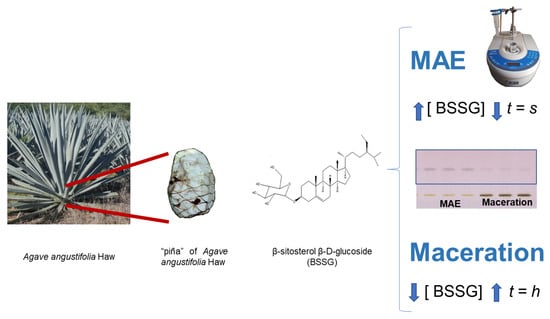
Identification and Quantification of β-Sitosterol β-d-Glucoside of an Ethanolic Extract Obtained by Microwave-Assisted Extraction from Agave angustifolia Haw
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
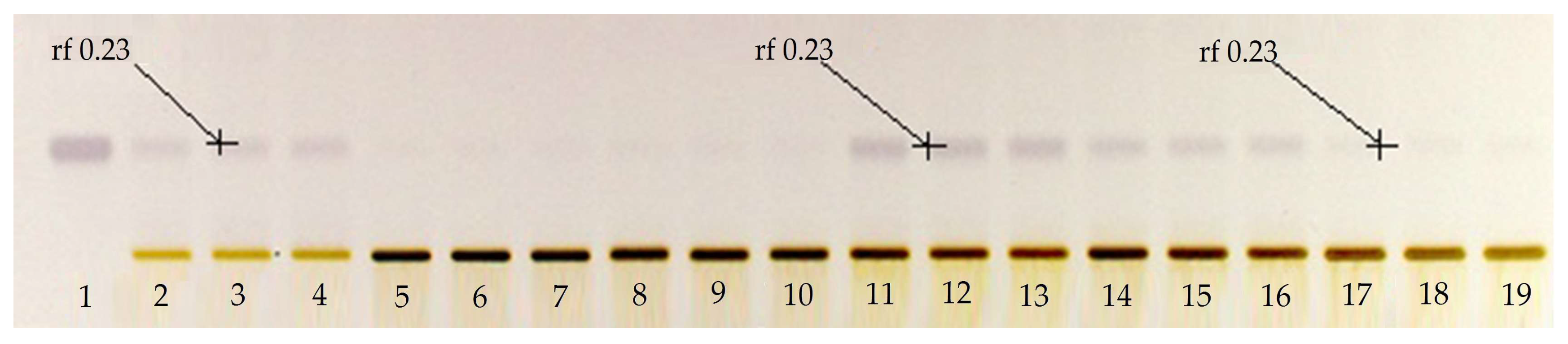
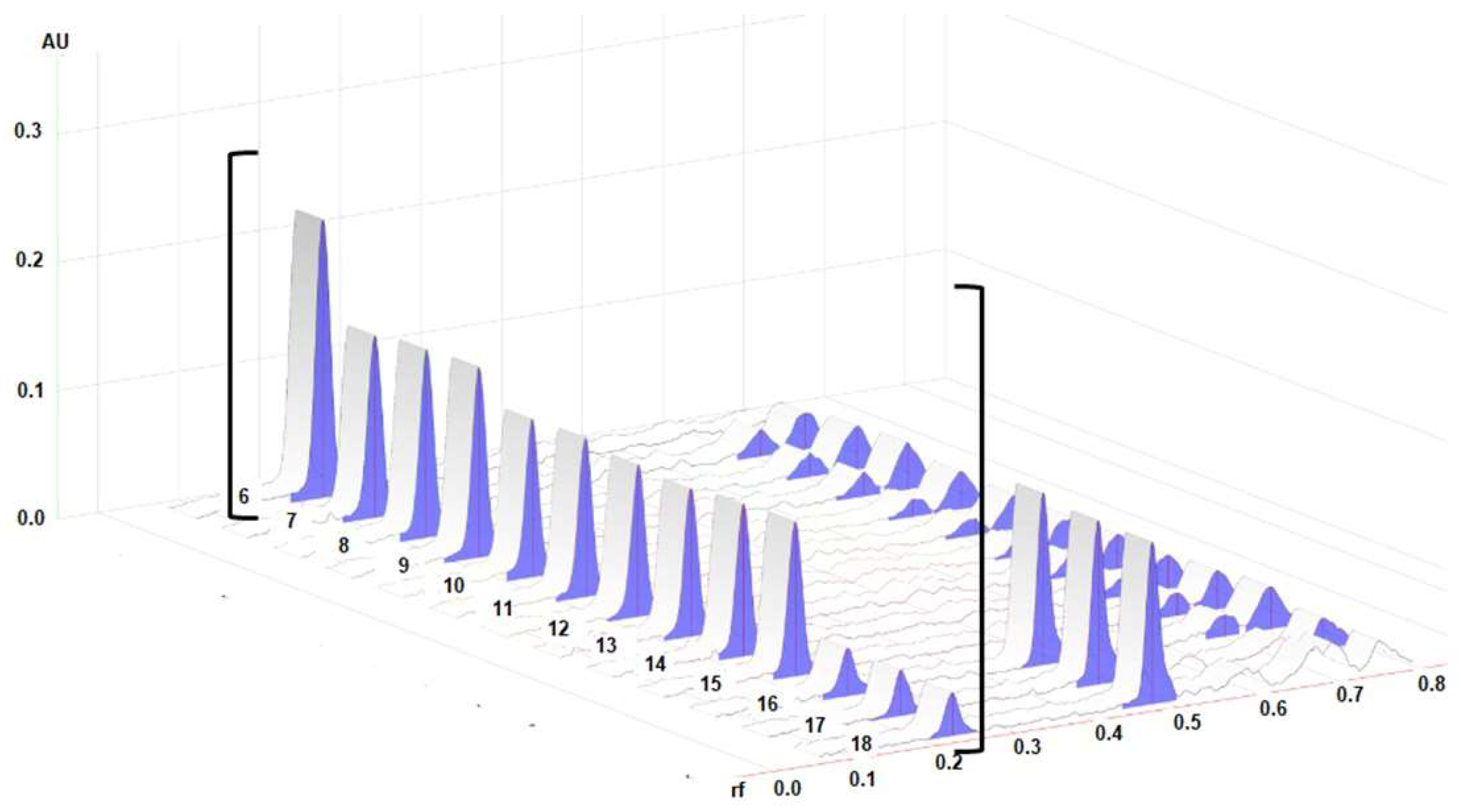
2.1. High-Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic (HPTLC) Analysis
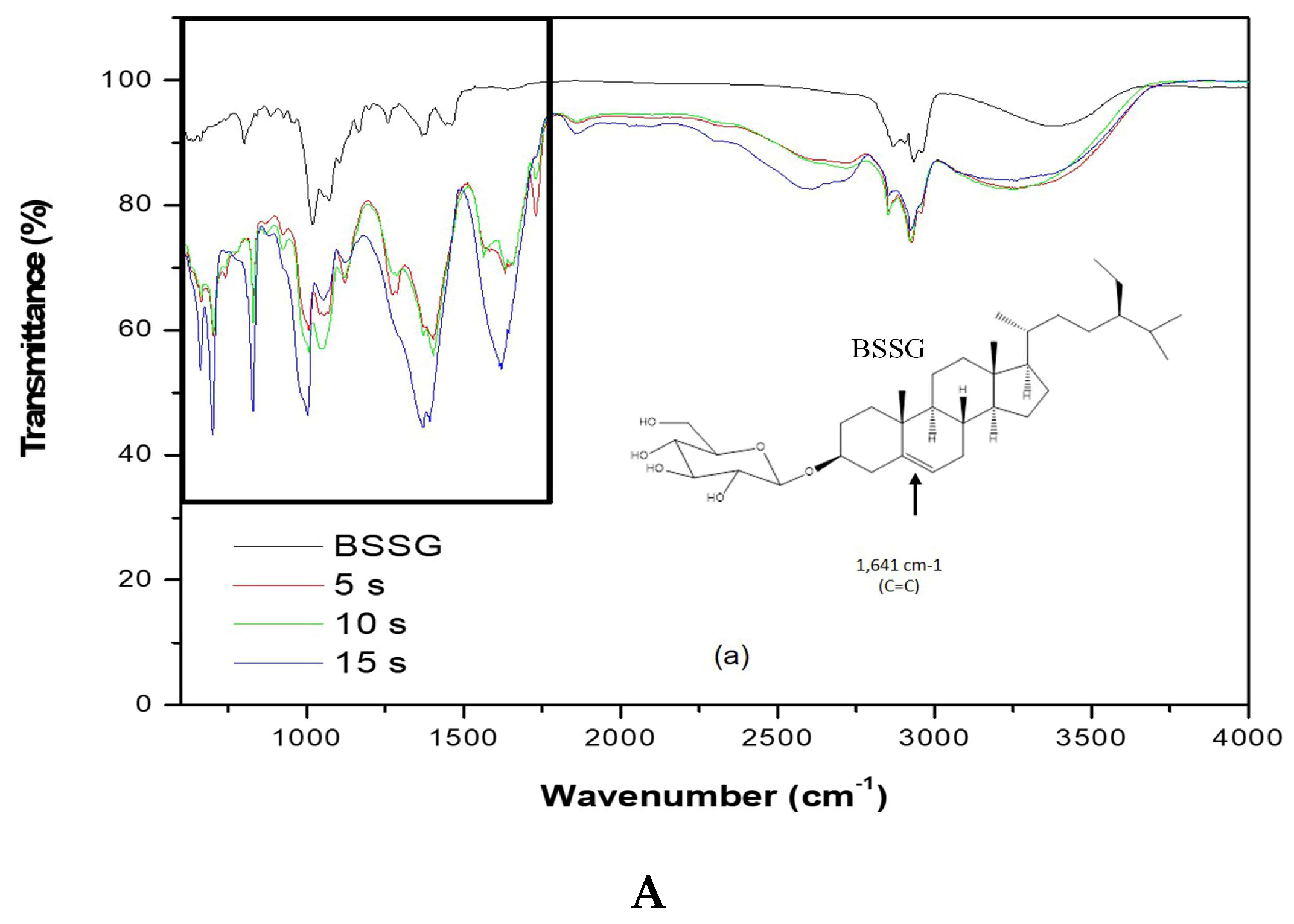
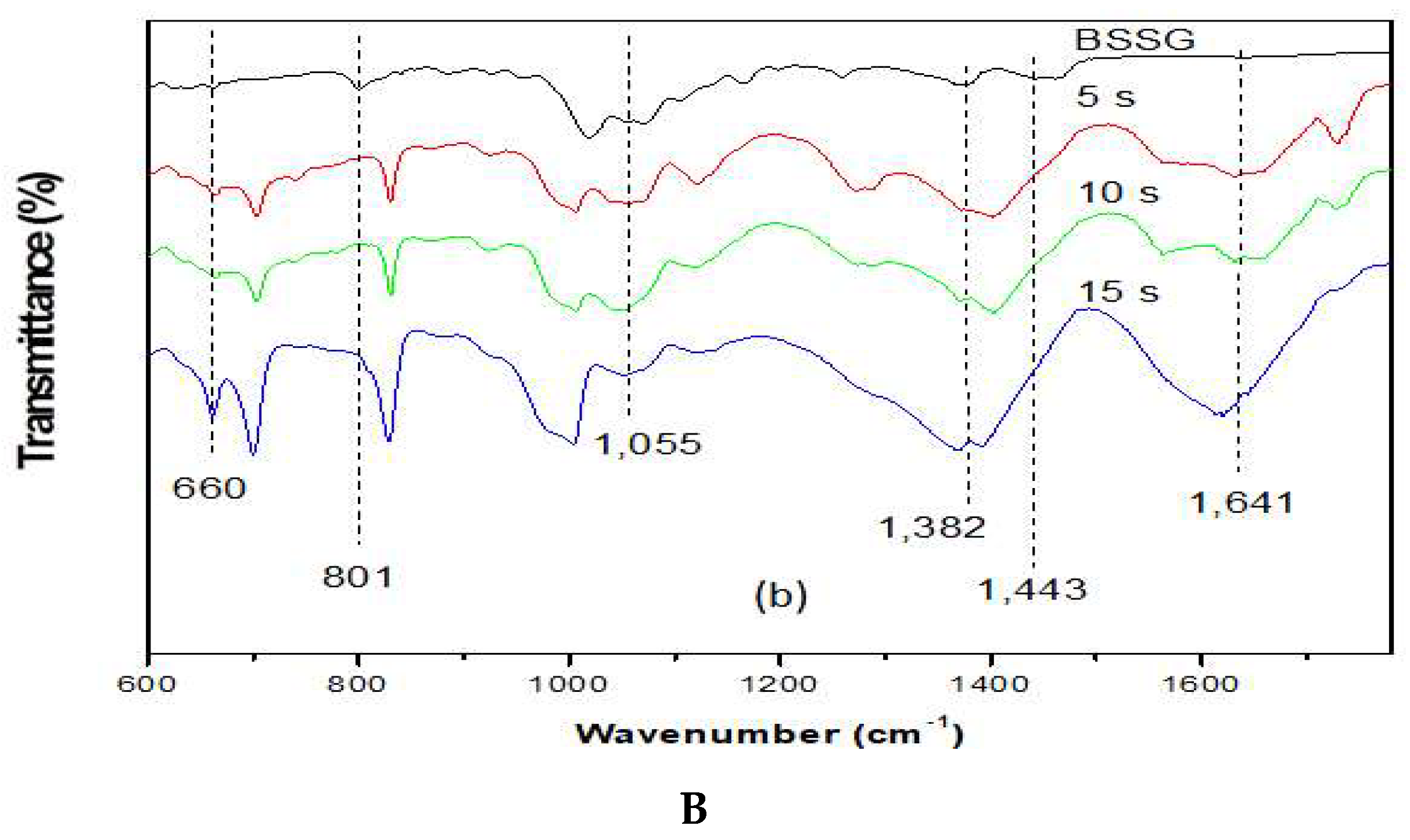
2.2. Identification of the Functional Groups of BSSG by FT-IR
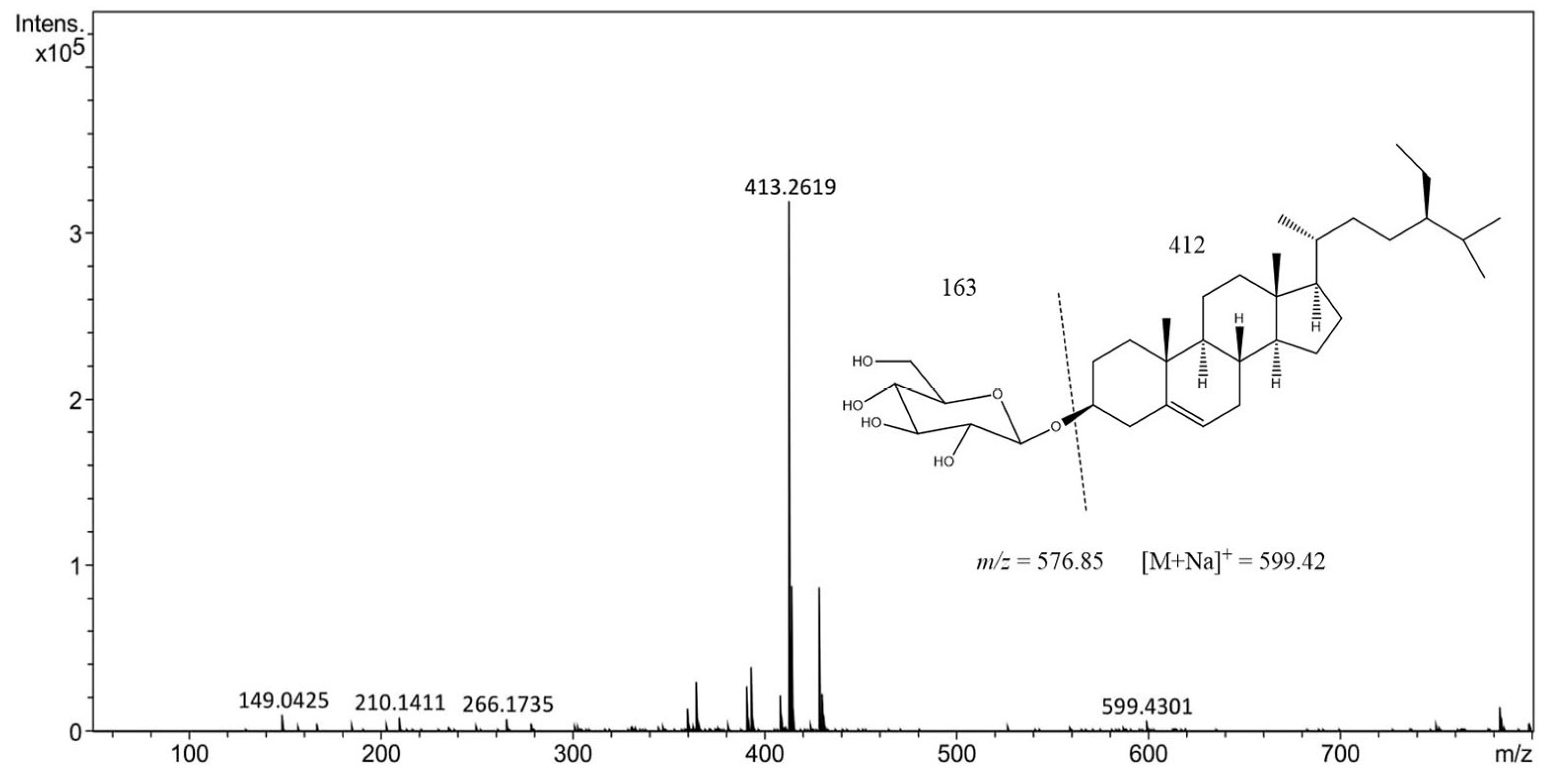
2.3. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography−Electrospray Ionization−Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS) Analysis
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Extraction Techniques
3.1.1. Plant Material
3.1.2. Sample Preparation
3.1.3. Innovation Extraction Technique: Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
3.1.4. Conventional Extraction Technique: Maceration
3.2. High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatographic (HPTLC) Method
3.2.1. Reagents
3.2.2. Standard Solution
3.2.3. Preparation of Samples
3.2.4. Application
3.2.5. Chromatography
3.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopic
3.4. HPLC-ESI-MS
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gentry, H.S. Agaves of Continental North America; The University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1982; p. 670. [Google Scholar]
- García-Mendoza, A. Sistemática y Distribución Actual de los Agave Smezcaleros. CONABIO. Fina Report. Project V029. Available online: http://www.conabio.gob.mx/institucion/cgi-bin/datos.cgi?Letras=V&Numero=29ISBN (accessed on 23 May 2019).
- Hodgson, W.C. Food Plants of the Sonoran Desert; The University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, N.B.; Araiza, P.L.S. El mezcal en Sonora, México, más que una bebida espirituosa. Etnobotánica de Agave angustifolia Haw. In Estudios Sociales. Revista de Alimentación Contemporánea y Desarrollo Regional; CIAD: Hermosillo Sonora, Mexico, 2012; pp. 173–197. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez Nava, Z.; Jiménez-Aparicio, A.R.; Herrera-Ruiz, M.L.; Jiménez-Ferrer, E. Immunomodulatory Effect of Agave tequilana Evaluated on an Autoimmunity Like-SLE Model. Induced in Balb/c Mice with Pristane. Molecules 2017, 22, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Valle, E.; Herrera-Ruiz, M.; Salgado, G.; Zamilpa, A.; Ocampo, M.; Jiménez-Aparicio, A.R.; Jiménez-Ferrer, E. Anti-inflammatory effect of 3-O-[(6′-O-palmitoyl)-β-d-glucopyranosyl sitosterol] from Agave angustifolia on ear edema in mice. Molecules 2014, 19, 15624–15637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monterrosas-Brisson, N.; Ocampo, M.; Jiménez-Ferrer, E.; Jiménez-Aparicio, A.R.; Zamilpa, A.; Gonzalez-Cortazar, M.; Herrera-Ruiz, M. Anti-inflammatory activity of different Agave plants and the compound Cantalasaponin-1. Molecules 2013, 18, 8136–8146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-Martínez, J.R.; González-Cervantes, R.M.; Hernández-Gallegos, M.A.; Mendiola, R.C.; Jiménez-Aparicio, A.R.; Ocampo, M.L.A. Prebiotic potential of Agave angustifolia Haw fructans with different degrees of polymerization. Molecules 2014, 19, 12660–12675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahumada-Santos, Y.P.; Montes-Avila, J.; De Jesús Uribe-Beltrán, M.; Díaz-Camacho, S.P.; López-Angulo, G.; Vega-Aviña, R.; Delgado-Vargas, F. Chemical characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of six Agave species from Sinaloa, Mexico. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 49, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaraz-Abarca, N.; Delgado-Alvarado, E.A.; Ávila-Reyes, J.A.; Uribe-Soto, J.N.; González-Valdez, L.S. The phenols of the genus Agave (Agavaceae). J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriada-Bernal, L.G.; Almaraz-Abarca, N.; Delgado-Alvarado, E.A.; Gallardo-Velázquez, T.; Ávila-Reyes, J.A.; Torres-Morán, M.I.; Herrera-Arrieta, Y. Flavonoid composition and antioxidant capacity of the edible flowers of Agave durangensis (Agavaceae). CYTA J. Food 2014, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Serna, J.A.; Jiménez-Aparicio, A.R.; Estrada-Reyes, R.; Marquez, C.; Cárdenas, J.; Salmón, M. Homoisoflavanones from Agave tequilana weber. Molecules 2010, 15, 3295–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, K.; Zubair, M.; Rasool, N.; Riaz, M.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; De Feo, V. Phytochemical and biological studies of Agave attenuata. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 6440–6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botura, M.B.; Silva, G.D.; Lima, H.G.; Oliveira, J.V.A.; Souza, T.S.; Santos, J.D.G.; Batatinha, M.J.M. In vivo anthelmintic activity of an aqueous extract from sisal waste (Agave sisalana Perr.) against gastrointestinal nematodes in goats. Veterinary Parasitol. 2011, 177, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, S.A.; Melek, F.R.; Abdel-khalik, S.M.; Gabr, N.M. Two steroidal saponins from Agave franzosinii and Agave angustifolia leaves and Biological activities of Agave franzosinii. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 6, 188–197. [Google Scholar]
- Loizou, S.; Lekakis, I.; Chrousos, G.P.; Moutsatsou, P. β-Sitosterol exhibits anti-inflammatory activity in human aortic endothelial cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouic, P.J. The role of phytosterols and phytosterolins in immune modulation: A review of the past 10 years. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2001, 4, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, A.B.; Fink, C.S. Phytosterols as anticancer dietary components: Evidence and mechanism of action. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2127–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.J.; Raeini-Sarjaz, M.; Ntanios, F.Y.; Vanstone, C.A.; Feng, J.Y.; Parsons, W.E. Modulation of plasma lipid levels and cholesterol kinetics by phytosterol versus phytostanol esters. J. Lipid Res. 2000, 41, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Naraniwal, M.; Kothari, V. Modern extraction methods for preparation of bioactive plant extracts. Int. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2012, 1, 8–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Gu, F.; Xu, F.; Wang, Q. Comparison of four kinds of extraction techniques and kinetics of microwave-assisted extraction of vanillin from Vanilla planifolia Andrews. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinatoru, M.; Mason, T.J.; Calinescu, I. Ultrasonically assisted extraction (UAE) and microwave assisted extraction (MAE) of functional compounds from plant materials. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Ugarte, G.A.; Juárez-Becerra, G.P.; Sosa Morales, M.E.; López-Malo, A. Microwave-assisted extraction of essential oils from herbs. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 2013, 47, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusheva, B.; Trunkova, D.; Bankova, V. Different extraction methods of biologically active components from propolis: A preliminary study. Chem. Cent. J. 2007, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azwanida, N.N. A review on the extraction methods use in medicinal plants, principle, strength and limitation. Med. Aromat. Plants 2015, 4, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Gaber, A.S.; El Gendy, A.N.G.; Elkhateeb, A.; Saleh, I.A.; El-Seedi, H.R. Microwave Extraction of Essential Oil from Anastatica hierochuntica (L): Comparison with Conventional Hydro-Distillation and Steam Distillation. J. Essential Oil Bear. Plants 2018, 21, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapa, A.N.; Martin, A.; Mato, R.B.; Cocero, M.J. Extraction of phytocompounds from the medicinal plant Clinacanthus nutans Lindau by microwave-assisted extraction and supercritical carbon dioxide extraction. Ind. Crops Product. 2015, 74, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.H.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Li, G.K. Preparation of phytosterols and phytol from edible marine algae by microwave-assisted extraction and high-speed counter-current chromatography. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 104, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Xiao, X.; Xu, P.; Li, G. Ionic liquid-based microwave-assisted extraction and HPLC analysis of dehydrocavidine in corydalis saxicola Bunting. Acta Chromatogr. 2010, 22, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Xiao, X.; Li, G.; Cai, Z. Study of polyethylene glycol as a green solvent in the microwave-assisted extraction of flavone and coumarin compounds from medicinal plants. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 3608–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirge, S.S.; Tatke, P.A.; Gabhe, S.Y. Development and validation of a novel HPTLC method for simultaneous estimation of beta- sitosterol d-glucoside and withaferin A. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3, 227–230. [Google Scholar]
- Belwal, T.; Ezzat, S.M.; Rastrelli, L.; Bhatt, I.D.; Daglia, M.; Baldi, A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. A critical analysis of extraction techniques used for botanicals: Trends, priorities, industrial uses and optimization strategies. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 100, 82–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Massarani, S.M.; El Gamal, A.A.; Alam, P.; Al-Sheddi, E.S.; Al-Oqail, M.M.; Farshori, N.N. Isolation, biological evaluation and validated HPTLC-quantification of the marker constituent of the edible Saudi plant Sisymbrium irio L. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.H.; Yusoff, R.; Ngoh, G.C.; Kung, F.W.L. Microwave-assisted extractions of active ingredients from plants. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 37, 6213–6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, M.; Handa, S.S. Antiinflammatory activity and chemical composition of extracts of Verbena officinalis. Phytother. Res. 2000, 14, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilango, K. β-Sitosterol Glucoside from Pisonia grandis R. Br. Stem Bark in Ethyl Acetate Extract. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ododo, M.M.; Choudhury, M.K.; Dekebo, A.H. Structure elucidation of β-sitosterol with antibacterial activity from the root bark of Malva parviflora. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barriuso, B.; Otaegui-Arrazola, A.; Menéndez-Carreño, M.; Astiasarán, I.; Ansorena, D. Sterols heating: Degradation and formation of their ring-structure polar oxidation products. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkacheva, O.; Sukhov, D. Investigation of lignins by FTIR spectroscopy. Macromol. Symp. 2008, 265, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, R.; Ramaswamy, M. Phytochemical screening by FTIR spectroscopic analysis of leaf extracts of selected Indian Medicinal plants. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 395–406. [Google Scholar]
- Rutckeviski, R.; Xavier-Júnior, F.; Morais, A.; Alencar, E.; Amaral-Machado, L.; Genre, J.; Egito, E. Thermo-oxidative stability evaluation of bullfrog (rana catesbeiana shaw) oil. Molecules 2017, 22, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hattab, N.; Daghbouche, Y.; El Hattab, M.; Piovetti, L.; Garrigues, S.; De la Guardia, M. FTIR-determination of sterols from the red alga Asparagopsis armata: Comparative studies with HPLC. Talanta 2006, 68, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbusola, E.M.; Fagbemi, T.N.; Osundahunsi, O.F. Fatty acid characterisation, sterol composition and spectroscopic analysis of selected Cucurbitaceae seed oils. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 696–702. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer, A.; Altabella, T.; Arró, M.; Boronat, A. Emerging roles for conjugated sterols in plants. Progr. Lipid Res. 2017, 67, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Liu, S.; Luo, Z.; Tang, K. Direct saponification preparation and analysis of free and conjugated phytosterols in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.W.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.F.; Lin, J.M. Simultaneous extraction and determination of free and conjugated phytosterols in tobacco. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 2466–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, S.; Tatke, P. Charantin: An important lead compound from Momordica charantia for the treatment of diabetes. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2015, 3, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Khatun, M.; Billah, M.; Quader, M.A. Sterols and sterol glucoside from Phyllanthus species. Dhaka Univer. J. Sci. 2012, 60, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithambo, B.; Noundou, X.S.; Krause, R.W. Anti-malarial synergy of secondary metabolites from Morinda lucida Benth. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 199, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SigmaPlot for Windows Version 11.0, Build 11.1.0.102; Systat Software, Inc.: Wpcubed GmbH, Germany, 2018.
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |


| Method | Extraction Time (s) | Extraction Time (h) | Mg B-Sitosterol B-d-Glucoside/Dry Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | 5 | - | 124.76 ± 0.0000655 a |
| MAE | 10 | - | 106.19 ± 0.0000793 b |
| MAE | 15 | - | 103.96 ± 0.0000321 c |
| Maceration | - | 48 | 26.66 ± 0.0000100 d |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Salazar, H.; Camacho-Díaz, B.H.; Ávila-Reyes, S.V.; Pérez-García, M.D.; González- Cortazar, M.; Arenas Ocampo, M.L.; Jiménez-Aparicio, A.R. Identification and Quantification of β-Sitosterol β-d-Glucoside of an Ethanolic Extract Obtained by Microwave-Assisted Extraction from Agave angustifolia Haw. Molecules 2019, 24, 3926. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213926
López-Salazar H, Camacho-Díaz BH, Ávila-Reyes SV, Pérez-García MD, González- Cortazar M, Arenas Ocampo ML, Jiménez-Aparicio AR. Identification and Quantification of β-Sitosterol β-d-Glucoside of an Ethanolic Extract Obtained by Microwave-Assisted Extraction from Agave angustifolia Haw. Molecules. 2019; 24(21):3926. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213926
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Salazar, Herminia, Brenda Hildeliza Camacho-Díaz, Sandra Victoria Ávila-Reyes, Ma Dolores Pérez-García, Manases González- Cortazar, Martha L. Arenas Ocampo, and Antonio R. Jiménez-Aparicio. 2019. "Identification and Quantification of β-Sitosterol β-d-Glucoside of an Ethanolic Extract Obtained by Microwave-Assisted Extraction from Agave angustifolia Haw" Molecules 24, no. 21: 3926. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213926
APA StyleLópez-Salazar, H., Camacho-Díaz, B. H., Ávila-Reyes, S. V., Pérez-García, M. D., González- Cortazar, M., Arenas Ocampo, M. L., & Jiménez-Aparicio, A. R. (2019). Identification and Quantification of β-Sitosterol β-d-Glucoside of an Ethanolic Extract Obtained by Microwave-Assisted Extraction from Agave angustifolia Haw. Molecules, 24(21), 3926. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213926