Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay for Determination of Enrofloxacin in Pork Liver and Chicken
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
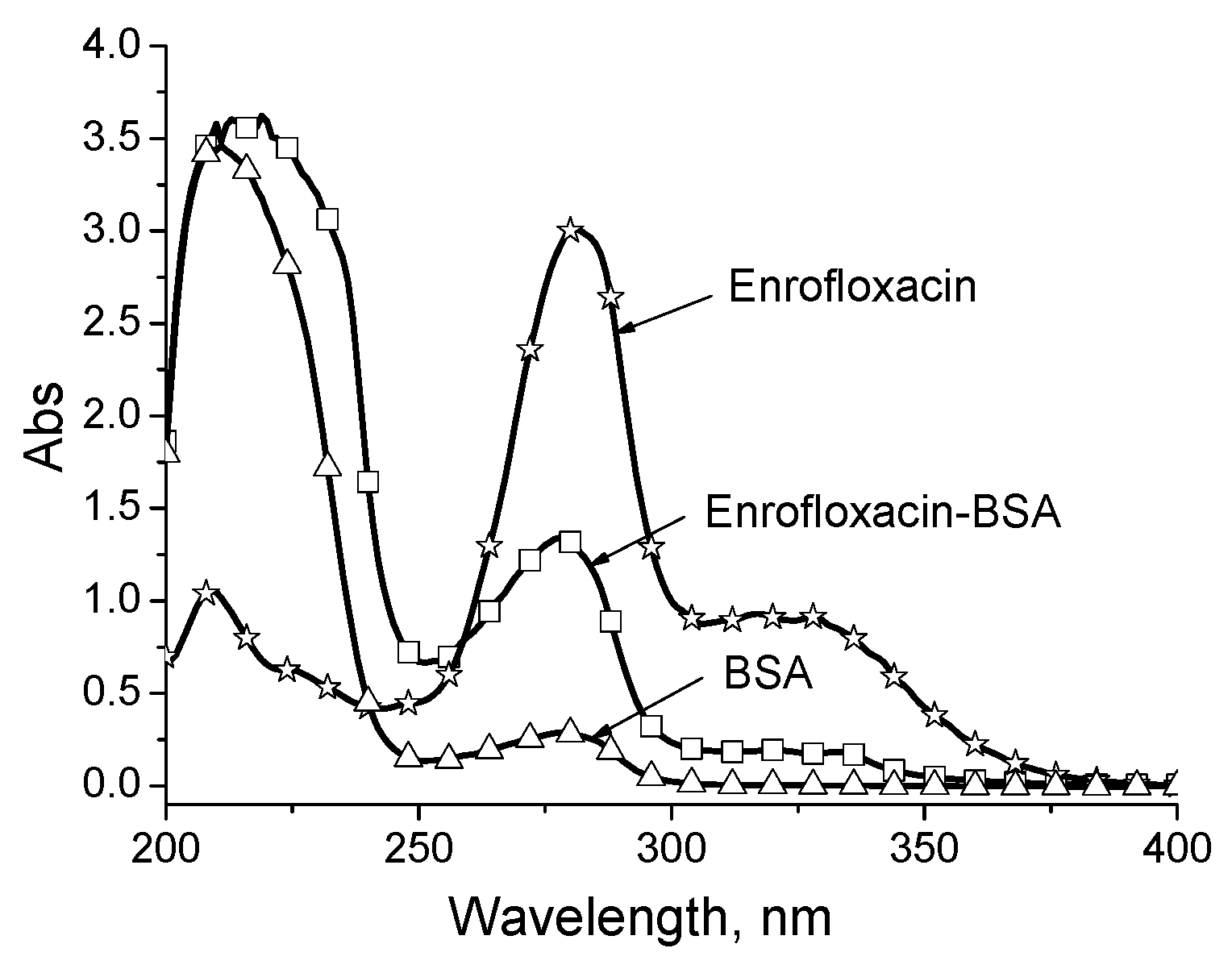
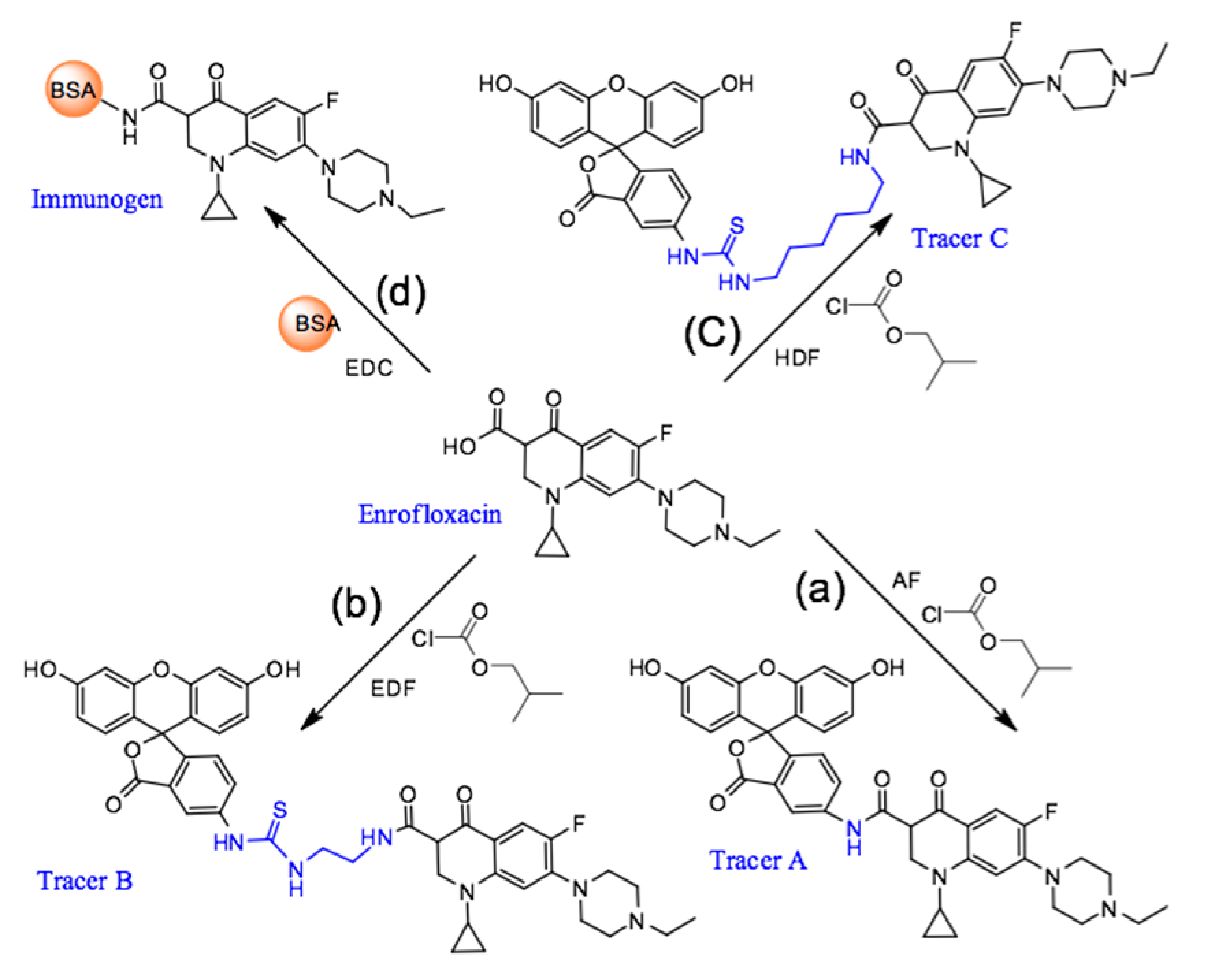
2.1. Immunoreagent Preparation
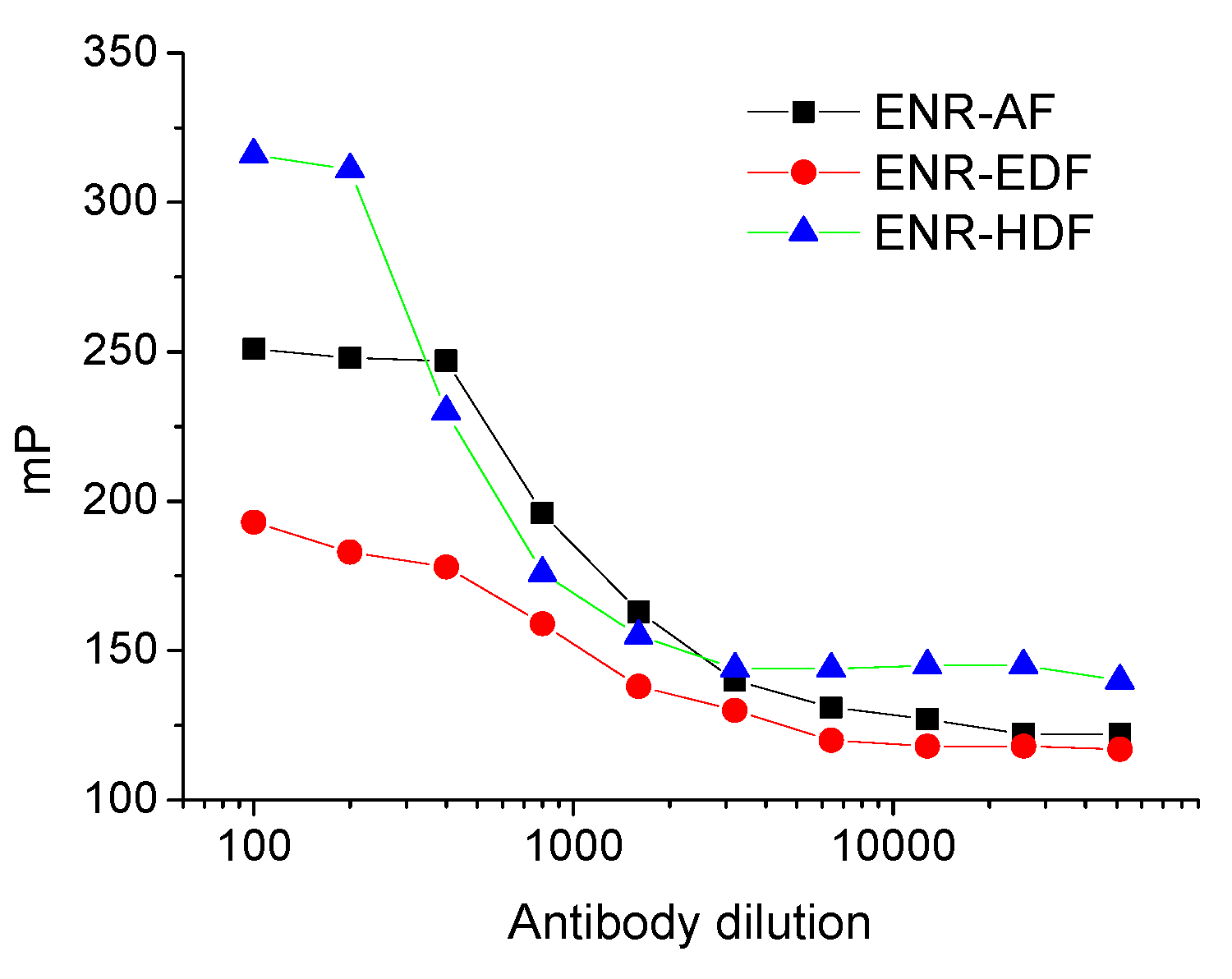
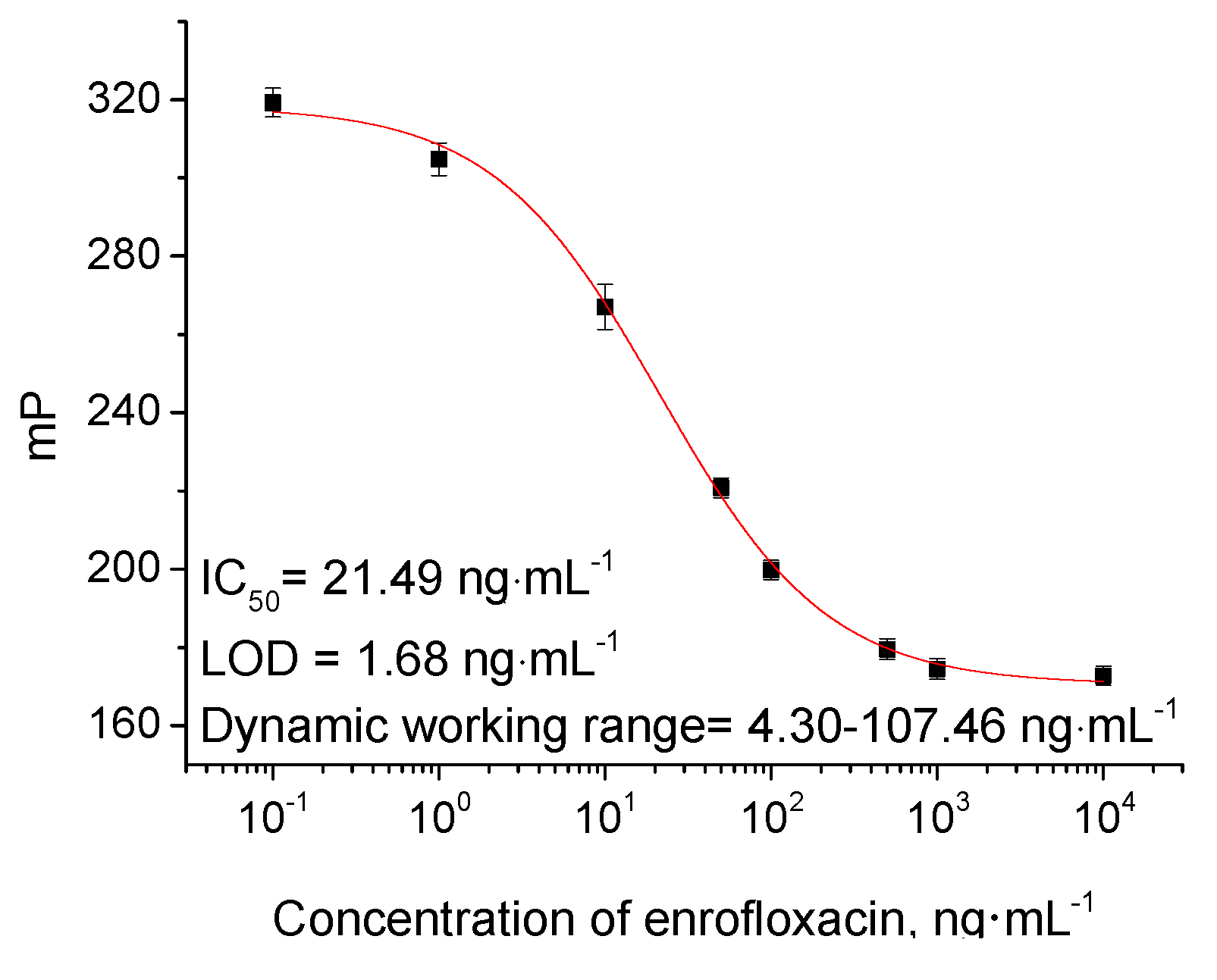
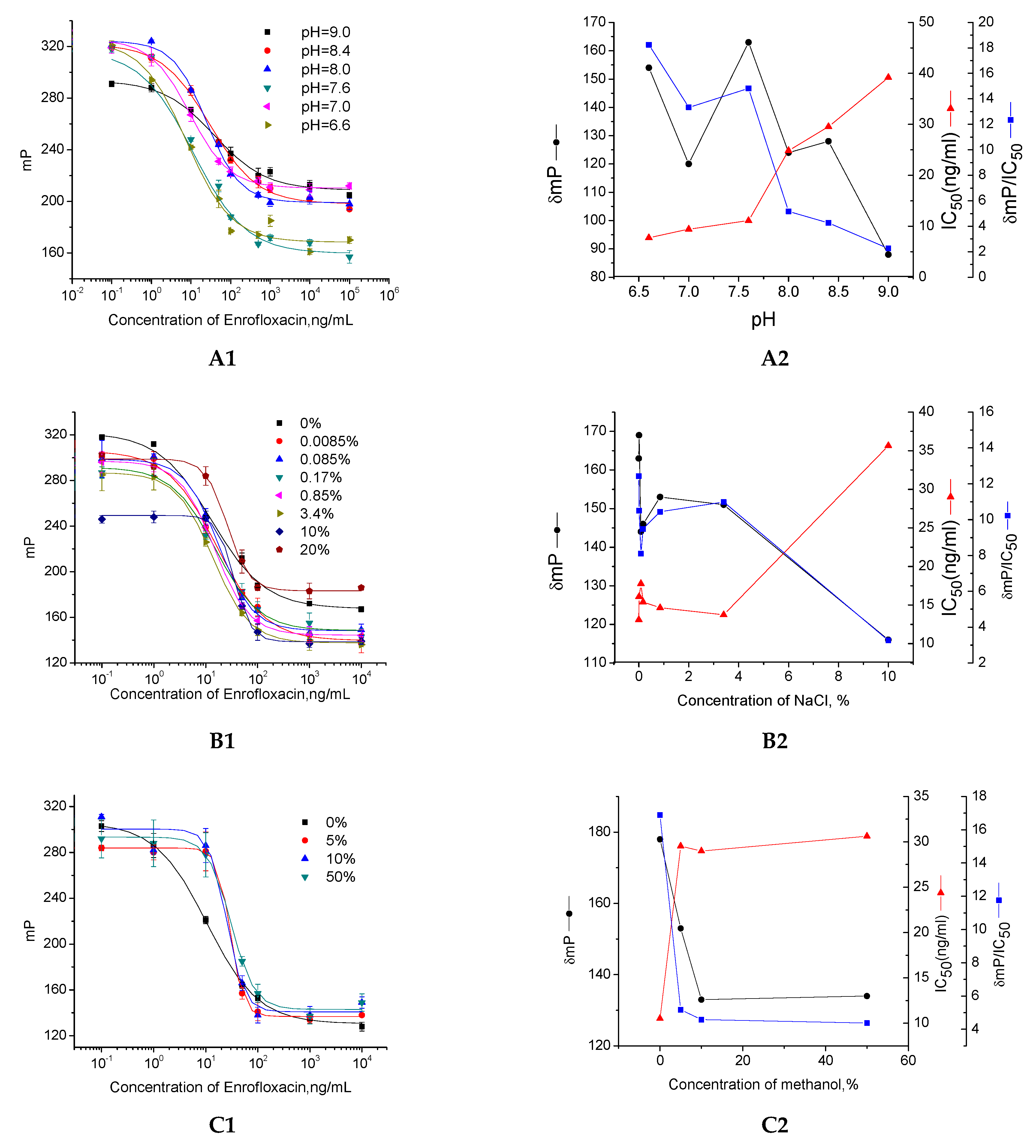
2.2. Optimization of FPIA
2.3. Specificity
2.4. Matrix Effect
2.5. Recovery
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Instruments
3.2. Generation of Polyclonal Antibody
3.3. Preparation of Fluorescein-Labeled Enrofloxacin Tracers
3.4. FPIA Procedure
3.5. Optimization of Immunoreagents
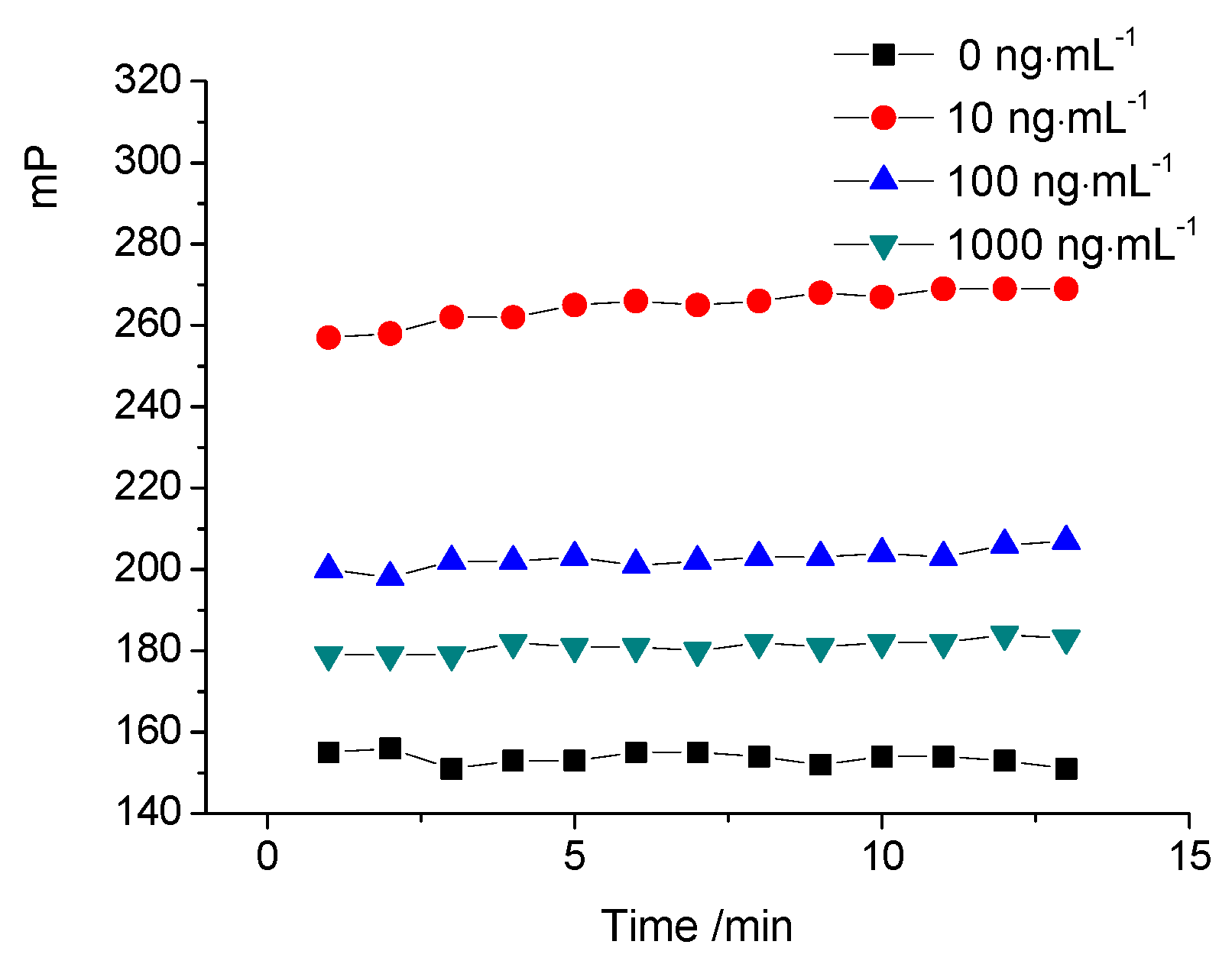
3.6. Kinetics of FPIA
3.7. Specificity
3.8. Recovery Matrix Effects
3.9. Sample Extraction and Recovery Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsepo Ramatla, L.N.; Modupeade, A.; Mulunda, M. Evaluation of antibiotic residues in raw meat using different analytical methods. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Trouchon, T.; Lefebvre, S. A review of enrofloxacin for veterinary use. Open J. Vet. Med. 2016, 6, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Du, Y.P.; Li, Q.Q.; Wang, X.; Pan, Y.C.; Zhang, H.; Wu, T.; Hu, H.L. Ultrasensitive detection of enrofloxacin in chicken muscles by surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy using amino-modified glycidyl methacrylate-ethylene dimethacrylate (GMA-EDMA) powdered porous material. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolo, M.; Pedreira, S.; Fente, C.; Vázquez, B.; Franco, C.; Cepeda, A. Study of enrofloxacin depletion in the eggs of laying hens using diphasic dialysis extraction/purification and determinative HPLC-MS analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2849–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet, A.C.; Charlier, C.; Tittlemier, S.A.; Singh, G.; Benrejeb, S.; Delahaut, P. Simultaneous determination of (fluoro) quinolone antibiotics in kidney, marine products, eggs, and muscle by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2822–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Martín, B.; Cornejo, J.; Lapierre, L.; Iragüen, D.; Pérez, F.; Hidalgo, H.; Andre, F. Withdrawal time of four pharmaceutical formulations of enrofloxacin in poultry according to different maximum residues limits. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 33, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.T.; Jiang, J.Q.; Wang, Z.L.; Chang, X.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Zhao, K.; Chen, J.S. Development of an indirect competitive ELISA for simultaneous detection of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2011, 12, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Ni, H.J.; Zhang, S.X.; Shen, J.Z. Development of a highly sensitive and specific immunoassay for enrofloxacin based on heterologous coating haptens. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2014, 820, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.K.; Zhao, M.G.; Zhang, D.; Yan, H.Y. Enrofloxacin-imprinted monologhic HPLC columns synthesized by in situ copolymerization for chromatographic separation. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2011, 34, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, F.; Hegnerová, K.; Piliarik, M.; Sanchez-Baeza, F.; Homola, J.; Marco, M.P. A label-free and portable multichannel surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for on site analysis of antibiotics in milk samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet, A.C.; Charlier, C.; Singh, G.; Godefroy, S.B.; Leivo, J.; Vehniäinen, M.; Nielen, M.; Weigel, S.; Delahaut, P. Development of an optical surface plasmon resonance biosensor assay for (fluoro) quinolones in egg, fish, and poultry meat. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2008, 623, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wang, P.P.; Jiang, P.; Dong, X.C.; Lin, S. Preparation and application of a restricted access material with hybrid poly(glycerol mono-methacrylate) and cross-linked bovine serum albumin as hydrophilic out layers for directly on-line high performance liquid chromatography analysis of enrofloxacin and gatifloxacin in milk samples. J. Chromatography. A 2018, 1573, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, M.; Xi, R. Review: Current development of immunoassay for analyzing veterinary drug residue in foods and food products. Anal. Lett. 2011, 44, 2543–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.G.; Kim, M.; Park, Y.I.; Jung, T.S.; Son, S.W.; So, B.; Kang, H.G. Magnetic nanoparticle based purification and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using monoclonal antibody against enrofloxacin. J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 16, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Yu, S.C.; Yu, L.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Wu, Y.J.; Zhang, H.Q.; Qu, L.B.; Harrington, P.B. Determination of residual enrofloxacin in food samples by a sensitive method of chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.C.; Yu, F.; Zhang, H.Q.; Qu, L.B.; Wu, Y.J. Optimization of condition for conjugation of enrofloxacin to enzymes in chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay. Spectrochim. Acta. Part. A 2014, 127, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Wu, Y.J.; Yu, S.C.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, H.Q.; Qu, L.B.; Harrington, P.B. A competitive chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for rapid and sensitive determination of enrofloxacin. Spectrochim. Acta. Part. A 2012, 93, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.L.; Wang, Q.; Lei, H.T.; Eremin, S.A.; Shen, Y.D.; Wang, H.; Beier, R.C.; Yang, J.Y.; Maksimova, K.A.; Sun, Y.M. A simple, rapid and high-throughput fluorescence polarization immunoassay for simultaneous detection of organophosphorus pesticides in vegetable and environmental water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2011, 708, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Kai, W.; Tao, X.Q.; Ding, S.Y.; Xie, J.; Yu, X.Z.; Li, J.C.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.L.; et al. A novel multiplexed fluorescence polarisation immunoassay based on a recombinant bi-specific single-chain diabody for simultaneous detection of fluoroquinolones and sulfonamides in milk. Food Addit. Contam.: Part. A 2014, 31, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, T.J.; Wang, Z.H.; Eremin, S.A.; Shen, J.Z.; Zhang, S.X. Simultaneous determination of multiple (fluoro)quinolone antibiotics in food samples by a one-step fluorescence polarization immunoassay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9347–9355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, T.J.; Liang, X.; Ding, L.; Zhang, S.X.; Eremin, S.A.; Beier, R.C.; Shen, J.Z.; Wang, Z.H. Development and optimization of a fluorescence polarization immunoassay for orbifloxacin in milk. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 3849–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Shanin, I.A.; Lv, S.W.; Wang, Q.; Mao, C.B.; Xu, Z.L.; Sun, Y.M.; Wu, Q.; Eremin, S.A.; Lei, H.T. Heterologous strategy enhancing the sensitivity of the fluorescence polarization immunoassay of clinafloxacin in goat milk. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.T.; Xue, G.; Yu, C.F.; Haughey, S.A.; Eremin, S.A.; Sun, Y.M.; Wang, Z.H.; Xu, Z.L.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.D. Fluorescence polarization as a tool for the detection of a widely used herbicide, butachlor, in polluted waters. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 2334–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, S.X.; Nesterenko, I.S.; Eremin, S.A.; Shen, J.Z. Monoclonal antibody-based fluorescence polarization immunoassay for sulfamethoxypyridazine and sulfachloropyridazine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6871–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, I.; Nakata, K.; Ono, K.; Sugimoto, M.; Sekiguchi, A. Kinetic resolution of the racemic 2-hydroxyalkanoates using the enantioselective mixed-anhydride method with pivalic anhydride and a chiral acyl-transfer catalyst. Chem. –A Eur. J. 2010, 16, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Peterson, J.R.; Gooding, J.J.; Lee, N.A. Development of sensitive direct and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) for monitoring bisphenol-A in canned foods and beverages. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Satake, A.; Kido, Y.; Tsuji, A. Monoclonal-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunochromatographic assay for enrofloxacin in biological matrices. Analyst 2001, 127, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.S.; Eremin, S.A. Fluorescence polarization immunoassays and related methods for simple, high-throughput screening of small molecules. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.L.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Li, H.M.; Lai, W.H.; Wei, H.; Xu, H.Y.; Xiong, Y.H. Fluorescent Ru(phen)32+-doped silica nanoparticles-based ICTS sensor for quantitative detection of enrofloxacin residues in chicken meat. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5120–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Xu, F.; Jiang, H.Y.; Hou, Y.L.; Rao, Q.X.; Guo, P.J.; Ding, S.Y. A novel quantum dot-based fluoroimmunoassay method for detection of Enrofloxacin residue in chicken muscle tissue. Anal. Methods 2009, 113, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Xie, H.; Xu, L.X. A long lifetime chemical sensor: Study on fluorescence property of fluorescein isothiocyanate and preparation of pH chemical sensor. Spectrochim. Acta. Part. A 2004, 60, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Dixit, N.; Zhou, L.L.; Fraunhofer, W. Impact of short range hydrophobic interactions and long range electrostatic forces on the aggregation kinetics of a monoclonal antibody and a dual-variable domain immunoglobulin at low and high concentrations. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 421, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Huang, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.S.; Fang, W.; Yang, X.L. Monoclonal antibody based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the specific detection of ciprofloxacin and enrofloxacin residues in fishery products. Aquaculture 2010, 310, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.T.; Shen, Y.D.; Song, L.J.; Yang, J.Y.; Chevallier, O.P.; Haughey, S.A.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.M.; Elliott, C.T. Hapten synthesis and antibody production for the development of a melamine immunoassay. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2010, 665, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Haughey, S.A.; Sun, Y.M.; Eremin, S.A.; Li, Z.F.; Liu, H.; Xu, Z.L.; Shen, Y.D.; Lei, H.T. Development of a fluorescence polarization immunoassay for the detection of melamine in milk and milk powder. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 2275–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakovleva, J.N.; Lobanova, A.Y.; Shutaleva, E.A.; Kourkina, M.A.; Mart’ianov, A.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Eremin, S.A. Express detection of nonylphenol in water samples by fluorescence polarization immunoassay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
| Tracer | Titer | δmP | IC50 (ng·mL−1) | LOD (ng·mL−1) | Dynamic Working Range (ng·mL−1) | δmP/IC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tracer A | 1/600 | 89 | 49.93 | 2.01 | 6.59–378.48 | 1.74 |
| Tracer B | 1/300 | 39 | 9.34 | 0.75 | 1.80–48.60 | 4.18 |
| Tracer C | 1/300 | 124 | 21.82 | 3.85 | 5.04–108.33 | 5.68 |
| Method | LOD (ng·mL−1) | LOQ (ng·mL−1) | IC50 (ng·mL−1) | Linear Range (ng·mL−1) | Testing Samples | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC | 7.99 | 26.6 | - | - | Milk | Huang, 2018 [12] |
| SPR | 0.3 | - | 3.21 | - | Milk | Fernández, 2010 [10] |
| icELISA | 0.2 | 0.6 | 9.4 | 0.6–148.0 | Beef, pork | Zhang, 2011 [7] |
| CLEIA | 0.03 | 0.35 | - | 0.35–1.0 | Milk, eggs, honey | Yu, 2014 [15] |
| cFLISA | 2.5 | - | 8.3 | 1–100 | Chicken | Chen, 2009 [30] |
| FN-ICA | 0.02 | - | 0.22 | 0.025–3.5 | Chicken | Huang, 2013 [29] |
| No. | Compound | Structure | IC50(nmol·mL−1) | CR (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moiety | Substituent Group | ||||
| 1 | Enrofloxacin | 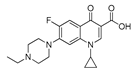 | ethyl | 0.027 | 100.0 |
| 2 | Ofloxacin | 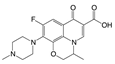 | methyl | 1.50 | 1.8 |
| 3 | Levofloxacin | 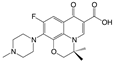 | methyl | 1.62 | 1.6 |
| 4 | Ciprofloxacin | 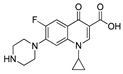 | H | 2.21 | 1.2 |
| 5 | Gatifloxacin | 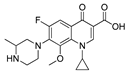 | H | 4.65 | 0.6 |
| 6 | Flumequine | 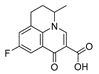 | H | ND a | ≤0.01 |
| Sample | Spiked Level (μg·kg−1) | Observed Value (μg·kg−1) | Recovery (%, n = 3) | Mean Recovery (%) | CV (%) | Mean CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pork liver | 5 | 5.64 ± 0.46 | 112.9 ± 9.1 | 105.7 | 8.07 | 3.83 |
| 10 | 10.46 ± 0.33 | 104.6 ± 3.3 | 3.13 | |||
| 50 | 49.79 ± 0.15 | 99.6 ± 0.3 | 0.30 | |||
| Chicken | 5 | 4.56 ± 0.31 | 91.3 ± 6.2 | 95.6 | 6.76 | 5.13 |
| 10 | 10.36 ± 0.26 | 103.6 ± 2.6 | 2.47 | |||
| 50 | 45.99 ± 2.84 | 92.0 ± 5.7 | 6.17 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, X.; Chen, J.; Lv, S.; Sun, X.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Eremin, S.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Lei, H. Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay for Determination of Enrofloxacin in Pork Liver and Chicken. Molecules 2019, 24, 4462. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244462
Shen X, Chen J, Lv S, Sun X, Dzantiev BB, Eremin SA, Zherdev AV, Xu J, Sun Y, Lei H. Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay for Determination of Enrofloxacin in Pork Liver and Chicken. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4462. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244462
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Xing, Jiahong Chen, Shuwei Lv, Xiulan Sun, Boris B. Dzantiev, Sergei A. Eremin, Anatoly V. Zherdev, Jianfa Xu, Yuanming Sun, and Hongtao Lei. 2019. "Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay for Determination of Enrofloxacin in Pork Liver and Chicken" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4462. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244462
APA StyleShen, X., Chen, J., Lv, S., Sun, X., Dzantiev, B. B., Eremin, S. A., Zherdev, A. V., Xu, J., Sun, Y., & Lei, H. (2019). Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay for Determination of Enrofloxacin in Pork Liver and Chicken. Molecules, 24(24), 4462. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244462









