LncMirNet: Predicting LncRNA–miRNA Interaction Based on Deep Learning of Ribonucleic Acid Sequences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Datasets
2.1.2. Constructing Positive and Negative Samples
2.2. Methods
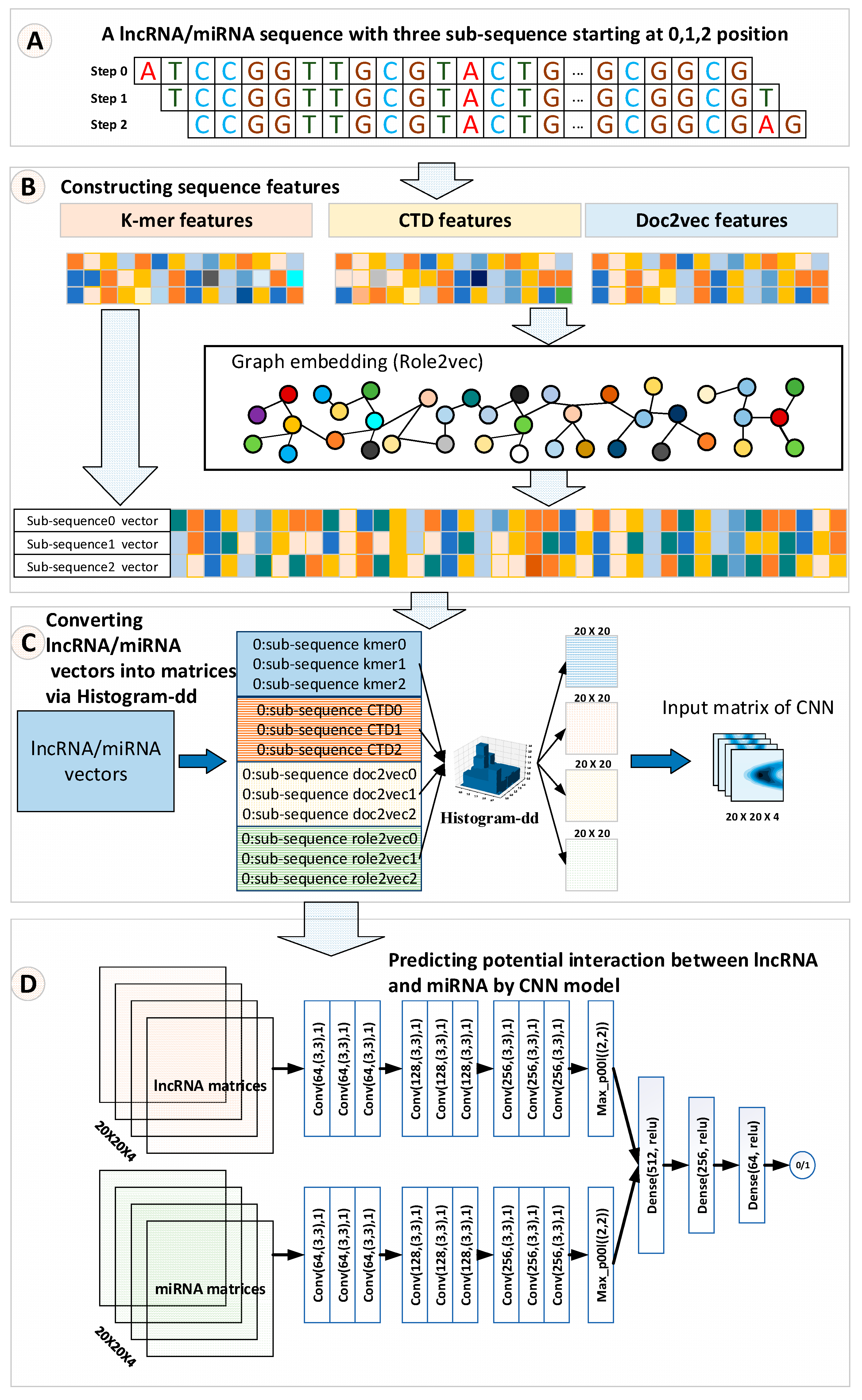
2.2.1. Overall Workflow
2.2.2. Construction Features
k-mer Features of RNA Sequence
Composition/Transition/Distribution (CTD) Features
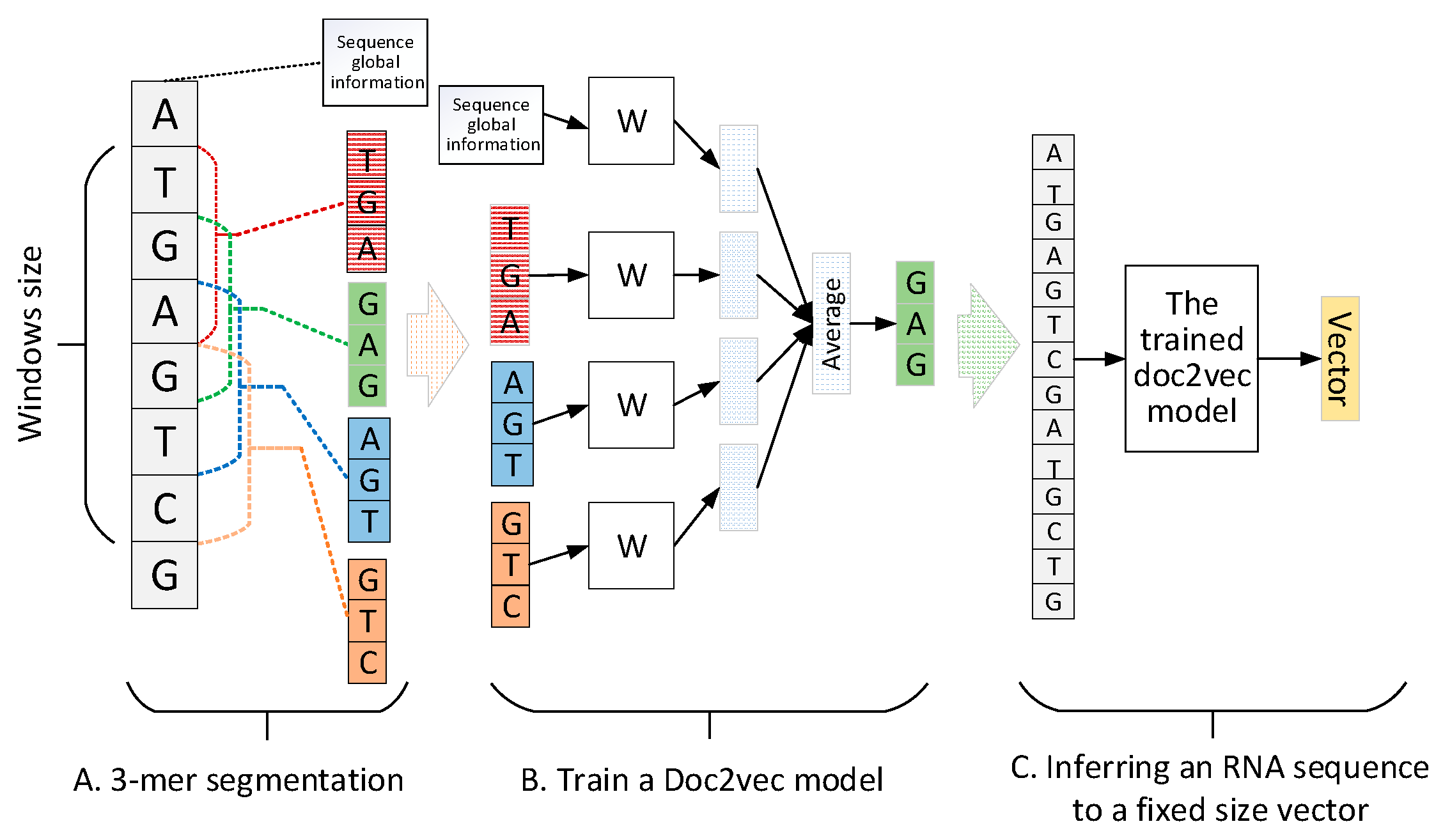
Distributed Representation Feature of RNA Sequence by doc2vec
Graph Embedding Methods to Represent RNA Sequence
Constructing Matrix Features by Histogram-Dd
2.2.3. Prediction Model by Convolutional Neural Networks
2.3. Implementation of LncMirNet
2.4. Evaluation Criteria
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Settings
3.2. The Effects of Feature Combination
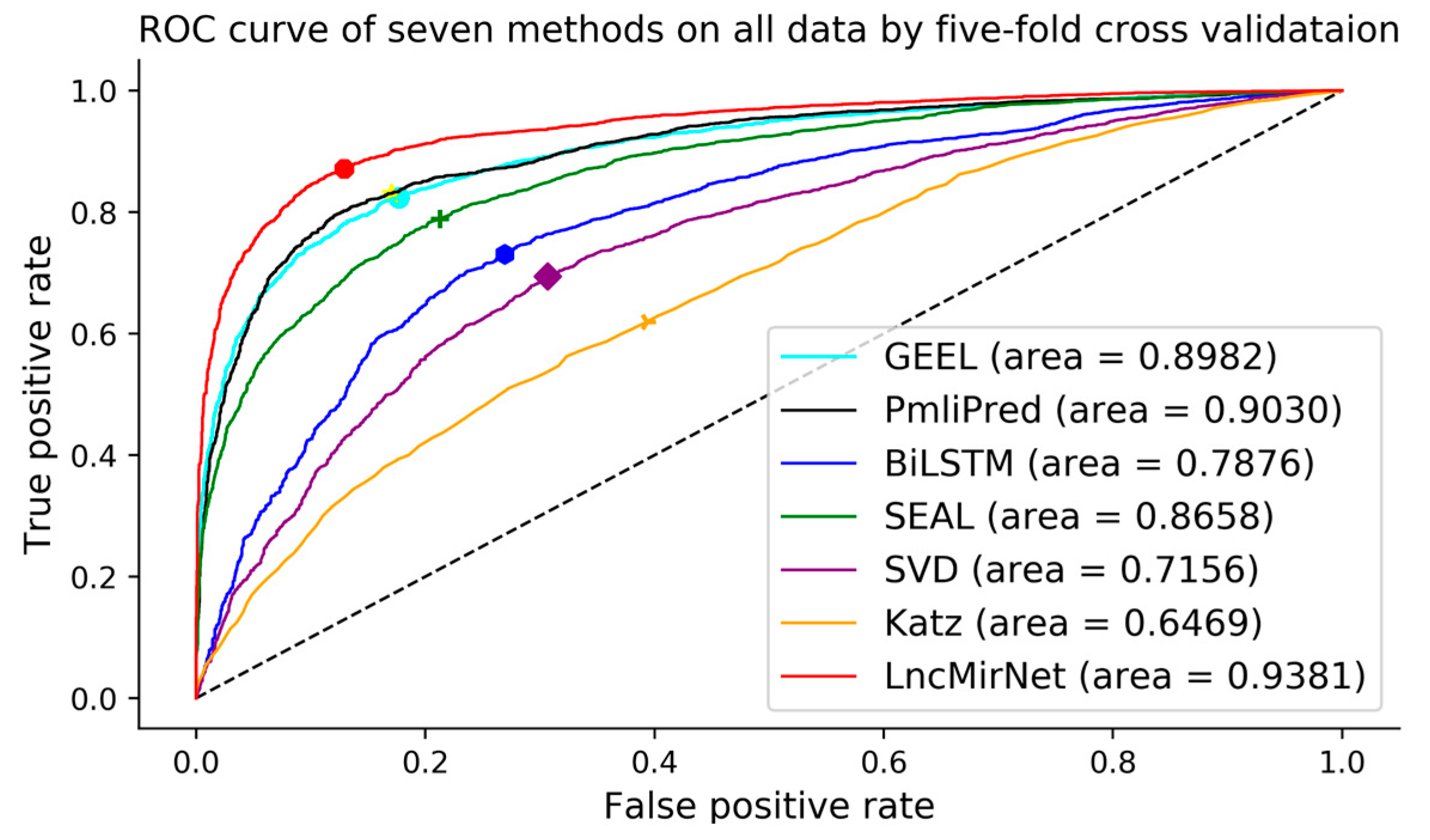
3.3. Comparison with Six Other Methods on All Data
3.4. Negative Samples Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Data Availability Statement
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Ma, Q.; Tian, Y. NCResNet: Noncoding Ribonucleic Acid Prediction Based on a Deep Resident Network of Ribonucleic Acid Sequences. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Z.; Chen, M.; Chen, D.; Gao, X.C.; Zhu, S.; Huang, H.; Hu, M.; Zhu, H.; Yan, G.R. A Peptide Encoded by a Putative lncRNA HOXB-AS3 Suppresses Colon Cancer Growth. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 171–184.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, D.; Sboner, A.; Nair, S.S.; Giannopoulou, E.; Li, R.; Hennig, S.; Mosquera, J.M.; Pauwels, J.; Park, K.; Kossai, M.; et al. The oestrogen receptor alpha-regulated lncRNA NEAT1 is a critical modulator of prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhan, A.; Mandal, S.S. LncRNA HOTAIR: A master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2015, 1856, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Nie, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, J.; He, D.; Xie, M.; Xu, L.; De, W.; Wang, Z.; et al. LncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by scaffolding the chromatin modification factors PRC2, LSD1, and DNMT1. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6299–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Yang, Y.A.; Zhang, A.; Fong, K.W.; Kim, J.; Song, B.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.C.; Yu, J. LncRNA HOTAIR enhances ER signaling and confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Liu, W.; Li, F.; Zhao, W.; Qin, C. Decreased expression of lncRNA GAS5 predicts a poor prognosis in cervical cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 6776–6783. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Yu, X.; Hu, S.; Yu, J. A Brief Review on the Mechanisms of miRNA Regulation. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2009, 7, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.X.; Koirala, P.; Mo, Y.Y. LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5661–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.A.; Huang, Y.A.; You, Z.H.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, Y. Novel link prediction for large-scale miRNA-lncRNA interaction network in a bipartite graph. BMC Med. Genom. 2018, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.A.; Chan, K.C.C.; You, Z.H. Constructing prediction models from expression profiles for large scale lncRNA-miRNA interaction profiling. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.A.; Huang, Z.A.; You, Z.H.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, W.Z.; Guo, J.X.; Yu, C.Q. Predicting lncRNA-miRNA Interaction via Graph Convolution Auto-Encoder. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yue, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Niu, Y. LncRNA-miRNA interaction prediction from the heterogeneous network through graph embedding ensemble learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, BIBM 2019, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 November 2019; pp. 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Meng, J.; Cui, J.; Luan, Y.; Chen, M. PmliPred: A method based on hybrid model and fuzzy decision for plant miRNA–lncRNA interaction prediction. Bioinformatics 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Liu, S. CPPred: Coding potential prediction based on the global description of RNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.R.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, A.Y. LncRNASNP2: An updated database of functional SNPs and mutations in human and mouse lncRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D276–D280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankish, A.; Diekhans, M.; Ferreira, A.M.; Johnson, R.; Jungreis, I.; Loveland, J.; Mudge, J.M.; Sisu, C.; Wright, J.; Armstrong, J.; et al. GENCODE reference annotation for the human and mouse genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D766–D773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. MiRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Luo, J.; Pan, C.; Liu, Y. SG-LSTM-FRAME: A computational frame using sequence and geometrical information via LSTM to predict miRNA–gene associations. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, R.M.; Šulc, M.; Vaníček, J. Searching the coding region for microRNA targets. RNA 2013, 19, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Fang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Chou, K.C. Identification of microRNA precursor with the degenerate K-tuple or Kmer strategy. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 385, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.H.; Baldwin, T. An Empirical Evaluation of doc2vec with Practical Insights into Document Embedding Generation. In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Representation Learning for NLP, Berlin, Germany, 11 August 2016; pp. 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Rossi, R.A.; Lee, J.; Willke, T.; Zhou, R.; Kong, X.; Eldardiry, H. Role-based Graph Embeddings. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 4347, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubchak, I.; Muchnik, I.; Holbrook, S.R.; Kim, S.H. Prediction of protein folding class using global description of amino acid sequence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8700–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambria, E.; White, B. Jumping NLP curves: A review of natural language processing research. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2014, 9, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, E.A.; Katahira, I.; da Rocha Vicente, F.F.; Pereira, L.F.P.; Lopes, F.M. BASiNET—Biological sequences network: A case study on coding and non-coding RNAs identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Q.; Mikolov, T. Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2014; Xing, E.P., Jebara, T., Eds.; PMLR: Beijing, China, 2014; Volume 4, pp. 2931–2939. [Google Scholar]
- Simonovsky, M.; Komodakis, N. GraphVAE: Towards generation of small graphs using variational autoencoders. In International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Lee, B.; Yoon, S. Deep learning in bioinformatics. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 18, 851–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: All data and code are available from the authors. |
| k-mer | k-mer, CTD | k-mer, CTD, doc2vec | k-mer, CTD, doc2vec, Graph Embedding | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 0.8609 | 0.8802 | 0.9048 | 0.9140 |
| Test | 0.8004 | 0.8188 | 0.8321 | 0.8534 |
| Sensitivity | Specificity | F1-Score | Accuracy | AUC | MCC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEEL | 0.8040 | 0.8401 | 0.8187 | 0.8220 | 0.8982 | 0.6445 |
| PmliPred | 0.8800 | 0.7118 | 0.8117 | 0.7959 | 0.9030 | 0.6004 |
| BiLSTM | 0.8027 | 0.6263 | 0.7239 | 0.7145 | 0.7876 | 0.4359 |
| SEAL | 0.7650 | 0.8097 | 0.7825 | 0.7874 | 0.8658 | 0.5754 |
| SVD | 0.6548 | 0.6594 | 0.6595 | 0.6571 | 0.7156 | 0.3142 |
| Katz | 0.5969 | 0.5961 | 0.5953 | 0.5964 | 0.6459 | 0.1930 |
| LncMirNet | 0.9158 | 0.7910 | 0.8620 | 0.8534 | 0.9381 | 0.7124 |
| Number of Positive Samples | Number of Negative Samples | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 15,386 | 3846 | 0.8519 |
| 0.5 | 15,386 | 7693 | 0.8729 |
| 1.0 | 15,386 | 15,386 | 0.9381 |
| 2.0 | 15,386 | 30,772 | 0.9067 |
| 4.0 | 15,386 | 61,544 | 0.8834 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Shao, D.; He, K.; Huang, L. LncMirNet: Predicting LncRNA–miRNA Interaction Based on Deep Learning of Ribonucleic Acid Sequences. Molecules 2020, 25, 4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194372
Yang S, Wang Y, Lin Y, Shao D, He K, Huang L. LncMirNet: Predicting LncRNA–miRNA Interaction Based on Deep Learning of Ribonucleic Acid Sequences. Molecules. 2020; 25(19):4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194372
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Sen, Yan Wang, Yu Lin, Dan Shao, Kai He, and Lan Huang. 2020. "LncMirNet: Predicting LncRNA–miRNA Interaction Based on Deep Learning of Ribonucleic Acid Sequences" Molecules 25, no. 19: 4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194372
APA StyleYang, S., Wang, Y., Lin, Y., Shao, D., He, K., & Huang, L. (2020). LncMirNet: Predicting LncRNA–miRNA Interaction Based on Deep Learning of Ribonucleic Acid Sequences. Molecules, 25(19), 4372. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194372






