New Heteroleptic Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Sulfamethoxypyridazine and Diimines as Potential Antitumor Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
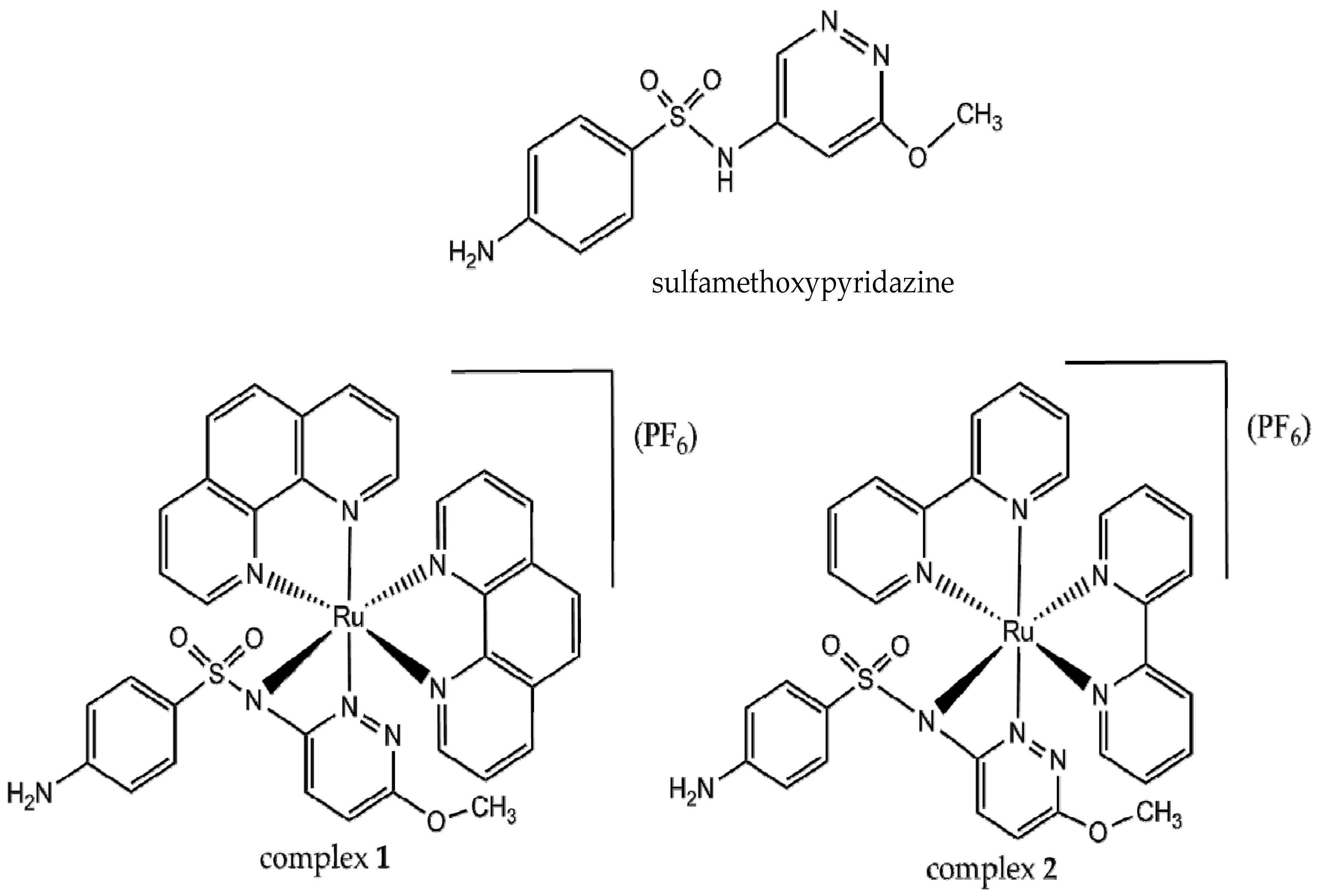
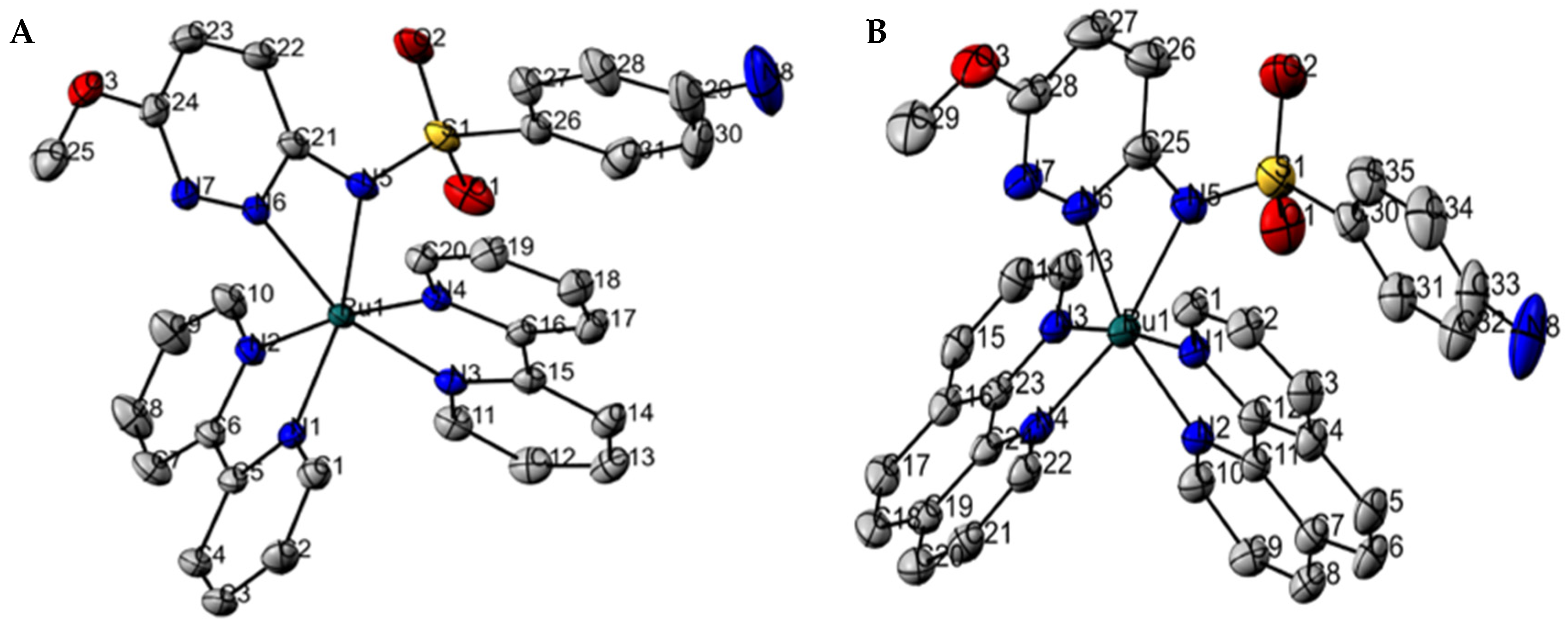
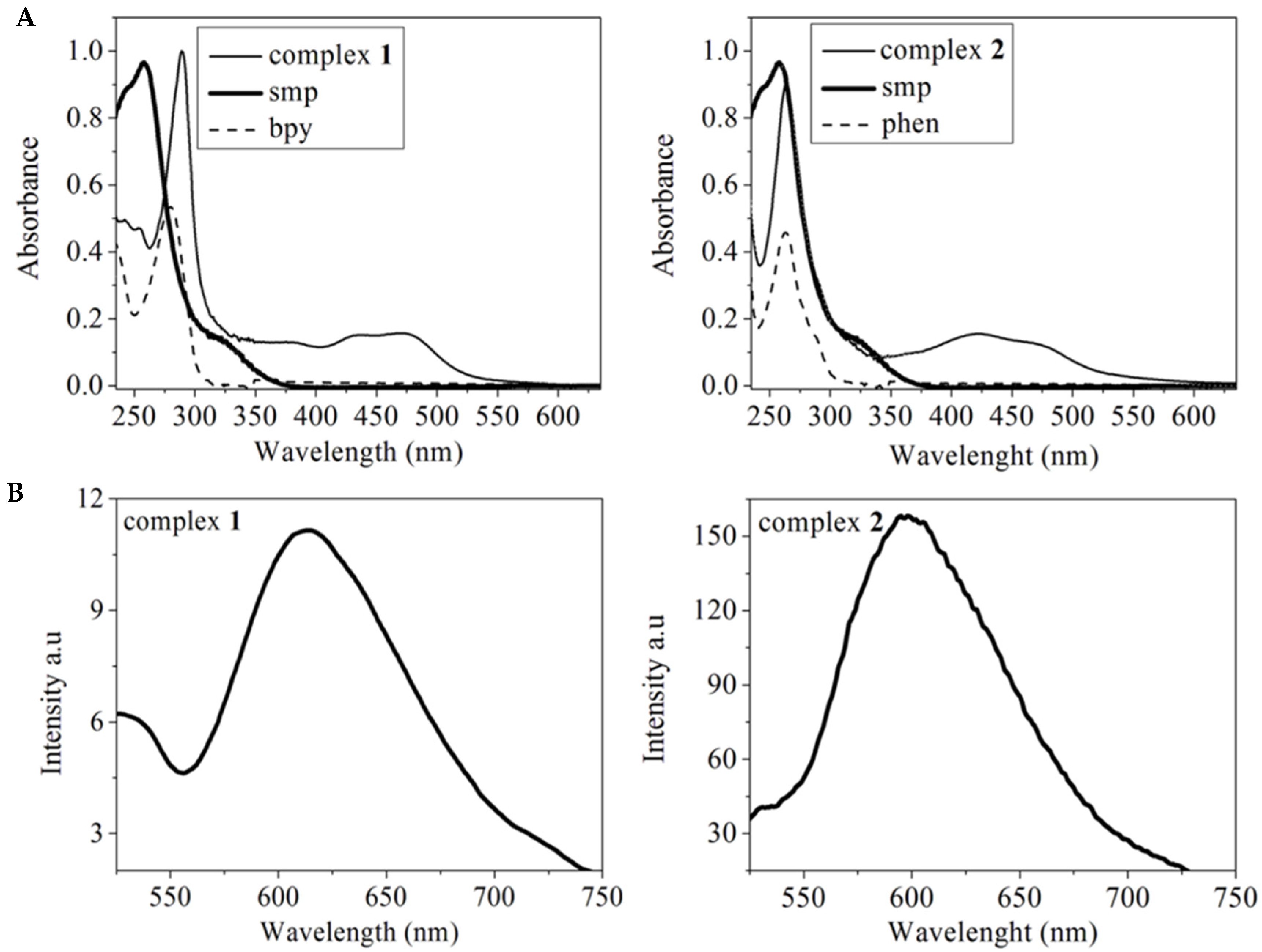
2.1. Characterization of Complexes 1 and 2
2.2. Cytotoxic Effect on Myelogenous Leukemia Cells
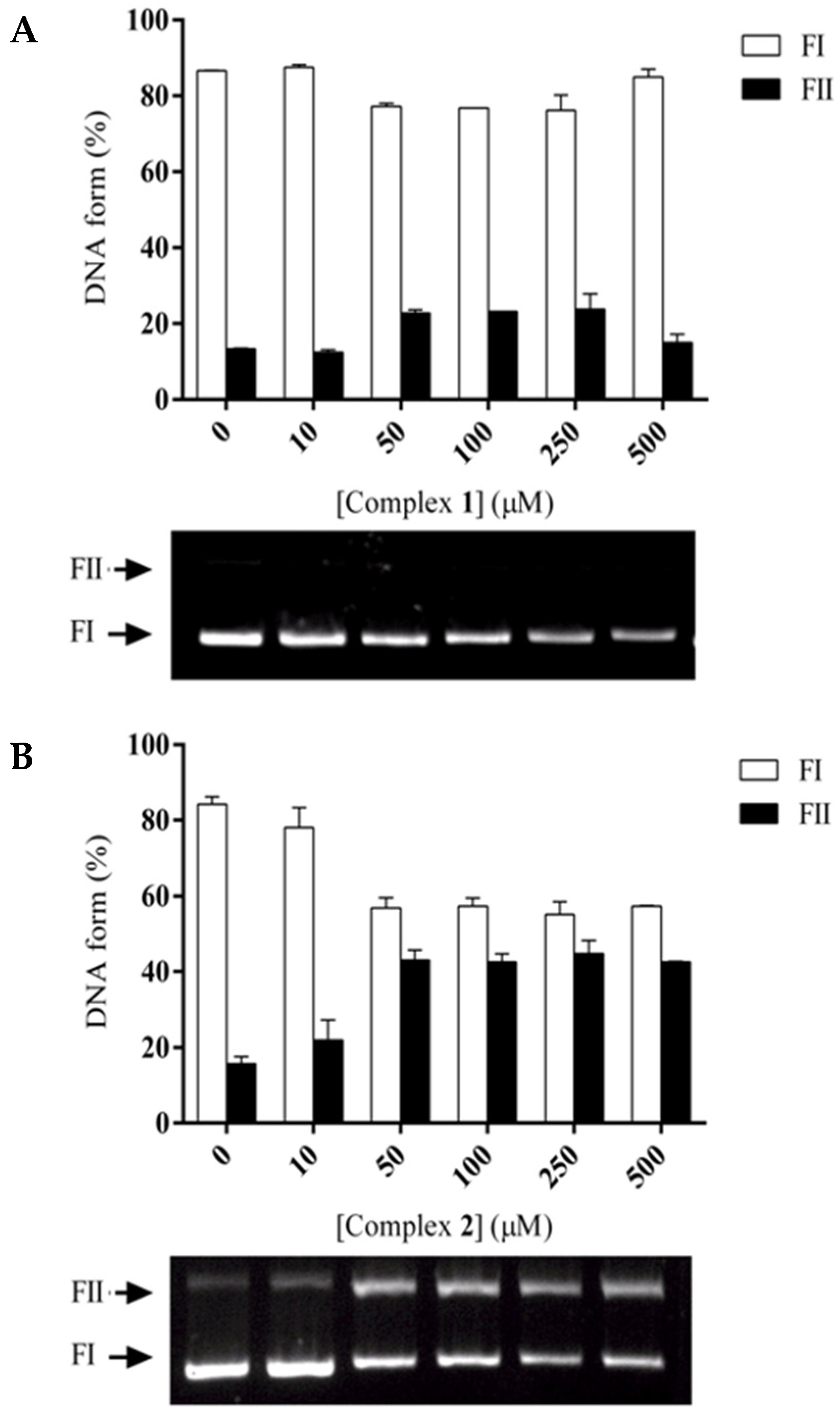
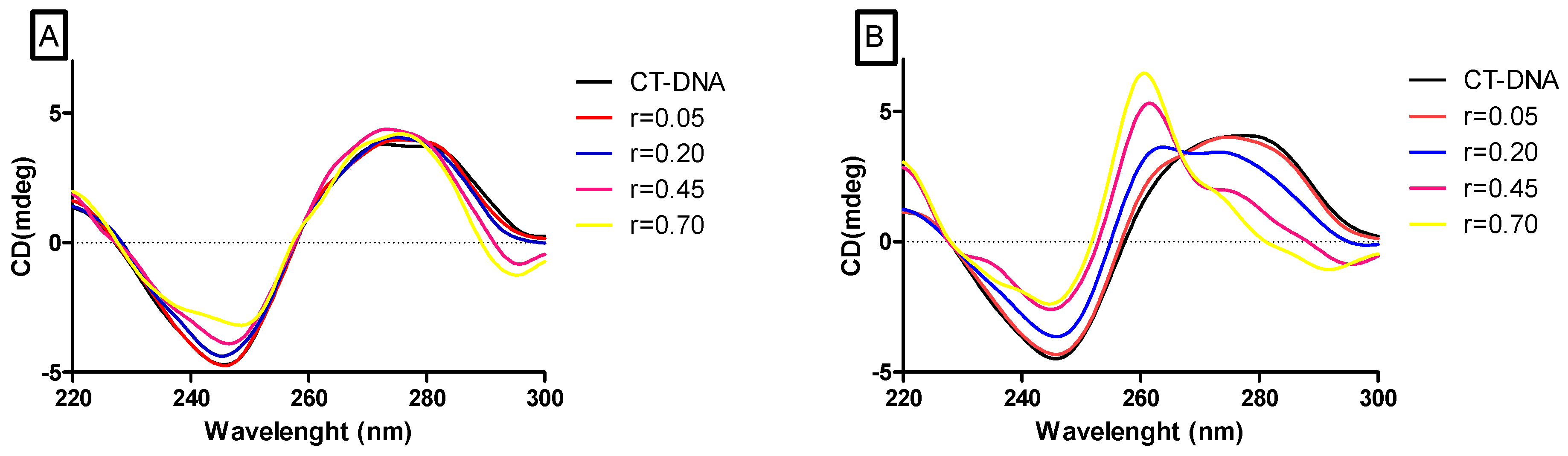
2.3. DNA Binding and Photocleavage
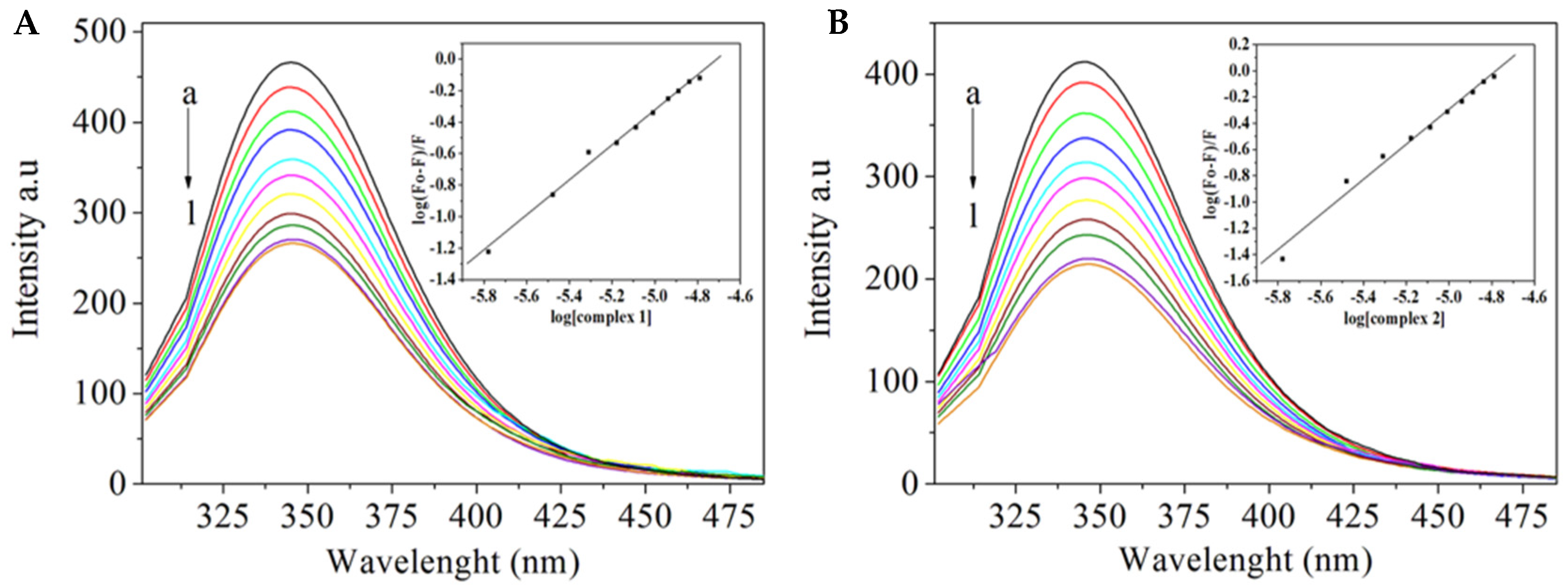
2.4. BSA Binding Studies
2.5. Interaction with the ABL-SH3 Domain
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General and Instruments
3.2. Synthesis of Complexes [Ru(bpy)2smp](PF6) and [Ru(phen)2smp](PF6)
3.3. Crystal Structure Determination
3.4. Cells, Culture and Drug Sensitivity Assays
3.5. DNA Cleavage Assays
3.6. Circular Dichroism
3.7. Fe(II)-EDTA (Hydroxyl radical) DNA Footprinting
3.8. Abl-SH3 Binding Assays
3.9. BSA Binding Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberg, B.; VanCamp, L. The successful regression of large solid sarcoma 180 tumors by platinum compounds. Cancer Res. 1970, 30, 1799–1802. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sherman, S.E.; Gibson, D.; Wang, A.H.; Lippard, S.J. X-ray structure of the major adduct of the anticancer drug cisplatin with DNA: Cis-[Pt(NH3)2(d(pGpG))]. Science 1985, 230, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, E.R.; Lippard, S.J. Structure, Recognition, and Processing of Cisplatin-DNA Adducts. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2467–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruijnincx, P.C.A.; Sadler, P.J. New trends for metal complexes with anticancer activity. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domotor, O.; de Almeida, R.F.M.; Corte-Real, L.; Matos, C.P.; Marques, F.; Matos, A.; Real, C.; Kiss, T.; Enyedy, E.A.; Garcia, H.M.; et al. Studies on the mechanism of action of antitumor bis(aminophenolate)ruthenium(III) complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 168, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zheng, K.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C.; Tan, W.; Mei, W. Ruthenium(II) Complexes as Potential Apoptosis Inducers in Chemotherapy. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Garza-Ortiz, A.; Maheswari, P.U.; Lutz, M.; Siegler, M.A.; Reedijk, J. Tuning the cytotoxic properties of new ruthenium(III) and ruthenium(II) complexes with a modified bis(arylimino)pyridine Schiff base ligand using bidentate pyridine-based ligands. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 19, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, J.S.; Ramos, L.C.; Ferreira, L.P.; Campo, V.L.; de Rezende, L.C.D.; da Silva, E.F.; Santana, R.S. Cytotoxicity, cellular uptake, and subcellular localization of a nitrogen oxide and aminopropyl-β-lactose derivative ruthenium complex used as nitric oxide delivery agent. Nitric Oxide 2019, 86, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, M.C.; Kljun, J.; Turel, I.; Di Virgilio, A.L.; León, I.E. Comparative antitumor studies of organoruthenium complexes with 8-hydroxyquinolines on 2D and 3D cell models of bone, lung and breast cancer. Metallomics 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Emadi, A. Ruthenium-based chemotherapeutics: Are they ready for prime time? Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamo, A.; Sava, G. Ruthenium complexes can target determinants of tumour malignancy. Dalton Trans. 2007, 13, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamo, A.; Sava, G. Linking the future of anticancer metal-complexes to the therapy of tumour metastases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8818–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartinger, C.G.; Zorbas-Seifried, S.; Jakupec, M.A.; Kynast, B.; Zorbas, H.; Keppler, B.K. From bench to bedside--preclinical and early clinical development of the anticancer agent indazolium trans-[tetrachlorobis(1H-indazole)ruthenate(III)] (KP1019 or FFC14A). J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamo, A.; Masi, A.; Jakupec, M.A.; Keppler, B.K.; Sava, G. Inhibitory Effects of the Ruthenium Complex KP1019 in Models of Mammary Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Metal-Based Drugs 2009, 681270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habtemariam, A.; Melchart, M.; Fernandez, R.; Parsons, S.; Oswald, I.D.H.; Parkin, A.; Fabbiani, F.P.A.; Davidson, J.E.; Dawson, A.; Aird, R.E.; et al. Structure-activity relationships for cytotoxic ruthenium(II) arene complexes containing N,N-, N,O-, and O,O-chelating ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6858–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uršic, M.; Lipec, T.; Meden, A.; Turel, I. Synthesis and Structural Evaluation of Organo-Ruthenium Complexes with β-Diketonates. Molecules 2017, 22, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artner, C.; Holtkamp, H.U.; Hartinger, C.G.; Meier-Menches, S.M. Characterizing activation mechanisms and binding preferences of ruthenium metallo-prodrugs by a competitive binding assay. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 177, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.J. Ruthenium metallopharmaceuticals. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003, 236, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlino, A. Interactions between proteins and Ru compounds of medicinal interest: A structural perspective. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 326, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, A.C.C.; Santana, J.M.S.V.P.; Nunes, K.J.R.C.; Marques, M.A.; de Oliveira, G.A.P.; Moraes, A.H.; Pereira-Maia, E.C. Interactions of ruthenium(II) compounds with sulfasalazine and N,N-heterocyclic ligands with proteins. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2017, 467, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzada, D.; Salvadó, I.; Barka, G.; Rama, G.; Martínez-Costas, J.; Lorca, R.; Somoza, A.; Melle-Franco, M.; Vázquez, M.E.; Vázquez López, M. Selective G-quadruplex binding by oligoarginine-Ru(dppz) metallopeptides. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillozzi, S.; Gasparoli, L.; Stefanini, M.; Ristori, M.; D’amico, M.; Alessio, E.; Scaletti, F.; Becchetti, A.; Arcangeli, A.; Messori, L. NAMI-A is highly cytotoxic toward leukaemia cell lines: Evidence of inhibition of KCa 3.1 channels. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 12150–12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobec, M.; Kljun, J.; Sosič, I.; Mlinarič-Raščan, I.; Uršič, M.; Gobec, S.; Turel, I. Structural characterization and biological evaluation of a clioquinol–ruthenium complex with copper-independent antileukaemic activity. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 9045–9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badger, J.; Grover, P.; Shi, H.; Panjarian, S.B.; Engen, J.R.; Smithgall, T.E.; Makowski, L. c-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Adopts Multiple Active Conformational States in Solution. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 3251–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbi-Verge, C.; Marinelli, F.; Zafra-Ruano, A.; Ruiz-Sanz, J.; Luque, I.; Faraldo-Gómez, J.D. Two-state dynamics of the SH3-SH2 tandem of Abl kinase and the allosteric role of the N-cap. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3372–E3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, R.A. Is there a best TKI for chronic phase CML? Blood 2015, 126, 2370–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazuryk, O.; Magiera, K.; Rys, B.; Suzenet, F.; Kieda, C.; Brindell, M. Multifaceted interplay between lipophilicity, protein interaction and luminescence parameters of non-intercalative ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes controlling cellular imaging and cytotoxic properties. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 19, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, N.; Mehanna, S.; Mroueh, M.A.; Audi, H.; Bodman-Smith, K.; Daher, C.F.; Taleb, R.I.; El-Sibai, M.; Khnayzer, R.S. Photoactivatable RuII Complex Bearing 2,9-Diphenyl-1,10- phenanthroline: Unusual Photochemistry and Significant Potency on Cisplatin-Resistant Cell Lines. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 22, 2524–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, D.F.; Audi, H.; Farhat, S.; El-Sibai, M.; Abi-Habib, R.J.; Khnayzer, R.S. Phototoxicity of strained Ru(II) complexes: Is it the metal complex or the dissociating ligand? Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 11529–11532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, T.; Pierroz, V.; Mari, C.; Gemperle, L.; Ferrari, S.; Gasser, G. A bis(dipyridophenazine)(2-(2-pyridyl)pyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid)ruthenium(II) complex with anticancer action upon photodeprotection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2960–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, C.; Pierroz, V.; Rubbiani, R.; Patra, M.; Hess, J.; Spingler, B.; Oehninger, L.; Schur, J.; Ott, I.; Salassa, L.; et al. DNA intercalating Ru(II) polypyridyl complexes as effective photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy. Chemistry 2014, 20, 14421–14436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łakomska, I.; Fandzloch, M.; Muzioł, T.; Lis, T.; Jezierska, J. Synthesis, characterization and antitumor properties of two highly cytotoxic ruthenium(III) complexes with bulky triazolopyrimidine ligands. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 6219–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albani, B.A.; Penña, B.; Leed, N.A.; de Paula, N.A.B.G.; Pavani, C.; Baptista, M.S.; Dunbar, K.R.; Turro, C. Marked improvement in photoinduced cell death by a new tris-heteroleptic complex with dual action: Singlet oxygen sensitization and ligand dissociation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 17095–17101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cream, C.W.; Kavanagh, Y.T.; O’Keeffe, C.M.; Lawler, M.P.; Stevenson, C.; Davies, R.J.; Boyle, P.H.; Kelly, J.M. Targeting of photooxidative damage on single-stranded DNA representing the bcr-abl chimeric gene using oligonucleotide-conjugates containing [Ru(phen)3](2+)-like photosensitiser groups. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2002, 1, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, W.; Silva-Caldeira, P.P.; Terenzi, H.; Pereira-Maia, E.C. Impact of metal coordination on the antibiotic and non-antibiotic activities of tetracycline-based drugs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 327–328, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet, M.; Ota, E.; Chibueze, C.E.; Oladapo, O.T. Routine antibiotic prophylaxis after normal vaginal birth for reducing maternal infectious morbidity. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD012137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, L.L.; de Oliveira, G.M.; Lang, E.S.; de Campos, M.M.A.; Gris, L.R.S. New gold(I) and silver(I) complexes of sulfamethoxazole: Synthesis, X-ray structural characterization and microbiological activities of triphenylphosphine(sulfamethoxazolato-N2)gold(I) and (sulfamethoxazolato)silver(I). Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2007, 10, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.H.B.; de Paiva, R.E.F.; Cuin, A.; Lustri, W.R.; Corbi, P.P. Silver complexes with sulfathiazole and sulfamethoxazole: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, crystal structure and antibacterial assays Silver complexes with sulfathiazole and sulfamethoxazole: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, crystal structure and antibacterial assays. Polyhedron 2015, 85, 437–444. [Google Scholar]
- Borrás, E.; Alzuet, G.; Borrás, J.; Server-Carrió, J.; Castiñeiras, A.; Liu-González, M.; Sanz-Ruiz, F. Coordination chemistry of sulfamethizole: Crystal structures of [Cu(sulfamethizolate)2(py)2(OH2)]·H2O, [M(sulfamethizolate)2(py)2(OH2)2] [M=Co and Ni] and {Cu(sulfamethizolate)2(dmf)2}∞. Polyhedron 2000, 19, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Raso, Á.; Fiol, J.J.; Rigo, S.; López-López, A.; Molins, E.; Espinosa, E.; Borrás, E.; Alzuet, G.; Borrás, J.; Castiñeiras, A. Coordination behaviour of sulfanilamide derivatives.: Crystal structures of [Hg(sulfamethoxypyridazinato)2], [Cd(sulfadimidinato)2(H2O)]·2H2O and [Zn(sulfamethoxazolato)2-(pyridine)2(H2O)2]. Polyhedron 2000, 19, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, E.; Facchin, G.; Estévez, E.; Alborés, P.; Baran, E.J.; Ellena, J.; Torre, M.H. Copper complexes with heterocyclic sulfonamides: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, microbiological and SOD-like activities: Crystal structure of [Cu(sulfisoxazole)2(H2O)4]. 2H2O. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzano, I.M.; Franco, M.S.; Silva, P.P.; Augusti, R.; Santos, G.C.; Fernandes, N.G.; Bucciarelli-Rodrigues, M.R.; Chartone-Souza, E.; Pereira-Maia, E.C. Crystal Structure, Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Activities of a New Complex of Bismuth(III) with Sulfapyridine. Molecules 2013, 18, 1464–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refat, M.S.; Sharshar, T.; Elsabawy, K.M.; El-Sayed, M.Y.; Adam, A.M.A. Synthesis, physicochemical characterization and anticancer screening of sulfa drug ruthenium complexes as anticancer agent. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 222, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, W.J. The use of conductivity measurements in organic solvents for the characterisation of coordination compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1971, 7, 81–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, B.P.; Salmon, D.J.; Meyer, T. Mixed phosphine 2,2’-bipyridine complexes of ruthenium. Inorg. Chem. 1978, 17, 3334–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotto, T.; Silva-Caldeira, P.P.; Pich, C.T.; Pereira-Maia, E.C.; Terenzi, H. Tunable DNA cleavage activity promoted by copper(II) ternary complexes with N-donor heterocyclic ligands. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 7130–7133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T. Chiral ruthenium complexes induce apoptosis of tumor cell and interact with bovine serum albumin. Chirality 2012, 24, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colina-Vegas, L.; Dutra, J.L.; Villarreal, W.; Neto Cominetti, J.A.M.R.; Pavan, F.; Navarro, M.; Batista, A.A. Ru(II)/clotrimazole/diphenylphosphine/bipyridine complexes: Interaction with DNA, BSA and biological potential against tumor cell lines and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 162, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, P.; Viswanathamurthi, P.; Silambarasan, V.; Velmurugan, D.; Velmurugan, K.; Nandhakumar, R.; Butcher, R.J.; Silambarasan, T.; Dhandapani, R. Dissymmetric thiosemicarbazone ligands containing substituted aldehyde arm and their ruthenium(II) carbonyl complexes with PPh3/AsPh3 as ancillary ligands: Synthesis, structural characterization, DNA/BSA interaction and in vitro anticancer activity. J. Organomet. Chem. 2014, 768, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarushi, A.; Totta, X.; Papadopoulos, A.; Kljun, J.; Turel, I.; Kessissoglou, D.P.; Psoma, G. Antioxidant activity and interaction with DNA and albumins of zinc–tolfenamato complexes. Crystal structure of [Zn(tolfenamato)2(2,2′-dipyridylketoneoxime)2]. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 74, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurty, R.; Brigham, J.L.; Leonard, S.E.; Ranjitkar, P.; Larson, E.T.; Dale, E.J.; Merritt, E.A.; Maly, D.J. Active site profiling reveals coupling between domains in SRC-family kinases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohidov, F.; Knudsen, S.E.; Leonard, P.G.; Ohata, J.; Wheadon, M.J.; Popp, B.V.; Ladbury, J.E.; Ball, Z.T. Potent and selective inhibition of SH3 domains with dirhodium metalloinhibitors. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4778–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRYSALIS PRO; Agilent Technologies Ltd.: Oxfordshire, UK, 2014.
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. 2008, A64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, I.J.; Cole, J.C.; Edgington, P.R.; Kessler, M.; Macrae, C.F.; Mccabe, P.; Pearson, J.; Taylor, R. New software for searching the Cambridge Structural Database and visualizing crystal structures. Acta Crystallogr. B 2002, 58, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, L.J. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: An update. J. Appl. Cryst. 2012, 45, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, L.J. WinGX suite for small-molecule single-crystal crystallography. J. Appl. Cryst. 1999, 32, 837–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotto, T.; Silva, P.P.; Neves, A.; Pereira-Maia, E.C.; Terenzi, H. Photoinduced DNA Cleavage Promoted by Two Copper(II) Complexes of Tetracyclines and 1,10-Phenanthroline. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 10519–10521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.P.; Guerra, W.; Silveira, J.N.; Ferreira, A.M.C.; Bortolotto, T.; Fischer, F.L.; Terenzi, H.; Neves, A.; Pereira-Maia, E.C. Two New Ternary Complexes of Copper(II) with Tetracycline or Doxycycline and 1,10-Phenanthroline and Their Potential as Antitumoral: Cytotoxicity and DNA Cleavage. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 6414–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.S.; Tullius, T.D. Footprinting protein–DNA complexes using the hydroxyl radical. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, S.S.; Perkins, R.S.; Louka, F.R.; Xu, W.; Le Roux, A.; Dutercq, Q.; Fischer, R.C.; Mautner, F.A.; Handa, M.; Hiraoka, Y.; et al. Efficient hydrolytic cleavage of plasmid DNA by chloro-cobalt(II) complexes based on sterically hindered pyridyl tripod tetraamine ligands: Synthesis, crystal structure and DNA cleavage. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 10086–10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, G.A.P.; Pereira, E.G.; Ferretti, G.D.S.; Valente, A.P.; Cordeiro, Y.; Silva, J.L. Intramolecular Dynamics within the N-Cap-SH3-SH2 Regulatory Unit of the c-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Reveal Targeting to the Cellular Membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 28331–28345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of compounds are available from the authors. |


| Complex | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3.80 ± 0.19 |
| 2 | 2.00 ± 0.10 |
| cis-[RuCl2(bpy)2] | >100 |
| cis-[RuCl2(phen)2] | >100 |
| kcat (h−1) | KM (M) | kcat/KM (h−1 M) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.38 | 4.5 × 10−6 | 2.7 × 105 |
| 2 | 2.03 | 3.1 × 10−6 | 6.5 × 105 |
| Complex | Ksv (L mol−1) | Kq (L mol−1 s−1) | Kb (L mol−1) | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.02 × 105 | 1.02 × 1013 | 8.19 × 104 | 0.99 | 0.9733 |
| 2 | 1.28 × 105 | 1.28 × 1013 | 2.47 × 106 | 0.99 | 0.9793 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Melo, A.C.C.; Santana, J.M.S.V.P.; Nunes, K.J.R.C.; Rodrigues, B.L.; Castilho, N.; Gabriel, P.; Moraes, A.H.; Marques, M.d.A.; de Oliveira, G.A.P.; de Souza, Í.P.; et al. New Heteroleptic Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Sulfamethoxypyridazine and Diimines as Potential Antitumor Agents. Molecules 2019, 24, 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112154
de Melo ACC, Santana JMSVP, Nunes KJRC, Rodrigues BL, Castilho N, Gabriel P, Moraes AH, Marques MdA, de Oliveira GAP, de Souza ÍP, et al. New Heteroleptic Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Sulfamethoxypyridazine and Diimines as Potential Antitumor Agents. Molecules. 2019; 24(11):2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112154
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Melo, Ariane C.C., Jaime M.S.V.P. Santana, Kelen J.R.C. Nunes, Bernardo L. Rodrigues, Nathalia Castilho, Philipe Gabriel, Adolfo H. Moraes, Mayra de A. Marques, Guilherme A.P. de Oliveira, Ívina P. de Souza, and et al. 2019. "New Heteroleptic Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Sulfamethoxypyridazine and Diimines as Potential Antitumor Agents" Molecules 24, no. 11: 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112154
APA Stylede Melo, A. C. C., Santana, J. M. S. V. P., Nunes, K. J. R. C., Rodrigues, B. L., Castilho, N., Gabriel, P., Moraes, A. H., Marques, M. d. A., de Oliveira, G. A. P., de Souza, Í. P., Terenzi, H., & Pereira-Maia, E. C. (2019). New Heteroleptic Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Sulfamethoxypyridazine and Diimines as Potential Antitumor Agents. Molecules, 24(11), 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112154








