Discovery of Farnesoid X Receptor Antagonists Based on a Library of Oleanolic Acid 3-O-Esters through Diverse Substituent Design and Molecular Docking Methods
Abstract
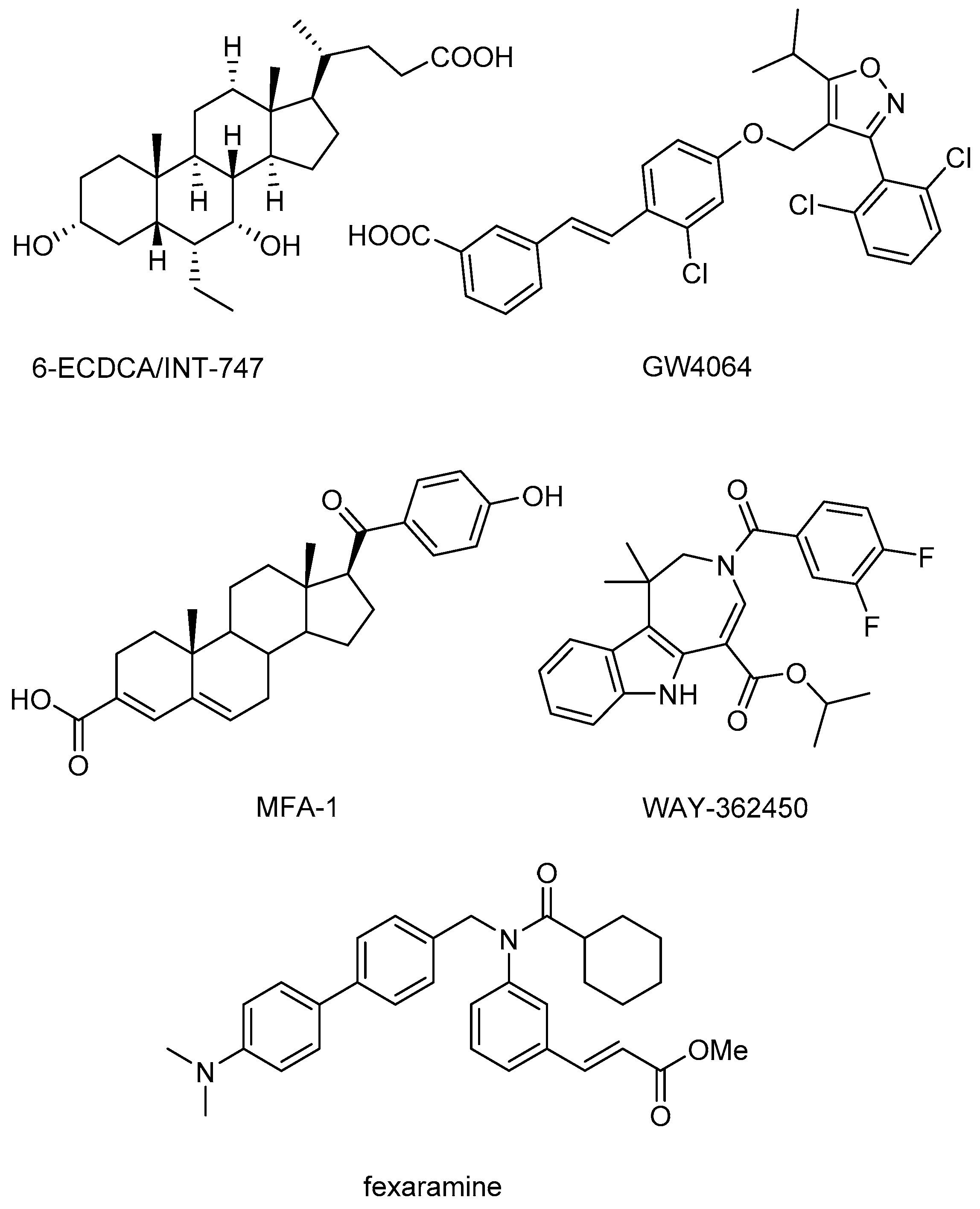
:1. Introduction
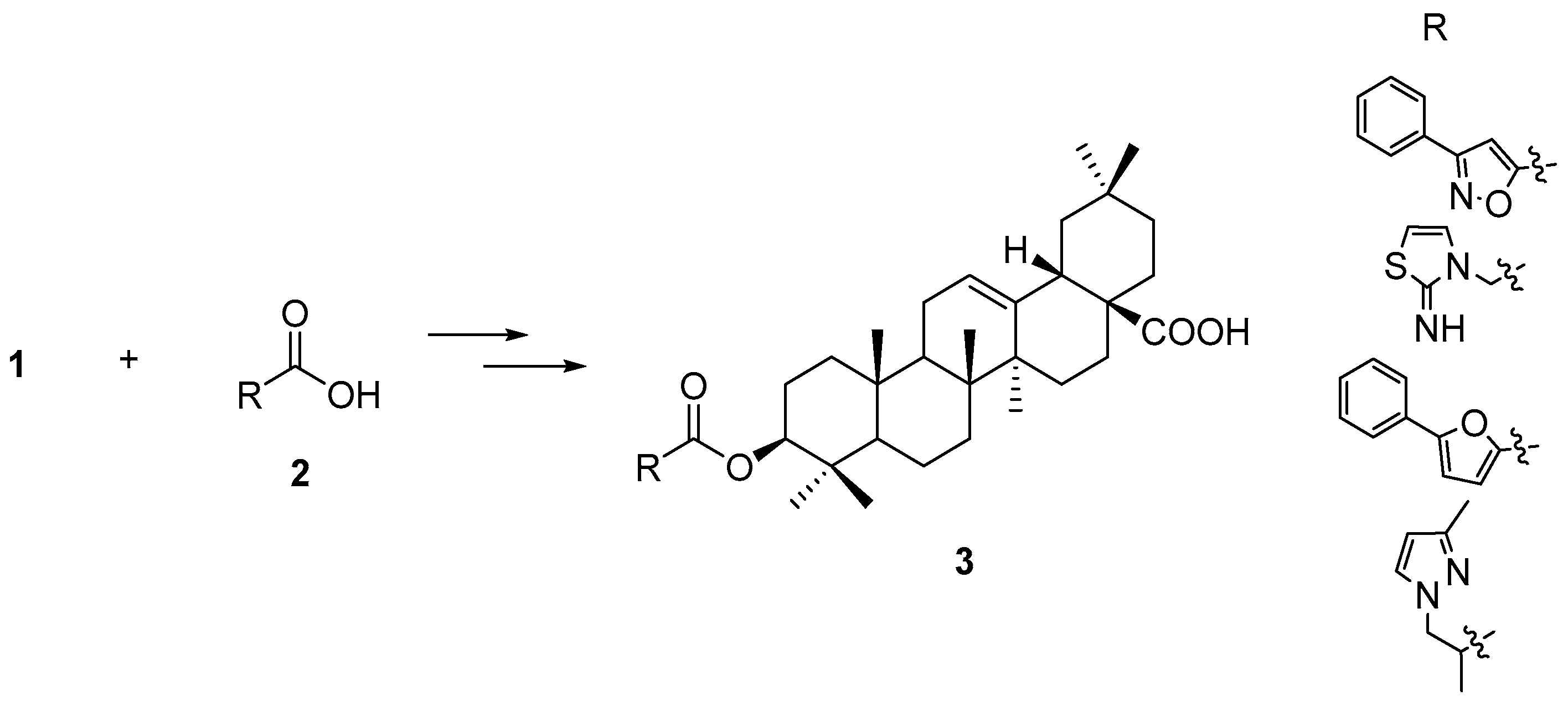
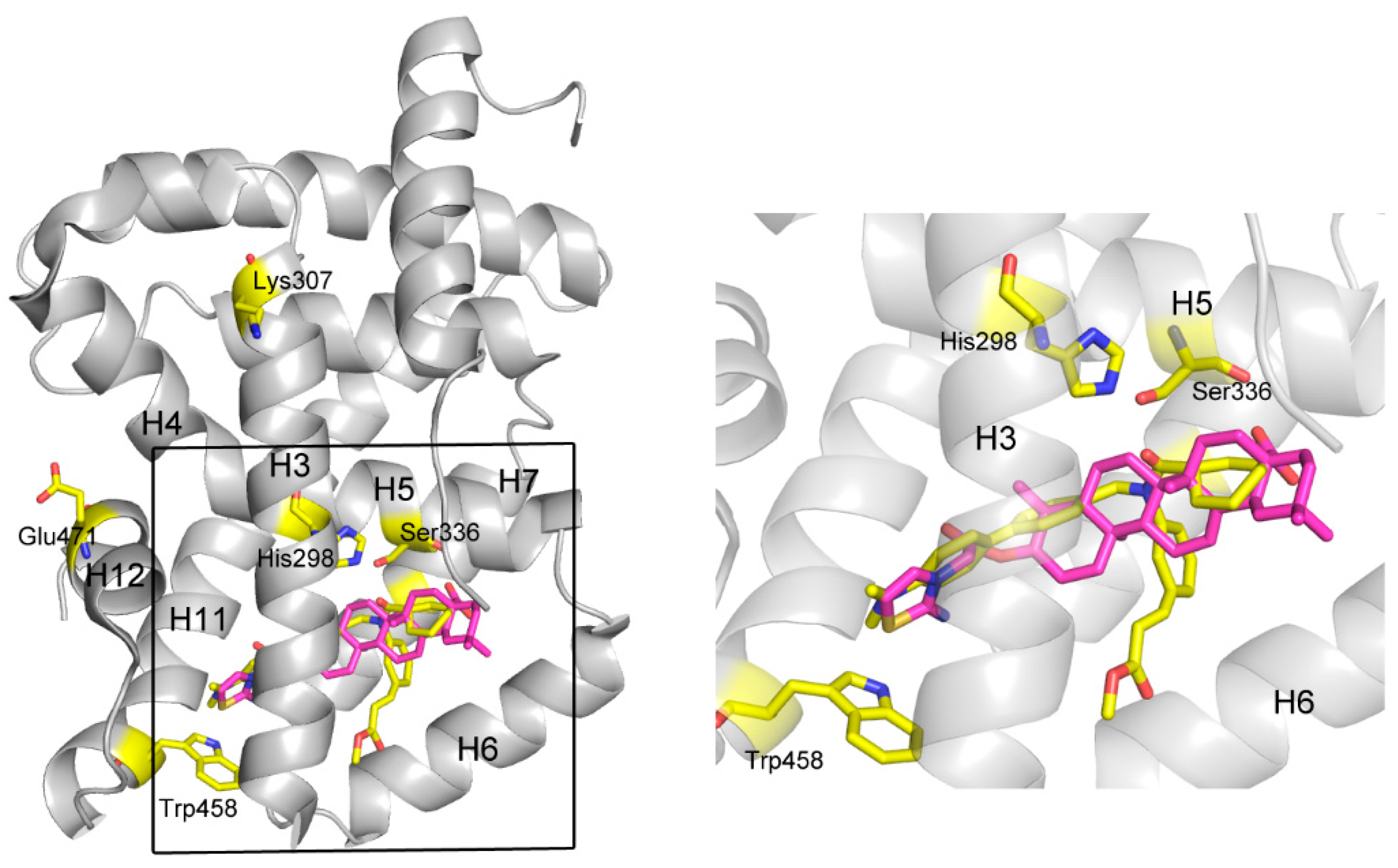
2. Results and Discussion
- (1)
- For a balance between more choice of building blocks and drug-like properties, i.e., not too large a molecular weight (MW), we set the upper MW limit of the carboxylic acids to 200. In Lipinkski’s rule, the MW is set to below 500 for orally active compounds. Considering the MW of 1 itself is 456, using MW 500 for 3-O-esters of OA would significantly limit the choice of carboxylic acids.
- (2)
- For other parameter settings, e.g., hydrogen bond donors (HBD) and hydrogen bond acceptors (HBA), the functional groups presenting already in OA (at C-3 and C-28) are also considered, so these parameters were set as follows: HBD equal or less than 4, HBA equal or less than 8, the number of rotatable bonds equal or less than 7, the number of rings equal or less than 2, the number of aromatic rings equal or less than 2.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
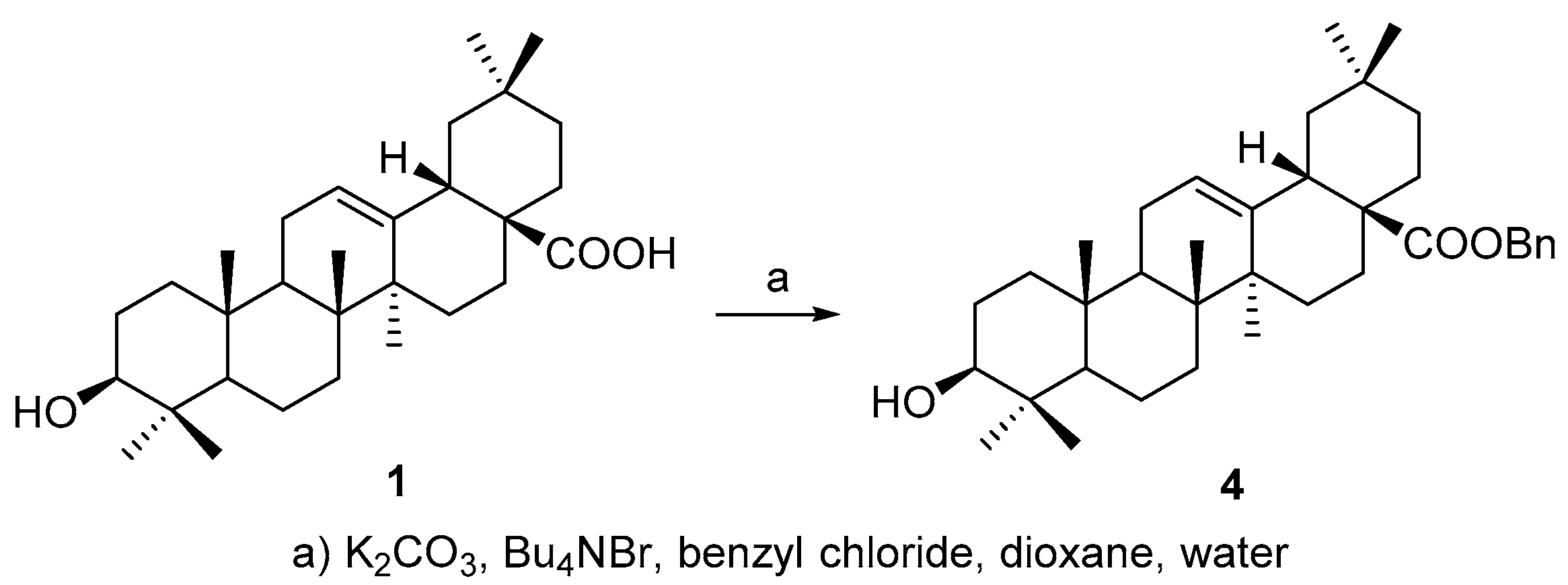
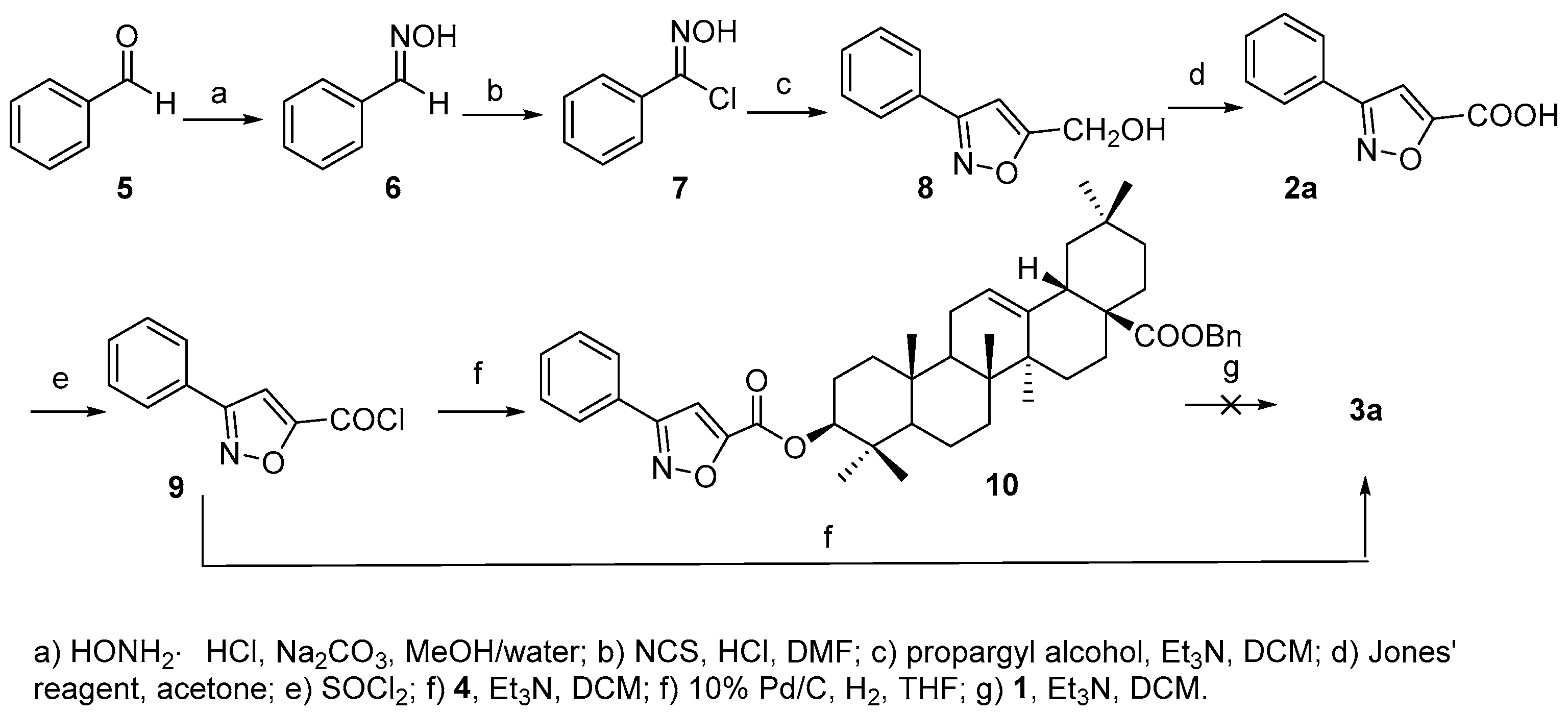
3.2. Synthesis of Compound 10
3.3. Synthesis of Compound 3a
3.4. Synthesis of Compound 12
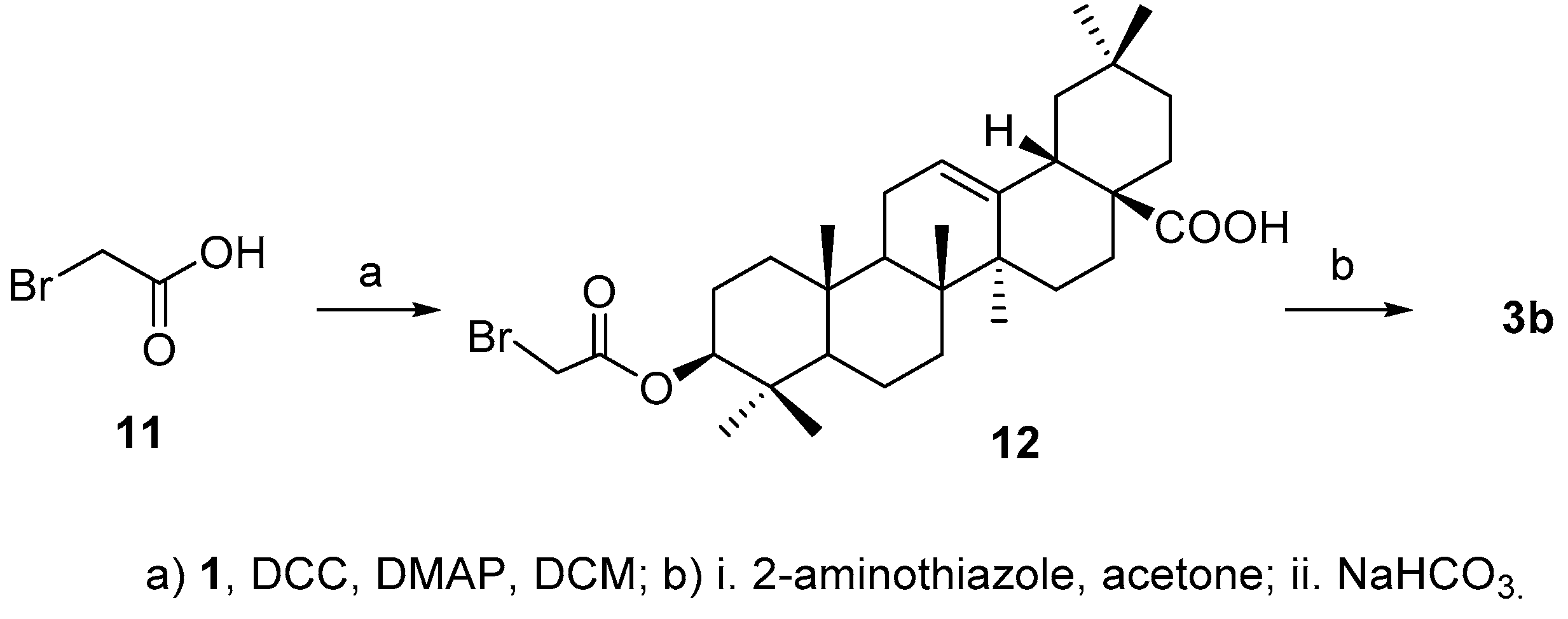
3.5. Synthesis of Compound 3b
3.6. Synthesis of Compound 13
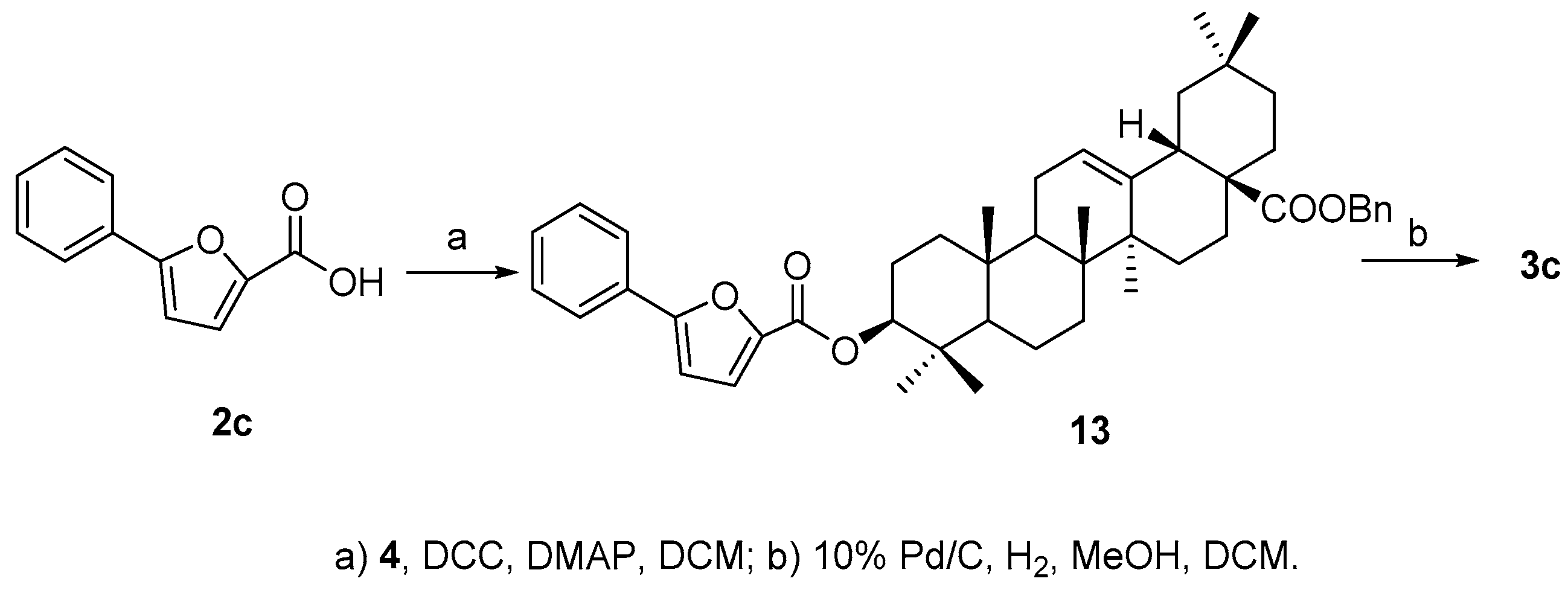
3.7. Synthesis of Compound 3c
3.8. Synthesis of Compound 16
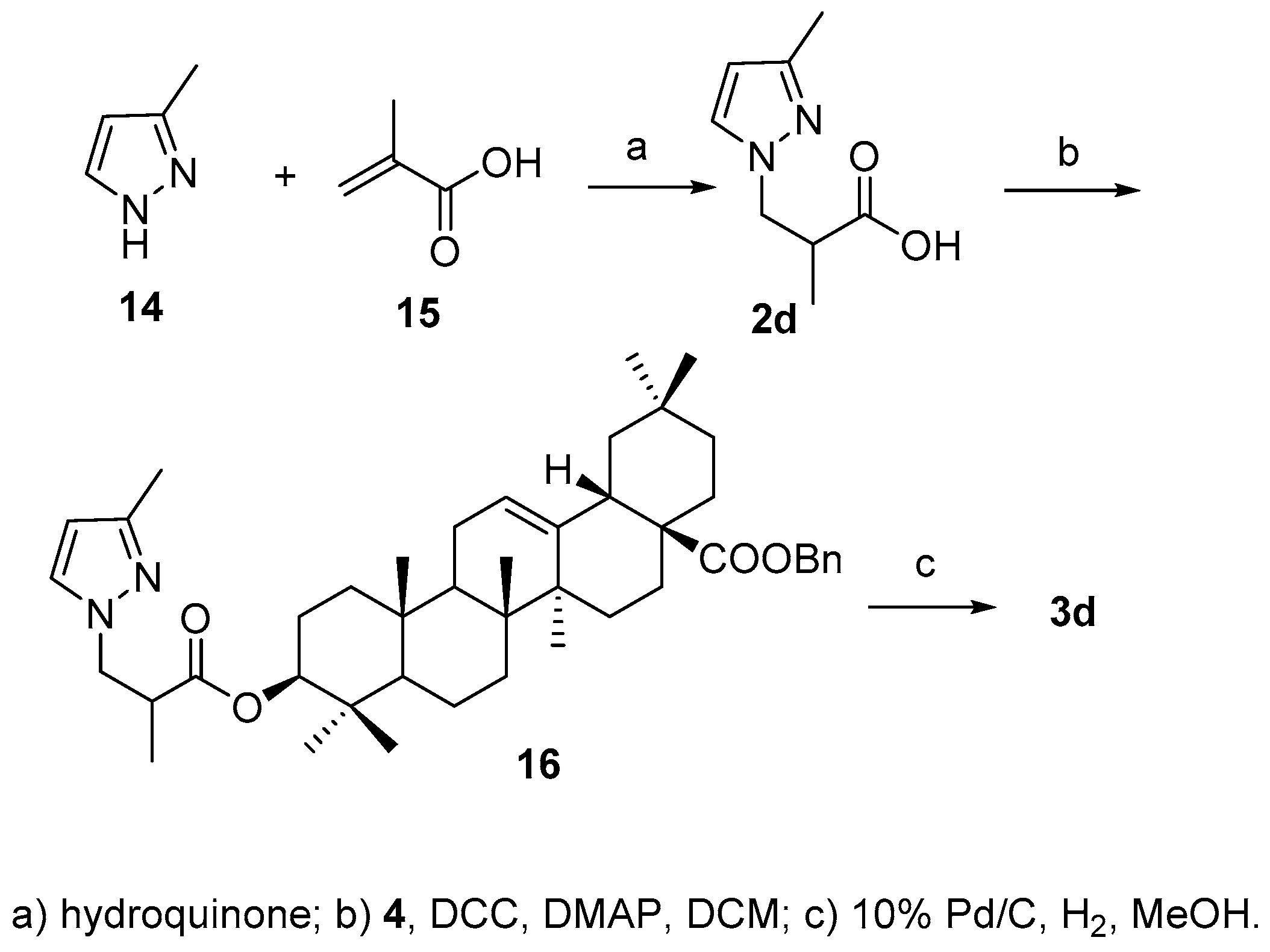
3.9. Synthesis of Compound 3d
3.10. Assembling the Database of Carboxylic Acids
3.11. Evaluating the Diversity of the Carboxylic Acids Database
3.12. Docking
3.13. Cell Culture
3.14. Transient Transfection and Luciferase Reporter Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Makishima, M.; Okamoto, A.Y.; Repa, J.J.; Tu, H.; Learned, R.M.; Luk, A.; Hull, M.V.; Lustig, K.D.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Shan, B. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science 1999, 284, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.J.; Blanchard, S.G.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Chandra, G.; Consler, T.G.; Kliewer, S.A.; Stimmel, J.B.; Willson, T.M.; Zavacki, A.M.; Moore, D.D.; et al. Bile acids: Natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science 1999, 284, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorucci, S.; Rizzo, G.; Donini, A.; Distrutti, E.; Santucci, L. Targeting farnesoid X receptor for liver and metabolic disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modica, S.; Murzilli, S.; Salvatore, L.; Schmidt, D.R.; Moschetta, A. Nuclear bile acid receptor FXR protects against intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9589–9594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorucci, S.; Mencarelli, A.; Distrutti, E.; Palladino, G.; Cipriani, S. Targetting farnesoid-X-receptor: From medicinal chemistry to disease treatment. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merk, D.; Steinhilber, D.; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M. Medicinal chemistry of farnesoid X receptor ligands: From agonists and antagonists to modulators. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 1015–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Lavine, J.E.; Van Natta, M.L.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Chalasani, N.; Dasarathy, S.; Diehl, A.M.; Hameed, B.; et al. Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorucci, S.; Distrutti, E.; Ricci, P.; Giuliano, V.; Donini, A.; Baldelli, F. Targeting FXR in cholestasis: Hype or hope. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Yu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Jin, H.; Yan, W.; Ma, R.; Zhu, J.; et al. Discovery and optimization of 1,3,4-trisubstituted-pyrazolone derivatives as novel, potent, and nonsteroidal farnesoid X receptor (FXR) selective antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7037–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wong, C. Oleanolic acid is a selective farnesoid X receptor modulator. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J.; Klingler, F.M.; Proschak, E.; Steinhilber, D.; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M.; Merk, D. NSAIDs ibuprofen, indometacin, and diclofenac do not interact with farnesoid X receptor. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zeng, H.; Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Xu, C.; Deng, R.; Zhou, X.; Bi, H.; Huang, M. Low dose of oleanolic acid protects against lithocholic acid–induced cholestasis in mice: Potential involvement of nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2-mediated upregulation of multidrug resistance-associated proteins. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Li, J.; Fan, X.; Zeng, H.; Deng, R.; Li, D.; Huang, M.; Bi, H. Oleanolic acid attenuates obstructive cholestasis in bile duct-ligated mice, possibly via activation of NRF2-MRPs and FXR antagonism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 765, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.; Du, X.; Chen, S.; Feng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, S.; He, X.; Wang, R.; et al. Oral administration of oleanolic acid, isolated from Swertia mussotii Franch, attenuates liver injury, inflammation, and cholestasis in bile duct-ligated rats. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.L.; Cho, K.H.; Ha, Y.W.; Jeong, T.S.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, Y.S. Cholesterol-lowering effect of platycodin D in hypercholesterolemic ICR mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 537, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Shen, H.; Hu, L.H.; Jiang, H.L.; Shen, X. Oleanolic acid derivative NPLC441 potently stimulates glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via a multi-target mechanism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, P. Similarity-based virtual screening using 2D fingerprints. Drug Discov. Today 2006, 11, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.S.; Yan, M.C.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, L.G.; Liu, J. Synthesis of β-hederin and Hederacolchiside A1: Triterpenoid saponins bearing a unique cytotoxicity-inducing disaccharide moiety. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 341, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Z.; Jia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.R.; Liu, W.; Shi, F.N.; Wang, J.W. Concise Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activities of New Substituted 5-Isoxazolpenicillins. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2007, 54, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.; Singh, V.; Batra, S. Studies on the catalytic hydrogenation of Baylis–Hillman derivatives of substituted isoxazolecarbaldehydes. Unusual retention of isoxazole ring during Pd–C-promoted hydrogenation of Baylis–Hillman adducts. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 10311–10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachir, L.; D’Amour, K.; Casida, J.E. Novel and potent 6-chloro-3-pyridinyl ligands for the α4β2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 2227–2234. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, L.; Huang, Z.; Lai, Y.; Ji, H.; Peng, S.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Y. Hybrid molecule from O2-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)diazeniumdiolate and oleanolic acid: A glutathione S-transferase π-activated nitric oxide prodrug with selective anti-human hepatocellular carcinoma activity and improved stability. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 4641–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaran, O.S.; Baltayan, A.O.; Matsoyan, S.G. Synthesis of α-methyl-β-(3-methylpyrazol-1-yl)-and α-methyl-β-(5-methylpyrazol-1-yl)propionic acids and their esterification with vinyl acetate. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2007, 77, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, L.Z.; Devarakonda, S.; Harp, J.M.; Han, Q.; Pellicciari, R.; Willson, T.M.; Khorasanizadeh, S.; Rastinejad, F. Structural basis for bile acid binding and activation of the nuclear receptor FXR. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soisson, S.M.; Parthasarathy, G.; Adams, A.D.; Sahoo, S.; Sitlani, A.; Sparrow, C.; Cui, J.; Becker, J.W. Identification of a potent synthetic FXR agonist with an unexpected mode of binding and activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5337–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte, R.T.; Wisely, G.B.; Westin, S.; Cobb, J.E.; Lambert, M.H.; Kurokawa, R.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Willson, T.M.; Glass, C.K.; Milburn, M.V. Ligand binding and co-activator assembly of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ. Nature 1998, 395, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Downes, M.; Verdecia, M.A.; Roecker, A.J.; Hughes, R.; Hogenesch, J.B.; Kast-Woelbern, H.R.; Bowman, M.E.; Ferrer, J.L.; Anisfeld, A.M.; Edwards, P.A.; et al. A chemical, genetic, and structural analysis of the nuclear bile acid receptor FXR. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Autodock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexiblity. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 16, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

| Prediction | 1 | 3a | 3b | 3c | 3d | Fexaramine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pKi (Autodock) | 8.87 | 8.67 | 9.35 | 8.00 | 9.68 | 10.39 |
| IC50 (μM) | 13.69 | 19.41 | 7.03 | 13.74 | 9.03 | / |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.-R.; Xu, T.; Deng, K.; Wong, C.-W.; Liu, J.; Fang, W.-S. Discovery of Farnesoid X Receptor Antagonists Based on a Library of Oleanolic Acid 3-O-Esters through Diverse Substituent Design and Molecular Docking Methods. Molecules 2017, 22, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050690
Wang S-R, Xu T, Deng K, Wong C-W, Liu J, Fang W-S. Discovery of Farnesoid X Receptor Antagonists Based on a Library of Oleanolic Acid 3-O-Esters through Diverse Substituent Design and Molecular Docking Methods. Molecules. 2017; 22(5):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050690
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shao-Rong, Tingting Xu, Kai Deng, Chi-Wai Wong, Jinsong Liu, and Wei-Shuo Fang. 2017. "Discovery of Farnesoid X Receptor Antagonists Based on a Library of Oleanolic Acid 3-O-Esters through Diverse Substituent Design and Molecular Docking Methods" Molecules 22, no. 5: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050690
APA StyleWang, S.-R., Xu, T., Deng, K., Wong, C.-W., Liu, J., & Fang, W.-S. (2017). Discovery of Farnesoid X Receptor Antagonists Based on a Library of Oleanolic Acid 3-O-Esters through Diverse Substituent Design and Molecular Docking Methods. Molecules, 22(5), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050690






