Nrf2–ARE Signaling Acts as Master Pathway for the Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Fisetin
Abstract
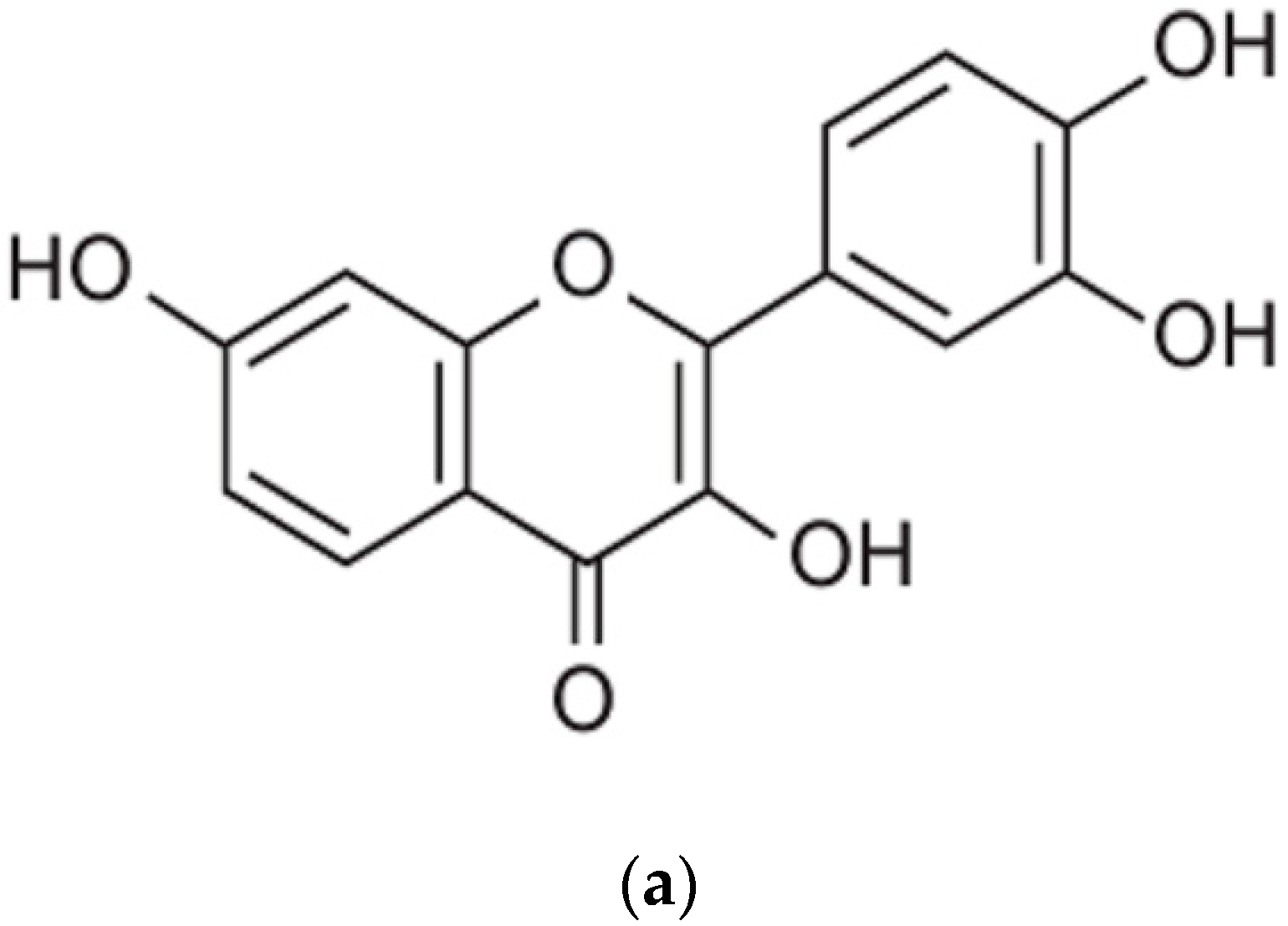
1. Introduction
2. Results
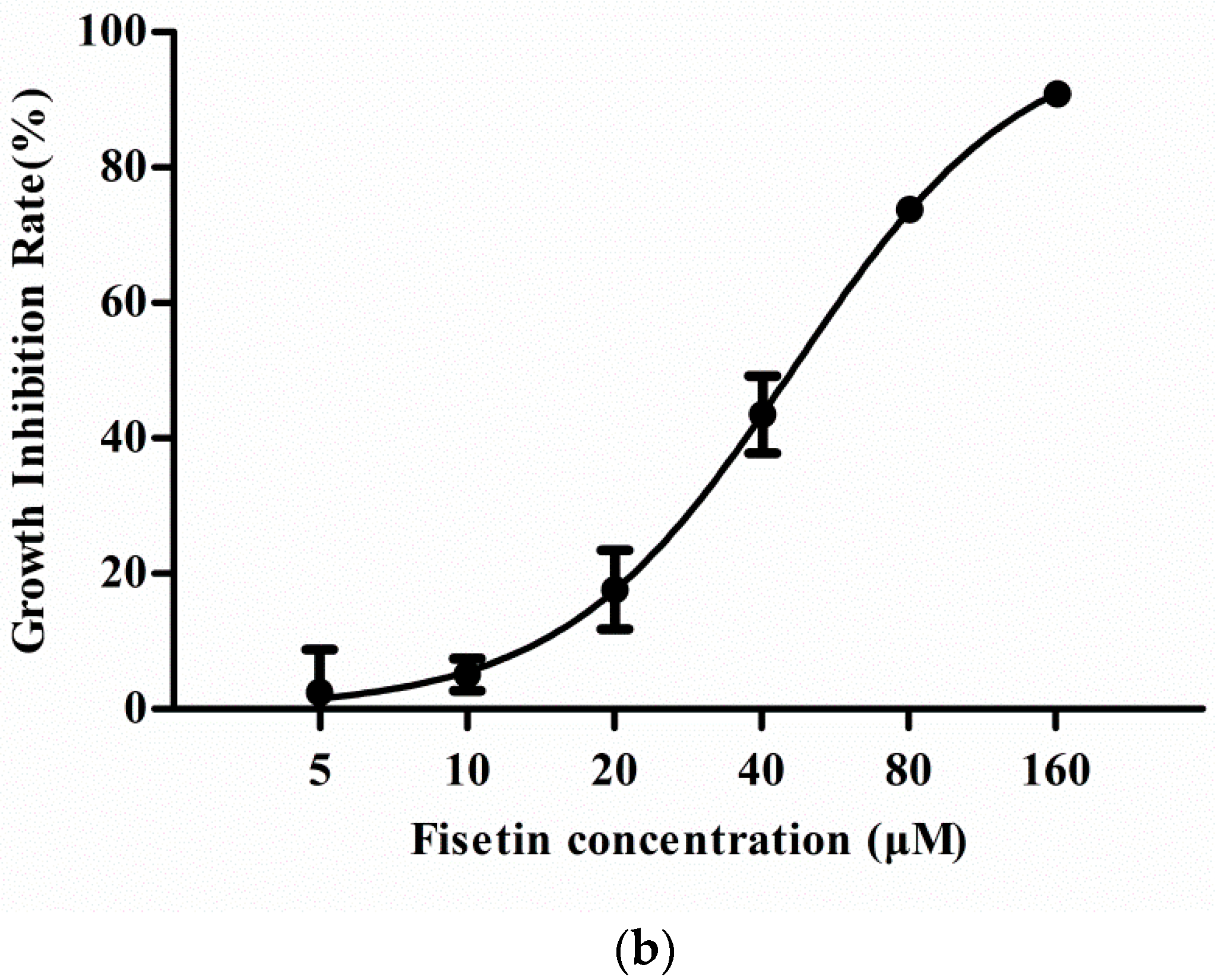
2.1. Effect of Fisetin on Cell Viability
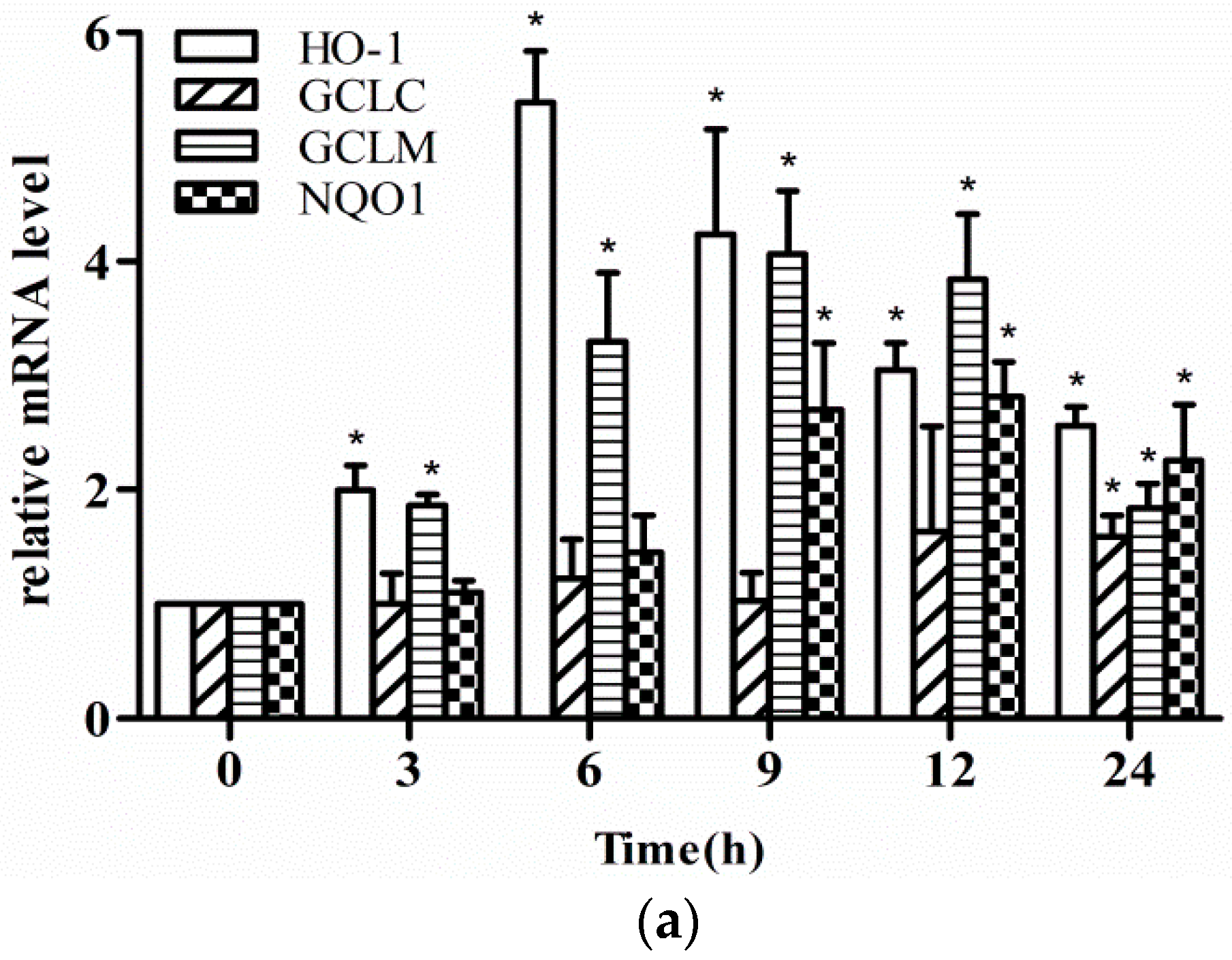
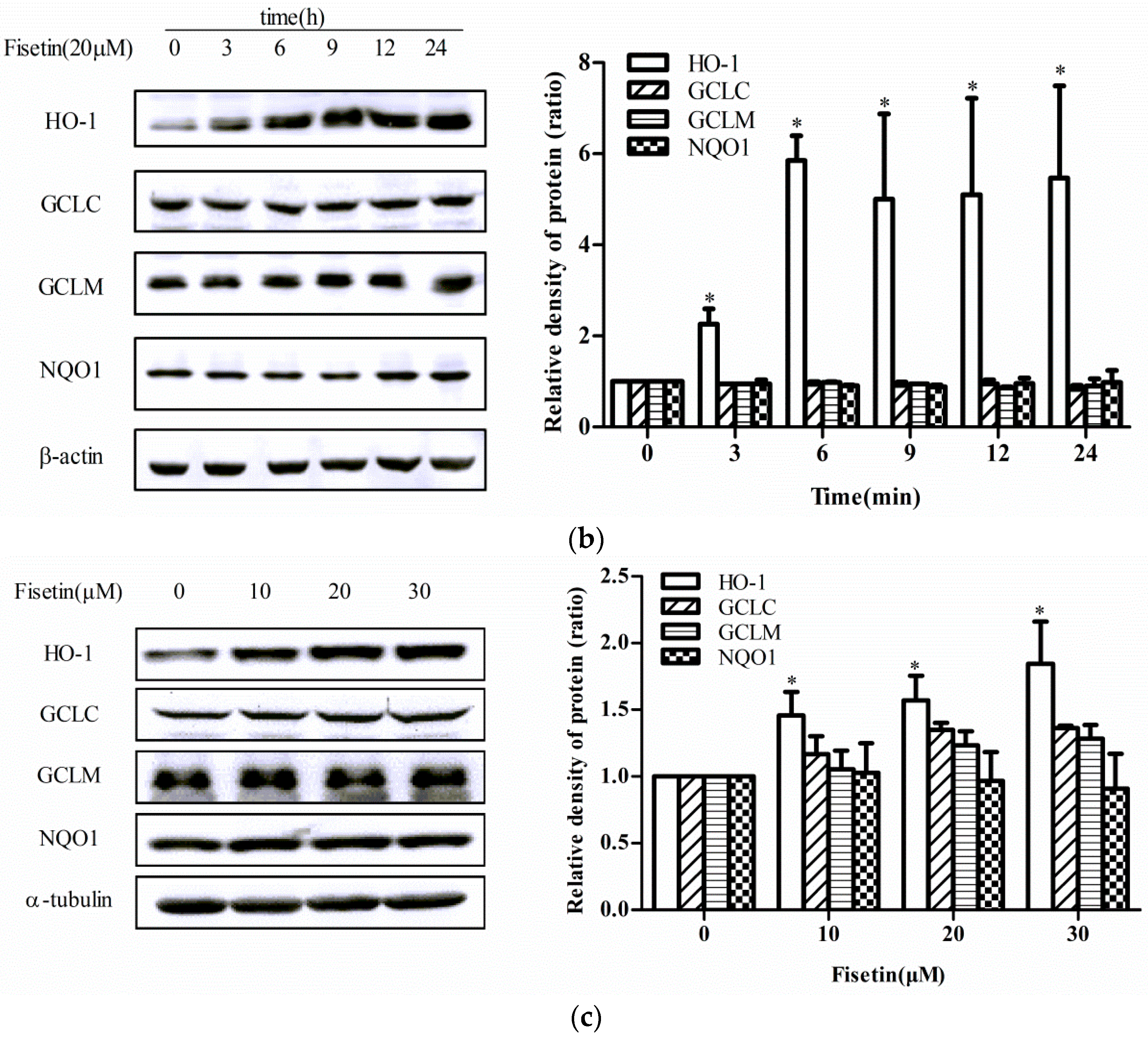
2.2. Effect of Fisetin on the Level of Phase II Enzyme
2.3. Fisetin-Induced Nuclear Accumulation of Nrf2
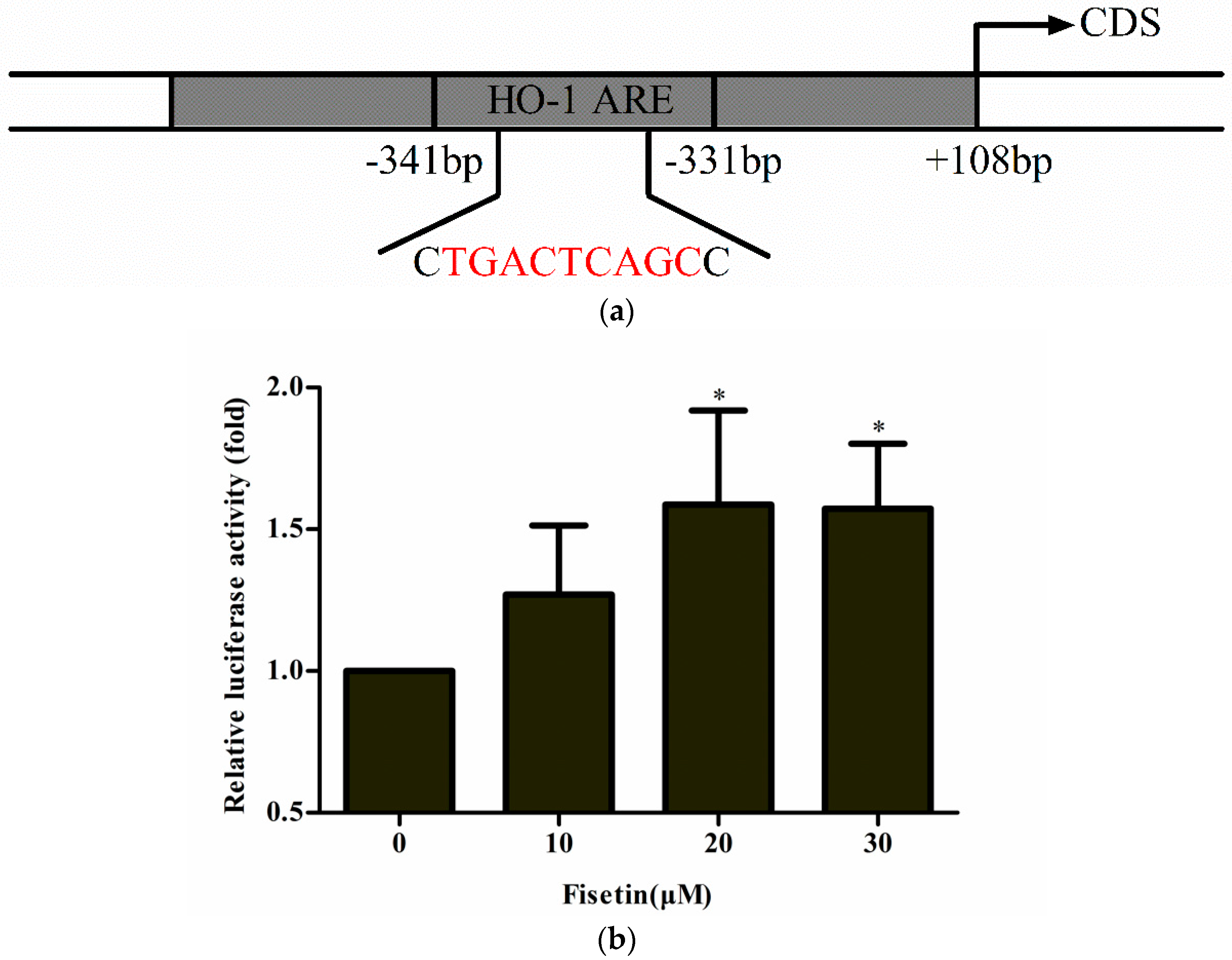
2.4. Effect of Fisetin on the Transcriptional Activity of ARE-Regulated Luciferase Activity
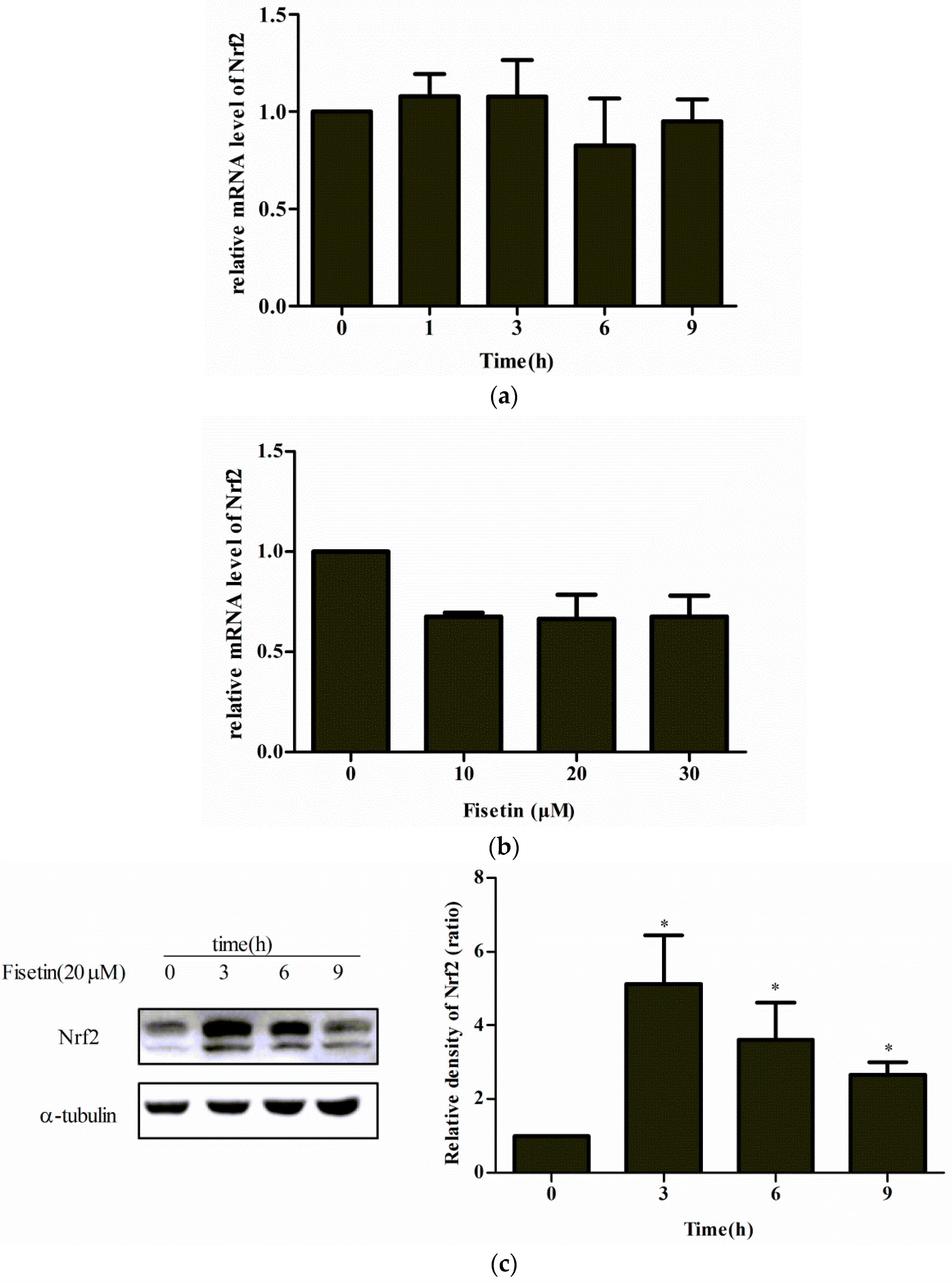
2.5. Effect of Fisetin on Nrf2 Expression
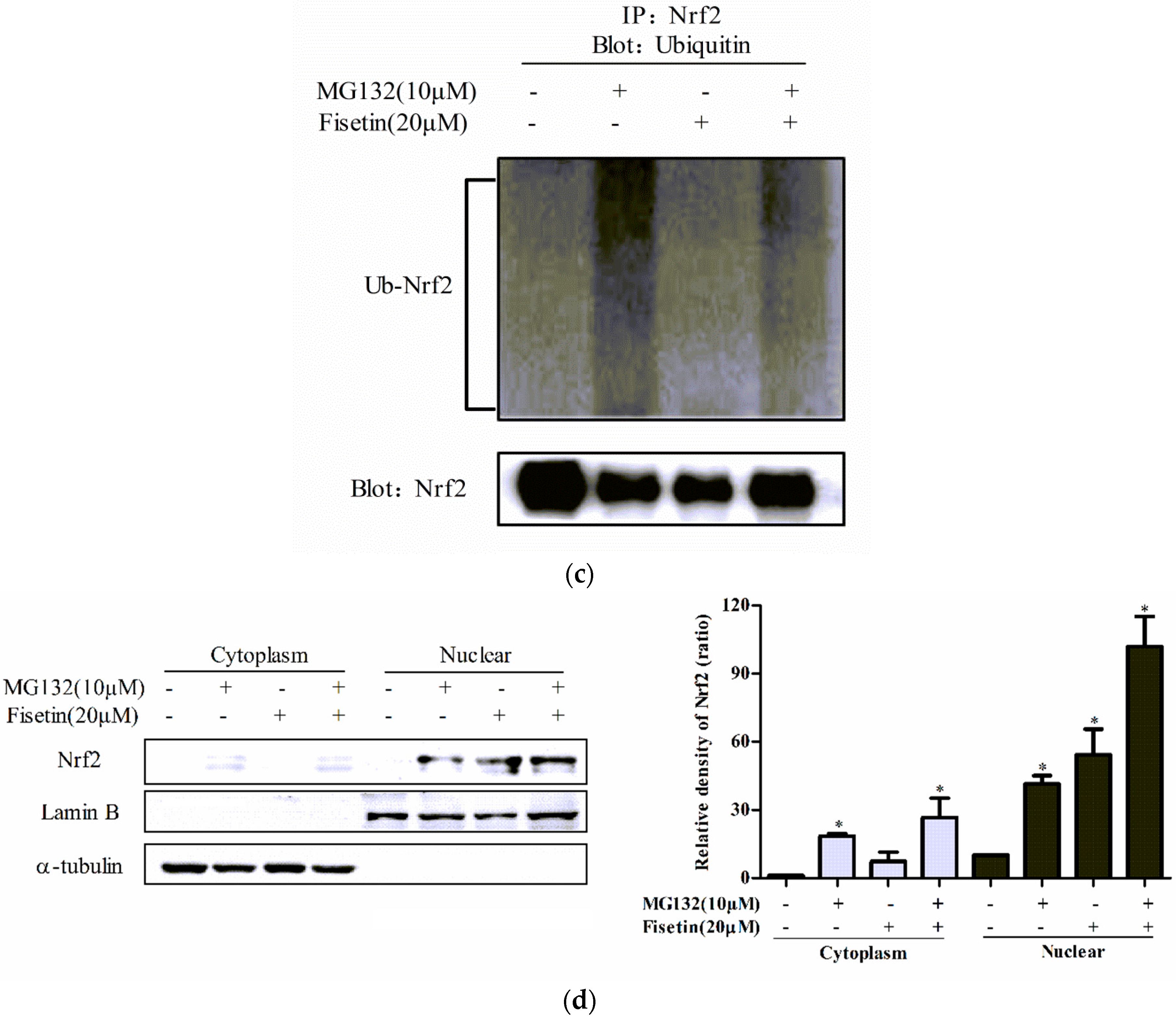
2.6. Fisetin Increased the Stability of Nrf2 Protein
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Immunofluorescence Assay
4.7. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
- 5′-GACTGAGGGTGACTCAGCAAAATCACTGAGGGTGACTCAGCAAAATC-3′
- 3′-CTGACTCCCACTGAGTCGTTTTAGTGACTCCCACTGAGTCGTTTTAG-5′.
4.8. Immunoprecipitation
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayyan, M.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Superoxide Ion: Generation and Chemical Implications. Chemical Reviews. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3029–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasagayam, T.P.; Tilak, J.C.; Boloor, K.K.; Sane, K.S.; Ghaskadbi, S.S.; Lele, R.D. Free radicals and antioxidants in human health: Current status and future prospects. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2004, 52, 794–804. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W.; Ijaz, B.; Shabbiri, K.; Ahmed, F.; Rehman, S. Oxidative toxicity in diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms behind ROS/ RNS generation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspita, L.; Chung, S.Y.; Shim, J.W. Oxidative stress and cellular pathologies in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheignon, C.; Tomas, M.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; Collin, F. Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Redox. Biol. 2018, 14, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santilli, F.; Guagnano, M.T.; Vazzana, N.; La, B.S.; Davi, G. Oxidative stress drivers and modulators in obesity and cardiovascular disease: From biomarkers to therapeutic approach. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, B.S.; Chavez-Moreno, A.; Koh, W.; Akar, J.G.; Akar, F.G. Oxidative stress and inflammation as central mediators of atrial fibrillation in obesity and diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Chen, J.; Tanigawa, S.; Hou, D.X. Gene expression profiling and pathway network analysis of hepatic metabolic enzymes targeted by baicalein. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 140, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dong, H.; Song, E.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Song, Y. Nrf2/ARE pathway activation, HO-1 and NQO1 induction by polychlorinated biphenyl quinone is associated with reactive oxygen species and PI3K/AKT signaling. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 209, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.S. Protopanaxatriol Ginsenoside Rh1 Upregulates Phase II Antioxidant Enzyme Gene Expression in Rat Primary Astrocytes: Involvement of MAP Kinases and Nrf2/ARE Signaling. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Chang, Z.; Han, W.; Wang, L.; Hong, G. Curcumin reduces paraquat-induced oxidative injury in A549 cells by activation of the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2014, 32, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.; Chen, J.; Tanigawa, S.; Hou, D.X. Microarray and pathway analysis highlight Nrf2/ARE-mediated expression profiling by polyphenolic myricetin. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanigawa, S.; Fujii, M.; Hou, D.X. Action of Nrf2 and Keap1 in ARE-mediated NQO1 expression by quercetin. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 1690–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Kimira, M.; Shimoi, K.; Mochizuki, R.; Kinae, N. Dietary intakes of flavonols, flavones and isoflavones by Japanese women and the inverse correlation between quercetin intake and plasma LDL cholesterol concentration. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.A.; Piao, M.J.; Madduma, H.S.; Ryu, Y.S.; Oh, M.C.; Kwon, T.K.; Chae, S.; Hyun, J.W. Fisetin induces apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in human non-small cell lung cancer through inhibition of the MAPK signaling pathway. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 9615–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, E.M.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, H.R.; Song, H.K.; Hong, O.Y.; So, H.S.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Fisetin regulates TPA-induced breast cell invasion by suppressing matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation via the PKC/ROS/MAPK pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 764, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hytti, M.; Piippo, N.; Korhonen, E.; Honkakoski, P.; Kaarniranta, K.; Kauppinen, A. Fisetin and luteolin protect human retinal pigment epithelial cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death and regulate inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.H.; Wang, C.X.; Xie, G.B.; Wu, L.Y.; Wei, Y.X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.S.; Hang, C.H.; Zhou, M.L.; Shi, J.X. Fisetin alleviates early brain injury following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats possibly by suppressing TLR 4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Brain Res. 2015, 1629, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, D.; Sudhandiran, G. Dietary flavonoid fisetin regulates aluminium chloride-induced neuronal apoptosis in cortex and hippocampus of mice brain. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.A.; Piao, M.J.; Kim, K.C.; Cha, J.W.; Zheng, J.; Yao, C.W.; Chae, S.; Hyun, J.W. Fisetin attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced cell damage by scavenging reactive oxygen species and activating protective functions of cellular glutathione system. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2014, 50, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaee, S.B.; Beetham, K.S.; Howden, E.J.; Stanton, T.; Isbel, N.M.; Coombes, J.S. Oxidative stress is associated with decreased heart rate variability in patients with chronic kidney disease. Redox Rep. 2017, 22, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, T.; Farrar, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, X. Antioxidants Maintain Cellular Redox Homeostasis by Elimination of Reactive Oxygen Species. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 532–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Gasparrini, M.; Afrin, S.; Cianciosi, D.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Mezzetti, B.; Quiles, J.L.; Battino, M.; Giampieri, F.; et al. Strawberry (cv. Romina) Methanolic Extract and Anthocyanin-Enriched Fraction Improve Lipid Profile and Antioxidant Status in HepG2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Ho, Y.R.; Wu, M.J.; Huang, S.P.; Chen, P.K.; Tai, M.H.; Ho, C.T.; Yen, J.H. Cytoprotective effects of fisetin against hypoxia-induced cell death in PC12 cells. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, P. A comparison of the neurotrophic activities of the flavonoid fisetin and some of its derivatives. Free Radic. Res. 2006, 40, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.H.; Wu, P.S.; Chen, S.F.; Wu, M.J. Fisetin Protects PC12 Cells from Tunicamycin-Mediated Cell Death via Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging and Modulation of Nrf2-Driven Gene Expression, SIRT1 and MAPK Signaling in PC12 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehren, J.L.; Maher, P. Concurrent regulation of the transcription factors Nrf2 and ATF4 mediates the enhancement of glutathione levels by the flavonoid fisetin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1816–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, G.; Bin, P.; Meng, T.; Niu, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L.; Duan, H.; Yu, T.; Dai, Y.; et al. Time-course effects of antioxidants and phase II enzymes on diesel exhaust particles-induced oxidative damage in the mouse lung. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, E.; Shimada-Sugawara, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Sakamoto, H.; Fumimoto, R.; Fukuma, Y.; Nishishita, K.; Okamoto, K.; Tsukuba, T. Fisetin inhibits osteoclastogenesis through prevention of RANKL-induced ROS production by Nrf2-mediated up-regulation of phase II antioxidant enzymes. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 121, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Fei, M. Fisetin alleviates oxidative stress after traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 118, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Sherratt, P.J.; Huang, H.C.; Yang, C.S.; Pickett, C.B. Increased protein stability as a mechanism that enhances Nrf2-mediated transcriptional activation of the antioxidant response element. Degradation of Nrf2 by the 26 S proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 4536–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Chen, M.G.; Lin, G.X.; Ma, Q. Arsenic induces NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase I by disrupting the Nrf2·Keap1·Cul3 complex and recruiting Nrf2·Maf to the antioxidant response element enhancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 23620–23631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Motohashi, H.; Yamamoto, M. Toward clinical application of the Keap1–Nrf2 pathway. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilenko, M.; Studzinski, G.P. Keep Harm at Bay: Oxidative Phosphorylation Induces Nrf2-Driven Antioxidant Response Via ERK5/MEF2/miR-23a Signaling to Keap-1. Ebiomedicine 2016, 3, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.L.; He, H.T.; Li, M.X.; Zhu, J.W.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, N.; Wang, G.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.Q.; He, Y.; et al. APE1 promotes antioxidant capacity by regulating Nrf-2 function through a redox-dependent mechanism. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 78, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tertil, M.; Golda, S.; Skrzypek, K.; Florczyk, U.; Weglarczyk, K.; Kotlinowski, J.; Maleszewska, M.; Czauderna, S.; Pichon, C.; Kieda, C.; et al. Nrf2-heme oxygenase-1 axis in mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the lung: Antitumoral effects associated with down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 89, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saw, C.L.; Guo, Y.; Yang, A.Y.; Paredes-Gonzalez, X.; Ramirez, C.; Pung, D.; Kong, A.N. The berry constituents quercetin, kaempferol, and pterostilbene synergistically attenuate reactive oxygen species: Involvement of the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 72, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.G.; Zhang, G.D.; Shi, P.Q.; Du, B.S. Expression and antioxidation of Nrf2/ARE pathway in traumatic brain injury. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2013, 6, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Jeong, S.I.; Yang, H.; Park, C.S.; Jin, Y.H.; Park, Y.S. Fisetin induces Nrf2-mediated HO-1 expression through PKC-delta and p38 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2011, 112, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, A.; Kang, M.I.; Okawa, H.; Ohtsuji, M.; Zenke, Y.; Chiba, T.; Igarashi, K.; Yamamoto, M. Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Nioi, P.; Pickett, C.B. The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13291–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, G.; Zhou, M.; Xiang, L.; Ren, D.; Lou, H.; Wang, X.; Shen, T. Discovery of natural flavonoids as activators of Nrf2-mediated defense system: Structure-activity relationship and inhibition of intracellular oxidative insults. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 5140–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyninck, K.; Sabbe, L.; Chirumamilla, C.S.; Szarc, V.S.; Vander, V.P.; Lemmens, K.J.A.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Naulaerts, S.; Op, B.K.; Laukens, K.; et al. Withaferin A induces heme oxygenase (HO-1) expression in endothelial cells via activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 109, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korenori, Y.; Tanigawa, S.; Kumamoto, T.; Qin, S.; Daikoku, Y.; Miyamori, K.; Nagai, M.; Hou, D.X. Modulation of Nrf2/Keap1 system by Wasabi 6-methylthiohexyl isothiocyanate in ARE-mediated NQO1 expression. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zheng, W.; Feng, X.; Yang, F.; Qin, H.; Wu, S.; Hou, D.-X.; Chen, J. Nrf2–ARE Signaling Acts as Master Pathway for the Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Fisetin. Molecules 2019, 24, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040708
Zhang H, Zheng W, Feng X, Yang F, Qin H, Wu S, Hou D-X, Chen J. Nrf2–ARE Signaling Acts as Master Pathway for the Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Fisetin. Molecules. 2019; 24(4):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040708
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huihui, Wan Zheng, Xiangling Feng, Fei Yang, Hong Qin, Shusong Wu, De-Xing Hou, and Jihua Chen. 2019. "Nrf2–ARE Signaling Acts as Master Pathway for the Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Fisetin" Molecules 24, no. 4: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040708
APA StyleZhang, H., Zheng, W., Feng, X., Yang, F., Qin, H., Wu, S., Hou, D.-X., & Chen, J. (2019). Nrf2–ARE Signaling Acts as Master Pathway for the Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Fisetin. Molecules, 24(4), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040708





