3,7-Dihydroxytropolones Inhibit Initiation of Hepatitis B Virus Minus-Strand DNA Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
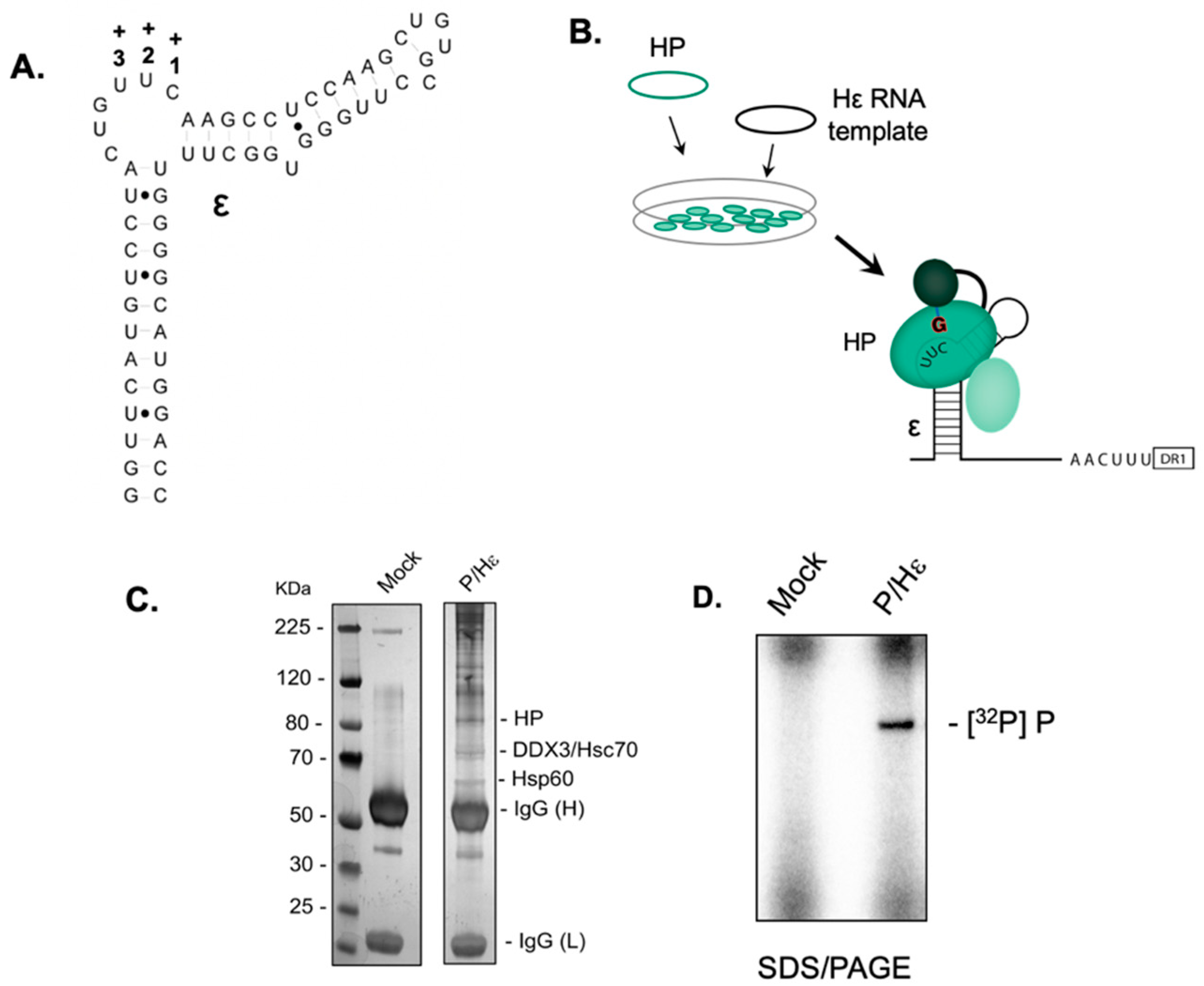
2.1. Establishing the HBV Minus-Strand DNA Priming System
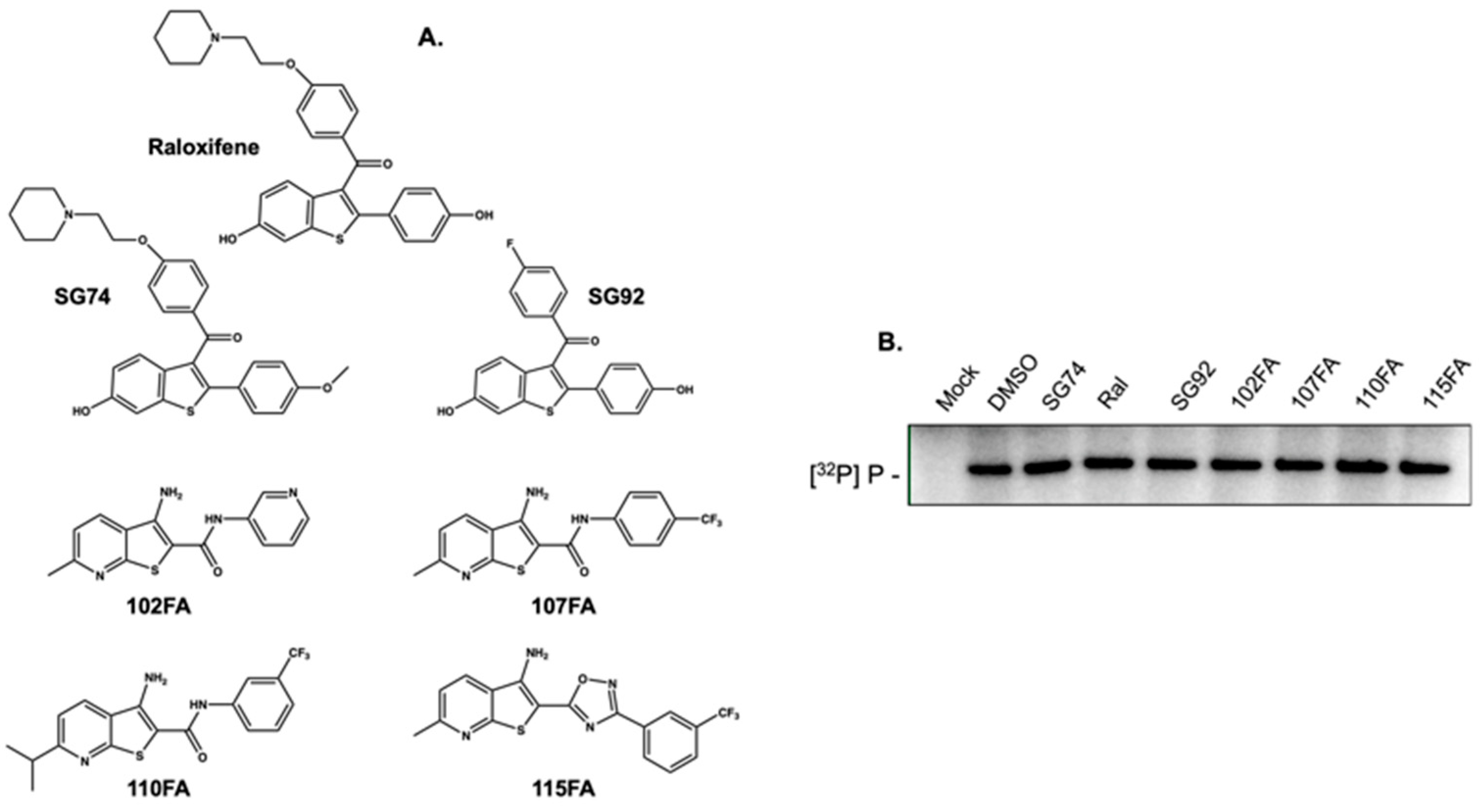
2.2. Small Molecules that Recognize HBV Epsilon Do not Inhibit Priming
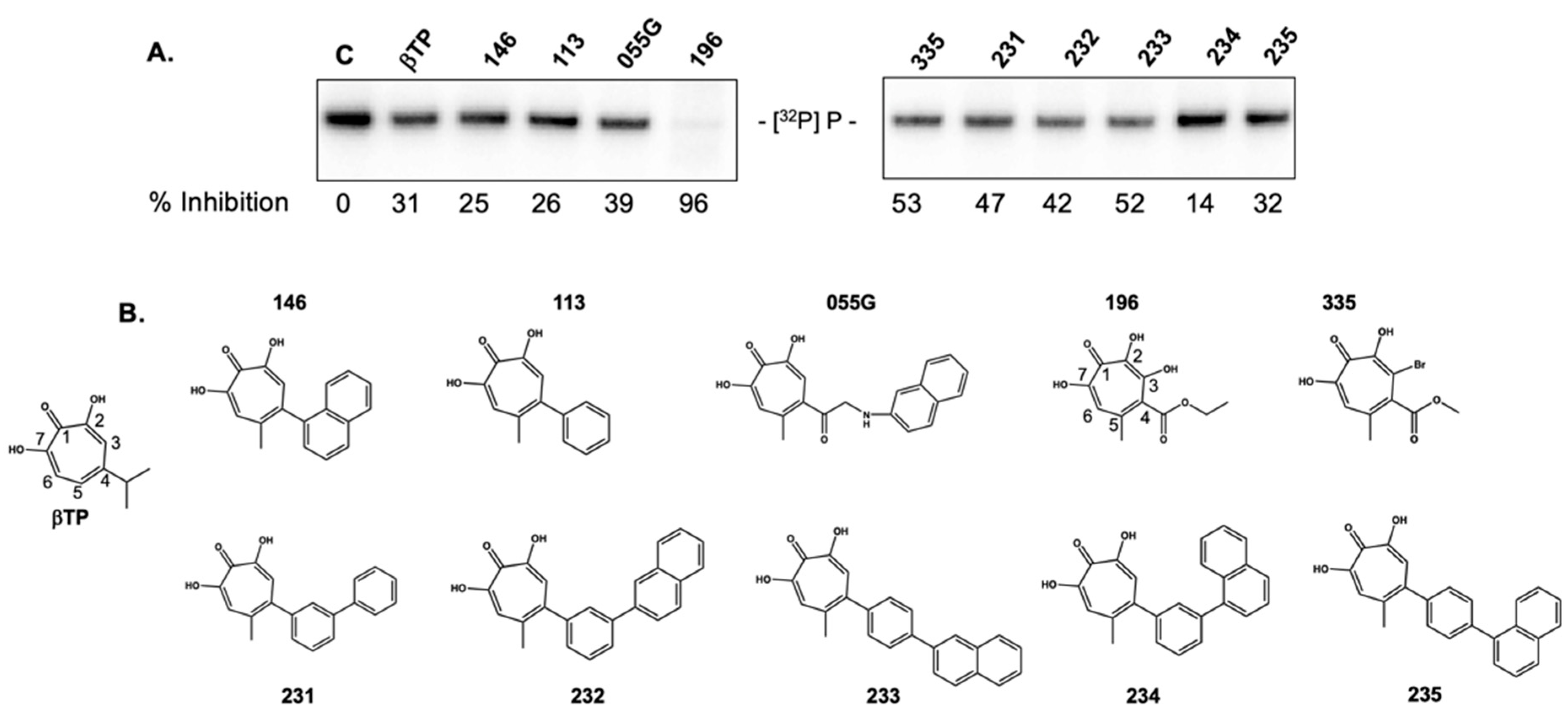
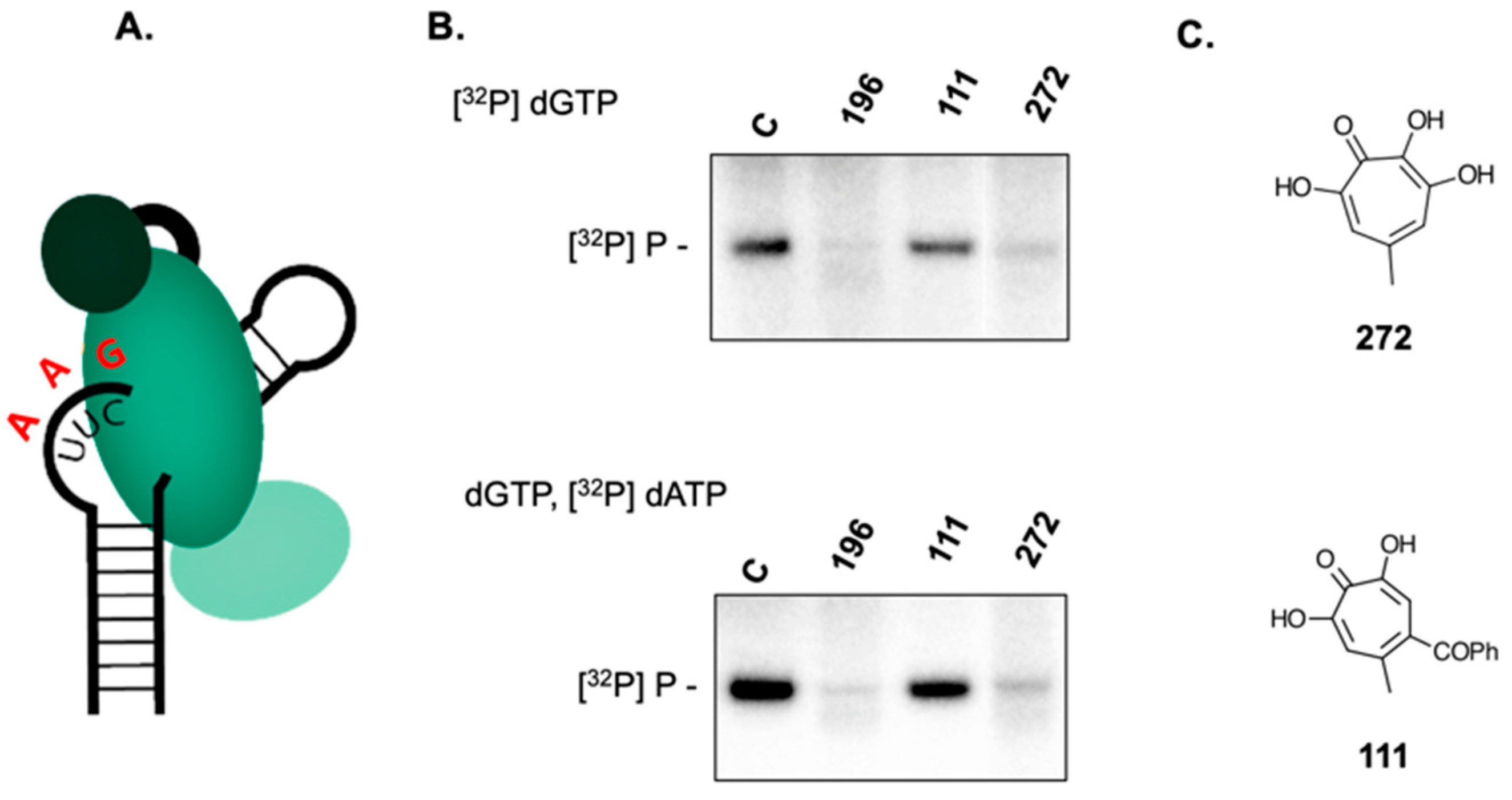
2.3. 3,7 Dihydroxytropolones Inhibit HBV (-) Strand DNA Synthesis
2.4. 3,7-dHTs Inhibit Covalent Attachment of dGTP to HBV P Protein
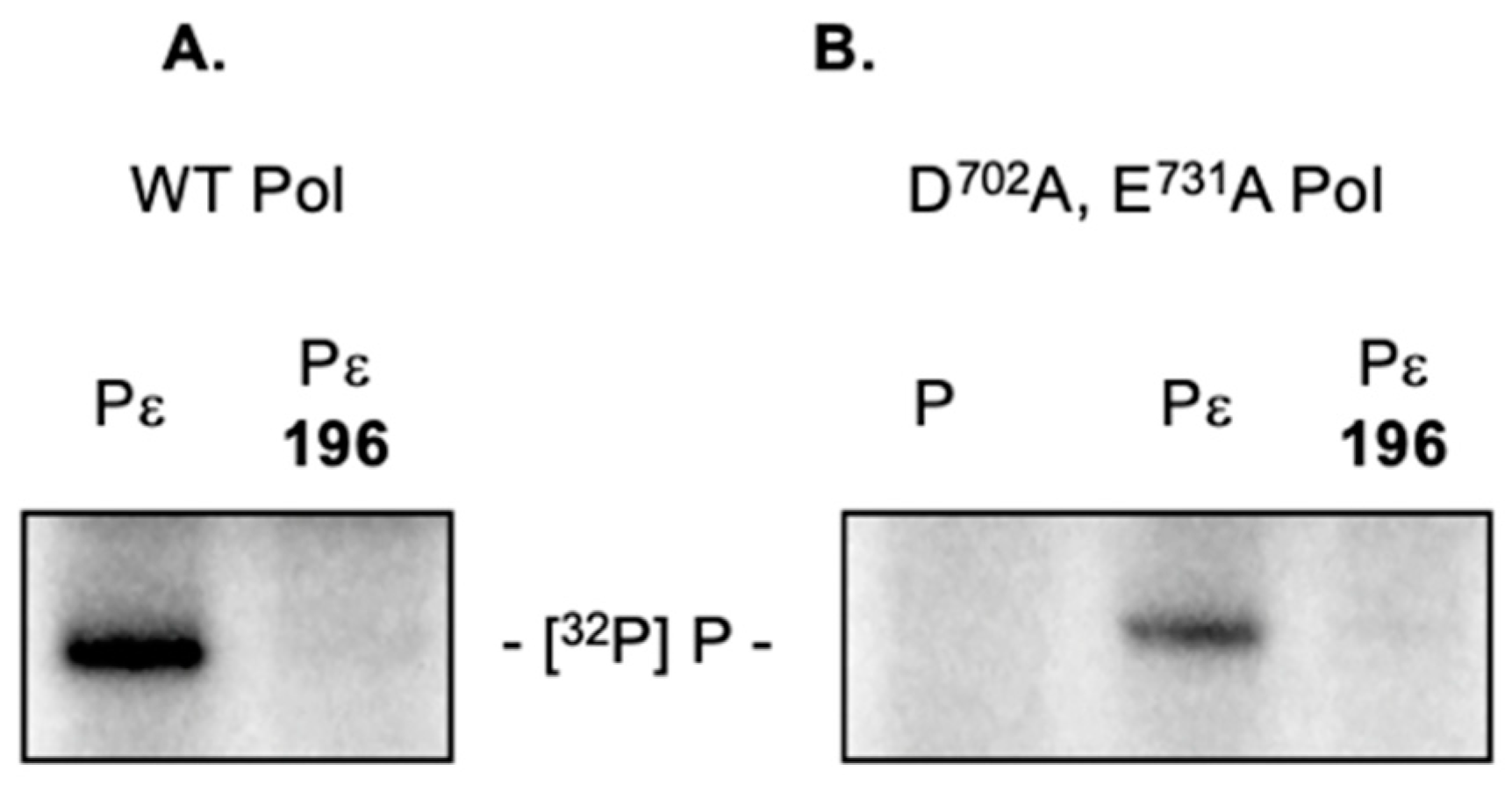
2.5. 3,7-dHTs Inhibit Priming by an RNase H-Deficient HBV Polymerase
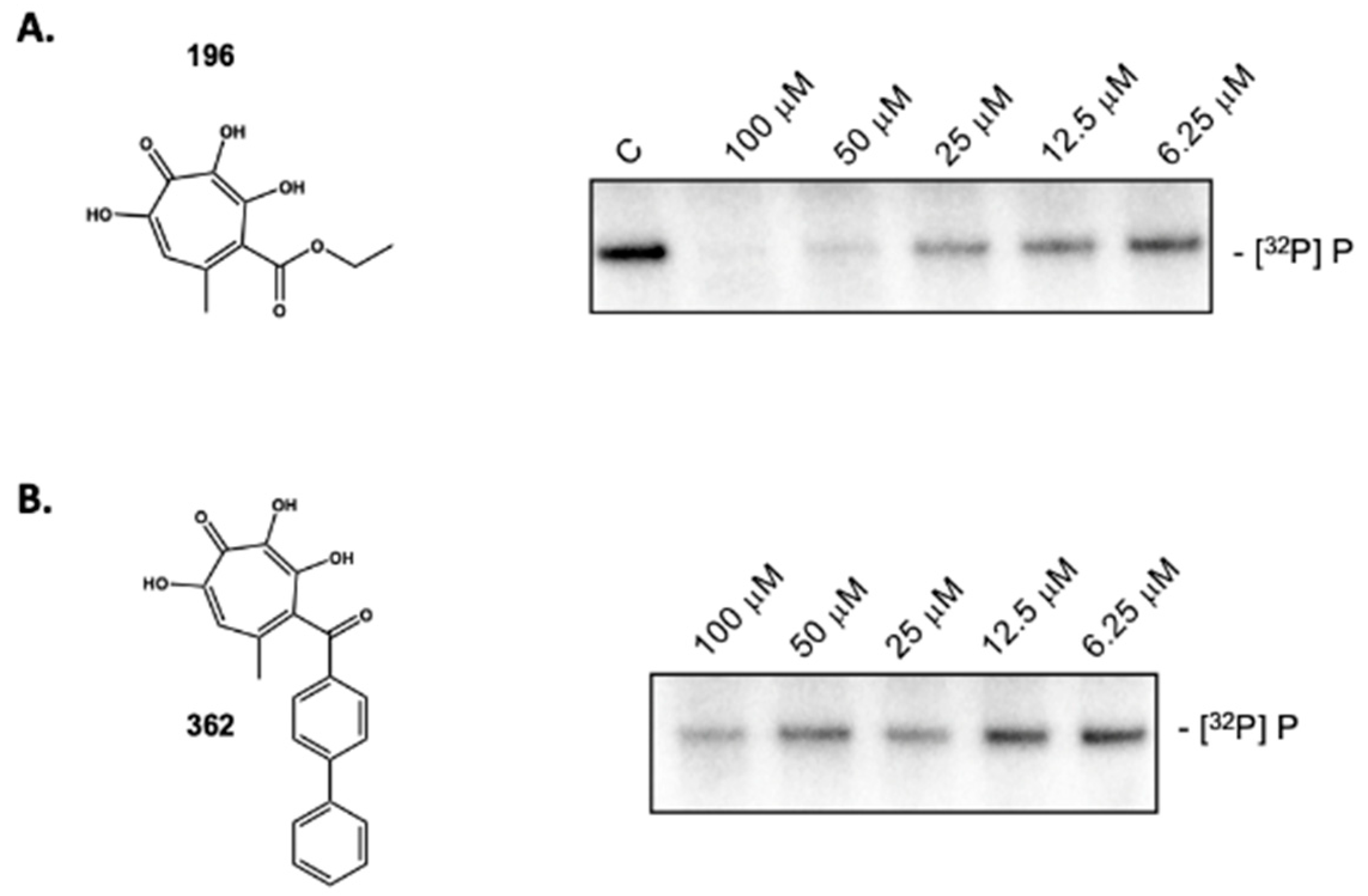
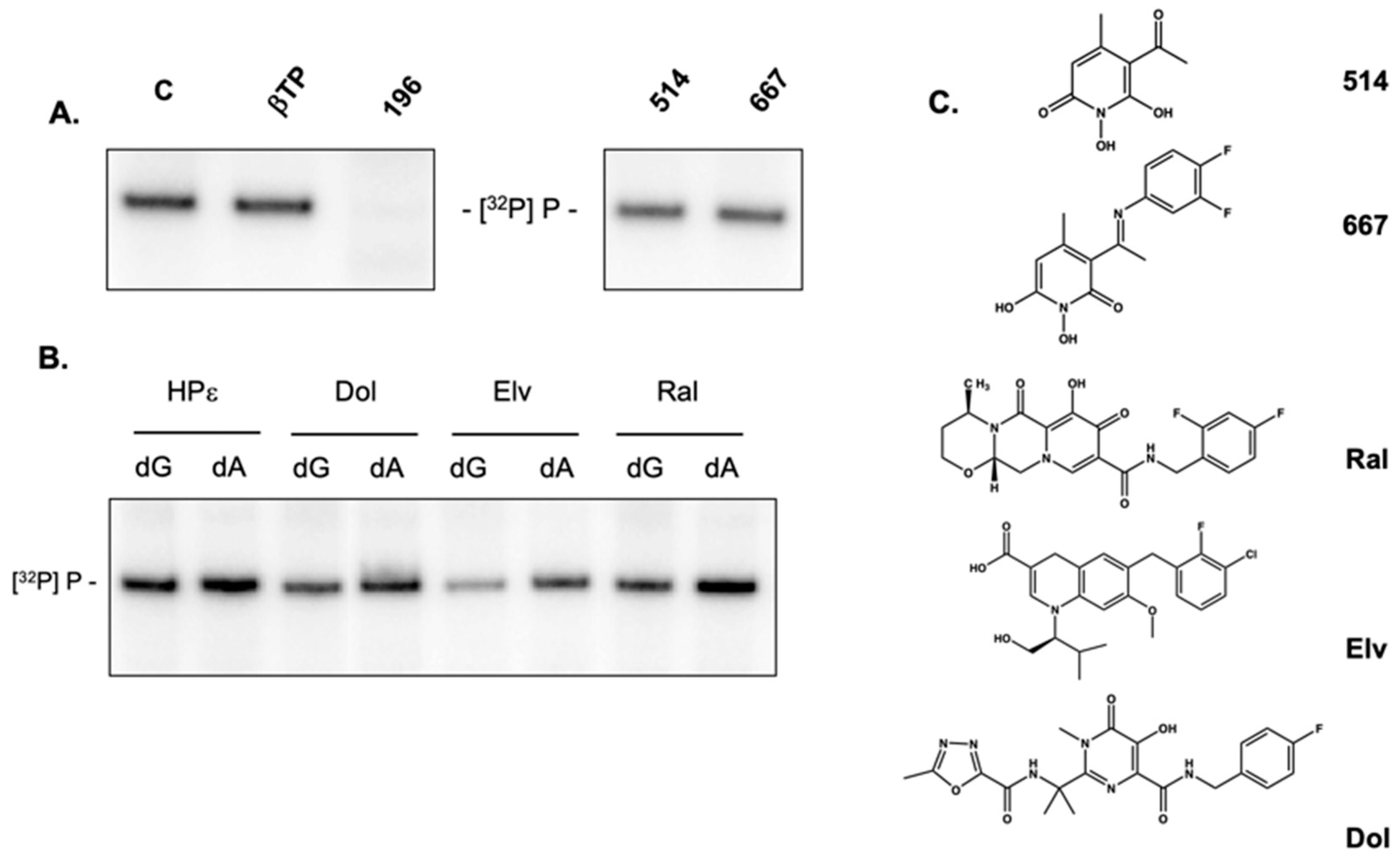
2.6. Activity of Non-Troponoid Nucleotidyltransferase Inhibitors
2.7. 3,7-dHT 196 Does Not Induce Dissociation of the HBV Initiation Complex
2.8. Modeling Supports Additional Interactions of 3,7-dHTs at the HBV Polymerase Active Site
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. α–HTs and 3,7-dHTs
4.2. Plasmids
4.3. Protein, RNA Expression and Purification
4.4. In Vitro Protein Priming
4.5. In Vitro Binding of ε RNA to HBV Polymerase
4.6. HBV ε RNA Detection
4.7. Modeling Ligand Binding within the HBV Polymerase Active Site
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanaway, J.D.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Fitzmaurice, C.; Vos, T.; Abubakar, I.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Assadi, R.; Bhala, N.; Cowie, B.; et al. The global burden of viral hepatitis from 1990 to 2013: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2016, 388, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganem, D.; Prince, A.M. Hepatitis B Virus Infection—Natural History and Clinical Consequences. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, B.S.; Alter, H.J. A “New” Antigen in Leukemia Sera. JAMA 1965, 191, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galibert, F.; Mandart, E.; Fitoussi, F.; Tiollais, P.; Charnay, P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature 1979, 281, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Jones, S.; Hu, J. Hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase: Diverse functions as classical and emerging targets for antiviral intervention. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, J.; Nassal, M. Hepatitis B virus replication. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, J.; Lai, C.-L.; Seto, W.; Yuen, M.-F. Nucleoside/nucleotide analogues in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 2715–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revill, P.; Penicaud, C.; Brechot, C.; Zoulim, F. Meeting the Challenge of Eliminating Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. Genes 2019, 10, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavis, J.E.; Zoidis, G.; Meyers, M.J.; Murelli, R.P. Chemical Approaches to Inhibiting the Hepatitis B Virus Ribonuclease H. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.C.; Ponzar, N.L.; Tavis, J.E. Shedding light on RNaseH: A promising target for hepatitis B virus (HBV). Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budihas, S.R.; Gorshkova, I.; Gaidamakov, S.; Wamiru, A.; Bona, M.K.; Parniak, M.A.; Crouch, R.J.; McMahon, J.B.; Beutler, J.A.; Le Grice, S.F.J. Selective inhibition of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H activity by hydroxylated tropolones. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Cao, F.; Huang, A.; Tavis, J.E. β-Thujaplicinol inhibits hepatitis B virus replication by blocking the viral ribonuclease H activity. Antivir. Res. 2013, 99, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meck, C.; D’Erasmo, M.P.; Hirsch, D.R.; Murelli, R.P. The biology and synthesis of α-hydroxytropolones. Med.Chem.Comm. 2014, 5, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.W.; Lomonosova, E.; Moran, E.A.; Cheng, X.; Patel, K.B.; Bailly, F.; Cotelle, P.; Meyers, M.J.; Tavis, J.E. Hepatitis B virus replication is blocked by a 2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione (HID) inhibitor of the viral ribonuclease H activity. Antivir. Res. 2014, 108, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.R.; Lomonosova, E.; Li, Q.; Ponzar, N.L.; Villa, J.A.; Touchette, E.; Rapp, S.; Liley, R.M.; Murelli, R.P.; Grigoryan, A.; et al. Efficacy of hepatitis B virus ribonuclease H inhibitors, a new class of replication antagonists, in FRG human liver chimeric mice. Antivir. Res. 2018, 149, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, J.A.; Pike, D.P.; Patel, K.B.; Lomonosova, E.; Lu, G.; Abdulqader, R.; Tavis, J.E. Purification and enzymatic characterization of the hepatitis B virus ribonuclease H, a new target for antiviral inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2016, 132, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.N.; Hu, J. Unveiling the roles of HBV polymerase for new antiviral strategies. Futur. Virol. 2015, 10, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B.; Thapa, R.J.; Guo, H.; Block, T.M. Host functions used by hepatitis B virus to complete its life cycle: Implications for developing host-targeting agents to treat chronic hepatitis B. Antivir. Res. 2018, 158, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.A.; Boregowda, R.; Spratt, T.E.; Hu, J. In Vitro Epsilon RNA-Dependent Protein Priming Activity of Human Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5134–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.A.; Murakami, E.; Delaney, W.; Furman, P.; Hu, J. Noncompetitive Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus Reverse Transcriptase Protein Priming and DNA Synthesis by the Nucleoside Analog Clevudine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4181–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulwerdi, F.A.; Le Grice, S.F. Recent Advances in Targeting the HIV-1 Tat/TAR Complex. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 4112–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abulwerdi, F.A.; Shortridge, M.D.; Sztuba-Solinska, J.; Wilson, R.; Le Grice, S.F.J.; Varani, G.; Schneekloth, J.J.S. Development of Small Molecules with a Noncanonical Binding Mode to HIV-1 Trans Activation Response (TAR) RNA. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 11148–11160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, R.A.; Anderson, K.S.; Johnson, K.A. HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Resistance to Nonnucleoside Inhibitors†. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figiel, M.; Krepl, M.; Poznanski, J.; Golab, A.; Šponer, J.; Nowotny, M. Coordination between the polymerase and RNase H activity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 3341–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Lomonosova, E.; Cheng, X.; Moran, E.A.; Meyers, M.J.; Le Grice, S.F.J.; Thomas, C.J.; Jiang, J.-K.; Meck, C.; Hirsch, D.R.; et al. Hydroxylated Tropolones Inhibit Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Blocking Viral Ribonuclease H Activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 59, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonosova, E.; Daw, J.; Garimallaprabhakaran, A.K.; Agyemang, N.B.; Ashani, Y.; Murelli, R.P.; Tavis, J.E. Efficacy and cytotoxicity in cell culture of novel α-hydroxytropolone inhibitors of hepatitis B virus ribonuclease H. Antivir. Res. 2017, 144, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonosova, E.; Zlotnick, A.; Tavis, J.E. Synergistic Interactions between Hepatitis B Virus RNase H Antagonists and Other Inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didierjean, J.; Isel, C.; Querré, F.; Mouscadet, J.-F.; Aubertin, A.-M.; Valnot, J.-Y.; Piettre, S.R.; Marquet, R. Inhibition of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Reverse Transcriptase, RNase H, and Integrase Activities by Hydroxytropolones. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4884–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majorek, K.A.; Dunin-Horkawicz, S.; Steczkiewicz, K.; Muszewska, A.; Nowotny, M.; Ginalski, K.; Bujnicki, J.M. The RNase H-like superfamily: New members, comparative structural analysis and evolutionary classification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 4160–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavis, J.E.; Cheng, X.; Hu, Y.; Totten, M.; Cao, F.; Michailidis, E.; Aurora, R.; Meyers, M.J.; Jacobsen, E.J.; Parniak, M.A.; et al. The Hepatitis B Virus Ribonuclease H Is Sensitive to Inhibitors of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Ribonuclease H and Integrase Enzymes. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, E.P.; Johns, B.A.; Gartland, M.J.; Foster, S.A.; Miller, W.H.; Ferris, R.G.; Hazen, R.J.; Underwood, M.R.; Boros, E.E.; Thompson, J.B.; et al. The Naphthyridinone GSK364735 Is a Novel, Potent Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Integrase Inhibitor and Antiretroviral. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 52, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.D.; Staas, D.D.; Venkatraman, S.; Loughran, H.M.; Ruzek, R.D.; Booth, T.M.; Lyle, T.A.; Wai, J.S.; Vacca, J.P.; Feuston, B.P.; et al. Potent and selective HIV-1 ribonuclease H inhibitors based on a 1-hydroxy-1,8-naphthyridin-2(1H)-one scaffold. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6754–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.; Xiong, X.; Yang, H.; Westland, C.E.; Gibbs, C.S.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Arnold, E. Molecular Modeling and Biochemical Characterization Reveal the Mechanism of Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase Resistance to Lamivudine (3TC) and Emtricitabine (FTC). J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4771–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, T.C.-F.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Chan, H.L.-Y.; Tse, Y.-K.; Lui, G.C.-Y.; Wong, G.L. Tenofovir Is Associated With Lower Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Than Entecavir in Patients With Chronic HBV Infection in China. Gastroenterology 2019, 158, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Wang, C.; Yan, S.; Liu, G. Past, Current, and Future Developments of Therapeutic Agents for Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 6461–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesa, L.C.; Patury, S.; Komiyama, T.; Ahmad, A.; Zuiderweg, E.R.P.; Gestwicki, J.E. Inhibitors of Difficult Protein–Protein Interactions Identified by High-Throughput Screening of Multiprotein Complexes. ACS Chem. Boil. 2013, 8, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenney, D.J.; Levine, S.M.; Rose, R.E.; Walsh, A.W.; Weinheimer, S.P.; Discotto, L.; Plym, M.; Pokornowski, K.; Yu, C.F.; Angus, P.; et al. Clinical Emergence of Entecavir-Resistant Hepatitis B Virus Requires Additional Substitutions in Virus Already Resistant to Lamivudine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3498–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, K.M. Structure-enhanced methods in the development of non-nucleoside inhibitors targeting HIV reverse transcriptase variants. Futur. Microbiol. 2015, 10, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, D.R.; Schiavone, D.V.; Berkowitz, A.J.; Morrison, L.A.; Masaoka, T.; Wilson, J.A.; Lomonosova, E.; Zhao, H.; Patel, B.S.; Datla, S.H.; et al. Synthesis and biological assessment of 3,7-dihydroxytropolones. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 16, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steitz, T.A.; Steitz, J.A. A general two-metal-ion mechanism for catalytic RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6498–6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Harrison, S.C.; Verdine, G.L. Trapping of a catalytic HIV reverse transcriptase*template:primer complex through a disulfide bond. Chem. Boil. 2000, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piettre, S.R.; André, C.; Chanal, M.-C.; Ducep, J.-B.; Lesur, B.; Piriou, F.; Raboisson, P.; Rondeau, J.-M.; Schelcher, C.; Zimmermann, P.; et al. Monoaryl- and Bisaryldihydroxytropolones as Potent Inhibitors of Inositol Monophosphatase. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 4208–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkowitz, A.J.; Franson, A.D.; Cassals, A.G.; Donald, K.A.; Yu, A.J.; Garimallaprabhakaran, A.K.; Morrison, L.A.; Murelli, R.P. Importance of lipophilicity for potent anti-herpes simplex virus-1 activity of α-hydroxytropolones. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Erasmo, M.P.; Murelli, R.P. Fluorous-Phase Approach to α-Hydroxytropolone Synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bak, E.; Miller, J.T.; Noronha, A.; Tavis, J.; Gallicchio, E.; Murelli, R.P.; Le Grice, S.F.J. 3,7-Dihydroxytropolones Inhibit Initiation of Hepatitis B Virus Minus-Strand DNA Synthesis. Molecules 2020, 25, 4434. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194434
Bak E, Miller JT, Noronha A, Tavis J, Gallicchio E, Murelli RP, Le Grice SFJ. 3,7-Dihydroxytropolones Inhibit Initiation of Hepatitis B Virus Minus-Strand DNA Synthesis. Molecules. 2020; 25(19):4434. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194434
Chicago/Turabian StyleBak, Ellen, Jennifer T. Miller, Andrea Noronha, John Tavis, Emilio Gallicchio, Ryan P. Murelli, and Stuart F. J. Le Grice. 2020. "3,7-Dihydroxytropolones Inhibit Initiation of Hepatitis B Virus Minus-Strand DNA Synthesis" Molecules 25, no. 19: 4434. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194434
APA StyleBak, E., Miller, J. T., Noronha, A., Tavis, J., Gallicchio, E., Murelli, R. P., & Le Grice, S. F. J. (2020). 3,7-Dihydroxytropolones Inhibit Initiation of Hepatitis B Virus Minus-Strand DNA Synthesis. Molecules, 25(19), 4434. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194434





