Development of Technetium-99m-Labeled BODIPY-Based Probes Targeting Lipid Droplets Toward the Diagnosis of Hyperlipidemia-Related Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
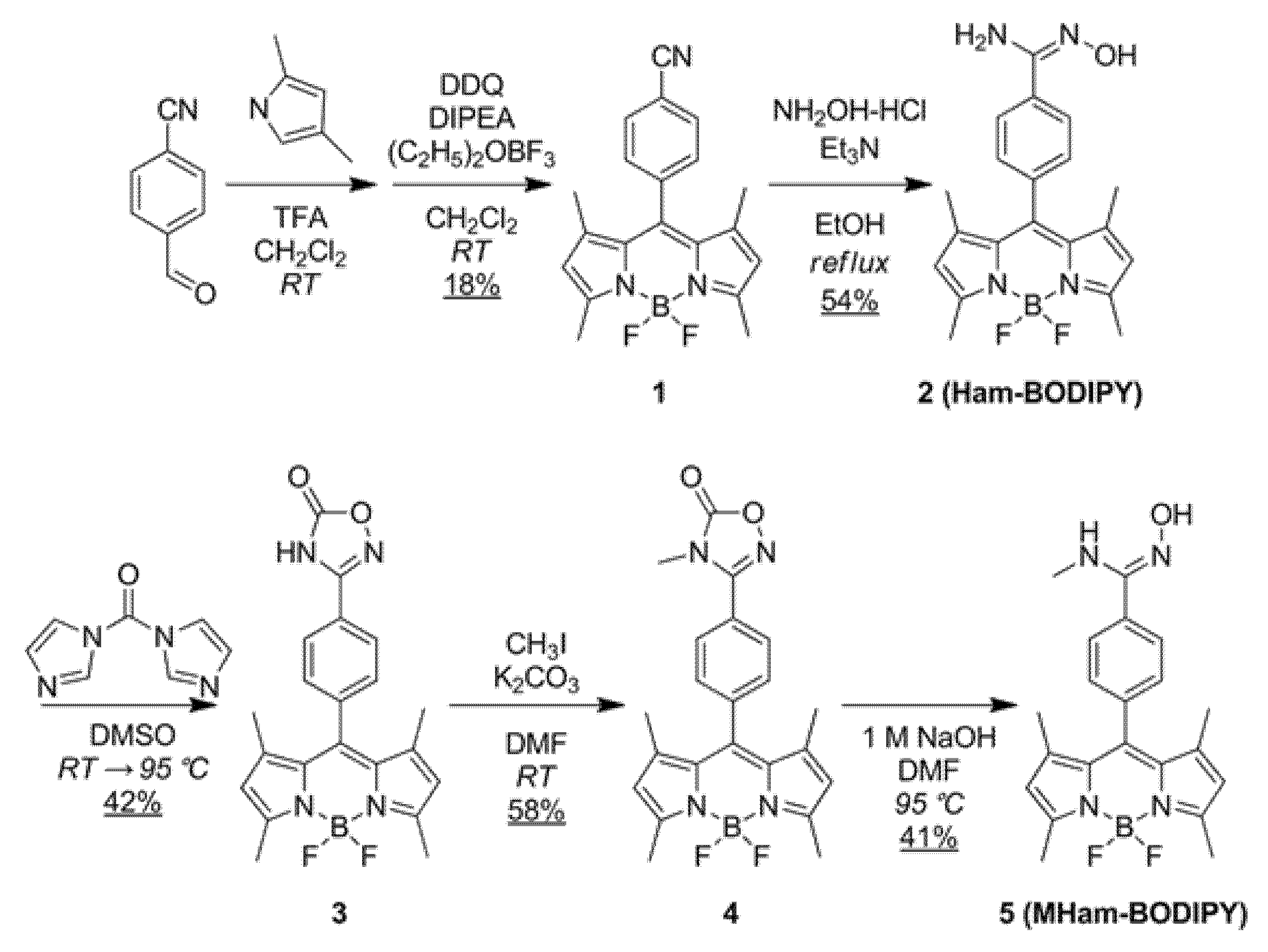
2.1. Chemistry
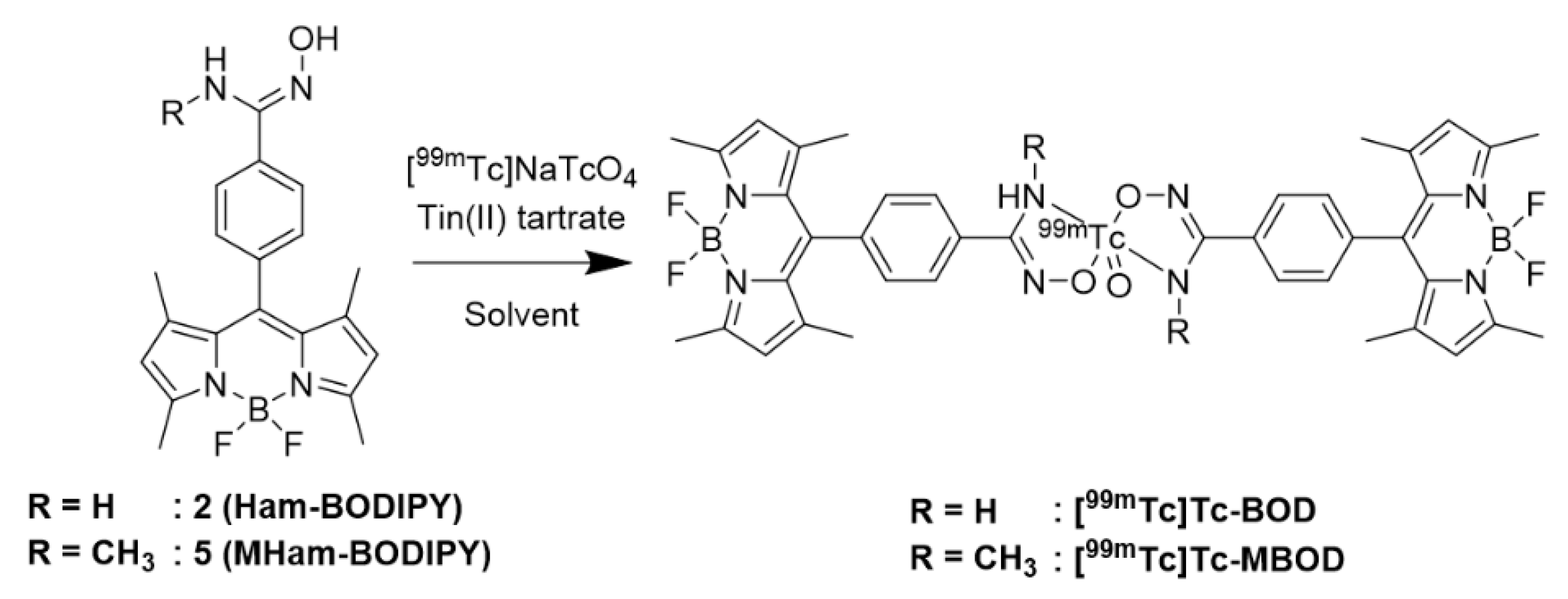
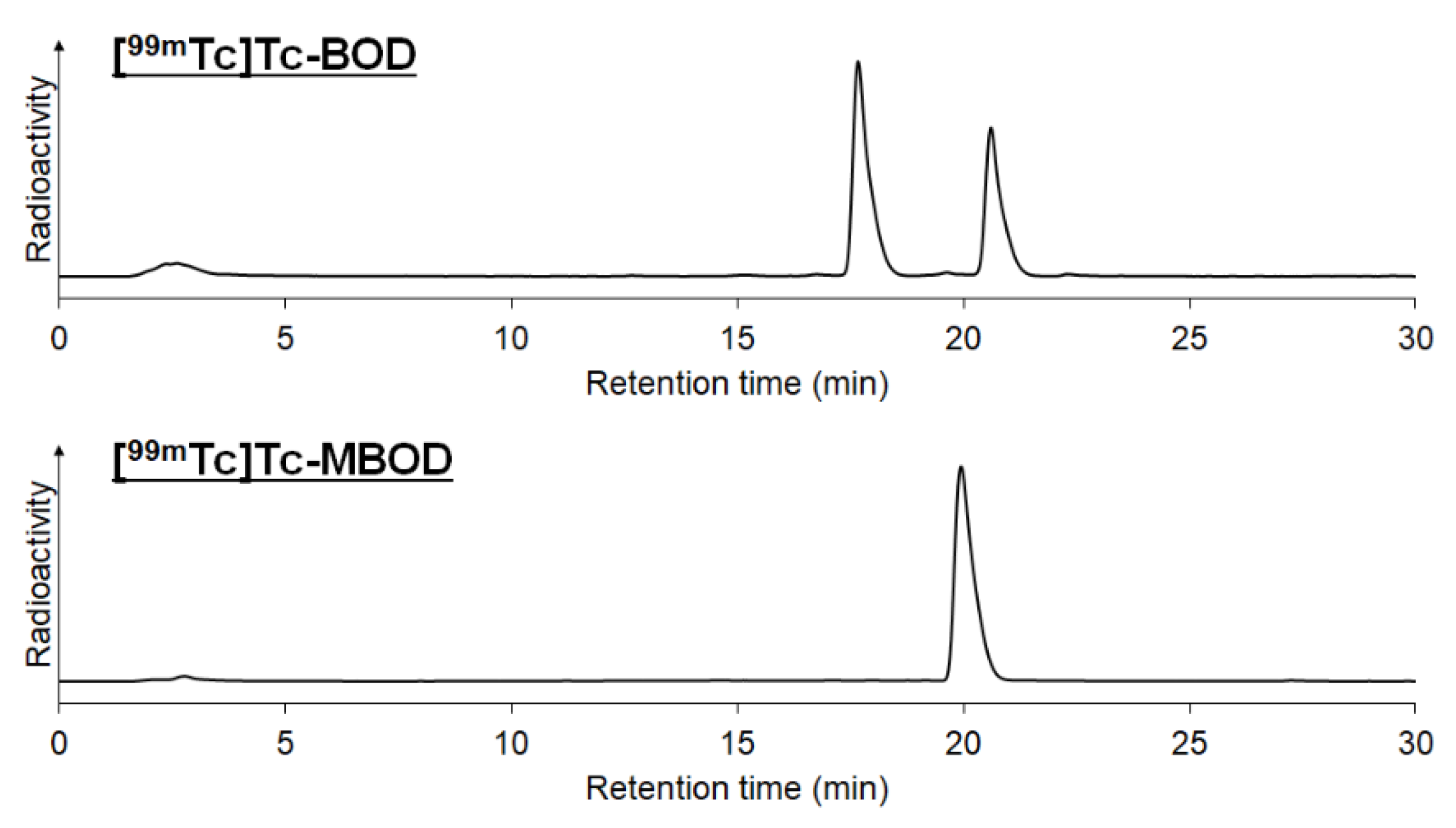
2.2. Radiolabeling
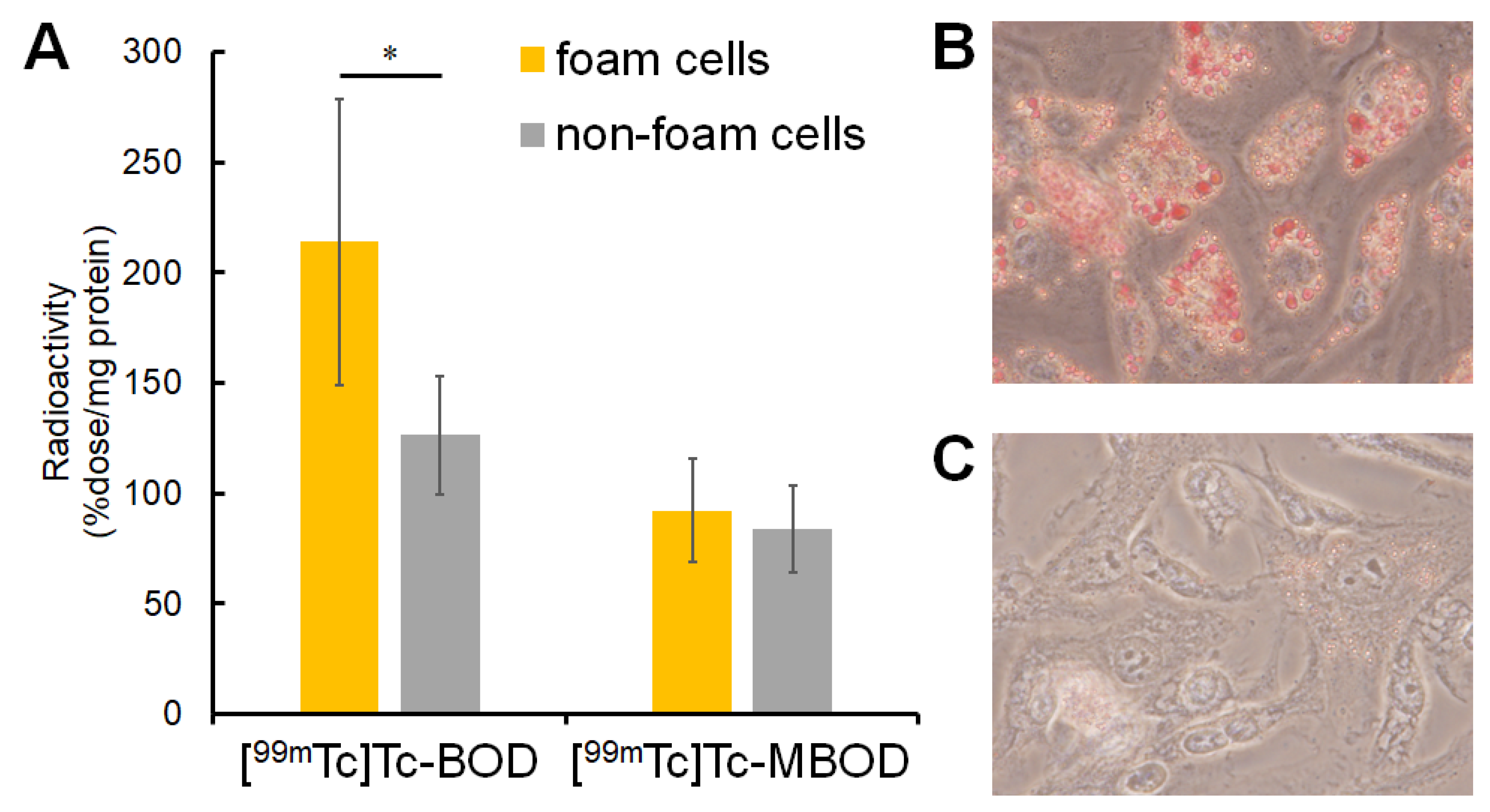
2.3. In Vitro Cellular Uptake Study
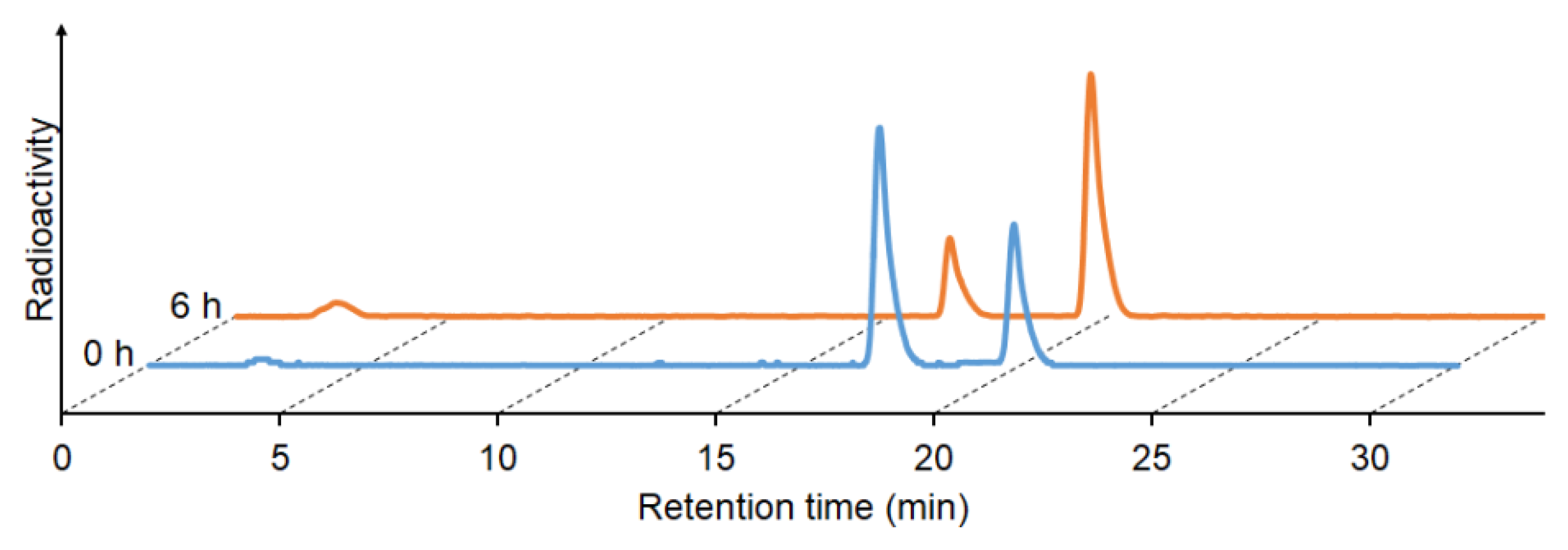
2.4. Stability in Murine Plasma
2.5. In Vivo Biodistribution
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General
4.2. Chemistry
4.2.1. Synthesis of 1
4.2.2. Synthesis of 2 (Ham-BODIPY)
4.2.3. Synthesis of 3
4.2.4. Synthesis of 4
4.2.5. Synthesis of 5 (MHam-BODIPY)
4.3. Radiolabeling
4.4. Preparation of Foam Cells
4.5. In Vitro Cellular Uptake Study
4.6. Stability in Murine Plasma
4.7. In Vivo Biodistribution
4.8. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knopp, R.H. Drug treatment of lipid disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assy, N.; Kaita, K.; Mymin, D.; Levy, C.; Rosser, B.; Minuk, G. Fatty infiltration of liver in hyperlipidemic patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2000, 45, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R. Cell biology of atherosclerosis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1995, 57, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.C.; Horton, J.D.; Hobbs, H.H. Human fatty liver disease: old questions and new insights. Science 2011, 332, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, E.; Shah, P.K.; Fuster, V. Coronary plaque disruption. Circulation 1995, 92, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Coleman, R.A.; Kraemer, F.B.; McManaman, J.L.; Obin, M.S.; Puri, V.; Yan, Q.-W.; Miyoshi, H.; Mashek, D.G. The role of lipid droplets in metabolic disease in rodents and humans. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, T.; Ohsaki, Y.; Cheng, J.; Suzuki, M.; Shinohara, Y. Lipid droplets: a classic organelle with new outfits. Histochem. Cell Bio. 2008, 130, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluchowski, N.L.; Becuwe, M.; Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Lipid droplets and liver disease: From basic biology to clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stary, H.C.; Chandler, A.B.; Dinsmore, R.E.; Fuster, V.; Glagov, S.; Insull, W., Jr.; Rosenfeld, M.E.; Schwartz, C.J.; Wagner, W.D.; Wissler, R.W. A definition of advanced types of atherosclerotic lesions and a histological classification of atherosclerosis: a report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Circulation 1995, 92, 1355–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Lipid droplets and cellular lipid metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 687–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, L.H.; Kasten, B.B.; Benny, P.D.; Arrowsmith, R.L.; Ge, H.; Pascu, S.I.; Botchway, S.W.; Clegg, W.; Harrington, R.W.; Higham, L.J. Re and 99m Tc complexes of BodP 3–multi-modality imaging probes. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15503–15505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listenberger, L.L.; Studer, A.M.; Brown, D.A.; Wolins, N.E. Fluorescent Detection of Lipid Droplets and Associated Proteins. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2016, 71, 4.31.1–4.31.14. [Google Scholar]
- Pysz, M.A.; Gambhir, S.S.; Willmann, J.K. Molecular imaging: Current status and emerging strategies. Clin. Radiol. 2010, 65, 500–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaki, S.; Hokamura, K.; Ogawa, M.; Takehara, Y.; Muramatsu, Y.; Yamane, T.; Hirabayashi, K.; Morimoto, Y.; Hagisawa, K.; Nakahara, K.; et al. A design strategy for small molecule-based targeted MRI contrast agents: their application for detection of atherosclerotic plaques. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 8611–8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceulemans, M.; Nuyts, K.; De Borggraeve, W.M.; Parac-Vogt, T.N. Gadolinium (III)-DOTA complex functionalized with BODIPY as a potential bimodal contrast agent for MRI and optical imaging. Inorganics 2015, 3, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Saigo, H.; Kai, E.; Koda, A.; Ozeki, H.; Harada, K.; Sugii, A.; Tomiguchi, S.; Kojima, A.; Hara, M. Hydroxamamide as a chelating moiety for the preparation of 99mTc radiopharmaceuticals (I). Nucl. Med. Commun. 1992, 13, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, M.; Saigo, H.; Koda, A.; Ozeki, K.; Harada, K.; Sugii, A.; Tomiguchi, S.; Kojima, A.; Hara, M.; Nakashima, R. Hydroxamamide as a chelating moiety for the preparation of 99mTc radiopharmaceuticals—II. The 99mTc complexes of hydroxamanide derivatives. Appl. Radiat. Isotopes 1994, 45, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Xu, L.; Koga, Y.; Harada, K.; Sugii, A.; Nakayama, H.; Tomiguchi, S.; Kojima, A.; Ohyama, Y.; Takahashi, M. Hydroxamamide as a chelating moiety for the preparation of 99mTc-radiopharmaceuticals III. Characterization of various 99mTc-hydroxamamides. Appl. Radiat. Isotopes. 1997, 48, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iikuni, S.; Ono, M.; Watanabe, H.; Matsumura, K.; Yoshimura, M.; Harada, N.; Kimura, H.; Nakayama, M.; Saji, H. Enhancement of binding affinity for amyloid aggregates by multivalent interactions of 99mTc-hydroxamamide complexes. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thipyapong, K.; Uehara, T.; Tooyama, Y.; Braband, H.; Alberto, R.; Arano, Y. Insight into technetium amidoxime complex: oxo technetium(V) complex of N-substituted benzamidoxime as new basic structure for molecular imaging. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iikuni, S.; Ono, M.; Watanabe, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Ihara, M.; Saji, H. Novel Bivalent 99mTc-Complex with N-Methyl-Substituted Hydroxamamide as Probe for Imaging of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, M.; Nakamura, S.; Saito, Y.; Kosugi, M.; Magata, Y. What can be seen by 18F-FDG PET in atherosclerosis imaging? The effect of foam cell formation on 18F-FDG uptake to macrophages in vitro. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Thien Quach, C.; Jung, K.-H.; Paik, J.-Y.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.W.; Lee, K.-H. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein stimulates macrophage 18F-FDG uptake via hypoxia-inducible factor-1a activation through Nox2-dependent reactive oxygen species generation. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.C.; Nakayama, M.; Harada, K.; Nakayama, H.; Tomiguchi, S.; Kojima, A.; Takahashi, M.; Arano, Y. Synthesis and evaluation of hydroxamamide-based tetradentate ligands as a new class of thiol-free chelating molecules for 99mTc radiopharmaceuticals. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1998, 25, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Kuge, Y. Recent Advances in the Development of PET/SPECT Probes for Atherosclerosis Imaging. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 50, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Lin, T.P.; Li, D.; Leamer, L.; Shan, H.; Li, Z.; Gabbai, F.P.; Conti, P.S. Lewis acid-assisted isotopic 18F-19F exchange in BODIPY dyes: facile generation of positron emission tomography/fluorescence dual modality agents for tumor imaging. Theranostics 2013, 3, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendricks, J.A.; Keliher, E.J.; Wan, D.; Hilderbrand, S.A.; Weissleder, R.; Mazitschek, R. Synthesis of [18F]BODIPY: bifunctional reporter for hybrid optical/positron emission tomography imaging. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 4603–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Watanabe, H.; Ikehata, Y.; Ding, N.; Yoshimura, M.; Sano, K.; Saji, H. Radioiodination of BODIPY and its application to a nuclear and optical dual functional labeling agent for proteins and peptides. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, L.E.; Long, N.J. ‘Two is better than one’—Probes for dual-modality molecular imaging. Chem. Commun. 2009, 3511–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
| Organ | Time after Injection | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 h | 1 h | 3 h | 6 h | |
| Blood | 4.98 ± 0.35 | 3.33 ± 0.29 | 2.70 ± 0.33 | 1.94 ± 0.12 |
| Spleen | 6.46 ± 1.09 | 5.47 ± 1.34 | 5.44 ± 0.79 | 5.58 ± 0.65 |
| Pancreas | 1.41 ± 0.15 | 1.08 ± 0.17 | 0.96 ± 0.16 | 0.79 ± 0.10 |
| Stomach* | 23.87 ± 2.56 | 28.77 ± 3.52 | 29.80 ± 3.48 | 25.25 ± 5.30 |
| Intestine | 2.03 ± 0.31 | 2.94 ± 0.41 | 5.28 ± 0.37 | 7.90 ± 1.72 |
| Kidney | 2.43 ± 0.30 | 2.16 ± 0.35 | 2.07 ± 0.26 | 2.07 ± 0.39 |
| Liver | 17.43 ± 1.87 | 14.99 ± 2.63 | 15.93 ± 1.32 | 15.22 ± 1.72 |
| Heart | 1.96 ± 0.15 | 1.22 ± 0.14 | 1.19 ± 0.13 | 0.89 ± 0.08 |
| Lung | 8.85 ± 2.42 | 4.80 ± 0.82 | 3.22 ± 0.70 | 2.33 ± 0.44 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimizu, Y.; Tanimura, K.; Iikuni, S.; Watanabe, H.; Saji, H.; Ono, M. Development of Technetium-99m-Labeled BODIPY-Based Probes Targeting Lipid Droplets Toward the Diagnosis of Hyperlipidemia-Related Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122283
Shimizu Y, Tanimura K, Iikuni S, Watanabe H, Saji H, Ono M. Development of Technetium-99m-Labeled BODIPY-Based Probes Targeting Lipid Droplets Toward the Diagnosis of Hyperlipidemia-Related Diseases. Molecules. 2019; 24(12):2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122283
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimizu, Yoichi, Keiichi Tanimura, Shimpei Iikuni, Hiroyuki Watanabe, Hideo Saji, and Masahiro Ono. 2019. "Development of Technetium-99m-Labeled BODIPY-Based Probes Targeting Lipid Droplets Toward the Diagnosis of Hyperlipidemia-Related Diseases" Molecules 24, no. 12: 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122283
APA StyleShimizu, Y., Tanimura, K., Iikuni, S., Watanabe, H., Saji, H., & Ono, M. (2019). Development of Technetium-99m-Labeled BODIPY-Based Probes Targeting Lipid Droplets Toward the Diagnosis of Hyperlipidemia-Related Diseases. Molecules, 24(12), 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122283





