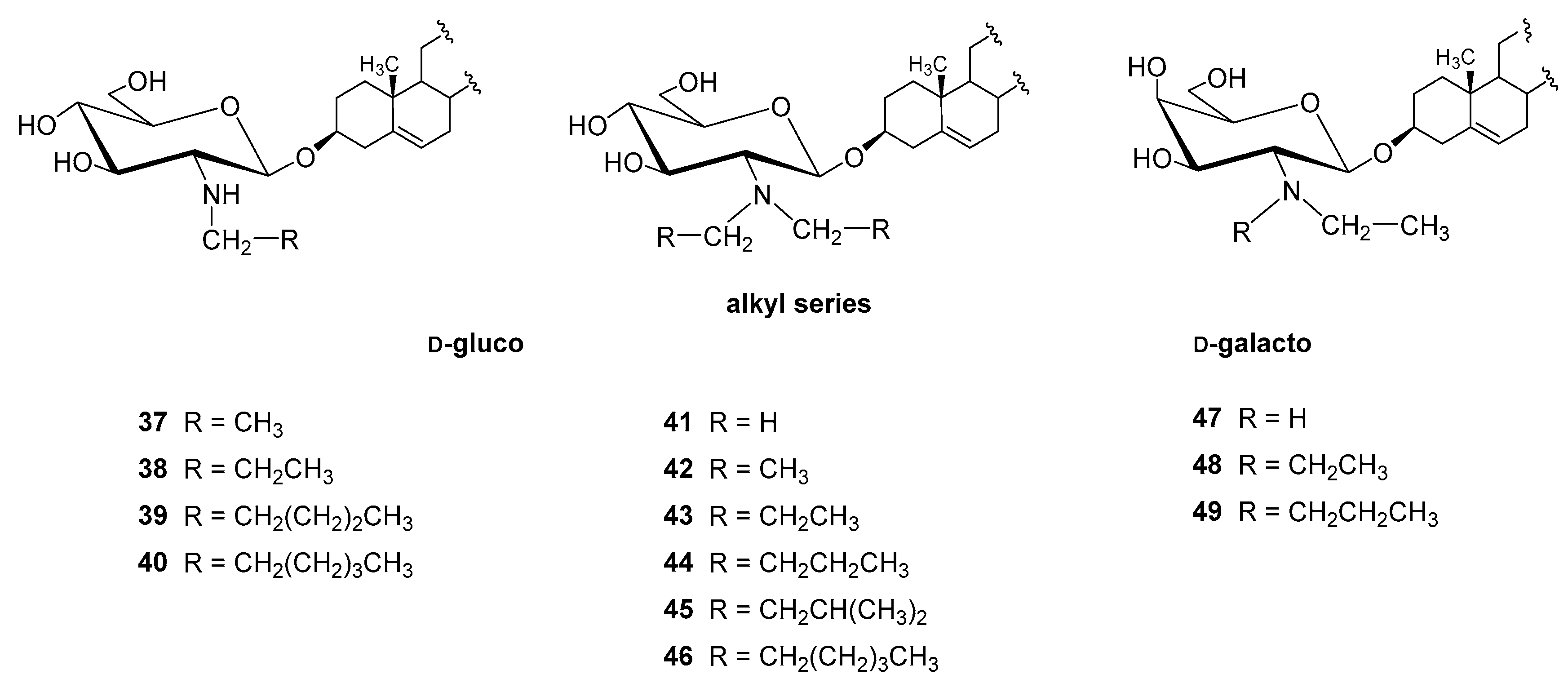
4.2.1. N-alkyl and N,N-dialkyl Derivatives
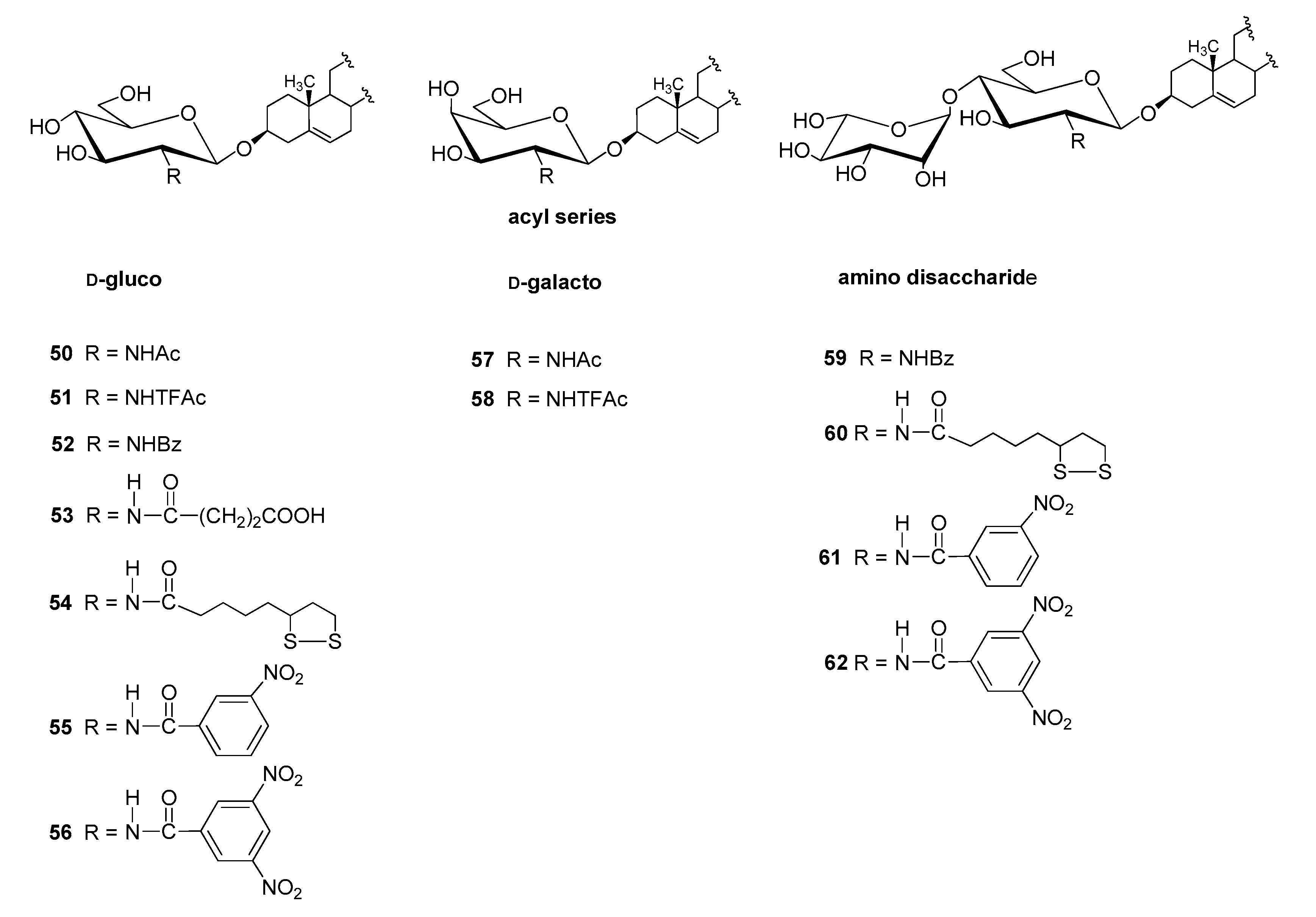
4.2.2. N-acyl Derivatives
4.2.3. Other Derivatives
4.3. Pharmacological Properties
4.3.1. Antibacterial Activity
4.3.2. Antifungal Activity
4.3.3. Anti-Cancer Activity
4.3.4. Hemolytic Activity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sparg, S.G.; Light, M.E.; van Staden, J. Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 94, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincken, J.P.; Heng, L.; de Groot, A.; Gruppen, H. Saponins, classification and occurrence in the plant kingdom. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyarenko, T.; Malyarenko, O.; Ivanchina, N.; Kalinovsky, A.; Popov, R.; Kicha, A. Four New Sulfated Polar Steroids from the Far Eastern Starfish Leptasterias ochotensis: Structures and Activities. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4418–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.R.; Gong, H. Isolation and synthesis of shark-repelling saponins. Lipids 2004, 39, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smułek, W.; Zdarta, A.; Łuczak, M.; Krawczyk, P.; Jesionowski, T.; Kaczorek, E. Sapindus saponins’ impact on hydrocarbon biodegradation by bacteria strains after short- and long-term contact with pollutant. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 142, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhao, W.; Xu, J.; Shao, B.; Qin, G. Studies on bioactive saponins from Chinese medicinal plants. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1996, 404, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, R.; Tay, I. Saponins Properties, Applications and Health Benefits; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Barky, A.; Hussein, S.A.; AlmEldeen, A.; Hafez, Y.A.; Mohamed, T.M. Saponins and their potential role in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Manag. 2017, 7, 148–158. [Google Scholar]
- Elekofehinti, O.O. Saponins: Anti-diabetic principles from medicinal plants—A review. Pathophysiology 2015, 22, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Liu, C. Chemical study and medical application of saponins as anti-cancer agents. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-Y.; Chan, S.-H.; Juang, Y.-P.; Hsiao, H.-M.; Guh, J.-H.; Liang, P.-H. Design, synthesis and cytotoxic activity of N-modified oleanolic saponins bearing a glucosamine. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 1942–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Melzig, M.F.; Fuchs, H.; Weng, A. Chemistry and pharmacology of saponins: Special focus on cytotoxic properties. Bot. Targets Ther. 2011, 1, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.S.; Sule, I.M.; Musa, M.A.; Musa, Y.K.; Abubakar, S.M.; Hassan, S.A. Anti-inflammatory activity of crude saponin extracts from five Nigerian medicinal plants. Afr. J. Tradit. Complementary Altern. Med. 2012, 9, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, K.J.; Kim, H.K.; Han, M.H.; Oh, Y.N.; Yoon, H.M.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, B.W.; Choi, Y.H. CytoAnti-inflammatory effects of saponins derived from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorus in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; Gong, L.; Zhou, F.; Long, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Ouyang, B.; Liu, M. Anti-inflammatory effect of traditional Chinese medicine preparation Penyanling on pelvic inflammatory disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 23, 113405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallelli, L. Escin: A review of its anti-edematous, anti-inflammatory, and venotonic properties. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 27, 3425–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, J.M.; Kuzina, V.; Andersen, S.B.; Bak, S. Molecular activities, biosynthesis and evolution of triterpenoid saponins. Phytochem 2011, 72, 435–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, T.; Papadopoulou, K.K.; Osbourn, A. Metabolic and functional diversity of saponins, biosynthetic intermediates and semi-synthetic derivatives. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, A.; Jenett-Siems, K.; Schmieder, P.; Bachran, D.; Bachran, C.; Görick, C.; Thakur, M.; Fuchs, H.; Melzig, M. A convenient method for saponin isolation in tumour therapy. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 1, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.S.; Ferdosh, S.; Haque Akanda, M.J.; Ghafoor, K.; Rukshana, A.H.; Ali, M.E.; Kamaruzzaman, B.Y.; Fauzi, M.B.; Shaarani, S.; Islam Sarker, M.Z. Techniques for the extraction of phytosterols and their benefits in human health: A review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2206–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netala, V.R.; Ghosh, S.B.; Bobbu, P.; Anitha, D.; Tartte, V. Triterpenoid saponins: A review on biosynthesis, applications and mechanism of their action. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Negi, J.S.; Negi, P.S.; Pant, G.J.; Rawat, M.S.; Negi, S.K. Naturally occurring saponins: Chemistry and biology. J. Poisonous Med. Plant Res. 2013, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Gao, W.Y.; Man, S.L.; Wang, Y. In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of steroid saponins of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Exp. Oncol. 2009, 31, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.-C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Ke, Y.; Xua, Q.-C.; Cheng, M.-S. Synthesis and antitumor activity of two natural N-acetylglucosamine-bearing triterpenoid saponins: Lotoidoside D and E. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 4200–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ni, J. Treatment of wastewater from Dioscorea zingiberensis tubers used for producing steroid hormones in a microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2731–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Gadewar, M.; Tahilyani, V.; Kumar, D.P. A review on pharmacological and analytical aspects of diosgenin: A concise report. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2012, 2, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-R.; Zhang, Y.; Jacob, M.R.; Khan, S.I.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Li, X.-C. Antifungal activity of C-27 steroidal saponins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1710–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Huang, B.; Du, D.; Guo, X.; Xin, G.; Xing, Z.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; He, Y.; et al. Anti-thrombosis effect of diosgenyl saponins in vitro and in vivo. Steroids 2013, 78, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cong, X.; Zheng, L.; Xu, L.; Yin, L.; Peng, J. Dioscin, a natural steroid saponin, shows remarkable protective effect against acetaminophen-induced liver damage in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 214, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Han, X.; Yu, B. Synthesis of monomethylated dioscin derivatives and their antitumor activities. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, B. Synthesis, cytotoxicity, and hemolytic activity of 6′-O-substituted dioscin derivatives. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2705–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chun, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.-S.; Joo, E.-J.; Kim, Y.S.; Cheng, M.S. Synthesis of novel diosgenyl saponin analogues and apoptosis-inducing activity on A549 human lung adenocarcinoma. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 8822–8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravikumar, P.R.; Hammesfahr, P.; Sih, C.J. Cytotoxic saponins form the Chinese herbal drug Yunnan Bai Yao. J. Pharm. Sci. 1979, 68, 900–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimaki, Y.; Yokosuka, A.; Kuroda, M.; Sashida, Y. Cytotoxic activities and structure–cytotoxic relationships of steroidal saponins. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 24, 1286–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, B. Exploration of the correlation between the structure, hemolytic activity, and cytotoxicity of steroid saponins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 2528–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.C.; Leon, F.; Brouard, I.; Torres, F.; Rubio, S.; Quintana, J.; Estevez, F.; Bermejo, J. Synthesis of novel spirostanic saponins and their cytotoxic activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 2063–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banoub, J.; Boullanger, P.; Lafont, D. Synthesis of oligosaccharides of 2-amino-2-deoxy sugars. Chem. Rev. 1992, 92, 1167–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demchenko, A.V. Stereoselective Chemical 1,2-cis O-Glycosylation: From ‘Sugar Ray’ to Modern Techniques of the 21st Century. Curr. Org. Chem. 2003, 7, 35–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarczyk, D.; Kaca, W.; Myszka, H.; Serwecińska, L.; Smiatacz, Z.; Zaborowski, A. The synthesis of diosgenyl 2-amino-2-deoxy-β-d-glucopyranoside hydrochloride. Carbohydr. Res. 2000, 328, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfrom, M.L.; Bhat, H.M. Trichloroacetyl and trifluoroacetyl as N-blocking groups in nucleoside synthesis with 2-amino sugars. J. Org. Chem. 1967, 32, 1821–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszka, H.; Bednarczyk, D.; Najder, M.; Kaca, W. Synthesis and induction of apoptosis in B cell chronic leukemia by diosgenyl 2-amino-2-deoxy-β-d-glucopyranoside hydrochloride and its derivatives. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, S.L.; Madsen, R.; Fraser-Reid, B. Studies towards lipid A: Synthesis of Differentially Protected Disaccharide Fragments. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 3654–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarczyk, D.; Walczewska, A.; Grzywacz, D.; Sikorski, A.; Liberek, B.; Myszka, H. Differently N-protected 3,4,6-tri-O-acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-d-glucopyranosyl chlorides and their application in the synthesis of diosgenyl 2-amino-2-deoxy-β-d-glucopyranoside. Carbohydr. Res. 2013, 367, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, H. Advances in Selective Chemical Syntheses of Complex Oligosaccharides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1982, 21, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, B. N-Dimethylphosphoryl-protected glucosamine trichloroacetimidate as an effective glycosylation donor. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 4557–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskiw, M.J.; Tassotto, M.L.; Th’ng, J.; Jiang, Z.-H. Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of diosgenyl saponin analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 3209–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaskiw, M.J.; Tassotto, M.L.; Mok, M.; Tokar, S.L.; Pycko, R.; Th’ng, J.; Jiang, Z.-H. Structural analogues of diosgenyl saponins: Synthesis and anticancer activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 7670–7679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Herrera, M.A.; Lopez-Munoz, H.; Hernandez-Vazquez, J.M.V.; Sanchez-Sanchez, L.; Escobar-Sanchez, M.L.; Pinto, B.M.; Sandoval-Ramirez, J. Synthesis and selective anticancer activity of steroidal glycoconjugates. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Xiao, X.; Yao, J.; Han, F.; Lou, H.; Luo, H.; Liang, G.; Ben-David, Y.; Pan, W. Syntheses and anti-cancer activities of glycosylated derivatives of diosgenin. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2017, 33, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczewska, A.; Grzywacz, D.; Bednarczyk, D.; Dawgul, M.; Nowacki, A.; Kamysz, W.; Liberek, B.; Myszka, H. N-Alkyl derivatives of diosgenyl 2-amino-2-deoxy-β-d-glucopyranoside; synthesis and antimicrobial activity. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, U.; Ray, A.K.; Magnusson, G. Efficient syntheses of 3,4,6-tri-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-2- phthalimido-β- and -α-d-galactopyranosyl chloride. Carbohydr. Res. 1990, 208, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Tao, H. Glycosyl trifluoroacetimidates. Part 1: Preparation and application as new glycosyl donors. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 2405–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Sun, J. Glycosylation with glycosyl N-phenyltrifluoroacetimidates (PTFAI) and a perspective of the future development of new glycosylation methods. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4668–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszka, H.; Sokołowska, P.; Cieślińska, A.; Nowacki, A.; Jaśkiewicz, M.; Kamysz, W.; Liberek, B. Diosgenyl 2-amino-2-deoxy-β-d-galactopyranoside: Synthesis, derivatives and antimicrobial activity. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 2310–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.R.; Toepfer, A. Glycosylation with highly reactive glycosyl donors: Efficiency of the inverse procedure. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 2405–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cheng, M.-S. Syntheses and structure–activity relationship studies of N-substituted-β-d-glucosaminides as selective cytotoxic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 7110–7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debenham, J.S.; Rodebaugh, R.; Fraser-Reid, B. Recent Advances in N-Protection for Amino Sugar Synthesis. Liebigs Ann. 1997, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, T.; Josephson, S.; Bundle, D.R. The synthesis of streptococcal groups A, C and variant—A antigenic determinants. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin I 1981, 2379–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xin, G.; He, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhao, H.; Xing, Z.; Chen, Q.; Huang, W.; He, Y. Novel organic gelators based on pentose derivatized diosgenyl saponins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Herrera, M.; Lopez-Munoz, H.; Hernandes-Vazquez, J.; Lopez-Davila, M.; Mohan, S.; Escobar-Sanchez, M.; Sanchez-Sanches, L.; Pinto, B.; Sandoval-Ramirez, J. Synthesis and biological evaluation of the glycoside (25R)-3β,16β-diacetoxy-22-oxo-cholest-5-en-26-yl β-d-glucopyranoside: A selective anticancer agent in cervicouterine cell lines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 3877–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberek, B.; Melcer, A.; Osuch, A.; Wakieć, R.; Milewski, S.; Wiśniewski, A. N-Alkyl derivatives of 2-amino-2-deoxy-d-glucose. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 1876–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzywacz, D.; Paduszyńska, M.; Norkowska, M.; Kamysz, W.; Myszka, H.; Liberek, B. N-Aminoacyl and N-hydroxyacyl derivatives of diosgenyl 2-amino-2-deoxy-β-d-glucopyranoside: Synthesis, antimicrobial and hemolytic activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 114923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Panda, S.S.; Birs, A.S.; Serrano, J.C.; Gonzalez, C.F. Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of amino acid-antibiotic conjugates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1856–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.S.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Kucukbay, H.; Meyers, M.J.; Sverdrup, F.M.; El-Feky, S.A.; Katritzky, A.R. Synthesis and antimalarial bioassay of quinine–peptide conjugates. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2013, 82, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalbetti, C.A.; Falque, V. Amide bond formation and peptide coupling. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 10827–10852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, M.J.; Nguyen, H.M. Recent developments in glycosyl urea synthesis. Carbohydr. Res. 2014, 385, 18–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porwański, S. New ureas containing glycosyl and diphenylphosphinyl scaffolds: Synthesis and the first attempts to use them in asymmetric synthesis. Carbohydr. Res. 2014, 394, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharana, A.K.; Dash, R.N.; Subudhi, B.B. Thiosemicarbazides: Updates on antivirals strategy. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 32811412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsanu, V.; Lisa, G. Composites containing metal and thiosemicarbazone: Thermal, antimicrobial and antifungal properties. Polyhedron 2020, 191, 114800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.R.S.; Andrade, J.T.; Sousa, C.D.F.; Fernandes, J.S.; Carmo, L.F.; Araújo, M.G.F.; Ferreira, J.M.S.; Villar, J.A.F.P. Synthesis and Evaluation of the in vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Triazoles, Morpholines and Thiosemicarbazones. Med. Chem. 2019, 15, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharkwal, H.; Panthari, P.; Pant, M.K.; Kharkwal, H.; Kharkwal, A.C.; Joshi, D.D. Foaming glycosides: A Review. IOSR J. Pharm. 2012, 2, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Ahhmed, A.; Shin, J.H.; Baek, J.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, J.D. Green Tea Seed Isolated Saponins Exerts Antibacterial Effects against Various Strains of Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria, a Comprehensive Study In Vitro and In Vivo. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2018, 3486106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Yang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, F.; Hou, Z.; Xue, P. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action saponins from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. husks against foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 112350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trdá, L.; Janda, M.; Macková, D.; Pospíchalová, R.; Dobrev, P.I.; Burketová, L.; Matušinsky, P. Dual Mode of the Saponin Aescin in Plant Protection: Antifungal Agent and Plant Defense Elicitor. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirioni, O.; Myszka, H.; Dawgul, M.; Ghiselli, R.; Orlando, F.; Silvestri, C.; Brescini, L.; Kamysz, W.; Guerrieri, M.; Giacometti, A. In vitro activity and in vivo efficacy of the saponin diosgenyl 2-amino-2-deoxy-β-d-glucopyranoside hydrochloride (HSM1) alone and in combination with daptomycin and vancomycin against Gram-positive cocci. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.E. Overview of the changing epidemiology of candidemia. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2009, 25, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawgul, M.A.; Grzywacz, D.; Liberek, B.; Kamysz, W.; Myszka, H. Activity of Diosgenyl 2-amino-2-deoxy-β-D-glucopyranoside, its Hydrochloride, and N,N-dialkyl Derivatives against Non-albicans Candida Isolates. Med. Chem. 2018, 14, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolak, I.; Galanty, A.; Sobolewska, D. Saponins as cytotoxic agents; a review. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
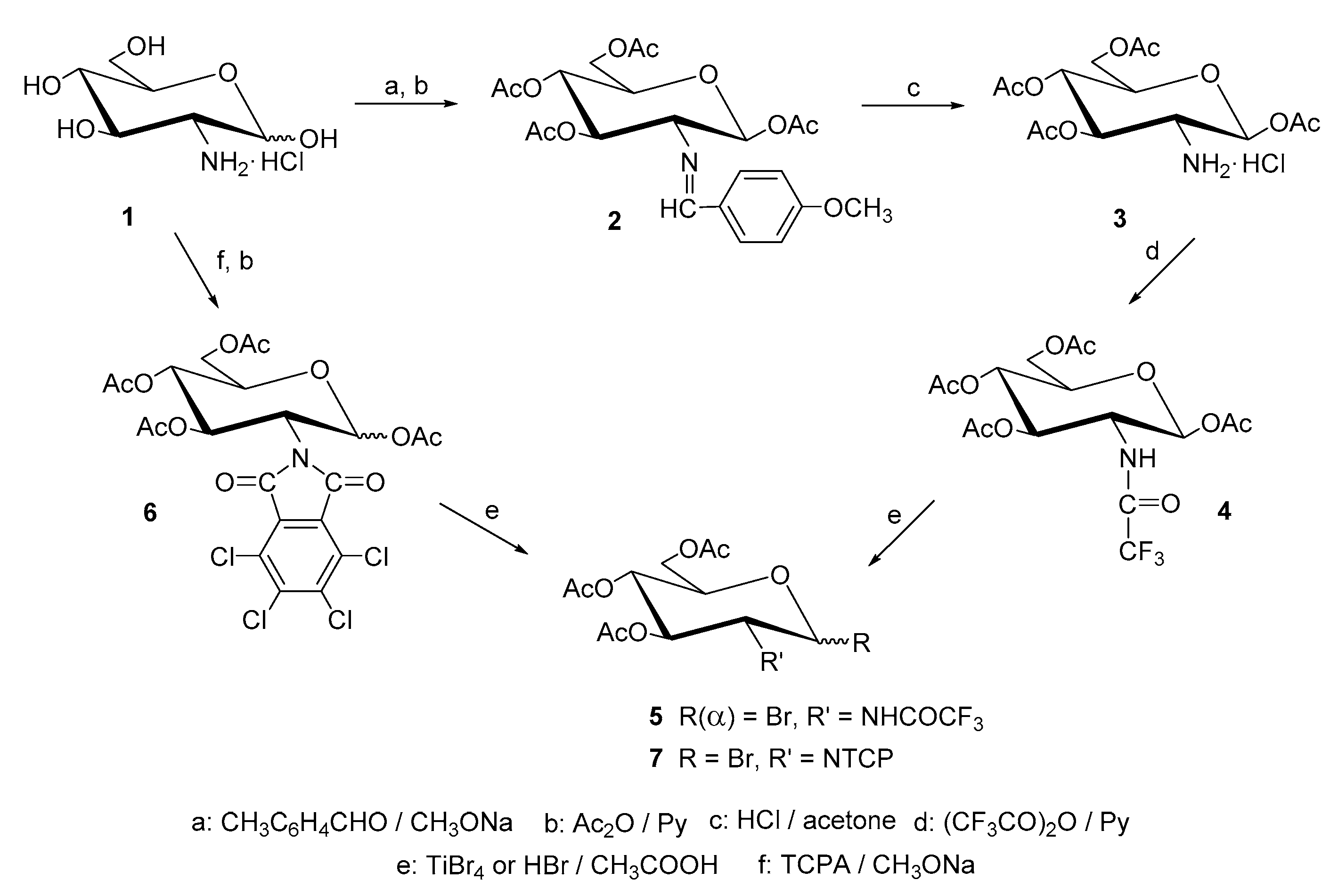
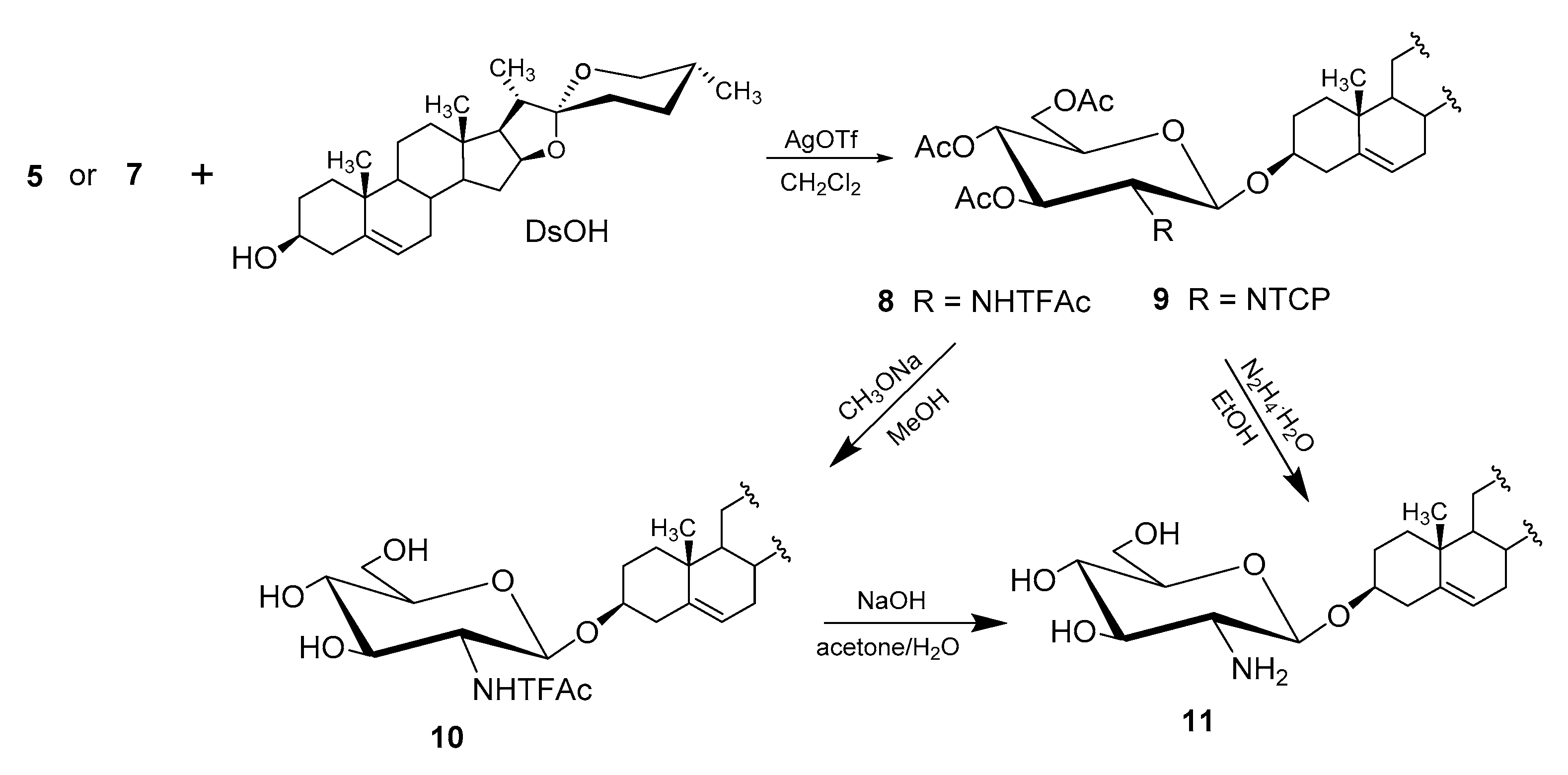
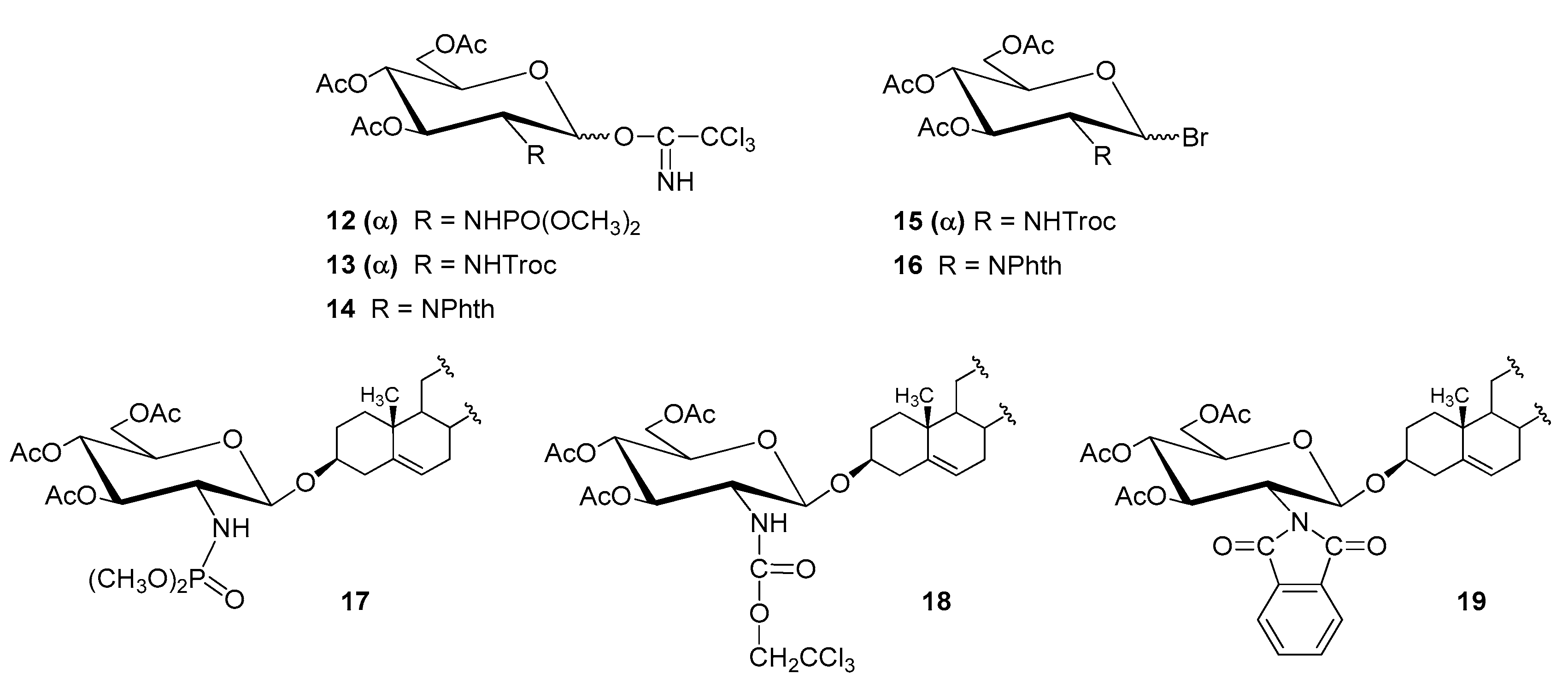
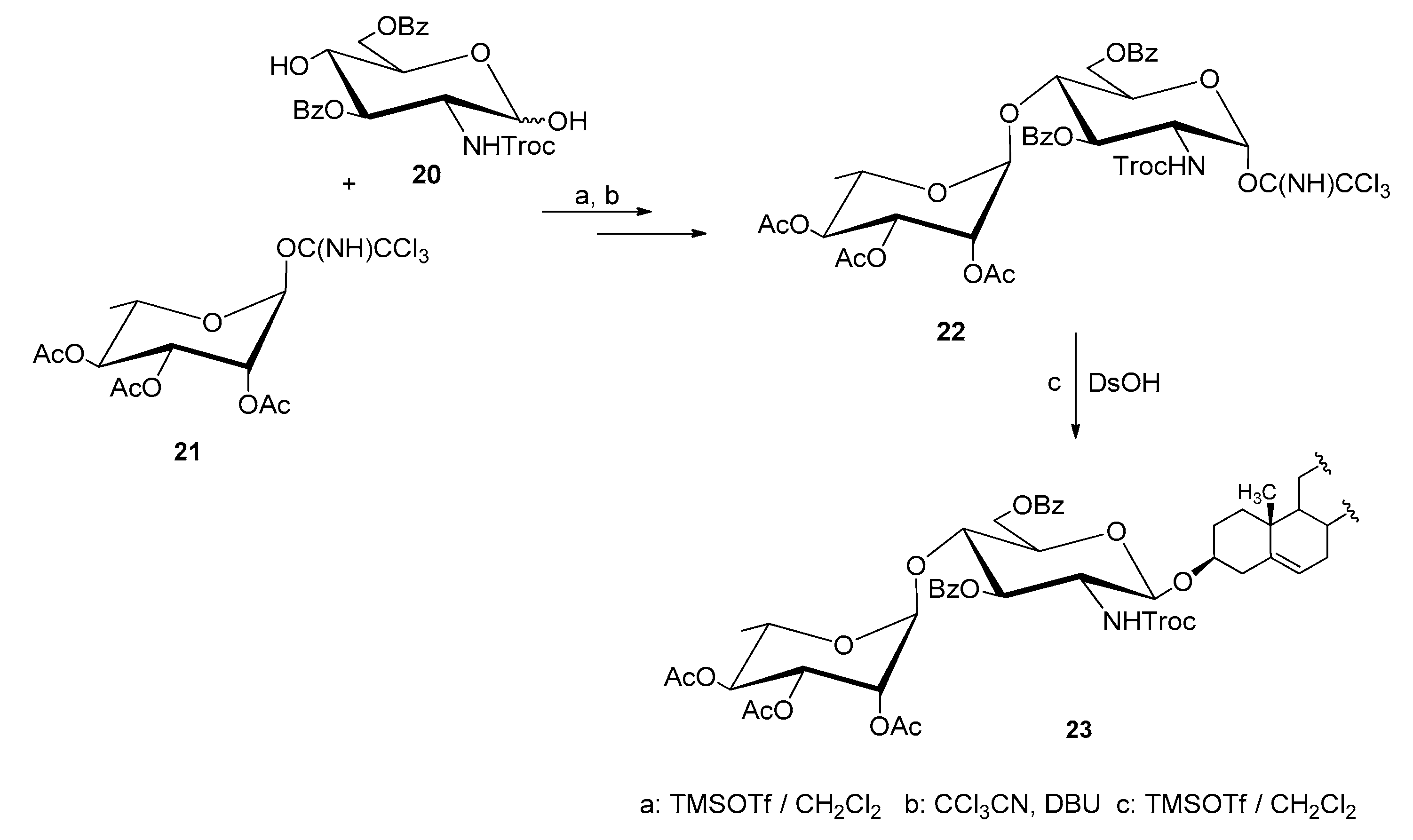
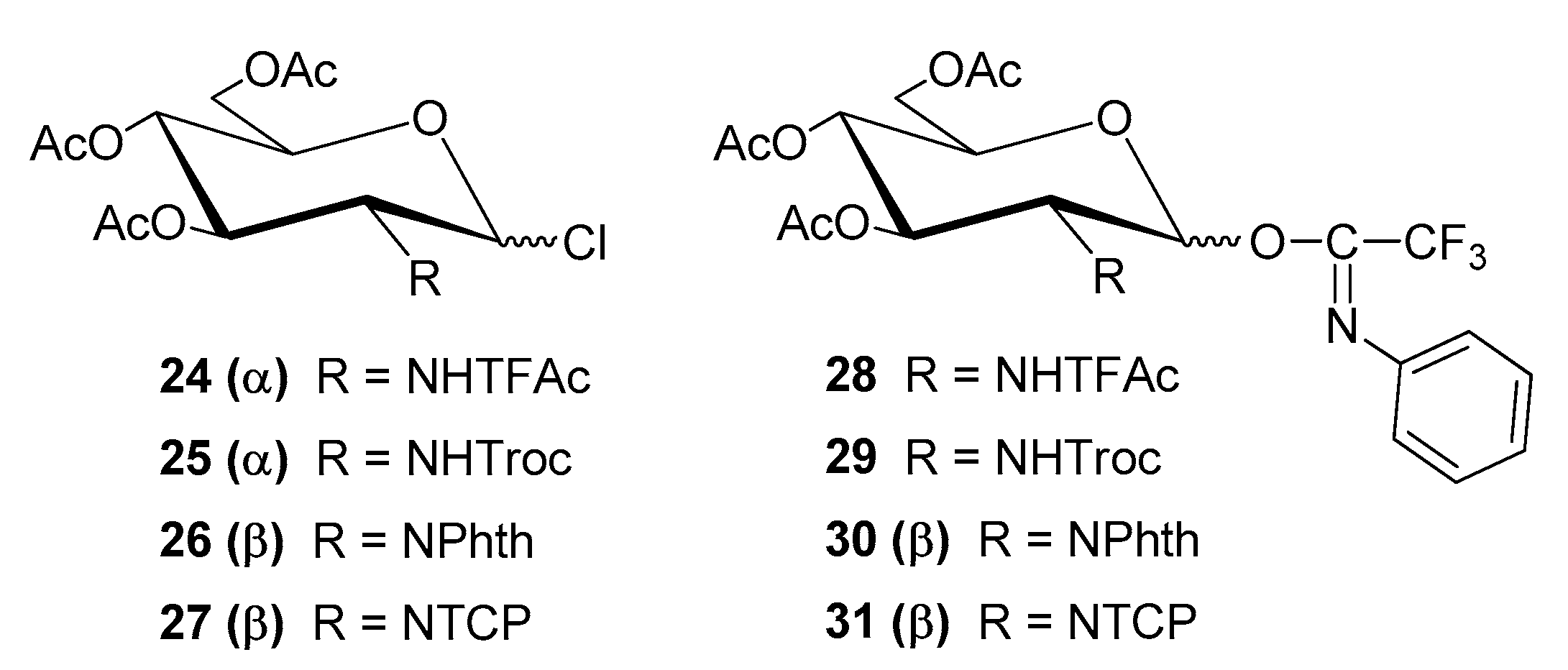
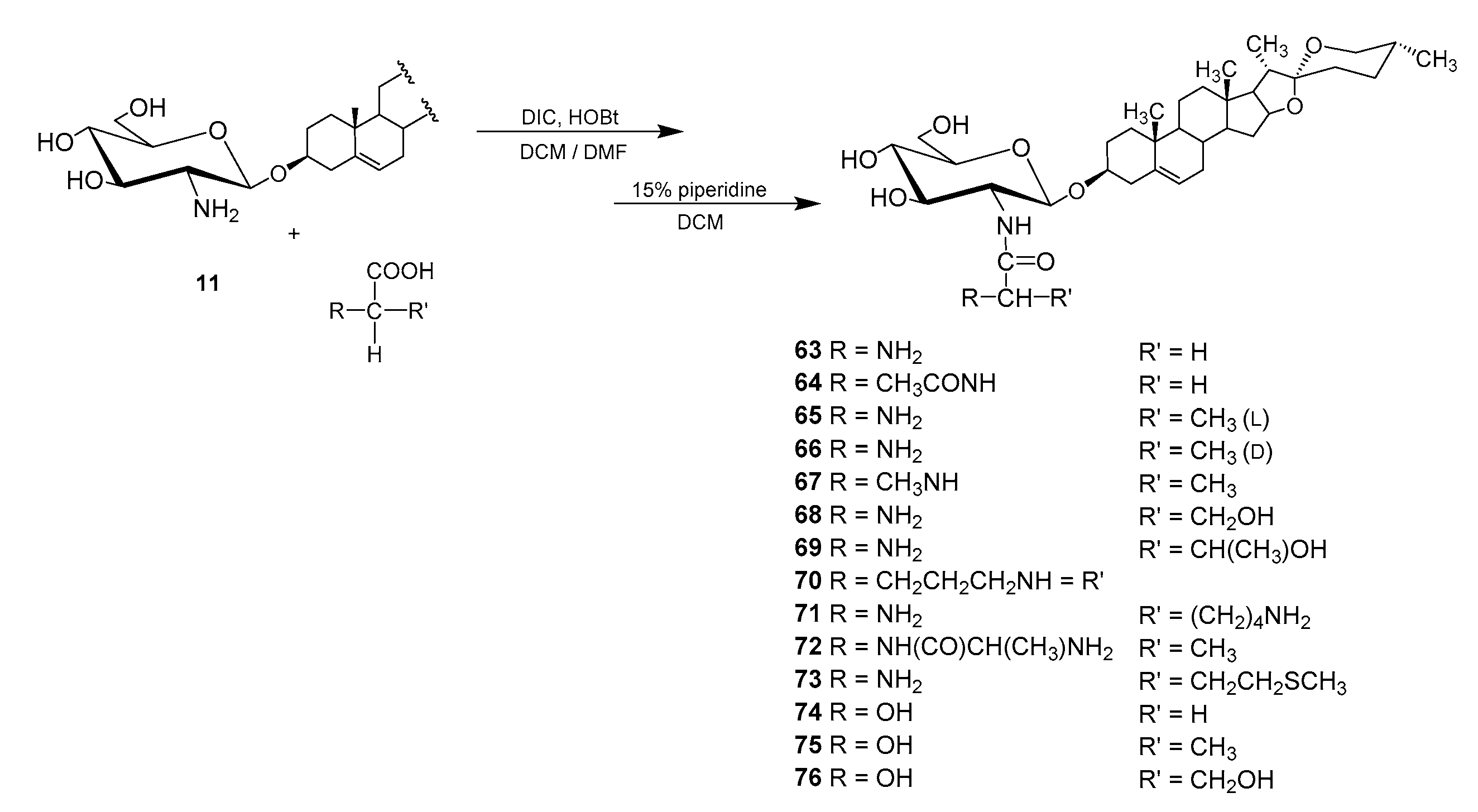
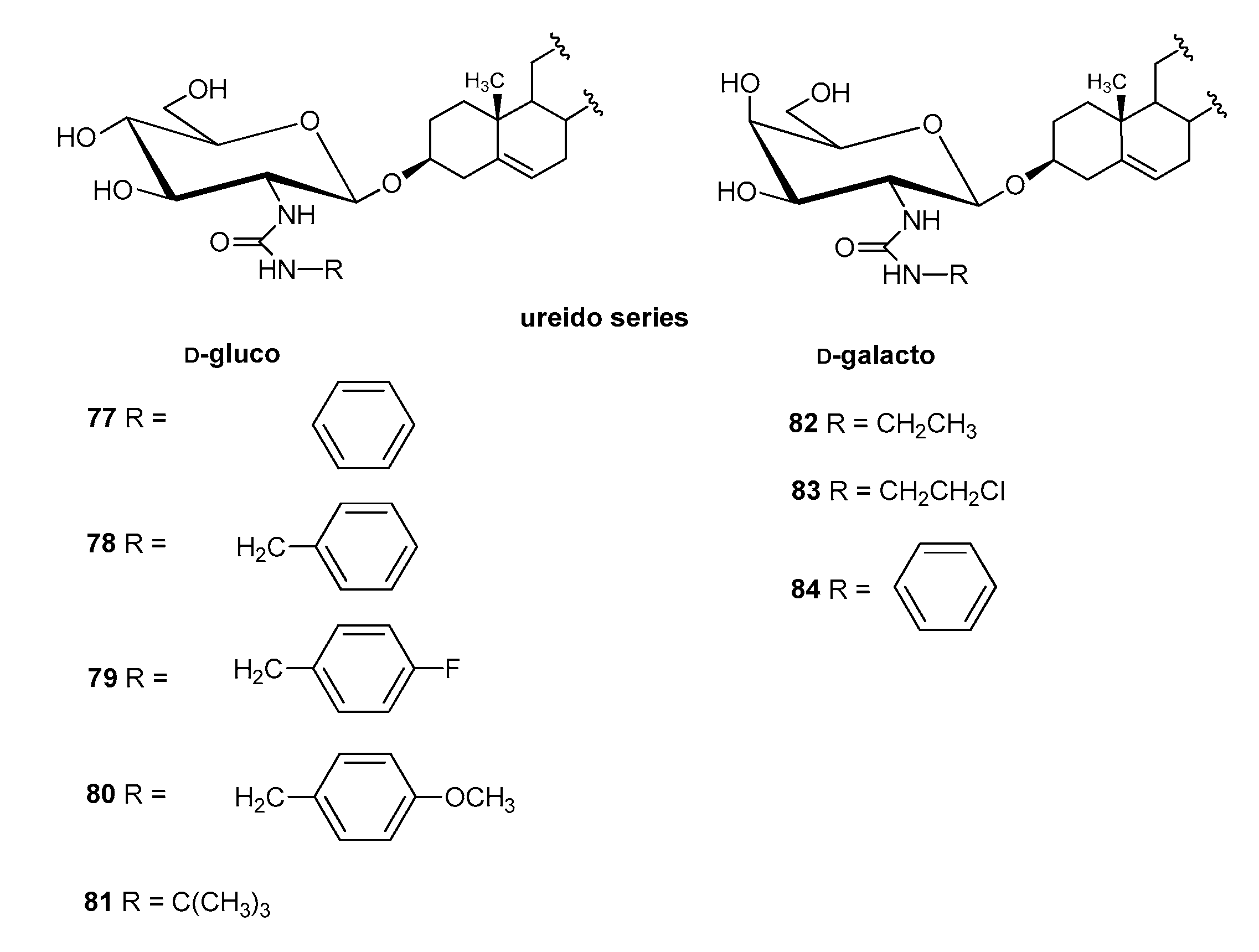
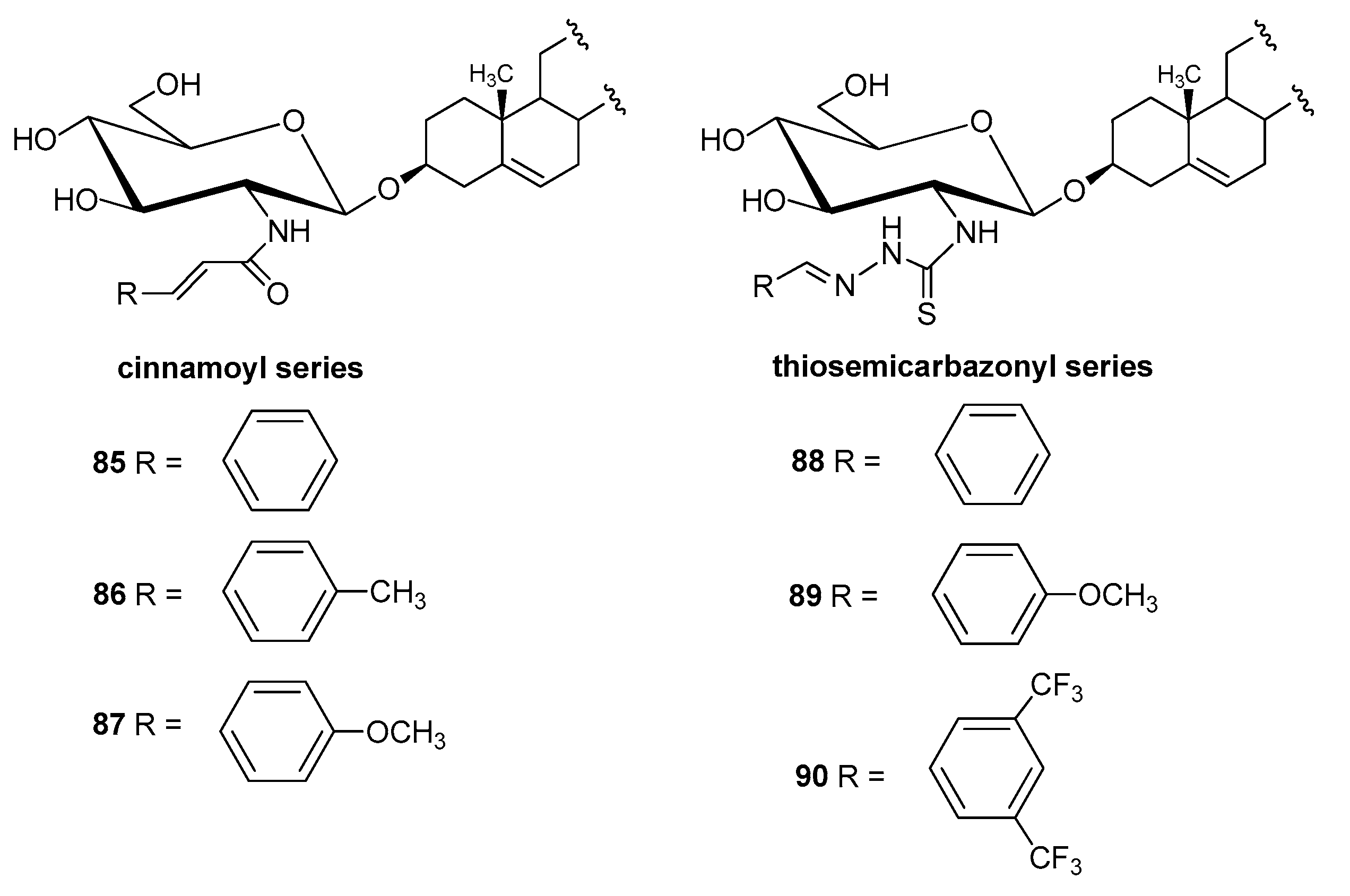
| Entry | Procedure | Glycosyl Donor | Solvent | Promotor | Product | Yield (%) | Lit. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | normal | 5 (α) | Bromide | NHTFAc | CH2Cl2 | AgOTf | 8 | 65 | [39] |
| 2 | normal | 5 (α) | Bromide | NHTFAc | CH2Cl2/Et2O | AgOTf | 8 | 69 | [41] |
| 3 | reverse | 5 (α) | Bromide | NHTFAc | CH2Cl2/Et2O | AgOTf | 8 | 77 | [50] |
| 4 | normal | 7 (α + β) | Bromide | NTCP | CH2Cl2 | AgOTf | 9 | 65 | [39] |
| 5 | normal | 7 (α + β) | Bromide | NTCP | CH2Cl2/Et2O | AgOTf | 9 | 73 | [41] |
| 6 | reverse | 7 (α + β) | Bromide | NTCP | CH2Cl2 | AgOTf | 9 | 93 | [50] |
| 7 | normal | 10 (α) | TCAI | NDMP | CH2Cl2 | TMSOTf | 15 | 92 | [45] |
| 8 | normal | 11 (α) | TCAI | NHTroc | CH2Cl2 | TMSOTf | 16 | 98; 84 | [47,56] |
| 9 | normal | 12 (α + β) | TCAI | NPhth | CH2Cl2 | TMSOTf | 17 | 96; 80 | [48,49] |
| 10 | reverse | 13 (α) | Bromide | NHTroc | CH2Cl2/Et2O | AgOTf | 16 | 98 | [50] |
| 11 | normal | 14 (α + β) | Bromide | NPhth | CH2Cl2/Et2O | AgOTf | 17 | 51 | [50] |
| 12 | reverse | 14 (α + β) | Bromide | NPhth | CH2Cl2/Et2O | AgOTf | 17 | 55 | [50] |
| 13 | reverse | 14 (α + β) | Bromide | NPhth | CH2Cl2 | AgOTf | 17 | 90 | [50] |
| 14 | reverse | 18 (α) | Chloride | NHTFAc | CH2Cl2/Et2O | AgOTf | 8 | 69 | [43] |
| 15 | reverse | 19 (α) | Choride | NHTroc | CH2Cl2/Et2O | AgOTf | 16 | 86 | [43] |
| 16 | reverse | 20 (β) | Chloride | NPhth | CH2Cl2 | AgOTf | 17 | 99 | [43] |
| 17 | reverse | 21 (β) | Chloride | NTCP | CH2Cl2 | AgOTf | 9 | 87 | [43] |
| 18 | normal | 22 (α + β) | PTFAI | NHTFAc | CH2Cl2 | TMSOTf | 8 | 85 | [50] |
| 19 | normal | 23 (α + β) | PTFAI | NHTroc | CH2Cl2 | TMSOTf | 16 | 81 | [50] |
| 20 | normal | 24 (β) | PTFAI | NPhth | CH2Cl2 | TMSOTf | 17 | 83 | [50] |
| 21 | normal | 25 (β) | PTFAI | NTCP | CH2Cl2 | TMSOTf | 9 | 52 | [50] |
| 22 | reverse | 27 (α + β) | Bromide | NTCP | CH2Cl2 | AgOTf | 28 | 80 | [54] |
| MIC50 (MIC90) * | MBC50 (MBC90) ** | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR S. aureus (n = 20) *** | MS S. aureus (n = 20) | VR E. faecalis (n = 10) | VS E. faecalis (n = 20) | S. pyogenes (n = 20) | R. equi (n = 20) | MR S. aureus (n = 20) | MS S. aureus (n = 20) | VR E. faecalis (n = 10) | VS E. faecalis (n = 20) | S. pyogenes (n = 20) | R. equi (n = 20) | |
| 11.HCl | 4 (8) | 2 (4) | 8 (32) | 8 (16) | 2 (4) | 2 (4) | 8 (16) | 8 (16) | 16 (64) | 16 (32) | 4 (8) | 4 (16) |
| Imipenem | 16 (128) | 1 (2) | 16 (64) | 4 (16) | 0,5 (1) | 0,25 (1) | 64 (256) | 4 (8) | 64 (128) | 16 (64) | 1 (4) | 8 (32) |
| Doxycycline | 4 (16) | 4 (8) | 16 (32) | 8 (16) | 4 (8) | 1 (2) | 8 (32) | 8 (32) | 16 (64) | 16 (64) | 8 (16) | 32 (128) |
| Erythromycin | 4 (16) | 2 (8) | 16 (64) | 8 (32) | 2 (8) | 0,5 (2) | 32 (128) | 16 (64) | 32 (128) | 16 (128) | 8 (32) | 32 (64) |
| Ciprofloxacin | 4 (8) | 2 (8) | 8 (32) | 4 (8) | 2 (8) | 1 (2) | 8 (16) | 4 (16) | 16 (128) | 8 (16) | 8 (16) | 16 (64) |
| Saponin Antibiotic | C. glabrata (n = 22) ** | C. krusei (n = 12) | C. parapsilosis (n = 19) | C. tropicalis (n = 13) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fungus | 50% | 90% | 50% | 90% | 50% | 90% | 50% | 90% | |
| 11.HCl | 2 | 4 | 16 | 1024 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1024 | |
| 41 | 4 | 4 | 16 | 1024 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1024 | |
| 42 | 4 | 4 | 64 | 1024 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 512 | |
| 43 | 4 | 8 | 1024 | 1024 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 1024 | |
| 44 | 8 | 16 | 1024 | 1024 | 8 | 16 | 128 | 1024 | |
| Amphotericin B | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | |
| Clotrimazole | 4 | 8 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 4 | 16 | |
| Fluconazole | 128 | 128 | 32 | 64 | 4 | 8 | 128 | 1024 | |
| Itrakonazol | 4 | 32 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 256 | 1024 | |
| Natamycin | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | |
| Nystatin | 8 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 4 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grzywacz, D.; Liberek, B.; Myszka, H. Synthesis, Modification and Biological Activity of Diosgenyl β-d-Glycosaminosides: An Overview. Molecules 2020, 25, 5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225433
Grzywacz D, Liberek B, Myszka H. Synthesis, Modification and Biological Activity of Diosgenyl β-d-Glycosaminosides: An Overview. Molecules. 2020; 25(22):5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225433
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrzywacz, Daria, Beata Liberek, and Henryk Myszka. 2020. "Synthesis, Modification and Biological Activity of Diosgenyl β-d-Glycosaminosides: An Overview" Molecules 25, no. 22: 5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225433
APA StyleGrzywacz, D., Liberek, B., & Myszka, H. (2020). Synthesis, Modification and Biological Activity of Diosgenyl β-d-Glycosaminosides: An Overview. Molecules, 25(22), 5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225433






