Microneedle-Assisted Percutaneous Delivery of a Tetramethylpyrazine-Loaded Microemulsion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of Formulation for TMP-ME
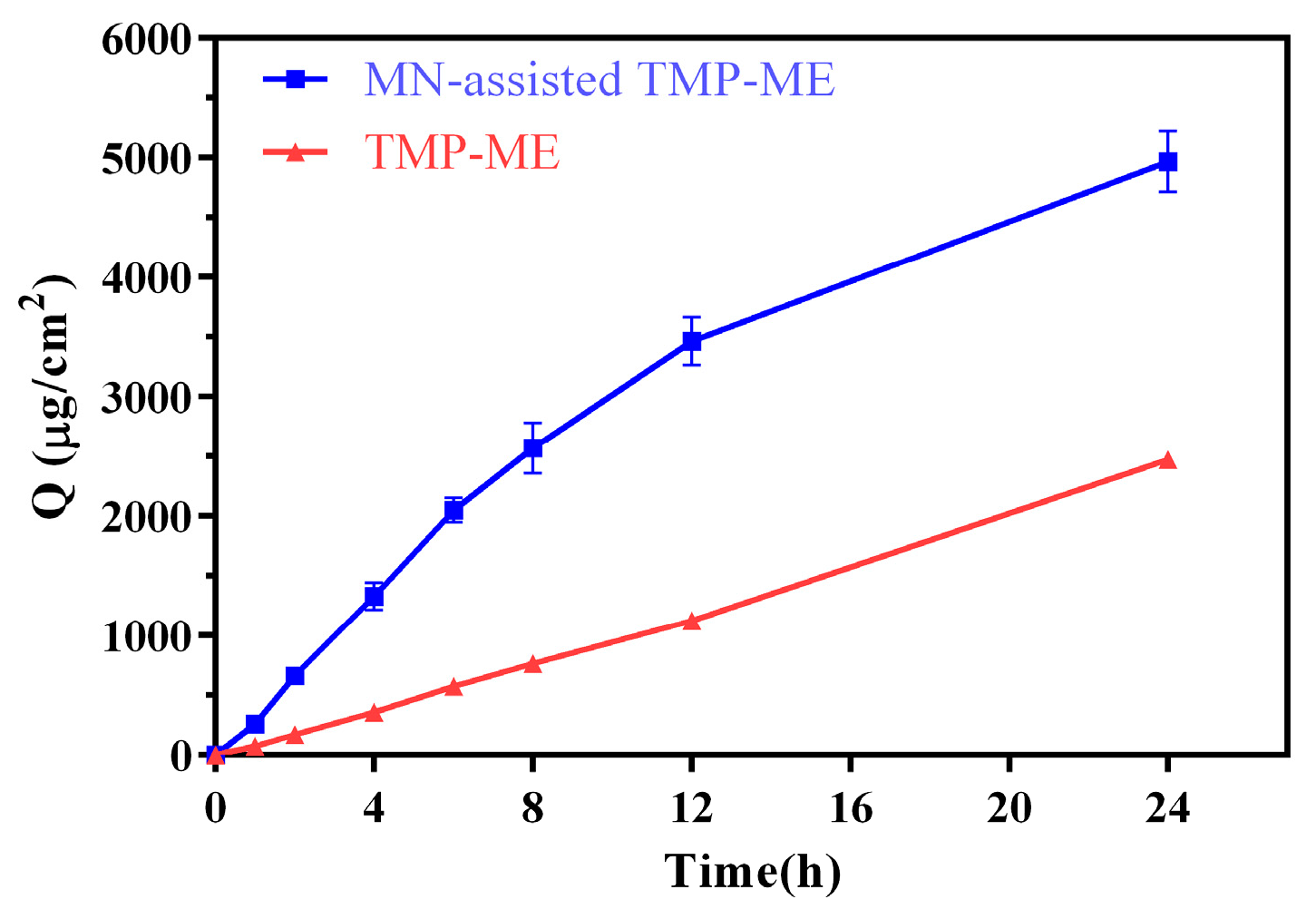
2.2. In Vitro Skin Permeation of MN-Assisted TMP-ME
2.3. In Vivo Skin Microdialysis of MN-Assisted TMP-ME
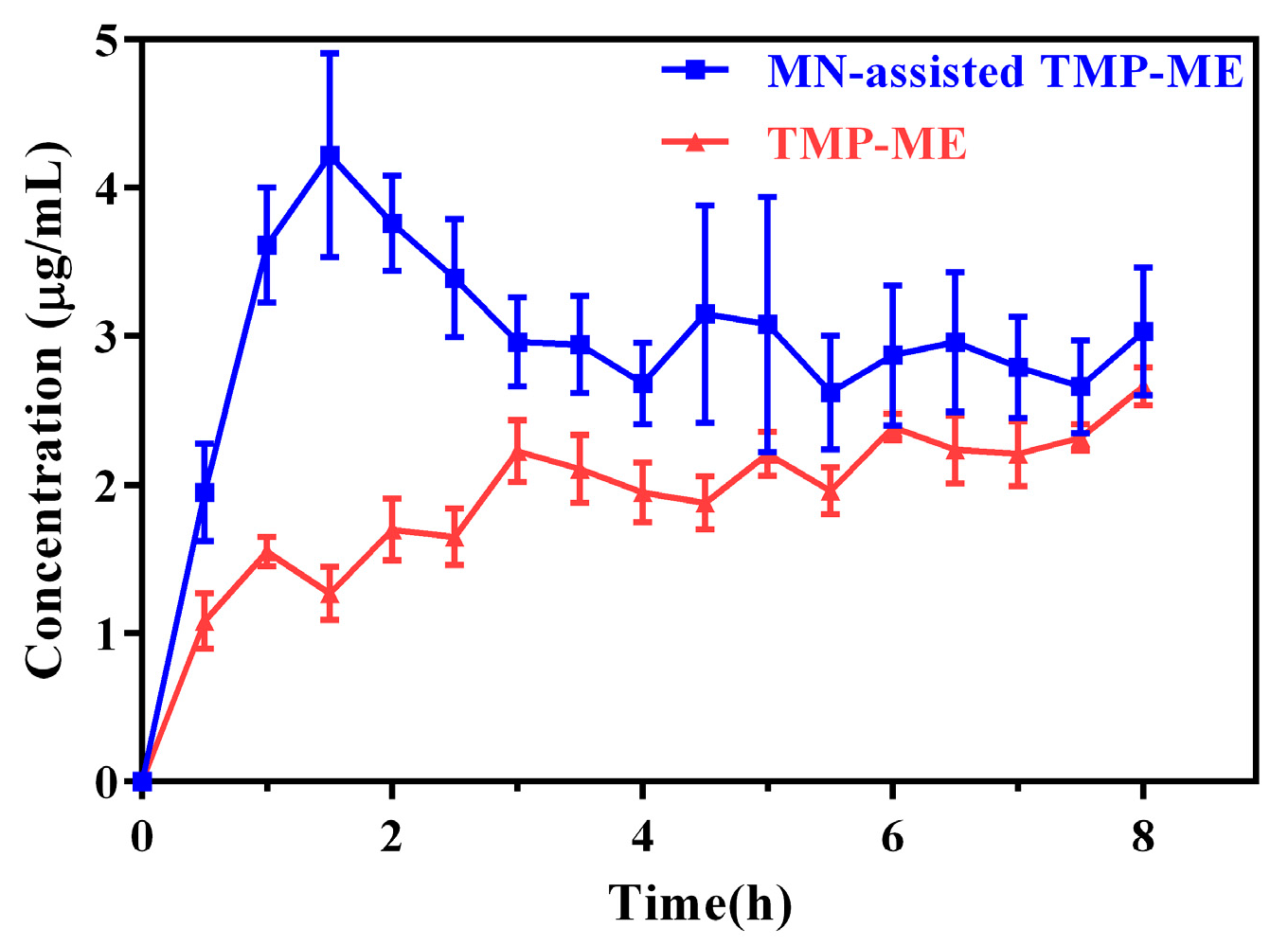
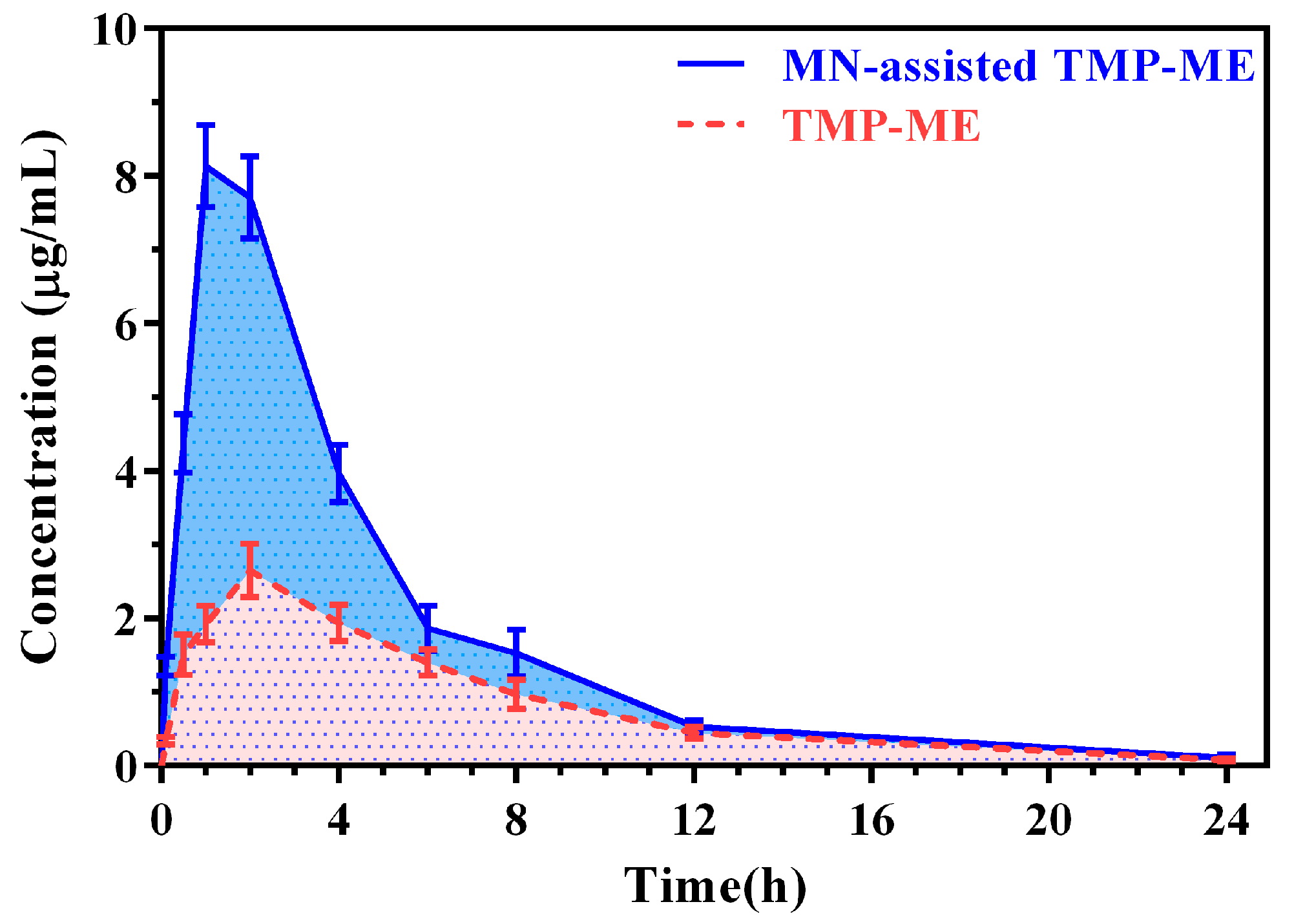
2.4. Pharmacokinetic Study of MN-Assisted TMP-ME
2.5. Influence of MN Treatment on Transcutaneous Electrical Resistance
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Formulation Optimization of TMP-ME
3.3. In Vitro Skin Permeation of MN-Assisted TMP-ME
3.4. In Vivo Skin Microdialysis of MN-Assisted TMP-ME
3.5. Pharmacokinetics of MN-Assisted TMP-ME
3.6. Influence of MN Treatment on Transcutaneous Electrical Resistance
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexander, A.; Dwivedi, S.; Ajazuddin; Giri, T.K.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S.; Tripathi, D.K. Approaches for breaking the barriers of drug permeation through transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, V.F.M.; Migotto, A.; Giacone, D.V.; de Lemos, D.P.; Zanoni, T.B.; Maria-Engler, S.S.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V.; Lopes, L.B. Co-encapsulation of paclitaxel and C6 ceramide in tributyrin-containing nanocarriers improve co-localization in the skin and potentiate cytotoxic effects in 2D and 3D models. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 109, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Wu, D.; Shi, D.; Wang, T.; Zhu, X. Mechanism of transdermal permeation promotion of lipophilic drugs by ethosomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engkagul, V.; Klaharn, I.Y.; Sereemaspun, A.; Chirachanchai, S. Chitosan whisker grafted with oligo(lactic acid) nanoparticles via a green synthesis pathway: Potential as a transdermal drug delivery system. Nanomedicine 2017. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andar, A.U.; Karan, R.; Pecher, W.T.; DasSarma, P.; Hedrich, W.D.; Stinchcomb, A.L.; DasSarma, S. Microneedle-Assisted Skin Permeation by Nontoxic Bioengineerable Gas Vesicle Nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikkath, J.; Hegde, A.R.; Kalthur, G.; Parekh, H.S.; Mutalik, S. Influence of peptide dendrimers and sonophoresis on the transdermal delivery of ketoprofen. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinovskaja-Gomez, K.; Espuelas, S.; Garrido, M.J.; Hirvonen, J.; Laaksonen, T. Comparison of liposomal drug formulations for transdermal iontophoretic drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Hu, M.; Liu, W.; Xue, C.; Xu, H.; Yang, X. Investigation of the carbopol gel of solid lipid nanoparticles for the transdermal iontophoretic delivery of triamcinolone acetonide acetate. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hu, K.; Li, F. Enhancement of skin permeation of docetaxel: a novel approach combining microneedle and elastic liposomes. J. Control. Release 2008, 129, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mutoh, M.; Ueda, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Hirayama, K.; Atobe, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Morimoto, Y. Characterization of transdermal solute transport induced by low-frequency ultrasound in the hairless rat skin. J. Control. Release 2003, 92, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenjarla, S. Microemulsions: An overview and pharmaceutical applications. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 1999, 16, 461–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, V.; Yadav, P.; Verma, A.; Pandit, J.K. Ex vivo and in vivo evaluation of microemulsion based transdermal delivery of E. coli specific T4 bacteriophage: A rationale approach to treat bacterial infection. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 107, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dave, K.; Alsharif, F.M.; Islam, S.; Dwivedi, C.; Perumal, O. Chemoprevention of Breast Cancer by Transdermal Delivery of α-Santalol through Breast Skin and Mammary Papilla (Nipple). Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.L.; Silva, J.A.; Lira, A.A.; Conceição, T.M.; Nunes Rde, S.; de Albuquerque Junior, R.L.; Sarmento, V.H.; Leal, L.B.; de Santana, D.P. Evaluation of Microemulsion and Lamellar Liquid Crystalline Systems for Transdermal Zidovudine Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2188–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffatt, K.; Wang, Y.; Raj Singh, T.R.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedles for enhanced transdermal and intraocular drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 36, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, M.; Mönkäre, J.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Kersten, G. Dissolving Microneedle Patches for Dermal Vaccination. Pharm. Res. 2017. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Wu, C. Microneedle, bio-microneedle and bio-inspired microneedle: A review. J. Control. Release 2017, 251, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, S.P.; Koutsonanos, D.G.; Del Pilar Martin, M.; Lee, J.W.; Zarnitsyn, V.; Choi, S.O.; Murthy, N.; Compans, R.W.; Skountzou, I.; Prausnitz, M.R. Dissolving polymer microneedle patches for influenza vaccination. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vučen, S.R.; Vuleta, G.; Crean, A.M.; Moore, A.C.; Ignjatović, N.; Uskoković, D. Improved percutaneous delivery of ketoprofen using combined application of nanocarriers and silicon microneedles. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolli, C.S.; Xiao, J.; Parsons, D.L.; Babu, R.J. Microneedle assisted iontophoretic transdermal delivery of prochlorperazine edisylate. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2012, 38, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkor, P.O.; Chen, Y.; Ding, L.; Qiu, F. Locally and traditionally used Ligusticum species—A review of their phytochemistry, pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 530–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Dong, S.N.; Lou, Y.Q. HPLC determination of tetramethylpyrazine in human serum and its pharmacokinetic parameters. Yao Xue Xue Bao 1989, 24, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.; Cao, X.; Chen, M.L. The pharmacokinetics and disposition of tetramethylpyrazine phosphate in dogs and rats. Yao Xue Xue Bao 1986, 21, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.L. Clinical use of tetramethylpyrazine: A review. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 1994, 14, 465–468. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; He, Z.; Ding, C.; Huang, G.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, L. Preparation of a ligustrazine ethosome patch and its evaluation in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Xu, H.; Weng, W.; Zhang, J. Development of a reservoir-type transdermal delivery system containing eucalyptus oil for tetramethylpyrazine. Drug Deliv. 2013, 20, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Cong, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Luo, G. Microemulsion-based patch for transdermal delivery of huperzine A and ligustrazine phosphate in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2012, 38, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Ita, K.B.; Popova, I.E.; Parikh, S.J.; Bair, D.A. Microneedle-assisted delivery of verapamil hydrochloride and amlodipine besylate. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, A.; Murthy, S.N. Pretreatment with skin permeability enhancers: Importance of duration and composition on the delivery of diclofenac sodium. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Song, C.; Baik, S.; Kim, D.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.-H. Device-assisted transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanke, S.S.; Kolli, C.S.; Strom, J.G.; Banga, A.K. Enhanced transdermal delivery of low molecular weight heparin by barrier perturbation. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 365, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachakonda, V.K.; Yerramsetty, K.M.; Madihally, S.V.; Robinson, R.L., Jr.; Gasem, K.A. Screening of chemical penetration enhancers for transdermal drug delivery using electrical resistance of skin. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2697–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.H.; Ji, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.T.; Liu, Y.; Feng, N.P. Microemulsion-based novel transdermal delivery system of tetramethylpyrazine: Preparation and evaluation in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhong, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shi, F.; Feng, N.P. Enhanced transdermal delivery of evodiamine and rutaecarpine using microemulsion. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2469–2482. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Sample- of 2,3,5,6-Tetramethylpyrazone is available from the authors. |
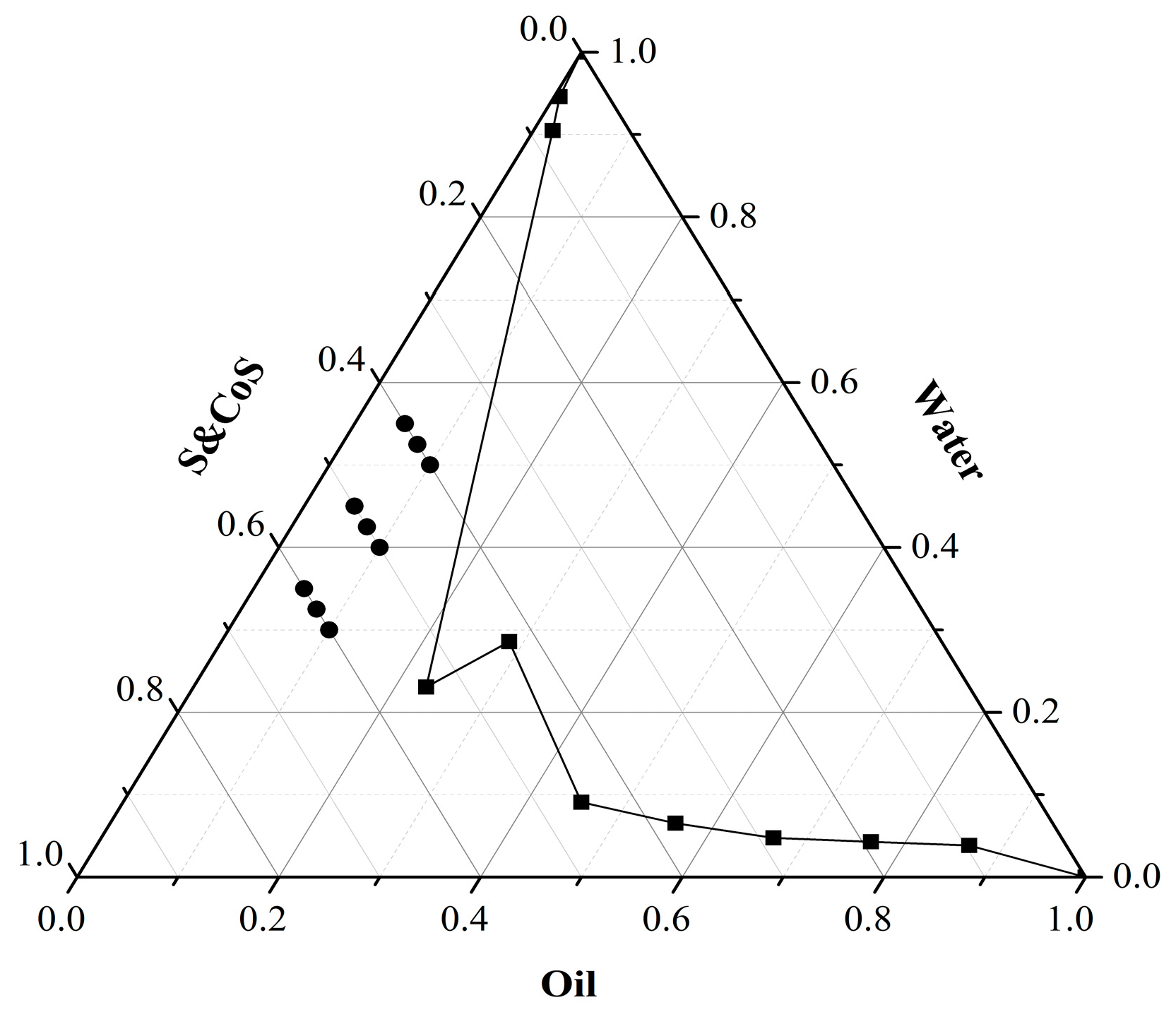
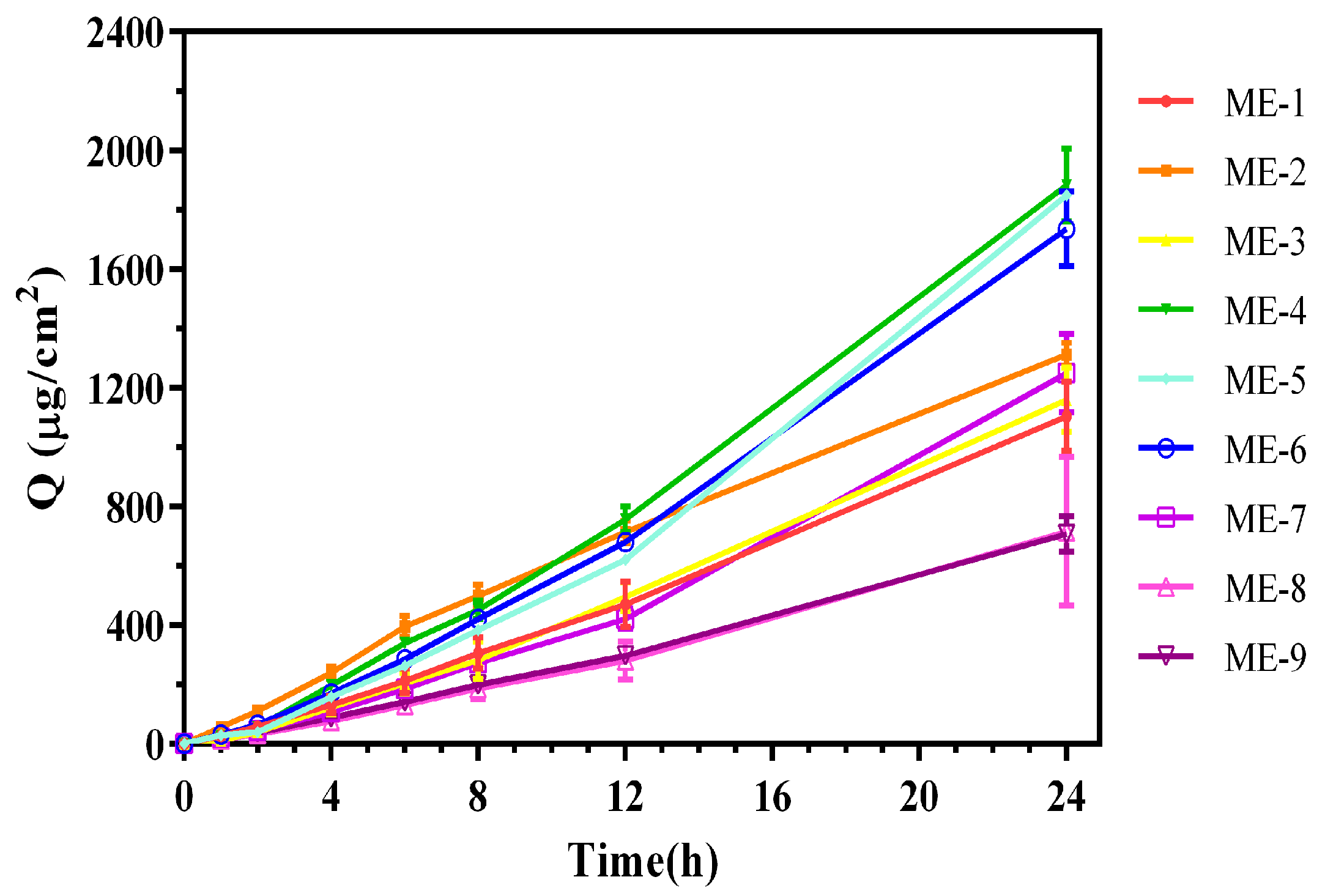
| Formulation | TMP 24-h Cumulative Skin Permeation (µg/cm2) | Mean Particle Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1103.90 ± 117.32 | 63.61 ± 0.72 |
| 2 | 1311.12 ± 40.24 | 86.84 ± 0.41 |
| 3 | 1158.98 ± 109.01 | 55.96 ± 0.34 |
| 4 | 1883.34 ± 123.26 | 101.2 ± 0.65 |
| 5 | 1849.33 ± 16.63 | 83.57 ± 0.59 |
| 6 | 1735.46 ± 125.78 | 96.04 ± 0.28 |
| 7 | 1248.86 ± 132.42 | 119.4 ± 0.15 |
| 8 | 714.97 ± 252.10 | 117.4 ± 0.35 |
| 9 | 1103.90 ± 117.32 | 189.2 ± 0.45 |
| Parameter | MN-Assisted TMP-ME | TMP-ME |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 4.79 ± 0.68 * | 2.13 ± 0.16 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.60 ± 0.22 * | 3.10 ± 0.22 |
| AUC (h * µg/mL) | 21.90 ± 2.14 * | 11.65 ± 0.58 |
| Parameter | MN-Assisted TMP-ME | TMP-ME |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 8.25 ± 0.51 * | 2.65 ± 0.36 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.20 ± 0.45 * | 2.00 ± 0.00 |
| AUC (h * µg/mL) | 41.11 ± 3.11 * | 19.87 ± 2.40 |
| t1/2 (h) | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.16 ± 0.01 |
| V (mL) | 2219.01 ± 401.80 * | 4642.66 ± 634.70 |
| Cl (mL/h) | 360.47 ± 28.82 * | 746.00 ± 90.89 |
| MRT (h) | 4.56 ± 0.17 * | 6.03 ± 0.33 |
| Formulation | Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| X1 (%) | X2 (%) | Water (%) | |
| 1 | 1 (5.0) | 4 (50.0) | 45.0 |
| 2 | 2 (5.0) | 8 (60.0) | 35.0 |
| 3 | 3 (5.0) | 3 (40.0) | 55.0 |
| 4 | 4 (7.5) | 7 (60.0) | 32.5 |
| 5 | 5 (7.5) | 2 (40.0) | 52.5 |
| 6 | 6 (7.5) | 6 (50.0) | 42.5 |
| 7 | 7 (10.0) | 1 (40.0) | 50.0 |
| 8 | 8 (10.0) | 5 (50.0) | 40.0 |
| 9 | 9 (10.0) | 9 (60.0) | 30.0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Bi, X.; Zhang, R.; Di, L. Microneedle-Assisted Percutaneous Delivery of a Tetramethylpyrazine-Loaded Microemulsion. Molecules 2017, 22, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112022
Zu Q, Yu Y, Bi X, Zhang R, Di L. Microneedle-Assisted Percutaneous Delivery of a Tetramethylpyrazine-Loaded Microemulsion. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112022
Chicago/Turabian StyleZu, Qiang, Yanyan Yu, Xiaolin Bi, Ren Zhang, and Liuqing Di. 2017. "Microneedle-Assisted Percutaneous Delivery of a Tetramethylpyrazine-Loaded Microemulsion" Molecules 22, no. 11: 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112022
APA StyleZu, Q., Yu, Y., Bi, X., Zhang, R., & Di, L. (2017). Microneedle-Assisted Percutaneous Delivery of a Tetramethylpyrazine-Loaded Microemulsion. Molecules, 22(11), 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112022




