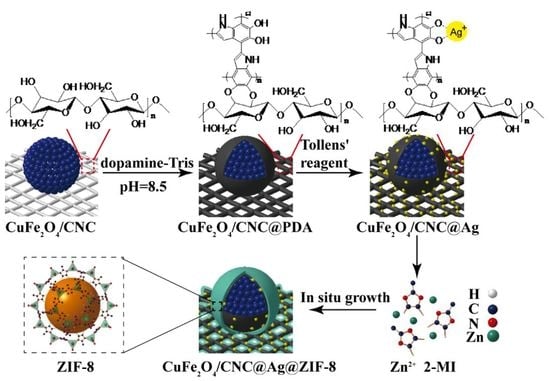
Preparation of Magnetic CuFe2O4@Ag@ZIF-8 Nanocomposites with Highly Catalytic Activity Based on Cellulose Nanocrystals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
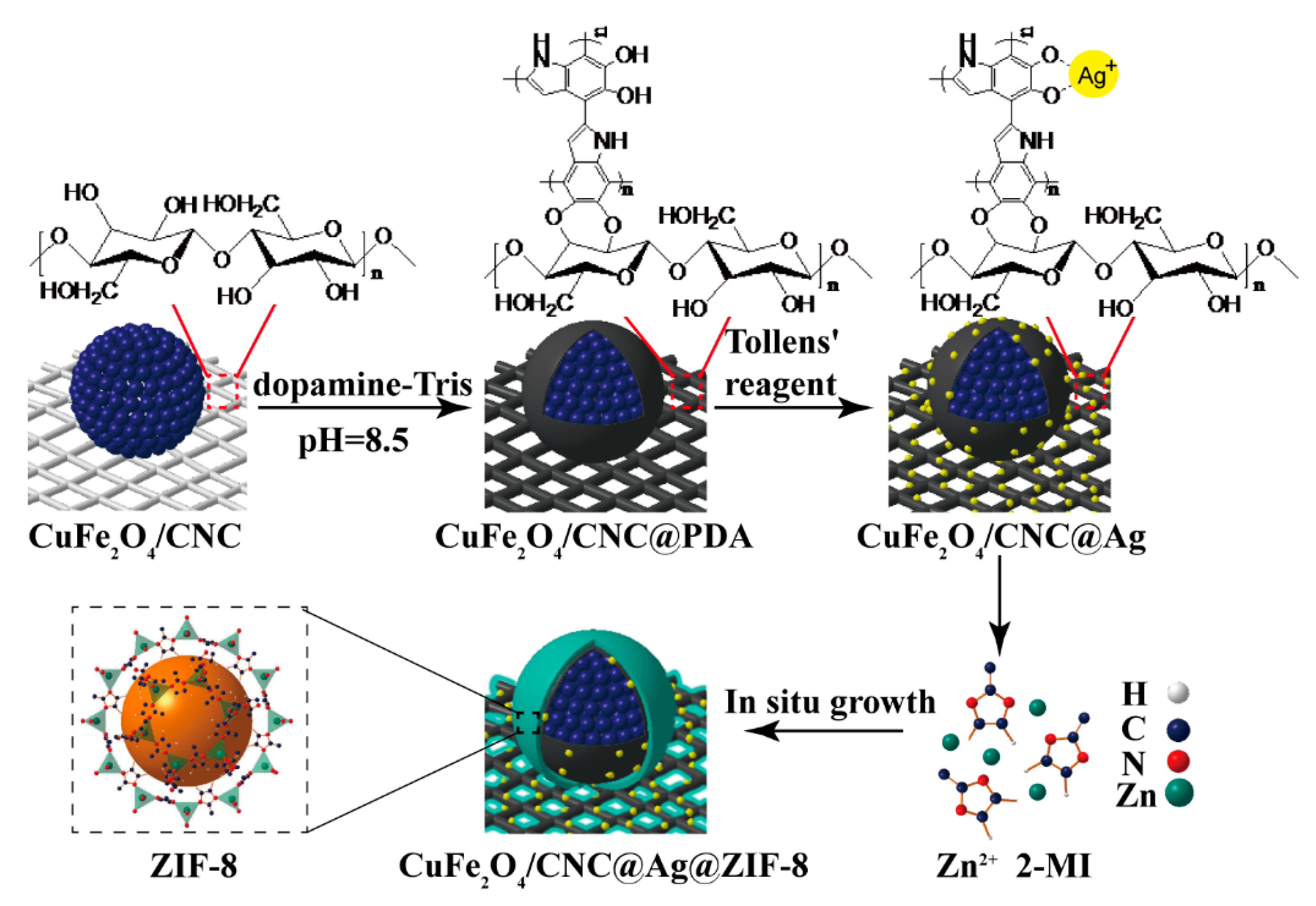
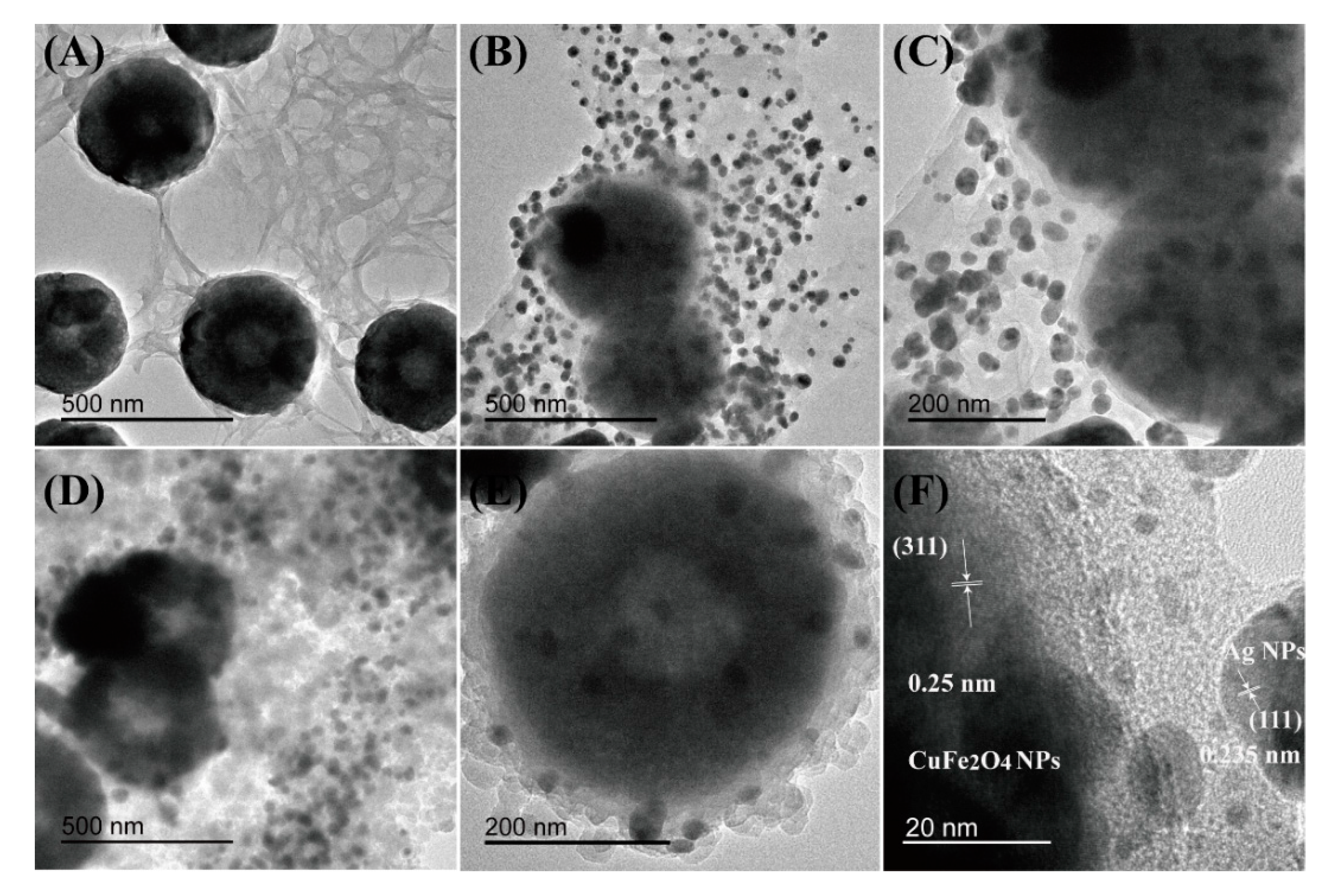
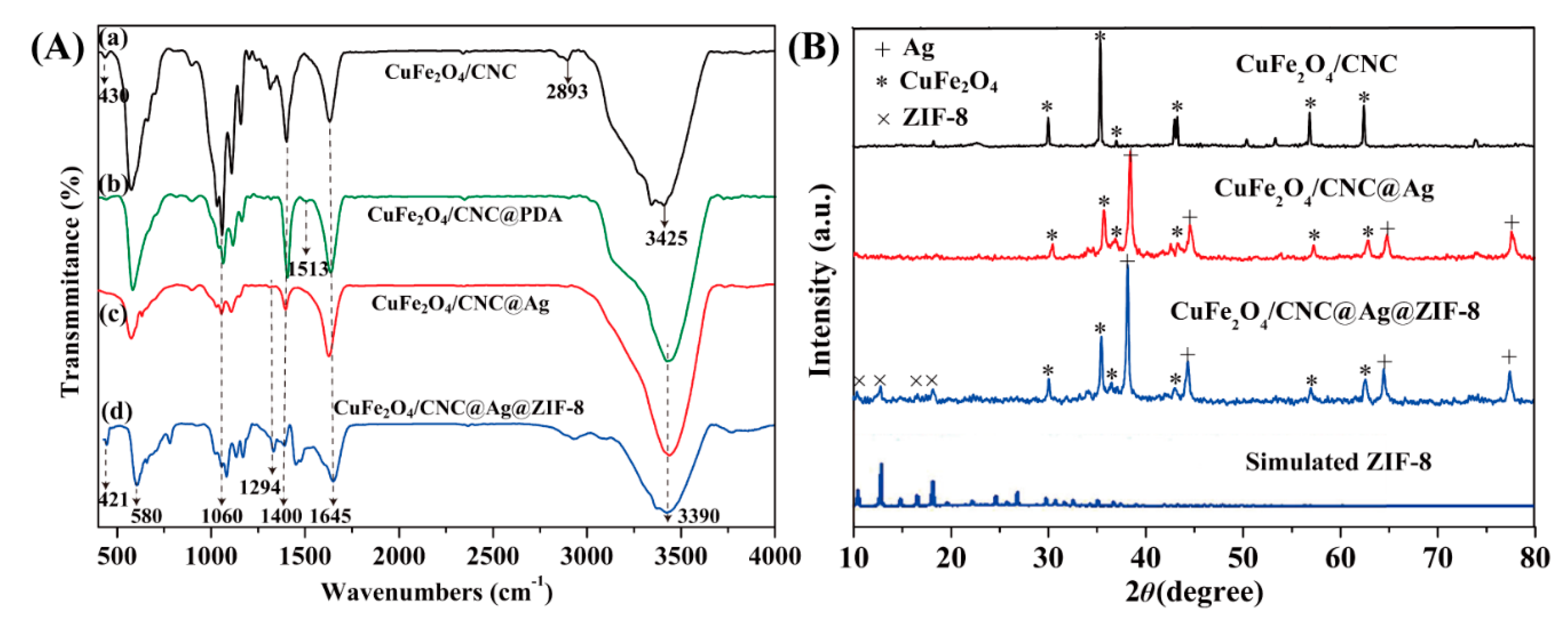
2.1. Characterization of CuFe2O4/CNC@Ag and CuFe2O4/CNC@Ag@ZIF-8 Nanocomposites
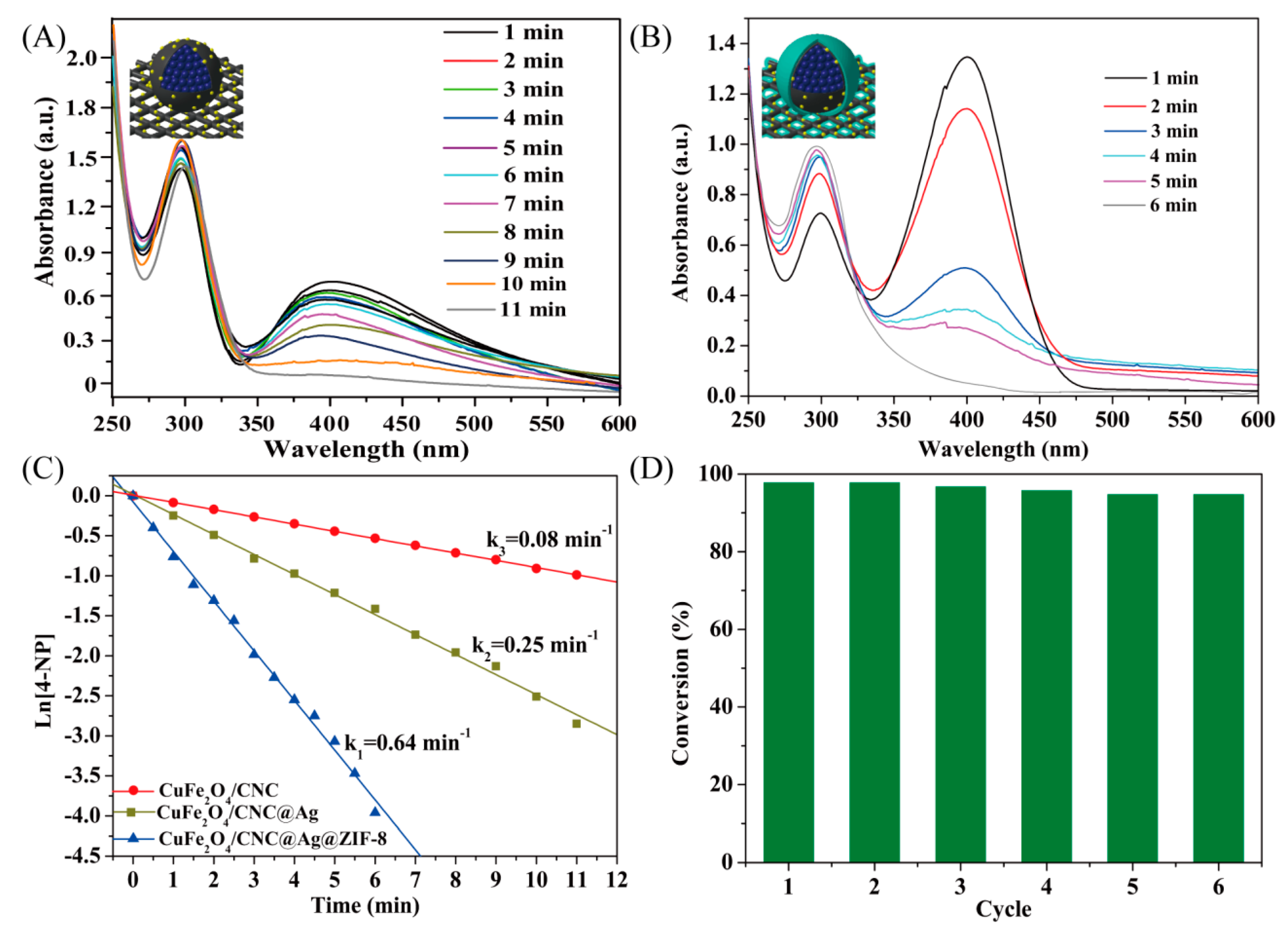
2.2. Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol
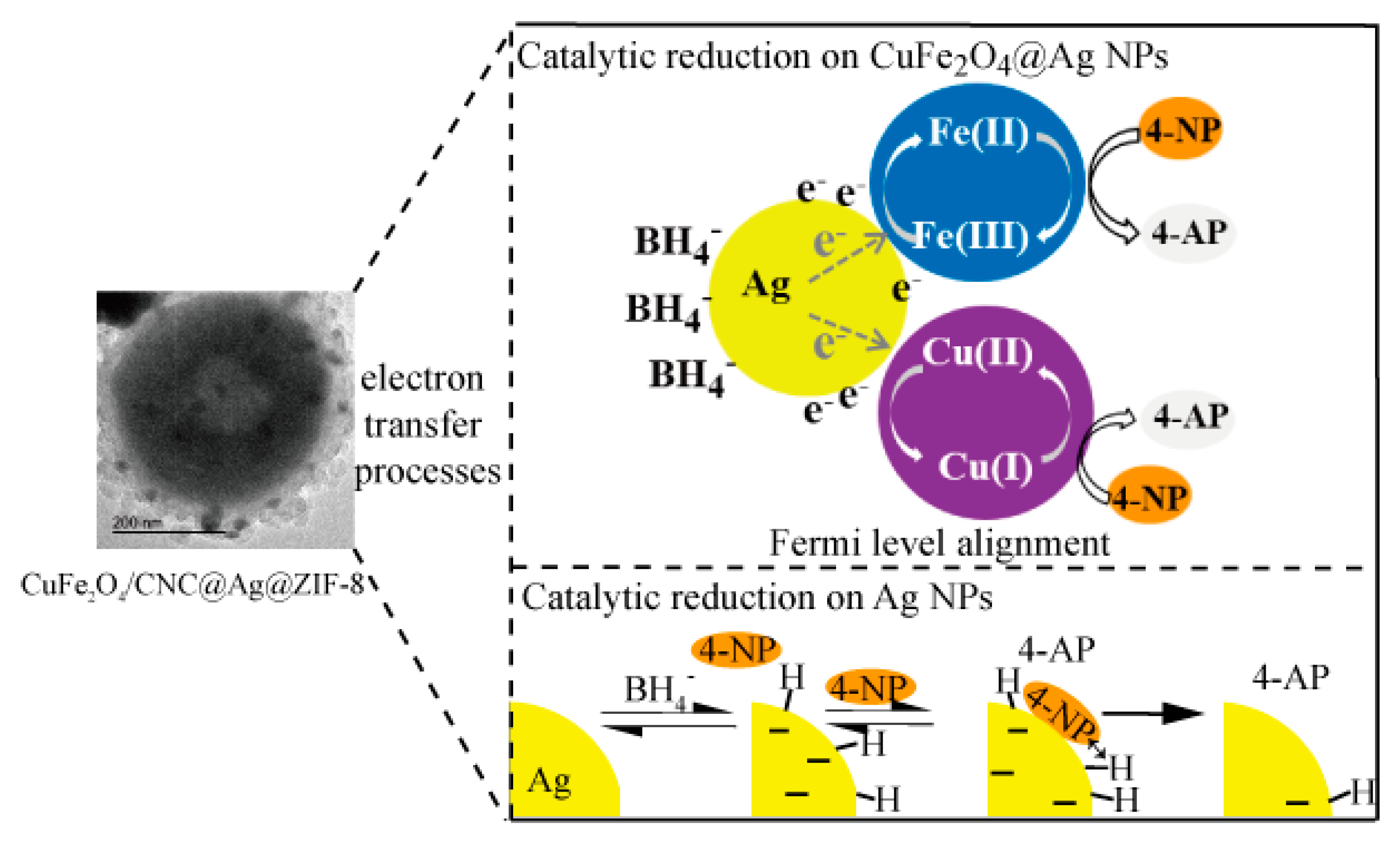
2.3. Reaction Mechanism of CuFe2O4/CNC@Ag@ZIF-8 Nanocomposites
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Measurements
3.3. Preparation of CuFe2O4/CNC Nanocomposites
3.4. In Situ Reduction of Ag+ Ions
3.5. Preparation of CuFe2O4/CNC@Ag@ZIF-8 Nanocomposites
3.6. General Procedure for the Reduction of 4-NP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leung, K.C.; Xuan, S.; Zhu, X. Gold and iron oxide hybrid nanocomposite materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1911–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Li, E.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, J.; Lu, S.; Ge, C.; Pan, Y.; Gu, H. Facile preparation of hybrid core-shell nanorods for photo thermal and radiation combined therapy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3895–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.X.; Zou, M.Z.; Wen, W.W.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Lin, B.; Chen, L.Z.; Lai, H.; Guan, L.H.; Huang, Z.G. Spinel MFe2O4 (M = Co, Ni) nanoparticles coated on multi-walled carbon nanotubes as electrocatalysts for Li-O2 batteriesm. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 10257–10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Qin, W.J.; Zhang, H.; Rahman, Z.U.; Ren, C.L.; Ma, S.; Chen, X. The peroxidase/catalase-like activities of MFe2O4 (M= Mg, Ni, Cu) MNPs and their application in colorimetric biosensing of glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, F.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J. Multifunctional Au-Fe3O4@MOF core-shell nanocomposite catalysts with controllable reactivity and magnetic recyclability. Nanoscale 2014, 7, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yang, P.; Ma, Y. Facile synthesis of magnetic hierarchical core-shell structured Fe3O4@PDA-Pd@MOF nanocomposites: Highly integrated multifunctional catalysts. Chemcatchem Catal. 2018, 10, 446–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, W. In situ loading of gold nanoparticles on Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic nanocomposites and their high catalytic activity. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4894–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chook, S.W.; Yau, S.X.; Chia, C.H.; Chin, S.X.; Zakaria, S. Carboxylated nanoncellulose as a template for the synthesis of silver nanoprism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.W.; Ul-Islam, M.; Khan, S.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.K. Innovative production of bio-cellulose using a cell-free system derived from a single cell line. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Choi, Y.S.; Yoo, C.G.; Kim, T.H.; Brown, R.C.; Shanks, B.H. Cellulose-hemicellulose and cellulose-lignin interactions during fast pyrolysis. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, M.; Li, A.Y.; Hudson, R.; Masnadi, M.; Li, C.J.; Moores, A. Reversing aggregation: Direct synthesis of nanocatalysts from bulk metal. Cellulose nanocrystals as active support to access efficient hydrogenation silver nanocatalysts. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.F.; Zhao, D.Y.; Hou, C.; Li, H.; Liang, C. Facile one-pot synthesis of cellulose nanocrystal-supported hollow CuFe2O4 nanoparticles as efficient catalyst for 4-nitrophenol reduction. J. Nanopart. Res. 2018, 20, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.B.; Branco, P.S.; Varma, R.S. Nano-magnetite (Fe3O4) as a support for recyclable catalysts in the development of sustainable methodologies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3371–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Mendoza-Garcia, A.; Li, Q.; Sun, S. Organic phase syntheses of magnetic nanoparticles and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10473–10512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.; Lu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.H.; Zhang, X. Nanofibrillated cellulose as the support and reductant for the facile synthesis of Fe3O4/Ag nanocomposites with catalytic and antibacterial activity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 14910–14918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Ni, Y.; Li, S. Chain-like Fe3O4@resorcinol-formaldehyde resins Ag composite microstructures: Facile construction and applications in antibacterial and catalytic fields. Rsc Adv. 2016, 6, 15831–15837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokouhimehr, M.; Shin, K.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Hackett, M.J.; Jun, S.W.; Oh, M.H.; Hyeon, T.; Jang, J. Magnetically recyclable core-shell nanocatalysts for efficient heterogeneous oxidation of alcohols. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7593–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, Q.; Duan, J. Magnetically separable nanocatalyst with the Fe3O4 core and polydopamine-sandwiched Au nanocrystal shell. Langmuir 2018, 34, 4298–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasaki, S.A.; Zhao, C.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Yang, M. Facile synthesis approach for preparation of robust and recyclable Ag/ZnO nanorods with high catalytic activity for 4-nitrophenol reduction. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 119, 110536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Sun, R. Facile synthesis of bifunctional Fe3O4/Au nanocomposite and their application in catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 57, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, B.; Yao, J.; Wang, A. TEMPO-oxidized bacterial cellulose nanofibers-supported gold nanoparticles with superior catalytic properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 160, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, C. One-pot achieving well-dispersed copper nanoparticles on N-doped carbon films. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 656, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.D.; Lu, C.H.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, G.P.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, X.X. A novel reagentless approach for synthesizing cellulose nanocrystal-supported palladium nanoparticles with enhanced catalytic performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8645–8652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Yue, R.; Zhang, X.D.; Huang, Y.M. Removal of silver nanoparticles by mussel-inspired Fe3O4@ polydopamine core-shell microspheres and its use as efficient catalyst for methylene blue reduction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Yuran, S.; Yan, J.; Lee, P.S.; Reches, M. Sticky tubes and magnetic hydrogels co-assembled by a short peptide and melanin-like nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 5432–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.H.; Zheng, Z.F.; Deng, C.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Yang, P.Y. Facile synthesis of Ti4+-immobilized Fe3O4@polydopamine core-shell microspheres for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5055–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryou, M.H.; Kim, J.B.; Lee, I.H.; Kim, S.J.; Jeong, Y.K.; Hong, S.K.; Choi, J.W.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, H.; Kim, T.S.; et al. Mussel-inspired adhesive binders for high-performance silicon nanoparticle anodes in lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.J.; Yang, Z.H.; Jia, J.L.; Li, X.; Luo, Y.; Fang, Y. Synthesis of yolk/shell Fe3O4-polydopamine-graphene-Pt nanocomposite with high electro catalytic activity for fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Zhang, X.L.; Niu, H.Y.; Ma, Y.R.; Li, W.H.; Cai, Y.Q. In situ growth of gold nanoparticles onto polydopamine-encapsulated magnetic microspheres for catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene. Appl. Catal. B 2013, 134, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Y.; Shi, Z.Q.; Fu, S.D.; Chen, J.L.; Berry, R.M.; Tam, K.C. Strategy for synthesizing porous cellulose nanocrystal supported metal nanocatalysts. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5929–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, C. Dual functional biocomposites based on polydopamine modified cellulose nanocrystal for Fe3+-pollutant detecting and autoblocking. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5667–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Song, Y.; Tanvir, S.; Anderson, W.A.; Berry, R.M.; Tam, K.C. Polyrhodanine coated cellulose nanocrystals: A sustainable antimicrobial agent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.L.; Akita, T.; Ishida, T.; Haruta, M.; Xu, Q. Synergistic catalysis of Au@Ag core-shell nanoparticles stabilizedon metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1304–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zeng, H.C. Immobilization of metal-organic framework nanocrystals for advanced design of supported nanocatalysts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29551–29564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Spatial confinement of a Co3O4 catalyst in hollow metal-organic frameworks as a nanoreactor for improved degradation of organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2350–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.J.; Wang, P.C.; Wang, X.; Goh, Y.T.; Fang, Z.; Messersmith, P.B.; Duan, H. Versatile core-shell nanoparticle@metal-organic framework nanohybrids: Exploiting mussel-inspired polydopamine for tailored structural integration. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6951–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, E.J.; Duan, W.Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, A.Q.; Zheng, Y. Natural cellulose fiber derived hollow-tubular-orientedpolydopamine: In-situ formation of Ag nanoparticles for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 158, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.Y.; Long, Y.D.; Ni, Y.H. Cellulose nanocrystal/hexadecyl-trimethyl ammonium bromide/silvernanoparticle composite as a catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Gao, S.T.; Shang, N.Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Preparation of magnetically separable Cu6/7Co1/7Fe2O4-graphene catalyst and its application in selective reduction of nitroarenes. Catal. Commun. 2015, 59, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Kou, Q.W.; Chen, Y.; Han, D.L.; Wang, D.D.; Lu, Z.Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.H.; Xing, S. Eco-friendly seeded Fe3O4-Ag nanocrystals: A new type of highly efficient and low cost catalyst for methylene blue reduction. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 2209–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandia, A.; Jain, A.K.; Sharma, S. CuFe2O4 nanoparticles as a highly efficient and magnetically recoverable catalyst for the synthesis of medicinally privileged spiropyrimidine scaffolds. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 2924–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, M.; Qu, R.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. Catalytic degradation of diethyl phthalate in aqueous solution by persulfate activated with nano-scaled magnetic CuFe2O4/MWCNTs. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 301, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Meng, Q.; Liu, R.; Fu, S.Y.; Lucia, L.A. Physical study of the primary and secondary photo thermal events in gold/cellulose nanocrystals (Au NP/CNC) nanocomposites embedded in PVA matrices. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Zhang, C.H. A universal route for the simultaneous extraction and functionalization of cellulose nanocrystals from industrial and agricultural celluloses. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.C.; Wu, F.C.; Ye, G.; Yi, R.; Lu, Y.X. Surface-initiated SET-LRP mediated by mussel-inspired polydopamine chemistry for controlled building of novel core-shell magnetic nanoparticles for highly-efficient uranium enrichment. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.P.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Shi, J.F.; Wu, H. Facile preparation of porous magnetic polydopamine microspheres through an inverse replication strategy for efficient enzyme immobilization. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7194–7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X. Synthesis of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 magnetic core-shell microspheres and their potential application in a capillary microreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Wang, S.; Jia, J.; Xu, F.; Long, Z.; Hou, X. Ultrasensitive determination of inorganic arsenic by hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry using Fe3O4@ZIF-8 nanoparticles for preconcentration. Microchem. J. 2015, 124, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehria, S.M.; Almuqatia, T.; Almuqatib, N.; Al-Farraja, E.; Alhokbanya, N.; Ahamada, T. Chitosan based polymer matrix with silver nanoparticles decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenl. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarringhadam, P.; Farhadi, S. Flower-like Bi2O2CO3/NiFe2O4, magnetically recoverable nanocomposites: Preparation, characterization and their catalytic application in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 729, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.B.; Ning, R.; Qin, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Chang, G.H.; Liu, S.; Luo, Y.L.; Sun, X.P. Synthesis of Au nanoparticles decorated graphene oxide nanosheets: Noncovalent functionalization by TWEEN 20 in situ reduction of aqueous chloroaurate ions for hydrazine detection and catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 197, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Polavarapu, L.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Q. Mesoporous SnO2-Coated Metal Nanoparticles with Enhanced Catalytic Efficiency. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4844–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pach, P.; Kandambeth, S.; Díaz, D.D.; Banerjee, R. Highly stable covalent organic framework-Au nanoparticles hybrids for enhanced activity for nitrophenol reduction. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3169–3172. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.; Tu, J.; Wang, M.; Li, X. One-pot synthesis of ordered mesoporous silver nanoparticle/carbon composites for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 423, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Ma, B.; Jin, A. Facile loading of Ag nanoparticles onto magnetic microsphere by the aid of a tannic acid-metal polymer layer to synthesize magnetic disinfectant with high antibacterial activity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 342, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, C.; Rong, Z. Silver coated magnetic microflowers as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for catalytic reduction. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 14199–14208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yao, Y.; Xu, Y. Imparting catalytic activity to a covalent organic framework material by nanoparticle encapsulation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7481–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are unavailable from the authors. |

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Hou, C. Preparation of Magnetic CuFe2O4@Ag@ZIF-8 Nanocomposites with Highly Catalytic Activity Based on Cellulose Nanocrystals. Molecules 2020, 25, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010124
Zhang S, Xu Y, Zhao D, Chen W, Li H, Hou C. Preparation of Magnetic CuFe2O4@Ag@ZIF-8 Nanocomposites with Highly Catalytic Activity Based on Cellulose Nanocrystals. Molecules. 2020; 25(1):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010124
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Sufeng, Yongshe Xu, Dongyan Zhao, Wenqiang Chen, Hao Li, and Chen Hou. 2020. "Preparation of Magnetic CuFe2O4@Ag@ZIF-8 Nanocomposites with Highly Catalytic Activity Based on Cellulose Nanocrystals" Molecules 25, no. 1: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010124
APA StyleZhang, S., Xu, Y., Zhao, D., Chen, W., Li, H., & Hou, C. (2020). Preparation of Magnetic CuFe2O4@Ag@ZIF-8 Nanocomposites with Highly Catalytic Activity Based on Cellulose Nanocrystals. Molecules, 25(1), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010124