A Novel Lipopeptaibol Emericellipsin A with Antimicrobial and Antitumor Activity Produced by the Extremophilic Fungus Emericellopsis alkalina
Abstract
1. Introduction
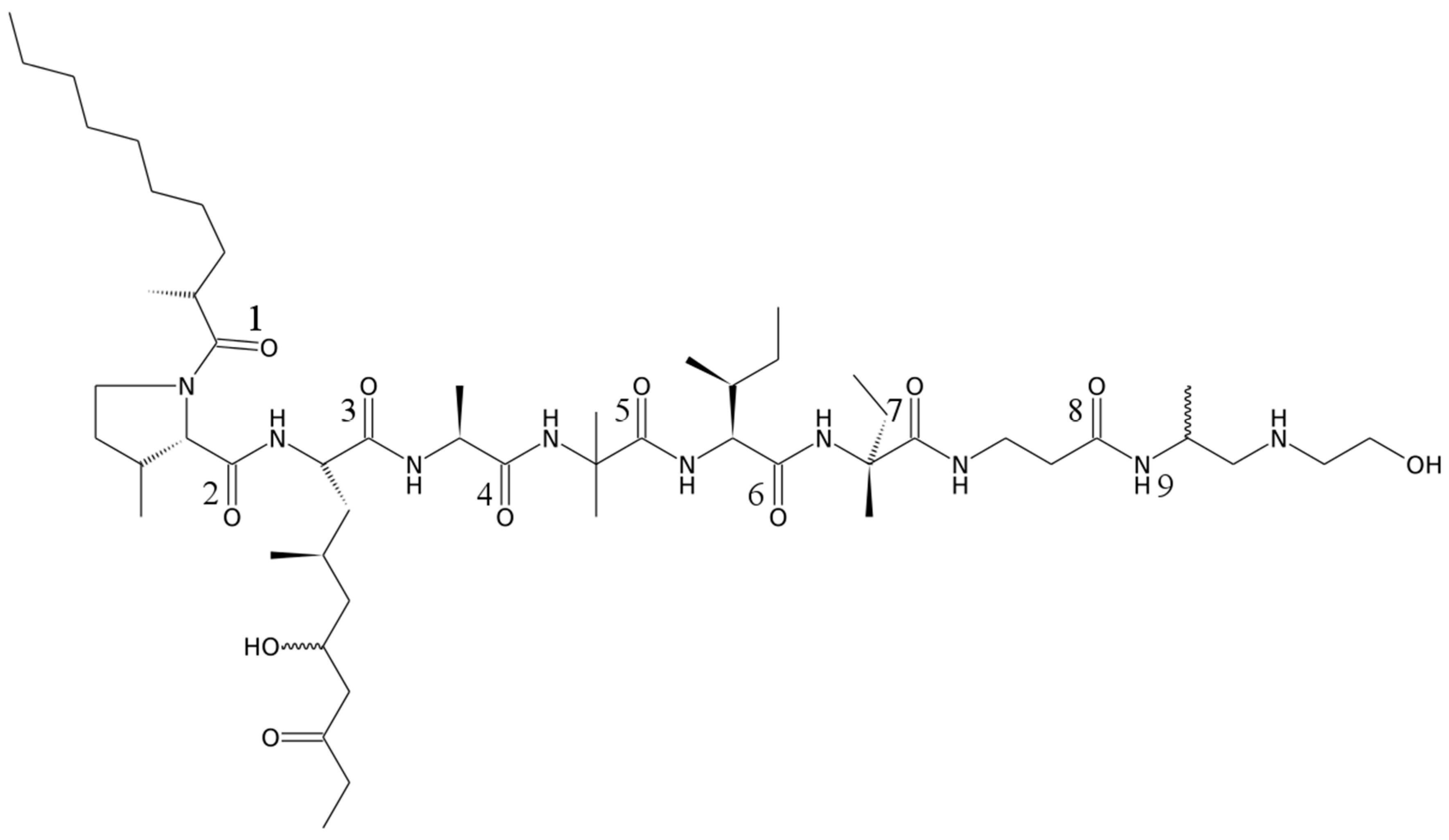
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Fungal Strain and Cultivation
3.2. Microorganisms
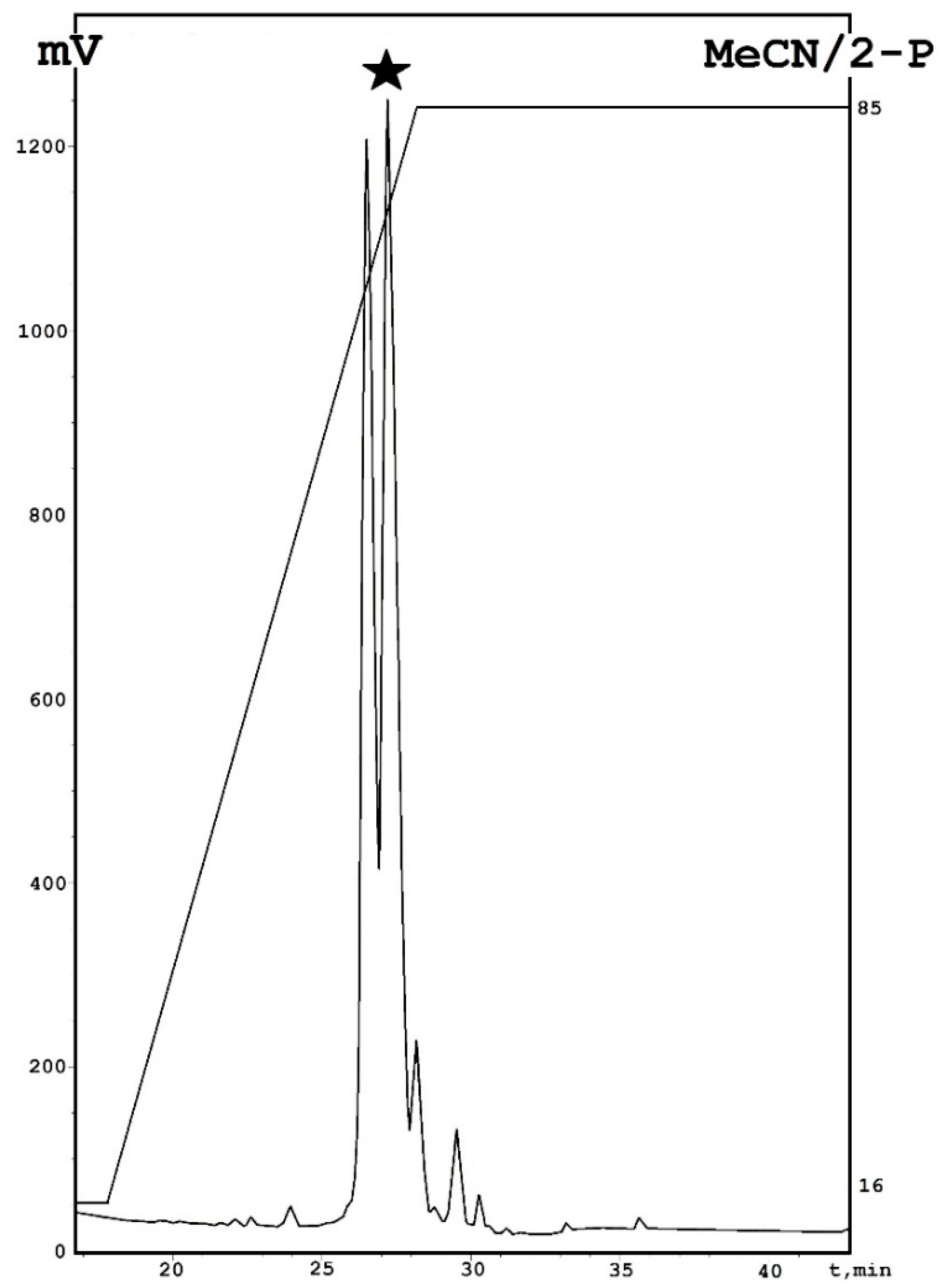
3.3. Isolation and Purification of Emericellipsin A
3.4. Mass Spectrometry
3.5. NMR Spectrometry
3.6. Antibacterial Activity
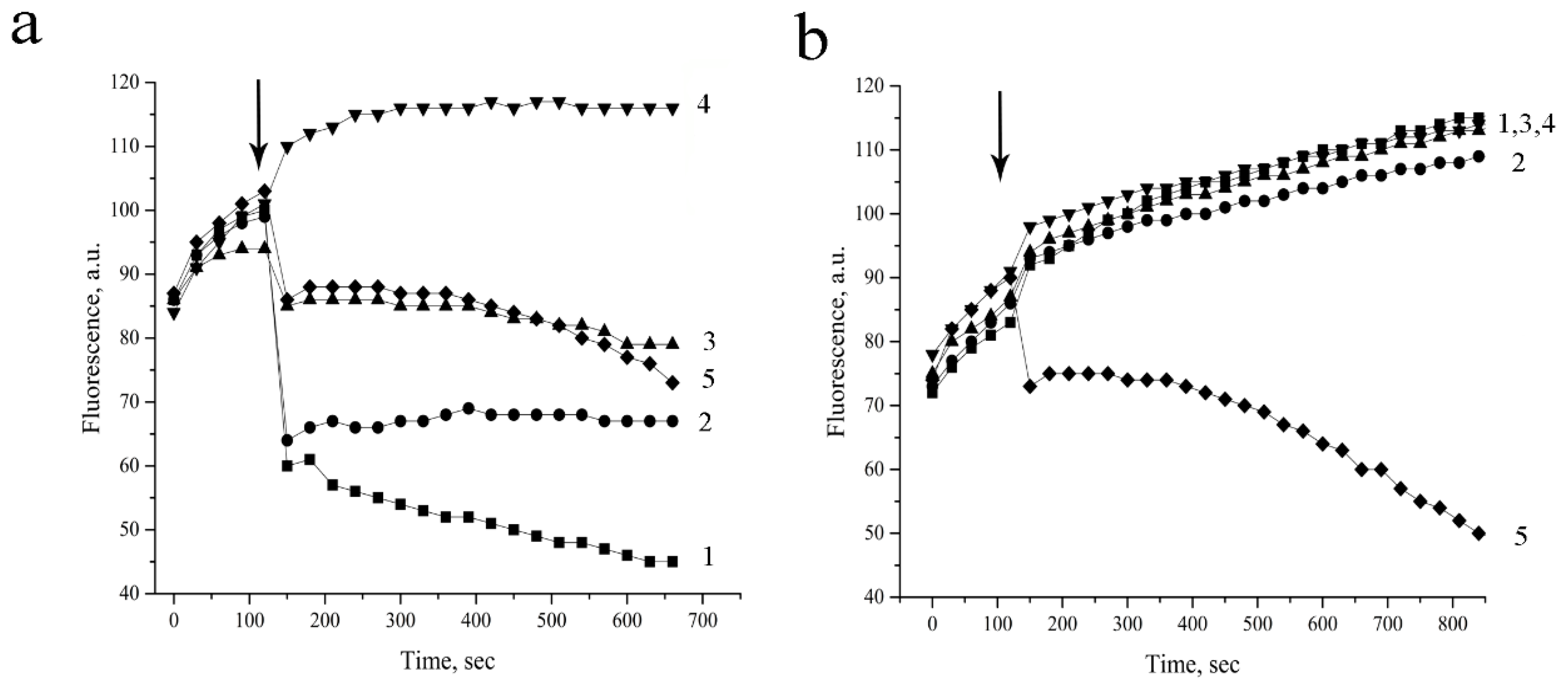
3.7. Permeabilization of the Bacterial Cell Wall. Evaluation of the Outer Membrane Disturbance
3.8. Permeabilization of the Bacterial Cytoplasmatic Membrane
3.9. Antifungal Activity
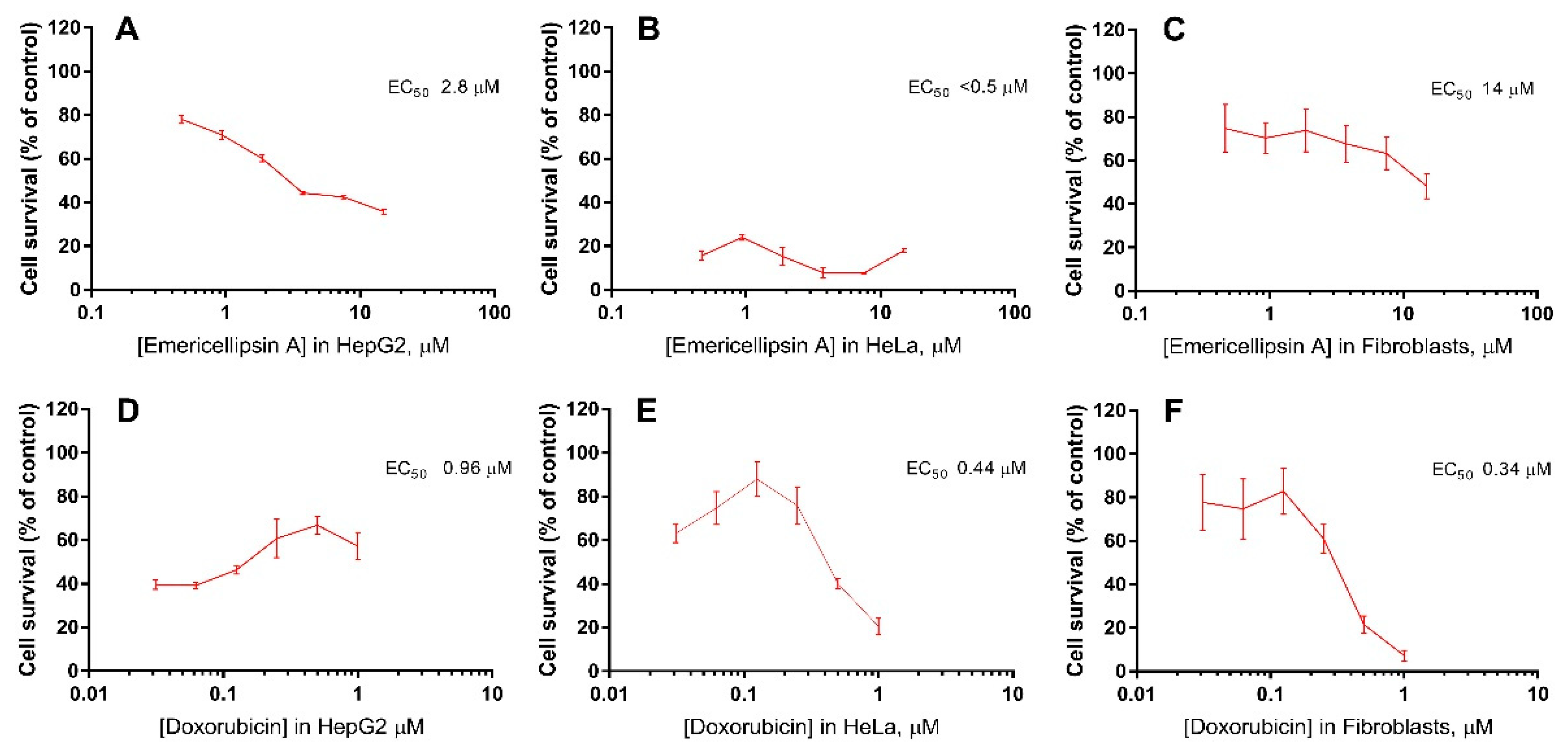
3.10. Cytotoxic Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ovchinnikova, T.V.; Levitskaya, N.G.; Voskresenskaya, O.G.; Yakimenko, Z.A.; Tagaev, A.A.; Ovchinnikova, A.Y.; Murashev, A.N.; Kamenskii, A.A. Neuroleptic properties of the ion-channel-forming peptaibol zervamicin: Locomotor activity and behavioral effects. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 1374–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argoudelis, A.D.; Johnson, L.E. Emerimicins II, 3 and IV, antibiotics produced by Emericellopsis microspora in media supplemented with trans-4-n-propyl-L-proline. J. Antibiot. 1974, 27, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessmann, R.; Axford, D.; Brückner, H.; Berg, A.; Petratos, K. A natural, single-residue substitution yields a less active peptaibiotic: The structure of bergofungin A at atomic resolution. Acta Cryst. 2017, 73, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, A.; Ritzau, M.; Ihn, W.; Schlegel, B.; Fleck, W.F.; Heinze, S.; Gräfe, U. Isolation and structure of bergofungin, a new antifungal peptaibol from Emericellopsis donezkii HKI 0059. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Berg, A.; Schlegel, B.; Ihn, W.; Demuth, U.; Gräfe, U. Isolation and structural elucidation of new peptaibols, bergofungins B, C and D, from Emericellopsis donezkii HKI 0059. J. Antibiot. 1999, 52, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, D.; Satou, T.; Senda, H.; Fujimaki, T.; Honda, R.; Kanazawa, S. Heptaibin, a novel antifungal peptaibol antibiotic from Emericellopsis sp. BAUA8289. J. Antibiot. 2000, 53, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranova, A.A.; Georgieva, M.L.; Bilanenko, E.N.; Andreev, Y.A.; Rogozhin, E.A.; Sadykova, V.S. Antimicrobial potential of alkalophilic micromycetes Emericellopsis alkalina. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2017, 53, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvin-Guette, C.; Rebuffat, S.; Prigent, Y.; Bodo, B. Trichogin A IV, an 11-residue lipopeptaibol from Trichoderma longibrachiatum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 2170–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Janso, J.E.; Yang, H.Y.; Bernan, V.S.; Lin, S.L.; Yu, K. Culicinin D, an antitumor peptaibol produced by the fungus Culicinomyces clavisporus, strain LL-12I252. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, K.Y.; Harris, P.W.; Brimble, M.A. Synthesis of the peptaibol framework of the anticancer agent culicinin D: Stereochemical assignment of the AHMOD moiety. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5784–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenkolb, T.; Berg, A.; Gams, W.; Schlegel, B.; Gräfe, U. The occurrence of peptaibols and structurally related peptaibiotics in fungi and their mass spectrometric identification via diagnostic fragment ions. J. Pept. Sci. 2003, 9, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, J.F.; Filho, E.R. Peptaibols of trichoderma. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 1128–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmoll, M.; Esquivel-Naranjo, E.U.; Herrera-Estrella, A. Trichoderma in the light of day-physiology and development. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2010, 47, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henson, K.E.; Levine, M.T.; Wong, E.A.; Levine, D.P. Glycopeptide antibiotics: Evolving resistance, pharmacology and adverse event profile. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 1265–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inostroza, A.; Lara, L.; Paz, C.; Perez, A.; Galleguillos, F.; Hernandez, V.; Becerra, J.; Gonzalez-Rocha, G.; Silva, M. Antibiotic activity of Emerimicin IV isolated from Emericellopsis minima from Talcahuano Bay, Chile. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenkarev, Z.O.; Paramonov, A.S.; Lyukmanova, E.N.; Gizatullina, A.K.; Zhuravleva, A.V.; Tagaev, A.A.; Yakimenko, Z.A.; Telezhinskaya, I.N.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Ovchinnikova, T.V.; et al. Peptaibol antiamoebin I: Spatial structure, backbone dynamics, interaction with bicelles and lipid-protein nanodiscs, and pore formation in context of barrel-stave model. Chem. Biodivers. 2013, 10, 838–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugh, J.K.; Brückner, H.; Wallace, B.A. Model for a helical bundle channel based on the high-resolution crystal structure of trichotoxin_A50E. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 12934–12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csermely, P.; Radics, L.; Rossi, C.; Szamel, M.; Ricci, M.; Mihály, K.; Somogyi, J. The nonapeptide leucinostatin A acts as a weak ionophore and as an immunosuppressant on T lymphocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1221, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Reffuveille, F.; Fernández, L.; Hancock, R.E. Bacterial biofilm development as a multicellular adaptation: Antibiotic resistance and new therapeutic strategies. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the 30 years from 1981 to 2010. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Tailhades, J.; Pantarat, N.; Dawson, R.M.; Otvos, L.; Reynolds, E.C.; Separovic, F.; Hossain, M.A.; Wade, J.D. Multimerization of a Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptide, Chex-Arg20, Alters Its Mechanism of Interaction with the Escherichia coli Membrane. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Pantarat, N.; Attard, T.J.; Walsh, K.A.; Reynolds, E.C. A Rapid and Quantitative Flow Cytometry Method for the Analysis of Membrane Disruptive Antimicrobial Activity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocks, S.M. Mechanism and use of the commercially available viability stain, BacLight. Cytometry A 2004, 61, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berney, M.; Hammes, F.; Bosshard, F.; Weilenmann, H.-U.; Egli, T. Assessment and Interpretation of Bacterial Viability by Using the LIVE/DEAD BacLight Kit in Combination with Flow Cytometry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3283–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilchenko, A.S.; Vasilchenko, A.V.; Valyshev, A.V.; Rogozhin, E.A. A novel high-molecular-mass bacteriocin produced by Enterococcus faecium: Biochemical features and mode of action. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilchenko, A.S.; Vasilchenko, A.V.; Pashkova, T.M.; Smirnova, M.P.; Kolodkin, N.I.; Manukhov, I.V.; Zavilgelsky, G.B.; Sizova, E.A.; Kartashova, O.L.; Simbirtsev, A.S.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of the indolicidin-derived novel synthetic peptide In-58. J. Pept. Sci. 2017, 23, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helander, I.M.; Mattila-Sandholm, T. Fluorometric assessment of Gram-negative bacterial permeabilization. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilchenko, A.S.; Rogozhin, E.A.; Vasilchenko, A.V.; Kartashova, O.L.; Sycheva, M.V. Novel hemoglobin-derived antimicrobial peptides from chicken (Gallus gallus) blood: Purification, structural aspects, and biological activity. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1546–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenkolb, T.; Karimi Aghcheh, R.; Dieckmann, R.; Neuhof, T.; Baker, S.E.; Druzhinina, I.S.; Kubicek, C.P.; Breckner, H.; von Dahren, H. The production of multiple small peptaibol families by single 14-module peptide synthetases in Trichoderma/Hypocrea. Chem. Biodivers. 2012, 9, 499–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadykova, V.S.; Kurakov, A.V.; Korshun, V.A.; Rogozhin, E.A.; Gromovykh, T.I.; Kuvarina, A.E.; Baranova, A.A. Antimicrobial Activity of Substances Produced by Trichoderma citrinoviride Strain VKPM F-1228: Optimization of Cultivation and Assessment of Spectrum of Individual Peptaibols. Antibiot. Chemother. 2015, 60, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, W.H.; Khalil, Z.; Dewapriya, P.; Salim, A.A.; Lin, H.W.; Capon, R.J. Trichodermides A-E: New Peptaibols Isolated from the Australian Termite Nest-Derived Fungus Trichoderma virens CMB-TN16. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Wang, H.N.; Xie, S.T.; Luo, Y.; Sun, C.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, Y.Z. Antimicrobial peptaibols, novel suppressors of tumor cells, targeted calcium-mediated apoptosis and autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grum-Grzhimaylo, A.A.; Georgieva, M.L.; Debets, A.J.M.; Bilanenko, E.N. Are alkalitolerant fungi of the Emericellopsis lineage (Bionectriaceae) of marine origin? IMA Fungus 2013, 4, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds of emericellipsin A are available from the authors. |
| Microorganisms | Strains | MIC, μg/mL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indolicidin | Emericellipsin A | Vancomycin | Norfloxacin | ||
| Gram-negative | Escherichia coli MG1655 | 25 | >300 | >200 | 0.08 |
| Salmonella enterica ATCC 14028 | 100 | >300 | >200 | 1.25 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 100 | >300 | >200 | 2.5 | |
| Gram-positive | Bacillus cereus ATCC 14893 | 12.5 | 16 | 12.5 | >28 |
| Staphylococcus aureus FDA 209 P | 12.5 | 4 | 3.1 | 0.31 | |
| Listeria monocytogenes EGDe | 3.25 | 32.5 | 0.38 | 1.75 | |
| Samples | NPN Uptake Factor ± SD |
|---|---|
| Escherichia coli MG1655 | 1.5 ± 0.05 |
| Escherichia coli MG1655 treated with 0.5 M EDTA | 1.83 ± 0.1 |
| Escherichia coli MG1655 treated with 7 µg/mL of emericellipsin A | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| Escherichia coli MG1655 treated with 15 µg/mL of emericellipsin A | 2.3 ± 0.2 |
| Escherichia coli MG1655 treated with 30 µg/mL of emericellipsin A | 4.7 ± 0.2 |
| Microorganism | Emericellipsin A | Fluconazol | Amphotericin B |
|---|---|---|---|
| C. tropicales 1402 | 2 | R * | 1.0 |
| C. albicans 1582 | 2 | R | 1.0 |
| C. albicans ATCC14053 | 2 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| A. niger ATCC 16404 | 4 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| A. niger 219 | 4 | R | 0.5 |
| A. fumigatus 163 | 4 | R | 1.0 |
| A. flavus 905 | 4 | R | 0.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rogozhin, E.A.; Sadykova, V.S.; Baranova, A.A.; Vasilchenko, A.S.; Lushpa, V.A.; Mineev, K.S.; Georgieva, M.L.; Kul’ko, A.B.; Krasheninnikov, M.E.; Lyundup, A.V.; et al. A Novel Lipopeptaibol Emericellipsin A with Antimicrobial and Antitumor Activity Produced by the Extremophilic Fungus Emericellopsis alkalina. Molecules 2018, 23, 2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112785
Rogozhin EA, Sadykova VS, Baranova AA, Vasilchenko AS, Lushpa VA, Mineev KS, Georgieva ML, Kul’ko AB, Krasheninnikov ME, Lyundup AV, et al. A Novel Lipopeptaibol Emericellipsin A with Antimicrobial and Antitumor Activity Produced by the Extremophilic Fungus Emericellopsis alkalina. Molecules. 2018; 23(11):2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112785
Chicago/Turabian StyleRogozhin, Eugene A., Vera S. Sadykova, Anna A. Baranova, Alexey S. Vasilchenko, Vladislav A. Lushpa, Konstantin S. Mineev, Marina L. Georgieva, Alexander B. Kul’ko, Mikhail E. Krasheninnikov, Alexey V. Lyundup, and et al. 2018. "A Novel Lipopeptaibol Emericellipsin A with Antimicrobial and Antitumor Activity Produced by the Extremophilic Fungus Emericellopsis alkalina" Molecules 23, no. 11: 2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112785
APA StyleRogozhin, E. A., Sadykova, V. S., Baranova, A. A., Vasilchenko, A. S., Lushpa, V. A., Mineev, K. S., Georgieva, M. L., Kul’ko, A. B., Krasheninnikov, M. E., Lyundup, A. V., Vasilchenko, A. V., & Andreev, Y. A. (2018). A Novel Lipopeptaibol Emericellipsin A with Antimicrobial and Antitumor Activity Produced by the Extremophilic Fungus Emericellopsis alkalina. Molecules, 23(11), 2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112785







