Elucidating Direct Photolysis Mechanisms of Different Dissociation Species of Norfloxacin in Water and Mg2+ Effects by Quantum Chemical Calculations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Computational Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Geometries of Three Dissociation Species (NOR0, NOR+, and NOR2+) in Water
3.2. Direct Photolysis Pathways of Three Dissociation Species (NOR0, NOR+, and NOR2+) in Water
3.3. Complex Geometries of Three Dissociation Species (NOR0, NOR+, and NOR2+) with Metal Ion Mg2+ in Water
3.4. Effects of Mg2+ on Direct Photolysis of Three Dissociation Species (NOR0, NOR+, and NOR2+) in Water
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part I. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Chu, L.M. Fate of antibiotics in soil and their uptake by edible crops. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Bagnati, R.; Melis, M.; Fanelli, R. Source, occurrence and fate of antibiotics in the Italian aquatic environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moellering, R.C. Norfloxacin: A fluoroquinolone carboxylic acid antimicrobial agent. Am. J. Med. 1987, 82, 1–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Kolpin, D.W.; Costanzo, S.D. The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: From wastewater to drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2711–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, G.; Zou, S.; Ling, Z.; Wang, G.; Yan, W. A preliminary investigation on the occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the Yellow River and its tributaries, China. Water Environ. Res. 2009, 81, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Wang, Y.; Tong, L.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; Guo, W.; Gan, Y. Seasonal variation of antibiotics concentration in the aquatic environment: A case study at Jianghan Plain, central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527–528, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Liang, H.; Gao, D. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the Songhua River in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19282–19292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Du, J.; Qu, Y.; Shen, C.; Tan, F.; Chen, J.; Quan, X. Occurrence, removal, and risk assessment of antibiotics in 12 wastewater treatment plants from Dalian, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16478–16487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, D.; Wu, J. Photodegradation of Norfloxacin in aqueous solution containing algae. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Bano, R.; Musharraf, S.G.; Sheraz, M.A.; Ahmed, S.; Tahir, H.; ulArfeen, Q.; Bhatti, M.S.; Shad, Z.; Hussain, S.F. Photodegradation of norfloxacin in aqueous and organic solvents: A kinetic study. J. Photoch. Photobiol. A 2015, 302, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.V.d.S.; Meireles, A.M.; Lange, L.C. Degradation of antibiotics norfloxacin by Fenton, UV and UV/H2O2. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 154, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Chen, J.; Wei, X.; Zhang, S.; Qiao, X.; Cai, X.; Xie, Q. Aquatic photochemistry of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: Kinetics, pathways, and multivariate effects of main water constituents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2400–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Niu, J.; Wang, W. Photolysis of enrofloxacin in aqueous systems under simulated sunlight irradiation: Kinetics, mechanism and toxicity of photolysis products. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babić, S.; Periša, M.; Škorić, I. Photolytic degradation of norfloxacin, enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in various aqueous media. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wammer, K.H.; Korte, A.R.; Lundeen, R.A.; Sundberg, J.E.; McNeill, K.; Arnold, W.A. Direct photochemistry of three fluoroquinoloneantibacterials: Norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and enrofloxacin. Water Res. 2013, 47, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ge, L.; Qiao, X. Distinct photolytic mechanisms and products for different dissociation species of ciprofloxacin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4284–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Zhao, H.; Deng, M.; Quan, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, H. Impact of dissolved organic matter on the photolysis of the ionizable antibiotic norfloxacin. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 27, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zepp, R.G.; Cline, D.M. Rates of direct photolysis in aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1977, 11, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, X.; Hao, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, J.; Qiu, J. Elucidating triplet-sensitized photolysis mechanisms of sulfadiazine and metal ions effects by quantum chemical calculations. Chemosphere 2015, 122, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Yao, S.; Wang, W. Effects of pH and polarity on the excited states of norfloxacin and its 4’-N-acetyl derivative: A steady-state and time-resolved study. Sci. China Chem. 2014, 57, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J.J.; Arnold, W.A.; Mcneill, K. Water hardness as a photochemical parameter: Tetracycline photolysis as a function of calcium concentration, magnesium concentration, and pH. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7236–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, L.; Bilski, P.; Chignell, C.F. Effect of magnesium and calcium complexation on the photochemical properties of norfloxacin. Photochem. Photobiol. 1996, 64, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, X.; Hao, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, J.; Qiu, J. Elucidating photodehalogenation mechanisms of polychlorinated and polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans and Mg2+ effects by quantum chemical calculations. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2014, 1042, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafuka, A.; Yoshikawa, H.; Yamada, K.; Kato, T.; Takahashi, M.; Okabe, S.; Satoh, H. Application of fluorescence spectroscopy using a novel fluoroionophore for quantification of zinc in urban runoff. Water Res. 2014, 54, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabljic, A. QSAR models for estimating properties of persistent organic pollutants required in evaluation of their environmental fate and risk. Chemosphere 2001, 43, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hao, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, J.; Qiu, J. Effects of excited-state structures and properties on photochemical degradation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers: A TDDFT study. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Hao, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, J.; Qiu, J. Theoretical investigation on photodechlorination mechanism of polychlorinated biphenyls. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Hao, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, J.; Qiu, J. Theoretical investigations on direct photolysis mechanisms of polychlorinated diphenyl ethers. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacevic, G.; Sabljic, A. Theoretical study on the mechanism and kinetics of addition of hydroxyl radicals to fluorobenzene. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacevic, G.; Sabljic, A. Mechanisms and reaction-path dynamics of hydroxyl radical reactions with aromatic hydrocarbons: The case of chlorobenzene. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohn, W.; Becke, A.D.; Parr, R.G. Density functional theory of electronic structure. J. Chem. Phys. 1996, 100, 12974–12980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, J.; Mennucci, B.; Cammi, R. Quantum mechanical continuum solvation models. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2999–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, K.; Werschnik, J.; Gross, E.K.U. Time-dependent density functional theory: Past, present, and future. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123, 062206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.-J.; Han, K.-L. Excited state electronic structures and photochemistry of heterocyclic annulated perylene (HAP) materials tuned by heteroatoms: S, Se, N, O, C, Si, and B. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 4788–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.-J.; Han, K.-L. Hydrogen bonding in the electronic excited state. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albini, A.; Monti, S. Photophysics and photochemistry of fluoroquinolones. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2003, 32, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, K. The path of chemical reactions—The IRC approach. Acc. Chem. Res. 1981, 14, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Rev. B. 01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, Z.; Adams, C. Potentiometric determination of acid dissociation constants (pKa) for human and veterinary antibiotics. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2874–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds is not available from authors. |
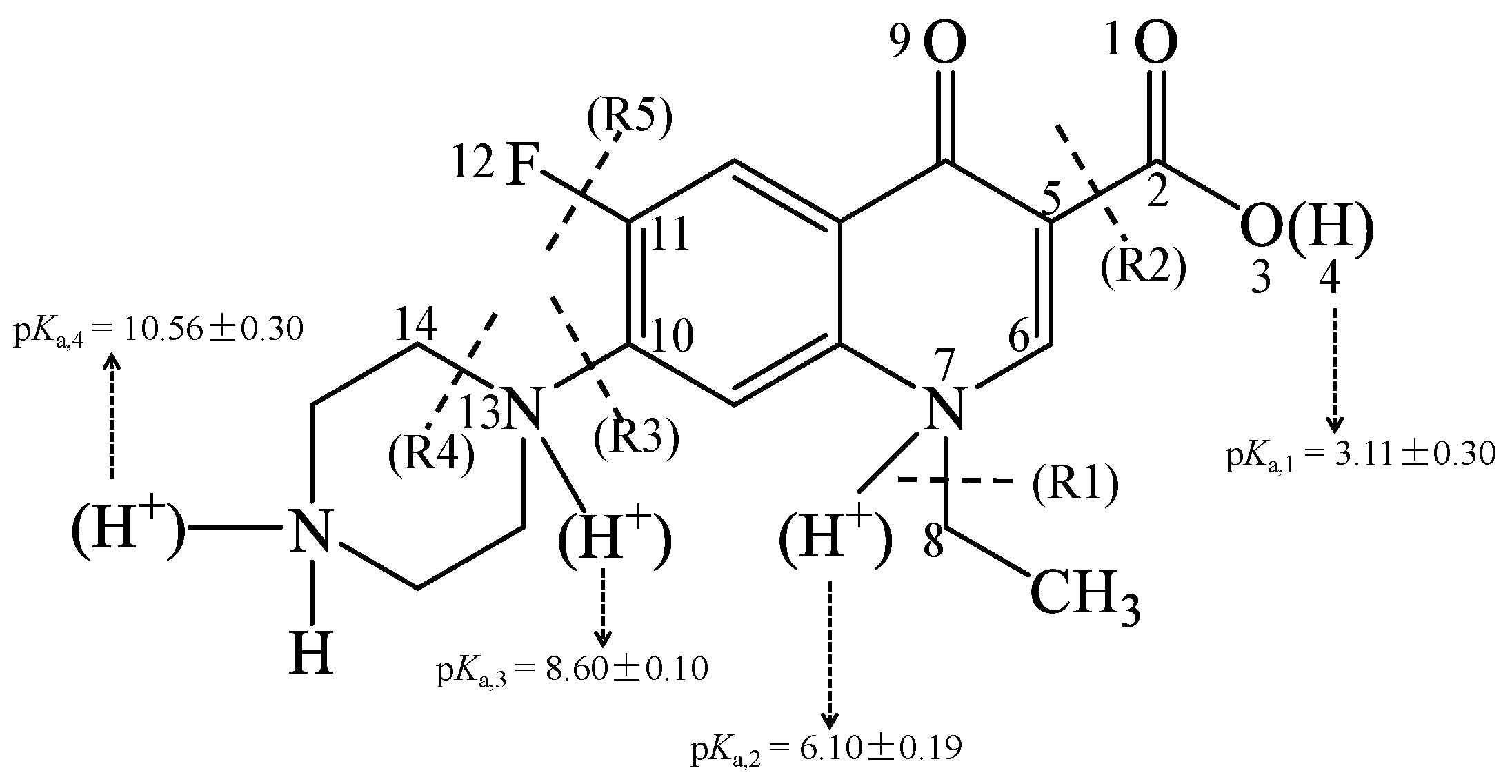



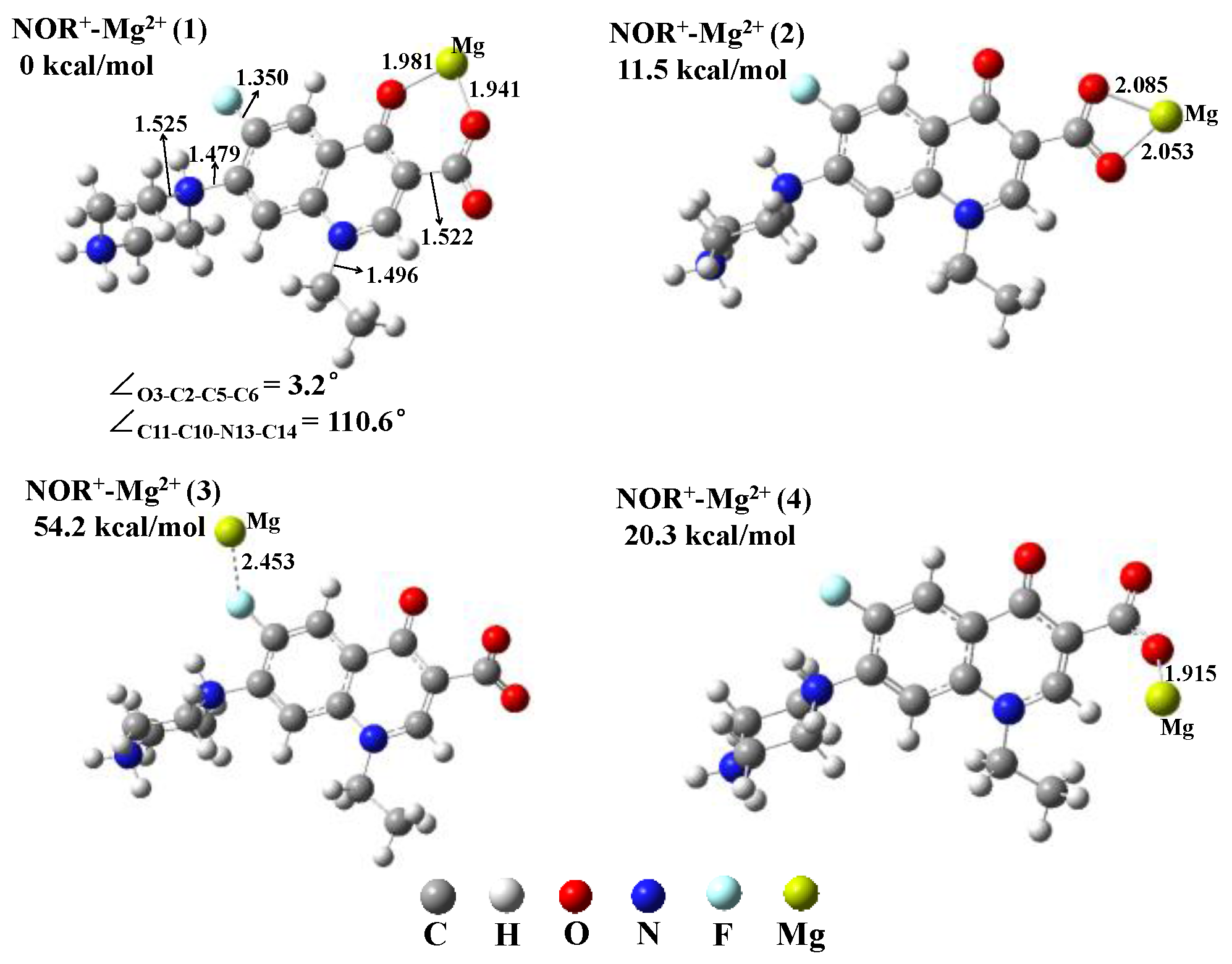
| R1 (Cleavage of N7–C8 Bond) | R2 (Cleavage of C2–C5 Bond) | R3 (Cleavage of C10–N13 Bond) | R4 (Cleavage of N13–C14 Bond) | R5 (Cleavage of C11–F12 Bond) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOR0 | 21.0 | 27.6 | 31.2 | 26.3 | - |
| NOR0-Mg2+ | 23.0 | 36.5 | 26.3 | 18.6 | - |
| NOR+ | 25.4 | 23.0 | 9.5 | 7.7 | 18.7 |
| NOR+-Mg2+ | 27.9 | 31.2 | 17.1 | 12.7 | 11.4 |
| NOR2+ | 5.4 | 8.9 | 30.0 | 20.5 | 42.5 |
| NOR2+-Mg2+ | 5.2 | 12.5 | 35.3 | 27.3 | 55.4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Elucidating Direct Photolysis Mechanisms of Different Dissociation Species of Norfloxacin in Water and Mg2+ Effects by Quantum Chemical Calculations. Molecules 2017, 22, 1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111949
Wang S, Wang Z. Elucidating Direct Photolysis Mechanisms of Different Dissociation Species of Norfloxacin in Water and Mg2+ Effects by Quantum Chemical Calculations. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111949
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Se, and Zhuang Wang. 2017. "Elucidating Direct Photolysis Mechanisms of Different Dissociation Species of Norfloxacin in Water and Mg2+ Effects by Quantum Chemical Calculations" Molecules 22, no. 11: 1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111949
APA StyleWang, S., & Wang, Z. (2017). Elucidating Direct Photolysis Mechanisms of Different Dissociation Species of Norfloxacin in Water and Mg2+ Effects by Quantum Chemical Calculations. Molecules, 22(11), 1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111949






