Selenocompounds as Novel Antibacterial Agents and Bacterial Efflux Pump Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
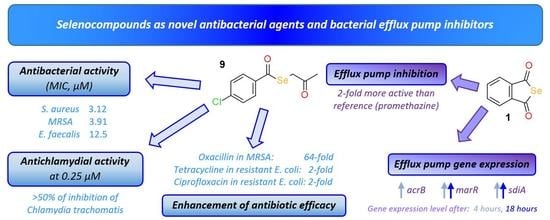
2. Results
2.1. Antibacterial Activity: Determination of the MIC
2.2. Enhancement of the Activity of Antibiotics
2.3. Anti-Chlamydial Activity
2.4. Real-Time Accumulation Assay
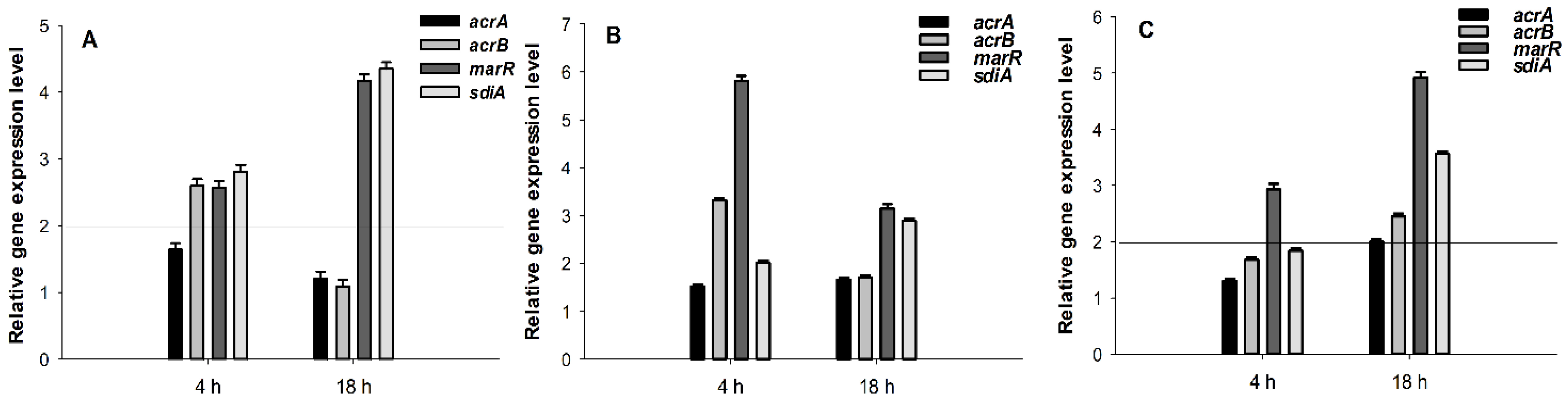
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis by Quantitative PCR
3. Discussion
3.1. Antibacterial Activity
3.2. Enhancement of the Activity of Antibiotics
3.3. Anti-Chlamydial Activity
3.4. Interaction of the Compounds with Bacterial Efflux Pumps
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.2. Bacterial Strains
4.3. Propagation of C. trachomatis D
4.4. Determination of MIC
4.5. Enhancement of the Activity of Antibiotics
4.6. Anti-Chlamydial Assay
4.7. Real-Time Accumulation Assay
4.8. Expression Analyses of Genes by Quantitative PCR
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drusano, G.L.; Louie, A.; MacGowan, A.; Hope, W. Suppression of Emergence of Resistance in Pathogenic Bacteria: Keeping Our Powder Dry, Part 1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 60, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobanov, A.V.; Hatfield, D.L.; Gladyshev, V.N. Eukaryotic selenoproteins and selenoproteomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1424–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinggi, U. Selenium: Its role as antioxidant in human health. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2008, 13, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, A.; Abbas, G.; del Prete, S.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Selenides bearing benzenesulfonamide show potent inhibition activity against carbonic anhydrases from pathogenic bacteria Vibrio cholerae and Burkholderia pseudomallei. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 79, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, H.; Gao, Y.; Shan, H.; Lin, Y. Preparation and antibacterial activity studies of degraded polysaccharide selenide from Enteromorpha prolifera. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 107, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek, K.; Nasim, M.; Bischoff, M.; Gaupp, R.; Arsenyan, P.; Vasiljeva, J.; Marć, M.; Olejarz, A.; Latacz, G.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; et al. Selenazolinium Salts as “Small Molecule Catalysts” with High Potency against ESKAPE Bacterial Pathogens. Molecules 2017, 22, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Gajdács, M.; Spengler, G.; Palop, J.A.; Marć, M.A.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; Amaral, L.; Molnár, J.; Jacob, C.; Handzlik, J.; et al. Identification of selenocompounds with promising properties to reverse cancer multidrug resistance. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2821–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajdács, M.; Spengler, G.; Sanmartín, C.; Marć, M.A.; Handzlik, J.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E. Selenoesters and selenoanhydrides as novel multidrug resistance reversing agents: A confirmation study in a colon cancer MDR cell line. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handzlik, J.; Matys, A.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. Recent Advances in Multi-Drug Resistance (MDR) Efflux Pump Inhibitors of Gram-Positive Bacteria S. aureus. Antibiotics 2013, 2, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, G.; Iannelli, F.; Oggioni, M.R.; Santagati, M.; Stefani, S. Genetic elements carrying macrolide efflux genes in streptococci. Curr. Drug Targets Infect. Disord. 2004, 4, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, E.; Ross, J.I.; Cove, J.H. Msr(A) and related macrolide/streptogramin resistance determinants: Incomplete transporters? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2003, 22, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, G.T.; Doyle, T.B.; Lynch, A.S. Use of an efflux-deficient streptococcus pneumoniae strain panel to identify ABC-class multidrug transporters involved in intrinsic resistance to antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4781–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daury, L.; Orange, F.; Taveau, J.-C.; Verchère, A.; Monlezun, L.; Gounou, C.; Marreddy, R.K.R.; Picard, M.; Broutin, I.; Pos, K.M.; et al. Tripartite assembly of RND multidrug efflux pumps. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Pande, A.; Sabrin, A.; Thapa, S.S.; Gioe, B.W.; Grove, A. MarR Family Transcription Factors from Burkholderia Species: Hidden Clues to Control of Virulence-Associated Genes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2018, 83, e00039-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovic, S.; Brown, M.H.; Skurray, R.A. Regulation of bacterial drug export systems. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 671–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavío, M.M.; Aquili, V.D.; Poveda, J.B.; Antunes, N.T.; Sánchez-Céspedes, J.; Vila, J. Quorum-sensing regulator sdiA and marA overexpression is involved in in vitro-selected multidrug resistance of Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holinka, J.; Pilz, M.; Kubista, B.; Presterl, E.; Windhager, R. Effects of selenium coating of orthopaedic implant surfaces on bacterial adherence and osteoblastic cell growth. Bone Joint J. 2013, 95, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.S.; Tiwari, S.K.; Manoj, G.; Kunwar, A.; Amrita, N.; Sivaram, G.; Abid, Z.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, A.A.; Priyadarsini, K.I. Anti-unlcer and antimicrobial activities of sodium selenite against Helicobacter pylori: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 42, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aribi, M.; Meziane, W.; Habi, S.; Boulatika, Y.; Marchandin, H.; Aymeric, J.-L. Macrophage Bactericidal Activities against Staphylococcus aureus Are Enhanced In Vivo by Selenium Supplementation in a Dose-Dependent Manner. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhwani, S.A.; Shedbalkar, U.U.; Singh, R.; Chopade, B.A. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles: Current status and future prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2555–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihalova, K.; Chudobova, D.; Michalek, P.; Moulick, A.; Guran, R.; Kopel, P.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA Growth and Biofilm Formation after Treatment with Antibiotics and SeNPs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 24656–24672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudobova, D.; Cihalova, K.; Dostalova, S.; Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Rodrigo, M.A.M.; Tmejova, K.; Kopel, P.; Nejdl, L.; Kudr, J.; Gumulec, J.; et al. Comparison of the effects of silver phosphate and selenium nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus growth reveals potential for selenium particles to prevent infection. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 351, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, M.; Filipović, N.; Djurdjević, J.; Lukić, M.; Milenković, M.; Boccaccini, A. 45S5Bioglass®-based scaffolds coated with selenium nanoparticles or with poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/selenium particles: Processing, evaluation and antibacterial activity. Colloid. Surf. B 2015, 132, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Yu, Q.; Sun, D.; Liu, J. Investigation of functional selenium nanoparticles as potent antimicrobial agents against superbugs. Acta Biomater. 2016, 30, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkusre, P.; Singh Cameotra, S. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles inhibit Staphylococcus aureus adherence on different surfaces. Colloid. Surf. B 2015, 136, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, N.; Mukhopadhyay, M. Green synthesis and structural characterization of selenium nanoparticles and assessment of their antimicrobial property. Bioproc. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoz, K.M.; Rockey, D.D. Antibiotic resistance in Chlamydiae. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1427–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestrovic, T.; Ljubin-Sternak, S. Molecular mechanisms of Chlamydia trachomatis resistance to antimicrobial drugs. Front Biosci. 2018, 23, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, C.A.; Nikaido, H. Substrate specificity of the RND-type multidrug efflux pumps AcrB and AcrD of Escherichia coli is determined predominantly by two large periplasmic loops. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 6490–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, V.; Piddock, L.J.V. Only for substrate antibiotics are a functional AcrAB-TolC efflux pump and RamA required to select multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paixão, L.; Rodrigues, L.; Couto, I.; Martins, M.; Fernandes, P.; de Carvalho, C.C.C.R.; Monteiro, G.A.; Sansonetty, F.; Amaral, L.; Viveiros, M. Fluorometric determination of ethidium bromide efflux kinetics in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Eng. 2009, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmartín, C.; Plano, D.; Domínguez, E.; Font, M.; Calvo, A.; Prior, C.; Encío, I.; Palop, J.A. Synthesis and pharmacological screening of several aroyl and heteroaroyl selenylacetic acid derivatives as cytotoxic and antiproliferative agents. Molecules 2009, 14, 3313–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Plano, D.; Font, M.; Calvo, A.; Prior, C.; Jacob, C.; Palop, J.A.; Sanmartín, C. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of novel selenoester derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 73, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Argelich, N.; Encío, I.; Plano, D.; Fernandes, A.P.; Palop, J.A.; Sanmartín, C. Novel Methylselenoesters as Antiproliferative Agents. Molecules 2017, 22, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, G.; Gajdács, M.; Marć, M.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Sanmartín, C. Organoselenium Compounds as Novel Adjuvants of Chemotherapy Drugs—A Promising Approach to Fight Cancer Drug Resistance. Molecules 2019, 24, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Rubio, C.; Campbell, D.; Vacas, A.; Ibañez, E.; Moreno, E.; Espuelas, S.; Calvo, A.; Palop, J.A.; Plano, D.; Sanmartin, C.; et al. Leishmanicidal Activities of Novel Methylseleno-Imidocarbamates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5705–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martín-Montes, Á.; Plano, D.; Martín-Escolano, R.; Alcolea, V.; Díaz, M.; Pérez-Silanes, S.; Espuelas, S.; Moreno, E.; Marín, C.; Gutiérrez-Sánchez, R.; et al. Library of Seleno-Compounds as Novel Agents against Leishmania Species. Antimicrobial. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02546-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Z.; Plésiat, P.; Nikaido, H. The challenge of efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 337–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, H.; Pagès, J.-M. Broad-specificity efflux pumps and their role in multidrug resistance of Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 340–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, A.; Endrész, V.; Urbán, S.; Lantos, I.; Deák, J.; Burián, K.; Önder, K.; Ayaydin, F.; Balázs, P.; Virok, D.P. Application of DNA chip scanning technology for automatic detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Chlamydia pneumoniae inclusions. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute: CLSI Guidelines. Available online: https://clsi.org/ (accessed on 24 July 2017).
- Balogh, E.P.; Faludi, I.; Virók, D.P.; Endrész, V.; Burián, K. Chlamydophila pneumoniae induces production of the defensin-like MIG/CXCL9, which has in vitro antichlamydial activity. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viveiros, M.; Martins, A.; Paixão, L.; Rodrigues, L.; Martins, M.; Couto, I.; Fähnrich, E.; Kern, W.V.; Amaral, L. Demonstration of intrinsic efflux activity of Escherichia coli K-12 AG100 by an automated ethidium bromide method. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 31, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincses, A.; Szabó, Á.M.; Saijo, R.; Watanabe, G.; Kawase, M.; Molnár, J.; Spengler, G. Fluorinated Beta-diketo Phosphorus Ylides Are Novel Efflux Pump Inhibitors in Bacteria. In Vivo 2016, 30, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viveiros, M.; Dupont, M.; Rodrigues, L.; Couto, I.; Davin-Regli, A.; Martins, M.; Pagès, J.-M.; Amaral, L. Antibiotic stress, genetic response and altered permeability of E. coli. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |

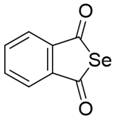 | 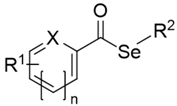 | ||||
| I. Cyclic selenoanhydride (1) | II. Selenoesters (2–11) | ||||
| Compound | Group | R1 | X | n | R2 |
| 1 | I | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | II | 5-COSeCH3 | S | 0 | -CH3 |
| 3 | II | 6-COSeCH3 | N | 1 | -CH3 |
| 4 | II | 3-COSeCH3 | C | 1 | -CH3 |
| 5 | II | 4-COSeCH3 | C | 1 | -CH3 |
| 6 | II | -H | C | 1 | -CH2CONH2 |
| 7 | II | 4−Cl | C | 1 | -CH2COOCH3 |
| 8 | II | -H | C | 1 | -CH2COOPh |
| 9 | II | 4−Cl | C | 1 | -CH2COCH3 |
| 10 | II | 4−Cl | C | 1 | -CH2COC(CH3)3 |
| 11 | II | 3,5-diOCH3 | C | 1 | -CH2COC(CH3)3 |
| Compounds | MIC (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | Staphylococcus aureus HEMSA 5 | Enterococcus Faecalis ATCC 29212 | |
| 1 | >100 | >125 | >100 |
| 2 | 100 | >125 | >100 |
| 3 | 100 | >125 | >100 |
| 4 | 100 | >125 | >100 |
| 5 | >100 | >125 | >100 |
| 6 | >100 | >125 | >100 |
| 7 | 100 | 125 | >100 |
| 8 | 100 | >125 | >100 |
| 9 | 3.12 | 3.91 | 12.5 |
| 10 | 25 | >125 | >100 |
| 11 | 50 | >125 | >100 |
| Cpd1 | MRSA HEMSA 5 | Escherichia coli AG100 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration of Compound [µM]2 | Reduction of Oxacillin MIC | Concentration of Compound [µM] | Reduction of Tetracycline mic | Reduction of Ciprofloxacin mic | |
| 1 | 62.5 | no effect | 50 | no effect | no effect |
| 2 | ND | ND 3 | 50 | no effect | no effect |
| 3 | 62.5 | 2-fold | 50 | no effect | no effect |
| 4 | 62.5 | no effect | 50 | no effect | no effect |
| 5 | 62.5 | no effect | 50 | no effect | no effect |
| 6 | 62.5 | no effect | 50 | no effect | no effect |
| 7 | 62.5 | ≥ 2-fold | 50 | no effect | no effect |
| 8 | 62.5 | 2-fold | 50 | no effect | no effect |
| 9 | 1.95 | 64-fold | 25 | 2-fold | 2-fold |
| 10 | 62.5 | no effect | 50 | no effect | 2-fold |
| 11 | 62.5 | no effect | 50 | no effect | no effect |
| Compound | RFIa | Compound | RFIa | Compound | RFIa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli AG100 | Escherichia coli AG100 | Escherichia coli AG100 | |||
| 1 | 0.28 | 5 | 0.04 | 9 | 0.11 |
| 2 | 0.03 | 6 | 0.06 | 10 | 0.12 |
| 3 | 0.04 | 7 | 0.13 | 11 | 0.11 |
| 4 | 0.18 | 8 | 0.08 | PMZ | 0.15 |
| Gene | Full Name | Primer Sequence (5’–3’) | Amplicon size (bp) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| acrA | Acridine resistance protein A | CTTAGCCCTAACAGGATGTG TTGAAATTACGCTTCAGGAT | 189 | [45] |
| acrB | Acridine resistance protein B | CGTACACAGAAAGTGCTCAA CGCTTCAACTTTGTTTTCTT | 183 | [45] |
| marR | Multiple antibiotic resistance protein R | AGCGATCTGTTCAATGAAAT TTCAGTTCAACCGGAGTAAT | 170 | [45] |
| sdiA | Quorum-sensing transcriptional activator | CTGATGGCTCTGATGCGTTTA TCTGGTGGAAATTGACCGTATT | 163 | [44] |
| gapdh | Glyceraldehyde-3-phospate dehydrogenase | ACTTACGAGCAGATCAAAGC AGTTTCACGAAGTTGTCGTT | 170 | [45] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mosolygó, T.; Kincses, A.; Csonka, A.; Tönki, Á.S.; Witek, K.; Sanmartín, C.; Marć, M.A.; Handzlik, J.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; et al. Selenocompounds as Novel Antibacterial Agents and Bacterial Efflux Pump Inhibitors. Molecules 2019, 24, 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081487
Mosolygó T, Kincses A, Csonka A, Tönki ÁS, Witek K, Sanmartín C, Marć MA, Handzlik J, Kieć-Kononowicz K, Domínguez-Álvarez E, et al. Selenocompounds as Novel Antibacterial Agents and Bacterial Efflux Pump Inhibitors. Molecules. 2019; 24(8):1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081487
Chicago/Turabian StyleMosolygó, Tímea, Annamária Kincses, Andrea Csonka, Ádám Szabó Tönki, Karolina Witek, Carmen Sanmartín, Małgorzata Anna Marć, Jadwiga Handzlik, Katarzyna Kieć-Kononowicz, Enrique Domínguez-Álvarez, and et al. 2019. "Selenocompounds as Novel Antibacterial Agents and Bacterial Efflux Pump Inhibitors" Molecules 24, no. 8: 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081487
APA StyleMosolygó, T., Kincses, A., Csonka, A., Tönki, Á. S., Witek, K., Sanmartín, C., Marć, M. A., Handzlik, J., Kieć-Kononowicz, K., Domínguez-Álvarez, E., & Spengler, G. (2019). Selenocompounds as Novel Antibacterial Agents and Bacterial Efflux Pump Inhibitors. Molecules, 24(8), 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081487