Determination of Chemical Stability of Two Oral Antidiabetics, Metformin and Repaglinide in the Solid State and Solutions Using LC-UV, LC-MS, and FT-IR Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Elaboration of Quantitative LC-UV Method
2.2. Validation of Quantitative LC-UV Method
2.3. Percentage Degradation of Metformin and Repaglinide in Solutions
2.4. Kinetics of Degradation
2.5. Identification of Degradation Products
2.6. Degradation in a Solid State and Impact of Excipients
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Standards
3.2. LC-UV Method
3.2.1. Chromatography
3.2.2. Stock Solutions
3.2.3. Robustness
3.2.4. Linearity
3.2.5. Precision and Accuracy
3.2.6. Specificity
3.3. Degradation in Solutions
3.3.1. Quantitative Analysis after Degradation
3.3.2. Parameters of LC-MS Method
3.4. Degradation in the Solid State
3.5. FT-IR Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kinaan, M.; Ding, H.; Triggle, C.R. Metformin: An old drug for the treatment of diabetes but a new drug for the protection of the endothelium. Med. Princ. Pract. 2015, 24, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardado-Mendoza, R.; Prioletta, A.M.; Jiménez-Ceja, L.M.; Sosale, A.; Folli, F. The role of nateglinide and repaglinide, derivatives of meglitinide, in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Med. Sci. 2013, 9, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Guideline for Industries Impurities in Drug Product, Draft Guidance, Centre for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER); FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH). Guidance for Industry Q1A(R2): Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products; International Conference on Harmonization (ICH): Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Hsu, J.C.; Bretz, F.; Hayter, A.J.; Han, Y. Shelf-life and its estimation in drug stability studies. J. Appl. Stat. 2014, 41, 1989–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blessy, M.N.; Patel, R.D.; Prajapati, P.N.; Agrawal, Y.K. Development of forced degradation and stability indicating studies of drugs—A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2014, 4, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geetha Swarupa, P.; Lakshmana Rao, K.; Prasad, K.R.S.; Suresh Babu, K. Development and validation of stability indicating reversed phase high-pressure liquid chromatography method for simultaneous estimation of metformin and empagliflozin in bulk and tablet dosage form. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 9, 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- Runja, C.; Ravikumar, P.; Avanapu, S.R. Stability indicating RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of alogliptin benzoate and metformin hydrochloride in tablet dosage form. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 8, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Vaingankar, P.N.; Amin, P.D. Development and validation of stability-indicating RP-HPLC method for simultaneous determination of metformin HCl and glimepiride in fixed-dose combination. Anal. Chem. Insights 2016, 2016, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, Y.A.S.; Mohamed, A.M.I.; Mohamed, F.A.F.; Ahmed, S.A. New salting out stability-indicating and kinetic thin layer chromatographic method for determination of glimepiride and metformin HCl binary mixture. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 53, 1603–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammad, Y.; Gowri, S.D. A validated stability indicating high-performance liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of metformin HCl and dapagliflozin in bulk drug and tablet dosage form. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2015, 8, 320–326. [Google Scholar]
- Mallikarjuna Rao, N.; Gowri Sankar, D. RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation and stability indicating study of metformin and linagliptin in pure and pharmaceutical dosage forms. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Gite, S.; Patravale, V. Validation of RP-HPLC method and stress degradation for the combination of metformin HCl, atorvastatin calcium and glimepiride: Application to nanoparticles. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 53, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satheeshkumar, N.; Pradeepkumar, M.; Shanthikumar, S.; Rao, V.J. Development of validated stability indicating assay method for simultaneous estimation of metformin hydrochloride and vildagliptin by RP-HPLC. Drug Res. 2014, 64, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elrefay, H.; Ismaiel, O.A.; Hassan, W.S.; Shalaby, A. Development and validation of a stability-indicating HPLC-UV method for the determination of pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride in bulk drug and combined dosage form. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6 (Suppl. 4), 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Raghava Raju, T.V.; Jagan Mohan, T.S.S.; Bhavani Prasad, S.V.S.G.; Suresh Kumar, P.; Someswara Rao, N.; Mrutyunjaya Rao, I. Development, validation and resolving mass balance issue by using alternative oxidizing reagents for the determination of metformin hydrochloride impurities in API and pharmaceutical dosage forms. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6 (Suppl. 4), 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Peraman, R.; Gowra, C.S.; Reddy, Y.P.; Peruru, K.K. Stability-indicating RP-HPLC method for simultaneous determination of metformin hydrochloride and sitagliptin phosphate in dosage forms. Chromatographia 2013, 76, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, K.Y.; Geetha, G.; Hariprasad, R.; Kaviarasu, M.; Venkatnarayanan, R. Development and validation of stability indicating RP-HPLC method for the simultaneous estimation of linagliptin and metformin in pure and pharmaceutical dosage form. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2013, 5, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Rank, M.; Kapupara, P.; Shah, K. Development and validation of stability indicating HPTLC method for pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2016, 9, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivani, J.; Umamahesh, B.; Veeresham, C. Development and validation of stability indicating hptlc method for simultaneous determination of linagliptin and metformin. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 8, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Thakkar, P.P.; Patel, N.R.; Kothari, C.S.; Patel, R.; Mehta, P.J. Validated stability indicating high performance thin layer chromatographic method for repaglinide API. Indian Drugs 2015, 52, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, J.; Fareed, S.; Aqil, M. Stability-indicating assay of repaglinide in bulk and optimized nanoemulsion by validated high performance thin layer chromatography technique. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2013, 5, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, P.; Patel, M.; Surana, S. Development and validation of stability-indicating high-performance thin-layer chromatography method for estimation of repaglinide in bulk and in pharmaceutical formulation. Acta Chromatogr. 2013, 25, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deshpande, K.; Ranaware, P.; Madgulkar, A.R.; DamLe, M.C. Development and validation of stability indicating HPTLC method for determination of repaglinide. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2013, 6, 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, C.M.; Basavaiah, K. Development and validation of a simple stability indicating UPLC method for the determination of repaglinide in pharmaceuticals. Thai J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 37, 84–94. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, D.R.; Patel, L.J.; Patel, M.M. Development and validation of stability indicating method for the determination of repaglinide in pharmaceutical dosage form using high performance liquid chromatography. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2011, 3, 539–546. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.C.; Sharma, S. Stability indicating RP-HPLC method for determination and validation of repaglinide in pharmaceutical dosage form. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2011, 3, 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.S.; Nahire, R.R.; Shastri, N.R.; Surendranath, K.V.; Satish, J. Validated stability-indicating RP-HPLC UV method for simultaneous determination of metformin and repaglinide. Acta Chromatogr. 2012, 24, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonia, K.; Nappinnai, M.; Manikandan, K. Stability indicating RP-HPLC method for the estimation of metformin hydrochloride and repaglinide as API and estimation in tablet dosage form. Int. J. Pharm. Qual. Assur. 2016, 7, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Council of Europe. European Pharmacopeia, 9th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Markiewicz, M.; Jungnickel, C.; Stolte, S.; Białk-Bielińska, A.; Kumirska, J.; Mrozik, W. Primary degradation of antidiabetic drugs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Levons, J.; Narang, A.S.; Raghavan, K.; Rao, V.M. Reactive impurities in excipients: Profiling, identification and mitigation of drug-excipient incompatibility. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2011, 12, 1248–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, P.A.; Shrivastav, P.S.; Shah, J.V.; George, A. Simultaneous quantitation of metformin and dapagliflozin in human plasma by LC-MS/MS: Application to a pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 33, e4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas Moussa, B.; Mahrouse, M.A.; Fawzy, M.G. A validated LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of linagliptin and metformin in spiked human plasma coupled with solid phase extraction: Application to a pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 163, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintao, F.J.O.; Freitas, J.R.L.; de Fatima Machado, C.; Aquino, S.F.; de Queiroz Silva, S.; de Cassia Franco Afonso, J. Characterization of metformin by-products under photolysis, photocatalysis, ozonation and chlorination by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 30, 2360–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Pawar, G.; Yadam, S.; Giri, S.; Rajagopal, S.; Mullangi, R. LC-MS/MS-ESI method for simulateneous quantitation of metformin and repaglinide in rat plasma and its application to pharmacokinetic study in rats. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 356–364. [Google Scholar]
- Kancherla, P.; Keesari, S.; Alevegete, P.; Khagga, M. Das Parthasarathi, Identification, isolation and synthesis of seven novel impurities of anti-diabetic drug repaglinide. Drug Test. Anal. 2018, 10, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Purna Chander, C.; Raju, B.; Ramesh, M.; Shankar, G.; Srinivas, R. Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry study of repaglinide and its forced degradation products. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 32, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balpande, H.M.; Raut, N.S.; Umekar, M.J.; Kotagale, N.R. Compatibility study of metformin with pharmaceutical excipients. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2013, 5, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdary, Y.A.; Raparla, R.; Madhuri, M. Formulation and evaluation of multilayered tablets of pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride. J. Pharm. 2014, 2014, 848243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Basilio, I.; de Souza, F.; Medeiros, A.; Pinto, M.F.; de Santana, D.; Macedo, R. Application of thermal analysis in study of binary mixtures with metformin. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2008, 93, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y. Lubricants in pharmaceutical dosage forms. Lubricants 2014, 2, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, H.A.; Javadzadehl, Y.; Hamidi, M.; Jalali, M.B. Repaglinide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Effect of using different surfactants/stabilizers on physicochemical properties of nanoparticles. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceban, I.; Blajovan, R.; Vlase, G.; Albu, P.; Koppandi, O.; Vlase, T. Thermoanalytical measurements conducted on repaglinide to estimate the kinetic triplet followed by compatibility studies between the antidiabetic agent and various experiments. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH). Guidance for Industry Q1B: Photostability Testing of New Active Substances and Medicinal Products; International Conference on Harmonization (ICH): Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of metformin and repaglinide are available from the authors. |












| Compound | [M + H]+ | Name | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
 N-cyanoguanidine | Imp A | [30] | |
 N-(4,6-diamino-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)guanidine | Imp B | [30] | |
 N2,N2-dimethyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine | Imp C | [30] | |
 1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine | Imp D=DP2 | [17,30] | |
 N-methyltriimidodicarbonic diamide (1-methylbiguanide) | 116.0931 | Imp E=DP3=DPIV | [17,30] |
 N-methylmethanamine (dimethylamine) | Imp F | [30] | |
 1-carbamimidoylurea (guanylurea) | 103 | DP1 | [31] |
| Compound | [M + H]+ | Name |
|---|---|---|
 4-(carboxymethyl)-2-ethoxybenzoic acid | Imp A | |
 3-ethoxy-4-(ethoxycarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid | Imp B | |
 (1S)-3-methyl-1-[2-(piperidin-1-yl)phenyl]butan-1-amine | 247.2169 | Imp C=DPIII |
 ethyl 2-ethoxy-4-[2-[[(1S)-3-methyl-1-[2-(piperidin-1-yl) phenyl]butyl]amine]-2-ethoxy]benzoate | Imp D | |
 2-ethoxy-4-[2-[[(1R)-3-methyl-1-[2-(piperidin-1-yl)phenyl]butyl]amine]-2-ethoxy]benzoic acid (isomer) | 453.2753 | Imp E=DPV |
| Parameter | Metformin | Repaglinide |
|---|---|---|
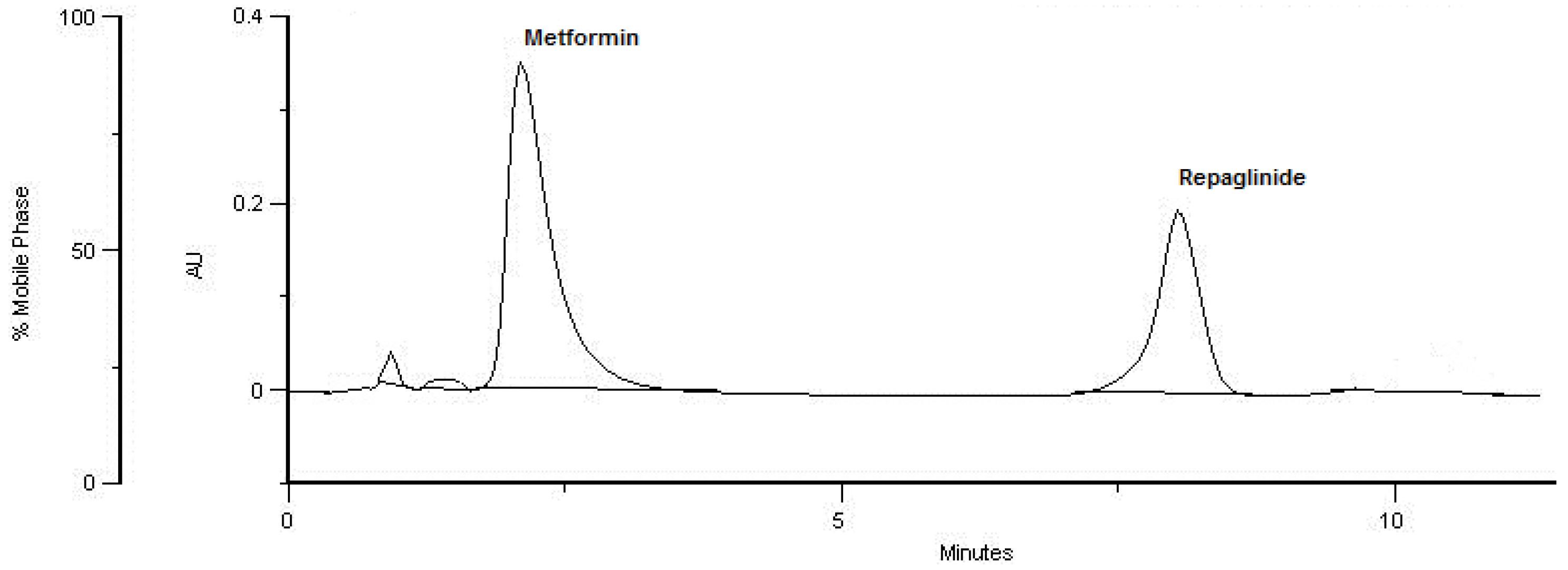
| tR (min) | 2.55 | 7.68 |
| Asymmetry factor | 1.5 | 0.8 |
| Linearity range (mg/mL) | 0.015–0.09 | 0.015–0.09 |
| Slope | 44.4609 | 9.2725 |
| SD of slope | 0.5807 | 0.0738 |
| Intercept | 0.1877 | 0.0039 |
| SD for intercept | 0.0189 | 0.0017 |
| R2 | 0.9993 | 0.9995 |
| SD of R2 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 |
| LOD (mg/mL) | 0.001 | 0.0006 |
| LOQ (mg/mL) | 0.004 | 0.002 |
| Precision (RSD) | ||
| Intra-day | 1.07–1.55 | 0.67–0.95 |
| Inter-day | 1.28–1.60 | 0.82–1.15 |
| Accuracy (%) | 99.81–100.98 | 98.48–101.63 |
| Metformin tR | Metformin Peak Area | Repaglinide tR | Repaglinide Peak Area | Rs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow rate (mL/min) | |||||
| 0.8 | 2.51 | 2.43189 | 7.65 | 0.46497 | 7.35 |
| 1.0 | 2.55 | 2.39286 | 7.68 | 0.46730 | 7.25 |
| 1.2 | 2.53 | 2.38583 | 7.65 | 0.46674 | 7.21 |
| Acetonitrile (%) | |||||
| 35 | 2.53 | 2.38583 | 7.70 | 0.47090 | 7.23 |
| 40 | 2.55 | 2.39286 | 7.68 | 0.46730 | 7.25 |
| 45 | 2.56 | 2.38111 | 7.62 | 0.47090 | 7.25 |
| UV detection (nm) | |||||
| 232 | 2.55 | 2.38320 | 7.67 | 0.46672 | 7.24 |
| 235 | 2.55 | 2.39286 | 7.68 | 0.46730 | 7.25 |
| 238 | 2.53 | 2.38229 | 7.68 | 0.46719 | 7.27 |
| Conditions | Degradation [%] | y = ax + b | R2 | K [s−1] | t0.1 [h] | t0.5 [h] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metformin | ||||||
| 0.01 M HCl | 5.73 | y = −0.0003x + 1.6154 | 0.9816 | 1.15 × 10−5 | 2.55 | 16.74 |
| 0.1 M HCl | 6.73 | y = −0.0003x + 1.6035 | 0.9743 | 1.15 × 10−5 | 2.55 | 16.74 |
| 0.01 M NaOH | 9.11 | y = −0.0004x + 1.5817 | 0.9585 | 1.54 × 10−5 | 1.90 | 12.50 |
| 0.1 M NaOH | 60.92 | y = −0.0052x + 1.6011 | 0.9984 | 1.99 × 10−4 | 0.15 | 0.97 |
| 0.3% H2O2 | 6.58 | y = −0.0001x + 1.5717 | 0.9770 | 3.84 × 10−5 | 7.62 | 50.13 |
| 3% H2O2 | 7.95 | y = −0.0003x + 1.6076 | 0.9699 | 1.15 × 10−5 | 2.55 | 16.74 |
| Repaglinide | ||||||
| 0.01 M HCl | 19.93 | y = −0.0012x + 1.6041 | 0.9748 | 4.61 × 10−5 | 0.64 | 4.18 |
| 0.1 M HCl | 38.32 | y = −0.0024x + 1.6435 | 0.9340 | 9.21 × 10−5 | 0.32 | 2.09 |
| 0.01 M NaOH | 6.13 | y = −0.0003x + 1.5762 | 0.9275 | 1.15 × 10−5 | 2.55 | 16.74 |
| 0.1 M NaOH | 7.24 | y = −0.0004x + 1.6013 | 0.9666 | 1.54 × 10−5 | 1.90 | 12.50 |
| 0.3% H2O2 | 9.16 | y = −0.0006x + 1.6033 | 0.9546 | 2.30 × 10−5 | 1.09 | 8.37 |
| 3% H2O2 | 21.75 | y = −0.0014x + 1.6225 | 0.9691 | 5.37 × 10−5 | 0.55 | 3.58 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gumieniczek, A.; Berecka-Rycerz, A.; Mroczek, T.; Wojtanowski, K. Determination of Chemical Stability of Two Oral Antidiabetics, Metformin and Repaglinide in the Solid State and Solutions Using LC-UV, LC-MS, and FT-IR Methods. Molecules 2019, 24, 4430. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244430
Gumieniczek A, Berecka-Rycerz A, Mroczek T, Wojtanowski K. Determination of Chemical Stability of Two Oral Antidiabetics, Metformin and Repaglinide in the Solid State and Solutions Using LC-UV, LC-MS, and FT-IR Methods. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4430. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244430
Chicago/Turabian StyleGumieniczek, Anna, Anna Berecka-Rycerz, Tomasz Mroczek, and Krzysztof Wojtanowski. 2019. "Determination of Chemical Stability of Two Oral Antidiabetics, Metformin and Repaglinide in the Solid State and Solutions Using LC-UV, LC-MS, and FT-IR Methods" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4430. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244430
APA StyleGumieniczek, A., Berecka-Rycerz, A., Mroczek, T., & Wojtanowski, K. (2019). Determination of Chemical Stability of Two Oral Antidiabetics, Metformin and Repaglinide in the Solid State and Solutions Using LC-UV, LC-MS, and FT-IR Methods. Molecules, 24(24), 4430. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244430