Efficient Degradation of Acesulfame by Ozone/Peroxymonosulfate Advanced Oxidation Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
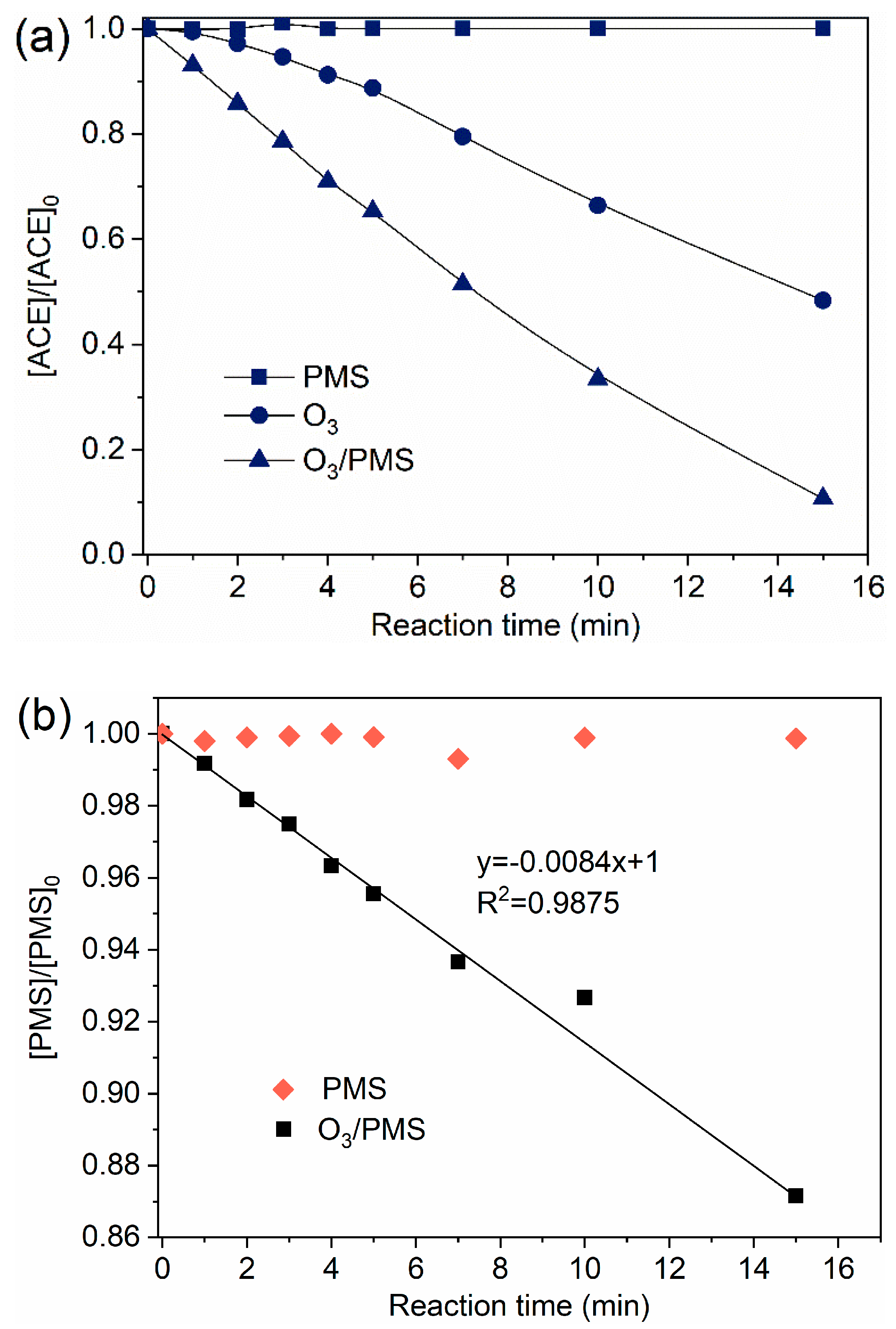
2.1. Degradation Effeciency of ACE by O3/PMS
2.2. Degradation Mechanism
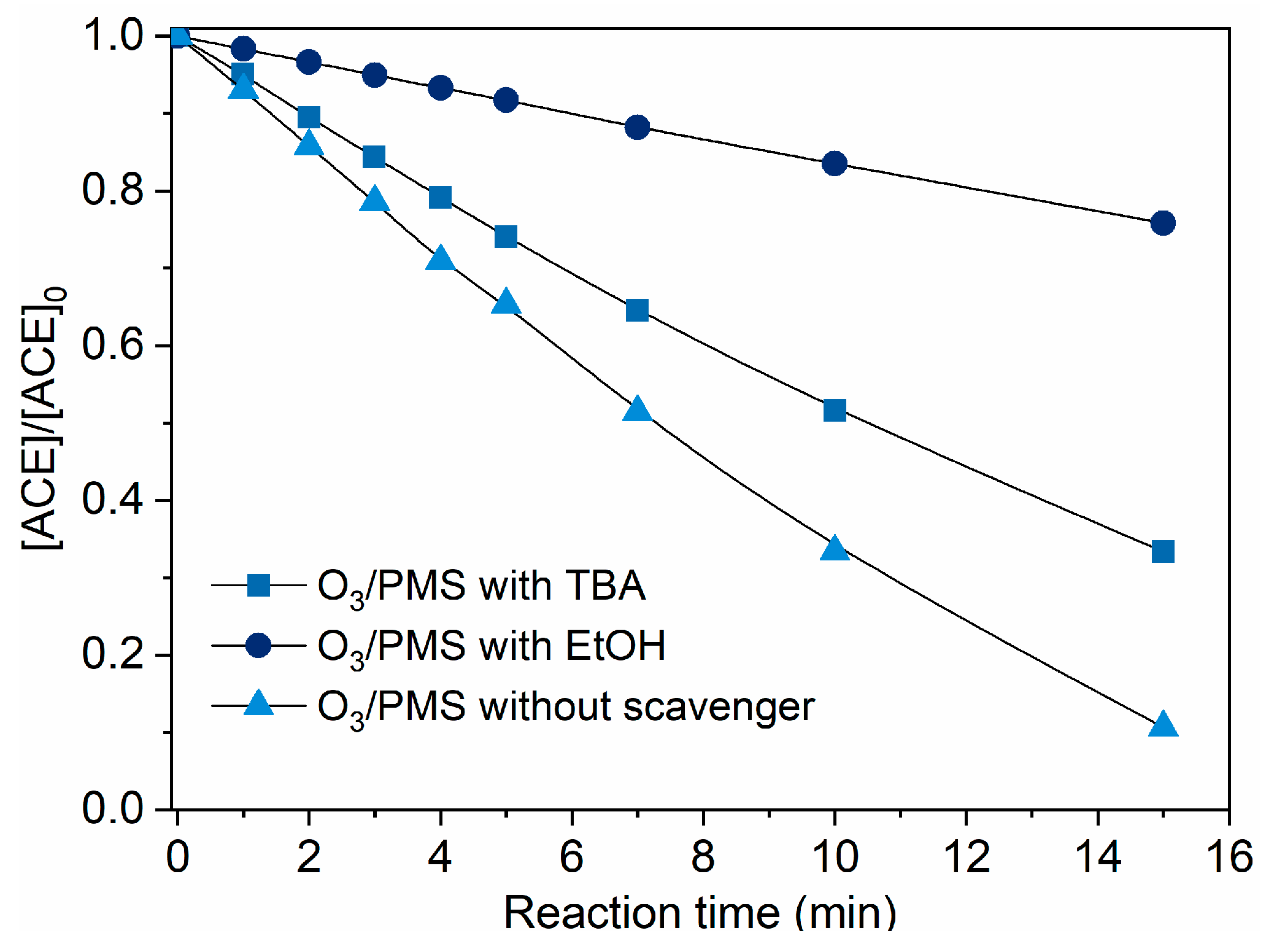
2.2.1. Contributions of Different Reactive Species
2.2.2. Degradation Products
2.3. Effect Water Matrix Components on ACE Degradation
2.4. EE/O Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experimental Procedures
3.3. Analysis Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.L.; Ren, Y.H.; Fu, Y.Y.; Gao, X.S.; Jiang, C.; Wu, G.; Ren, H.Q.; Geng, J.J. Fate of artificial sweeteners through wastewater treatment plants and water treatment processes. Plos One 2018, 13, e0189867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, M.; Brauch, H.-J.; Lange, F.T. Analysis and occurrence of seven artificial sweeteners in german waste water and surface water and in soil aquifer treatment (sat). Anal. Bioanal.Chem. 2009, 394, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, F.T.; Scheurer, M.; Brauch, H.-J. Artificial sweeteners—a recently recognized class of emerging environmental contaminants: A review. Anal. Bioanal.Chem. 2012, 403, 2503–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Raychaudhuri, U.; Chakraborty, R. Artificial sweeteners–a review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subedi, B.; Kannan, K. Fate of artificial sweeteners in wastewater treatment plants in new york state, USA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13668–13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheurer, M.; Storck, F.R.; Brauch, H.-J.; Lange, F.T. Performance of conventional multi-barrier drinking water treatment plants for the removal of four artificial sweeteners. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3573–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Sun, H.; Feng, B.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y. Occurrence of seven artificial sweeteners in the aquatic environment and precipitation of tianjin, china. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4928–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawhinney, D.B.; Young, R.B.; Vanderford, B.J.; Borch, T.; Snyder, S.A. Artificial sweetener sucralose in us drinking water systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8716–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.-N.; Cho, H.; Han, J.; Her, N.; Yoon, J. Photocatalytic degradation of acesulfame k: Optimization using the box–behnken design (bbd). Process Saf. Environ. 2018, 113, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Deng, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, C. Oxidative transformation of artificial sweetener acesulfame by permanganate: Reaction kinetics, transformation products and pathways, and ecotoxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 330, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, M.; Godejohann, M.; Wick, A.; Happel, O.; Ternes, T.A.; Brauch, H.J.; Ruck, W.K.; Lange, F.T. Structural elucidation of main ozonation products of the artificial sweeteners cyclamate and acesulfame. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Sohn, M.; Anquandah, G.A.K.; Nesnas, N. Kinetics of the oxidation of sucralose and related carbohydrates by ferrate(vi). Chemosphere 2012, 87, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, P.W.; Khan, N.A.; Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of artificial sweeteners from water using metal-organic frameworks functionalized with urea or melamine. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29799–29807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheurer, M.; Schmutz, B.; Happel, O.; Brauch, H.J.; Wulser, R.; Storck, F.R. Transformation of the artificial sweetener acesulfame by UV light. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, Z.Y.; Zhang, H. Mineralization of sucralose by uv-based advanced oxidation processes: Uv/pds versus uv/h2o2. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. The UV/peroxymonosulfate process for the mineralization of artificial sweetener sucralose. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Oturan, N.; Wu, J.; Sharma, V.K.; Zhang, H.; Oturan, M.A. Removal of artificial sweetener aspartame from aqueous media by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2017, 167, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, R.; Salazar, G.; Buehlmann, P.; Nading, T.; Schimmoller, L.; Wilson, C.; Bott, C. Carbon vs. membrane: A pilot scale comparison of two different treatment strategies for managed aquifer recharge. In Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation 2017, Chicago, IL, USA, 30 September 2017; Water Environment Federation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, L.; Shao, Y. Degradation of atenolol by uv/peroxymonosulfate: Kinetics, effect of operational parameters and mechanism. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2717–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.-H.; Ma, J.; Li, X.-C.; Fang, J.-Y.; Chen, L.-W. Influence of pH on the formation of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in the uv/peroxymonosulfate system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9308–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, T.; Shao, Y. Comparison of UV/PDS and UV/H2O2 processes for the degradation of atenolol in water. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzek, L.W.; Carter, K.E. Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: A review. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Lu, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y. Production of sulfate radical and hydroxyl radical by reaction of ozone with peroxymonosulfate: A novel advanced oxidation process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7330–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, J. Degradation of bisphenol a using ozone/persulfate process: Kinetics and mechanism. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthamuthu, P.; Neta, P. Radiolytic chain decomposition of peroxomonophosphoric and peroxomonosulfuric acids. J. Phys. Chem. 1977, 81, 937–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gunten, U. Ozonation of drinking water: Part i. Oxidation kinetics and product formation. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1443–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, J.; Merényi, G.; Johansson, E.; Brinck, T. Reaction of peroxyl radicals with ozone in water. The J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.K.; Easwaramoorthy, D.; Bilal, I.M.; Palanichamy, M. Studies on mn(ii)-catalyzed oxidation of alpha-amino acids by peroxomonosulphate in alkaline medium-deamination and decarboxylation: A kinetic approach. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2009, 369, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, P.; Ren, X. Transformation of acesulfame in water under natural sunlight: Joint effect of photolysis and biodegradation. Water Res. 2014, 64, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, M.G.; de la Cruz, A.A.; Dionysiou, D.D. Intermediates and reaction pathways from the degradation of microcystin-lr with sulfate radicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7238–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neta, P.; Madhavan, V.; Zemel, H.; Fessenden, R.W. Rate constants and mechanism of reaction of sulfate radical anion with aromatic compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chu, S.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Shao, Y.; Liu, X.; Ye, M. Efficient degradation of aqueous carbamazepine by bismuth oxybromide-activated peroxide oxidation. Catalysts 2017, 7, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelkowska, K.; Grasso, D.; Fábián, I.; Gordon, G. Numerical simulations of aqueous ozone decomposition. Ozone Sci.-Eng. 1992, 14, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, O.S.; Teel, A.L.; Watts, R.J. Mechanism of base activation of persulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6423–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, J.E.; Rickman, K.A.; Venter, A.R.; Kiddle, J.J.; Mezyk, S.P. Reaction kinetics and efficiencies for the hydroxyl and sulfate radical based oxidation of artificial sweeteners in water. J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 116, 9819–9824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X. Degradation of aqueous polycyclic musk tonalide by ultraviolet-activated free chlorine. Processes 2019, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebel, J.E.; Pignatello, J.J.; Mitch, W.A. Effect of halide ions and carbonates on organic contaminant degradation by hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes in saline waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6822–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neta, P.; Huie, R.E.; Ross, A.B. Rate constants for reactions of inorganic radicals in aqueous-solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 1027–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Gschwend, P.M. Environmental organic chemistry, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Pignatello, J.J.; Ma, J.; Mitch, W.A. Effect of matrix components on uv/h2o2 and uv/s2o82− advanced oxidation processes for trace organic degradation in reverse osmosis brines from municipal wastewater reuse facilities. Water Res. 2016, 89, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Kwon, M.; Jung, Y.; Hwang, T.-M.; Kang, J.-W. Application of O3 and O3/H2O2 as post-treatment processes for color removal in swine wastewater from a membrane filtration system. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2801–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Zhang, T.Q.; Wang, L.L.; Shao, Y.; Fang, L. Hydrated electron-based degradation of atenolol in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.; Sayed, M.; Khan, J.A.; Shah, N.S.; Khan, H.M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Oxidative removal of brilliant green by UV/S2O82−, UV/HSO5− and UV/H2O2 processes in aqueous media: A comparative study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, J.; Gottschalk, C.; Jekel, M. Comparison of advanced oxidation processes in flow-through pilot plants (Part II). Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Shao, Y. Aqueous bromate reduction by uv activation of sulfite. Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, N.; Shen, J.; Ye, M. Degradation and detoxification of microcystin-lr in drinking water by sequential use of uv and ozone. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1897–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Pollution Control Federation; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 2320–2330. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Not available. |






| Water Matrices | Units | RW-1 | RW-2 | RW-3 | RW-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.3 | 7.5 | 7.2 | 7.5 | |
| DOC | mg C·L−1 | 2.80 | 4.41 | 1.93 | 4.45 |
| Alkalinity (as CO32−) | mg·L−1 | 24 | 10.31 | 7.89 | 7.26 |
| Cl− | mg·L−1 | 4.21 | 57.2 | 15.708 | 3.653 |
| NO3− | mg·L−1 | 0.802 | 1.480 | 9.392 | 6.573 |
| UV254 | cm−1·(mg·L−1)−1 | 0.008 | 0.020 | 0.015 | 0.108 |
| SO42− | mg·L−1 | 6.970 | 55.0 | 18.331 | 26.481 |
| Ca2+ | mg·L−1 | 44.5 | 137 | 8.253 | -- |
| Mn2+ | mg·L−1 | 2.48 × 10−3 | <0.05 | 0.012 | -- |
| Cu2+ | mg·L−1 | 7.64 × 10−4 | <0.1 | 0.076 | -- |
| Total Fe | mg·L−1 | 7.21 × 10−3 | <0.05 | 0.155 | -- |
| P | t | V | U/P(PMS) | U/P(Ele) | C | M | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kW) | (h) | (L) | (kWh·m−3) | ($/g) | ($/kWh) | (mM) | (g·mol−1) | (kWh·m−3) | (kWh·m−3) |
| 0.0036 | 0.25 | 0.48 | 1.875 | 0.0042 | 0.1132 | 0.4 | 307.35 | 2.7 | 4.575 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, Y.; Pang, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X. Efficient Degradation of Acesulfame by Ozone/Peroxymonosulfate Advanced Oxidation Process. Molecules 2019, 24, 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162874
Shao Y, Pang Z, Wang L, Liu X. Efficient Degradation of Acesulfame by Ozone/Peroxymonosulfate Advanced Oxidation Process. Molecules. 2019; 24(16):2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162874
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Yu, Zhicheng Pang, Lili Wang, and Xiaowei Liu. 2019. "Efficient Degradation of Acesulfame by Ozone/Peroxymonosulfate Advanced Oxidation Process" Molecules 24, no. 16: 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162874
APA StyleShao, Y., Pang, Z., Wang, L., & Liu, X. (2019). Efficient Degradation of Acesulfame by Ozone/Peroxymonosulfate Advanced Oxidation Process. Molecules, 24(16), 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162874







