A G-Quadruplex-Binding Small Molecule and the HDAC Inhibitor SAHA (Vorinostat) Act Synergistically in Gemcitabine-Sensitive and Resistant Pancreatic Cancer Cells †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Inhibition of chromatin condensation by the HDAC inhibitor SAHA, thus exposing potential G4 sites within a gene, for example in regulatory or non-coding regions.
- G4-binding compounds can maintain the unwinding of duplex regions of G4-containing genes within active chromatin by stabilizing G4 structures within these genes.
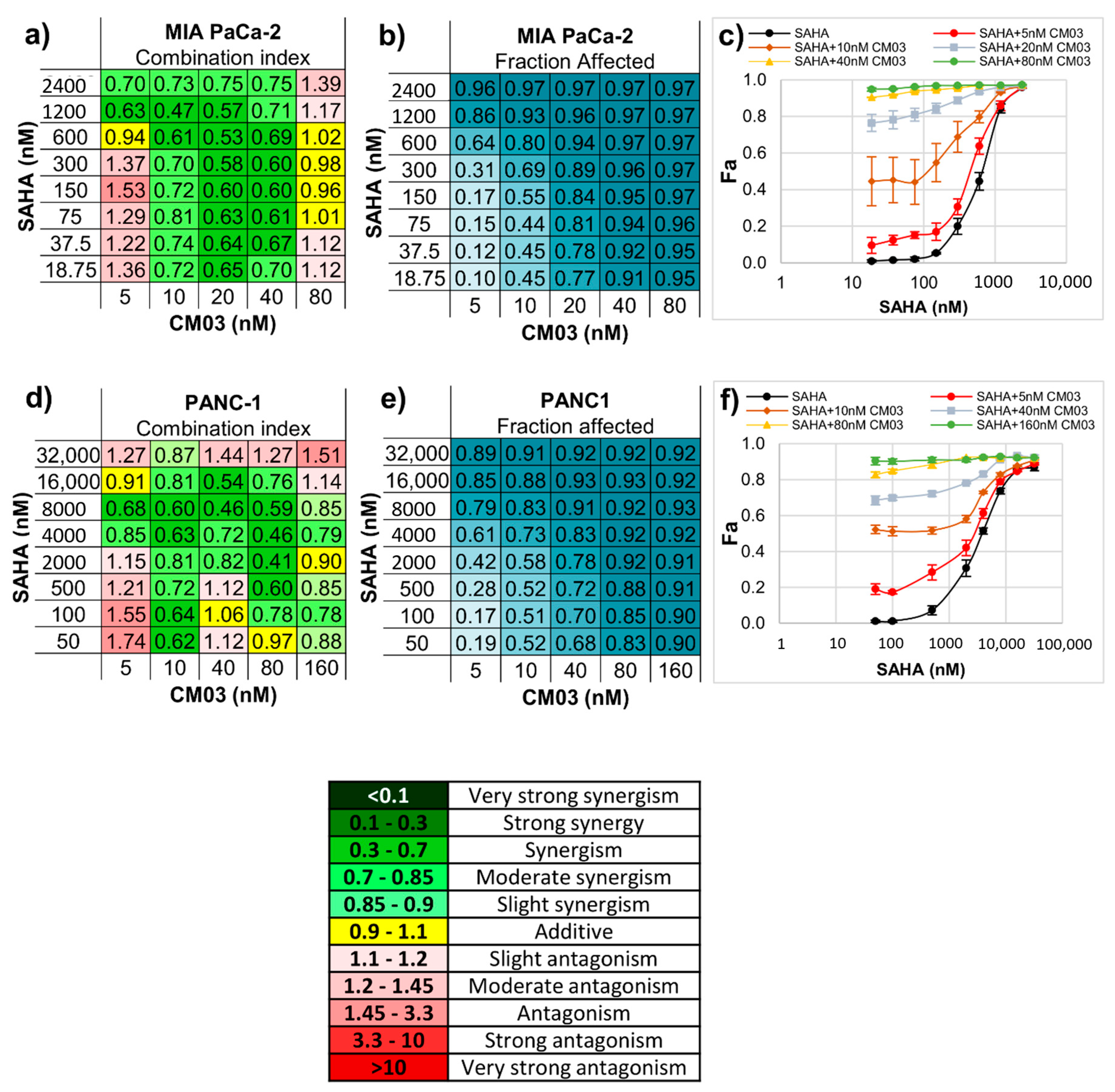
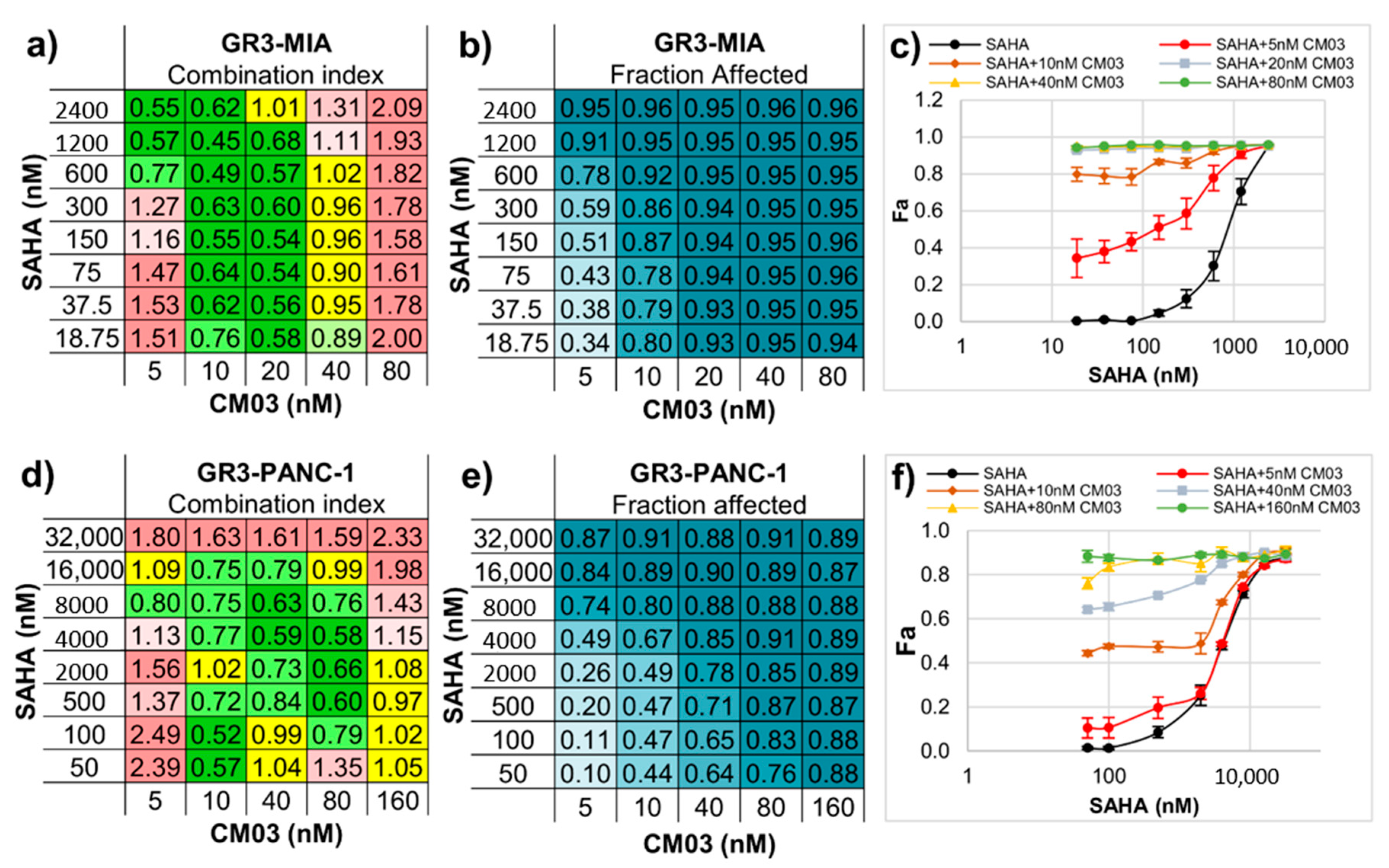
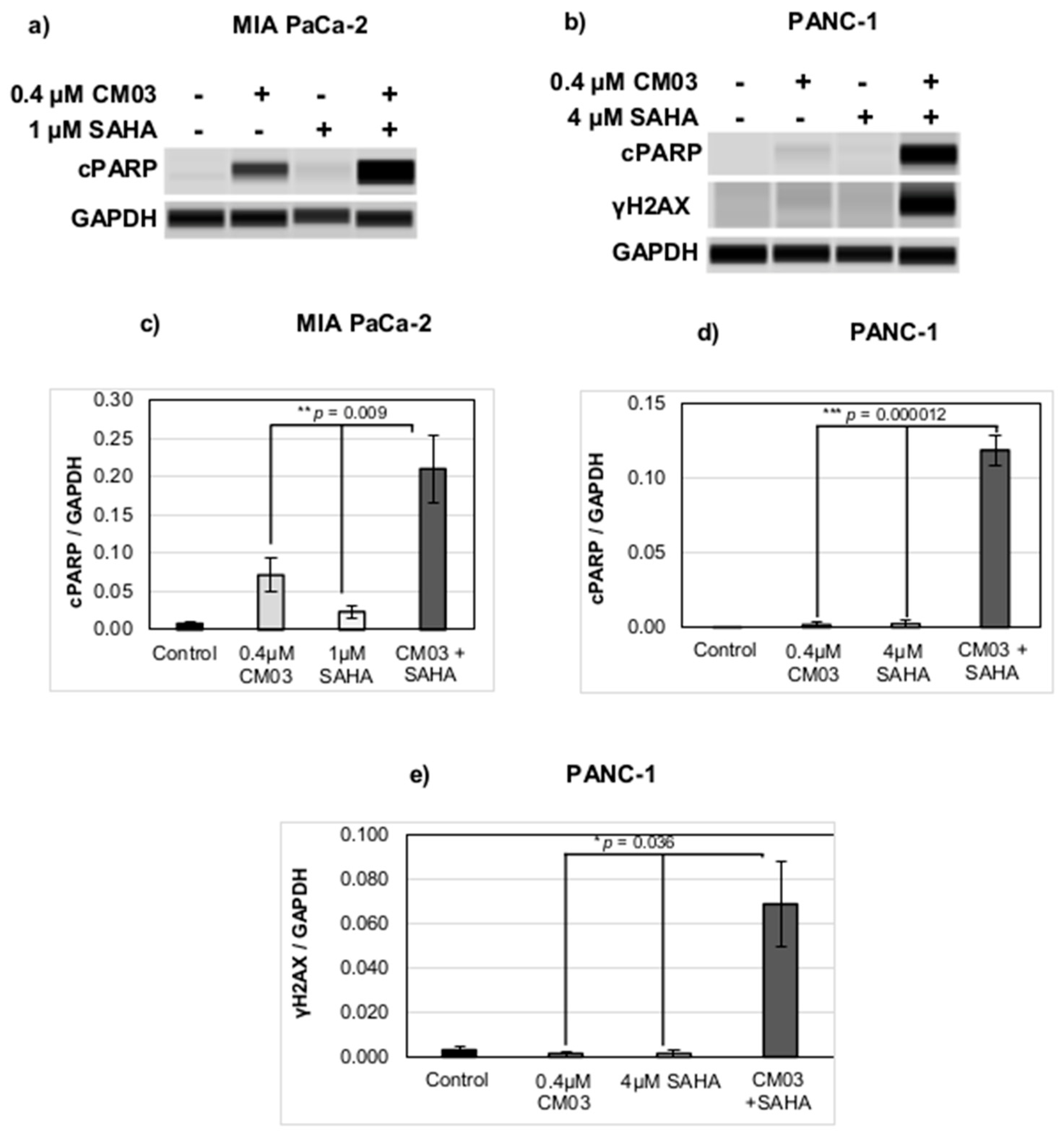
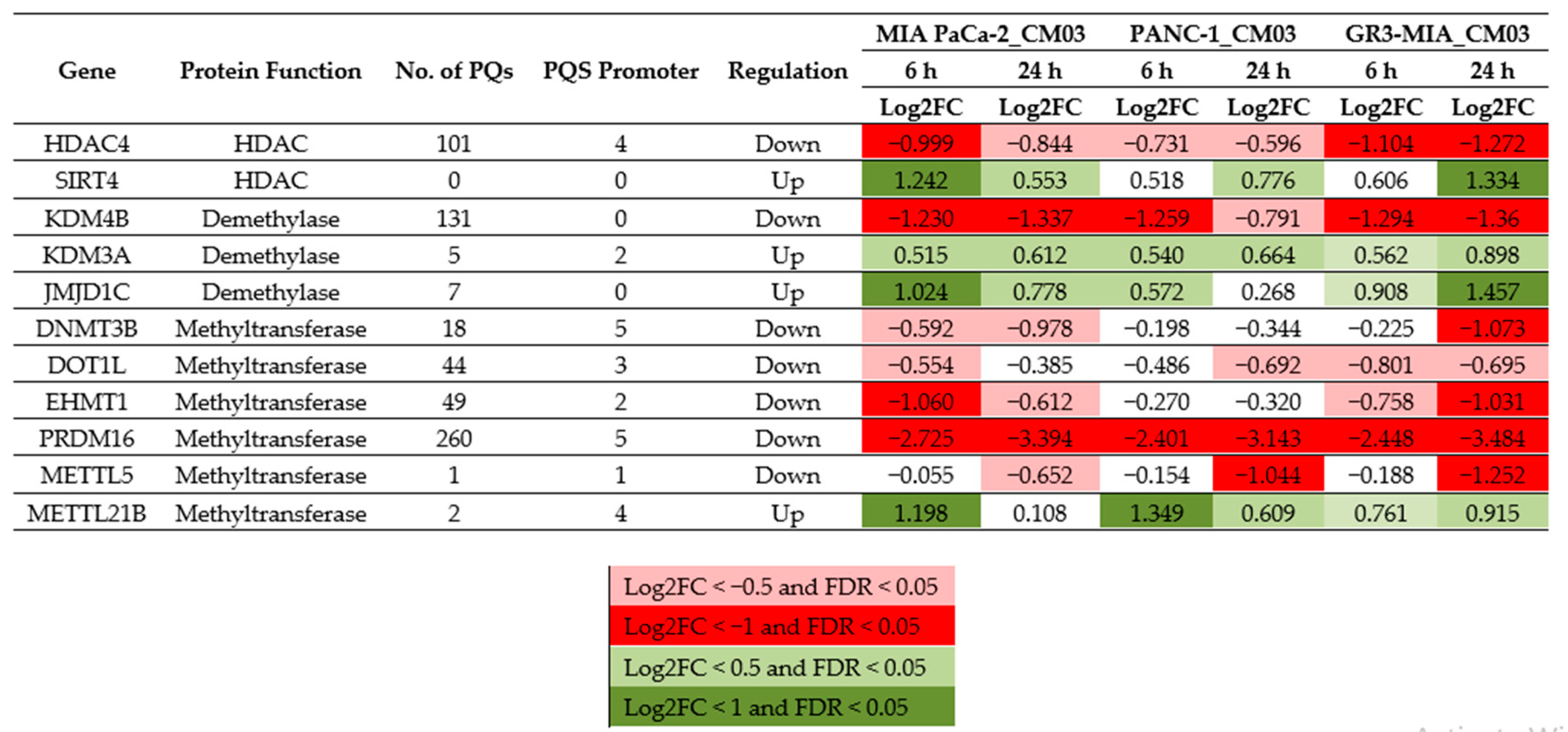
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. SRB Assays: Synergy Experiments
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambert, A.L. An update on treatment options for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919875568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samulitis, B.K.; Pond, K.W.; Pond, E.; Cress, A.E.; Patel, H.; Wisner, L.; Patel, C.; Dorr, R.T.; Landowski, T.H. Gemcitabine resistant pancreatic cancer cell lines acquire an invasive phenotype with collateral hypersensitivity to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirota, V.; Nadai, M.; Doria, F.; Richter, S.N. Naphthalene diimides as multimodal G-quadruplex-selective ligands. Molecules 2019, 24, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recagni, M.; Greco, M.L.; Milelli, A.; Minarini, A.; Zaffaroni, N.; Folini, M.; Sissi, C. Distinct biological responses of metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer cells upon exposure to G-quadruplex interacting naphthalenediimide derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 177, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collie, G.W.; Promontorio, R.; Hampel, S.M.; Micco, M.; Neidle, S.; Parkinson, G.N. Structural basis for telomeric G-quadruplex targeting by naphthalene diimide ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micco, M.; Collie, G.W.; Dale, A.G.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Pazitna, I.; Gunaratnam, M.; Reszka, A.P.; Neidle, S. Structure-based design and evaluation of naphthalene diimide G-quadruplex ligands as telomere targeting agents in pancreatic cancer cells. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2959–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnmacht, S.A.; Marchetti, C.; Gunaratnam, M.; Besser, R.J.; Haider, S.M.; Di Vita, G.; Lowe, H.L.; Mellinas-Gomez, M.; Diocou, S.; Robson, M.; et al. A G-quadruplex-binding compound showing antitumour activity in an in vivo model for pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, C.; Zyner, K.G.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Robson, M.; Haider, S.M.; Morton, J.P.; Marsico, G.; Vo, T.; Laughlin-Toth, S.; Ahmed, A.A.; et al. Targeting multiple effector pathways in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with a G-quadruplex-binding small molecule. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2500–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Angell, R.; Oxenford, S.; Worthington, J.; Williams, N.; Barton, N.; Fowler, T.G.; O’Flynn, D.E.; Sunose, M.; McConville, M.; et al. Asymmetrically substituted quadruplex-binding naphthalene diimide showing potent activity in pancreatic cancer models. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Marchetti, C.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Neidle, S. A G-quadruplex-binding compound shows potent activity in human gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehar, J.; Krueger, A.S.; Avery, W.; Heilbut, A.M.; Johansen, L.M.; Price, E.R.; Rickles, R.J.; Iii, G.F.S.; Staunton, J.E.; Jin, X.; et al. Synergistic drug combinations tend to improve therapeutically relevant selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, Z.B.; Kuru, N.; Kiriakov, S.; Palmetr, A.C.; Khalil, A.S.; Clemons, P.A.; Zaman, M.H.; Roth, F.P.; Cokol, M. Modeling the impact of drug interactions on therapeutic selectivity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burge, S.; Parkinson, G.N.; Hazel, P.; Todd, A.K.; Neidle, S. Quadruplex DNA: Sequence, topology and structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5402–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. G-quadruplexes in promoters throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugaut, A.; Balasubramanian, S. 5′-UTR RNA G-quadruplexes: Translation regulation and targeting. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4727–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Beraldi, D.; Lensing, S.V.; Marsico, G.; Zyner, K.; Parry, A.J.; Di Antonio, M.; Pike, J.; Kimura, H.; Narita, M.; et al. G-quadruplex structures mark human regulatory chromatin. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, T.M. Mechanisms of DNA replication and repair: Insights from the study of G-quadruplexes. Molecules 2019, 24, 3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, L.K.; Sale, J.E. Replication of G quadruplex DNA. Genes 2019, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, J.; Adhikari, S.; Balasubramanian, S. The structure and function of DNA G-quadruplexes. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, D.; Spiegel, J.; Zyner, K.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. The regulation and functions of DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, C.; Seimiya, H. G-quadruplex in cancer biology and drug discovery. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 531, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Antonio, M.; Ponjavic, A.; Radzevičius, A.; Ranasinghe, R.T.; Catalano, M.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Needham, L.-M.; Lee, S.F.; Klenerman, D.; et al. Single-molecule visualization of DNA G-quadruplex formation in live cells. Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Simeone, A.; Shea, A.; Hui, W.W.I.; Zyner, K.G.; Marsico, G.; Rueda, O.M.; Bruna, A.; Martin, A.; Zhang, X.; et al. Landscape of G-quadruplex DNA structural regions in breast cancer. Nat Genet. 2020, 52, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, A.; Ganguly, A.; Chowdhury, S. Promise of G-quadruplex structure binding ligands as epigenetic modifiers with anti-cancer effects. Molecules 2019, 24, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varizhuk, A.; Isaakova, E.; Pozmogova, G. DNA G-quadruplexes (G4s) modulate epigenetic (re)programming and chromatin remodeling: Transient genomic G4s assist in the establishment and maintenance of epigenetic marks, while persistent G4s may erase epigenetic marks. Bioessays 2019, 41, e1900091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, C.; Cavalieri, V. Epigenetic modulation of chromatin states and gene expression by G-quadruplex structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cree, S.L.; Fredericks, R.; Miller, A.; Pearce, F.G.; Filichev, V.; Fee, C.M.; Kennedy, A. DNA G-quadruplexes show strong interaction with DNA methyltransferases in vitro. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 2870–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbaud, G.; Murat, P.; Recolin, B.; Campbell, B.C.; Maiter, A.; Sale, J.E.; Balasubramanian, S. Local epigenetic reprogramming induced by G-quadruplex ligands. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Snyder, N.; Leary, M.; Rollinson, S.; Sarkar, S. Use of epigenetic drugs in disease: An overview. Genet. Epigenet. 2014, 6, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Seto, E. HDACs and HDAC Inhibitors in cancer development and therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellacci, L.; Perinelli, D.R.; Maggi, F.; Grifantini, M.; Petrelli, R. Recent progress in histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 2449–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, N.B.; Arkus, N.; Gunn, J.; Korc, M. The histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid induces growth inhibition and enhances gemcitabine-induced cell death in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, T.; Wakimoto, N.; Yin, D.; Gery, S.; Kawamata, N.; Takai, N.; Komatsu, N.; Chumakov, A.; Imai, Y.; Koeffler, P. Histone deacetylase inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (Vorinostat, SAHA) profoundly inhibits the growth of human pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haefner, M.; Bluethner, T.; Niederhagen, M.; Moebius, C.; Wittekind, C.; Mossner, J.; Caca, K.; Wiedmann, M. Experimental treatment of pancreatic cancer with two novel histone deacetylase inhibitors. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 3681–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, P.K.; Herner, A.; Mello, S.S.; Wirth, M.; Hausmann, S.; Sanchez-Rivera, F.J.; Lofgren, S.M.; Kuschma, T.; A Hahn, S.; Vangala, D.; et al. Combined inhibition of BET family proteins and histone deacetylases as a potential epigenetics-based therapy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Patel, V.K.; Jain, D.K.; Patel, P.H.; Rajak, H. Panobinostat as pan-deacetylase inhibitor for the treatment of pancreatic cancer: Recent progress and future prospects. Oncol. Ther. 2016, 4, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.; Chiorean, E.G.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Alcindor, T.; Potvin, D.; Chao, R.; Hurwitz, H. Phase I/II study of mocetinostat in combination with gemcitabine for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer and other advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 81, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschanzky, R.S.; Humphrey, L.E.; Ma, J.; Smith, L.M.; Enke, T.; Shukla, S.K.; Dasgupta, A.; Singh, P.K.; Howell, G.M.; Brattain, M.G.; et al. Selective inhibition of histone deacetylases 1/2/6 in combination with gemcitabine: A promising combination for pancreatic cancer therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, P.A. Discovery and development of SAHA as an anticancer agent. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, J.J.; Li, X.; Chou, C.J. Advances and challenges of HDAC inhibitors in cancer therapeutics. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 138, 183–211. [Google Scholar]
- Hassell, K.N. Histone deacetylases and their inhibitors in cancer epigenetics. Diseases 2019, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Jing, H.; Lin, H. Sirtuin inhibitors as anticancer agents. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 945–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvati, E.; Leonetti, C.; Rizzo, A.; Scarsella, M.; Mottolese, M.; Galati, R.; Sperduti, I.; Stevens, M.F.; D’Incalci, M.; Blasco, M.; et al. Telomere damage induced by the G-quadruplex ligand RHPS4 has an antitumor effect. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3236–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauchi, T.; Shin-ya, K.; Sashido, G.; Sumi, M.; Nakajima, A.; Shimamoto, T.; Ohyashiki, J.H.; Ohyashiki, K. Activity of a novel G-quadruplex-interactive telomerase inhibitor, telomestatin (SOT-095), against human leukemia cells: Involvement of ATM-dependent DNA damage response pathways. Oncogene 2003, 22, 5338–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.; Miller, K.M.; Forment, J.V.; Bradshaw, C.R.; Nikan, M.; Britton, S.; Oelschlaegel, T.; Xhemalce, B.; Balasubramanian, S.; Jackson, S.P. Small-molecule-induced DNA damage identifies alternative DNA structures in human genes. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, P.; Isenberg, D.; Muller, S. Inhibition of caspase-3-mediated poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) apoptotic cleavage by human PARP autoantibodies and effect on cells undergoing apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9043–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, I.; Margueron, R.; Shukeir, N.; Eisold, M.; Fritzsch, C.; Richter, F.M.; Mittler, G.; Genoud, C.; Goyama, S.; Kurokawa, M.; et al. Prdm3 and Prdm16 are H3K9me1 methyltransferases required for mammalian heterochromatin integrity. Cell 2012, 150, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowan, S.M.; Harrison, J.R.; Patterson, L.; Valenti, M.; Read, M.A.; Neidle, S.; Kelland, L.R. A G-quadruplex-interactive potent small-molecule inhibitor of telomerase exhibiting in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaratnam, M.; Green, C.; Moreira, J.B.; Moorhouse, A.D.; Kelland, L.R.; Moses, J.E.; Neidle, S. G-quadruplex compounds and cis-platin act synergistically to inhibit cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phatak, P.; Cookson, J.C.; Dai, F.; Smith, V.; Gartenhaus, R.B.; Stevens, M.F.; Burger, A.M. Telomere uncapping by the G-quadruplex ligand RHPS4 inhibits clonogenic tumour cell growth in vitro and in vivo consistent with a cancer stem cell targeting mechanism. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.J.; Turnidge, M.A.; Wai, D.H.; Patel, A.R.; Lee, D.W.; Gokhale, V.; Hurley, L.H.; Arceci, R.J.; Wetmore, C.; Azorsa, D.O. In vitro activity of a G-quadruplex stabilizing small molecule that synergizes with Navitoclax to induce cytotoxicity in acute myeloid leukemia cells. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, A.M.; Dai, F.; Schultes, C.M.; Reszka, A.P.; Moore, M.J.; Double, J.A.; Neidle, S. The G-quadruplex-interactive molecule BRACO-19 inhibits tumor growth, consistent with telomere targeting and interference with telomerase function. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidle, S. Challenges in developing small-molecule quadruplex therapeutics. Ann. Rep. Med Chem. 2020, 54, 517–546. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.F.; Qin, Q.P.; Qin, J.L.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.L.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.C.; Liang, H. Water-Soluble ruthenium(ii) complexes with chiral 4-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-formamide oxoaporphine (FOA): In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity by stabilization of G-quadruplex DNA, inhibition of telomerase activity, and induction of tumor cell apoptosis. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4771–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porru, M.; Zizza, P.; Franceschin, M.; Leonetti, C.; Biroccio, A. EMICORON: A multi-targeting G4 ligand with a promising preclinical profile. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1861, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Surana, R.; Valle, J.W.; Shroff, R.T. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2020, 395, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.J.; Schultes, C.M.; Cuesta, J.; Cuenca, F.; Gunaratnam, M.; Tanious, F.A.; Wilson, W.D.; Neidle, S. Trisubstituted acridines as G-quadruplex telomere targeting agents. Effects of extensions of the 3,6- and 9-side chains on quadruplex binding, telomerase activity, and cell proliferation. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 582–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
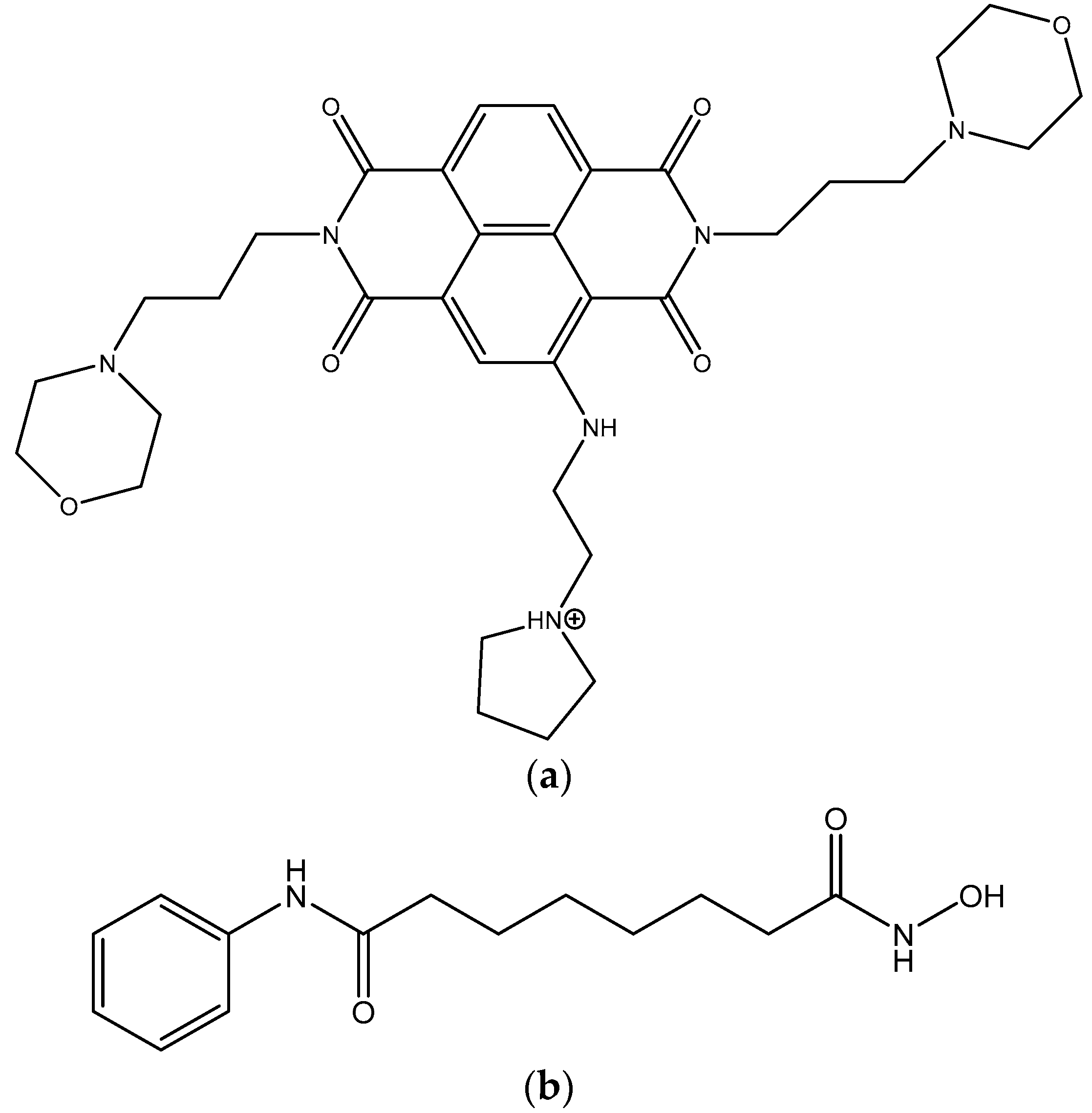

| Compound | MIA PaCa-2 Parental | MIA PaCa-2 GemResist 3 µM | PANC-1 Parental | PANC-1 GemResist 3 µM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gemcitabine | 6.5 ± 0.7 | 11,055.7 ± 540.0 | 23.3 ± 8.4 | 28,750.9 ± 6121.3 |
| CM03 | 13.0 ± 8.4 | 14.9 ± 8.3 | 10.4 ± 1.2 | 15.5 ± 1.8 |
| SAHA | 1292.7 ± 204.5 | 1055.9 ± 80.5 | 3986.5 ± 646.6 | 4499.3 ± 932.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, A.A.; Neidle, S. A G-Quadruplex-Binding Small Molecule and the HDAC Inhibitor SAHA (Vorinostat) Act Synergistically in Gemcitabine-Sensitive and Resistant Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 5407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225407
Ahmed AA, Neidle S. A G-Quadruplex-Binding Small Molecule and the HDAC Inhibitor SAHA (Vorinostat) Act Synergistically in Gemcitabine-Sensitive and Resistant Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2020; 25(22):5407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225407
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Ahmed Abdullah, and Stephen Neidle. 2020. "A G-Quadruplex-Binding Small Molecule and the HDAC Inhibitor SAHA (Vorinostat) Act Synergistically in Gemcitabine-Sensitive and Resistant Pancreatic Cancer Cells" Molecules 25, no. 22: 5407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225407
APA StyleAhmed, A. A., & Neidle, S. (2020). A G-Quadruplex-Binding Small Molecule and the HDAC Inhibitor SAHA (Vorinostat) Act Synergistically in Gemcitabine-Sensitive and Resistant Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Molecules, 25(22), 5407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225407






