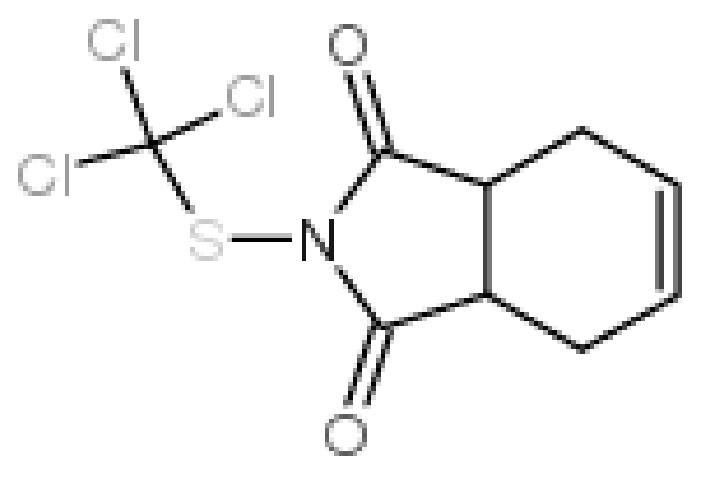
Physicochemical Parameters of Real Wastewater Originating from a Plant Protection Products Factory and Modification of the QuEChERS Method for Determination of Captan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
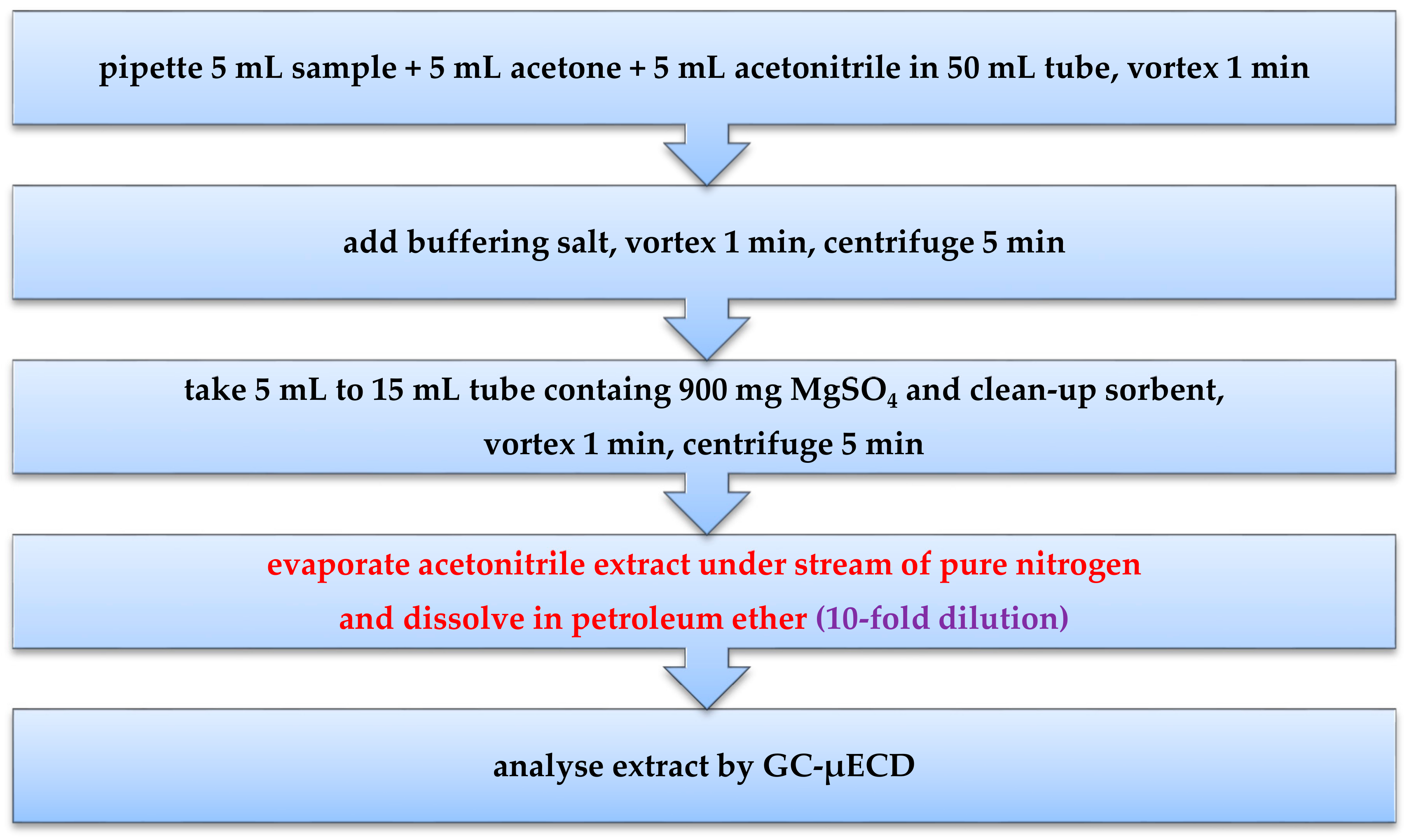
4.2. Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Cang, T.; Zhao, X.; Wu, S.; Qi, P.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q. Positive effects of an oil adjuvant on efficacy, dissipation and safety of pyrimethanil and boscalid on greenhouse strawberry. Ecotox Environ. Safe 2018, 160, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PCC Group Product Portal. Available online: https://www.products.pcc.eu/en/k/agrochemicals/ (accessed on 16 December 2018).
- EU Pesticide Database. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/public (accessed on 11 June 2018).
- The Pesticide Properties Database (PPDB). Available online: https://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/ (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- Plant Protection Products Search Engine. Available online: http://www.minrol.gov.pl/Informacje-branzowe/Wyszukiwarka-srodkowochrony-roslin (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- Anastassiades, M.; Lehotay, S.J.; Stajnbaher, D.; Schenck, F.J. Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid–phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- PN-EN 15662:2008 Foods of Plant Origin. Determination of Pesticide Residues Using GC-MS and/or LC-MS/MS Following Acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and Clean-Up by Dispersive SPE. QuEChERS-Method; The Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2008; pp. 1–81.
- González-Curbelo, M.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; González-Sálamo, J.; Hernández-Borges, J.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M. Evolution and applications of the QuEChERS method. TrAC—Trend Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.L.; Snow, N.H. Making the case for QuEChERS-gas chromatography of drugs. TrAC—Trend Anal. Chem. 2016, 75, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.B.; Ying, G.G.; Kookana, R.S. Rapid multiresidue determination for currently used pesticides in agricultural drainage waters and soils using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2010, 45, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łozowicka, B.; Kaczyński, P.; Szabuńko, J.; Ignatowicz, K.; Warentowicz, D.; Łozowicki, J. New rapid analysis of two classes of pesticides in food wastewater by quechers-liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. JEE 2016, 17, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E. Improved methods for analyzing wastewater and sediments. LC GC N. Am. 2017, 35, 336–337. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce-Robles, L.; Rivas, G.; Esteban, B.; Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Agüera, A. Determination of pesticides in sewage sludge from an agro-food industry using QuEChERS extraction followed by analysis with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 6181–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PN-EN ISO 10523:2012. Water Quality. Determination of pH; The Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2012; pp. 1–16.
- PN-EN 27888:1999. Water Quality. Determination of electrical conductivity; The Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1999; pp. 1–10.
- PN-EN ISO 7887:2012. Water Quality. Examination and Determination of Color; The Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2012; pp. 1–18.
- PN-EN ISO 7027:2003. Water Quality. Determination of Turbidity; The Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2003; pp. 1–17.
- PN-ISO 9297:1994. Water Quality. Determination of Chloride. Silver Nitrate Titration with Chromate Indicator (Mohr’s Method); The Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1994; pp. 1–7.
- PN-ISO 9280:2002. Water Quality. Determination of Sulfate. Gravimetric Method using Barium Chloride; The Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2002; pp. 1–10.
- PN-ISO 15705:2005. Water Quality. Determination of the Chemical Oxygen Demand (ST-COD) using the Sealed Tube Method; The Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2005; pp. 1–24.
- PN-EN 1484:1999. Water Analysis. Guidelines for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon and Dissolved Organic Carbon; The Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1999; pp. 1–14.
- PN-EN ISO 11885:2009. Water Quality. Determination of Selected Elements by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES); The Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2009; pp. 1–31.
- PN-EN ISO 12260:2004. Water Quality. Determination of Nitrogen. Determination of Bound Nitrogen following Oxidation to Nitrogen Oxides; The Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2004; pp. 1–13.
- SANTE/11813/2017. Guidance Document on Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation Procedures for Pesticide Residues and Analysis in Food and Feed. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/sites/ food/files/plant/docs/pesticides_mrl_guidelines_wrkdoc_2017-11813.pdf; (accessed on 6 November 2018).
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Available online: https://www.osha.gov/dts/sltc/methods/partial/t-pv2093-01-8707-ch/t-pv2093-01-8707-ch.html (accessed on 6 November 2018).
- Fang, Y.; Tian, W.; Pei, F.; Li, P.; Shao, X.; Fan, Y.; Hu, Q. Simultaneous determination of pesticide residues and antioxidants in blended oil using a liquid-liquid extraction combined with dispersive solid phase extraction method. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirahmadi, M.; Yazdanpanah, H.; Kobarfard, F.; Shoeibi, S.; Pirali-Hamedani, M.; Rastegar, H. Exposure assessment for some pesticides through rice consumption in Iran using a multiresidue analysis by GC-MS. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozdemir, C.; Sahinkaya, S.; Onucyildiz, M. Treatment of Pesticide Wastewater by Physicochemical and Fenton Processes. Asian J. Chem. 2008, 20, 3795–3804. [Google Scholar]
- Mistra, R.; Satyanarayan, S.; Potle, N. Treatment of agrochemical/Pesticide Wastewater by Coagulation/Flocculation Process. IRJCCS 2013, 2, 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Nesakumar, N.; Gumpu, M.B.; Nagarajan, S.; Ramanujam, S.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Simultaneous voltammetric determination of captan, carbosulfan, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin and pentachlorophenol in groundwater by ceria nanospheres decorated platinum electrode and chemometrics. Measurement 2017, 109, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, K.L.; Cerqueira, M.B.R.; Caldas, S.S.; Primel, E.G. Evaluation of alternative environmentally friendly matrix solid phase dispersion solid supports for the simultaneous extraction of 15 pesticides of different chemical classes from drinking water treatment sludge. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaly, A.E.; Dave, D. Kinetics of biological treatment of low level pesticide wastewater. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 8, 424–432. [Google Scholar]
- Sadło, S.; Szpyrka, E.; Piechowicz, B.; Antos, P.; Józefczyk, R.; Balawejder, M. Reduction of Captan, Boscalid and Pyraclostrobin Residues on Apples Using Water Only, Gaseous Ozone, and Ozone Aqueous Solution. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2017, 39, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmett, P.E.; Munch, J.W. Development of a US. EPA drinking water method for the analysis of emerging organic contaminants by GC/MS. In Proceedings of the Water Quality Technology Conference and Exposition, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 16–20 November 2008; pp. 492–502. [Google Scholar]
- Słowik-Borowiec, M.; Szpyrka, E. Multiresidue Analysis of Pesticides in Wine and Grape Using Gas Chromatography with Microelectron Capture and Nitrogen–Phosphorus Detection. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 3516–3530. [Google Scholar]
- Kwona, H.; Lehotay, S.J.; Geis-Asteggiante, L. Variability of matrix effects in liquid and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of pesticide residues after QuEChERS sample preparation of different food crops. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1270, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regulation of the Minister of Construction of July 14, 2006 on the Manner of Performing the Obligations of Suppliers of Industrial Wastewater and the Conditions for the Introduction of Sewage into Sewage Systems; Ministry of Construction: Warsaw, Poland, 2016.
Sample Availability: A-sample is available, B-sample is not available from the authors. |

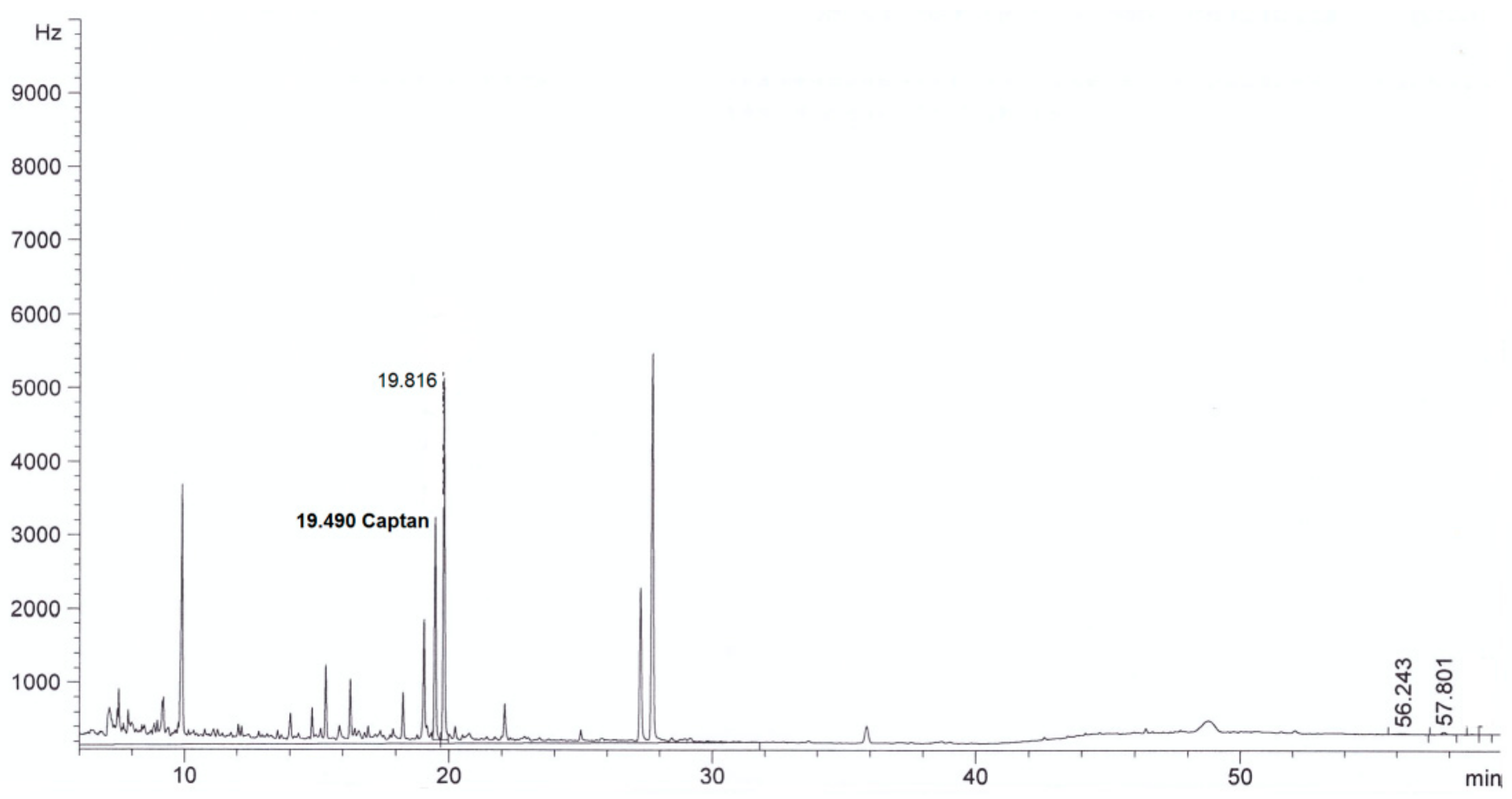
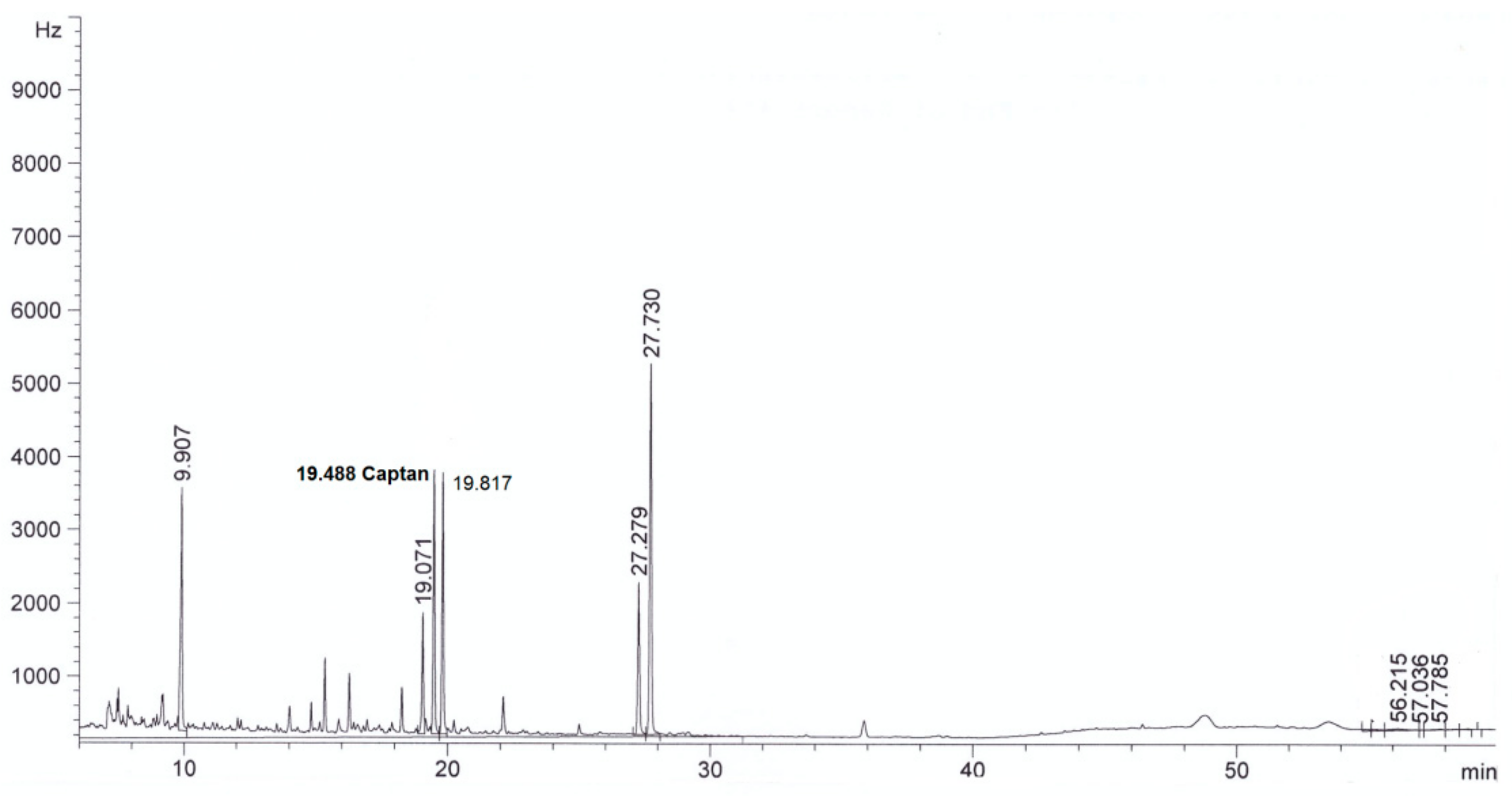
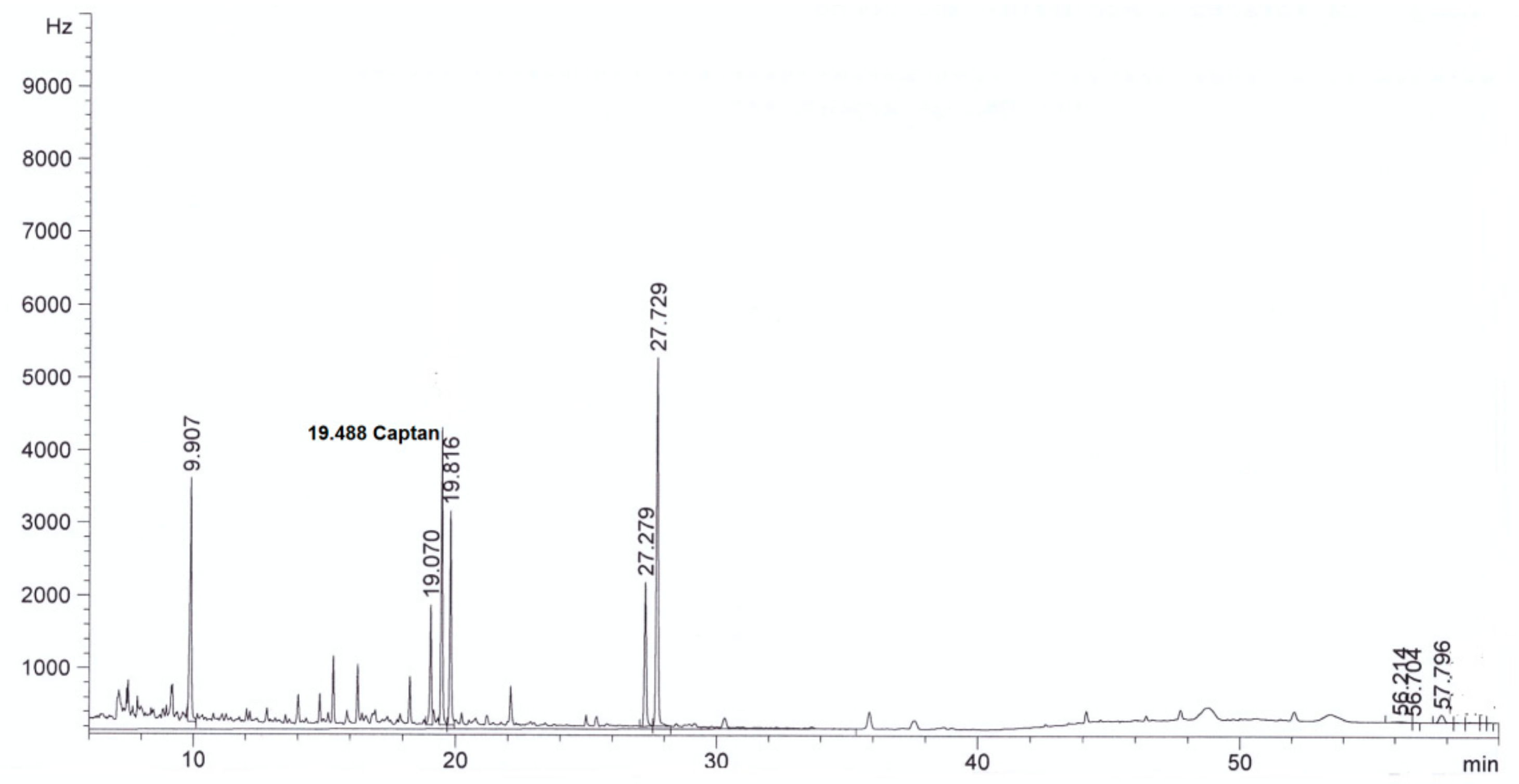
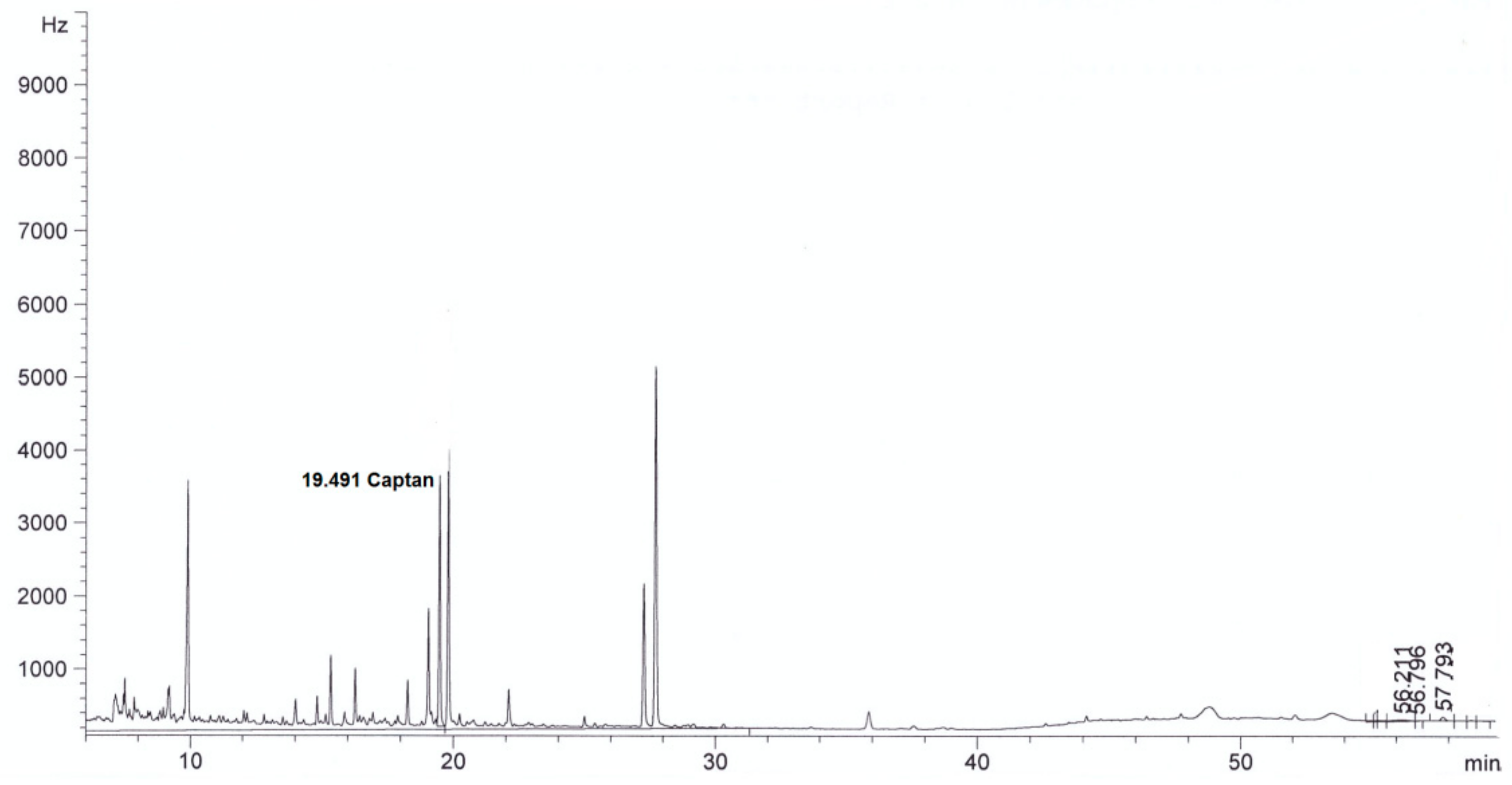
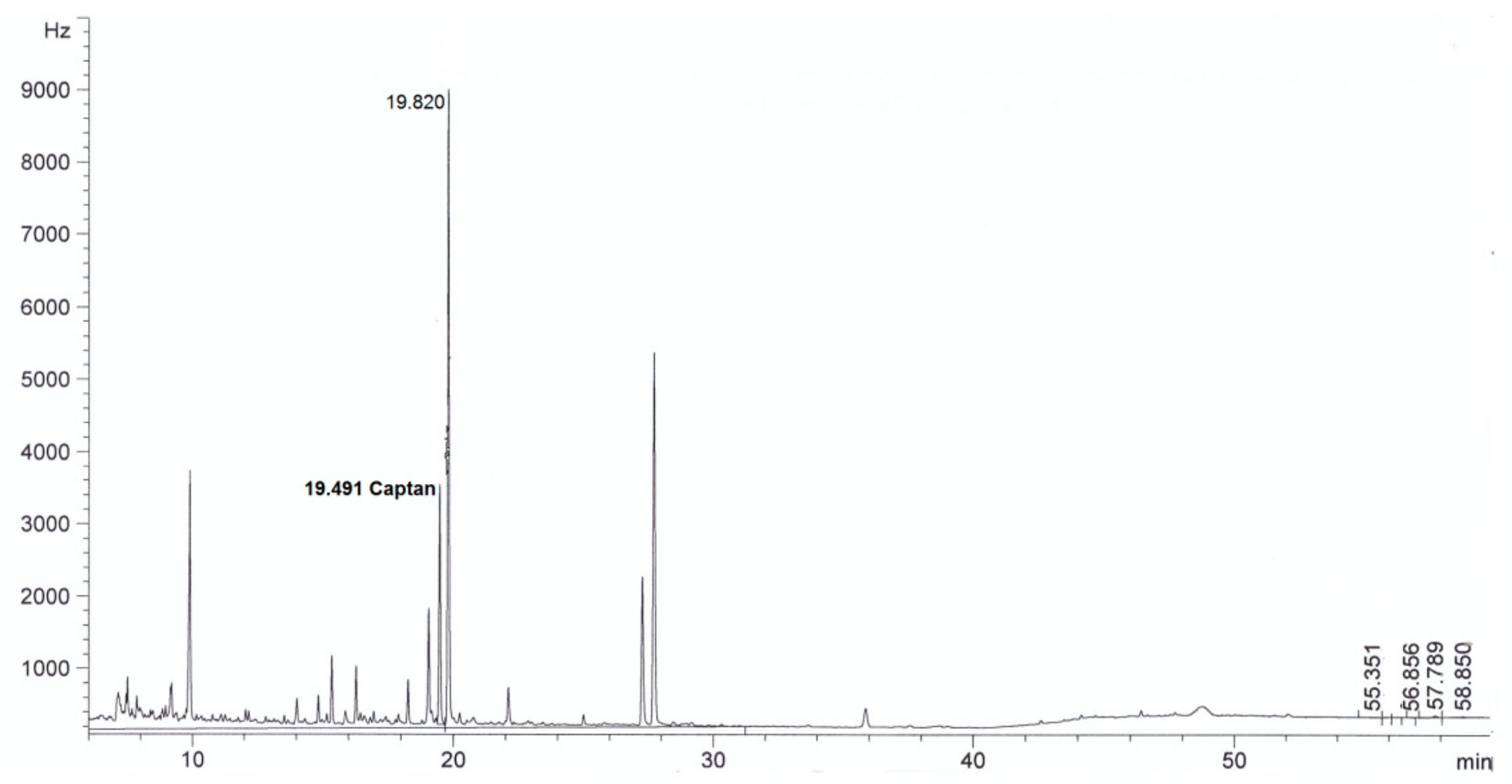
| Parameter | Method | Result | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-Sample | B-Sample | ||
| Captan, mg/L | This method | <0.003 in diluted extract | 4.0 ± 0.3 in diluted extract |
| pH | PN-EN ISO 10523:2012 [14] | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 7.6 ± 0.1 |
| Electrical conductivity, µS/cm | PN-EN 27888:1999 [15] | 900 ± 45 | 850 ± 43 |
| Salinity, mg NaCl/L | PN-EN 27888:1999 [15] | 430 ± 22 | 418 ± 21 |
| Color, mg Pt/L | PN-EN ISO 7887:2012 [16] | 50 ± 10 | 52 ± 10 |
| Turbidity, NTU | PN-EN ISO 7027:2003 [17] | 880 ± 90 | 900 ± 90 |
| Chloride, mg/L | PN-ISO 9297:1994 [18] | 75 ± 8 | 80 ± 8 |
| Sulfates, mg/L | PN-ISO 9280:2002 [19] | 95 ± 10 | 108 ± 11 |
| COD, mg O2/L | PN-ISO 15705:2005 [20] | 830 ± 120 | 856 ± 128 |
| TOC, mg/L | PN-EN 1484:1999 [21] | 58 ± 6 | 62 ± 9 |
| Total phosphorus, mg/L | PN-EN ISO 11885:2009 [22] | 0.5 ± 0.08 | 0.60 ± 0.06 |
| Total nitrogen, mg/L | PN-EN ISO 12260:2004 [23] | 2.00 ± 0.30 | 2.20 ± 0.33 |
| Copper, mg/L | PN-EN ISO 11885:2009 [22] | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 |
| Iron, mg/L | PN-EN ISO 11885:2009 [22] | 0.060 ± 0.006 | 0.040 ± 0.004 |
| Nickel, mg/L | PN-EN ISO 11885:2009 [22] | 0.050 ± 0.005 | 0.050 ± 0.005 |
| Zinc, mg/L | PN-EN ISO 11885:2009 [22] | 1.20 ± 0.12 | 1.30 ± 0.13 |
| Aluminum, mg/L | PN-EN ISO 11885:2009 [22] | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 0.24 ± 0.02 |
| Sorbent | Matrix-Match Calibration Curve Equation | Correlation Coefficient (R) | ME (%) | Recovery (%) at Spiking Level 0.1 mg/L | Recovery (%) at Spiking Level l50 mg/L | Overall Recover (%) | Intra-Day Relative Standard Deviation (%) | Inter-day Relative Standard Deviation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Florisil® | y = 3238 x − 381 | 0.997 | −44 | 95 | 97 | 96 | 9 | 10 |
| Al2O3 | y = 2333 x − 331 | 0.996 | −60 | 89 | 92 | 91 | 10 | 12 |
| ZrO2 | y = 1796 x − 237 | 0.996 | −69 | 93 | 103 | 98 | 8 | 10 |
| SiO2 | y =3093 x − 399 | 0.997 | −47 | 71 | 76 | 74 | 16 | 19 |
| PSA | y =1904 x − 247 | 0.996 | −67 | 95 | 89 | 92 | 18 | 20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szpyrka, E.; Thomas, M.; Podbielska, M. Physicochemical Parameters of Real Wastewater Originating from a Plant Protection Products Factory and Modification of the QuEChERS Method for Determination of Captan. Molecules 2019, 24, 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122203
Szpyrka E, Thomas M, Podbielska M. Physicochemical Parameters of Real Wastewater Originating from a Plant Protection Products Factory and Modification of the QuEChERS Method for Determination of Captan. Molecules. 2019; 24(12):2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122203
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzpyrka, Ewa, Maciej Thomas, and Magdalena Podbielska. 2019. "Physicochemical Parameters of Real Wastewater Originating from a Plant Protection Products Factory and Modification of the QuEChERS Method for Determination of Captan" Molecules 24, no. 12: 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122203
APA StyleSzpyrka, E., Thomas, M., & Podbielska, M. (2019). Physicochemical Parameters of Real Wastewater Originating from a Plant Protection Products Factory and Modification of the QuEChERS Method for Determination of Captan. Molecules, 24(12), 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122203