Mytoxin B and Myrothecine A Induce Apoptosis in Human Hepatocarcinoma Cell Line SMMC-7721 via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
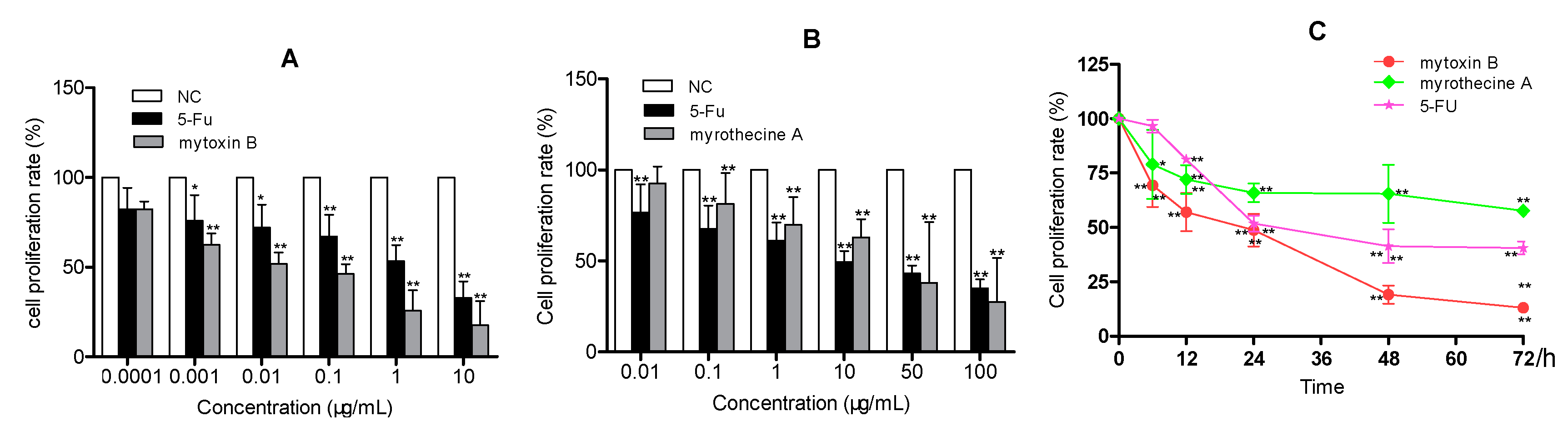
2.1. Anti-Proliferation Effects of Mytoxin B and Myrothecine A against SMMC-7721 Cells
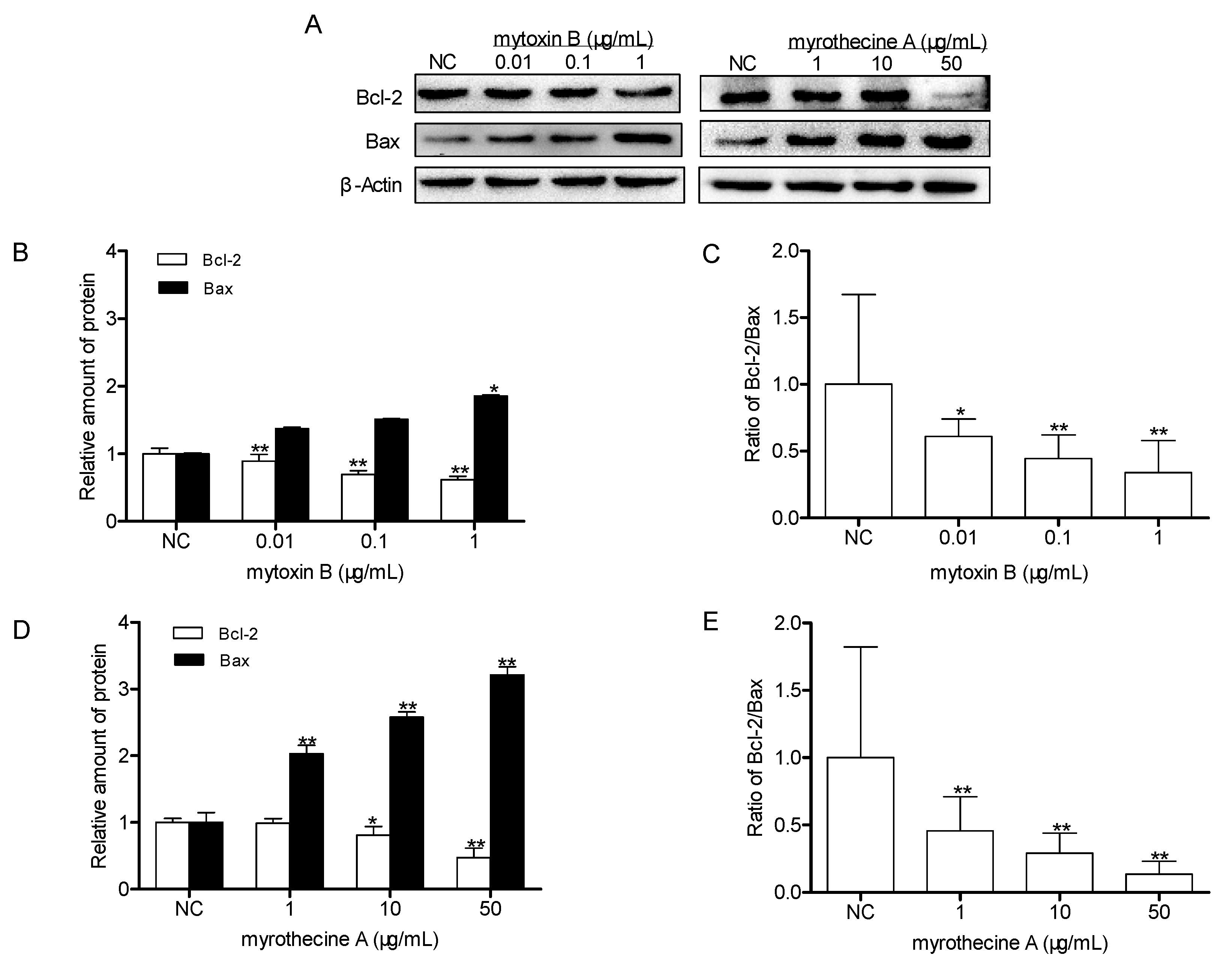
2.2. Mytoxin B and Myrothecine A Induced Apoptosis in SMMC-7721 Cells
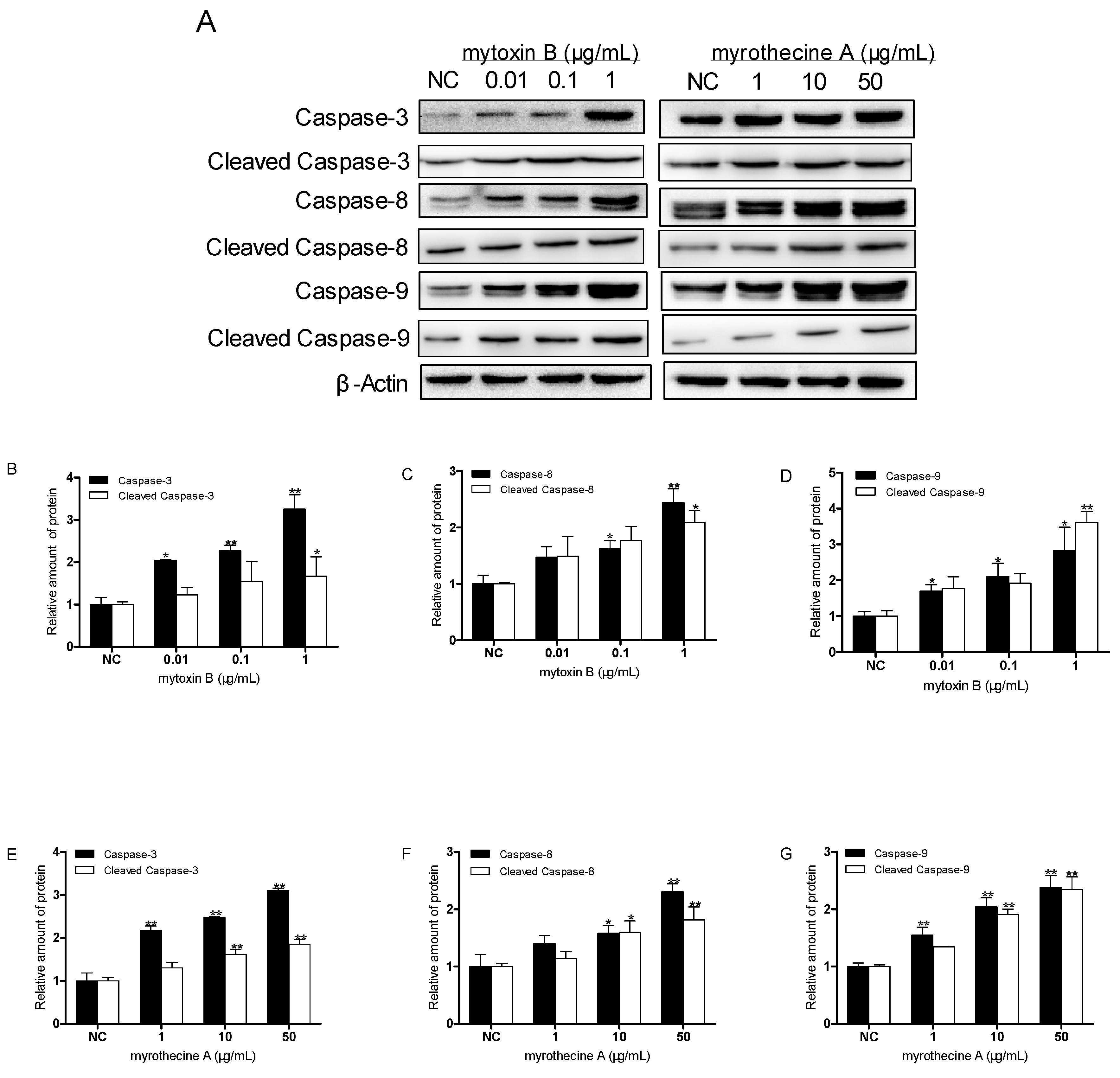
2.3. Induced Apoptosis by Mytoxin B and Myrothecine A in SMMC-7721 Cells Involved in Both the Death Receptor Pathway and the Mitochondrial Pathway
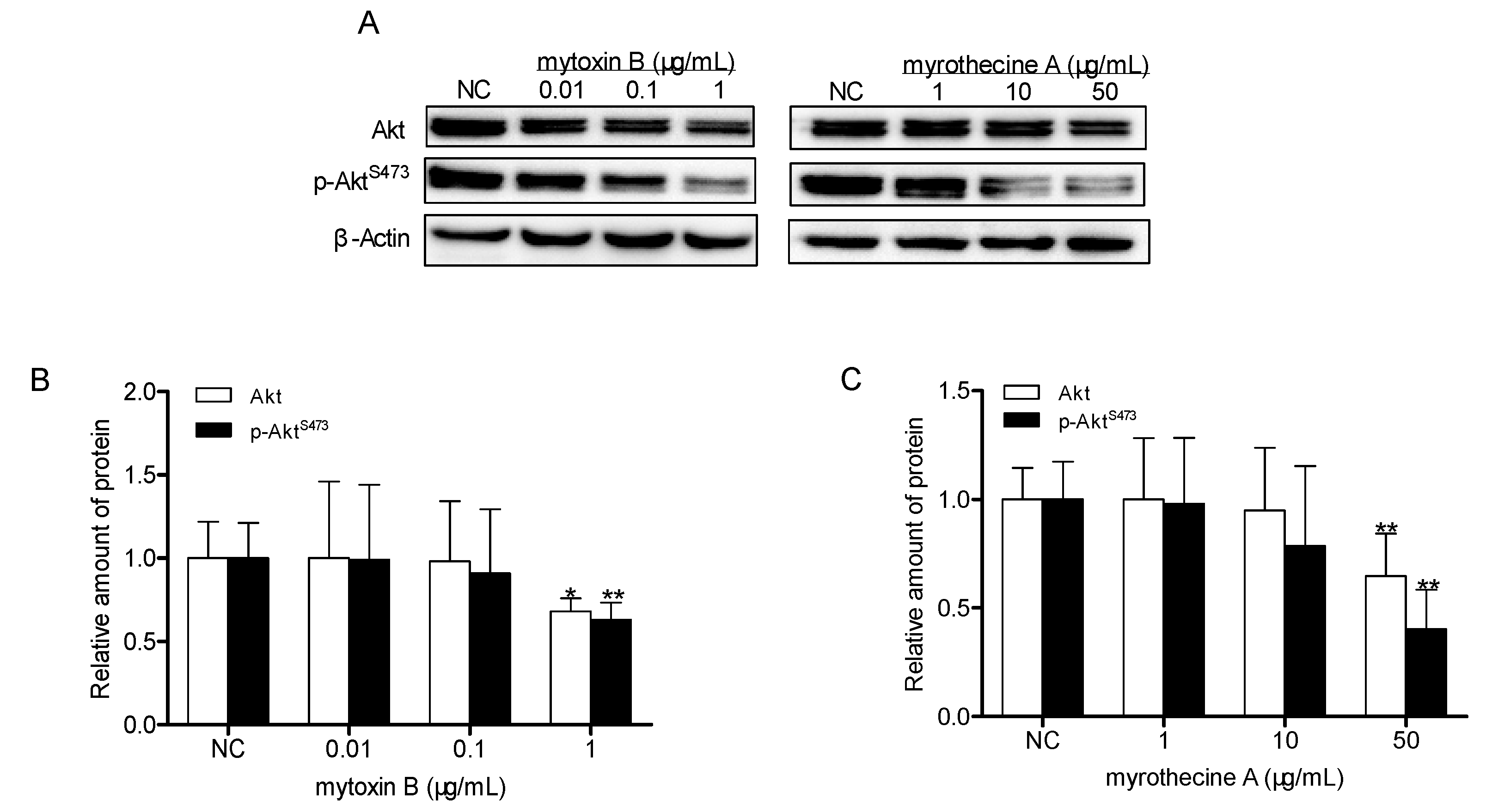
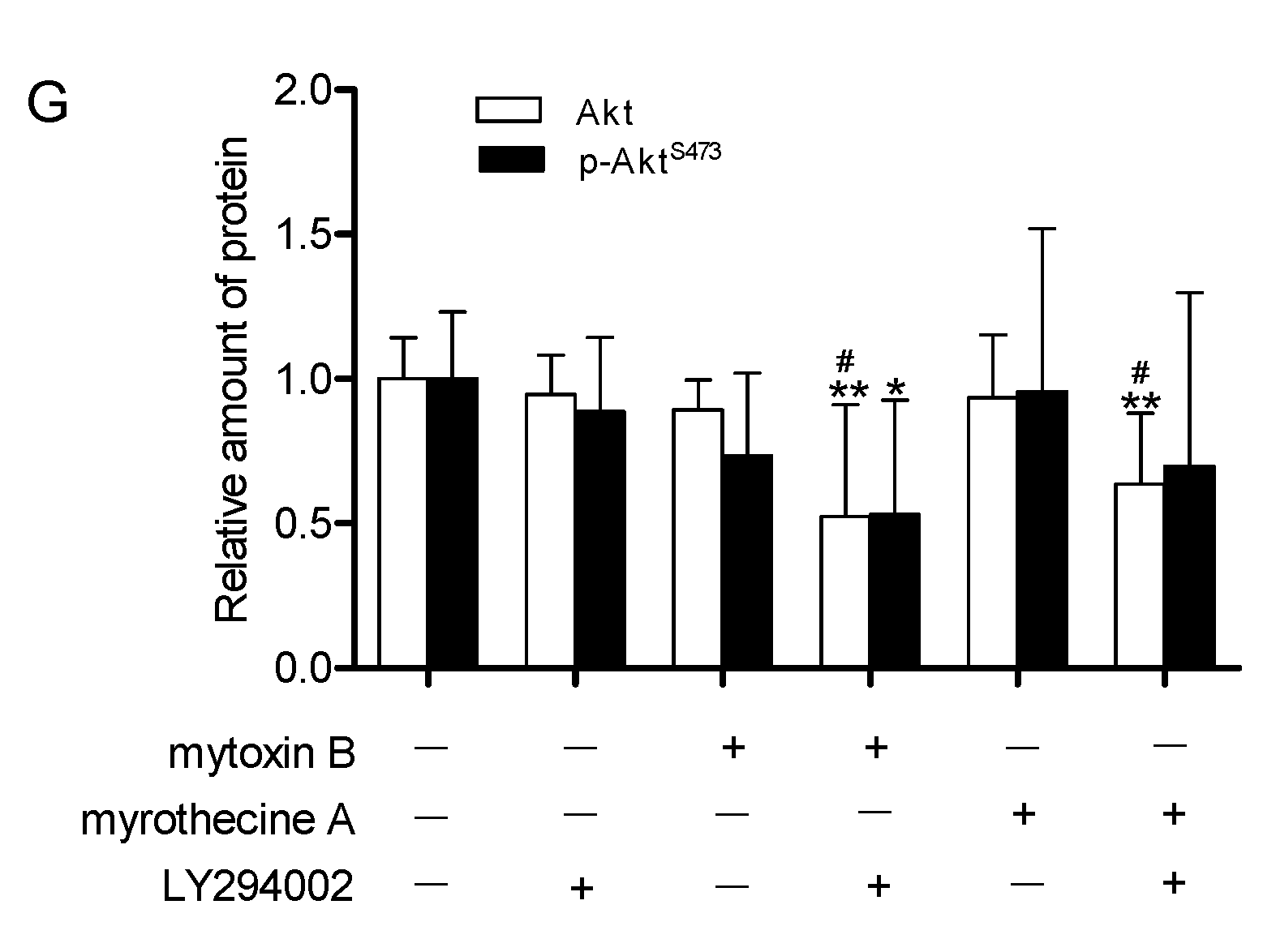
2.4. Involvement of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Mytoxin B- and Myrothecine A-Induced SMMC-7721 Cell Apoptosis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
3.3. Annexin V-FITC/PI Dual Staining Assay
3.4. Western Blot Analysis
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, L.; Jiao, R.H.; Ye, Y.H.; Wang, X.T.; Xu, C.; Song, Y.C.; Zhu, H.L.; Tan, R.X. Absolute configuration of new cytotoxic and other bioactive trichothecene macrolides. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 5596–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Maghraby, O.M.; Bean, G.A.; Jarvis, B.B.; Aboul-Nasr, M.B. Macrocyclic trichothecenes produced by Stachybotrys isolated from Egypt and eastern Europe. Mycopathologia 1991, 113, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minato, H.; Katayama, T.; Tori, K. Vertisporin, a new antibiotic from Verticimonosporium diffractum. Tetrahedron Lett. 1975, 16, 2579–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.J.; Guo, S.X.; Xiao, P.G. New sesquiterpene esters from the culture filtrate of Calcarisporium arbuscula isolated from Ganoderma lucidum. Acta Bot. Sin. 2002, 44, 878–882. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, A.; Takeuchi, S.; Kusano, M.; Fujioka, S.; Kimura, Y. Roridin A and verrucarin A, inhibitors of pollen development in Arabidopsis thaliana, produced by Cylindrocarpon sp. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, K.A.; Rabenstein, J.; Woodard, J.; Baker, D.D.; Bergthold, J.D.; Lynch, J.; Lieu, K.L.; Braude, I.A. 14′-Hydroxymytoxin B and 16-hydroxyroridin E, two new cytotoxic trichothecenes from Myrothecium roridum. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 742–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, B.B.; Stahly, G.P.; Pavanasasivam, G.; Mazzola, E.P. Antileukemic compounds derived from the chemical modification of macrocyclic trichothecenes. 1. Derivatives of Verrucarin A. J. Med. Chem. 1980, 23, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.Y.; Murphy, W.K.; DiStefano, A.; Blumenschein, G.R.; Bodey, G.P. Phase II study of anguidine in advanced breast cancer. Cancer Treat. Rep. 1979, 63, 789–791. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, J.W.; Bottomley, R.H.; Vaughn, C.B.; Frank, J.; Pugh, R.P. Phase II evaluation of anguidine in central nervous system tumors; a southwest oncology group study. Cancer Treat. Rep. 1983, 67, 285–286. [Google Scholar]
- Thigpen, J.T.; Vaughn, C.; Stuckey, W.J. Phase II trial of anguidine in patients with sarcomas unresponsive to prior chemotherapy: A southwest oncology group study. Cancer Treat. Rep. 1981, 65, 881–882. [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz, W.E.; Rodarte, C.B.; Lin, A. 3D QSAR study of the toxicity of trichothecene mycotoxins. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 4485–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amagata, T.; Rath, C.; Rigot, J.F.; Tarlov, N.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Crews, P. Structures and cytotoxic properties of trichoverroids and their macrolide analogues produced by saltwater culture of Myrothecium verrucaria. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 4342–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Ai, C.Z.; Song, Y.C.; Wang, F.W.; Jiao, R.H.; Zhang, A.H.; Man, H.Z.; Tan, R.X. Cytotoxic trichothecene macrolides produced by the endophytic Myrothecium roridum. J. Nat. Prod. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Sun, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, S. Two trichothecene mycotoxins from Myrothecium roridum induce apoptosis of HepG-2 cells via Caspase activation and disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential. Molecules 2016, 21, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.H.; Jarvis, B.B.; Chung, Y.J.; Pestka, J.J. Apoptosis Induction by the Satratoxins and Other Trichothecene Mycotoxins: Relationship to ERK, p38 MAPK, and SAPK/JNK Activation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2000, 164, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Lyu, F.; Cheng, W.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Shen, L.; Fu, Y. Molecular mechanism of mytoxin B and myrothecine A in inhibiting proliferation of SMMC-7721 of hepatocarcinoma cell. J. Clin. Med. Pract. 2014, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Alenzi, F.Q. Links between apoptosis, proliferation and the cell cycle. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2004, 61, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anding, A.L.; Baehrecke, E.H. Autophagy in cell life and cell death. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 114, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oral, O.; Akkoc, Y.; Bayraktar, O.; Gozuacik, D. Physiological and pathological significance of the molecular cross-talk between autophagy and apoptosis. Histol. Histopathol. 2016, 31, 479–498. [Google Scholar]
- Baggstrom, M.Q.; Qi, Y.; Koczywas, M.; Argiris, A.; Johnson, E.A.; Millward, M.J.; Murphy, S.C.; Erlichman, C.; Rudin, C.M.; Govindan, R. A phase II study of AT-101 (gossypol) in chemotherapy-sensitive recurrent extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1757–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.S.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Cooper, M.A. Natural product and natural product derived drugs in clinical trials. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1612–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A Review of Programmed Cell Death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degterev, A.; Boyce, M.; Yuan, J. A decade of caspases. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8543–8567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaleghpour, K.; Li, Y.; Banville, D.; Yu, Z.B.; Shen, S.-H. Involvement of the PI3-kinase signaling pathway in progression of colon adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, F.T.; Zhou, T.T.; Liu, B.; Bao, J.K. Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, F.R.; Qin, J.Q.; Shen, X.Y. Models of Bak and Bax activation in apoptosis pathways. Chem. Life 2011, 31, 858–862. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Bhalla, K.; Kim, C.N.; Ibrado, A.M.; Cai, J.; Peng, T.I.; Jones, D.P.; Wang, X. Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: Release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science 1997, 275, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorrano, L.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Mechanisms of cytochrome c release by proapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 304, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.H.; Cui, J.T.; Wang, T.; Zhang, A.H.; Tan, R.X. Trichothecin induces apoptosis of HepG2 cells via caspase-9 mediated activation of the mitochondrial death pathway. Toxicon 2012, 59, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuranaga, E.; Miura, M. Nonapoptotic functions of caspases: Caspases as regulatory molecules for immunity and cell-fate determination. Trends Cell Biol. 2007, 17, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyhenmeyer, B.; Murphy, A.C.; Prehn, J.H.M.; Murphy, B.M. Targeting the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members for the treatment of cancer. Exp. Oncol. 2012, 34, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Xie, W.; Kuhn, D.J.; Voorhees, P.M.; Lopez-Girona, A.; Mendy, D.; Corral, L.G.; Krenitsky, V.P.; Xu, W.; Moutouh-de Parseval, L.; et al. Targeting the p27 E3 ligase SCF(Skp2) results in p27- and Skp2-mediated cell-cycle arrest and activation of autophagy. Blood 2008, 111, 4690–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, U.; Janicke, R.U.; Schulze-Osthoff, K. Many cuts to ruin: A comprehensive update of caspase substrates. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 76–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassonneville, L.; Lansiaux, A.; Wattelet, A.; Wattez, N.; Mahieu, C.; Miert, S.V.; Pieters, L.; Bailly, C. Cytotoxicity and cell cycle effects of the plant alkaloids cryptolepine and neocryptolepine: Relation to drug-induced apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 409, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, W.; Wu, M.; Pan, G.; Yang, K.; Li, X.; Man, S.; Teng, Y.; Yu, P.; et al. Chemosensitizing effect of Paris Saponin I on Camptothecin and 10-hydroxycamptothecin in lung cancer cells via p38 MAPK, ERK, and Akt signaling pathways. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 125, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Ouyang, G.L.; Bao, S.D. The activation of Akt/PKB signalingpathway and cell survival. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2005, 9, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, M.G.; Deng, X.M. Nicotine inactivation of the proapoptotic function of bax through phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10781–10789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimmeler, S.; Zeiher, A.M. Akt takes center stage in angiogenesis signaling. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.J.; Li, H.H.; Li, J.F.; Shen, J.S. Signal transduction by protein tyrosine kinases and antitumor agents. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2008, 43, 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Gratton, J.-P.; Morales-Ruiz, M.; Kureishi, Y.; Fulton, D.; Walsh, K.; Sessa, W.C. Akt down-regulation of p38 signaling provides a novel mechanism of vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated cytoprotection in endothelial cells. J. Bio. Chem. 2001, 276, 30359–30365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.K.; Johnson, B.B.; Shier, W.T.; Tak, H.; Jarvis, B.B.; Boyette, C.D. Phytotoxicity and mammalian cytotoxicity of macrocyclic trichothecene mycotoxins from Myrothecium verrucaria. Phytochemistry 2002, 59, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, H.; Fu, Y.; Wan, D.; Xia, W.; Lyu, F.; Liu, L.; Shen, L. Mytoxin B and Myrothecine A Induce Apoptosis in Human Hepatocarcinoma Cell Line SMMC-7721 via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2019, 24, 2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122291
Song H, Fu Y, Wan D, Xia W, Lyu F, Liu L, Shen L. Mytoxin B and Myrothecine A Induce Apoptosis in Human Hepatocarcinoma Cell Line SMMC-7721 via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2019; 24(12):2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122291
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Huiliang, Yi Fu, Dan Wan, Wenjing Xia, Fengwei Lyu, Lijun Liu, and Li Shen. 2019. "Mytoxin B and Myrothecine A Induce Apoptosis in Human Hepatocarcinoma Cell Line SMMC-7721 via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway" Molecules 24, no. 12: 2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122291
APA StyleSong, H., Fu, Y., Wan, D., Xia, W., Lyu, F., Liu, L., & Shen, L. (2019). Mytoxin B and Myrothecine A Induce Apoptosis in Human Hepatocarcinoma Cell Line SMMC-7721 via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Molecules, 24(12), 2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122291




