Design of Tail-Clamp Peptide Nucleic Acid Tethered with Azobenzene Linker for Sequence-Specific Detection of Homopurine DNA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Design of PNAs and TC-PNAs
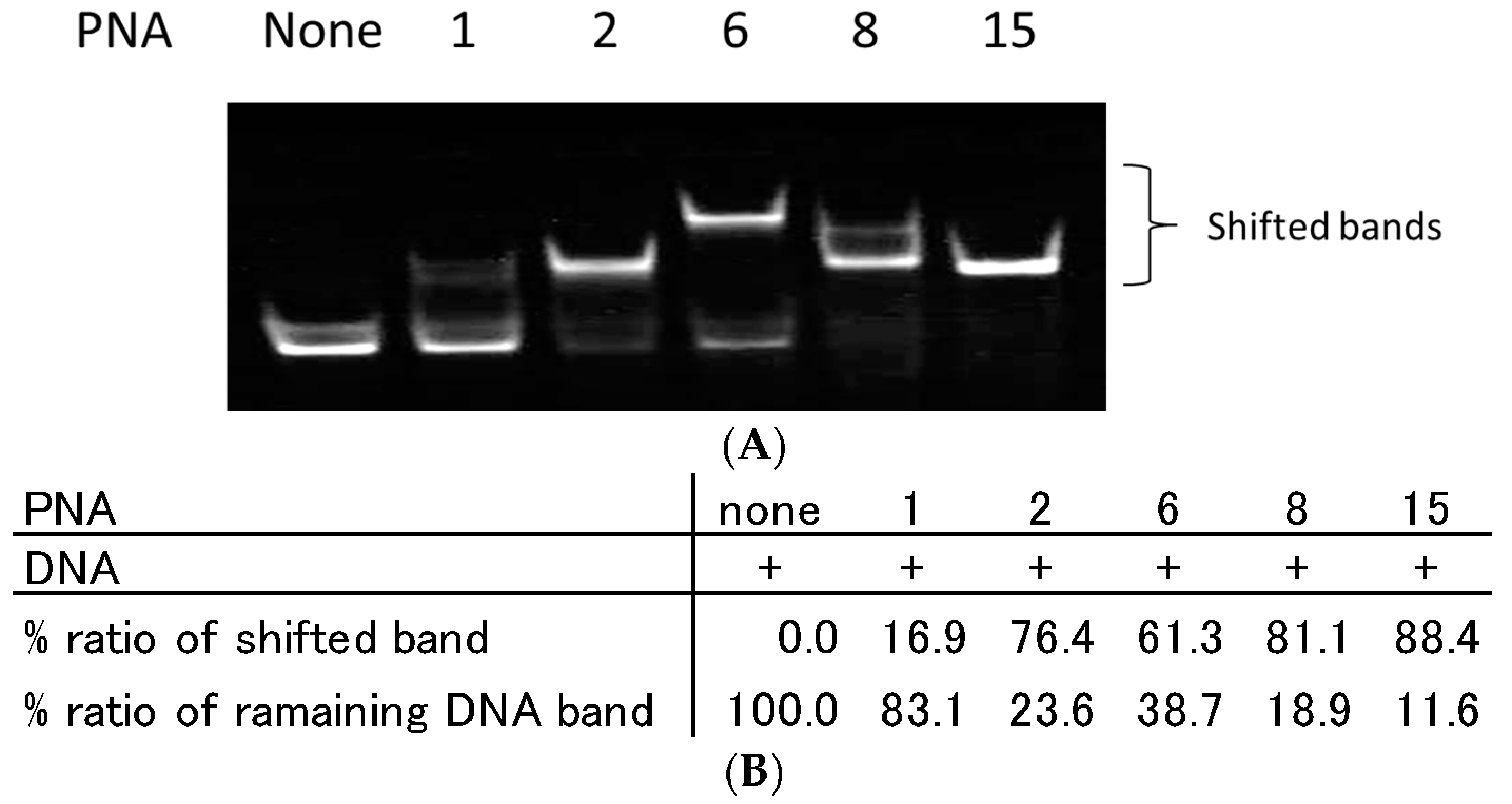
2.2. Recognition of Single Strand DNA by PNAs and TC-PNAs
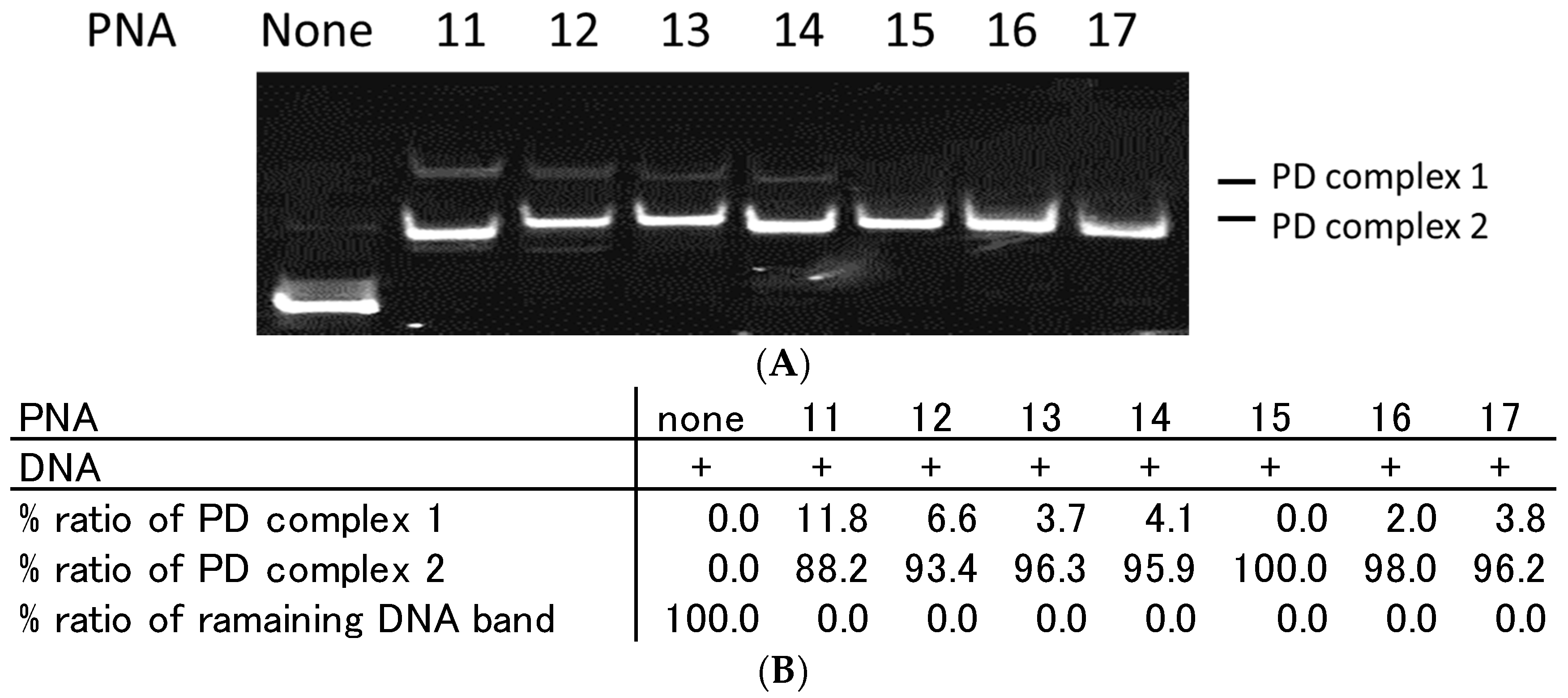
2.3. Effect of Homopyrimidine Bases of Azobenzene-Tethered PNAs on Complex Formation with Single Stranded DNA
2.4. Analysis of TC-PNA and DNA Complexes Using Nano ESI-MS
2.5. Thermal Stability of TC-PNA and ssDNA Complex
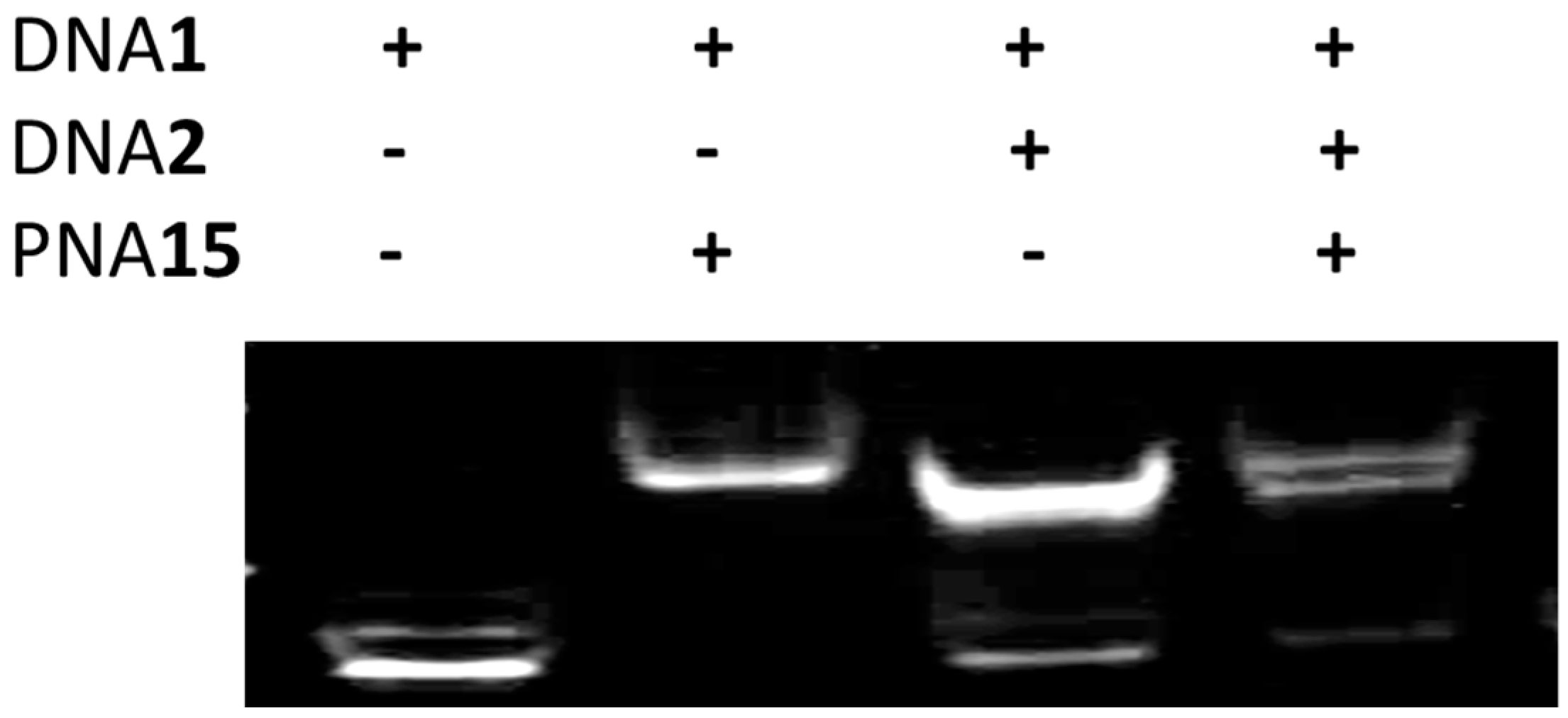
2.6. Strand Displacement of dsDNA by TC-PNA-AZO 9W5H-C4
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Fmoc-Lys-(Boc)-OH Loaded Resin
3.3. PNA Synthesis
3.4. PNA Purification and Analysis
3.5. Gel Mobility Shift Analysis of PNA/DNA Complexes
3.6. Analysis of TC-PNA/DNA Complexes Using Nano ESI-MS
3.7. Thermal Melting Analaysis of PNA/DNA and TC-PNA/DNA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEEA | Aminoethoxy-2-ethoxy acetic acid |
| BCIP | 5-Bromo-4-chloro-3′-indolylphosphatase p-toluidine salt |
| Bhoc | Benzhydryloxycarbonyl |
| Boc | Tert-butyloxycarbonyl |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| DMF | N,N-Dimethylformamide |
| Fmoc | 9-Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl |
| HBTU | 2-(1H-Benzotriazole-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate |
| HOBt | N-Hydroxybenzotriazole |
| NMM | N-Methylmorpholine |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| PNA | peptide nucleic acid |
References
- Nielsen, P.G.; Egholm, M.; Berg, R.H.; Buchardt, O. Sequence-selective recognition of DNA by strand displacement with a thymine-substituted polyamide. Science 1991, 254, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanvey, J.C.; Peffer, N.J.; Bisi, J.E.; Thomson, S.A.; Cadilla, R.; Josey, J.A.; Ricca, D.J.; Hassman, C.F.; Bonham, M.A.; Au, K.G.; et al. Antisense and antigene properties of peptide nucleic acids. Science 1992, 258, 1481–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, H.J.; Bentin, T.; Nielsen, P.E. Antisense properties of peptide nucleic acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1489, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Norden, B. Peptide nucleic acid (PNA): Its medical and biotechnical applications and promise for the future. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 1041–1060. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Egholm, M.; Buchardt, O.; Christensen, L.; Behrens, C.; Freier, S.M.; Driver, D.A.; Berg, R.H.; Kim, S.K.; Norden, B.; Nielsen, P.E. PNA hybridizes to complementary oligonucleotides obeying the Watson-Crick hydrogen-bonding rules. Nature 1993, 365, 566–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demidov, V.V.; Potaman, V.N.; Frank-Kamenetskii, M.D.; Egholm, M.; Buchard, O.; Sonnichsen, S.H.; Nielsen, P.E. Stability of peptide nucleic acids in human serum and cellular extracts. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 48, 1310–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.E.; Iyer, M.; Norton, J.C.; Corey, D.R. Specific and non-specific inhibition of RNA synthesis by DNA, PNA and phosphorothioate promoter analog duplexes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1996, 6, 2897–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherny, D.Y.; Belotserlovski, B.P.; Frank-Kamenetskii, M.D.; Egholm, M.; Buchardt, O.; Berg, R.H.; Nielsen, P.E. DNA unwinding upon strand-displacement binding of a thymine-substituted polyamide to double-stranded DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, P.E. Targeting Double Stranded DNA with Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA). Curr. Med. Chem. 2000, 8, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, H.; Demidov, V.V.; Nielsen, P.E.; Frank-Kamenetskii, M.D. An experimental study of mechanism and specificity of peptide nucleic acid (PNA) binding to duplex DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 286, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaihatsu, K.; Braasch, D.A; Cansizoglu, A.; Corey, D.R. Enhanced strand invasion by peptide nucleic acid-peptide conjugates. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 11118–11125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, H.J.; Nielsen, P.E. Transcription-mediated binding of peptide nucleic acid (PNA) to double-stranded DNA: Sequence-specific suicide transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaihatsu, K.; Shah, R.H.; Zhao, X.; Corey, D.R. Extending recognition by peptide nucleic acids (PNAs): Binding to duplex DNA and inhibition of transcription by tail-clamp PNA-Peptide conjugates. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 13996–14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleifman, E.B.; Bindra, R.; Leif, J.; del Campo, J.; Rogers, F.A.; Uchil, P.; Kutsch, O.; Shuults, L.D.; Kumar, P.; Greiner, D.L.; Glazer, P.M. Targeted disruption of the CCR5 gene in human hematopoietic stem cells stimulated by peptide nucleic acids. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahal, R.; McNeer, N.A.; Quijano, E.; Liu, Y.; Sulkowski, P.; Turchick, A.; Lu, Y.C.; Bhunia, D.C.; Manna, A.; Greiner, D.L.; et al. In vivo correction of anaemia in β-thalassemic mice by ΥPNA-mediated gene editing with nanoparticle delivery. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolina, I.; Miller, N.S.; Frank-Kamenetskii, M. PNA-based microbial pathogen identification and resistance marker detection: An accurate, isothermal rapid assay based on genome-specific features. Artif. DNA PNA XNA 2010, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, S.; Kato, N.; Kaihatsu, K. Synthesis and application of visible light sensitive azobenzene. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 2642–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaihatsu, K.; Sawada, S.; Nakamura, S.; Nakaya, T.; Yasunaga, T.; Kato, N. Sequence-specific and visual identification of the influenza virus NS gene by azobenzene-tethered bis-peptide nucleic acid. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, M.C.; Risen, L.M.; Greig, M.J.; Lesnik, E.A.; Sprankle, K.G.; Griffey, R.H.; Kiely, J.S.; Freier, S.M. Evaluation of pyrimidine PNA binding to ssDNA targets from nonequilibrium melting experiments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 831–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.I.; Bentin, T.; Larsen, H.J.; Nielsen, P.E. Structural isomers of bis-PNA to a target in duplex DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 307, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvester, N.C.; Bushell, G.R.; Searlesa, D.J.; Brown, C.L. Effect of terminal amino acids on the stability and specificity of PNA–DNA hybridisation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amodio, A.; Zhao, B.; Porchetta, A.; Idili, A.; Castronovo, M.; Fan, C.; Ricci, F. Rational design of pH-controlled DNA strand displacement. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16469–16472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available. |
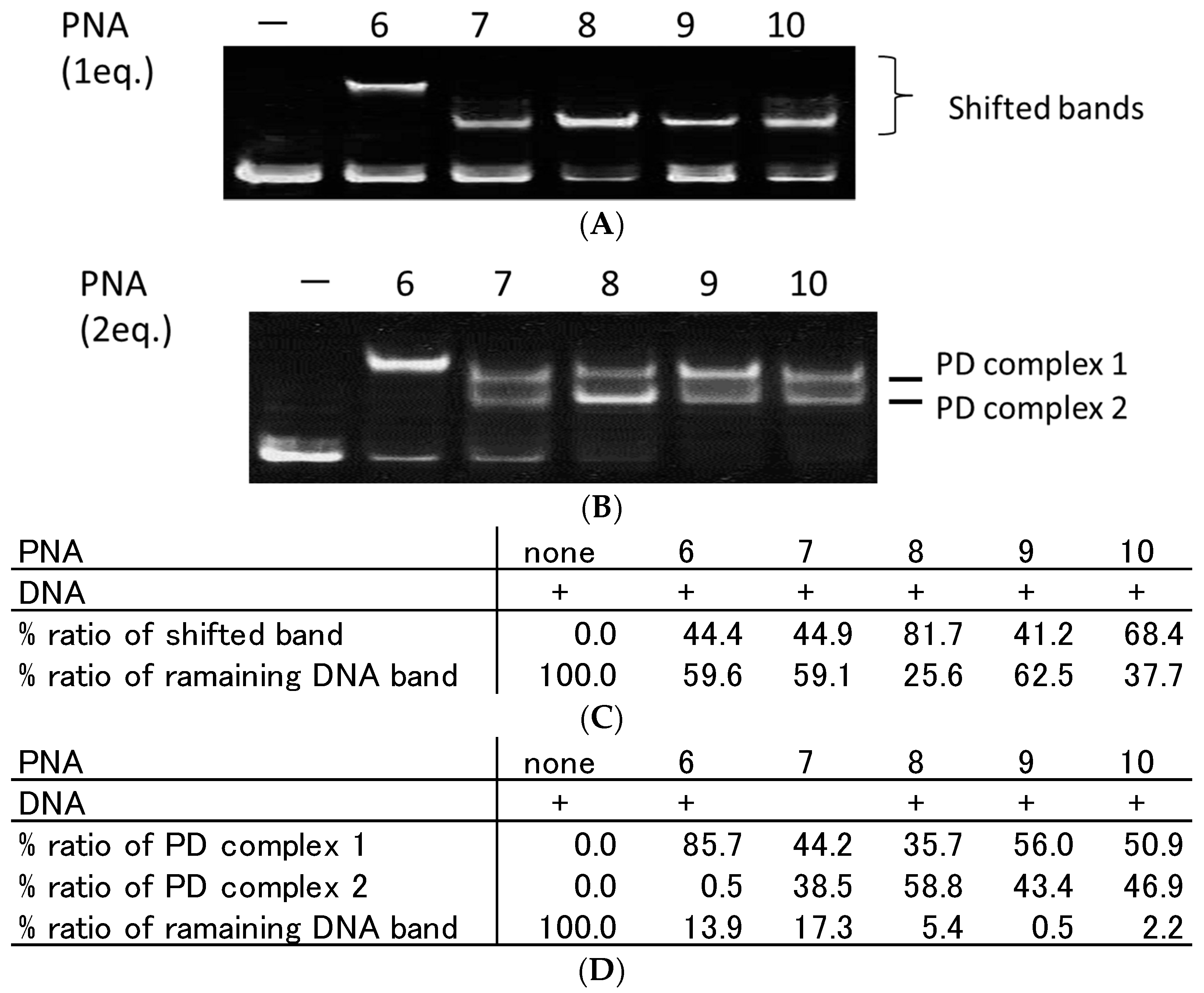



| Entry | Name | PNA Sequence (N to C)/DNA Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Mass | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcd. | Found | |||
| PNA1 | 12W | TCTCCCTTCTTT-Lys | 3266.44 | 3267.81 |
| PNA2 | 12W-C0-AZO | AZO-TCTCCCTTCTTT-Lys | 3549.80 | 3550.89 |
| PNA3 | 12W5H-(AEEA) | H-(Lys)3-CCTCT-(AEEA)-TCTCCCTTCTTT-Lys | 5082.51 | 5083.10 |
| PNA4 | 12W5H-(AEEA)2 | H-(Lys)3-CCTCT-(AEEA)2- TCTCCCTTCTTT-Lys | 5227.70 | 5228.86 |
| PNA5 | 12W5H-(AEEA)3 | H-(Lys)3-CCTCT-(AEEA)3-TCTCCCTTCTTT-Lys | 5372.80 | 5373.63 |
| PNA6 | 12W5H C0-AZO | H-(Lys)3-CCTCT-AZO-TCTCCCTTCTTT-Lys | 5220.74 | 5221.94 |
| PNA7 | 12W5H C3-AZO | H-(Lys)3-CCTCT-C3-AZO-TCTCCCTTCTTT-Lys | 5277.81 | 5278.77 |
| PNA8 | 12W5H C4-AZO | H-(Lys)3-CCTCT-C4-AZO-TCTCCCTTCTTT-Lys | 5291.82 | 5292.61 |
| PNA9 | 12W5H C5-AZO | H-(Lys)3-CCTCT-C5-AZO-TCTCCCTTCTTT-Lys | 5305.86 | 5306.59 |
| PNA10 | 12W5H C6-AZO | H-(Lys)3-CCTCT-C6-AZO-TCTCCCTTCTTT-Lys | 5319.89 | 5320.01 |
| PNA11 | 9W9H C4-AZO | H-(Lys)3-CTTCCCTCT-C4-AZO-TCTCCCTTC-Lys | 5528.17 | 5529.19 |
| PNA12 | 9W8H C4-AZO | H-(Lys)3-TTCCCTCT-C4-AZO-TCTCCCTTC-Lys | 5276.87 | 5277.21 |
| PNA13 | 9W7H C4-AZO | H-(Lys)3-TCCCTCT-C4-AZO-TCTCCCTTC-Lys | 5010.62 | 5011.17 |
| PNA14 | 9W6H C4-AZO | H-(Lys)3-CCCTCT-C4-AZO-TCTCCCTTC-Lys | 4744.37 | 4745.22 |
| PNA15 | 9W5H C4-AZO | H-(Lys)3-CCTCT-C4-AZO-TCTCCCTTC-Lys | 4493.07 | 4494.28 |
| PNA16 | 9W4H C4-AZO | H-(Lys)3-CTCT-C4-AZO-TCTCCCTTC-Lys | 4241.77 | 4242.89 |
| PNA17 | 9W3H C4-AZO | H-(Lys)3-TCT-C4-AZO-TCTCCCTTC-Lys | 3990.47 | 3991.77 |
| DNA1 | Cy3-CATCATCAAAGAAGGGAGATGGTG | 7982.50 | ||
| DNA2 | CCATCTCCCTTCTTTGATGATG | 6627.40 | ||
| DNA3 | Cy3-CATCATCAAATAAGGTAGATGGTG | 7932.40 | ||
| PNA | Name | Tm | ΔTm * | ΔTm ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12W | 68.0 | - | |
| 2 | 12W-C0-AZO | 72.9 | 4.9 | |
| 6 | 12W5H-C0-AZO | 81.5 | 13.5 | |
| 9 | 12W5H-C4-AZO | 79.3 | 11.3 | |
| 5 | 12W5H-(AEEA)3 | 86.3 | 18.3 | |
| 11 | 9W9H-C4-AZO | 79.6 | 19.9 | |
| 13 | 9W7H-C4-AZO | 74.3 | 14.6 | |
| 15 | 9W5H-C4-AZO | 68.0 | 8.3 | |
| 17 | 9W3H-C4-AZO | 59.7 | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sawada, S.; Takao, T.; Kato, N.; Kaihatsu, K. Design of Tail-Clamp Peptide Nucleic Acid Tethered with Azobenzene Linker for Sequence-Specific Detection of Homopurine DNA. Molecules 2017, 22, 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111840
Sawada S, Takao T, Kato N, Kaihatsu K. Design of Tail-Clamp Peptide Nucleic Acid Tethered with Azobenzene Linker for Sequence-Specific Detection of Homopurine DNA. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111840
Chicago/Turabian StyleSawada, Shinjiro, Toshifumi Takao, Nobuo Kato, and Kunihiro Kaihatsu. 2017. "Design of Tail-Clamp Peptide Nucleic Acid Tethered with Azobenzene Linker for Sequence-Specific Detection of Homopurine DNA" Molecules 22, no. 11: 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111840
APA StyleSawada, S., Takao, T., Kato, N., & Kaihatsu, K. (2017). Design of Tail-Clamp Peptide Nucleic Acid Tethered with Azobenzene Linker for Sequence-Specific Detection of Homopurine DNA. Molecules, 22(11), 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111840




