Simultaneous Quantitation of S(+)- and R(−)-Baclofen and Its Metabolite in Human Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid using LC–APCI–MS/MS: An Application for Clinical Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Optimization
2.2. Assay Validation
2.2.1. Sensitivity
2.2.2. Specificity and Selectivity
2.2.3. Calibration Curve and Linearity
2.2.4. Carry-Over
2.2.5. Accuracy and Precision
2.2.6. Recovery and Matrix Effect
2.2.7. Stability
2.2.8. Application of the Method for Clinical Sample Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Liquid Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric (LC/MS) Conditions
3.3. Preparation of Stock, Calibration Standards, and Quality Control Samples
3.4. Plasma and CSF Sample Preparation
3.5. Assay Validation
3.6. Recovery and Matrix Effect
3.7. Stability
3.8. Clinical Study and Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanchez-Ponce, R.; Wang, L.Q.; Lu, W.; von Hehn, J.; Cherubini, M.; Rush, R. Metabolic and Pharmacokinetic Differentiation of STX209 and Racemic Baclofen in Humans. Metabolites 2012, 2, 596–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.R.; Hirtz, D.; Aisen, M.; Ashwal, S.; Fehlings, D.; McLaughlin, J.; Morrison, L.; Shrader, M.; Tilton, A.; Vargus-Adams, J.J.N.; et al. Practice parameter: Pharmacologic treatment of spasticity in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy (an evidence-based review): Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology 2010, 74, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Navarrete-Opazo, A.A.; Gonzalez, W.; Nahuelhual, P.J.A. Effectiveness of oral baclofen in the treatment of spasticity in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 604–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogden, R.; Speight, T.; Avery, G.J.D. Baclofen: A preliminary report of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in spasticity. Drugs 1974, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesser, B.J.D. Multiple Sclerosis. Drugs 1985, 29, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Brunstrom-Hernandez, J.E.; Thio, L.L.; Lackey, S.; Gaebler-Spira, D.; Kuroda, M.M.; Stashinko, E.; Hoon, A.H., Jr.; Vargus-Adams, J.; Stevenson, R.D.; et al. Population pharmacokinetics of oral baclofen in pediatric patients with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. 2014, 164, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.J.; He, Y.; Brunstrom-Hernandez, J.; Thio, L.L.; Carleton, B.C.; Ross, C.J.D.; Gaedigk, A.; Lewandowski, A.; Dai, H.; Jusko, W.J.; et al. Pharmacogenomic Variability of Oral Baclofen Clearance and Clinical Response in Children With Cerebral Palsy. PM & R 2018, 10, 235–243. [Google Scholar]
- Faigle, J.; Keberle, H.J.P. The chemistry and kinetics of Lioresal. Postgrad. Med. J. 1972, 48, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kochak, G.M.; Rakhit, A.; Wagner, W.E.; Honc, F.; Waldes, L.; Kershaw, R.A. The pharmacokinetics of baclofen derived from intestinal infusion. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1985, 38, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri, L.E. (Ecole Nationale de Médecine Vétérinaire); Ghorbel, A. (Tunis El Manar University); Thameur, B.H. (Higher School of Communication of Tunis). Unpublished work. 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbut, K. General Muscle Relaxants in Medical Toxicology; Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 594–596. [Google Scholar]
- Vlavonou, R.; Perreault, M.M.; Barrière, O.; Shink, E.; Tremblay, P.O.; Larouche, R.; Pichette, V.; Tanguay, M.J.T.J. Pharmacokinetic characterization of baclofen in patients with chronic kidney disease: Dose adjustment recommendations. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 54, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, K.; Holmes, K.; Matthewson, K.J.P. Complications of baclofen overdosage. Postgrad. Med. J. 1980, 56, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froestl, W.; Mickel, S.J.; Hall, R.G.; von Sprecher, G.; Strub, D.; Baumann, P.A.; Brugger, F.; Gentsch, C.; Jaekel, J.; Olpe, H.R.; et al. Phosphinic acid analogues of GABA. 1. New potent and selective GABAB agonists. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 3297–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farì, G.; Oliva, M.; De Venuto, G.; Napolitano, M.; Schivardi, E.; Lanzilotta, P.; Lagioia, G.; Fiore, P.; Megna, M.J.S. Practical management of intrathecal baclofen therapy: Presence of symptoms of underdosing in absence of comorbidities and technical or pharmacological complications. In Proceedings of the 46th Congress National Seminar, Ancona, Italy, 20–23 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dario, A.; Di Stefano, M.G.; Grossi, A.; Casagrande, F.; Bono, G. Long-term intrathecal Baclofen infusion in supraspinal spasticity of adulthood. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2002, 105, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goda, R.; Murayama, N.; Fujimaki, Y.; Sudo, K. Simple and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for determination of the S(+)- and R(−)-enantiomers of baclofen in human plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2004, 801, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bree, J.B.; Audus, K.L.; Borchardt, R.T. Carrier-mediated transport of baclofen across monolayers of bovine brain endothelial cells in primary culture. Pharm. Res. 1988, 5, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sioufi, A.; Kaiser, G.; Leroux, F.; Dubois, J.P. Determination of the S(+)- and R(−)-enantiomers of baclofen in plasma and urine by gas chromatography using a chiral fused-silica capillary column and an electron-capture detector. J. Chromatogr. 1988, 450, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochak, G.; Honc, F. Improved gas-liquid chromatographic method for the determination of baclofen in plasma and urine. J. Chromatogr. 1984, 310, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, L.K.; Cordero, R.E.; Nutt, D.; Lingford-Hughes, A.; Turton, S.; Durant, C.; Wilson, S.; Paterson, S. Validated Method for the Quantification of Baclofen in Human Plasma Using Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 40, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, E.; Park, J.S.; Kim, C.K.J.J. Semi-microbore HPLC for the determination of baclofen in human plasma using column switching. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2004, 27, 3051–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.Y.; Zheng, N.-Y.; Chen, C.-S. Development and validation of a capillary electrophoresis method for the determination of baclofen in human plasma. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2004, 2, 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Schmidt, M.; Murry, D.J.; Donovan, M.D. Permeation and systemic absorption of R- and S-baclofen across the nasal mucosa. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 2717–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Larabi, I.A.; Fabresse, N.; Knapp, A.; Forcet, M.; Baud, F.J.; Lorin de la Grandmaison, G.; Alvarez, J.C. LC–MS/MS method for quantification of baclofen in hair: A useful tool to assess compliance in alcohol dependent patients? Drug Test. Anal. 2018, 10, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, F.T.; Wissenbach, D.K.; Busardo, F.P.; Marchei, E.; Pichini, S. Method Development in Forensic Toxicology. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 5455–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.R.; Delwaide, P.J. Drug therapy: Spasticity (second of two parts). N. Engl. J. Med. 1981, 304, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knutsson, E.; Lindblom, U.; Mårtensson, A.J.J. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid levels of baclofen (Lioresal®) at optimal therapeutic responses in spastic paresis. J. Neurol. Sci. 1974, 23, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Service; Food and Drug Administration; CDER; CVM. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation; FDA: Rockwell, MD, USA, 2018.
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

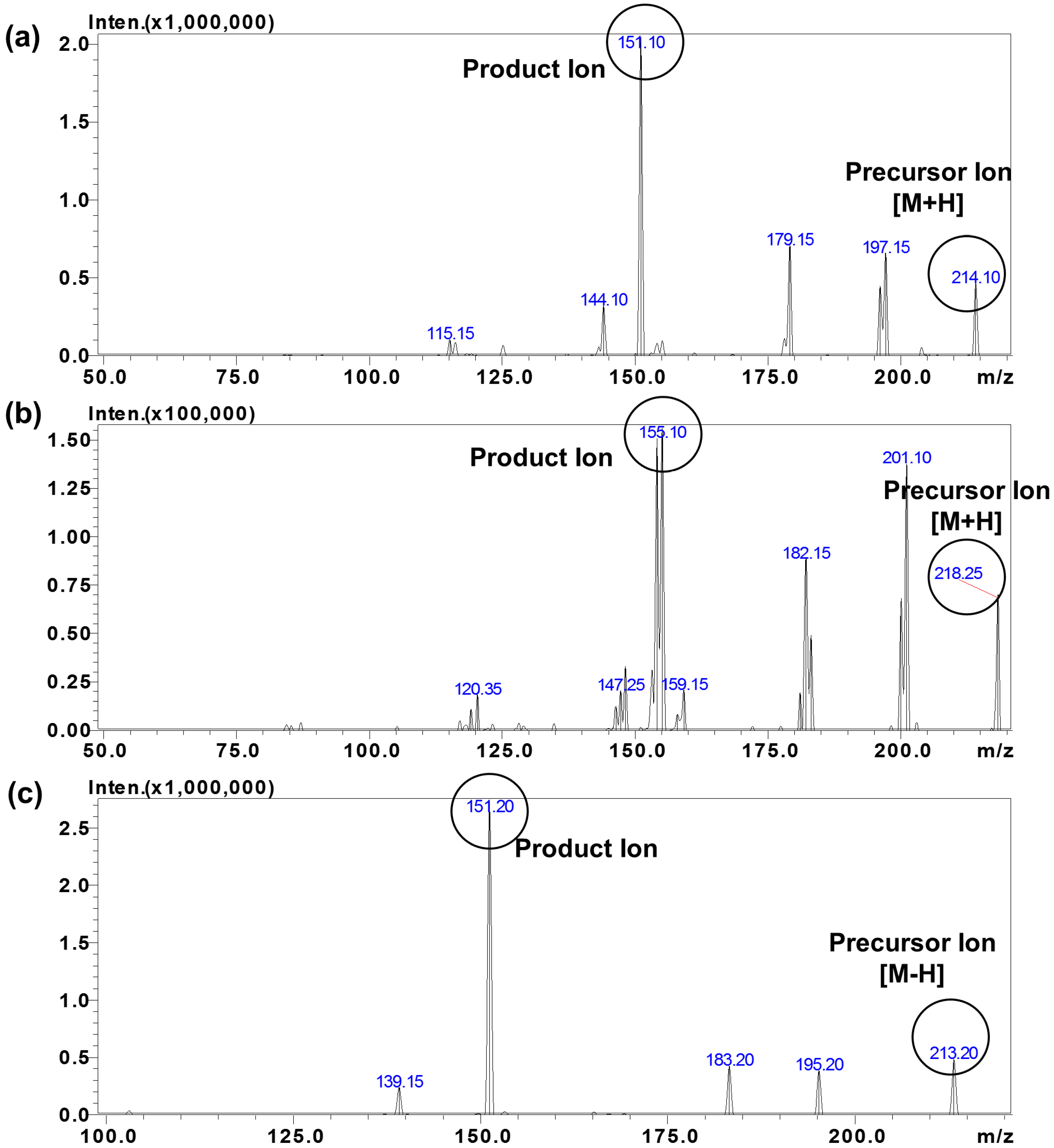

| S-Baclofen | R-Baclofen | S-CHBA | R-CHBA | S-BAC-d4 | R-BAC-d4 | |
| MRM transition m/z (Q1→Q3) | 214.10 > 151.05 | 213.15 > 151.10 | 218.10 > 155.10 | |||
| MS/MS Ionization | APCI (+) ve Mode | APCI (−) ve Mode | APCI (+) ve Mode | |||
| Q1(V) | −30 | 15 | −30 | |||
| CE(V) | −19 | 13 | −19 | |||
| Q3(V) | −15 | 13 | −16 | |||
| R-and S-Baclofen Separation and Racemic CHBA Method: | ||||||
| Column | Crownpak CR(+) 4.00 × 150 mm, 5μ (Part # 27714) | |||||
| Guard Column: | Crownpak CR(+) 4.00 × 10 mm, 5μ (Part # 27714) | |||||
| Run Time: | 11 min | |||||
| Mobile Phase | A-0.4% in formic acid water and B: 0.4% formic in acetonitrile | |||||
| Flow | 1 mL/min, Isocratic (86:16, A:B) | |||||
| Retention time | 3.5 | 5.4 | 8.7 | 3.5 | 5.4 | |
| R-and S-CHBA Separation and Racemic Baclofen Method: | ||||||
| Column | Chiralcel OJ R-RH 2.1 × 150 mm, 5μ (Part #17794) | |||||
| Guard Column: | Phenomex C18 | |||||
| Run Time: | 27 min | |||||
| Mobile Phase | A-0.4% in Formic acid water and B: 0.4% Formic in acetonitrile | |||||
| Flow | 0.1 mL/min, Isocratic (86:16, A:B) | |||||
| Retention time | 5.0 | 21.0 | 23.5 | 5.1 | ||
| Conc. (ng/mL) | S-Baclofen | R-Baclofen | CHBA (Racemic) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLOQ | LQC | MQC | HQC | LLOQ | LQC | MQC | HQC | LLOQ | LQC | MQC | HQC | |
| Theoretical Conc. | 1 ng/mL | 5 ng/mL | 500 ng/mL | 1500 ng/mL | 1 ng/mL | 5 ng/mL | 500 ng/mL | 1500 ng/mL | 2 ng/mL | 10 ng/mL | 1000 ng/mL | 3000 ng/mL |
| %Biasintra-assay | 11.1 | 0.4 | 1.7 | −1.3 | 7.4 | 0.6 | −0.9 | −3.4 | 6.0 | −5.2 | 2.9 | −3.9 |
| %Biasinter-assay | 14.1 | −1.3 | 4.0 | −2.3 | 7.9 | 8.9 | 0.2 | −3.8 | 18.4 | 4.1 | 4.2 | −2.3 |
| % RSDintra-assay | 7.7 | 2.4 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 2.1 | 5.2 | 3.6 | 1.1 | 11.0 | 5.0 | 3.2 | 1.2 |
| % RSDinter-assay | 16.6 | 4.2 | 3.9 | 4.3 | 5.8 | 8.1 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 12.1 | 9.8 | 5.5 | 3.3 |
| Bio-Matrix | Analytes | Absolute Extraction Recovery (%) | Absolute Matrix Effect (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LQC | MQC | HQC | LQC | MQC | HQC | ||
| Human plasma | S-baclofen | 94.2 ± 8 | 84.8 ± 2.3 | 85 ± 6.7 | 94.7 ± 7.4 | 85.8 ± 3.9 | 89.7 ± 7.7 |
| R-baclofen | 99.4 ± 7.7 | 99.2 ± 7.7 | 88.6 ± 10.6 | 87.7 ± 6.1 | 91.4 ± 2.0 | 94.7 ± 16.3 | |
| Racemic CHBA | 99.9 ± 9.3 | 107.7 ± 7.5 | 109.1 ± 6.2 | 96.4 ± 1.7 | 96.3 ± 4.9 | 100.2 ± 1.5 | |
| CSF: Plasma (1:1) | S-baclofen | 82.2 ± 2.4 | 103.0 ± 10.8 | 96.8 ± 0.2 | 83.4 ± 4.3 | 88.2 ± 5.3 | 89.9 ± 4.4 |
| R-baclofen | 95.8 ± 2.1 | 94.7 ± 3.2 | 97 ± 0.6 | 84 ± 3.9 | 86.5 ± 1.0 | 91.8 ± 5.3 | |
| Racemic CHBA | 97.9 ± 9.3 | 109.2 ± 0.9 | 101.7 ± 6.4 | 94.5 ± 10.6 | 105.2 ± 6.1 | 101.9 ± 7.9 | |
| Storage Conditions | Conc. | S-Baclofen | R-Baclofen | CHBA (Racemic) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Mean Conc. (ng/mL) | Accuracy (%) | Measured Mean Conc. (ng/mL) | Accuracy (%) | Measured Mean Conc. (ng/mL) | Accuracy (%) | ||
| Bench-top stability (20 °C, up to 6 h) | LQC | 4.9 ± 0.3 | 97.3 ± 6.1 | 5.0 ± 0.5 | 99.4 ± 9.1 | 10.7 ± 1.1 | 106.9 ± 11.0 |
| HQC | 1520.0 ± 32.3 | 101.3 ± 2.1 | 1490.1 ± 18.8 | 99.3 ± 1.3 | 2771.2 ± 829.0 | 104.4 ± 2.2 | |
| Freeze–thaw stability (−80 °C, up to three cycles) | LQC | 5.0 ± 0.3 | 100.5 ± 6.6 | 5.3 ± 0.4 | 105.9 ± 8.1 | 9.8 ± 0.9 | 98.1 ± 8.6 |
| HQC | 1551.2 ± 19.9 | 103.4 ± 1.3 | 1511.5 ± 10.7 | 100.8 ± 0.7 | 3148.8 ± 47.7 | 105.0 ± 1.6 | |
| Long-term stability (−80 °C, 40 days) | LQC | 4.6 ± 0.2 | 92.1 ± 4.2 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 94.3 ± 3.1 | 10.0 ± 1.4 | 100.4 ± 13.6 |
| HQC | 1533.1 ± 1.9 | 102.2 ± 0.1 | 1473.2 ± 22.4 | 98.3 ± 1.5 | 1533.1 ± 28.1 | 107.0 ± 0.9 | |
| Auto-sampler stability (4 °C, 72 h) | LQC | 5.3 ± 0.2 | 105.9 ± 3.6 | 5.4 ± 0.1 | 108.6 ± 2.1 | 5.3 ± 3.1 | 98.2 ± 0.1 |
| HQC | 1492.8 ± 7.0 | 99.5 ± 0.4 | 1501 ± 2.8 | 100.2 ± 0.2 | 1492.8 ± 118.0 | 100.8 ± 4.0 | |
| Processed Samples’ long-term stability (−80 °C, 40 days) | LQC | 5.3 ± 0.2 | 105.4 ± 3.5 | 5.6 ± 0.1 | 111.8 ± 1.1 | 5.3 ± 3.0 | 107.6 ± 0.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Q.; Chhonker, Y.S.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Murry, D.J. Simultaneous Quantitation of S(+)- and R(−)-Baclofen and Its Metabolite in Human Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid using LC–APCI–MS/MS: An Application for Clinical Studies. Molecules 2020, 25, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020250
He Q, Chhonker YS, McLaughlin MJ, Murry DJ. Simultaneous Quantitation of S(+)- and R(−)-Baclofen and Its Metabolite in Human Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid using LC–APCI–MS/MS: An Application for Clinical Studies. Molecules. 2020; 25(2):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020250
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Qingfeng, Yashpal S. Chhonker, Matthew J. McLaughlin, and Daryl J. Murry. 2020. "Simultaneous Quantitation of S(+)- and R(−)-Baclofen and Its Metabolite in Human Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid using LC–APCI–MS/MS: An Application for Clinical Studies" Molecules 25, no. 2: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020250
APA StyleHe, Q., Chhonker, Y. S., McLaughlin, M. J., & Murry, D. J. (2020). Simultaneous Quantitation of S(+)- and R(−)-Baclofen and Its Metabolite in Human Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid using LC–APCI–MS/MS: An Application for Clinical Studies. Molecules, 25(2), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020250





