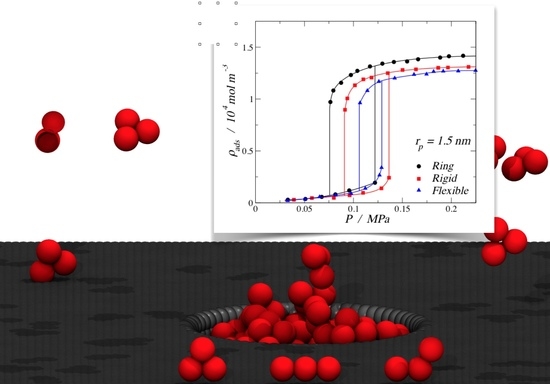
Molecular Simulation of the Adsorption and Diffusion in Cylindrical Nanopores: Effect of Shape and Fluid–Solid Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
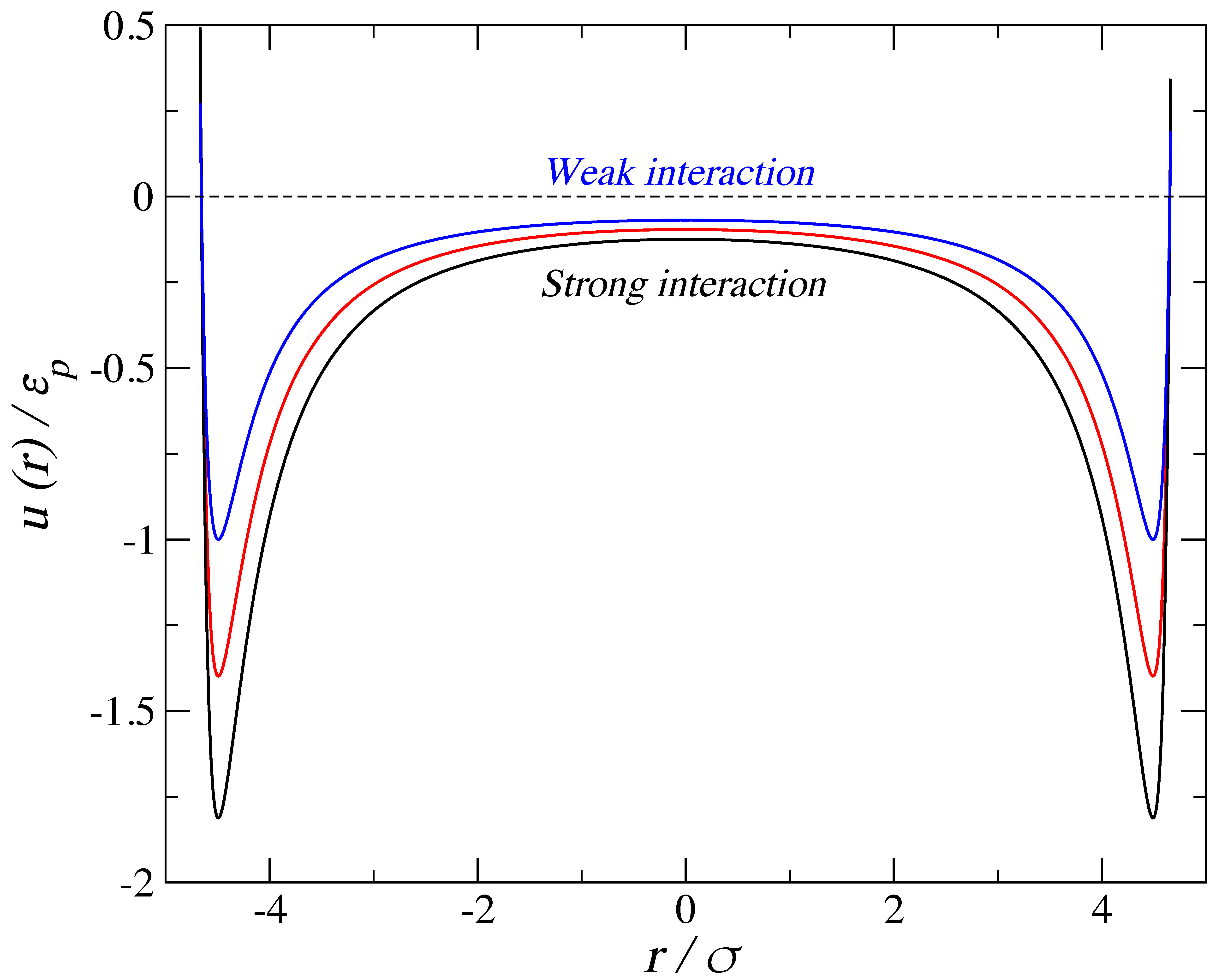
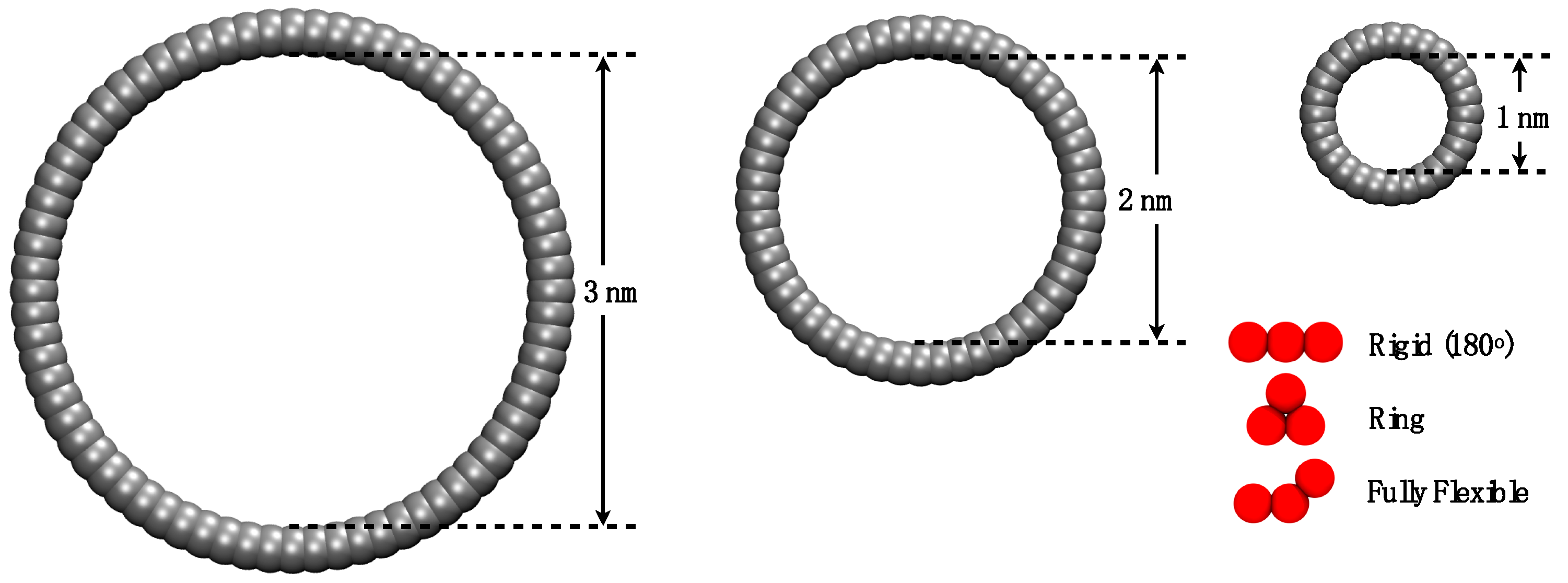
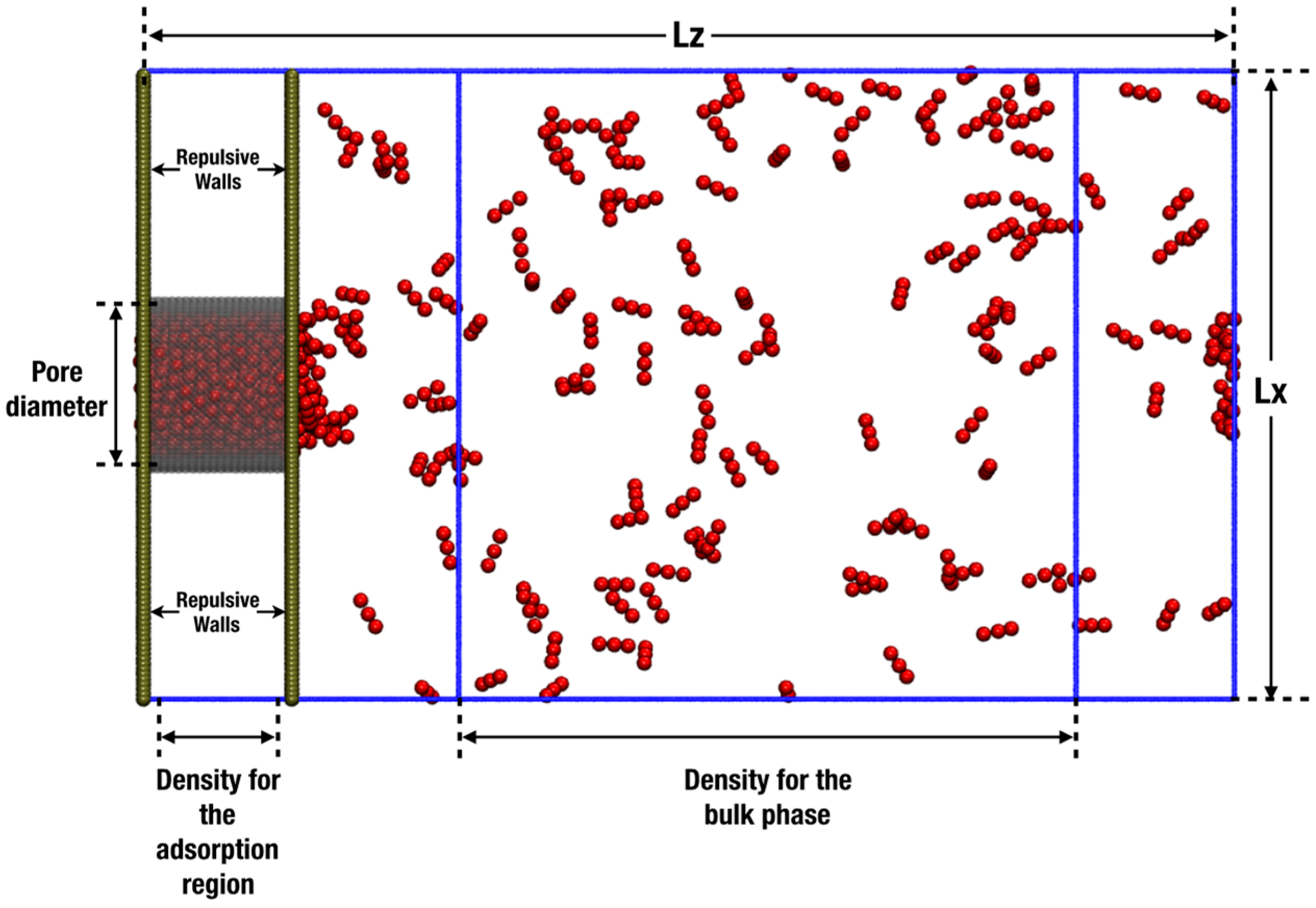
2. Simulation Details
3. Results
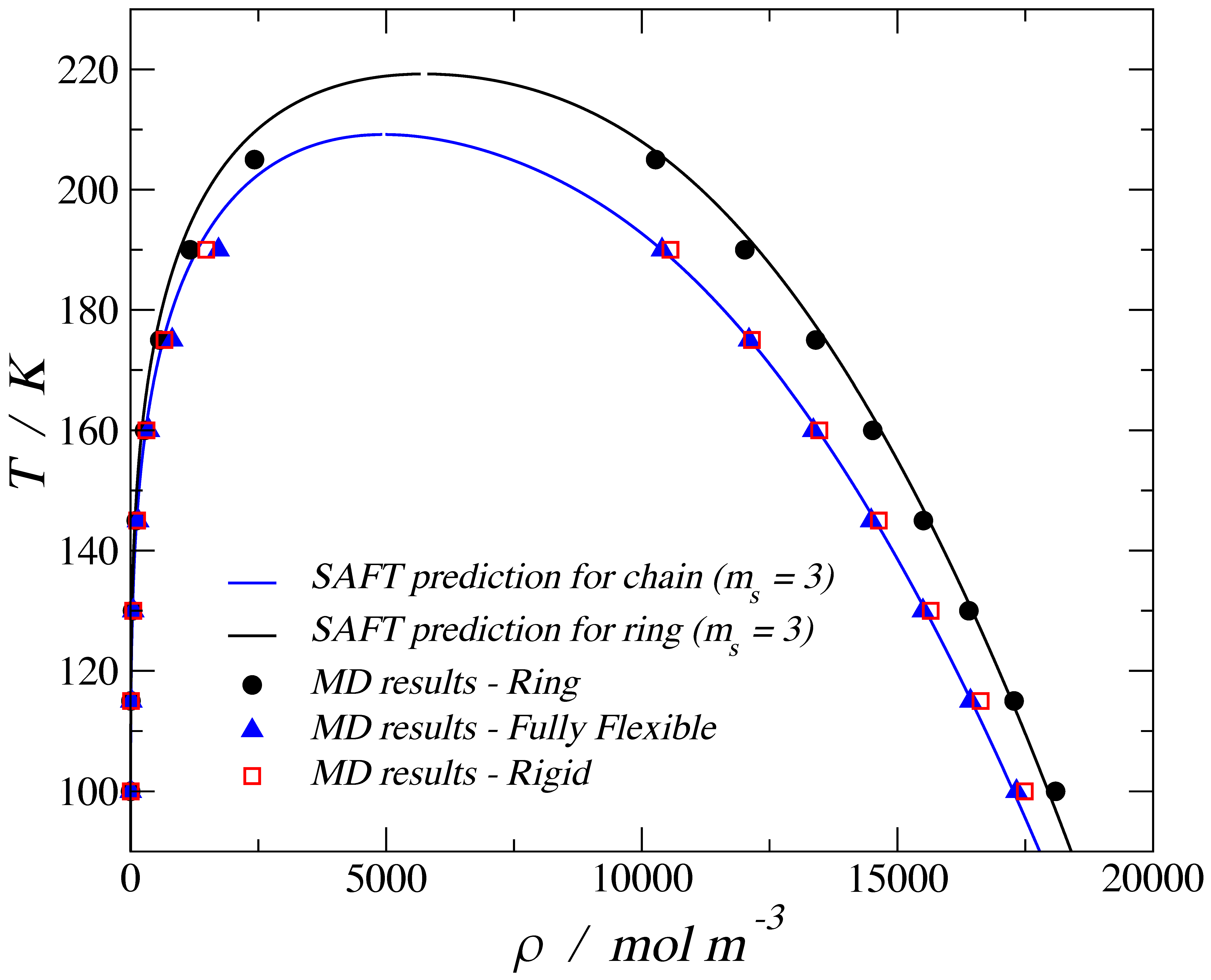
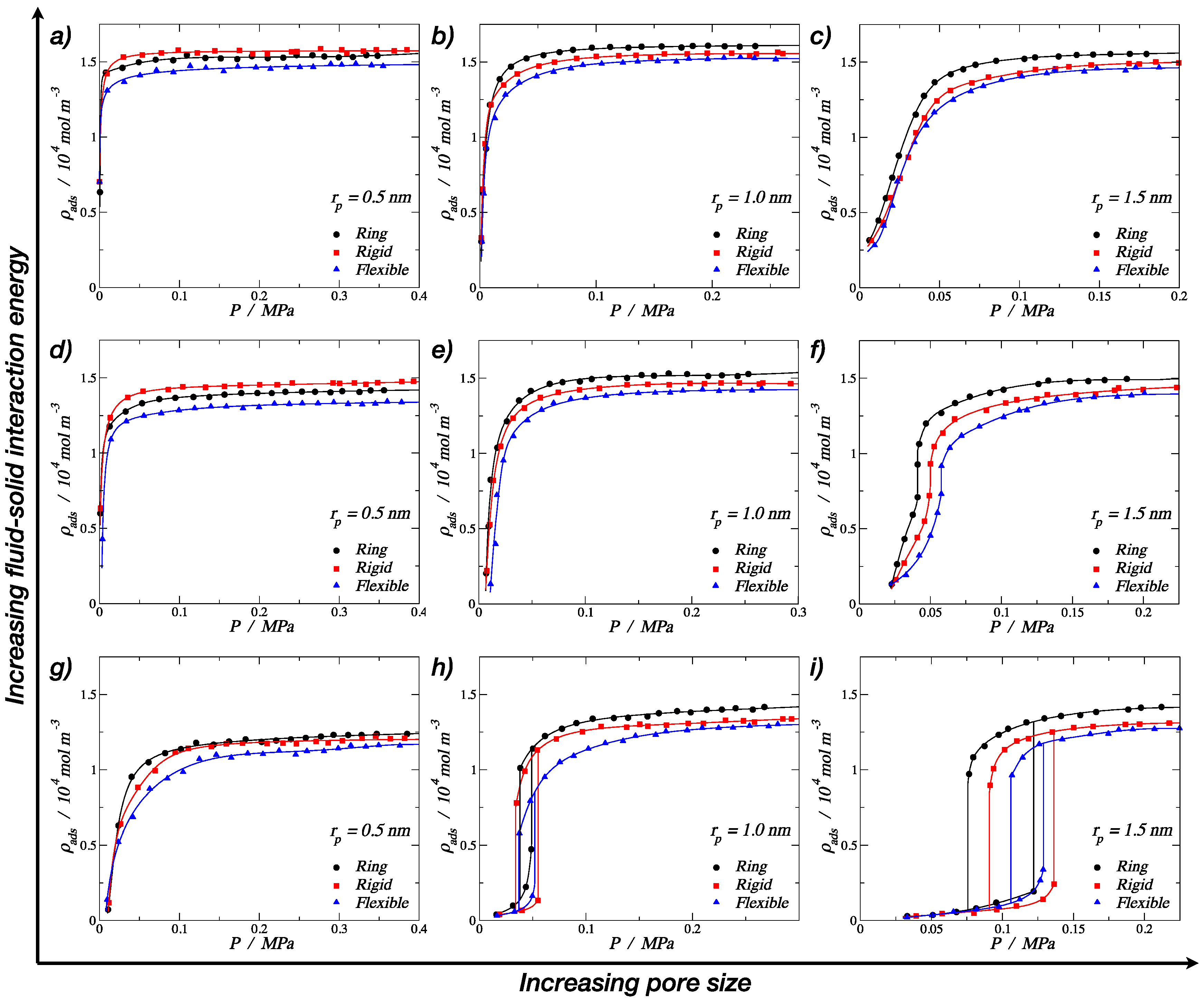
3.1. Adsorption of Trimers in Cylindrical Pores
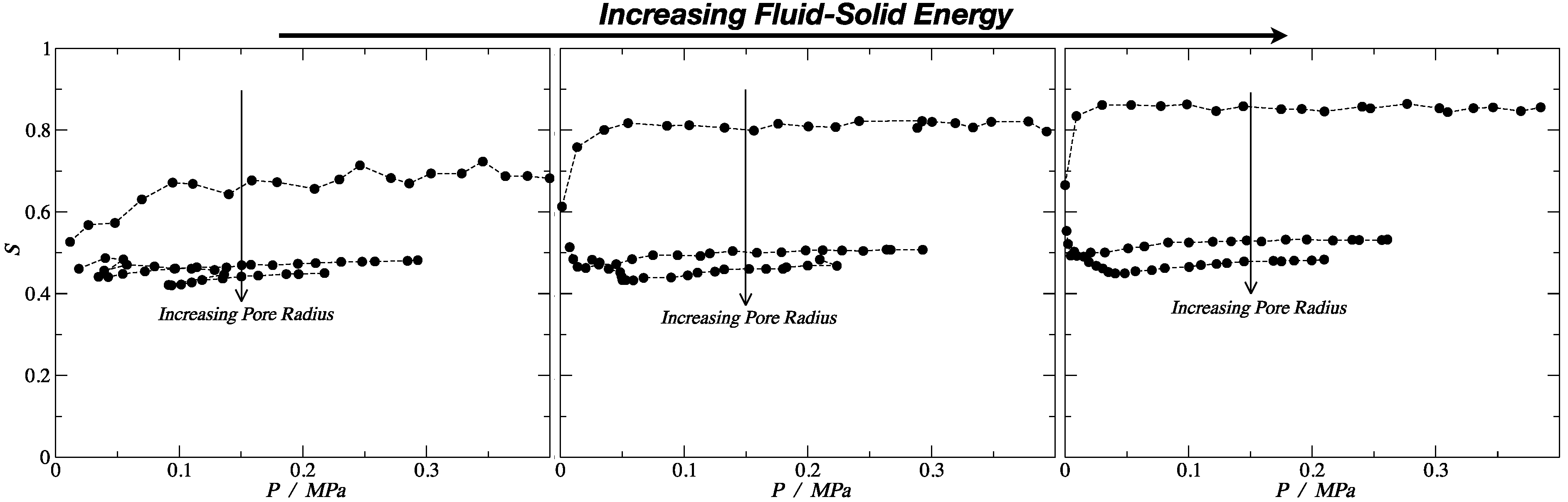
3.2. Nematic Order Parameter
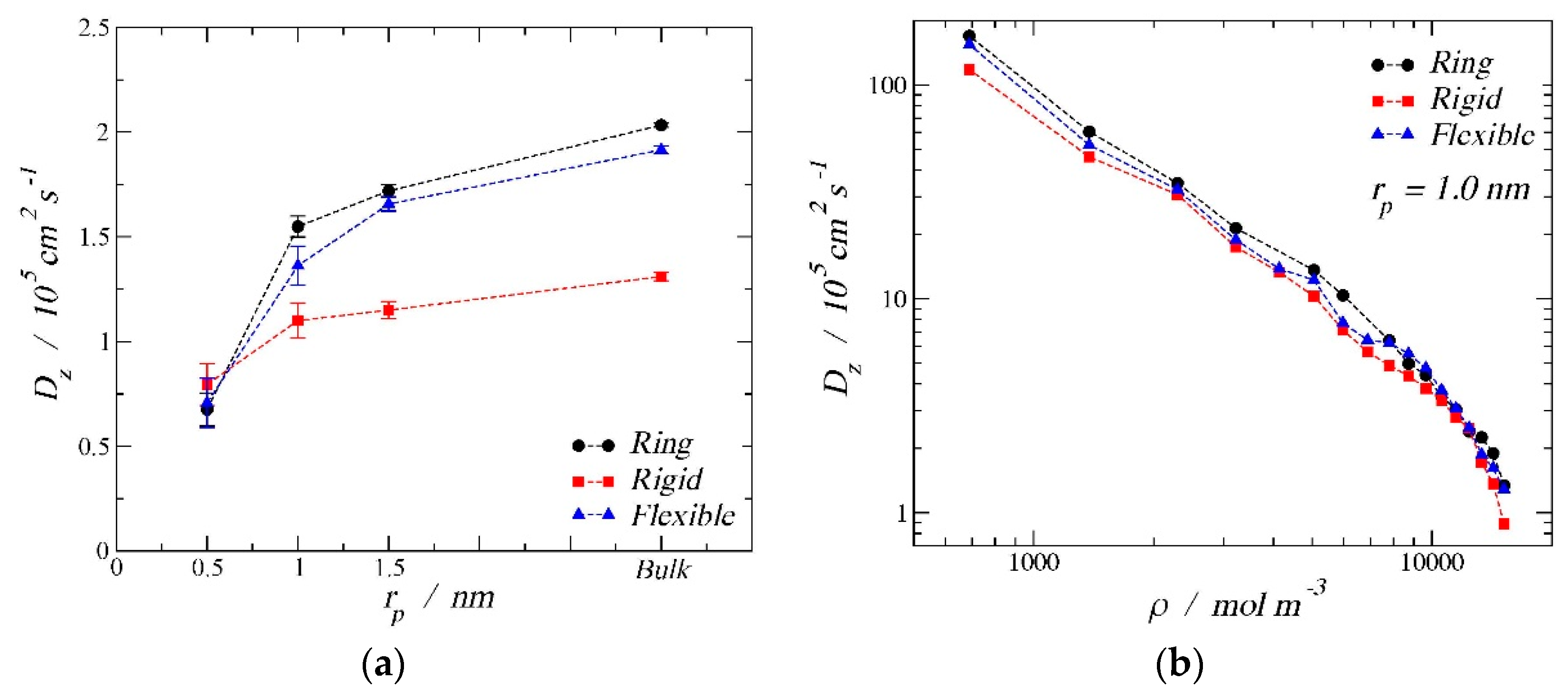
3.3. Diffusion Coefficients
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urita, K.; Shiga, Y.; Fujimori, T.; liyama, T.; Hattori, Y.; Kanoh, H.; Ohba, T.; Tanaka, H.; Yudasaka, M.; lijima, S.; et al. Confinement in Carbon Nanospace-Induced Production of KI Nanocrystals of High-Pressure Phase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10344–10347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.; Wu, H.; Jayaram, P.; Grigorieva, I. Unimpeded Permeation of Water Through Helium-Leak–Tight Graphene-Based Membranes. Science 2012, 335, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höfling, F.; Franosch, T. Anomalous transport in the crowded world of biological cells. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2013, 76, 046602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba-Simionesco, C.; Coasne, B.; Dosseh, G.; Dudziak, G.; Gubbins, K.E.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Sliwinska-Bartkowiak, M. Effects of confinement on freezing and melting. J. Phys-Condens. Mat. 2006, 18, R15–R68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiullin, R.; Kärger, J. Confined Fluids: NMR Perspectives on Confinements and on Fluid Dynamics. In Diffusion NMR of Confined Systems; Valiullin, R., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 390–434. [Google Scholar]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Oliver, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 89, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monson, P.A. Understanding adsorption/desorption hysteresis for fluids in mesoporous materials using simple molecular models and classical density functional theory. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2012, 160, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisov, L.; Monson, P.A. Modeling of Adsorption and Desorption in Pores of Simple Geometry using Molecular Dynamics. Langmuir 2001, 17, 7600–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, T.; Do, D.D.; Nicholson, D. Capillary condensation of adsorbates in porous materials. Advan. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2011, 169, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Sayari, A. Adsorption study of surface and structural properties of MCM-41 materials of different pore sizes. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Cychosz, K.A. Physical adsorption characterization of nanoporous materials: progress and challenges. Adsorption 2014, 20, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, B.; Maesen, T.L.M. Molecular simulations of zeolites: Adsorption, Diffusion, and Shape Selectivity. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 4125–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, B.; Siepmann, J.I. Simulating the Adsorption of Alkanes in Zeolites. Science 1994, 264, 1118–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, M.; Smit, B.; Vlugt, T.J.H.; Maesen, T.L.M. Shape Selectivity in Hydrocarbon Convertion. Angew. Chemie Inter. Ed. 2001, 40, 736–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Sandler, S.I. Monte Carlo simulation for the Adsorption and Separation of linear and branched alkanes in IRMOF-1. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5702–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkisov, L.; Düren, T.; Snurr, R.Q. Molecular modelling of adsorption in novel nanoporous metal-organic materials. Mol. Phys. 2006, 102, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärger, J.; Ruthven, D.M. Diffusion in Zeolites and Other Microporous Materials; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kärger, J.; Freude, D.; Haase, J. Diffusion in Nanoporous Materials: Novel Insights by Combining MAS and PFG NMR. Processes 2018, 6, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R. Diffusion in porous crystalline materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Baten, J.M.; Krishna, R. Entropy effects in adsorption and diffusion of alkane isomers in mordenite: An investigation using CBMC and MD simulations. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2005, 84, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.K.; Müller, E.A.; Gubbins, K.E. Equation of state for Lennard-Jones chains. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 6413–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, A.; Vega, C.; Sanz, E.; MacDowell, L.G.; de Miguel, E.; Blas, F.J. Computer simulation study of the global phase behavior of linear rigid Lennard-Jones chain molecules: Comparison with flexible models. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 3957–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Westen, T.; Oyarzún, B.; Vlugt, T.J.H.; Gross, J. An analytical equation of state for describing isotropic-nematic phase equilibria of Lennard-Jones chain fluids with variable degree of molecular flexibility. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 142, 244903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, E.A.; Mejía, A. Extension of the SAFT-VR Mie EoS to model homonuclear rings and its parametrization based on the principle of corresponding states. Langmuir 2017, 33, 11518–11529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafitte, T.; Apostolakou, A.; Avendaño, C.; Galindo, A.; Adjiman, C.S.; Müller, E.A.; Jackson, G. Accurate statistical associating fluid theory for chain molecules formed from Mie segments. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 154504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Sinha, A.; Deo, G.; Singh, J.K. Vapor-Liquid phase coexistence, critical properties, and surface tension of confined alkanes. J Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 7170–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, E.A.; Jackson, G. Force-Field Parameters from the SAFT-γ Equation of State for Use in Coarse-Grained Molecular Simulations. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2014, 5, 405–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ervik, Å.; Mejía, A.; Müller, E.A. Bottled SAFT: A Web App Providing SAFT-γ Mie Force Field Parameters for Thousands of Molecular Fluids. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herdes, C.; Totton, T.S.; Müller, E.A. Coarse grained force field for the molecular simulation of natural gases and condensates. Fluid Phase Equilibr. 2015, 406, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, F.; Matar, O.K.; Müller, E.A. Bulk viscosity of molecular fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 174504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdes, C.; Ervik, Å.; Mejía, A.; Müller, E.A. Prediction of the water/oil interfacial tension from molecular simulations using the coarse-grained SAFT-γ Mie force field. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2018, 476, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdes, C.; Petit, C.; Mejía, A.; Müller, E.A. Combined Experimental, Theoretical, and Molecular Simulation Approach for the Description of the Fluid-Phase Behavior of Hydrocarbon Mixtures within Shale Rocks. Energ. Fuel. 2018, 32, 5750–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreda, D.; Pérez-Mas, A.M.; Silvestre-Albero, A.; Casco, M.E.; Rudić, S.; Herdes, C.; Müller, E.A.; Blanco, C.; Santamaria, R.; Silvestre-Albero, J.; et al. Unusual flexibility of mesophase pitch-derived carbon materials: An approach to the synthesis of graphene. Carbon 2017, 115, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafitte, T.; Pérez-Mas, A.M.; Silvestre-Albero, A.; Casco, M.E.; Rudić, S.; Herdes, C.; Muller, E.A.; Blanco, C.; Santamaria, R.; Silvestre-Albero, J.; et al. SAFT-γ force field for the simulation of molecular fluids: 3. Coarse-grained models of benzene and hetero-group models of n−decylbenzene. Mol. Phy. 2012, 110, 1189–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R. Describing the Diffusion of Guest Molecules Inside Porous Structures. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 19756–19781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jover, J.; Haslam, A.J.; Galindo, A.; Jackson, G.; Müller, E.A. Pseudo Hard-Sphere potential for use in continuous molecular-dynamics simulation of spherical and chain molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 144505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowlinson, J.S.; Widom, B. Molecular Theory of Capillarity; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Low, R.J. Measuring order and biaxiality. Eur. J. Phys. 2002, 23, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Baker, R.W. The solution-diffusion model: A review. J. Memb. Sci. 1995, 107, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |
| σ [nm] | ε/kb [K] | λr | λa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ccylinder,1-LJfluid | 0.25 | 25.00 | 11.0 | 4.0 |
| Ccylinder,2-LJfluid | 0.25 | 19.30 | 11.0 | 4.0 |
| Ccylinder,3-LJfluid | 0.25 | 13.80 | 11.0 | 4.0 |
| LJfluid | 0.30 | 100.00 | 12.0 | 6.0 |
| εfluid-wall/kb[K] | 13.80 | 19.30 | 25.00 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rp [nm] | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 |
| S | 0.69 | 0.477 | 0.45 | 0.815 | 0.506 | 0.47 | 0.86 | 0.53 | 0.48 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cárdenas, H.; Müller, E.A. Molecular Simulation of the Adsorption and Diffusion in Cylindrical Nanopores: Effect of Shape and Fluid–Solid Interactions. Molecules 2019, 24, 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030608
Cárdenas H, Müller EA. Molecular Simulation of the Adsorption and Diffusion in Cylindrical Nanopores: Effect of Shape and Fluid–Solid Interactions. Molecules. 2019; 24(3):608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030608
Chicago/Turabian StyleCárdenas, Harry, and Erich A. Müller. 2019. "Molecular Simulation of the Adsorption and Diffusion in Cylindrical Nanopores: Effect of Shape and Fluid–Solid Interactions" Molecules 24, no. 3: 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030608
APA StyleCárdenas, H., & Müller, E. A. (2019). Molecular Simulation of the Adsorption and Diffusion in Cylindrical Nanopores: Effect of Shape and Fluid–Solid Interactions. Molecules, 24(3), 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030608