Inhibitory Effect of Hesperidin on the Expression of Programmed Death Ligand (PD-L1) in Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
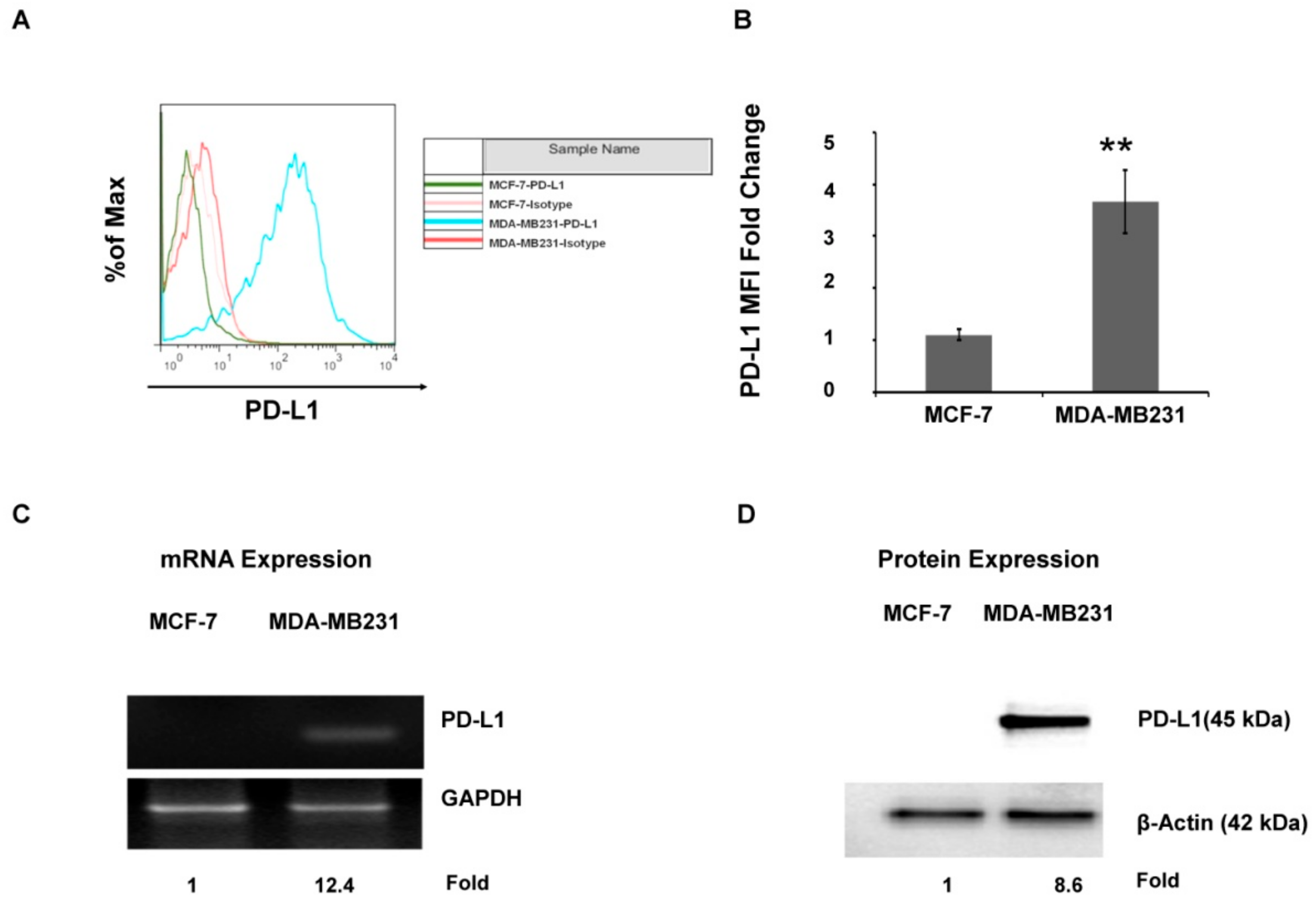
2.1. The PD-L1 Expression Level Is Associated with Aggressive Breast Cancer Cell Lines
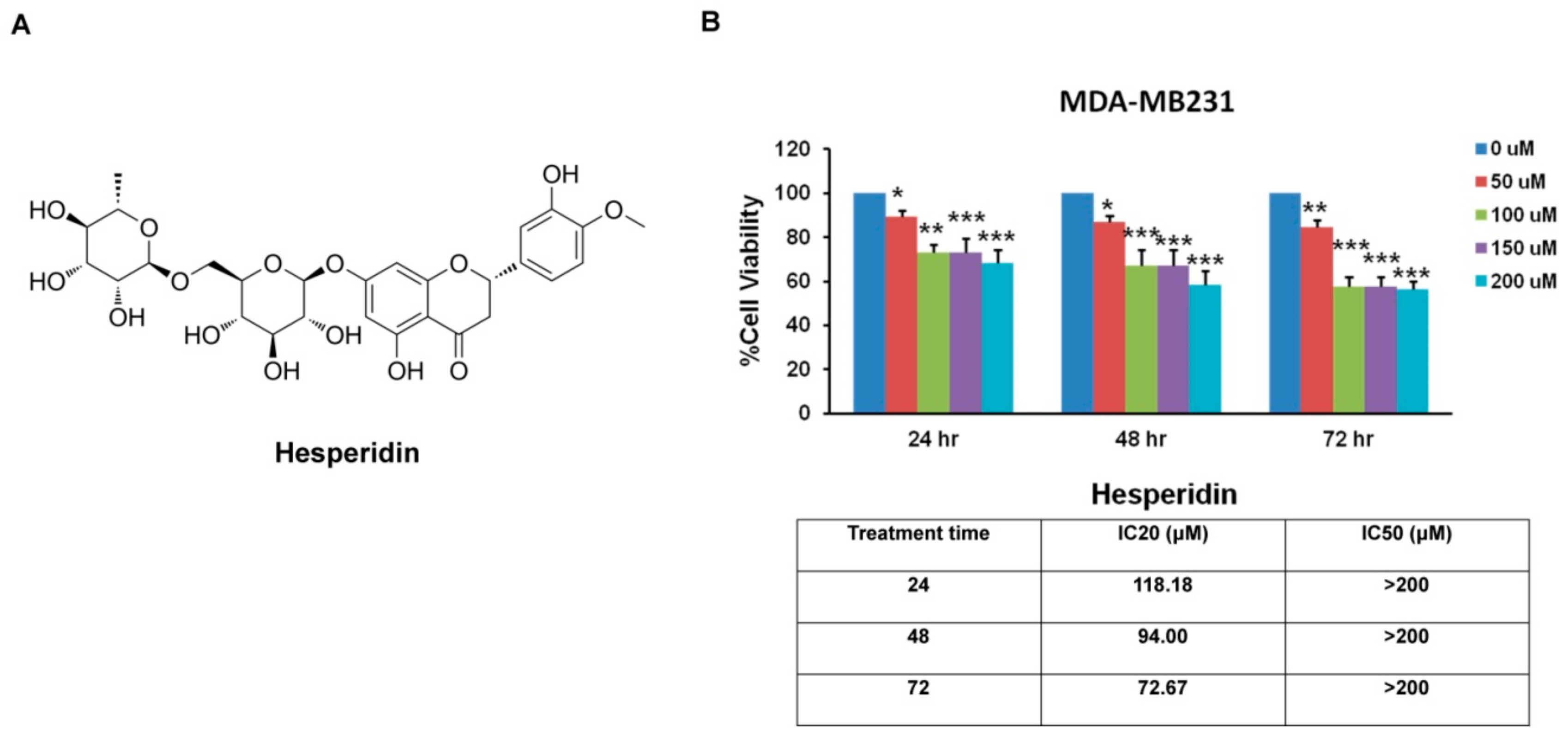
2.2. Hesperidin Inhibits MDA-MB231 Cells Viability
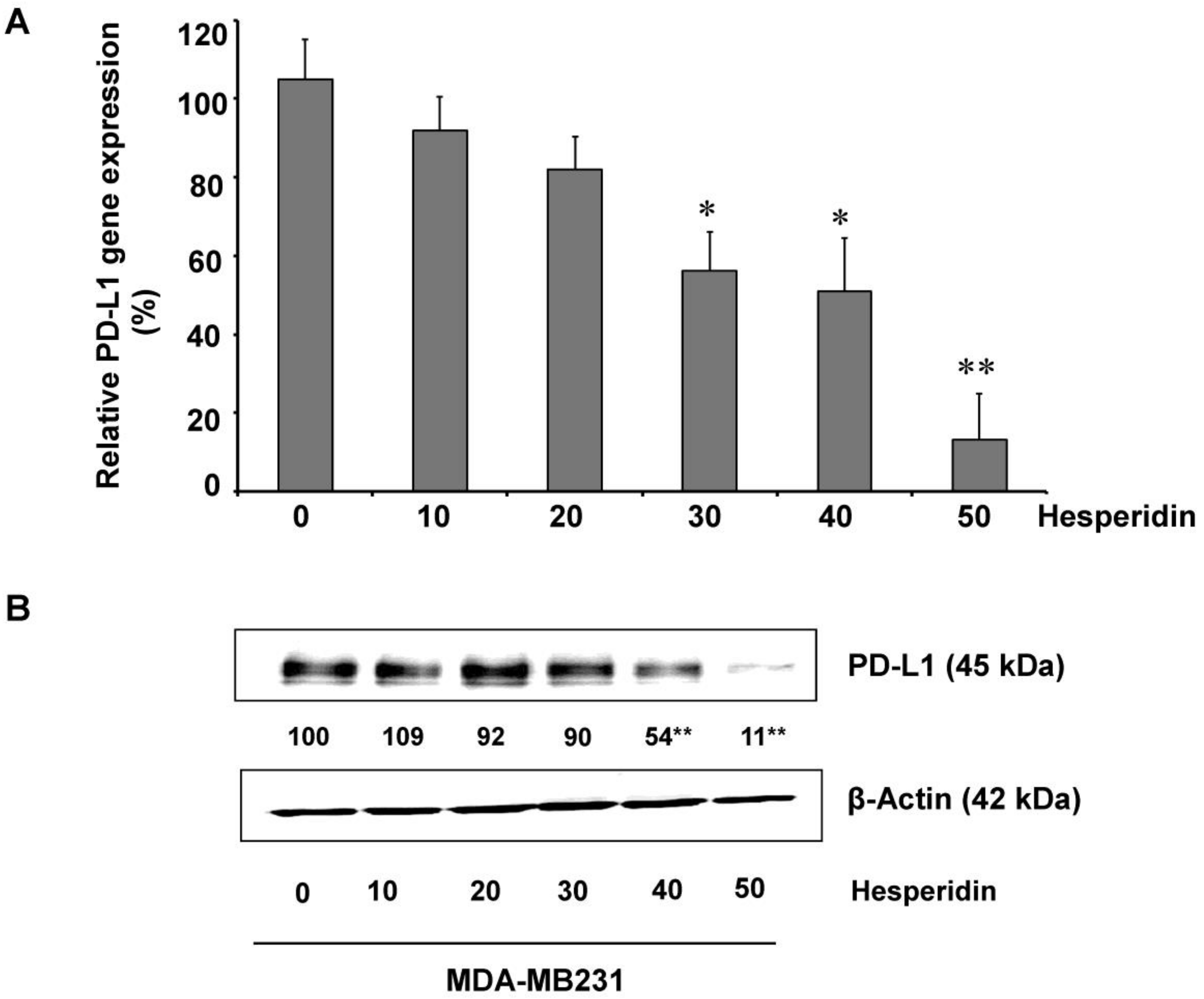
2.3. Hesperidin Decreases PD-L1 Expression in MDA-MB231 Cells
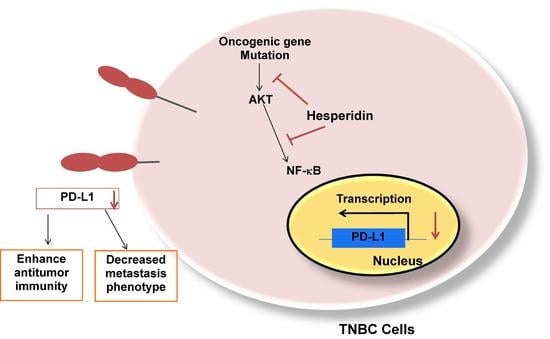
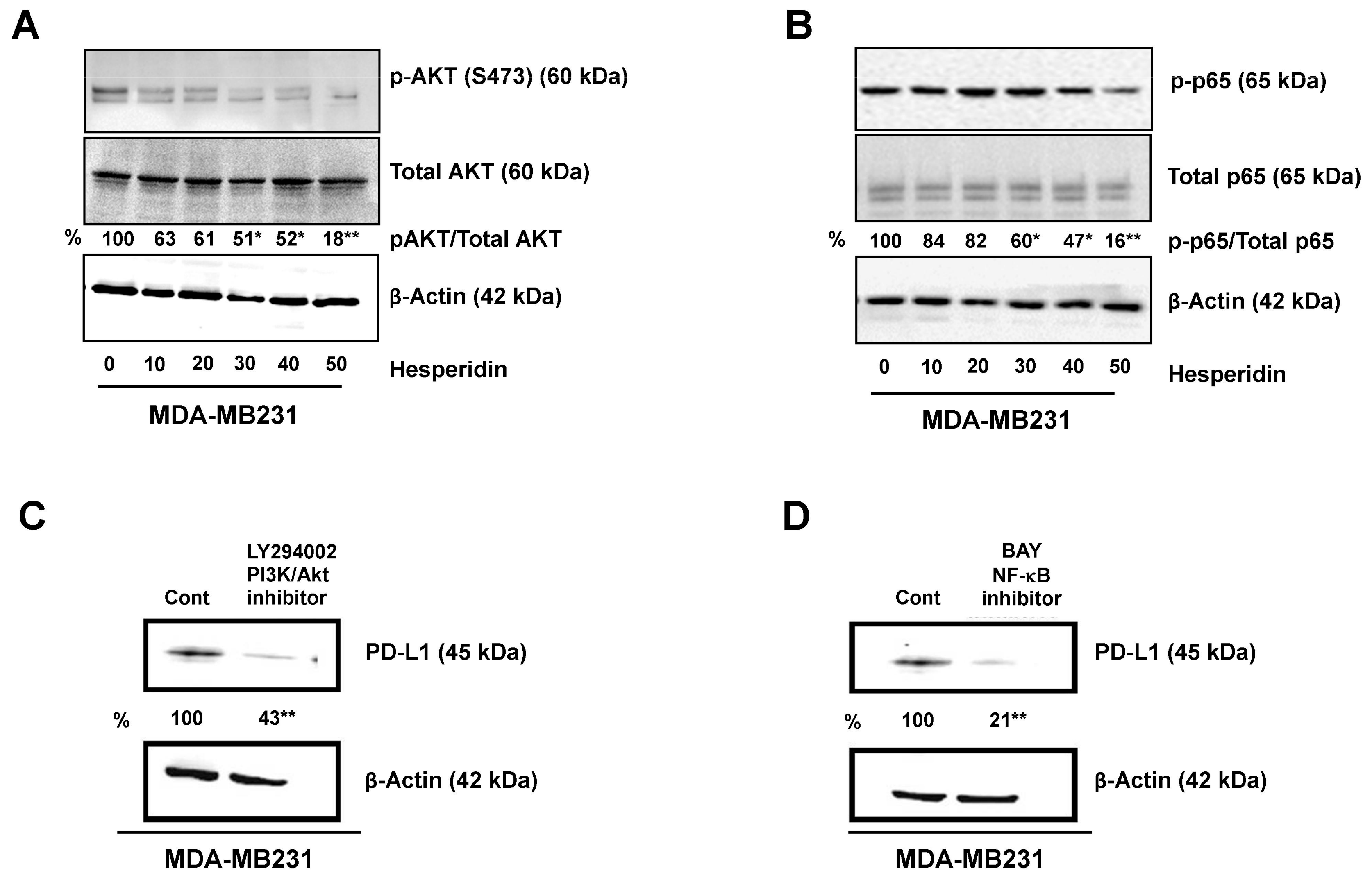
2.4. Hesperidin Decreases PD-L1 by Downregulating Akt and NF-κB in MDA-MB231 Cells
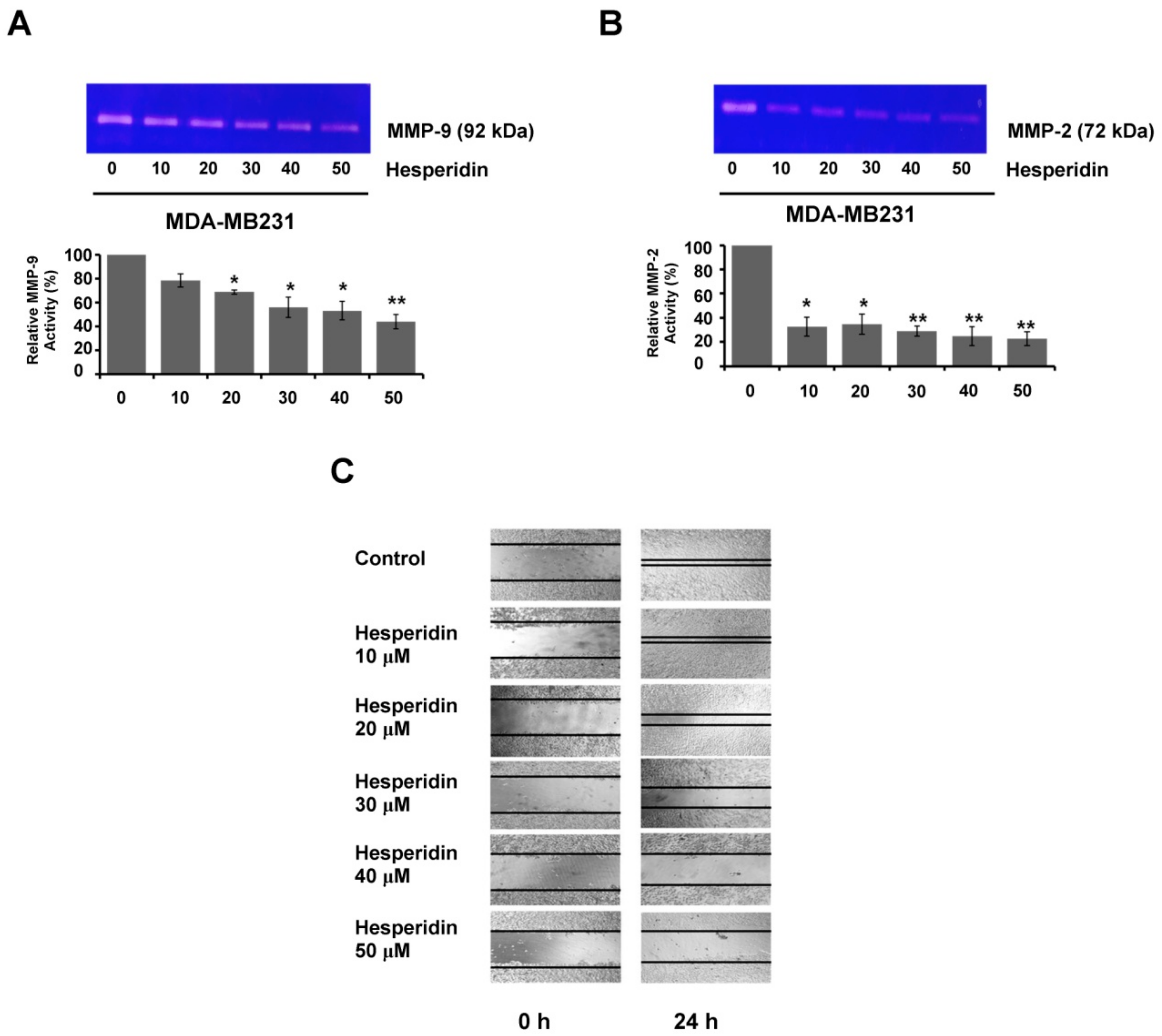
2.5. Hesperidin Suppresses Migration and MMP Secretion in High-Expressing PD-L1 MDA-MB231 Cells
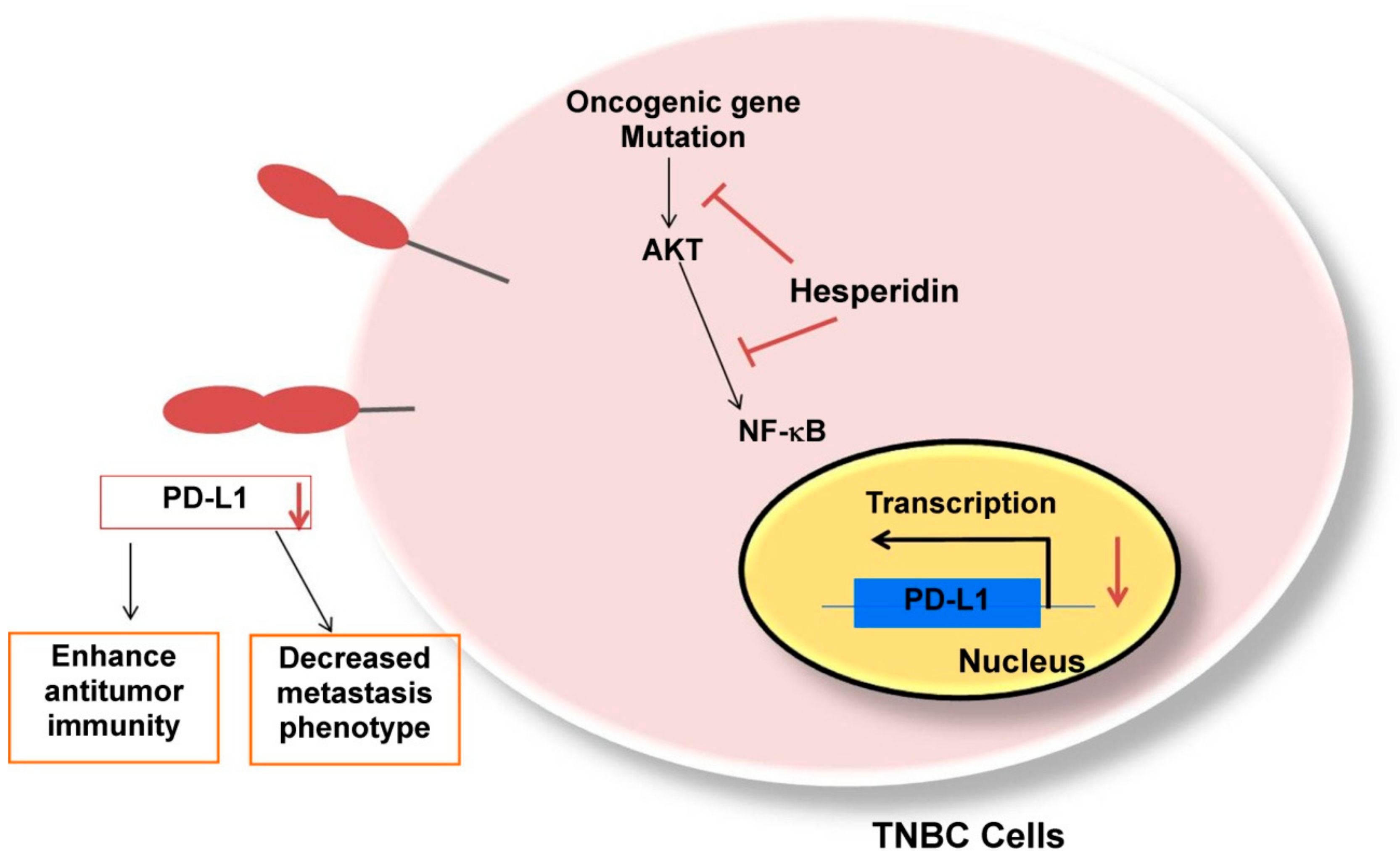
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cytotoxic Assay
4.4. Real-Time PCR (RT PCR)
- human PD-L1 forward primer 5′-GGACAAGCAGTGACCATCAAG-3′;
- human PD-L1 reverse primer 5′-CCCAGAATTTACCAAAGTGAGTCCT-3′;
- human GAPDH forward primer 5′-TGGTATCGTGGAAGGACTCATGAC-3′;
- human GAPDH reverse primer 5′-ATGCCACTCAGCTTCCCGTTCAGC-3.′
4.5. Western Blotting Assay
4.6. Flow Cytometry
4.7. Gelatin Zymography
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holliday, D.L.; Speirs, V. Choosing the right cell line for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haidari, F.; Heybar, H.; Jalali, M.T.; Ahmadi Engali, K.; Helli, B.; Shirbeigi, E. Hesperidin supplementation modulates inflammatory responses following myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2015, 34, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, O.; Robert, C.; Daud, A.; Hodi, F.S.; Hwu, W.J.; Kefford, R.; Wolchok, J.D.; Hersey, P.; Joseph, R.W.; Weber, J.S.; et al. Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in melanoma. New Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, H.; Strome, S.E.; Salomao, D.R.; Tamura, H.; Hirano, F.; Flies, D.B.; Roche, P.C.; Lu, J.; Zhu, G.; Tamada, K.; et al. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Wolchok, J.D.; Chen, L. PD-L1 (B7-H1) and PD-1 pathway blockade for cancer therapy: Mechanisms, response biomarkers, and combinations. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 328rv4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banjerdpongchai, R.; Wudtiwai, B.; Khaw-On, P.; Rachakhom, W.; Duangnil, N.; Kongtawelert, P. Hesperidin from Citrus seed induces human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell apoptosis via both mitochondrial and death receptor pathways. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.J.; Wilson, L.; Jordan, M.A.; Nguyen, V.; Tang, J.; Smiyun, G. Hesperidin suppressed proliferations of both human breast cancer and androgen-dependent prostate cancer cells. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, S15–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febriansah, R.; Putri, D.D.; Sarmoko; Nurulita, N.A.; Meiyanto, E.; Nugroho, A.E. Hesperidin as a preventive resistance agent in MCF-7 breast cancer cells line resistance to doxorubicin. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, R.; Sheng, X.; Xu, X.; Yu, C.; Lu, H. Hesperidin induces apoptosis and G0/G1 arrest in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Im, A.R.; Kim, S.M.; Kang, H.S.; Lee, J.D.; Chae, S. The flavonoid hesperidin exerts anti-photoaging effect by downregulating matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 expression via mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK)-dependent signaling pathways. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittendorf, E.A.; Philips, A.V.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Qiao, N.; Wu, Y.; Harrington, S.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Akcakanat, A.; et al. PD-L1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Ge, X.; Lou, G. Hesperidin inhibits HeLa cell proliferation through apoptosis mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways and cell cycle arrest. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Hu, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, B. Development of PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway in Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Treatment for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alsuliman, A.; Colak, D.; Al-Harazi, O.; Fitwi, H.; Tulbah, A.; Al-Tweigeri, T.; Al-Alwan, M.; Ghebeh, H. Bidirectional crosstalk between PD-L1 expression and epithelial to mesenchymal transition: Significance in claudin-low breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larue, L.; Bellacosa, A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: Role of phosphatidylinositol 3′ kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7443–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakin, A.V.; Tomlinson, A.K.; Bhowmick, N.A.; Moses, H.L.; Arteaga, C.L. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is required for transforming growth factor beta-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36803–36810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Z.; Huo, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, P. HIF-1 alpha had pivotal effects on downregulation of miR-210 decreasing viability and inducing apoptosis in hypoxic chondrocytes. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 876363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, R.V.; Chemnitz, J.M.; Frauwirth, K.A.; Lanfranco, A.R.; Braunstein, I.; Kobayashi, S.V.; Linsley, P.S.; Thompson, C.B.; Riley, J.L. CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T-cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 9543–9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Black, M.; Barsoum, I.B.; Truesdell, P.; Cotechini, T.; Macdonald-Goodfellow, S.K.; Petroff, M.; Siemens, D.R.; Koti, M.; Craig, A.W.; Graham, C.H. Activation of the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint confers tumor cell chemoresistance associated with increased metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10557–10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, J.; Zhuang, M.; Yu, X.; Li, N.; Mao, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; et al. MYC inhibition increases PD-L1 expression induced by IFN-gamma in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 101, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Uddin, M.M.; Padmanabhan, S.; Zhu, Y.; Bu, P.; Vancura, A.; Vancurova, I. The proto-oncogene Bcl3 induces immune checkpoint PD-L1 expression, mediating proliferation of ovarian cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 15483–15496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muenst, S.; Schaerli, A.R.; Gao, F.; Daster, S.; Trella, E.; Droeser, R.A.; Muraro, M.G.; Zajac, P.; Zanetti, R.; Gillanders, W.E.; et al. Expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is associated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 146, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colotta, F.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A. Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: Links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinstock, M.; McDermott, D. Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2015, 7, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, P.; Sayyed, U.; Tiwari, R.K.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Pathak, N.; Bajpai, P. Hesperidin Induces ROS-Mediated Apoptosis along with Cell Cycle Arrest at G2/M Phase in Human Gall Bladder Carcinoma. Nutr. Cancer 2018, 71, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Xu, G.; Huang, Y.; Sheng, X.; Xu, X.; Lu, H. Hesperidin suppresses the migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting the SDF-1/CXCR-4 pathway. Life Sci. 2018, 201, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, C.A.; Panner, A.; Murray, J.C.; Wilson, S.P.; Xu, H.; Chen, L.; Simko, J.P.; Waldman, F.M.; Pieper, R.O.; Parsa, A.T. PI(3) kinase is associated with a mechanism of immunoresistance in breast and prostate cancer. Oncogene 2009, 28, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bo, C.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q. Thymosin alpha1 suppresses migration and invasion of PD-L1 high-expressing non-small-cell lung cancer cells via inhibition of STAT3-MMP2 signaling. Oncotargets Ther. 2018, 11, 7255–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.M.; Li, X.M.; Li, G.M.; Du, W.C.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Xu, J.; Hu, M.; Zhu, Z. In vivo pharmacokinetics of hesperidin are affected by treatment with glucosidase-like BglA protein isolated from yeasts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5550–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kongtawelert, P.; Wudtiwai, B.; Shwe, T.H.; Pothacharoen, P.; Phitak, T. Inhibitory Effect of Hesperidin on the Expression of Programmed Death Ligand (PD-L1) in Breast Cancer. Molecules 2020, 25, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020252
Kongtawelert P, Wudtiwai B, Shwe TH, Pothacharoen P, Phitak T. Inhibitory Effect of Hesperidin on the Expression of Programmed Death Ligand (PD-L1) in Breast Cancer. Molecules. 2020; 25(2):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020252
Chicago/Turabian StyleKongtawelert, Prachya, Benjawan Wudtiwai, Thuzar Hla Shwe, Peraphan Pothacharoen, and Thanyaluck Phitak. 2020. "Inhibitory Effect of Hesperidin on the Expression of Programmed Death Ligand (PD-L1) in Breast Cancer" Molecules 25, no. 2: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020252
APA StyleKongtawelert, P., Wudtiwai, B., Shwe, T. H., Pothacharoen, P., & Phitak, T. (2020). Inhibitory Effect of Hesperidin on the Expression of Programmed Death Ligand (PD-L1) in Breast Cancer. Molecules, 25(2), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020252