Polyamines Disrupt the KaiABC Oscillator by Inducing Protein Denaturation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
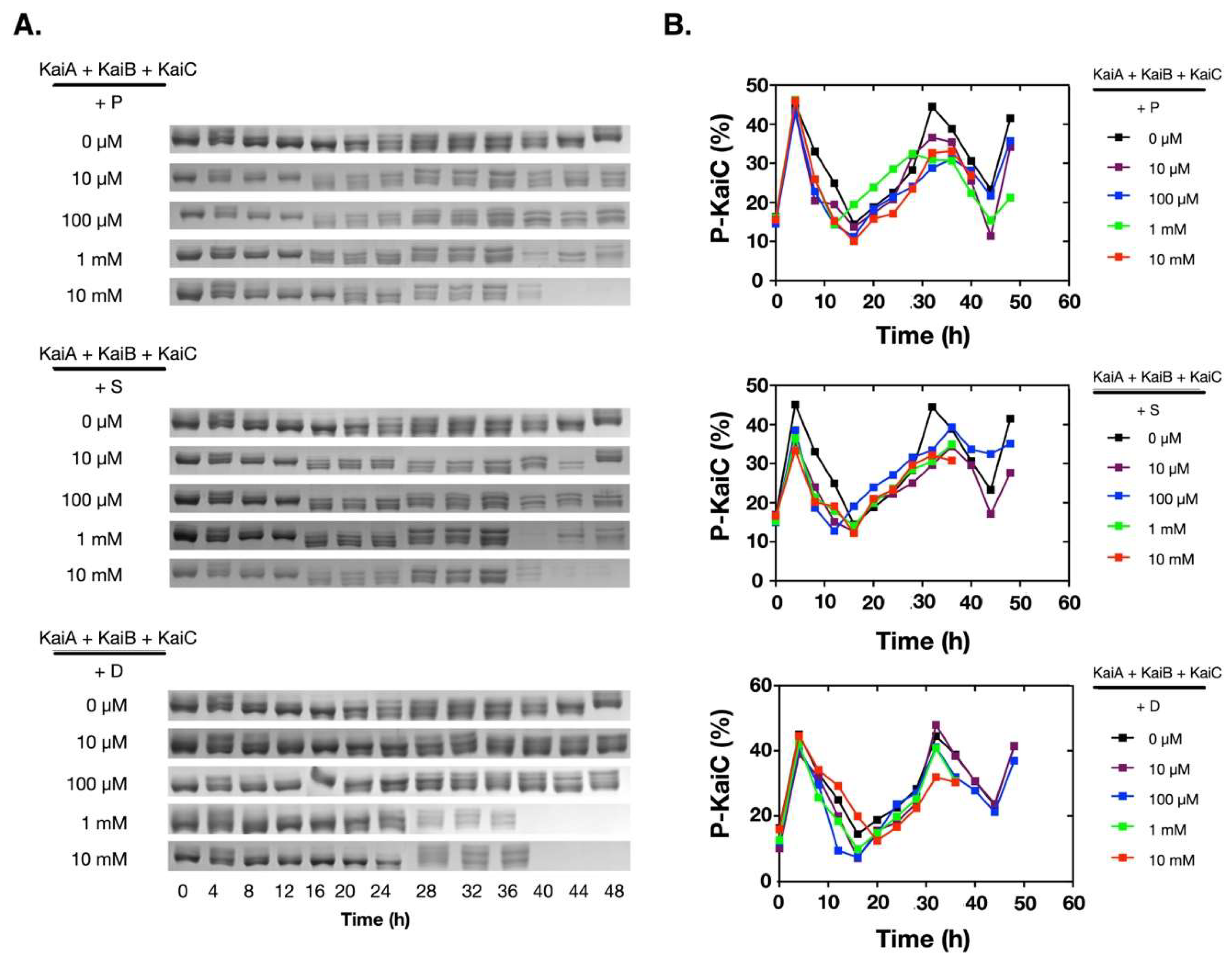
2.1. Polyamines can Disrupt the KaiABC Oscillator
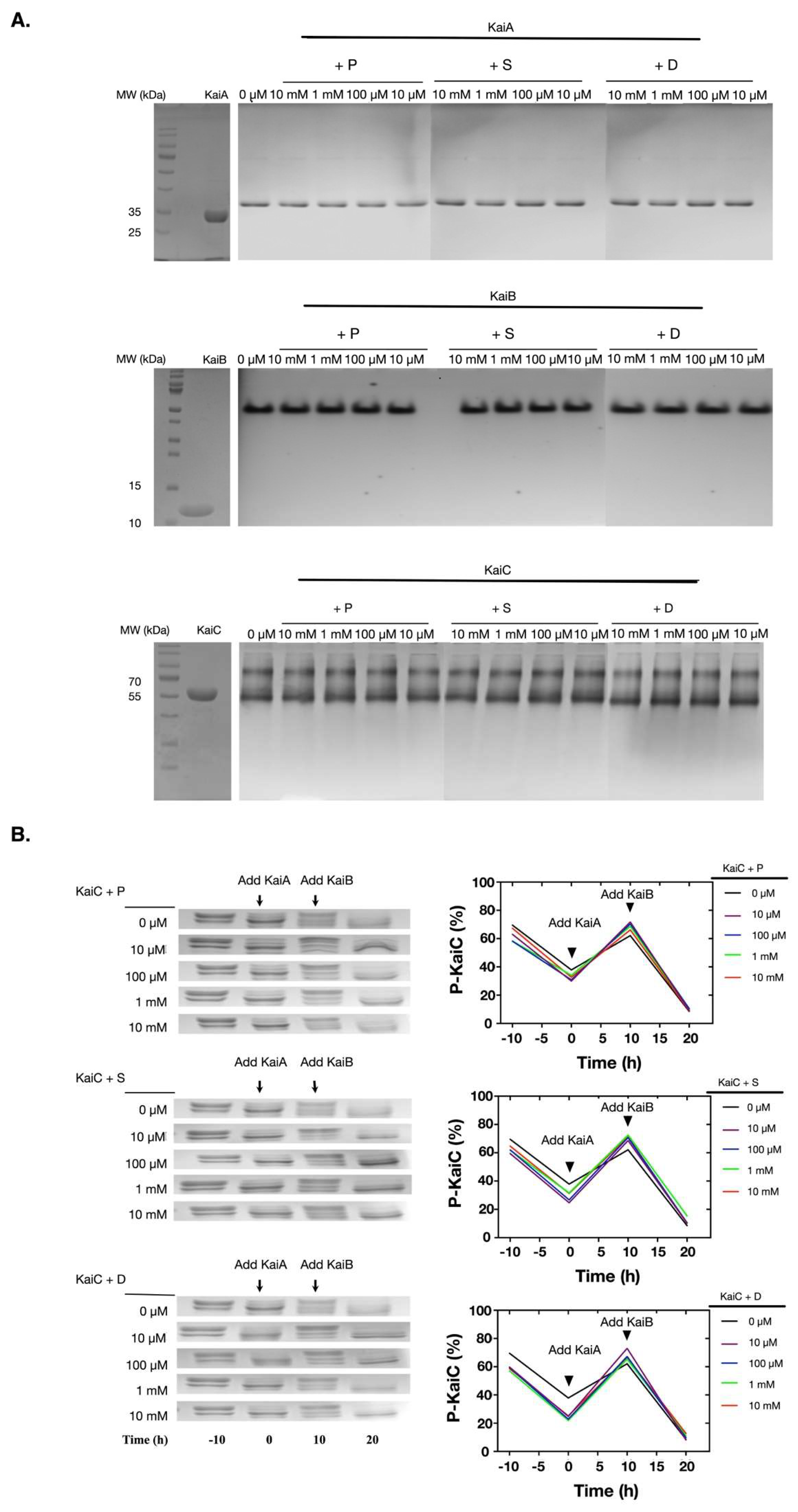
2.2. Polyamines did not Directly Disturb the Functions of the Clock Proteins
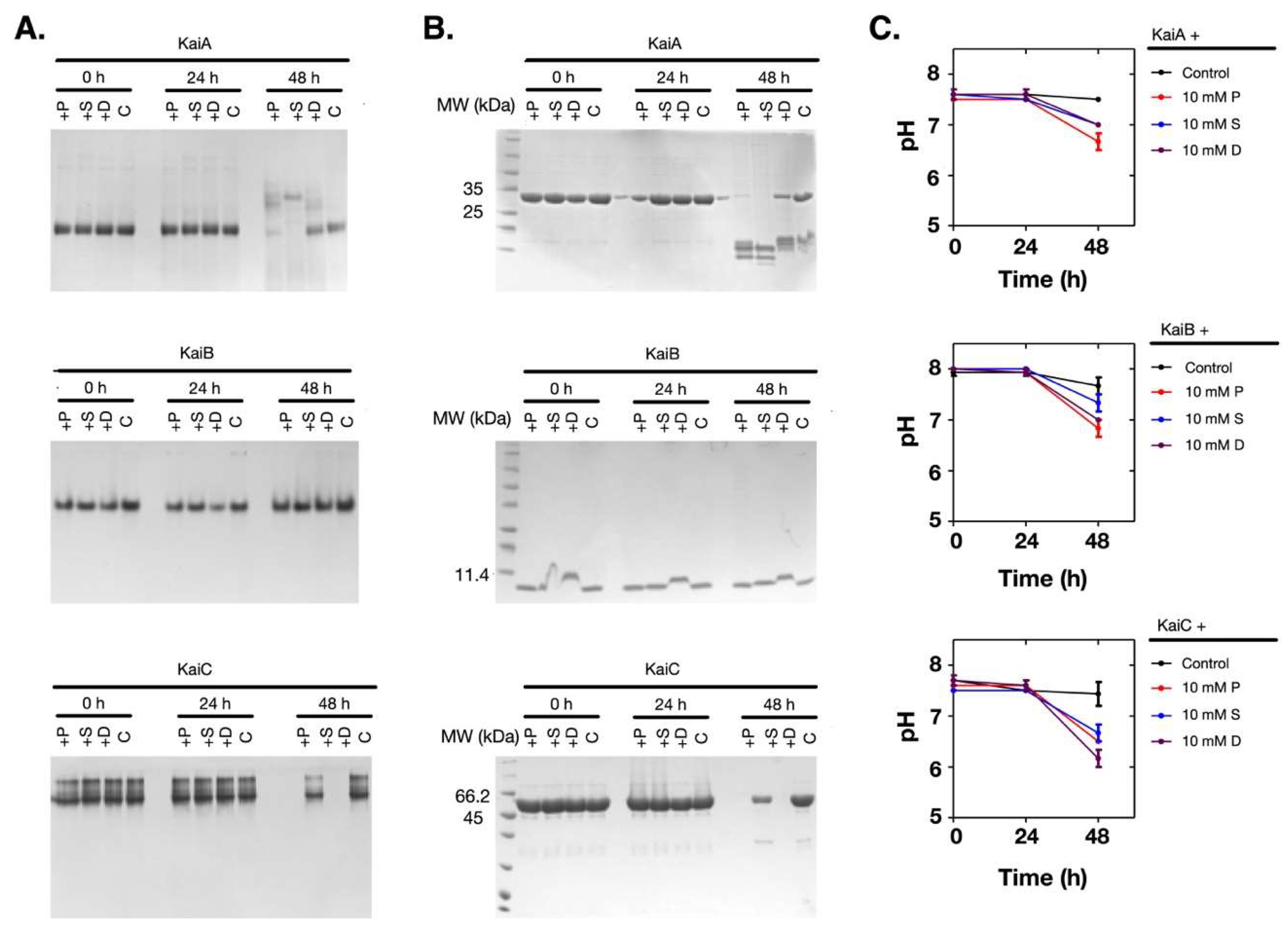
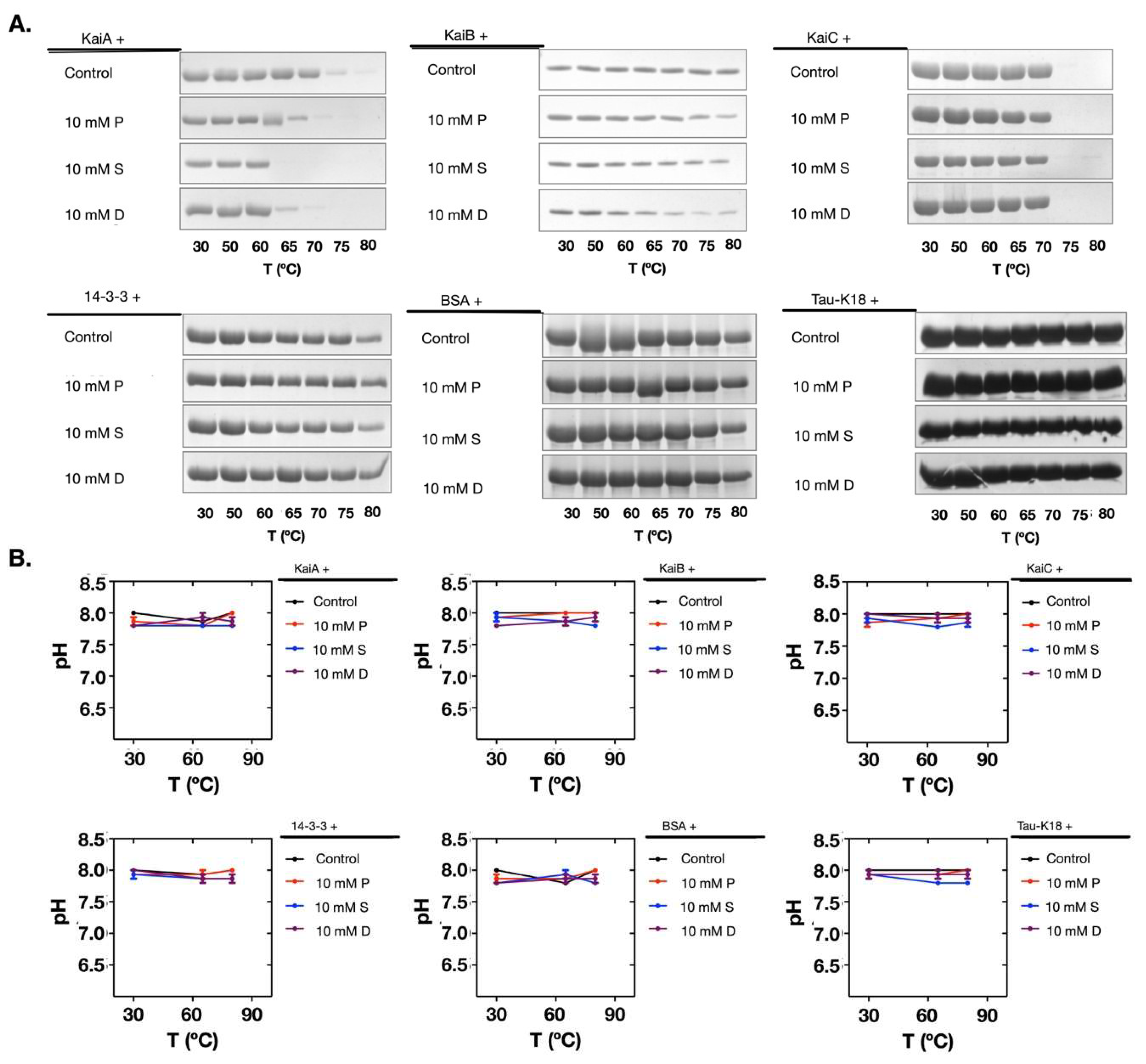
2.3. Polyamines Induced Denaturation of the Clock Proteins
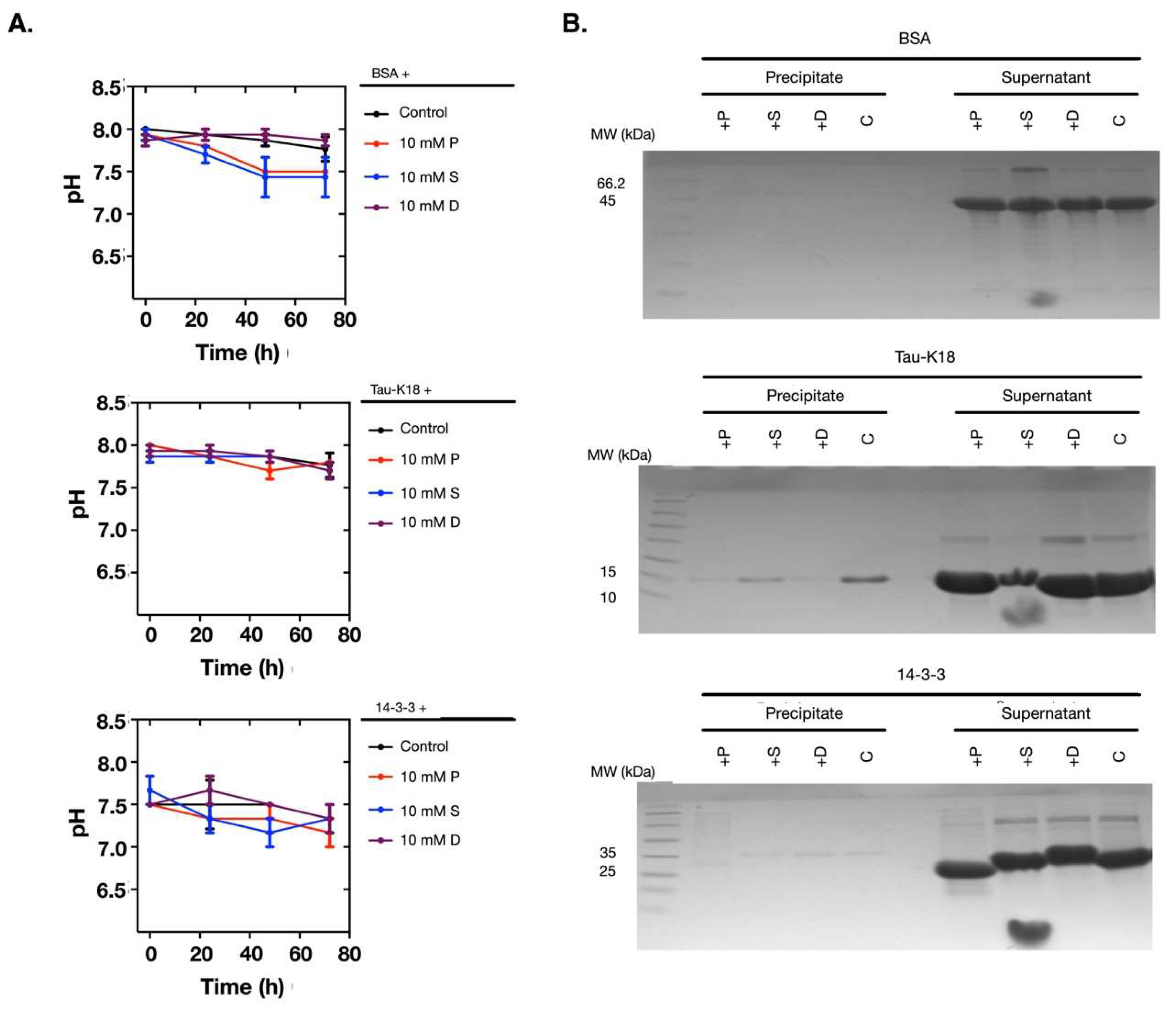
2.4. The Polyamine-Induced Denaturation is Protein-Dependent
2.5. Polyamines Induce the Decrease of the Thermal Stability of the Clock Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Protein Expression and Purification
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of the Protein Samples
4.5. Analysis of the Phosphorylation Level of KaiC
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arruabarrena-Aristorena, A.; Zabala-Letona, A.; Carracedo, A. Oil for the cancer engine: The cross-talk between oncogenic signaling and polyamine metabolism. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller-Fleming, L.; Olin-Sandoval, V.; Campbell, K.; Ralser, M. Remaining Mysteries of Molecular Biology: The Role of Polyamines in the Cell. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 3389–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamana, K.; Hamana, K.; Miyagawa, K.; Miyagawa, K.; Matsuzaki, S.; Matsuzaki, S. Occurrence of sym-homospermidine as the major polyamine in nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1983, 112, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeo, F.; Bauer, M.A.; Carmona-Gutiérrez, D.; Kroemer, G. Spermidine: a physiological autophagy inducer acting as an anti-aging vitamin in humans? Autophagy 2019, 15, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bograh, A.; Gingras, Y.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A.; Carpentier, R. The effects of spermine and spermidine on the structure of photosystem II proteins in relation to inhibition of electron transport. FEBS Lett. 1997, 402, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadian, S.; Shareghi, B.; Saboury, A.A. Exploring the thermal stability and activity of α-chymotrypsin in the presence of spermine. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 35, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.P.; Saha, I.; Nandi, I.; Swamy, M.J. Spermine and spermidine act as chemical chaperones and enhance chaperone-like and membranolytic activities of major bovine seminal plasma protein, PDC-109. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, S. [Progress in the effect of polyamines on proteins]. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 2018, 34, 352–359. [Google Scholar]
- Dierickx, P.; Van Laake, L.W.; Geijsen, N. Circadian clocks: from stem cells to tissue homeostasis and regeneration. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, C.; Markson, J.S.; Wilhoite, C.M.; Rust, M.J. Robust and tunable circadian rhythms from differentially sensitive catalytic domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlman, S.J.; Mackey, S.R.; Duffy, J.F. Biological Rhythms Workshop I: Introduction to Chronobiology. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2007, 72, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rust, M.J.; Markson, J.S.; Lane, W.S.; Fisher, D.S.; O’Shea, E.K. Ordered phosphorylation governs oscillation of a three-protein circadian clock. Science 2007, 318, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, S. Advances in the Molecular Mechanism of the Core Circadian Oscillator of Cyanobacteria. Acta Biophys. Sin. 2013, 29, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Imai, K.; Ito, H.; Nishiwaki, T.; Murayama, Y.; Iwasaki, H.; Oyama, T.; Kondo, T. Reconstitution of circadian oscillation of cyanobacterial KaiC phosphorylation in vitro. Science 2005, 308, 414–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rust, M.J.; Golden, S.S.; O’Shea, E.K. Light-Driven Changes in Energy Metabolism Directly Entrain the Cyanobacterial Circadian Oscillator. Science 2011, 331, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitayama, Y.; Nishiwaki-Ohkawa, T.; Sugisawa, Y.; Kondo, T. KaiC intersubunit communication facilitates robustness of circadian rhythms in cyanobacteria. Nat. Commun 2013, 4, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothipongsa, A.; Jantaro, S.; Incharoensakdi, A. Spermidine Synthase is Required for Growth of Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942 Under Osmotic Stress. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 73, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, R.; Hamana, K.; Itoh, T.; Hamana, K.; Isobe, M.; Benno, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Yokota, A. Polyamine distribution profiles of new members of the phylum Bacteroidetes. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z. Dry weight and cell density of individual algal and cyanobacterial cells for algae research and development. Ph.D Thesis, University of Missouri-Columbia Graduate School, Columbia, MO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Murray-Stewart, T.R.; Woster, P.M.; Casero, R.A. Targeting polyamine metabolism for cancer therapy and prevention. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 2937–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Stewart, P.L.; Egli, M. The cyanobacterial circadian system: from biophysics to bioevolution. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2011, 40, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagbrough, I.S.; Metwally, A.A.; Geall, A.J. Measurement of polyamine pKa values. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 720, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Cabo, R.; Navas, P. Spermidine to the rescue for an aging heart. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1389–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeo, F.; Eisenberg, T.; Pietrocola, F.; Kroemer, G. Spermidine in health and disease. Science 2018, 359, eaan2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.K.; Scheunemann, L.; Eisenberg, T.; Mertel, S.; Bhukel, A.; Koemans, T.S.; Kramer, J.M.; Liu, K.S.Y.; Schroeder, S.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; et al. Restoring polyamines protects from age-induced memory impairment in an autophagy-dependent manner. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, D.-H.; Lane, D.J.R.; Jansson, P.J.; Richardson, D.R. The old and new biochemistry of polyamines. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen. Subj 2018, 1862, 2053–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, F.; Li, W.; Zou, J.; Jiang, X.; Xu, G.; Huang, H.; Liu, L. Spermidine Prolongs Lifespan and Prevents Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Activating MAP1S-Mediated Autophagy. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2938–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini-Koupaei, M.; Shareghi, B.; Saboury, A.A. Conjugation of biogenic polyamine (putrescine) with proteinase K: Spectroscopic and theoretical insights. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, T.; Mutoh, R.; Onai, K.; Morishita, M.; Furukawa, Y.; Namba, K.; Ishiura, M. Importance of the monomer-dimer-tetramer interconversion of the clock protein KaiB in the generation of circadian oscillations in cyanobacteria. Genes Cells 2015, 20, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yu, C.-H.; Yu, H.; Borstnar, R.; Kamerlin, S.C.L.; Gräslund, A.; Abrahams, J.P.; Wärmländer, S.K.T.S. Cellular polyamines promote amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptide fibrillation and modulate the aggregation pathways. ACS Chem Neurosci 2013, 4, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swietach, P.; Vaughan-Jones, R.D.; Harris, A.L.; Hulikova, A. The chemistry, physiology and pathology of pH in cancer. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. BBiol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, S.; Yang, L. The reversible function switching of the circadian clock protein KaiA is encoded in its structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1861, 2535–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, P.; Fan, Y.; Sun, J.; Lv, M.; Yi, M.; Tan, X.; Liu, S. A dynamic interaction process between KaiA and KaiC is critical to the cyanobacterial circadian oscillator. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, L.; Tan, X.; Liu, S. Expression and Purification of Cyanobacterial Circadian Clock Protein KaiC and Determination of Its Auto-phosphatase Activity. BIO-PROTOCOL 2017, 7, e2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, J.; Cheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Su, Z.; Yi, M.; Liu, S. Polyamines Disrupt the KaiABC Oscillator by Inducing Protein Denaturation. Molecules 2019, 24, 3351. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183351
Li J, Zhang L, Xiong J, Cheng X, Huang Y, Su Z, Yi M, Liu S. Polyamines Disrupt the KaiABC Oscillator by Inducing Protein Denaturation. Molecules. 2019; 24(18):3351. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183351
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jinkui, Lingya Zhang, Junwen Xiong, Xiyao Cheng, Yongqi Huang, Zhengding Su, Ming Yi, and Sen Liu. 2019. "Polyamines Disrupt the KaiABC Oscillator by Inducing Protein Denaturation" Molecules 24, no. 18: 3351. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183351
APA StyleLi, J., Zhang, L., Xiong, J., Cheng, X., Huang, Y., Su, Z., Yi, M., & Liu, S. (2019). Polyamines Disrupt the KaiABC Oscillator by Inducing Protein Denaturation. Molecules, 24(18), 3351. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183351




