Acetylcholinesterase and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in Schistosomes and Other Parasitic Helminths
Abstract
1. Introduction
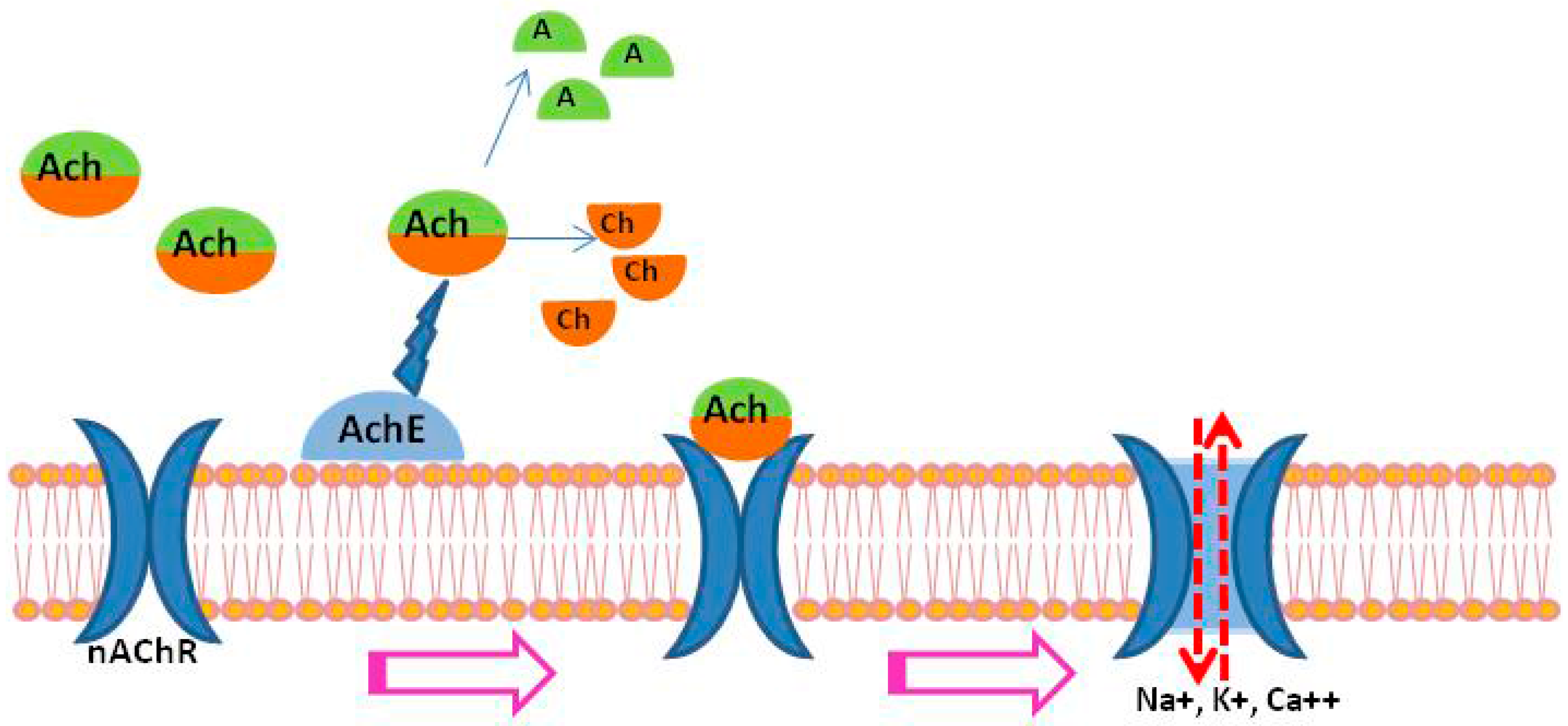
2. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in Schistosomes
3. Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors (nAChRs) in Schistosomes
4. AChE and AChRs in Other Helminths
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PZQ | praziquantel |
| AChE | acetylcholinesterase |
| ACh | acetylcholine |
| nAChRs | nicotinic acetylcholine receptors |
| GPI | glycophosphatidylinositol |
| PIPL-C | PI-specific phospholipase C |
| SmACCs | S. manosni acetylcholine gated chloride channels |
| ShAR1α | S. haematobium nicotinic acetylcholine receptor 1 α |
| ShAR1β | S. haematobium nicotinic acetylcholine receptor 1 β |
| ShAR2β | S. haematobium nicotinic acetylcholine receptor 2 β |
References
- Beaumier, C.M.; Gillespie, P.M.; Hotez, P.J.; Bottazzi, M.E. New vaccines for neglected parasitic diseases and dengue. Transl. Res. 2013, 162, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, A.P.; Martin, R.J. Ion-channels on parasite muscle: Pharmacology and physiology. Invert. Neurosci. 2007, 7, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminsky, R.; Gauvry, N.; Weber, S.S.; Skripsky, T.; Bouvier, J.; Wenger, A.; Schroeder, F.; Desaules, Y.; Hotz, R.; Goebel, T.; et al. Identification of the amino-acetonitrile derivative monepantel (AAD 1566) as a new anthelmintic drug development candidate. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueding, E.; Liu, C.L.; Rogers, S.H. Inhibition by metrifonate and dichlorvos of cholinesterases in schistosomes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1972, 46, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabtree, J.E.; Wilson, R.A. Schistosoma mansoni: A scanning electron microscope study of the developing schistosomulum. Parasitology 1980, 81, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Ridi, R.A.; Tallima, H.A. Novel therapeutic and prevention approaches for schistosomiasis: Review. J. Adv. Res. 2013, 4, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergquist, R. Strategies for Control of Infection and Disease: Current Practice and Future Potential. In Schistosomiasis; Mahmoud, A.A.F., Ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Salafsky, B.; Fusco, A.C.; Whitley, K.; Nowicki, D.; Ellenberger, B. Schistosoma mansoni: Analysis of cercarial transformation methods. Exp. Parasitol. 1988, 67, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.K.; Bentley, G.N.; Parra, W.G.O.; Agnew, A. Molecular characterization of an acetylcholinesterase implicated in the regulation of glucose scavenging by the parasite Schistosoma. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.J.; Lester, H.A.; Lummis, S.C. The structural basis of function in Cys-loop receptors. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2010, 43, 449–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, D.M. Acetylcholinesterase: Enzyme structure, reaction dynamics and virtual transition states. Chem. Rev. 1987, 87, 955–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, A.J. Ion channels and receptor as targets for the control of parasitic nematodes. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2011, 1, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennekou, P. The voltage-gated non-selective cation channel from human red cells is sensitive to acetylcholine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1147, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, L.R.; Bueding, E.; Timms, A.R. The possible role of acetylcholine in Schistosoma mansoni. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1966, 26, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, T.A.; Chen, G.Z.; Miller, C.; Tian, M.; Bennett, J.L.; Pax, R.A. Cholinergic inhibition of muscle fibres isolated from Schistosoma mansoni (Trematoda:Digenea). Parasitology 1996, 113, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouridakis, M.; Zisimopoulou, P.; Poulas, K.; Tzartos, S.J. Recent advances in understanding the structure of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, M.; Flood, P.; McArdle, J.J.; Brenner, H.R. Advances in neurobiology of the neuromuscular junction: Implications for the anesthesiologist. Anesthesiology 2002, 96, 202–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabbani, N.; Nordman, J.C.; Corgiat, B.A.; Veltri, D.P.; Shehu, A.; Seymour, V.A.; Adams, D.J. Are nicotinic acetylcholine receptors coupled to G proteins? Bioessays 2013, 35, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, G.N.; Jones, A.K.; Oliveros Parra, W.G.; Agnew, A. ShAR1alpha and ShAR1beta: Novel putative nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits from the platyhelminth blood fluke Schistosoma. Gene 2004, 329, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueding, E. Acetylcholinesterase activity of Schistosoma mansoni. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1952, 7, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pax, R.A.; Day, T.A.; Miller, C.L.; Bennett, J.L. Neuromuscular physiology and pharmacology of parasitic flatworms. Parasitology 1996, 113 (Suppl. 1), S83–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, B.; Tarrab-Hazdai, R.; Himmeloch, S.; Arnon, R. Acetylcholinesterase from Schistosoma mansoni: Immunological characterization. Immunol. Lett. 1991, 28, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, G.N.; Jones, A.K.; Agnew, A. Expression and comparative functional characterisation of recombinant acetylcholinesterase from three species of Schistosoma. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2005, 141, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.; Gobert, G.N.; Du, X.; Pali, G.; Cai, P.; Jones, M.K.; McManus, D.P. Functional characterisation of Schistosoma japonicum acetylcholinesterase. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi-Schaffer, F.; Tarrab-Hazdai, R.; Schryer, M.D.; Arnon, R.; Smolarsky, M. Isolation and partial characterization of the tegumental outer membrane of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1984, 13, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, M.S.; Becker, L.; Driguez, P.; Young, N.D.; Gaze, S.; Mendes, T.; Li, X.H.; Doolan, D.L.; Midzi, N.; Mduluza, T.; et al. Of monkeys and men: Immunomic profiling of sera from humans and non-human primates resistant to schistosomiasis reveals novel potential vaccine candidates. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnon, R.; Silman, I.; Tarrab-Hazdai, R. Acetylcholinesterase of Schistosoma mansoni—Functional correlates. Contributed in honor of Professor Hans Neurath’s 90th birthday. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 2553–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, B.; Parizade, M.; Ortega, E.; Tarrab-Hazdai, R.; Zilberg, D.; Arnon, R. Monoclonal antibodies against acetylcholinesterase of Schistosoma mansoni: Production and characterization. Hybridoma 1995, 14, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, M.; Agnew, A. Schistosoma: Rate of glucose import is altered by acetylcholine interaction with tegumental acetylcholine receptors and acetylcholinesterase. Exp. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-dos-Santos, G.; Verjovski-Almeida, S.; Leite, L.C. Schistosomiasis—A century searching for chemotherapeutic drugs. Parasitol. Res. 2006, 99, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, M.; Tarrab-Hazdai, R.; Espinoza, B.; Arnon, R.; Agnew, A. The amount of acetylcholinesterase on the parasite surface reflects the differential sensitivity of schistosome species to metrifonate. Parasitology 1994, 108, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, A. Chemotherapeutic approaches to schistosomes: Current knowledge and outlook. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.L. Why do some nematode parasites of the alimentary tract secrete acetylcholinesterase? Int. J. Parasitol. 1996, 26, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berriman, M.; Haas, B.J.; LoVerde, P.T.; Wilson, R.A.; Dillon, G.P.; Cerqueira, G.C.; Mashiyama, S.T.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Andrade, L.F.; Ashton, P.D.; et al. The genome of the blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni. Nature 2009, 460, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, N.D.; Jex, A.R.; Li, B.; Liu, S.; Yang, L.; Xiong, Z.; Li, Y.; Cantacessi, C.; Hall, R.S.; Xu, X.; et al. Whole-genome sequence of Schistosoma haematobium. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schistosoma japonicum Genome Sequencing and Functional Analysis Consortium. The Schistosoma japonicum genome reveals features of host-parasite interplay. Nature 2009, 460, 345–351. [Google Scholar]
- Massoulie, J.; Bon, S. The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1982, 5, 57–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarrab-Hazdai, R.; Toker, L.; Silman, I.; Arnon, R. Acetylcholinesterase from Schistosoma mansoni: Interaction of globular species with heparin. Biochem. J. 1999, 344, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarrab-Hazdai, R.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Gonzales, G.; Arnon, R. Acetylcholinesterase of Schistosoma mansoni. Molecular forms of the solubilized enzyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1984, 790, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, B.; Silman, I.; Arnon, R.; Tarrab-Hazdai, R. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C induces biosynthesis of acetylcholinesterase via diacylglycerol in Schistosoma mansoni. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 195, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, B.; Tarrab-Hazdai, R.; Silman, I.; Arnon, R. Acetylcholinesterase in Schistosoma mansoni is anchored to the membrane via covalently attached phosphatidylinositol. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1988, 29, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, K.; Buxton, S.; Kimber, M.J.; Day, T.A.; Robertson, A.P.; Ribeiro, P. Functional characterization of a novel family of acetylcholine-gated chloride channels in Schistosoma mansoni. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, M.; Alsford, S.; Jones, A.; Agnew, A. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the surface of the blood fluke Schistosoma. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1995, 71, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, G.N.; Jones, A.K.; Agnew, A. ShAR2beta, a divergent nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit from the blood fluke Schistosoma. Parasitology 2007, 134, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, M.; Agnew, A. Glucose uptake rates by Schistosoma mansoni, S. haematobium, and S. bovis adults using a flow in vitro culture system. J. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dani, J.A. Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine receptor structure and function and response to nicotine. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2015, 124, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beech, R.N.; Callanan, M.K.; Rao, V.T.; Dawe, G.B.; Forrester, S.G. Characterization of cys-loop receptor genes involved in inhibitory amine neurotransmission in parasitic and free living nematodes. Parasitol. Int. 2013, 62, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, T.E. Chemotherapeutic Targets in Parasites Contemporary Strategies; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhdeo, S.C.; Sangster, N.C.; Mettrick, D.F. Effects of cholinergic drugs on longitudinal muscle contractions of Fasciola hepatica. J. Parasitol. 1986, 72, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapson, E.B.; Chilwan, A.S.; Jenkins, D.C. Acetylcholinesterase secretion—A parameter for the interpretation of in vitro anthelmintic screens. Parasitology 1986, 92, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogilvie, B.M.; Rothwell, T.L.; Bremner, K.C.; Schnitzerling, H.J.; Nolan, J.; Keith, R.K. Acetylcholinesterase secretion by parasitic nematodes—I. Evidence for secretion of the enzyme by a number of species. Int. J. Parasitol. 1973, 3, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaux, R.; Schnoeller, C.; Berkachy, R.; Roberts, L.B.; Hagen, J.; Gounaris, K.; Selkirk, M.E. Modulation of the Immune Response by Nematode Secreted Acetylcholinesterase Revealed by Heterologous Expression in Trypanosoma musculi. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhdeo, S.C.; Sukhdeo, M.V.; Mettrick, D.F. Histochemical localization of acetylcholinesterase in the cerebral ganglia of Fasciola hepatica, a parasitic flatworm. J. Parasitol. 1988, 74, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemmerling, U.; Cabrera, G.; Campos, E.O.; Inestrosa, N.C.; Galanti, N. Localization, specific activity, and molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in developmental stages of the cestode Mesocestoides corti. J. Cell Physiol. 2006, 206, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.J. Modes of action of anthelmintic drugs. Vet. J. 1997, 154, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.K.; Sattelle, D.B. Functional genomics of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family of the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Bioessays 2004, 26, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richmond, J.E.; Jorgensen, E.M. One GABA and two acetylcholine receptors function at the C. elegans neuromuscular junction. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touroutine, D.; Fox, R.M.; Von Stetina, S.E.; Burdina, A.; Miller, D.M., 3rd; Richmond, J.E. acr-16 encodes an essential subunit of the levamisole-resistant nicotinic receptor at the Caenorhabditis elegans neuromuscular junction. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27013–27021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulin, T.; Gielen, M.; Richmond, J.E.; Williams, D.C.; Paoletti, P.; Bessereau, J.L. Eight genes are required for functional reconstitution of the Caenorhabditis elegans levamisole-sensitive acetylcholine receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18590–18595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, S.K.; Charvet, C.L.; Neveu, C.; Cabaret, J.; Cortet, J.; Peineau, N.; Abongwa, M.; Courtot, E.; Robertson, A.P.; Martin, R.J. Investigation of acetylcholine receptor diversity in a nematode parasite leads to characterization of tribendimidine- and derquantel-sensitive nAChRs. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duguet, T.B.; Charvet, C.L.; Forrester, S.G.; Wever, C.M.; Dent, J.A.; Neveu, C.; Beech, R.N. Recent Duplication and Functional Divergence in Parasitic Nematode Levamisole-Sensitive Acetylcholine Receptors. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, S.M.; Robertson, A.P.; Brown, L.; Williams, T.; Woods, D.J.; Martin, R.J.; Sattelle, D.B.; Wolstenholme, A.J. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of the parasitic nematode Ascaris suum: Formation of two distinct drug targets by varying the relative expression levels of two subunits. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.J.; Clark, C.L.; Trailovic, S.M.; Robertson, A.P. Oxantel is an N-type (methyridine and nicotine) agonist not an L-type (levamisole and pyrantel) agonist: Classification of cholinergic anthelmintics in Ascaris. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulin, T.; Fauvin, A.; Charvet, C.L.; Cortet, J.; Cabaret, J.; Bessereau, J.L.; Neveu, C. Functional reconstitution of Haemonchus contortus acetylcholine receptors in Xenopus oocytes provides mechanistic insights into levamisole resistance. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauvin, A.; Charvet, C.; Issouf, M.; Cortet, J.; Cabaret, J.; Neveu, C. cDNA-AFLP analysis in levamisole-resistant Haemonchus contortus reveals alternative splicing in a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2010, 170, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, M.A.; Reaves, B.J.; Maclean, M.J.; Storey, B.E.; Wolstenholme, A.J. Expression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits from parasitic nematodes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2015, 204, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Schistosome Species | AChE | nAChR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein ID | Description | Protein ID | Conserved Domains/Motifs | |||
| Ligand Domain | Trans-Membrane Region | Cys-Loop | ||||
| S. haematobium | A_03825 | AChR 1alpha | AAR84357 * | √ | √ | √ |
| KGB33661 * (XP_012793429 *) | AChR 2beta | AAR84358 * | √ | √ | √ | |
| AChR 2beta | AAX59989 * | √ | √ | √ | ||
| KGB33101 * (XP_012792873 *; A_04487 ~) | nAChR beta 3 (Dbeta 3) subunit | A_01504 ~ | ||||
| A_01761 ~ | √ | |||||
| KGB37011 * (XP_012796773 *; A_02007 ~) | Putative nAChR alpha 9b subunit | B_00805 ~ | √ | √ | ||
| AChR beta, putative | A_05298 ~ | √ | ||||
| AAO49838 * (AAO62355 *, AAQ14322 *) | AChR-related | A_06497 ~ | √ | √ | ||
| ACh-gated chloride channel-1 (ShACC-1) | A_02378 ~ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| ACh-gated chloride channel-2 (ShACC-2) | A_06346 ~ | |||||
| S. mansoni | AAQ14321 * (CCD58664 * XP_018645024 *) | AChR alpha subunit precursor | AAR84361 * | √ | ||
| AChR non-alpha subunit precursor | AAR84362 * | √ | ||||
| ACh-gated chloride channel-1 (SmACC-1) | Smp_176310 # | √ | √ | √ | ||
| ACh-gated chloride channel-2 (SmACC-2) | Smp_142690 # | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Putative nAChR alpha 9b subunit | Smp_135040 # | |||||
| AChR-related | Smp_012000 # | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Putative nAChR subunit | Smp_101990 # | |||||
| Smp_037960 # | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Smp_157790 # | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Smp_132070 # | √ | |||||
| Smp_180570 # | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Smp_197600 # | √ | √ | ||||
| Smp_142700 # | √ | √ | ||||
| Smp_031680 # | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Smp_139330 # | √ | √ | √ | |||
| S. japonicum | Sjp_0045440 # | Putative nAChR alpha 9b subunit | Sjp_0071780 # | |||
| Sjp_0034800 # | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Neuronal AChR subunit alpha-7 | Sjp_0082390 # | √ | √ | |||
| Sjp_0070510 # | AChR-related | Sjp_0131150 # | √ | √ | √ | |
| Sjp_0036280 # | Putative nAChR subunit | Sjp_0015560 # | √ | √ | ||
| Sjp_0066940 # | √ | |||||
| ANH56887 [24] * | ACh-gated chloride channel (SjACC-1) | Sjp_0115170 # | ||||
| Schistosome Species | nAChR | Cys-Loop Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| S. haematobium | AAR84357 | CNIDILWFPFDEQSC |
| AAR84358 | CDIEVNWFPFDSQNC | |
| AAX59989 | CQVEITYFPFDSQVC | |
| A_01761 | CSVDIKYFPFDRQKC | |
| A_06497 | CPLDVSFFPFDYQTC | |
| A_02378 | CPVKIKYFPYDKQVC | |
| S. mansoni | AAR84362 | CDIEVNWFPFDSQNC |
| Smp_139330 | CDIEVNWFPFDSQNC | |
| AAR84361 | CNIDILWFPFDEQSC | |
| Smp_031680 | CNIDILWFPFDEQSC | |
| Smp_197600 | CKIDITYFPFDDQSC | |
| Smp_157790 | CKIDIKSFPFDEQTC | |
| Smp_132070.1 | CPIDIKNFPFDYQHC | |
| Smp_132070.2 | CPIDIKNFPFDYQHC | |
| Smp_012000 | CPLDVSFFPFDYQTC | |
| Smp_142690 | CQVEITYFPFDSQVC | |
| Smp_037960 | CEVEITYFPFDTQIC | |
| Smp_176310 | CPVKIKYFPYDKQVC | |
| Smp_180570 | CQVDITLFPFDQQNC | |
| S. japonicum | Sjp_0034800 | CNVDVLYFPFDHQLC |
| Sjp_0131150 | CPLDVSFFPFDYQTC | |
| Sjp_0082390 | CDIEVNWFPFDSQNC |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, H.; Liu, C.; Du, X.; McManus, D.P. Acetylcholinesterase and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in Schistosomes and Other Parasitic Helminths. Molecules 2017, 22, 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091550
You H, Liu C, Du X, McManus DP. Acetylcholinesterase and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in Schistosomes and Other Parasitic Helminths. Molecules. 2017; 22(9):1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091550
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Hong, Chang Liu, Xiaofeng Du, and Donald P. McManus. 2017. "Acetylcholinesterase and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in Schistosomes and Other Parasitic Helminths" Molecules 22, no. 9: 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091550
APA StyleYou, H., Liu, C., Du, X., & McManus, D. P. (2017). Acetylcholinesterase and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in Schistosomes and Other Parasitic Helminths. Molecules, 22(9), 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091550





