Abstract
Melaleuca styphelioides, known as the prickly-leaf tea tree, contains a variety of bioactive compounds. The purposes of this study were to characterize the polyphenols extracted from Melaleuca styphelioides leaves and assess their potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. The polyphenol extracts were prepared by maceration with solvents of increasing polarity. The LC/MS-MS technique was used to identify and quantify the phenolic compounds. An assessment of the radical scavenging activity of all extracts was performed using 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), 2,2′-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonate) (ABTS+), and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assays. The anti-inflammatory activity was determined on interferon gamma (IFN-γ)/histamine (H)-stimulated human NCTC 2544 keratinocytes by Western blot and RT-PCR. Compared to other solvents, methanolic extract presented the highest level of phenolic contents. The most frequent phenolic compounds were quercetin, followed by gallic acid and ellagic acid. DPPH, ABTS+, and FRAP assays showed that methanolic extract exhibits strong concentration-dependent antioxidant activity. IFN-γ/H treatment of human NCTC 2544 keratinocytes induced the secretion of high levels of the pro-inflammatory mediator inter-cellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), which were inhibited by extract. In conclusion, the extract of Melaleuca styphelioides leaves is rich in flavonoids, and presents antioxidant and anti-inflammatory proprieties. It can be proposed as a useful compound to treat inflammatory skin diseases.
1. Introduction
Inflammation is a complicated series of protective responses, involving several cell types and various putative modulators and mediators [1]. Skin provides both chemical and physical barriers and contains the cellular components of a rapid innate immune response [2], which protects the organism against external invasions.
Keratinocytes are the major constituents of the epidermis and appear to be exposed to stressful conditions such as toxins and microbes. They are also the major players of the complex response in the skin, conducting the activation of a diversity of Toll-like receptors [3,4]. Histamine (H) and interferon gamma (IFN-γ) can induce inflammatory responses in keratinocytes, highlighted by the activation of the pro-inflammatory mediators, such as the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), inter-cellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) [5,6,7]. Inhibitors of these mediators are extensively used to treat several inflammatory diseases. However, the majority of such anti-inflammatory drugs (steroidal or non-steroidal molecules) are highly toxic, and their use is often associated with harmful effects on the gastrointestinal tract, such as mucosal lesions, bleeding, and peptic ulcers [8].
Currently, a regular growing interest in plant polyphenols is proposed as an alternative to treat skin inflammatory diseases. Plant polyphenols are one of the greatest groups, with the largest chemical diversity. In addition, polyphenols are widely used in traditional medicine to treat several skin diseases, like vitiligo, psoriasis [9], and atopic dermatitis [10], as well as to accelerate skin wound healing [9]. However, the mechanisms by which plant phenolic compounds exert their anti-inflammatory effect are poorly understood. The potential anti-inflammatory effects of polyphenols have been attributed to either their free radical scavenging activities or classical chain-breaking, antioxidant, and transition metal chelating activity [11]. Other in-vitro studies using skin cells suggest that polyphenols inhibit the activation of cellular functions by multiple mechanisms, such as the modulation of intracellular signal transduction and transcription of a number of genes, direct interaction with several receptors, and post-translational modulation of enzymatic activities [12,13]. It is well-documented that polyphenols inhibit major pro-inflammatory skin enzymes, such as COX, LOX, iNOS, NADPH oxidase, NF-κB, ICAM-1, and PLA2 [12]. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of plant polyphenols depends on various factors, such as chemical structure, synergy of other phenols, cell types, and inductor used [12].
Melaleuca (M.) styphelioides Sm. belongs to the Melaleuca genus, commonly known as the prickly-leaf tea tree. The Melaleuca genus, or tea tree, is presented by approximately 260 described species native to Australia and is widespread in Southeast Asia, the Caribbean, and the Southern United States. In different parts of world, tea tree is used in traditional medicine as a treatment for insect bites, bruises, skin infections, flu and colds, acne vulgaris, psoriasis, inflammation, dermatitis, an antimicrobial agent, and as an insect repellant. Moreover, Melaleuca species are used in the manufacture of cosmetics, such as shampoos, soaps, and some cosmetic products [14]. M. styphelioides is well-known species that has been reported to have the strongest production of scented essential oil and tannins, as well as amount of flavonoid compounds and phenolic acids [15]. Several studies have reported the antioxidant, antimicrobial, hepatoprotective, and anti-proliferative activities of the essential oil and extract isolated from M. styphelioides leaves [15,16,17,18].
Here, we aim to (i) characterize and quantify the polyphenol compounds present in M. styphelioides leaves, and (ii) evaluate their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities in IFN-γ/H-induced inflammation of human NCTC 2544 keratinocytes. To our knowledge, this is the first report that demonstrates the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of polyphenols extracted by M. styphelioides leaves.
2. Results and Discussion
In this work, four solvents of increasing polarities were chosen for the evaluation of phenolic compounds contents of M. styphelioides leaves, namely hexane, diethyl ether, ethyl acetate, and methanol.
The yields of total phenol, flavonoids, and tannins from M. styphelioides leaf extracts are shown in Table 1. The maximum content of phenols total (PT) (142.7 ± 3.15 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/g dry extract) and flavonoid total (FT) (31.54 ± 1.99 mg quercetin equivalents (QE)/g dry extract) was obtained in the MeOH extract. Lower amounts were found in the ethyl acetate and Et2O extracts, and even lower amounts in the hexane extract. The highest amount of TC (19.9 ± 2.9 mg Eq Catéchine/g dry extract) was determined in the EtOAc and MeOH extracts (15.2 ± 1.9 mg Eq Catéchine/g dry extract), while no TC was present in Et2O and hexane extracts (Table 1). The important phenolic compounds extraction yields, found in the MeOH extract, has been attributed to its high solubility, low toxicity, medium polarity, and high extraction capacity. Our results are in agreement with the previously report of Al-Sayed et al. [15], where the authors report a higher amount of phenolic and flavonoid components in the MeOH extract of M. styphelioides leaves.

Table 1.
Total phenols, flavonoids, and tannins content in M. styphelioides leaves.
Based on the optimization condition of LC/MS-MS, the MeOH extract of M. styphelioides leaves was subjected to identification and quantification of the polyphenol components, in order to better discuss its biological potential. The detailed phenolic composition was determined using our standard library information (peak retention time, [M − H−] (m2), and LC-MS/MS data). M. styphelioides leaf extract showed the presence of several types of phenols belonging to diverse phenolic families, such as phenolic acids and flavonoids. Fifteen phenolic compounds were identified and quantified, with a range of 3.04–5.61 min retention times (RT) in negative polarity mode (Figure 1 and Table 2). Qualitatively, the phenolic profile included seven phenolic acids (vanillic acid, gallic acid, caffeic acid, syringic acid, chlorogenic acid, ferulic acid, and ellagic acid), nine flavonoids (apigenin, kaempferol, myricetin, naringenin, quercetin, luteolin, pinocembrin, hesperidin, and rutin). In quantitative terms, M. styphelioides polyphenol extract contained a rich source of bioactive phenols, mainly phenolic acids (25%) and flavonoids (70.6%). Most of the detected flavonoids corresponded to quercetin (53.99%) and apigenin (4%), followed by kaempferol (3.2%). The major phenolic acid compound found in metanolic extract was gallic acid (13.5%), followed by ellagic acid (6.3%) and vanillic acid (4.3%).
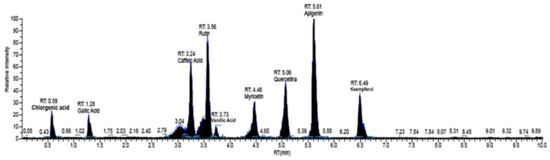
Figure 1.
Representative LC/MS-MS of phenolic components in leaf methanolic extract of M. styphelioides leaves.

Table 2.
Phenolic composition of M. styphelioides methanolic extract by LC/MS-MS.
Previous studies regarding the phenolic components of Melaleuca plants have reported a rich composition of bioactive compounds, such as ellagitannins and flavonoids [15,16]. According to Al-Sayed et al. [15,16], gallic acid, kaempferol-3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranoside, pedunculagin, pterocarinin A, tellimagrandin I, casuarinin, cellimagrandin II, 1,2,3,6-tetra-O-galloyl-β-d-glucopyranose and 1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-β-d-glucopyranose were the representative polyphenol compounds in M. styphelioides leaves. Al-Abd et al. [19] studied the phenolic composition of Melaleuca cajuputi leaves and indicate the presence of gingerol, caffeic acid, phenyl ester, aspidin, trans-2,3,4-trimethoxycinnamate, methyl orsellinic acid ester, ethyl ester, 5,6,3′-trimethoxyflavone, epigallocatechin 3-O-(4-hydroxybenzoate), polygonolide, and metyrosine. Compared to the aforementioned studies, our results show striking differences, presumably due to the species, origin, and analytical conditions [19]. Nevertheless, knowledge of M. styphelioides polyphenol compounds was extended by the identification of fourteen compounds (vanillic acid, gallic acid, caffeic acid, syringic acid, chlorogenic acid, ferulic acid, ellagic acid, apigenin, kaempferol, myricetin, naringenin, quercetin, luteolin, pinocembrin, hesperidin, and rutin) not previously reported in the M. styphelioides plant. From this finding, M. styphelioides appears as a source of bioactive compounds, justifying its pharmacological properties. Almost all of the identified phenolic compounds were well-known as antioxidants and anti-inflammatories.
The ability of M. styphelioides polyphenol extract to reduce the DPPH, ABTS radicals, and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) are shown in Table 3. DPPH and ABTS assays are frequently used as inexpensive, valid, and easy assays to evaluate the radical scavenging capacity of antioxidants. All extracts, excluding hexane extract, showed a concentration-dependent scavenging activity. The methanolic extract proved to be the highest DPPH and ABTS scavenger, with mean EC50 values of 22.13 and 21.39 µg/ml, respectively, followed by diethyl ether extract (73.24 ± 2.811 and 52.22 ± 1.40, respectively) and ethyl acetate (119.15 ± 1.66 and 75.84 ± 1.22, respectively). These results reflect the hydrogen-donating ability of the methanolic extracts from M. styphelioides leaves. On the other hand, the higher DPPH and ABTS scavenging activities of methanolic samples are most likely attributed to their higher total phenolic contents.

Table 3.
2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2′-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonate) (ABTS) scavenging activities, as well as the ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) of M. styphelioides leaf extracts.
The ferric reducing power method involves the reduction of the Fe(III)-tripyridyltriazine (Fe(III)-TPTZ) complex to Fe(II)-tripyridyltriazine (Fe(II)-TPTZ) at a low pH by electron-donating antioxidants, resulting in the absorbance increase at λ = 593 nm. As presented in Table 3, the FRAP values of the methanolic extract (3.66 mM FeSO4/g dw) was significantly (p < 0.05) higher than that ethyl acetate extract (0.85 mM FeSO4/g dw). The non-polar extracts with diethyl ether and hexane did not present any reducing power activity. As displayed in Table 3, it is clearly observed that the methanolic extracts can be considered as effective scavengers of DPPH and ABTS radicals, as well as potent reducing agents.
From a mechanistic standpoint, the observed antioxidant activity reflects the ability of the test extracts to donate electrons or hydrogen atoms to inactivate radical species [20]. Such properties have been reported for numerous phenolic compounds, namely gallic acid, syringic acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, rutin, chlorogenic acid, luteolin glucoside, apigenin derivative, and quercetin [21,22]. In addition, our results confirm the potential therapeutic uses of M. styphelioides extract for inflammatory diseases and cancers [15,16]. Moreover, our data, supported by analytical LC/MS-MS, are in agreement with those of Al-Sayed et al. [15,16], although their data are limited to evaluation of the antiradical activity of methanolic extracts from M. styphelioides leaves by DPPH assay only.
Keratinocytes are the major players of the innate immune response in the skin. They promote inflammation via expression of several key bio-mediators. However, these cells can also adapt an anti-inflammatory behavior, in order to stop acute inflammation and retrieve a steady state through the secretion of immuno-modulating agents, such as ICAM-1, COX-2, iNOS, and NF-κB. Human keratinocytes have been reported to be useful cellular barrier models for both host–pathogen interaction studies and synthetic or natural compound anti-inflammatory screening. Here, we used NCTC 2544 cells to assess the effect of M. styphelioides phenolic extract on IFN-γ/H-induced inflammation.
The cell toxicity of polyphenol extracts was assessed by an MTT assay after 72 h treatment with different concentrations of M. styphelioides polyphenols. The MTT assay revealed that the MeOH extract had a lower toxicity compared to other extracts (data not shown). Moreover, the dose of 50 µg/mL of M. MeOH extract showed no toxicity and a high antioxidant property (data not shown). Thus, we chose to use 50 µg/mL concentration in NCTC 2544 cells treated with IFN-γ/H, in order to investigate the potential anti-inflammatory activity of the M. MeOH extract.
In order to examine the anti-inflammatory activity of M. MeOH extract in human keratinocytes, we measured in IFN-γ/H-treated NCTC 2544 cell proteins and mRNA gene expression levels of ICAM-1 and COX-2 by Western blot and RT-PCR, respectively. As shown in Figure 2A, IFN-γ/H treatment for 72 h significantly increased the level of mRNA expression of ICAM-1, whereas M. MeOH extract treatment (50 µg/mL) for 72 h inhibited the IFN-γ/H induced expression of ICAM-1. Compared to M. MeOH, indomethacin (10 µM) inhibited the mRNA expression of ICAM-1 to a higher degree. The Western blot confirmed the results obtained by RT-PCR (Figure 2B). In inflamed keratinocytes, the expression of ICAM-1 is always increased providing retention and activation of lymphocytes (CD4+ and CD8+) in the epidermis. Moreover, the regulation of ICAM-1 expression on keratinocytes using phenols is considered as a recent strategy for the treatment of skin inflammatory diseases [23].
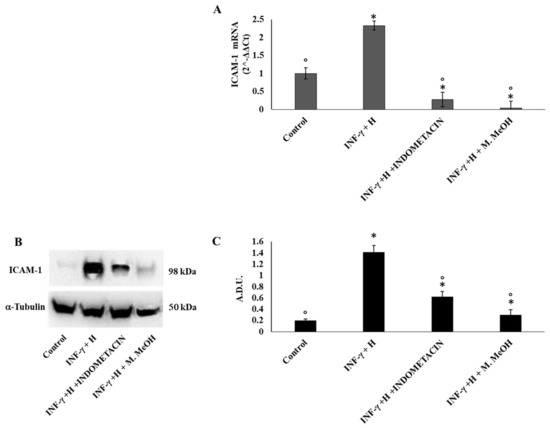
Figure 2.
Inter-cellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) mRNA expression (A) and protein production (B, and C). ICAM-1 mRNA expression was determined by RT-PCR (A), and ICAM-1 protein production was determined using Western blot (B: representative immunoblot; C: protein expression calculated as Arbitrary Densitometric Units; A.D.U.) in NCTC 2544 72 h after the addition of M. MeOH (50 µg/mL) with INF-γ + H. * Significantly different than control; ° significantly different from INF-γ/H-treated samples (p < 0.05).
Prostaglandins are also one of the major classes of mediators in the inflammatory response. They are generated from arachidonate by the action of cyclooxygenase isoenzymes (COX-1 and COX-2) [24]. In most tissues, COX-1 is constitutively expressed, whereas COX-2 is highly inducible by a variety of inflammatory and tumor-promoting stimuli, and is constitutively upregulated in skin carcinomas [25]. Our data demonstrates that COX-2 mRNA expressions were reduced significantly by the M. MeOH extract treatment in IFN-γ/H-induced inflammation, whereas its effect on protein levels was moderate compared to indomethacin (Figure 3).
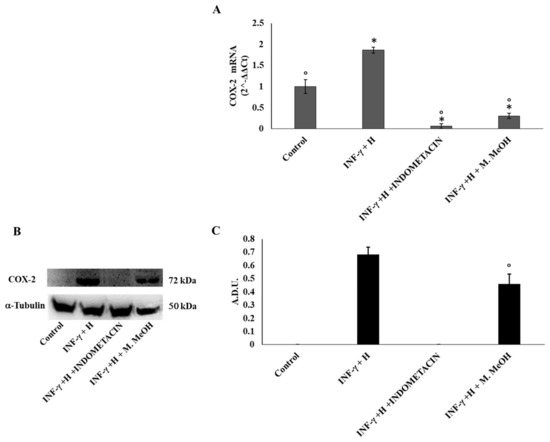
Figure 3.
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) mRNA expression (A) and protein production (B, and C). COX-2 mRNA expression was determined by RT-PCR (A), and COX-2 protein production was determined using Western blot (B: representative immunoblot; C: protein expression calculated as Arbitrary Densitometric Units; A.D.U.) in the NCTC 2544 72 h after the addition of M. MeOH (50 µg/mL) with INF-γ + H. * Significantly different than control; ° significantly different than INF-γ/H-treated samples (p < 0.05).
The expression of the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) is one of the direct consequences of an inflammatory process. Several methods such as RT-PCR, immunocytochemistry, and Western blot, have been used to describe the iNOS expression in many chronic human inflammatory diseases. The iNOS mRNA level is mainly regulated at the transcriptional level but also by other post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Phenolic acid and flavonoids have been reported to inhibit iNOS expression in several cell types, including endothelial cells, epithelial cells, and macrophages, yet in some cell types like chondrocytes [26]. Here, our data showed that the iNOS mRNA level was increased after cell stimulation with IFN-γ/H for 72 h, with respect to the non-treated control. A significant inhibition of iNOS mRNA expression was observed when the NCTC 2544 cells were co-treated with IFN-γ/H and 50 μg/mL of M. MeOH extract. Compared to M. MeOH extract, indomethacin weakly reduced iNOS mRNA levels (Figure 4B).
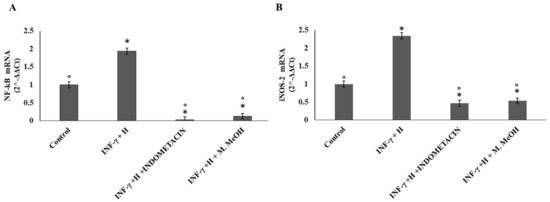
Figure 4.
Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) (A) and nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mRNA expression (B). The mRNA expression was determined by RT-PCR in the NCTC 2544 for 72 h after the addition of M. MeOH (50µg/mL) with INF-γ/H. * Significantly different than control; ° significantly different from INF-γ/H-treated samples (p < 0.05).
In addition, we examined the influence of M. MeOH extract treatment on IFN-γ/H-induced NF-κB mRNA expression. As shown in Figure 4A, NF-κB mRNA expression was increased after stimulation with IFN-γ and H for 72 h. Significant inhibition of NF-κB mRNA expression was observed when the NCTC 2544 was co-treated with IFN-γ/H and 50 μg/mL of M. MeOH extract. Compared to M. MeOH extract, indomethacin weakly reduced the NF-κB mRNA levels. Several studies have provided that the keratinocytes, when exposed to IFN-γ and histamine, activate NF-κB, leading to the expression of inflammatory genes. More than 150 genes have been identified that are regulated by NF-κB activation. These genes include iNOS, ICAM-1, COX-2, and chemokines [27]. Therefore, NF-κB is primarily an inducer of inflammatory cytokines, and its inhibitors could be useful as anti-inflammatory agents. In the present study, our data showed that M. MeOH extracts inhibited the mRNA expression of NF-κB in IFN-γ/H-activated NCTC 2544 keratinocytes. In addition, iNOS, ICAM-1, and COX-2 mRNA expression were markedly decreased with the M. MeOH extract treatment. Compared with indomethacin, the effect of M. MeOH extract was either higher or similar, probably due to the different active compounds present in M. styphelioides extracts.
In summary, our work represents the first report of an anti-inflammatory effect of M. styphelioides extract in IFN-γ/H-stimulated human NCTC 2544 cells. M. MeOH extract inhibited the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators by inflamed NCTC 2544 cells. This inhibition was primarily mediated by the modulation of the major cellular effectors of inflammation, such as NF-κB, iNOS, iCAM-1, and COX-2.
Quercetin, the major flavonoid molecule found in M. MeOH extract (53.99%), has been reported to down-regulate the activation of NF-κB, ICAM-1 [23], iNOS [28], and COX-2 [29]. Gallic acid (13.5%) and ellagic acid (6.3%), two important compounds of M. MeOH extract, have been reported to produce a beneficial antioxidant effect by regulating several pathways. These include inhibition of COX-2 [30] and cytokines activated by the NF-κB pathway [31]. All compounds identified and quantified in M. MeOH extract, like vanillic acid [32,33], apigenin [34], syringic acid [35], kaempferol [36], and rutin [37] have also been shown to have a potential anti-inflammatory activity. Our data suggest that each molecule may have contributed to the anti-inflammatory effect of the M. MeOH extract. However, additional work is needed to better characterize the contribution of each compound, even though the phenolic compounds probably act synergistically to generate a more potent anti-inflammatory effect.
3. Conclusions
Previously, M. styphelioides methanolic extract has been investigated for anti-proliferative and anti-cancer effects [38], but to our knowledge, we have shown for the first time that M. styphelioides extract also has an anti-inflammatory property. The cytoprotective, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory potential of M. styphelioides can be of great interest as an effective alternative for the treatment and prevention of inflammatory diseases.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
All chemicals and reagents were either analytical-reagent or HPLC grade. Ultrapure deionized water, with a resistivity of 18.2 MΩ cm, was obtained from a Milli-Q® Integral water purification system with a Q-pod purchased from Millipore (Bedford, MA, USA). Acetic acid, acetonitrile, and 2-propanol were purchased from VWR International S.r.l. (Milan, Italy); hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide were purchased from Carlo Erba (Milan, Italy). The methanol HPLC gradient grade was obtained from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Standard solutions of vanillic acid, trans-ferulic acid, syringic acid, myricetin, naringenin, pinocembrin, luteolin, and hesperidin were purchased from Extrasynthese (Genay Cedex, France). Chlorogenic acid was purchased from HWI Analytik GmbH (Rülzheim, Germany). Gallic acid, caffeic acid, apigenin, quercetin, kaempferol, catechin, epicatechin, indometacine, histamine, and anti-α-tubulin antibody were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich S.r.l. (Milan, Italy). The IFN-γ was obtained from Pepro Tech EC (London, England). The anti-ICAM-1 antibody (sc-51632) was purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Milan, Italy), anti-COX-2 (35-8200) from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Milan, Italy), and -α- tubulin (T6074) from Sigma-Aldrich (Milan, Italy).
4.2. Plant Material and Extracts Preparation
Leaves of M. styphelioides were collected from healthy trees in April 2016 from the botanical garden of the National Institute of Agricultural Research (INRAT, Tunis), Tunisia. Specimens were deposited at the Herbarium of the Department of Botany in the cited institute. Leaves were air-dried at room temperature (20 ± 2 °C) for one week, ground using a Retsch blender mill (Normandie-Labo, Normandy, France), sifted through a 0.5 mm mesh screen to obtain a uniform particle size, and subsequently assessed for their phenolic composition. Dried and ground leaves M. styphelioides were defatted three times by maceration with n-hexane for 48 h. The defatting process was used to extract lipophilic pigments and oil from lipid-containing samples and facilitate the polyphenol extract. The defatted samples were extracted with solvents of increasing polarity (diethyl ether, ethyl acetate, and methanol), sonicated for 30 min, and macerated for 24 h. The macerated organic extracts were filtered through Wattman filter paper, centrifuged for 10 min at 3000× g, and concentrated under reduced pressure in a Heidolph rotary evaporator. The obtained extracts were kept and stored at 4 °C until further analysis.
4.3. Phytochemical Analysis
4.3.1. The Phytochemical Screening
The phytochemical screening of total phenol, flavonoids, and tannins was determined according to the procedure reported by El Euch et al. [39].
4.3.2. LC/MS-MS Analysis
The mixture of polyphenols was determined according to previous work [40], using a Transcen II System with Multi-channel and Turbo Flow Technology (Dionex–Thermo Fisher Scientific) connected to a Q-Exactive Plus Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) equipped with HESI (heated electro spray ionization), used in negative polarity modes. The samples were extracted and purified using a Cyclone P column (50 mm × 0.5 m, 60 µm particle size, 60 Å pore size; Thermo Fisher Scientific). A Hypersil Gold (2.1 mm × 100 mm, 1.7 µm particle size) column was employed as the analytical separation column. The mobile phase consisted of eluent A (30 mM ammonium acetate (pH 5)), eluent B (methanol), eluent C (water containing 0.5% formic acid), and eluent D (acetonitrile/acetone/2 propanol (4:3:3)). Mobile phases A and B were used to optimize the chromatographic resolution. Mobile phases B, C, and D were required for purification in turbo flow. Extracts and standards were dissolved in the mobile phase A (ratio 1:10). The injection volume was 5 µL, and elution was performed at the rate of 0.2 mL/min with a gradient program as follows: 0–2 min with 95% A and 5% B; 4 min with 60% A and 40% B; 6 min with 0% A and 100% B; 9 min with 0% A and 100% B; 11.5 min with 95% A and 5% B; 14 min with 95% A and 5% B; and 18 min with 95% A and 5% B. The acquisition time was 10 min. Eluted components were detected by MS, used in negative polarity modes, using the ion source parameters as follows: sheath gas flow rate of 35 (arbitrary units); aux gas flow rate of 10 (arbitrary units); spray voltage at 3.50 kV; capillary temperature at 300 °C; tube lens voltage of 55 V; heater temperature of 305 °C; scan mode at full scan; scan range (m/z) at 100–700; microscans at 1 m/z; a positive resolution of 70,000; an FT automatic gain control (AGC) target of 3 × 106; a maximum IT of 100 ms; a negative resolution of 35,000; an automatic gain control (AGC) target of 1 × 106; and a maximum IT of 100 ms. The chromatographic parameters were as follows: column temperature at 30 °C and sample temperature at 6 °C. The auto-sampler sample holder temperature was maintained at 7 °C. The data analyses were performed using a Thermo Scientific XCalibur (Thermo Fisher Scientific) version 4.0 software and Qual and Quant Browser, and the concentration of the compounds were calculated using calibration curves; the results are expressed as calibration curves and as µg/kg of dry weight (DW). This method was validated according to the norm EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005. The limits of detection and quantification (LoDs and LoQs) were determined by the 3σ and 10σ approach [41,42]. The calibration curve was constructed with six standard additions (0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, and 2 mg/L), and was checked using the r2 value. The linearity range was considered to be acceptable when r2 was greater than 0.99 in the peak areas versus the concentration. A pool of 15 blank samples spiked with final concentrations of 5 µg/kg for all elements were analysed. The results were between 10 µg/kg for the LOD and 20 µg/kg for the LOQ for single analytes. The limit of repeatability and recovery has been evaluated, with the spike samples at three different concentration levels (0.1, 0.5, and 1 mg/L). The results were satisfactory for the limit of repeatability (metrological approach), less than the double value of the expanded uncertainty. The recovery was between 71% and 119%. The validation allowed us to identify the uncertainty contributions in order to calculate the expanded uncertainty [43]. The results show that the expanded uncertainty is less than 22% in all the analyzed levels.
4.4. Anti-Oxidant Activity Determination
The DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activity was assessed by the method described by El Euch et al. [39]. The antioxidant effect was expressed as IC50, which is the amount of extract required to scavenge the initial DPPH or ABTS radical by 50%, and is expressed as per mg of the sample [39]. The reducing power (FRAP) was determined by the method described in [44]. The results were expressed as FeSO4·7H2O-equivalent mM per gram of dry extract (mM/g DE), using a calibration curve.
4.5. Anti-Inflammatory Activity Evaluation
4.5.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
The NCTC 2544 keratinocyte cell line was obtained from Interlab Cell Line Collection (Genoa, Italy). Cells were grown in Minimum Essential Medium (Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy), containing 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and 100 U/mL penicillin. The cells were then incubated at 37 °C in a humidified, 95% air 5% CO2 atmosphere. The culture medium was changed every 2–3 days. For experiments, cells were trypsinized, counted, and plated in six- or 96-well plates. Cells were either treated or not treated with 200 U mL−1 of IFN-γ and 10−4 M of H, in the presence or absence of different concentrations of M. styphelioides polyphenol extracts (5, 10, 25, 50, and 75 μg/mL). Commercially available indomethacin was used as a positive control at 10 µM. After 72 h, each sample was tested for the experiments described below.
4.5.2. Cell Viability
The phenol extracts’ cytotoxicity was determined by an MTT assay, as previously described [45].
4.5.3. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR
As previously described [46], the total mRNA was isolated and prepared from the control and treated NCTC 2544 cells using the 1 mL Qiazol Reagent (Qiagen, Milan, Italy), 0.2 mL chloroform, and 0.5 mL isopropanol. An RNA pellet was washed with 75% ethanol, air-dried, and re-suspended in RNAse-free water. Reverse transcription was carried using the QuantiTect Reverse Transcription Kit (Qiagen), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Synthesis of cDNA was performed using 40-cycle PCR in a Rotor-gene Q real-time analyzer (Corbett, Qiagen). The amplification of ICAM-1, iNOS, COX-2, NF-κB, and GAPDH was performed using specific primers listed in Table 4. Each PCR reaction contained one Rotor-Gene SYBR Green PCR Master Mix, template cDNA (≤100 ng/reaction), primers (1 μM), and RNase-free water, with a final reaction volume of 25 μL. RT-PCR was carried out according to the following program: initial activation step at 95 °C for 10 min, denaturation at 95 °C for 10 s, annealing at 60 °C for 30 s, extension at 72 °C for 30 s (40 cycles), and final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. RT-PCR was followed by melting curve analysis to confirm PCR specificity. Each reaction was repeated three times, and the threshold cycle average was used for data analysis by Rotor-gene Q software. The identification was carried out using electrophoresis in a 2% agarose gel in 0.045 M Tris–borate/1 mM EDTA (TBE) buffer. The target gene expression was normalized to GAPDH using the 2−ΔΔCt method.

Table 4.
Primers used in RT-PCR analysis.
4.5.4. Western Blot
The ICAM-1 and COX-2 protein expression levels were determined by Western blot analysis according to standard procedures [47]. The NCTC 2544 cells were stimulated with IFN-γ/H and treated with 50 µg/mL of M. styphelioides polyphenol extract for 72 h at 37 °C. Western blot was performed following the method reported [24]. Briefly, equal protein amounts were resolved by 4–12% Novex Bis–Tris gel electrophoresis (NuPAGE, InVitrogen, Milan, Italy), and transferred into nitrocellulose membranes (InVitrogen) in a wet system. The membrane was blocked in Tris-buffered saline containing 0.01% Tween-20 (TBST) and 5% non-fat dry milk for 1 h at room temperature. The membrane was incubated overnight with specific primary antibodies at 4 °C. Mouse monoclonal anti-ICAM-1 (1:200) (1H4: sc-51632; Santa Cruz Biothechnology), anti-COX-2 (1:300) (35-8200; Thermo Fisher Scientific), and anti-α-tubulin antibodies (Sigma-Aldrich) were used. Blots were later washed three times with PBS, followed by incubation in a HRP-conjugated secondary antibody for 1 h at room temperature. Specific proteins bands were detected using enhanced chemiluminescent solution (Pierce, Fisher Scientific) and visualized by a Uvitec Alliance LD9 gel imaging system (Uvitec, Cambridge, UK). Bands were measured densitometrically, and their relative density was calculated based on the density of α-tubulin bands in each sample. Values were expressed as arbitrary densitometric units (A.D.U.) corresponding to signal intensity.
4.6. Statistical Analysis
The experiments were repeated independently at least three times in triplicate, and the mean ± SEM for each value was calculated. One-way statistical analyses of the results (Student’s t-test for paired and analysis of variance (ANOVA) for unpaired data) were used. All statistical analyses were performed using the statistical software package SYSTAT, version 11 (Systat Inc., Evanston, IL, USA). A value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.A. and V.C. (Venera Cardile); Funding acquisition, V.C. (Venera Cardile); Investigation, F.A., R.A. and A.C.E.G.; Methodology, F.A., G.M.L.D. and A.C.E.G.; Supervision, V.C. (Venera Cardile); Validation, R.A., M.A. and V.C. (Venera Cardile); Visualization, V.C. (Vittorio Calabrese); Writing—original draft, F.A.; Writing—review & editing, V.C. (Venera Cardile).
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Filippo Drago (Director of Department of Biomedical and Biotechnological Science, University of Catania, Catania, Italy) for his hospitality and scientific encouragement.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Abbreviations
| (H) | Histamine |
| (IFN-γ) | interferon gamma |
| (NF-κB) | nuclear factor kappa B |
| (ICAM-1) | inter-cellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| (iNOS) | nitric oxide synthase |
| (COX-2) | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| (DPPH) | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| (ABTS) | 2,2′-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonate) |
| (E. hex) | hexane extract |
| (E. Et2O) | diethyl ether extract |
| (E. EtOAc) | ethyl acetate extract |
| (E. MeOH) | methanol extract |
| (M. MeOH) | Melaleuca styphelioides methanolic extract |
References
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köllisch, G.; Kalali, B.N.; Voelcker, V.; Wallich, R.; Behrendt, H.; Ring, J.; Bauer, S.; Jakob, T.; Mempel, M.; Ollert, M. Various members of the Toll-like receptor family contribute to the innate immune response of human epidermal keratinocytes. Immunology 2005, 114, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInturff, J.E.; Modlin, R.L.; Kim, J. The role of toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis and treatment of dermatological disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, S.; Mascia, F.; Mariani, V.; Girolomoni, G. The epidermal growth factor receptor system in skin repair and inflammation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascia, F.; Mariani, V.; Girolomoni, G.; Pastore, S. Blockade of the EGF receptor induces a deranged chemokine expression in keratinocytes leading to enhanced skin inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkvliet, N.I. AHR-mediated immunomodulation: The role of altered gene transcription. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, S.; Mascia, F.; Mariotti, F.; Dattilo, C.; Mariani, V.; Girolomoni, G. ERK1/2 regulates epidermal chemokine expression and skin inflammation. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5047–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essafi-Benkhadir, K.; Refai, A.; Riahi, I.; Fattouch, S.; Karoui, H.; Essafi, M. Quince (Cydonia oblonga Miller) peel polyphenols modulate LPS-induced inflammation in human THP-1-derived macrophages through NF-κB, p38MAPK and Akt inhibition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 418, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkina, L.G. Phenylpropanoids as naturally occurring antioxidants: From plant defense to human health. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2017, 53, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kang, S.; Moon, N.R.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, N.R.; Kim, K.S.; Park, S. Topical treatments of Saussurea costus root and Thuja orientalis L. synergistically alleviate atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions by inhibiting protease-activated receptor-2 and NF-κB signaling in HaCaT cells and Nc/Nga mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 199, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.O.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, C.Y. Vitamin C equivalent antioxidant capacity (VCEAC) of phenolic phytochemicals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkina, L.G.; Pastore, S.; De Luca, C.; Kostyuk, V.A. Metabolism of plant polyphenols in the skin: Beneficial versus deleterious effects. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 710–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Kong, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yang, M.; Peng, X.; Efferth, T. In vitro antioxidant properties, DNA damage protective activity, and xanthine oxidase inhibitory effect of cajaninstilbene acid, a stilbene compound derived from pigeon pea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.] leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Salehi, B.; Varoni, E.M.; Sharopov, F.; Yousaf, Z.; Ayatollahi, S.A.; Kobarfard, F.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Afdjei, M.H.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; et al. Plants of the Melaleuca Genus as Antimicrobial Agents: From Farm to Pharmacy. Phyther. Res. 2017, 31, 1475–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sayed, E.; El-Lakkany, N.M.; Seif El-Din, S.H.; Sabra, A.N.A.; Hammam, O.A. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of Melaleuca styphelioides on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sayed, E.; Esmat, A. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effect of ellagitannins and galloyl esters isolated from Melaleuca styphelioides on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cells. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, R.S.; Shalaby, A.S.; El-Baroty, G.A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Ali, M.A.; Hassan, E.M. Chemical and Biological Evaluation of the Essential Oils of Different Melaleuca Species. Phyther. Res. 2004, 18, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amri, I.; Mancini, E.; de Martino, L.; Marandino, A.; Lamia, H.; Mohsen, H.; Bassem, J.; Scognamiglio, M.; Reverchon, E.; de Feo, V. Chemical composition and biological activities of the essential oils from three Melaleuca species grown in Tunisia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16580–16591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Abd, N.M.; Mohamed Nor, Z.; Mansor, M.; Azhar, F.; Hasan, M.S.; Kassim, M. Antioxidant, antibacterial activity, and phytochemical characterization of Melaleuca cajuputi extract. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.V.; Bone, D.E.; Carrington, M.F. Antioxidant activity of dulse (Palmaria palmata) extract evaluated in vitro. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albouchi, F.; Hassen, I.; Casabianca, H.; Hosni, K. Phytochemicals, antioxidant, antimicrobial and phytotoxic activities of Ailanthus altissima (Mill.) Swingle leaves. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2013, 87, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesjak, M.; Beara, I.; Simin, N.; Pintać, D.; Majkić, T.; Bekvalac, K.; Orčić, D.; Mimica-Dukić, N. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of quercetin and its derivatives. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, A.C.E.; Cardile, V.; Crascì, L.; Caggia, S.; Dugo, P.; Bonina, F.; Panico, A. Protective effects of an extract from Citrus bergamia against inflammatory injury in interferon-gamma and histamine exposed human keratinocytes. Life Sci. 2012, 90, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.L.; DeWitt, D.L.; Garavito, R.M. Cyclooxygenases: Structural, Cellular, and Molecular Biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 145–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Decker, K.; Scholz, K.; Neufang, G.; Marks, F.; Fürstenberger, G. Localization of prostaglandin-H synthase-1 and -2 in mouse skin: Implications for cutaneous function. Exp. Cell Res. 1998, 242, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suschek, C.; Schnorr, O.; Kolb-Bachofen, V. The Role of iNOS in Chronic Inflammatory Processes In Vivo: Is it Damage-Promoting, Protective, or Active at all? Curr. Mol. Med. 2004, 4, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Takada, Y.; Boriek, A.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-kappaB: Its role in health and disease. J. Mol. Med. 2004, 82, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Mediavilla, V.; Crespo, I.; Collado, P.S.; Esteller, A.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. The anti-inflammatory flavones quercetin and kaempferol cause inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and reactive C-protein, and down-regulation of the nuclear factor kappaB pathway in Chang Liver cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 557, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Shi, D.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Kang, T.; Deng, W. Quercetin suppresses cyclooxygenase-2 expression and angiogenesis through inactivation of P300 signaling. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Das, S.; Saha, A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K. Ellagic acid facilitates indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer healing via COX-2 up-regulation. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2012, 44, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahad, A.; Ganai, A.A.; Mujeeb, M.; Siddiqui, W.A. Ellagic acid, an NF-κB inhibitor, ameliorates renal function in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 219, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Chen, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Chung, H.Y.; Jin, Z. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of Australian tea tree (Melaleuca alternifolia) oil and its components. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2849–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.C.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, D.S.; Jeon, Y.D.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.S.; Um, J.Y.; Hong, S.H. Vanillic acid inhibits inflammatory mediators by suppressing NF-κB in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2011, 33, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.T.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Q.; Yan, T. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Apigenin in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory in Acute Lung Injury by Suppressing COX-2 and NF-kB Pathway. Inflammation 2014, 37, 2085–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, J.R.; Lee, H.-I.; Choi, R.-Y.; Sim, M.-O.; Seo, K.-I.; Lee, M.-K. Anti-steatotic and anti-inflammatory roles of syringic acid in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadioglu, O.; Nass, J.; Saeed, M.E.M.; Schuler, B.; Efferth, T. Kaempferol is an anti-inflammatory compound with activity towards NF-κB pathway proteins. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 2645–2650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Ku, S.K.; Baek, Y.D.; Bae, J.S. Anti-inflammatory effects of rutin on HMGB1-induced inflammatory responses in vitro and in vivo. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, D.; Al-Sayed, E.; Albert, A.; Paul, E.; Singab, A.N.B.; Govindan Sadasivam, S.; Saso, L. Antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds from extracts of Eucalyptus globulus and Melaleuca styphelioides and their protective role on d-glucose-induced hyperglycemic stress and oxalate stress in NRK-49Fcells. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Euch, S.K.; Bouajila, J.; Bouzouita, N. Chemical composition, biological and cytotoxic activities of Cistus salviifolius flower buds and leaves extracts. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gutiérrez, N.; del MAguilera-Luiz, M.; Romero-González, R.; Vidal, J.L.M.; Garrido Frenich, A. Fast analysis of polyphenols in royal jelly products using automated TurboFlowTM-liquid chromatography-Orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 973, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Standard Organization. ISO/IEC 17025 General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Eurachem, a Laboratory Guide to Method Validation and Related Topics. 2014. Available online: http://www.eurachem.org/images/stories/Guides/pdf/valid.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2017).
- Lo Dico, G.M.; Cammilleri, G.; Macaluso, A. Simultaneous Determination of As, Cu, Cr, Se, Sn, Cd, Sb and Pb Levels in Infant Formulas by ICP-MS after Microwave-Assisted Digestion: Method Validation. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Man, H.; Behera, S.K.; Park, H.S. Optimization of operational parameters for ethanol production from korean food waste leachate. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, A.C.E.; Parenti, R.; Avola, R.; Cardile, V. Krabbe disease: Involvement of connexin43 in the apoptotic effects of sphingolipid psychosine on mouse oligodendrocyte precursors. Apoptosis 2016, 21, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avola, R.; Graziano, A.C.E.; Pannuzzo, G.; Albouchi, F.; Cardile, V. New insights on Parkinson’s disease from differentiation of SH-SY5Y into dopaminergic neurons: An involvement of aquaporin4 and 9. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 88, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avola, R.; Graziano, A.C.E.; Pannuzzo, G.; Cardile, V. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Adipose Tissue Differentiated into Neuronal or Glial Phenotype Express Different Aquaporins. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 8308–8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).