Bridged Nucleic Acids Reloaded
Abstract
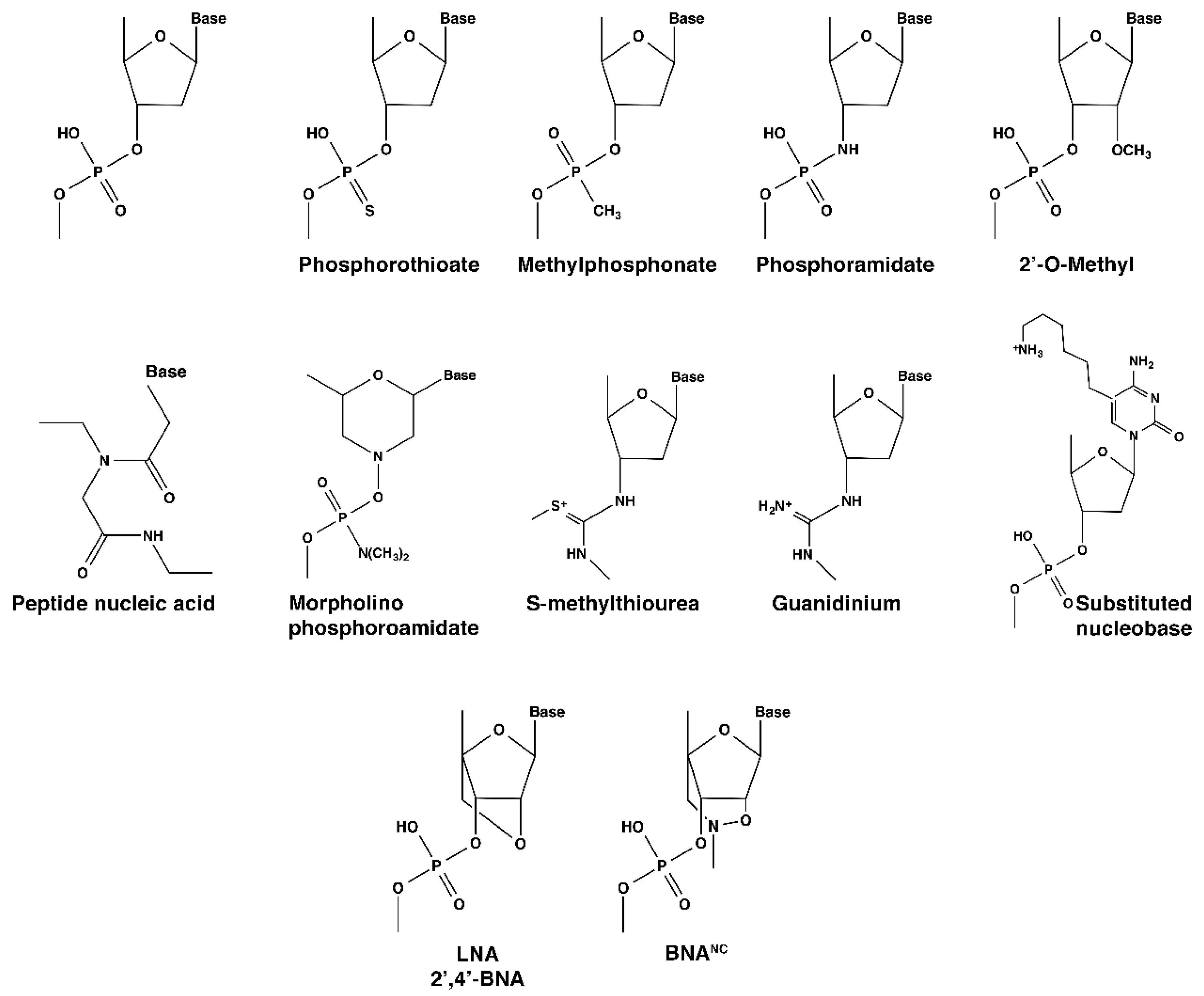
1. Oligonucleotides and Analogs
2. LNA—A Brief Overview
3. BNANC
3.1. Antisense Inhibition of Resistance to Amikacin by a BNANC-Containing Oligomer
3.2. Reversion of Splicing and Reduction of RNA Foci in Myotonic Dystrophy Cells by BNANC Gapmers
3.3. Reduction of Cholesterol Levels by BNANC Mixmers in Hypercholesterolemic Mice
3.4. Diagnostics of Hematologic Malignancies by the Detection of Somatic Mutations Using BNANC Mixmers
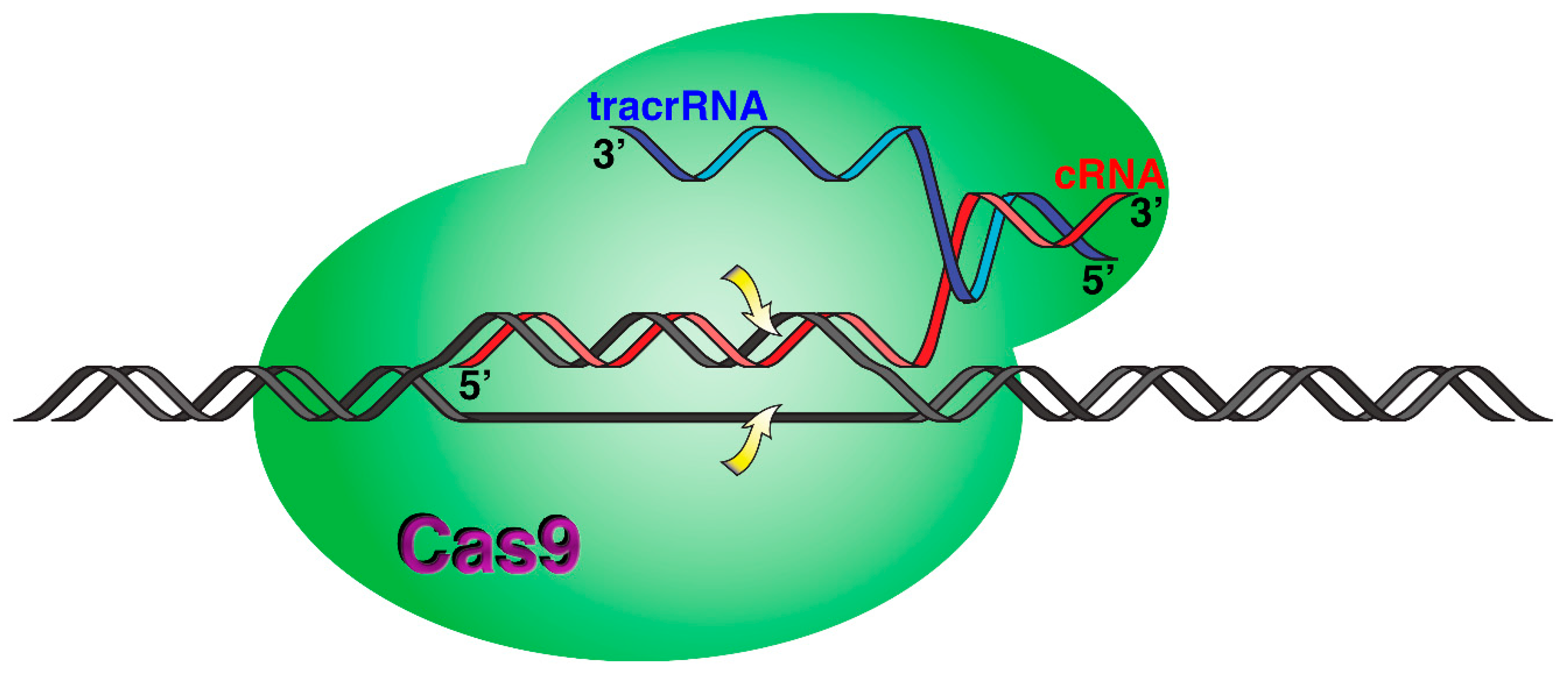
3.5. Incorporation of BNANC Residues to crRNA as an Enhancer of Cas9 Endonuclease Specificity
4. Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, C.F.; Swayze, E.E. RNA targeting therapeutics: Molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides as a therapeutic platform. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 259–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomason, M.K.; Storz, G. Bacterial antisense RNAs: How many are there, and what are they doing? Annu. Rev. Genet. 2010, 44, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.C.; Sperling-Petersen, H.U.; Mortensen, K.K. Hitting bacteria at the heart of the central dogma: Sequence-specific inhibition. Microb. Cell Fact. 2007, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies-Sala, C.; Soler-Bistue, A.; Bonomo, R.A.; Zorreguieta, A.; Tolmasky, M.E. External guide sequence technology: A path to development of novel antimicrobial therapeutics. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1354, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, A.C.; Altman, S. External guide sequences for an RNA enzyme. Science 1990, 249, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, J.C.; Rossi, J.J. RNA-based therapeutics: Current progress and future prospects. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.J.; Kim, J.; Li, S.; Zaia, J.; Yee, J.K.; Anderson, J.; Akkina, R.; Rossi, J.J. Long-term inhibition of HIV-1 infection in primary hematopoietic cells by lentiviral vector delivery of a triple combination of anti-HIV shRNA, anti-CCR5 ribozyme, and a nucleolar-localizing TAR decoy. Mol. Ther. 2005, 12, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Castanares, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Lupold, S.E. Nucleic acid aptamers: Clinical applications and promising new horizons. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4206–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooke, S.T.; Witztum, J.L.; Bennett, C.F.; Baker, B.F. RNA-Targeted Therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 714–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setten, R.L.; Rossi, J.J.; Han, S.P. The current state and future directions of RNAi-based therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 421–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplen, N.J.; Parrish, S.; Imani, F.; Fire, A.; Morgan, R.A. Specific inhibition of gene expression by small double-stranded RNAs in invertebrate and vertebrate systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9742–9747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rooij, E.; Kauppinen, S. Development of microRNA therapeutics is coming of age. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rooij, E.; Sutherland, L.B.; Qi, X.; Richardson, J.A.; Hill, J.; Olson, E.N. Control of stress-dependent cardiac growth and gene expression by a microRNA. Science 2007, 316, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, F. Nucleoside phosphorothioates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 4292–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, F. Phosphorothioates, essential components of therapeutic oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2014, 24, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ts’o, P.O.; Miller, P.S.; Aurelian, L.; Murakami, A.; Agris, C.; Blake, K.R.; Lin, S.B.; Lee, B.L.; Smith, C.C. An approach to chemotherapy based on base sequence information and nucleic acid chemistry. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1987, 507, 220–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, R.S.; Henry, S.P.; Grillone, L.R. Fomivirsen: Clinical pharmacology and potential drug interactions. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2002, 41, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellbye, B.L.; Weller, D.D.; Hassinger, J.N.; Reeves, M.D.; Lovejoy, C.E.; Iversen, P.L.; Geller, B.L. Cationic phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers efficiently prevent growth of Escherichia coli in vitro and in vivo. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Mishra, A.; Puri, N. Peptide nucleic acids: Advanced tools for biomedical applications. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 259, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.E. Peptide nucleic acids (PNA) in chemical biology and drug discovery. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, B.T.; Hornum, M.; Sharma, P.K.; Nielsen, P.; Veedu, R.N. Nucleobase-modified antisense oligonucleotides containing 5-(phenyltriazol)-2 ′-deoxyuridine nucleotides induce exon-skipping in vitro. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 54542–54545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Ducho, C. Oligonucleotide analogues with cationic backbone linkages. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 1293–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.; Wengel, J. LNA: A versatile tool for therapeutics and genomics. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Rungta, P.; Prasad, A.K. Nucleic acid therapeutics: Basic concepts and recent developments. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 16618–16631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sully, E.K.; Geller, B.L. Antisense antimicrobial therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 33, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, P.L. Phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers: Favorable properties for sequence-specific gene inactivation. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2001, 3, 235–238. [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita, K.; Rahman, S.M.; Seki, S.; Obika, S.; Imanishi, T. N-Methyl substituted 2′,4′- BNANC: A highly nuclease-resistant nucleic acid analogue with high-affinity RNA selective hybridization. Chem. Commun. 2007, 3765–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.; Seki, S.; Obika, S.; Yoshikawa, H.; Miyashita, K.; Imanishi, T. Design, synthesis, and properties of 2′,4′-BNA(NC): A bridged nucleic acid analogue. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 4886–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.; Seki, S.; Utsuki, K.; Obika, S.; Miyashita, K.; Imanishi, T. 2′,4′-BNA(NC): A novel bridged nucleic acid analogue with excellent hybridizing and nuclease resistance profiles. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2007, 26, 1625–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaka, A.; Hari, Y.; Takuma, H.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Yoshikawa, H.; Pang, J.; Imanishi, T.; Obika, S. Effective syntheses of 2′,4′-BNA(NC) monomers bearing adenine, guanine, thymine, and 5-methylcytosine, and the properties of oligonucleotides fully modified with 2′,4′-BNA(NC). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 1728–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshkin, A.A.; Nielsen, P.; Meldgaard, M.; Rajwanshi, V.K.; Singh, S.K.; Wengel, J. LNA (locked nucleic acid): An RNA mimic forming exceedingly stable LNA: LNA duplexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 13252–13253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshkin, A.A.; Rajwanshi, V.K.; Wengel, J. Novel convenient syntheses of LNA [2.2.1] bicyclo nucleosides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 4381–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshkin, A.A.; Singh, S.K.; Nielsen, P.; Rajwanshi, V.K.; Kumar, R.; Meldgaard, M.; Olsen, C.E.; Wengel, J. LNA (Locked Nucleic Acids): Synthesis of the adenine, cytosine, guanine, 5-methylcytosine, thymine and uracil bicyclonucleoside monomers, oligomerisation, and unprecedented nucleic acid recognition. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 3607–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Kumar, R.; Wengel, J. Synthesis of novel bicyclo [2.2.1] ribonucleosides: 2′-amino- and 2′-thio-LNA monomeric nucleosides. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 6078–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gunic, E.; Girardet, J.L.; Stoisavljevic, V. Conformationally locked nucleosides. Synthesis and hybridization properties of oligodeoxynucleotides containing 2′,4′-C-bridged 2′-deoxynucleosides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obika, S.; Nanbu, D.; Hari, Y.; Andoh, J.; Morio, K.; Doi, T.; Imanishi, T. Stability and structural features of the duplexes containing nucleoside analogues with a fixed N-type conformation, 2′-O,4′-C-methyleneribonucleosides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 5401–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veedu, R.N.; Wengel, J. Locked nucleic acids: Promising nucleic acid analogs for therapeutic applications. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, J.; Maiti, S.; Muhuri, S.; Nakano, S.; Miyoshi, D.; Sugimoto, N. Effect of locked nucleic acid modifications on the thermal stability of noncanonical DNA structure. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 7414–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braasch, D.A.; Corey, D.R. Locked nucleic acid (LNA): Fine-tuning the recognition of DNA and RNA. Chem. Biol. 2001, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.; Jani, S.; Sala, C.D.; Soler-Bistue, A.J.; Zorreguieta, A.; Tolmasky, M.E. Assessment of configurations and chemistries of bridged nucleic acids-containing oligomers as external guide sequences: A methodology for inhibition of expression of antibiotic resistance genes. Biol. Methods Protoc. 2016, 1, bpw001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler Bistue, A.J.; Martin, F.A.; Vozza, N.; Ha, H.; Joaquin, J.C.; Zorreguieta, A.; Tolmasky, M.E. Inhibition of aac(6′)-Ib-mediated amikacin resistance by nuclease-resistant external guide sequences in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13230–13235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzumanov, A.; Stetsenko, D.A.; Malakhov, A.D.; Reichelt, S.; Sorensen, M.D.; Babu, B.R.; Wengel, J.; Gait, M.J. A structure-activity study of the inhibition of HIV-1 Tat-dependent trans-activation by mixmer 2′-O-methyl oligoribonucleotides containing locked nucleic acid (LNA), alpha-L-LNA, or 2′-thio-LNA residues. Oligonucleotides 2003, 13, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzumanov, A.; Walsh, A.P.; Rajwanshi, V.K.; Kumar, R.; Wengel, J.; Gait, M.J. Inhibition of HIV-1 Tat-dependent trans activation by steric block chimeric 2′-O-methyl/LNA oligoribonucleotides. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 14645–14654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Wengel, J. Universality of LNA-mediated high-affinity nucleic acid recognition. Chem. Commun. 1998, 1247–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenvang, J.; Silahtaroglu, A.N.; Lindow, M.; Elmen, J.; Kauppinen, S. The utility of LNA in microRNA-based cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2008, 18, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritzen, P.; Nielsen, A.T.; Pfundheller, H.M.; Choleva, Y.; Kongsbak, L.; Moller, S. Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using locked nucleic acid (LNA). Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2003, 3, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, U.; Vogel, S. Mismatch discrimination of lipidated DNA and LNA-probes (LiNAs) in hybridization-controlled liposome assembly. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 6985–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simon, L.; Probst, A.V. High-affinity LNA-DNA mixmer probes for detection of chromosome-specific polymorphisms of 5S rDNA repeats in Arabidopsis thaliana. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1675, 481–491. [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaga, M.; Katsuragi, S.; Handa, Y.; Katsumata, H.; Chishaki, N.; Kawauchi, T.; Sakai, M. Improvements in bacterial primers to enhance selective SSU rRNA gene amplification of plant-associated bacteria by applying the LNA oligonucleotide-PCR clamping technique. Microbes Environ. 2018, 33, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, J.D.; Fiala, D.; Samala, M.F.; Kahn, J.D.; Peterson, R.J. Position-dependent effects of locked nucleic acid (LNA) on DNA sequencing and PCR primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakpour, N.; Cheung, K.W.; Souvannaseng, L.; Concordet, J.P.; Luckhart, S. Transfection and mutagenesis of target genes in mosquito cells by locked nucleic acid-modified oligonucleotides. J. Vis. Exp. 2010, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ravesteyn, T.W.; Dekker, M.; Fish, A.; Sixma, T.K.; Wolters, A.; Dekker, R.J.; Te Riele, H.P. LNA modification of single-stranded DNA oligonucleotides allows subtle gene modification in mismatch-repair-proficient cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4122–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh-Olmedo, H.; Drury, M.; Kmiec, E.B. Targeted nucleotide exchange in Saccharomyces cerevisiae directed by short oligonucleotides containing locked nucleic acids. Chem. Biol. 2002, 9, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtkowiak-Szlachcic, A.; Taylor, K.; Stepniak-Konieczna, E.; Sznajder, L.J.; Mykowska, A.; Sroka, J.; Thornton, C.A.; Sobczak, K. Short antisense-locked nucleic acids (all-LNAs) correct alternative splicing abnormalities in myotonic dystrophy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 3318–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmen, J.; Lindow, M.; Schutz, S.; Lawrence, M.; Petri, A.; Obad, S.; Lindholm, M.; Hedtjarn, M.; Hansen, H.F.; Berger, U.; et al. LNA-mediated microRNA silencing in non-human primates. Nature 2008, 452, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, H.L.; Reesink, H.W.; Lawitz, E.J.; Zeuzem, S.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Patel, K.; van der Meer, A.J.; Patick, A.K.; Chen, A.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ree, M.H.; de Vree, J.M.; Stelma, F.; Willemse, S.; van der Valk, M.; Rietdijk, S.; Molenkamp, R.; Schinkel, J.; van Nuenen, A.C.; Beuers, U.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and antiviral effect of RG-101 in patients with chronic hepatitis C: A phase 1B, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ree, M.H.; van der Meer, A.J.; de Bruijne, J.; Maan, R.; van Vliet, A.; Welzel, T.M.; Zeuzem, S.; Lawitz, E.J.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Kupcova, V.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of microRNA-targeted therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients. Antivir. Res. 2014, 111, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerard, M.; Andreas, Z.; Erich, K.; Christine, M.; Martina, M.B.; Christian, W.; Franz, S.; Thomas, S.; Yann, T. Locked nucleic acid (LNA): Based single-stranded oligonucleotides are not genotoxic. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, D.; Omlin, A.; Pezaro, C.; Lorente, D.; Ferraldeschi, R.; Mukherji, D.; Crespo, M.; Figueiredo, I.; Miranda, S.; Riisnaes, R.; et al. First-in-human Phase I study of EZN-4176, a locked nucleic acid antisense oligonucleotide to exon 4 of the androgen receptor mRNA in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2579–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swayze, E.E.; Siwkowski, A.M.; Wancewicz, E.V.; Migawa, M.T.; Wyrzykiewicz, T.K.; Hung, G.; Monia, B.P.; Bennett, C.F. Antisense oligonucleotides containing locked nucleic acid improve potency but cause significant hepatotoxicity in animals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiuchi-Kiyota, S.; Koza-Taylor, P.H.; Mantena, S.R.; Nelms, L.F.; Enayetallah, A.E.; Hollingshead, B.D.; Burdick, A.D.; Reed, L.A.; Warneke, J.A.; Whiteley, L.O.; et al. Comparison of hepatic transcription profiles of locked ribonucleic acid antisense oligonucleotides: Evidence of distinct pathways contributing to non-target mediated toxicity in mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 138, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuya, T.; Hori, S.; Watanabe, A.; Nakajima, M.; Gahara, Y.; Rokushima, M.; Yanagimoto, T.; Kugimiya, A. Ribonuclease H1-dependent hepatotoxicity caused by locked nucleic acid-modified gapmer antisense oligonucleotides. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C.A.; Hansen, J.B.; Lai, J.; Wu, S.; Voskresenskiy, A.; Hog, A.; Worm, J.; Hedtjarn, M.; Souleimanian, N.; Miller, P.; et al. Efficient gene silencing by delivery of locked nucleic acid antisense oligonucleotides, unassisted by transfection reagents. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traglia, G.M.; Sala, C.D.; Fuxman Bass, J.I.; Soler-Bistue, A.J.; Zorreguieta, A.; Ramirez, M.S.; Tolmasky, M.E. Internalization of locked nucleic acids/DNA hybrid oligomers into Escherichia coli. Biores. Open Access 2012, 1, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soifer, H.S.; Koch, T.; Lai, J.; Hansen, B.; Hoeg, A.; Oerum, H.; Stein, C.A. Silencing of gene expression by gymnotic delivery of antisense oligonucleotides. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 815, 333–346. [Google Scholar]
- Mettlen, M.; Pucadyil, T.; Ramachandran, R.; Schmid, S.L. Dissecting dynamin’s role in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajoie, P.; Nabi, I.R. Lipid rafts, caveolae, and their endocytosis. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 282, 135–163. [Google Scholar]
- Howes, M.T.; Mayor, S.; Parton, R.G. Molecules, mechanisms, and cellular roles of clathrin-independent endocytosis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.L. The delivery of therapeutic oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6518–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, L.; Lucchino, M. Current challenges in delivery and cytosolic translocation of therapeutic RNAs. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2018, 28, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabani, M.M.; Gait, M.J. miR-122 targeting with LNA/2′-O-methyl oligonucleotide mixmers, peptide nucleic acids (PNA), and PNA-peptide conjugates. RNA 2008, 14, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Fisker, N.; Asselin, M.C.; Lindholm, M.; Rosenbohm, C.; Orum, H.; Elmen, J.; Seidah, N.G.; Straarup, E.M. A locked nucleic acid antisense oligonucleotide (LNA) silences PCSK9 and enhances LDLR expression in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beane, R.; Gabillet, S.; Montaillier, C.; Arar, K.; Corey, D.R. Recognition of chromosomal DNA inside cells by locked nucleic acids. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 13147–13149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grunweller, A.; Wyszko, E.; Bieber, B.; Jahnel, R.; Erdmann, V.A.; Kurreck, J. Comparison of different antisense strategies in mammalian cells using locked nucleic acids, 2′-O-methyl RNA, phosphorothioates and small interfering RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3185–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.J.; Jones, S.; Fabani, M.M.; Ivanova, G.; Arzumanov, A.A.; Gait, M.J. RNA targeting with peptide conjugates of oligonucleotides, siRNA and PNA. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2007, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, S.; Jackson, A.; Davies-Sala, C.; Chiem, K.; Soler-Bistue, A.; Zorreguieta, A.; Tolmasky, M.E. Assessment of external guide sequences’ (EGS) efficiency as inducers of RNase P-mediated cleavage of mRNA target molecules. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1737, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Shu, D.; Guo, P. RNA micelles for systemic delivery of anti-miRNA for cancer targeting and inhibition without ligand. ACS Nano 2018, 13, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmen, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zuber, B.; Ljungberg, K.; Wahren, B.; Wahlestedt, C.; Liang, Z. Locked nucleic acid containing antisense oligonucleotides enhance inhibition of HIV-1 genome dimerization and inhibit virus replication. FEBS Lett. 2004, 578, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurreck, J.; Wyszko, E.; Gillen, C.; Erdmann, V.A. Design of antisense oligonucleotides stabilized by locked nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Babu, B.R.; Maiti, S. Perspectives on chemistry and therapeutic applications of Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA). Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4672–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagedorn, P.H.; Persson, R.; Funder, E.D.; Albaek, N.; Diemer, S.L.; Hansen, D.J.; Moller, M.R.; Papargyri, N.; Christiansen, H.; Hansen, B.R.; et al. Locked nucleic acid: Modality, diversity, and drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunweller, A.; Hartmann, R.K. Locked nucleic acid oligonucleotides: The next generation of antisense agents? Biodrugs 2007, 21, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadewasser, A.; Dietzel, E.; Michel, S.; Kluver, M.; Helfer, M.; Thelemann, T.; Klar, R.; Eickmann, M.; Becker, S.; Jaschinski, F. Anti-Niemann Pick C1 single-stranded oligonucleotides with locked nucleic acids potently reduce ebola virus infection in vitro. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, F.; Ostermann, P.N.; Muller, L.; Degrandi, D.; Erkelenz, S.; Widera, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Schaal, H. Gymnotic delivery of LNA mixmers targeting viral SREs induces HIV-1 mRNA degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Linse, K.; Retes, P.; Castro, P.; Castro, M. Bridged nucleic acids (BNAs) as molecular tools. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Res. 2015, 1, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Morita, K.; Koizumi, M. Synthesis of ENA nucleotides and ENA oligonucleotides. Curr. Protoc. Nucleic Acid Chem. 2018, 72, 4.79.01–4.79.21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuoka, Y.; Kodama, T.; Ohnishi, R.; Hari, Y.; Imanishi, T.; Obika, S. A bridged nucleic acid, 2′,4′-BNA COC: Synthesis of fully modified oligonucleotides bearing thymine, 5-methylcytosine, adenine and guanine 2′,4′-BNA COC monomers and RNA-selective nucleic-acid recognition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotkowiak, W.; Wengel, J.; Scotton, C.J.; Pasternak, A. Improved RE31 analogues containing modified nucleic acid monomers: Thermodynamic, structural, and biological effects. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2499–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferino, A.; Miglietta, G.; Picco, R.; Vogel, S.; Wengel, J.; Xodo, L.E. MicroRNA therapeutics: Design of single-stranded miR-216b mimics to target KRAS in pancreatic cancer cells. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Harada-Shiba, M.; Nakatani, M.; Wada, S.; Yasuhara, H.; Narukawa, K.; Sasaki, K.; Shibata, M.A.; Torigoe, H.; Yamaoka, T.; et al. Cholesterol-lowering action of BNA-based antisense oligonucleotides targeting PCSK9 in atherogenic diet-induced hypercholesterolemic mice. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.; Seki, S.; Obika, S.; Haitani, S.; Miyashita, K.; Imanishi, T. Highly stable pyrimidine-motif triplex formation at physiological pH values by a bridged nucleic acid analogue. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 4306–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Arivett, B.A.; Actis, L.A.; Tolmasky, M.E. Inhibition of AAC(6′)-Ib-mediated resistance to amikacin in Acinetobacter baumannii by an antisense peptide-conjugated 2′,4′-bridged nucleic acid-NC-DNA hybrid oligomer. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5798–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, K.S.; Rao, A.N.; Castro, M.; Cooper, T.A. BNA(NC) gapmers revert splicing and reduce RNA foci with low toxicity in myotonic dystrophy cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 2503–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivarov, V.; Ivanova, M.; Naumova, E. Rapid detection of DNMT3A R882 mutations in hematologic malignancies using a novel bead-based suspension assay with BNA(NC) probes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromwell, C.R.; Sung, K.; Park, J.; Krysler, A.R.; Jovel, J.; Kim, S.K.; Hubbard, B.P. Incorporation of bridged nucleic acids into CRISPR RNAs improves Cas9 endonuclease specificity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, L.; Nielsen, P.E. Antisense inhibition of gene expression in bacteria by PNA targeted to mRNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmasky, M.E. Strategies to prolong the useful life of existing antibiotics and help overcoming the antibiotic resistance crisis. In Frontiers in Clinical Drug Research-Anti Infectives; Atta-ur-Rhaman, Ed.; Bentham Books: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada, C.; Salavati, R.; Altman, S. Phenotypic conversion of drug-resistant bacteria to drug sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8468–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayhan, D.H.; Tamer, Y.T.; Akbar, M.; Bailey, S.M.; Wong, M.; Daly, S.M.; Greenberg, D.E.; Toprak, E. Sequence-specific targeting of bacterial resistance genes increases antibiotic efficacy. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.C.; Cheng, Z.; Fast, W.; Bonomo, R.A.; Crowder, M.W. The continuing challenge of metallo-beta-lactamase inhibition: Mechanism matters. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Akker, F.; Bonomo, R.A. Exploring additional dimensions of complexity in inhibitor design for serine beta-lactamases: Mechanistic and intra- and inter-molecular chemistry approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.S.; Tolmasky, M.E. Aminoglycoside modifying enzymes. Drug Resist. Updates 2010, 13, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; He, G.; Wang, H.; Jia, M.; Ma, X.; Da, F.; Wang, N.; Hou, Z.; Xue, X.; Li, M.; et al. Reversion of antibiotic resistance by inhibiting mecA in clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococci by antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotide. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2015, 68, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sully, E.K.; Geller, B.L.; Li, L.; Moody, C.M.; Bailey, S.M.; Moore, A.L.; Wong, M.; Nordmann, P.; Daly, S.M.; Sturge, C.R.; et al. Peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PPMO) restores carbapenem susceptibility to NDM-1-positive pathogens in vitro and in vivo. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 72, 782–790. [Google Scholar]
- Sarno, R.; Ha, H.; Weinsetel, N.; Tolmasky, M.E. Inhibition of aminoglycoside 6′-N-acetyltransferase type Ib-mediated amikacin resistance by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3296–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler Bistue, A.J.; Ha, H.; Sarno, R.; Don, M.; Zorreguieta, A.; Tolmasky, M.E. External guide sequences targeting the aac(6′)-Ib mRNA induce inhibition of amikacin resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakulenko, S.B.; Mobashery, S. Versatility of aminoglycosides and prospects for their future. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 430–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arivett, B.A.; Fiester, S.E.; Ream, D.C.; Centron, D.; Ramirez, M.S.; Tolmasky, M.E.; Actis, L.A. Draft genome of the multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strain A155 clinical isolate. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00212-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundblad, E.W.; Altman, S. Inhibition of gene expression by RNase P. New Biotechnol. 2010, 27, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, T.D. Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1. In GeneReviews; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Brook, J.D.; McCurrach, M.E.; Harley, H.G.; Buckler, A.J.; Church, D.; Aburatani, H.; Hunter, K.; Stanton, V.P.; Thirion, J.P.; Hudson, T.; et al. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: Expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3′ end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell 1992, 68, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, M.; Tsilfidis, C.; Sabourin, L.; Shutler, G.; Amemiya, C.; Jansen, G.; Neville, C.; Narang, M.; Barcelo, J.; O’Hoy, K.; et al. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: An unstable CTG repeat in the 3′ untranslated region of the gene. Science 1992, 255, 1253–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, J.R.; Willemsen, R.; Oostra, B.A. Microsatellite repeat instability and neurological disease. Bioessays 2009, 31, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Cooper, T.A. Pathogenic mechanisms of myotonic dystrophy. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, C.A. Myotonic dystrophy. Neurol. Clin. 2014, 32, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, V.; Khantalin, I.; Ramin-Mangata, S.; Chemello, K.; Nativel, B.; Lambert, G. PCSK9: From biology to clinical applications. Pathology 2019, 51, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abifadel, M.; Varret, M.; Rabes, J.P.; Allard, D.; Ouguerram, K.; Devillers, M.; Cruaud, C.; Benjannet, S.; Wickham, L.; Erlich, D.; et al. Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallman, D.M.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Chen, W.; Boerwinkle, E.; Berenson, G.S. Relation of PCSK9 mutations to serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in childhood and adulthood (from The Bogalusa Heart Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2007, 100, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, G.; Charlton, F.; Rye, K.A.; Piper, D.E. Molecular basis of PCSK9 function. Atherosclerosis 2009, 203, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, J.; Ranheim, T.; Kulseth, M.A.; Leren, T.P.; Berge, K.E. Berberine decreases PCSK9 expression in HepG2 cells. Atherosclerosis 2008, 201, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.J.; Wei, J.; Zuo, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Song, D.Q.; You, X.F.; Zhao, L.X.; Pan, H.N.; Jiang, J.D. Combination of simvastatin with berberine improves the lipid-lowering efficacy. Metabolism 2008, 57, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C.; Piper, D.E.; Cao, Q.; Liu, D.; King, C.; Wang, W.; Tang, J.; Liu, Q.; Higbee, J.; Xia, Z.; et al. A proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 neutralizing antibody reduces serum cholesterol in mice and nonhuman primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9820–9825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Grefhorst, A.; Anderson, N.N.; Racie, T.S.; Bramlage, B.; Akinc, A.; Butler, D.; Charisse, K.; Dorkin, R.; Fan, Y.; et al. Therapeutic RNAi targeting PCSK9 acutely lowers plasma cholesterol in rodents and LDL cholesterol in nonhuman primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11915–11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, R.; Garg, J.; Shah, N.; Sumner, A. PCSK9 inhibitors: A new era of lipid lowering therapy. World J. Cardiol. 2017, 9, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.J.; Lemonidis, K.M.; Whipple, C.P.; Subramaniam, A.; Monia, B.P.; Crooke, S.T.; Crooke, R.M. Antisense inhibition of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 reduces serum LDL in hyperlipidemic mice. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, L.; Gundry, M.C.; Goodell, M.A. DNMT3A in Leukemia. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a030320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetake, I.; Mishima, Y.; Kimura, H.; Lee, Y.H.; Goto, Y.; Takeshima, H.; Ikegami, T.; Tajima, S. Characterization of DNA-binding activity in the N-terminal domain of the DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3a. Biochem. J. 2011, 437, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkowska, R.Z.; Rajavelu, A.; Anspach, N.; Urbanke, C.; Jankevicius, G.; Ragozin, S.; Nellen, W.; Jeltsch, A. Oligomerization and binding of the Dnmt3a DNA methyltransferase to parallel DNA molecules: Heterochromatic localization and role of Dnmt3L. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 24200–24207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivarov, V.; Gueorguieva, R.; Stoimenov, A.; Tiu, R. DNMT3A mutation is a poor prognosis biomarker in AML: Results of a meta-analysis of 4500 AML patients. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itzykson, R.; Kosmider, O.; Fenaux, P. Somatic mutations and epigenetic abnormalities in myelodysplastic syndromes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2013, 26, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, A.M.; Makishima, H.; Tiu, R.V.; Szpurka, H.; Huang, Y.; Traina, F.; Visconte, V.; Sugimoto, Y.; Prince, C.; O’Keefe, C.; et al. Mutational spectrum analysis of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia includes genes associated with epigenetic regulation: UTX, EZH2, and DNMT3A. Blood 2011, 118, 3932–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucchi, A.M.; Lasho, T.L.; Guglielmelli, P.; Biamonte, F.; Pardanani, A.; Pereira, A.; Finke, C.; Score, J.; Gangat, N.; Mannarelli, C.; et al. Mutations and prognosis in primary myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traina, F.; Visconte, V.; Jankowska, A.M.; Makishima, H.; O’Keefe, C.L.; Elson, P.; Han, Y.; Hsieh, F.H.; Sekeres, M.A.; Mali, R.S.; et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism array lesions, TET2, DNMT3A, ASXL1 and CBL mutations are present in systemic mastocytosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, V.; Haferlach, C.; Weissmann, S.; Roller, A.; Schindela, S.; Poetzinger, F.; Stadler, K.; Bellos, F.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; et al. The molecular profile of adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Mutations in RUNX1 and DNMT3A are associated with poor prognosis in T-ALL. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2013, 52, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidzik, V.I.; Schlenk, R.F.; Paschka, P.; Stolzle, A.; Spath, D.; Kuendgen, A.; von Lilienfeld-Toal, M.; Brugger, W.; Derigs, H.G.; Kremers, S.; et al. Clinical impact of DNMT3A mutations in younger adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia: Results of the AML Study Group (AMLSG). Blood 2013, 121, 4769–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.Q.; Peng, L.; Zeng, W.J.; Jiang, B.Y.; Li, G.C.; Chen, X.P. DNMT3A R882 Mutations Predict a Poor Prognosis in AML: A Meta-Analysis From 4474 Patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, R.; Nagata, Y.; Kiyoi, H.; Kato, T.; Yamamoto, E.; Suzuki, K.; Chen, F.; Asou, N.; Ohtake, S.; Miyawaki, S.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of genetic alterations and their prognostic impacts in adult acute myeloid leukemia patients. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snetsinger, B.; Ferrone, C.K.; Rauh, M.J. Targeted, amplicon-based, next-generation sequencing to detect age-related clonal hematopoiesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Luthra, R.; Patel, K.P.; Reddy, N.G.; Haghshenas, V.; Routbort, M.J.; Harmon, M.A.; Barkoh, B.A.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Ravandi, F.; Cortes, J.E.; et al. Next-generation sequencing-based multigene mutational screening for acute myeloid leukemia using MiSeq: Applicability for diagnostics and disease monitoring. Haematologica 2014, 99, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcucci, G.; Metzeler, K.H.; Schwind, S.; Becker, H.; Maharry, K.; Mrozek, K.; Radmacher, M.D.; Kohlschmidt, J.; Nicolet, D.; Whitman, S.P.; et al. Age-related prognostic impact of different types of DNMT3A mutations in adults with primary cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, J.N.; Horne, G.A.; Bisling, K.E.; Stewart, H.J.; Chevassut, T.J. Rapid detection of DNMT3A R882 codon mutations allows early identification of poor risk patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 1336–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.R.; Bains, A.; Patel, K.P.; Rahimi, H.; Barkoh, B.A.; Paladugu, A.; Bisrat, T.; Ravandi-Kashani, F.; Cortes, J.E.; Kantarjian, H.M.; et al. Detection of high-frequency and novel DNMT3A mutations in acute myeloid leukemia by high-resolution melting curve analysis. J. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 14, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, M.A.; Hao, H.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Wu, Q.; Sattar, A.; Yuan, Z. Bacteria vs. bacteriophages: Parallel evolution of immune arsenals. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dy, R.L.; Richter, C.; Salmond, G.P.; Fineran, P.C. Remarkable mechanisms in microbes to resist phage infections. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2014, 1, 307–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arutyunov, D.; Frost, L.S. F conjugation: Back to the beginning. Plasmid 2013, 70, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishino, Y.; Krupovic, M.; Forterre, P. History of CRISPR-Cas from encounter with a mysterious repeated sequence to genome editing technology. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hille, F.; Charpentier, E. CRISPR-Cas: Biology, mechanisms and relevance. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strich, J.R.; Chertow, D.S. CRISPR-Cas Biology and Its Application to Infectious Diseases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01307-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.V.; Nunez, J.K.; Doudna, J.A. Biology and applications of CRISPR systems: Harnessing nature’s toolbox for genome engineering. Cell 2016, 164, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.S.L.; Yusa, K. Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screening in mammalian cells. Methods 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, P.; Esvelt, K.M.; Church, G.M. Cas9 as a versatile tool for engineering biology. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Ran, F.A.; Cox, D.; Lin, S.; Barretto, R.; Habib, N.; Hsu, P.D.; Wu, X.; Jiang, W.; Marraffini, L.A.; et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 2013, 339, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasiunas, G.; Barrangou, R.; Horvath, P.; Siksnys, V. Cas9-crRNA ribonucleoprotein complex mediates specific DNA cleavage for adaptive immunity in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2579–E2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, S.H.; LaFrance, B.; Kaplan, M.; Doudna, J.A. Conformational control of DNA target cleavage by CRISPR-Cas9. Nature 2015, 527, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, J.D.; Joung, J.K. CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, J.; Konermann, S.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Platt, R.J.; Brigham, M.D.; Sanjana, N.E.; Zhang, F. Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout and transcriptional activation screening. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 828–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, S.; Jain, N.; Singh, N.; Sreevathsa, R.; Dash, P.; Rai, R.; Yadav, S.; Kumar, P.; Sarkar, A.; Jain, A.; et al. CRISPR-cas 9 directed genome engineering for enhancing salt stress tolerance in rice. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, I.; Ramachandran, S.; Srivastava, S.K. CRISPR-Cas9: A multifaceted therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Geen, H.; Henry, I.M.; Bhakta, M.S.; Meckler, J.F.; Segal, D.J. A genome-wide analysis of Cas9 binding specificity using ChIP-seq and targeted sequence capture. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 3389–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Geen, H.; Yu, A.S.; Segal, D.J. How specific is CRISPR/Cas9 really? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 29, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, K.A.; Yang, Y. CRISPR/Cas-mediated base editing: Technical considerations and practical applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadic, V.; Josipovic, G.; Zoldos, V.; Vojta, A. CRISPR/Cas9-based epigenome editing: An overview of dCas9-based tools with special emphasis on off-target activity. Methods 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Kimberland, M.L.; Hou, W.; Alfonso-Pecchio, A.; Wilson, S.; Rao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Q. Strategies for controlling CRISPR/Cas9 off-target effects and biological variations in mammalian genome editing experiments. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 284, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilinger, J.P.; Thompson, D.B.; Liu, D.R. Fusion of catalytically inactive Cas9 to FokI nuclease improves the specificity of genome modification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaymaker, I.M.; Gao, L.; Zetsche, B.; Scott, D.A.; Yan, W.X.; Zhang, F. Rationally engineered Cas9 nucleases with improved specificity. Science 2016, 351, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinstiver, B.P.; Pattanayak, V.; Prew, M.S.; Tsai, S.Q.; Nguyen, N.T.; Zheng, Z.; Joung, J.K. High-fidelity CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases with no detectable genome-wide off-target effects. Nature 2016, 529, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tycko, J.; Myer, V.E.; Hsu, P.D. Methods for optimizing CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing specificity. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, D.; Kartje, Z.J.; Ageely, E.A.; Malek-Adamian, E.; Habibian, M.; Schofield, A.; Barkau, C.L.; Rohilla, K.J.; DeRossett, L.B.; Weigle, A.T.; et al. Extensive CRISPR RNA modification reveals chemical compatibility and structure-activity relationships for Cas9 biochemical activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendel, A.; Bak, R.O.; Clark, J.T.; Kennedy, A.B.; Ryan, D.E.; Roy, S.; Steinfeld, I.; Lunstad, B.D.; Kaiser, R.J.; Wilkens, A.B.; et al. Chemically modified guide RNAs enhance CRISPR-Cas genome editing in human primary cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Deng, Y.M.; Liu, X.R.; Cao, J.P.; Zhou, M.; Tang, Y.L.; Xiong, W.H.; Jiang, Z.S.; Tang, Z.H.; Liu, L.S. PCSK9: A new participant in lipophagy in regulating atherosclerosis? Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 495, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briata, P.; Di Blas, E.; Gulisano, M.; Mallamaci, A.; Iannone, R.; Boncinelli, E.; Corte, G. EMX1 homeoprotein is expressed in cell nuclei of the developing cerebral cortex and in the axons of the olfactory sensory neurons. Mech. Dev. 1996, 57, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, T.; Choong, C.J.; Nakamori, M.; Hayakawa, H.; Nishiyama, K.; Kasahara, Y.; Baba, K.; Nagata, T.; Yokota, T.; Tsuda, H.; et al. Amido-bridged nucleic acid (AmNA)-modified antisense oligonucleotides targeting alpha-synuclein as a novel therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Organism | Function or Disease | Target | Chemical Nature of Oligonucleotide | Sequence of Active Oligomer | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. baumannii | Resistance to aminoglycosides | aac(6′)-Ib | BNANC/DNA conjugated to (RXR)4XB 1 | (RXR)4XB-Cys-SMCC-C6 amino-cTgctGcgtAacaTc | [94] |
| Cell lines | Myotonic dystrophy type 1 | DMPK2 | BNANC/DNA gapmer | CGGAGcggttgtgaaCTGGC | [95] |
| Murine, human cell lines, and mice | Hypercholesterolemia | PCSK93 | BNANC/DNA mixmer | CCaggCCTaTgagggTgCCg | [92] |
| Human gene | Hematologic malignancies | DNTM3A4 | BNANC/DNA mixmers | cgccaAgcgGctcatgtt cgccAAgcagctcAtgtt cgccAAgtgGctcAtgtt cgccaAggggCtcatgtt cgccAAgctgCtcAtgtt | [96] |
| Human gene | CRISPR-Cas9 specificity | WAS5 | crRNA with BNANC substitutions | uggauggagGAAugaggagu | [97] |
| Human gene | CRISPR-Cas9 specificity | EXM16 | crRNA with BNANC substitutions | gaguccgagcaGAAgaagaa | [97] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soler-Bistué, A.; Zorreguieta, A.; Tolmasky, M.E. Bridged Nucleic Acids Reloaded. Molecules 2019, 24, 2297. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122297
Soler-Bistué A, Zorreguieta A, Tolmasky ME. Bridged Nucleic Acids Reloaded. Molecules. 2019; 24(12):2297. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122297
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoler-Bistué, Alfonso, Angeles Zorreguieta, and Marcelo E. Tolmasky. 2019. "Bridged Nucleic Acids Reloaded" Molecules 24, no. 12: 2297. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122297
APA StyleSoler-Bistué, A., Zorreguieta, A., & Tolmasky, M. E. (2019). Bridged Nucleic Acids Reloaded. Molecules, 24(12), 2297. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122297







