In Silico and In Vitro Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Effects of Combinations of Phytochemicals and Antibiotics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
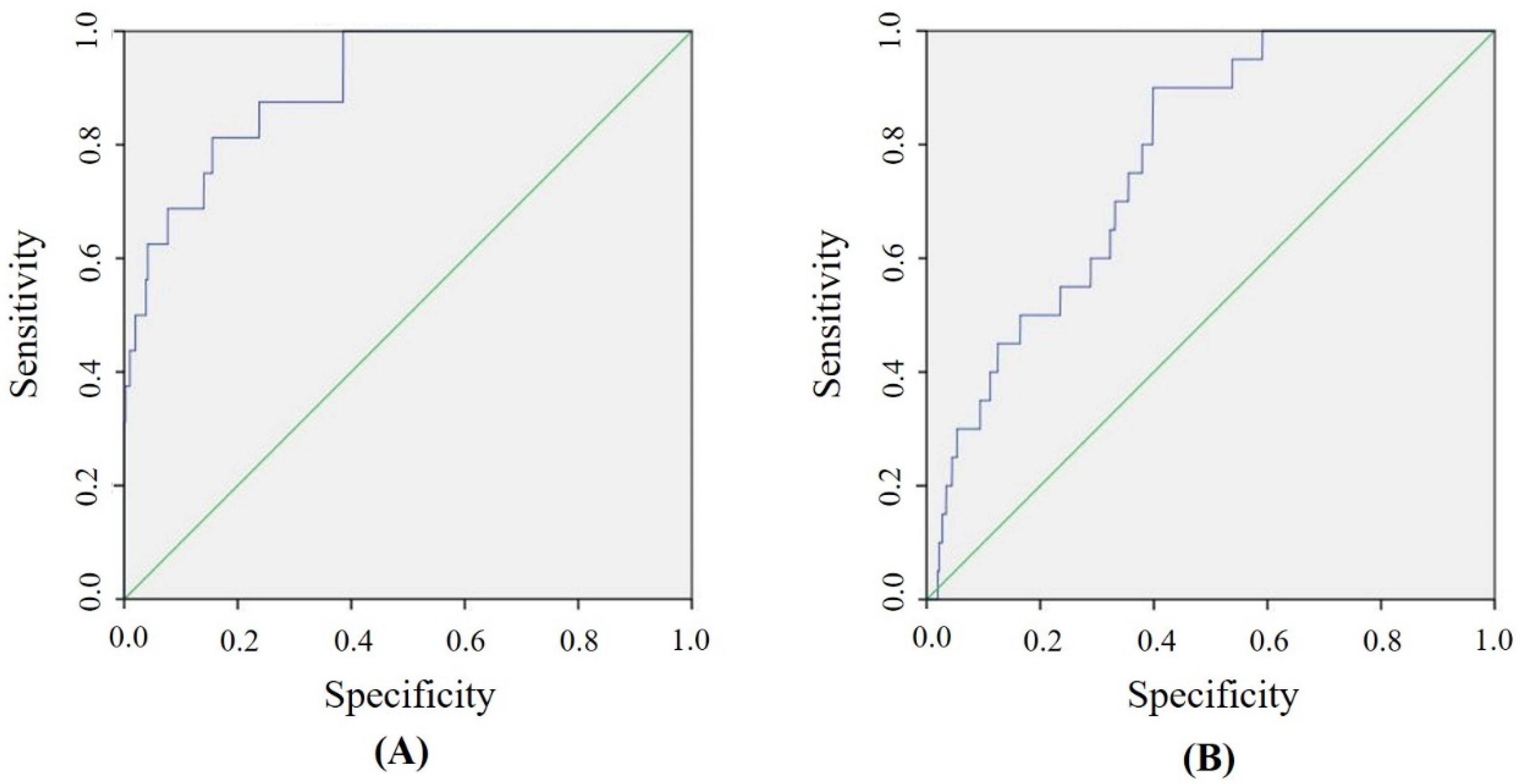
2.1. In Silico Simulations
2.2. In Vitro Susceptibility and Synergistic Testing
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Molecular Docking
3.2. Validation of Molecular Docking Methods
3.3. Drug-Like Properties Analysis
3.4. Susceptibility Testing
3.5. Synergistic Testing
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, C.Y.; Kuo, K.N.; Wu, M.S.; Chen, Y.J.; Wang, C.B.; Lin, J.T. Early Helicobacter pylori eradication decreases risk of gastric cancer in patients with peptic ulcer disease. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1641–1648.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoldi, A.; Carrara, E.; Graham, D.Y.; Conti, M.; Tacconelli, E. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: A systematic review and meta-analysis in World Health Organization regions. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1372–1382.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawla, P.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of gastric cancer: Global trends, risk factors and prevention. Prz Gastroenterol. 2019, 14, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagari, R.M.; Rabitti, S.; Eusebi, L.H.; Bazzoli, F. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: A clinical practice update. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thung, I.; Aramin, H.; Vavinskaya, V.; Gupta, S.; Park, J.; Crowe, S.; Valasek, M. the global emergence of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 514–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, F.F.; Oleastro, M. Overview of the phytomedicine approaches against Helicobacter pylori. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5594–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, H.M.; Zaidi, S.F.; Sugiyama, T.; Akhtar, N.; Usmanghani, K. Phytomedicine–based and quadruple therapies in Helicobacter pylori infection: A comparative, randomized trial. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2015, 21, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mobley, H.; Hu, L.; Foxall, P. Helicobacter pylori urease: Properties and role in pathogenesis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1991, 26, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Hsu, K.; Lin, S.; Chen, T.; Yang, J.; Wang, W. Structures of Helicobacter pylori shikimate kinase reveal a selective inhibitor–induced-fit mechanism. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Ngo, A.; Quinn, R.J.; Redburn, J.; Hooper, J.N. Petrosamine B, an Inhibitor of the Helicobacter p ylori Enzyme Aspartyl Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase from the Australian Sponge Oceanapia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 804–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Garg, P. Molecular Modeling and Active Site Binding Mode Characterization of Aspartate β-Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Family. Mol. Inform. 2013, 32, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puram, S.; Suh, H.C.; Kim, S.U.; Bethapudi, B.; Joseph, J.A.; Agarwal, A.; Kudiganti, V. Effect of GutGard in the Management of Helicobacter pylori: A Randomized Double Blind Placebo Controlled Study. Evid Based. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 263805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Salem, E.M.; Yar, T.; Bamosa, A.O.; Al-Quorain, A.; Yasawy, M.I.; Alsulaiman, R.M.; Randhawa, M.A. Comparative study of Nigella Sativa and triple therapy in eradication of Helicobacter Pylori in patients with non-ulcer dyspepsia. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adeniyi, B.A.; Anyiam, F.M. In vitro anti-Helicobacter pylori potential of methanol extract of Allium ascalonicum Linn.(Liliaceae) leaf: Susceptibility and effect on urease activity. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.L. A multicenter study of Chinese patent medicine wenweishu/yangweishu in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori positive patients with chronic gastritis and peptic ulcer. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2010, 90, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ncube, B.; Finnie, J.; Van Staden, J. Quality from the field: The impact of environmental factors as quality determinants in medicinal plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2012, 82, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.Y.; Meiler, J. Predictive power of different types of experimental restraints in small molecule docking: A review. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 58, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaddir, I.; Rasool, N.; Hussain, W.; Mahmood, S. Computer–aided analysis of phytochemicals as potential dengue virus inhibitors based on molecular docking, ADMET and DFT studies. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2017, 54, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Kataria, R.; Khatkar, A. Molecular docking, synthesis, kinetics study, structure–activity relationship and ADMET analysis of morin analogous as Helicobacter pylori urease inhibitors. BMC Chem. 2019, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, K.; Shen, X.; Jiang, H. Discovery of Helicobacter pylori shikimate kinase inhibitors: Bioassay and molecular modeling. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Park, J.; Devkota, A.K.; Cho, E.J.; Dalby, K.N.; Ren, P. Identification and validation of novel PERK inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, P.; Tong, H.H.; Ng, K.H.; Lao, C.K.; Chong, C.I.; Chao, C.M. In silico prediction of prostaglandin D2 synthase inhibitors from herbal constituents for the treatment of hair loss. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 175, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Dong, X.; Yin, X.; Wang, W.; You, L.; Ni, J. Radix Bupleuri: A review of traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zheng, R.; Xie, J.; Su, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Mo, Z.; Wu, X.; Wu, D.; et al. Biological evaluation and molecular docking of baicalin and scutellarin as Helicobacter pylori urease inhibitors. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 162, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Hu, D.; Wang, K.X. Study of Scutellaria baicalensis and Baicalin against antimicrobial susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori strains in vitro. Zhong Yao Cai 2008, 31, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- González-Segovia, R.; Quintanar, J.L.; Salinas, E.; Ceballos-Salazar, R.; Aviles-Jiménez, F.; Torres-López, J. Effect of the flavonoid quercetin on inflammation and lipid peroxidation induced by Helicobacter pylori in gastric mucosa of guinea pig. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberi, A.; Abbasloo, E.; Sepehri, G.; Yazdanpanah, M.; Mirkamandari, E.; Sheibani, V.; Safi, Z. The Effects of Methanolic Extract of Melissa officinalis on Experimental Gastric Ulcers in Rats. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2016, 18, e24271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhaei, M.M.; Malekzadeh, F.; Khaje-Karamoddin, M.; Ramezani, M. In vitro anti-Helicobacter pylori effects of sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) and purple basil (Ocimum basilicum var. purpurascens). Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2006, 9, 2887–2891. [Google Scholar]
- Salawu, S.; Ogundare, A.; Ola-Salawu, B.; Akindahunsi, A. Antimicrobial activities of phenolic containing extracts of some tropical vegetables. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 486–492. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnt, M.; Pröbstle, A.; Rimpler, H.; Bauer, R.; Heinrich, M. Biological and pharmacological activities and further constituents of Hyptis verticillata. Planta Med. 1995, 61, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohari, A.R.; Saeidnia, S.; Shahverdi, A.R.; Yassa, N.; Malmir, M.; Mollazade, K.; Naghinejad, A.R. Phytochemistry and antimicrobial compounds of Hymenocrater calycinus. Eur. Asia J. BioSci. 2009, 3, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, S.; Scheyer, T.; Romano, C.S.; Vojnov, A.A. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of rosemary extracts linked to their polyphenol composition. Free Radic. Res. 2006, 40, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekambaram, S.P.; Perumal, S.S.; Balakrishnan, A.; Marappan, N.; Gajendran, S.S.; Viswanathan, V. Antibacterial synergy between rosmarinic acid and antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Intercult Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 5, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, J.G.; de Liverant, J.G.; Martınez, A.; Martınez, G.; Munoz, J.L.; Arciniegas, A.; de Vivar, A.R. Mode of action of Buddleja cordata verbascoside against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 66, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didry, N.; Seidel, V.; Dubreuil, L.; Tillequin, F.; Bailleul, F. Isolation and antibacterial activity of phenylpropanoid derivatives from Ballota nigra. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 67, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masadeh, M.M.; Alkofahi, A.S.; Alzoubi, K.H.; Tumah, H.N.; Bani–Hani, K. Anti-Helicobactor pylori activity of some Jordanian medicinal plants. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazly Bazzaz, B.S.; Khameneh, B.; Zahedian Ostad, M.R.; Hosseinzadeh, H. In vitro evaluation of antibacterial activity of verbascoside, lemon verbena extract and caffeine in combination with gentamicin against drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli clinical isolates. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2018, 8, 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Shukla, N.; Singh, P.; Sharma, R.; Rajendran, S.; Maurya, R.; Palit, G. Verbascoside isolated from Tectona grandis mediates gastric protection in rats via inhibiting proton pump activity. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaad, A.S.; Al-Rifai, A.A.; El-Meligy, R.M.; Alafeefy, A.M.; Zain, M.E. New activities for isolated compounds from convolvulus austro-aegyptiacus as anti-ulcerogenic, anti-helicobacter pylori and their mimic synthesis using bio-guided fractionation. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahady, G.B.; Pendland, S.L.; Stoia, A.; Chadwick, L.R. In vitro susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori to isoquinoline alkaloids from Sanguinaria canadensis and Hydrastis canadensis. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nontakham, J.; Charoenram, N.; Upamai, W.; Taweechotipatr, M.; Suksamrarn, S. Anti–Helicobacter pylori xanthones of Garcinia fusca. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Q.; Xu, M.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, G.; Zhao, L. In vitro and in vivo bactericidal activity of Tinospora sagittata (Oliv.) Gagnep. var. craveniana (SY Hu) Lo and its main effective component, palmatine, against porcine Helicobacter pylori. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Gara, E.A.; Hill, D.J.; Maslin, D.J. Activities of garlic oil, garlic powder, and their diallyl constituents against Helicobacter pylori. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2269–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Sharopov, F.; Martorell, M.; Rajkovic, J.; Ademiluyi, A.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Fokou, P.; Martins, N.; Iriti, M.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Phytochemicals in Helicobacter pylori infections: What are we doing now? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattelman, E. Health effects of garlic. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 72, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Song, J.; Zhong, L.; Liao, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, X. Palmatine: A review of its pharmacology, toxicity and pharmacokinetics. Biochimie 2019, 162, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xia, T.; Yu, X. Wogonin suppresses inflammatory response and maintains intestinal barrier function via TLR4-MyD88-TAK1-mediated NF-κB pathway in vitro. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Song, H.E.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.; Koketsu, M.; Ngan, L.T.M.; Ahn, Y. Growth inhibitory, bactericidal, and morphostructural effects of dehydrocostus lactone from Magnolia sieboldii Leaves on antibiotic-susceptible and -resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Francesco, V.; Zullo, A.; Fiorini, G.; Saracino, I.M.; Pavoni, M.; Vaira, D. Role of MIC levels of resistance to clarithromycin and metronidazole in Helicobacter pylori eradication. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 74, 772–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehnke, K.F.; Valdivieso, M.; Bussalleu, A.; Sexton, R.; Thompson, K.C.; Osorio, S.; Novoa Reyes, I.; Crowley, J.J.; Baker, L.H.; Xi, C. Antibiotic resistance among Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates in Lima, Peru. Infect. Drug Resist. 2017, 10, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Yuan, Y. Resistance mechanisms of Helicobacter pylori and its dual target precise therapy. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobley, H. The role of Helicobacter pylori urease in the pathogenesis of gastritis and peptic ulceration. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 10, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C.; Leach, A.R.; Taylor, R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 267, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartshorn, M.J.; Verdonk, M.L.; Chessari, G.; Brewerton, S.C.; Mooij, W.T.; Mortenson, P.N.; Murray, C.W. Diverse, high-quality test set for the validation of protein-ligand docking performance. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 726–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, N.; Oh, S.; Sung, J.Y.; Cha, K.A.; Lee, M.H.; Oh, B. Supramolecular assembly and acid resistance of Helicobacter pylori urease. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2001, 8, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korb, O.; Stutzle, T.; Exner, T.E. Empirical scoring functions for advanced protein-ligand docking with PLANTS. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagadala, N.S.; Syed, K.; Tuszynski, J. Software for molecular docking: A review. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, J.J.; Sterling, T.; Mysinger, M.M.; Bolstad, E.S.; Coleman, R.G. ZINC: A free tool to discover chemistry for biology. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilson, M.K.; Liu, T.; Baitaluk, M.; Nicola, G.; Hwang, L.; Chong, J. BindingDB in 2015: A public database for medicinal chemistry, computational chemistry and systems pharmacology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, D1045–D1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. ACD/Percepta, Version 14.0. Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2015. Available online: www.acdlabs.com (accessed on 8 September 2019).
- Wang, J.; Hou, T. Advances in computationally modeling human oral bioavailability. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 86, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Cheng, F.; Chen, L.; Du, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Lee, P.W.; Tang, Y. In silico prediction of chemical Ames mutagenicity. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 2840–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; Easter, A.; Peters, D.; Kim, N.; Enyedy, I.J. In silico prediction of hERG inhibition. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Twenty-Fourth Informational Supplement M100-S24; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- White, R.L.; Burgess, D.S.; Manduru, M.; Bosso, J.A. Comparison of three different in vitro methods of detecting synergy: Time-kill, checkerboard, and E test. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 1914–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuok, C.F.; Hoi, S.O.; Hoi, C.F.; Chan, C.H.; Fong, I.H.; Ngok, C.K.; Meng, L.R.; Fong, P. Synergistic antibacterial effects of herbal extracts and antibiotics on methicillin–resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A computational and experimental study. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2017, 242, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doern, C. When does 2 plus 2 equal 5? A review of antimicrobial synergy testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4124–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |
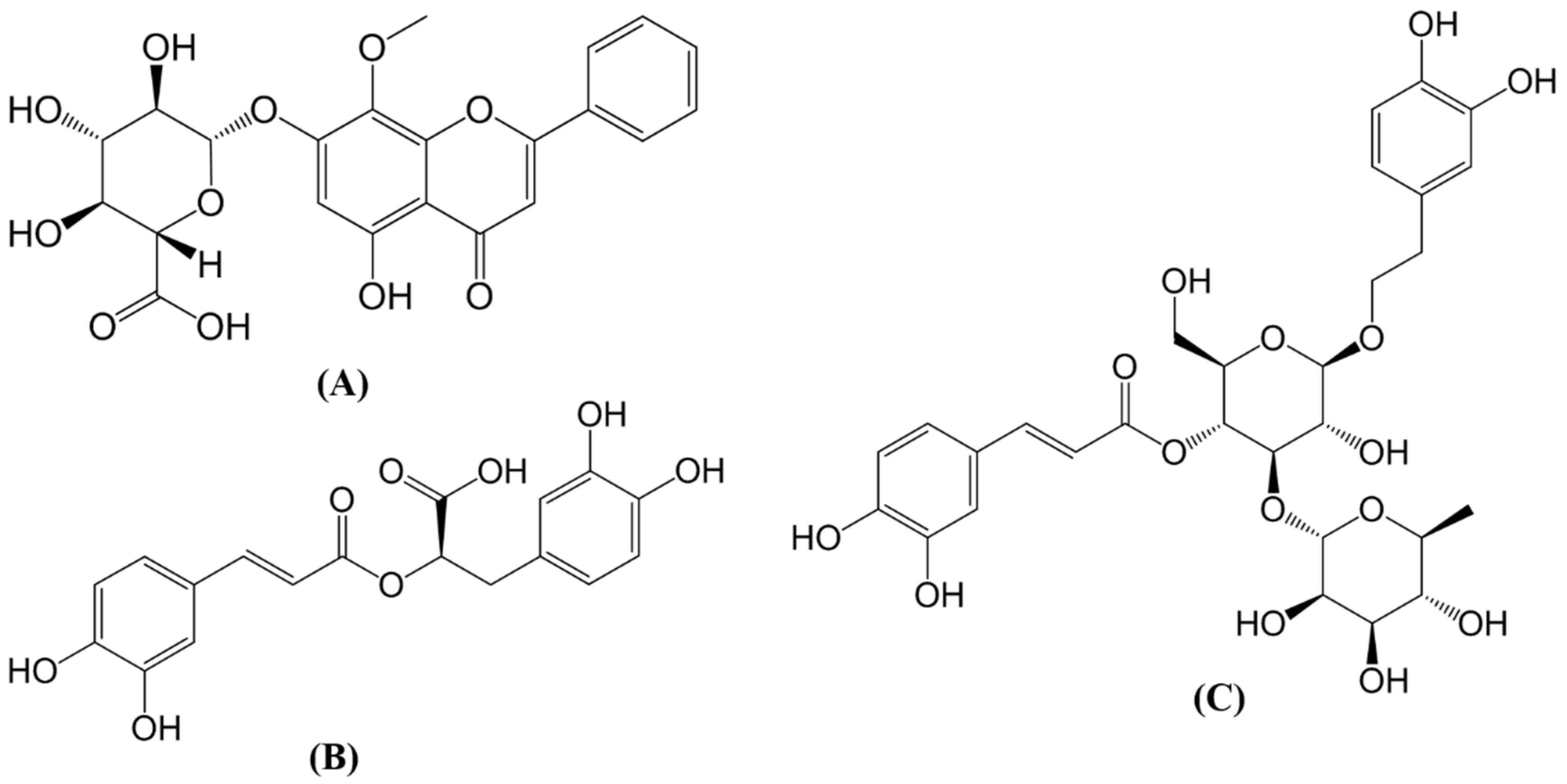
| Oroxindin | Verbascoside | Rosmarinic acid | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Docking Score 1 | 84.9 | 79.1 | 82.3 |
| MW | 460.4 | 624.6 | 360.3 |
| log P | -0.03 | 0.75 | 1.60 |
| Aqueous solubility (mg/mL) | 1000 | 15.7 | 1000 |
| Caco-2 | 0.0 × 10−6 | 0.1 × 10−6 | 0.2 × 10−6 |
| PPB (%) | 89 | 53 | 74 |
| CNS (cm/s) | −6.49 | −5.22 | −4.96 |
| HIA (%) | 1 | 9 | 8 |
| Ames | 0.49 | 0.44 | 0.34 |
| hERG | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.21 |
| CYP1A2 | NI | NI | NI |
| CYP2C9 | NI | NI | NI |
| CYP2C19 | NI | NI | NI |
| CYP2D6 | NI | NI | NI |
| CYP4A4 | NI | NI | NI |
| Test Samples | MIC90 (μg/mL) | Inhibitory % |
|---|---|---|
| Oroxindin | 50 | 97.6 3.5 |
| Verbascoside | 1200 | 97.73.2 |
| Rosmarinic acid | 800 | 96.96.4 |
| Positive control 1 | 0.250 | 92.02.2 |
| Test samples | FIC values | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Oroxindin plus amoxicillin | 0.750 | additive effect |
| Oroxindin plus verbascoside | 0.750 | additive effect |
| Oroxindin plus rosmarinic acid | 0.750 | additive effect |
| Verbascoside plus amoxicillin | 1.125 | indifference |
| Rosmarinic acid plus amoxicillin | 1.125 | indifference |
| Verbascoside plus rosmarinic acid | 1. 250 | indifference |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fong, P.; Hao, C.-H.; Io, C.-C.; Sin, P.-I.; Meng, L.-R. In Silico and In Vitro Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Effects of Combinations of Phytochemicals and Antibiotics. Molecules 2019, 24, 3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193608
Fong P, Hao C-H, Io C-C, Sin P-I, Meng L-R. In Silico and In Vitro Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Effects of Combinations of Phytochemicals and Antibiotics. Molecules. 2019; 24(19):3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193608
Chicago/Turabian StyleFong, Pedro, Chon-Hou Hao, Chi-Cheng Io, Pou-Io Sin, and Li-Rong Meng. 2019. "In Silico and In Vitro Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Effects of Combinations of Phytochemicals and Antibiotics" Molecules 24, no. 19: 3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193608
APA StyleFong, P., Hao, C.-H., Io, C.-C., Sin, P.-I., & Meng, L.-R. (2019). In Silico and In Vitro Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Effects of Combinations of Phytochemicals and Antibiotics. Molecules, 24(19), 3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193608





