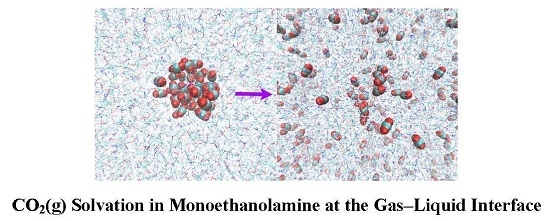
Solvation Dynamics of CO2(g) by Monoethanolamine at the Gas–Liquid Interface: A Molecular Mechanics Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Benchmark Using CO2 and (CO2)2 Models
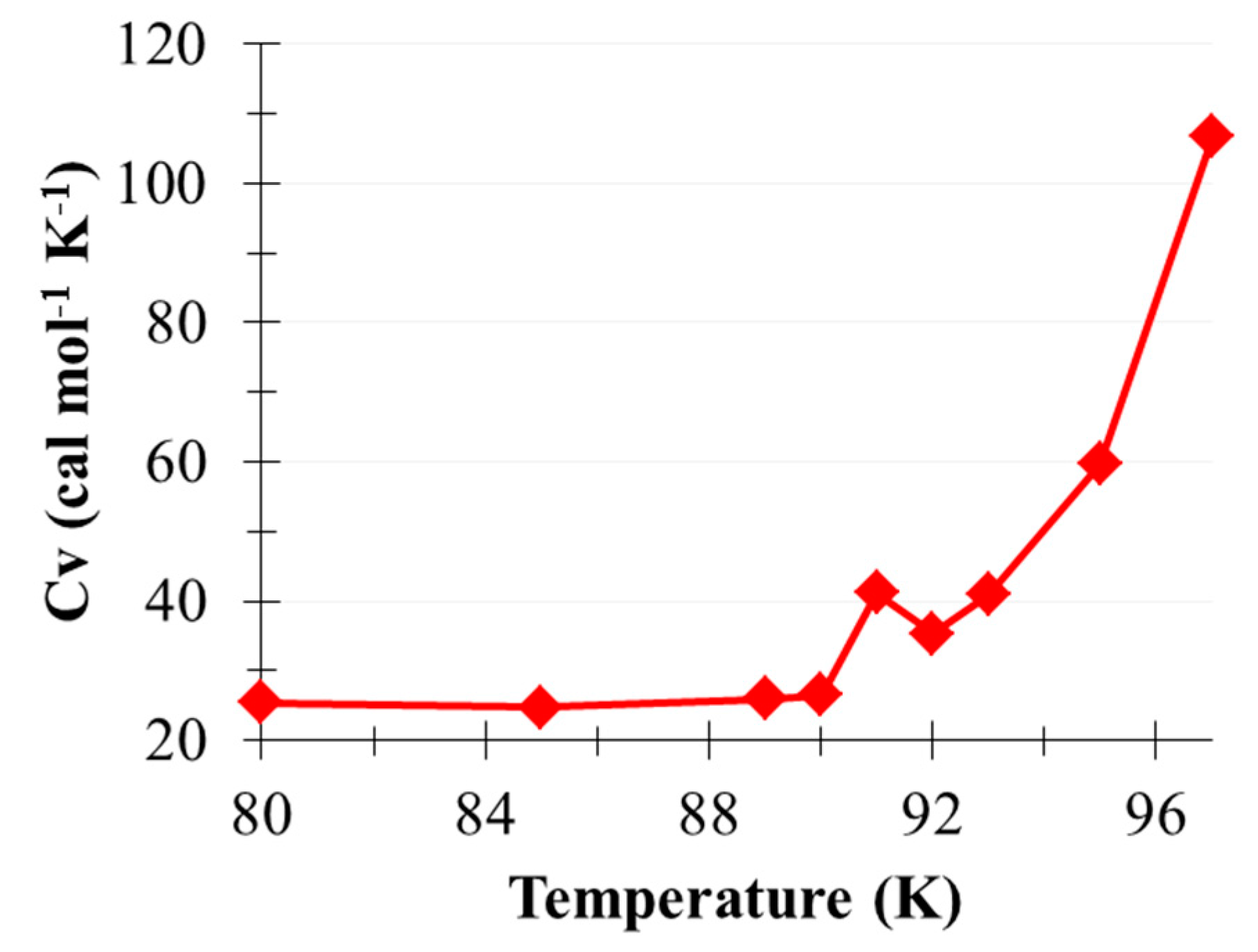
2.2. Phase Transition of (CO2)13
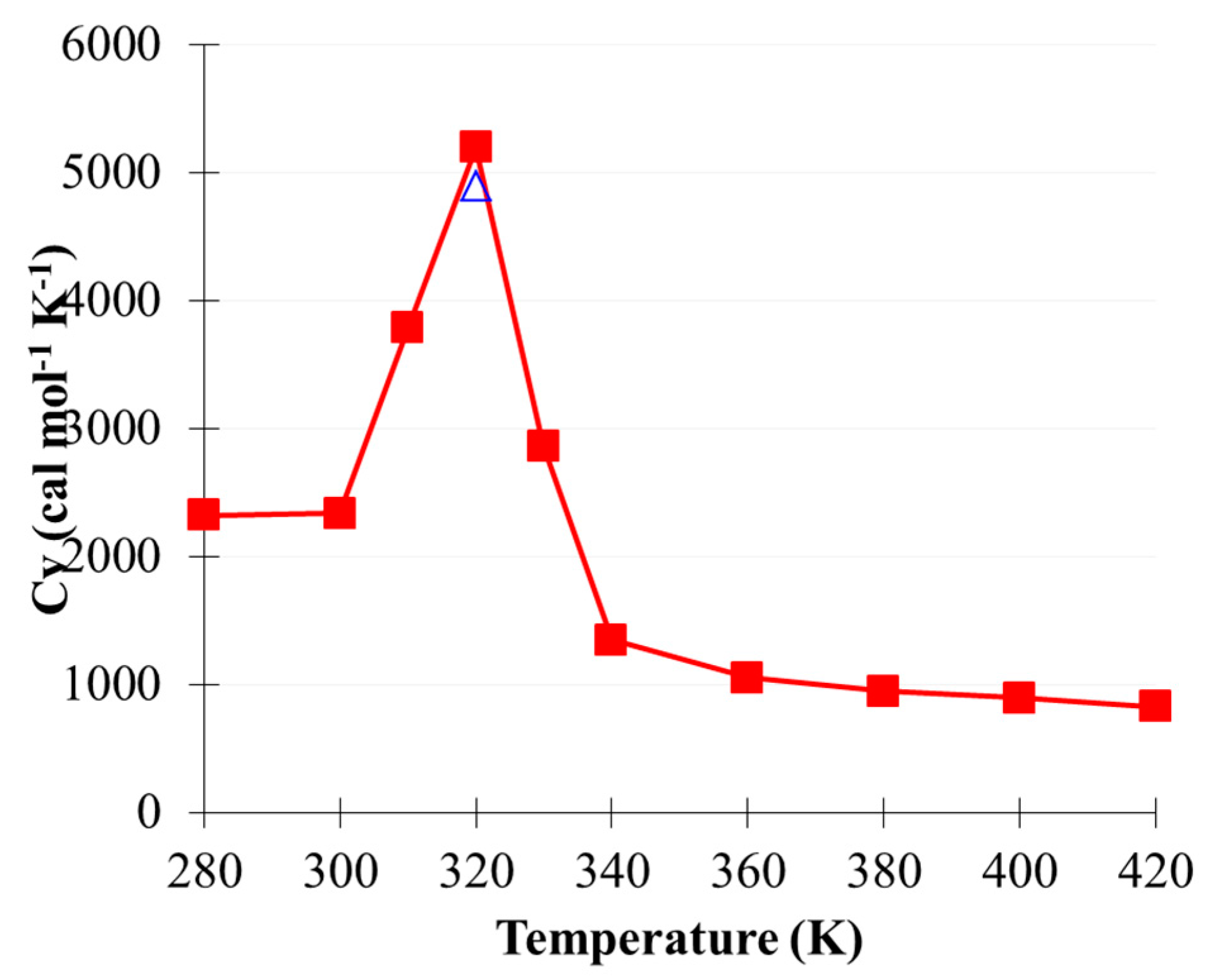
2.3. Benchmark of the MEA Potential
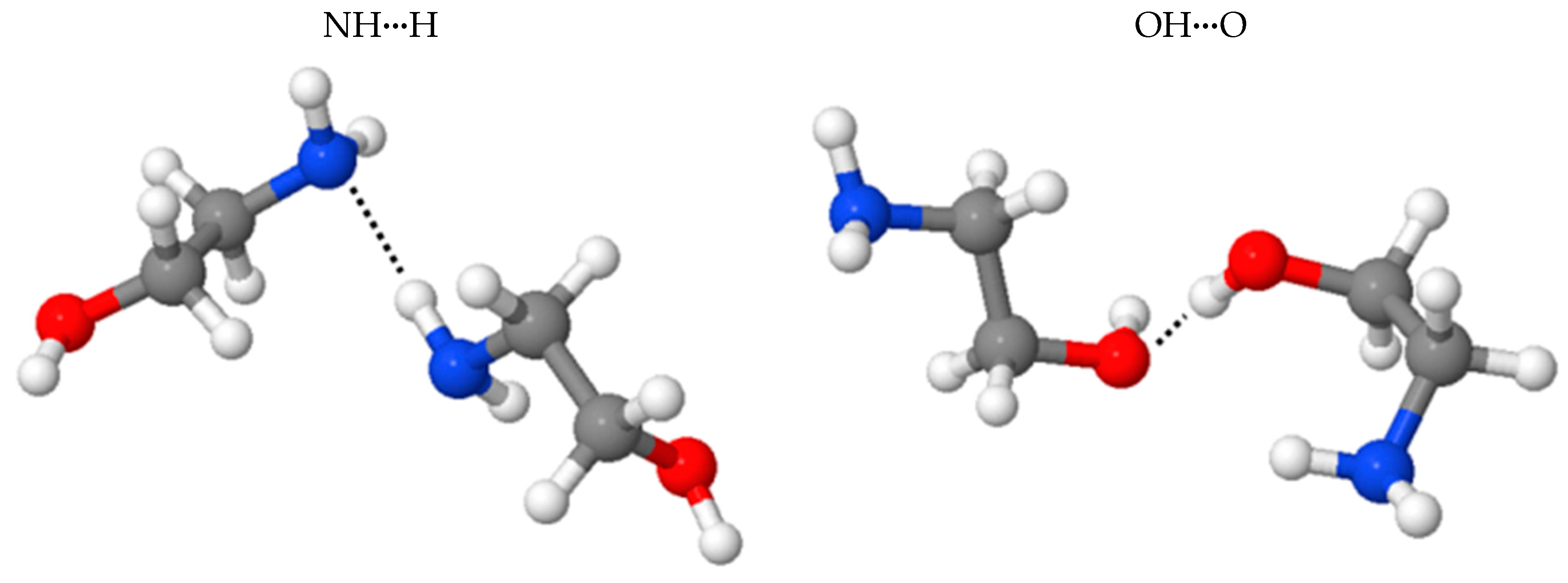
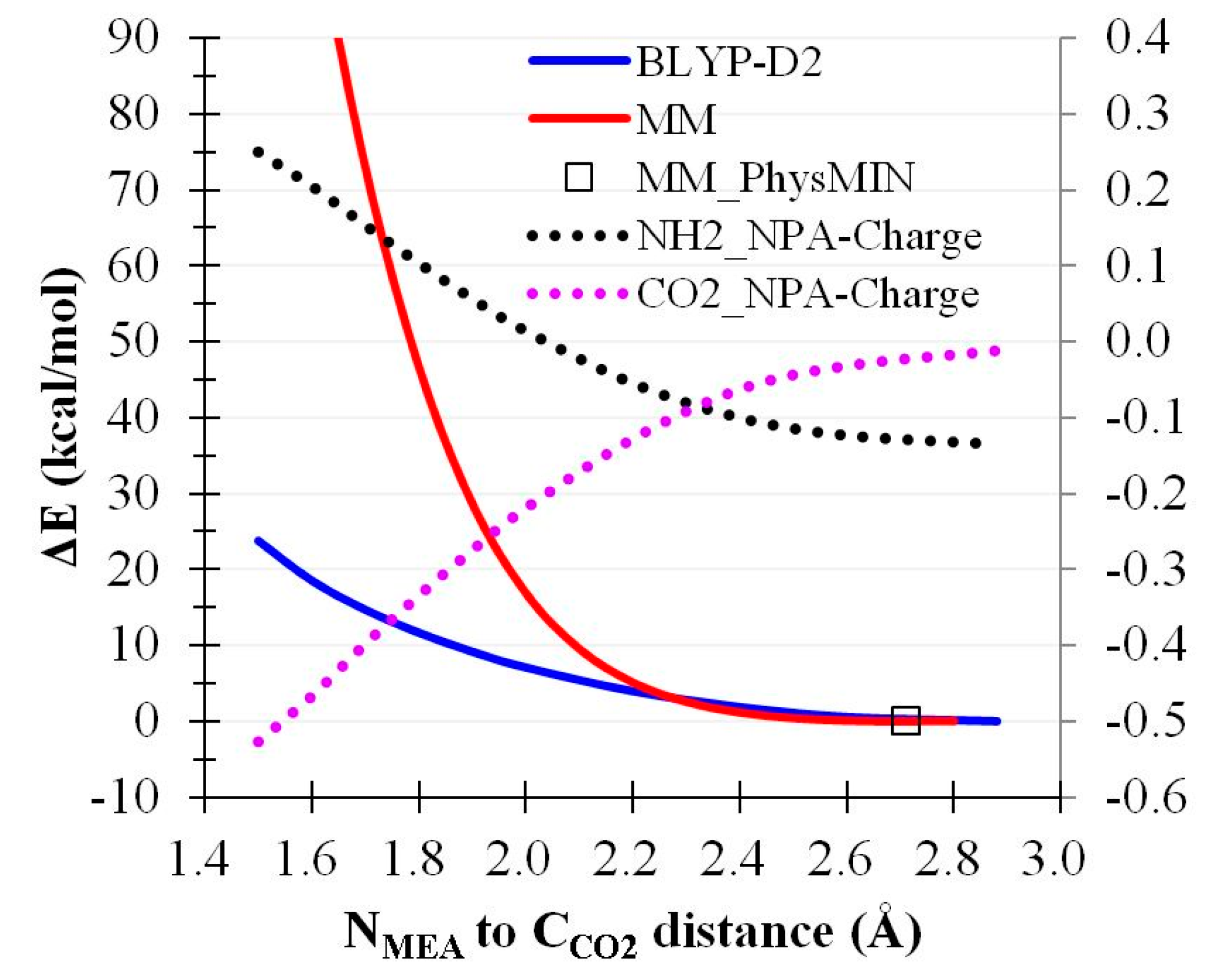
2.4. CO2 Binding Using MEA
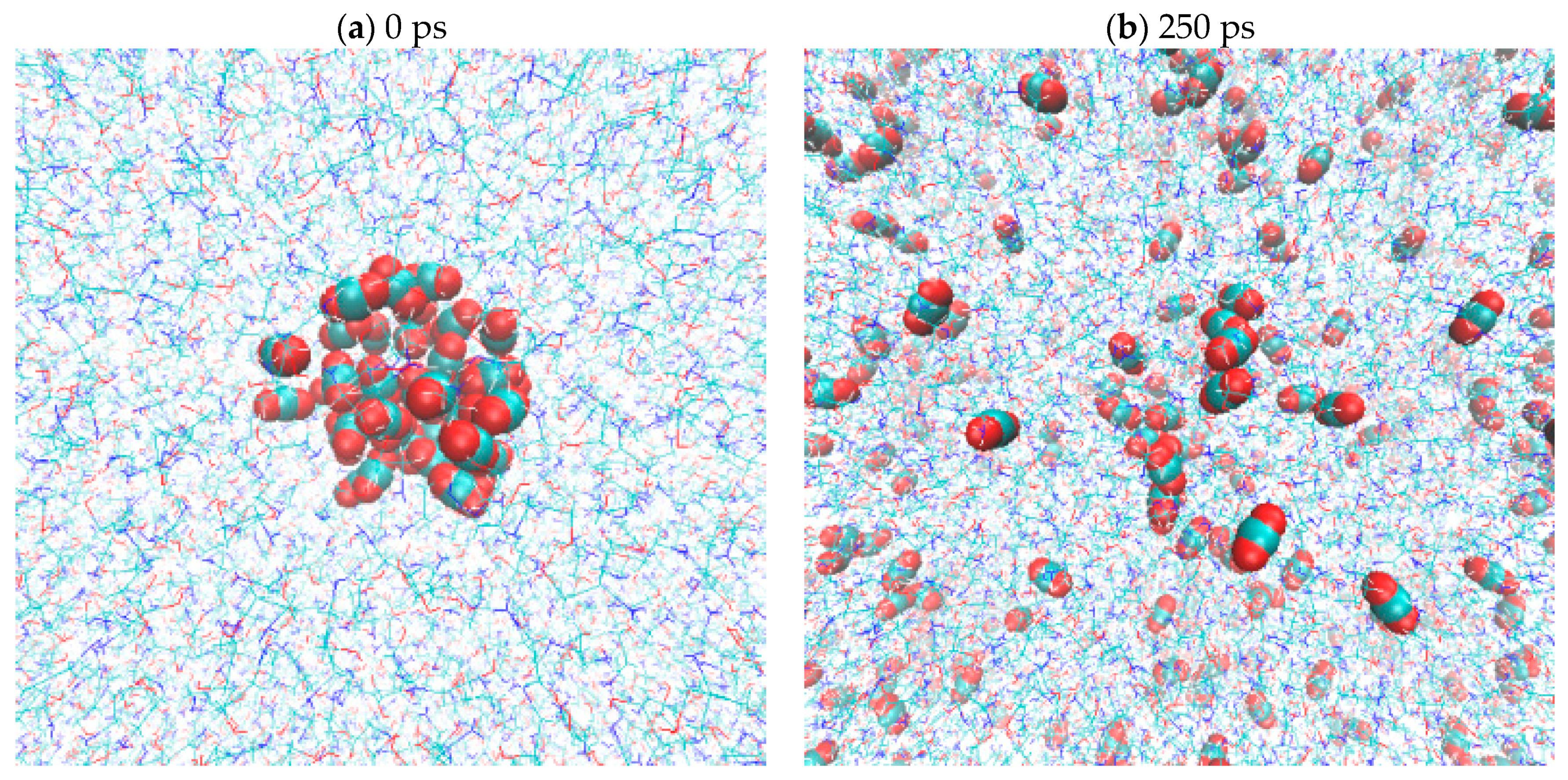
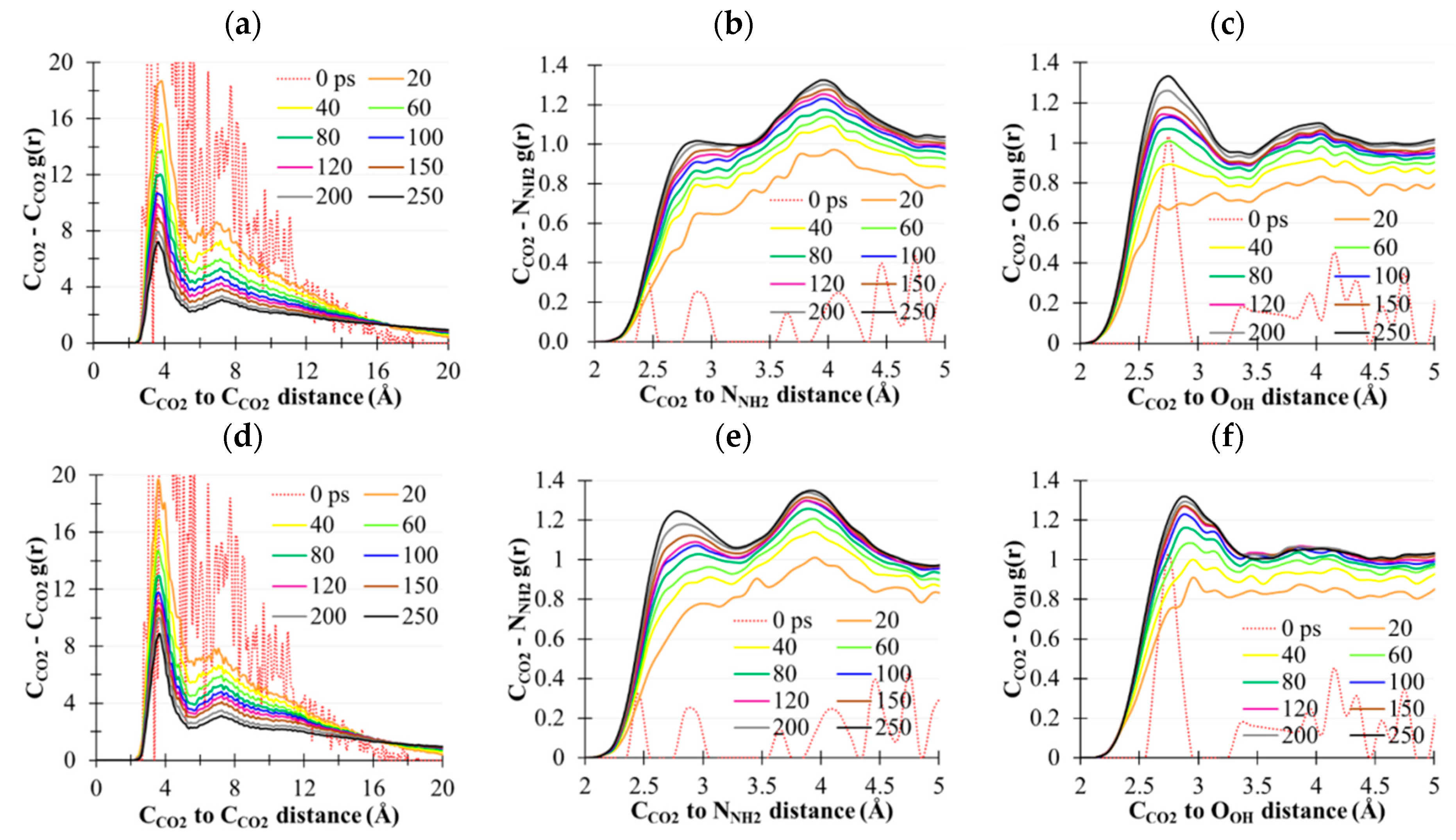
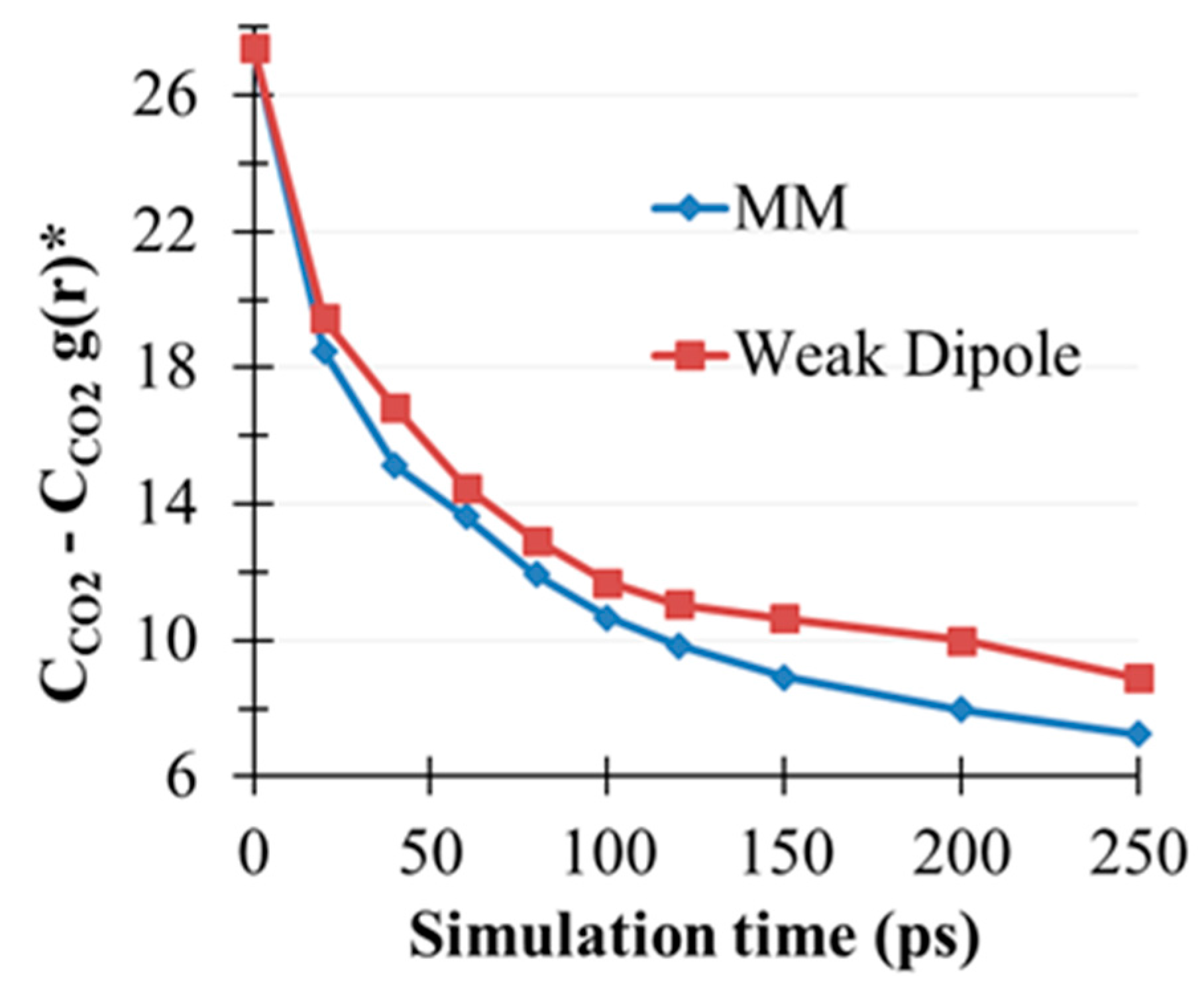
2.5. CO2(g) Dissolution by MEA(l)
3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rochelle, G.T. Amine scrubbing for CO2 capture. Science 2009, 325, 1652–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yih, S.M.; Shen, K.P. Kinetics of carbon-dioxide reaction with sterically hindered 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol aqueous-solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1988, 27, 2237–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alper, E. Reaction-mechanism and kinetics of aqueous-solutions of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol and carbon-dioxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1990, 29, 1725–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontiwachwuthikul, P.; Meisen, A.; Lim, C.J. CO2 absorption by naoh, monoethanolamine and 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol solutions in a packed column. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1992, 47, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.K.; Bandyopadhyay, S.S.; Biswas, A.K. Kinetics of aasorption of CO2 into aqueous-solutions of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1995, 50, 3587–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, B.; Sada, E. Kinetics of absorption of carbon dioxide into aqueous solutions of sterically hindered 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1996, 29, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, Y.W.; Otto, F.D.; Mather, A.E. Kinetics of the reaction of carbon dioxide with 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol solutions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1996, 51, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.J.; Hong, W.H. Effect of piperazine on the kinetics of carbon dioxide with aqueous solutions of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, C.W.; Li, M.H. Kinetics of absorption of carbon dioxide into aqueous solutions of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol plus monoethanolamine. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.P.; Bandyopadhyay, S.S. Simultaneous absorption of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide into aqueous blends of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol and diethanolamine. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 6438–6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.P.; Bandyopadhyay, S.S. Absorption of carbon dioxide into aqueous blends of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol and monoethanolamine. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 5440–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzagli, F.; Mani, F.; Peruzzini, M. A 13C nmr study of the carbon dioxide absorption and desorption equilibria by aqueous 2-aminoethanol and n-methyl-substituted 2-aminoethanol. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, W.; Wang, X.; Fernandes, D.; Burns, R.; Lawrance, G.; Puxty, G.; Maeder, M. Toward the understanding of chemical absorption processes for post-combustion capture of carbon dioxide: Electronic and steric considerations from the kinetics of reactions of CO2(aq) with sterically hindered amines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.-S.; Im, J.; Jeong, J.K.; Hong, S.Y.; Jang, H.G.; Cheong, M.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.S. CO2 absorption and desorption in an aqueous solution of heavily hindered alkanolamine: Structural elucidation of CO2-containing species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4163–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindrup, E.M.; Schneider, W.F. Computational comparison of the reactions of substituted amines with CO2. ChemSusChem 2010, 3, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.S.; Kitchin, J.R. Chemical and molecular descriptors for the reactivity of amines with CO2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 13609–13618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangarapu, S.; Marcelis, A.T.M.; Zuilhof, H. Carbamate stabilities of sterically hindered amines from quantum chemical methods: Relevance for CO2 capture. Chemphyschem 2013, 14, 3936–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-C.; Tsai, M.-K. A first-principle study of CO2 binding by monoethanolamine and mono-n-propanolamine solutions. Chem. Phys. 2015, 452, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, C.A.; Pietrucci, F.; Gallet, G.A.; Andreoni, W. The fate of a zwitterion in water from ab initio molecular dynamics: Monoethanolamine (mea)-CO2. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Sun, Y.; Fan, M.; Cheng, H. On the CO2 capture in water-free monoethanolamine solution: An ab initio molecular dynamics study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 5971–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.Q.; Dai, S.; Jiang, D.E. What can molecular simulation do for global warming? WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2016, 6, 173–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhon, Y.H.; Shim, J.G.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, K.R.; Kim, J. Nucleophilicity and accessibility calculations of alkanolamines: Applications to carbon dioxide absorption reactions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 12907–12913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgman-Cohen, S.; Giannelis, E.P.; Escobedo, F.A. Transport properties of amine/carbon dioxide reactive mixtures and implications to carbon capture technologies. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17603–17613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmahini, A.H.; Kvamme, B.; Kuznetsova, T. Molecular dynamics simulation studies of absorption in piperazine activated mdea solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 13070–13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.S.; Lu, H.F.; Wang, G.X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Rudolph, V. Characterizing the transport properties of multiamine solutions for CO2 capture by molecular dynamics simulation. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2013, 58, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Freysz, E.; Shen, Y.R. Surface vibrational spectroscopic studies of hydrogen bonding and hydrophobicity. Science 1994, 264, 826–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, I. Chemical reactions and solvation at liquid interfaces: A microscopic perspective. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 1449–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidovits, P.; Kolb, C.E.; Williams, L.R.; Jayne, J.T.; Worsnop, D.R. Mass accommodation and chemical reactions at gas-liquid interfaces. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1323–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett, B.C.; Schenter, G.K.; Morita, A. Molecular simulations of the transport of molecules across the liquid/vapor interface of water. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1355–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.K.; Yang, L.; Hayashi, M.; Zhu, C.Y.; Fujimura, Y.; Shen, Y.R.; Lin, S.H. Theory and applications of sum-frequency generations. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2014, 61, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, Y.; Ohto, T.; Backus, E.H.G.; Bonn, M. Molecular modeling of water interfaces: From molecular spectroscopy to thermodynamics. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 3785–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, A.; Neipert, C.; Space, B.; Moore, P.B. Theoretical modeling of interface specific vibrational spectroscopy: Methods and applications to aqueous interfaces. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1234–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.R.; Ostroverkhov, V. Sum-frequency vibrational spectroscopy on water interfaces: Polar orientation of water molecules at interfaces. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allinger, N.L.; Yuh, Y.H.; Lii, J.H. Molecular mechanics—The MM3 force-field for hydrocarbons.1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 8551–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allinger, N.L.; Li, F.B.; Yan, L.Q. Molecular mechanics—The MM3 force-field for alkenes. J. Comput. Chem. 1990, 11, 848–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allinger, N.L.; Rahman, M.; Lii, J.H. A molecular mechanics force-field (MM3) for alcohols and ethers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 8293–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lii, J.H.; Allinger, N.L. Molecular mechanics—The MM3 force-field for hydrocarbons. 2. Vibrational frequencies and thermodynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 8566–8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lii, J.H.; Allinger, N.L. Molecular mechanics—The MM3 force-field for hydrocarbons. 3. The vanderwaals potentials and crystal data for aliphatic and aromatic-hydrocarbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 8576–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lii, J.H.; Allinger, N.L. The MM3 force-field for amides, polypeptides and proteins. J. Comput. Chem. 1991, 12, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Akin-Ojo, O.; Pinnick, E.; Song, Y. Approaching post-hartree–fock quality potential energy surfaces with simple pair-wise expressions: Parameterising point-charge-based force fields for liquid water using the adaptive force matching method. Mol. Simul. 2011, 37, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin-Ojo, O.; Song, Y.; Wang, F. Developing ab initio quality force fields from condensed phase quantum-mechanics/molecular-mechanics calculations through the adaptive force matching method. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 064108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin-Ojo, O.; Wang, F. Improving the point-charge description of hydrogen bonds by adaptive force matching. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin-Ojo, O.; Wang, F. The quest for the best nonpolarizable water model from the adaptive force matching method. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillet, J.B.; Boutin, A.; Buttefey, S.; Calvo, F.; Fuchs, A.H. From molecular clusters to bulk matter: I. Structure and thermodynamics of small CO2, N2, and SF6 clusters. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 109, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Jordan, K.D. Finite temperature properties of (CO2)n clusters. J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 5703–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, C.S.; Oshea, S.F.; McDonald, I.R. Electrostatic interactions in molecular-crystals-lattice-dynamics of solid nitrogen and carbon-dioxide. Mol. Phys. 1983, 50, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monoethanolamine. Chemistry Webbook. Available online: http://webbook.nist.gov (accessed on 1 March 2015).
- Ponder, J.W. Tinker, Version 7.1. Available online: http://dasher.wustl.edu/tinker/ (accessed on 1 February 2015).
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional ecahcnage-energy approximation with correct asymptotic-behavior. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the colle-salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S. Semiempirical gga-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-C.; Chai, J.-D.; Tsai, M.-K. Assessment of dispersion-improved exchange-correlation functionals for the simulation of CO2 binding by alcoholamines. Int. J. Quantum. Chem. 2014, 114, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; Vangunsteren, W.F.; Dinola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecualr-dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.

| 1 Isomers | Min | Parallel | T-Type | (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 BE(BLYP-D2) | −1.06 | 0.25 | −0.77 | 636, 1302, 2310 |
| BE(BLYP) | 0.29 | 0.76 | 0.09 | |
| BE(disp) | −1.36 | −0.50 | −0.86 | |
| 2 BE(MP2) | −1.27 | −0.01 | −1.07 | 668, 1310, 2374 |
| BE(HF) | −0.05 | 0.83 | −0.16 | |
| BE(disp) | −1.22 | −0.84 | −0.91 | |
| 3 Eint(MM) | −1.23 | 0.16 | −0.92 | 629, 1240, 2374 |
| −1.00 | 0.32 | −0.70 | ||
| −0.23 | −0.15 | −0.22 |
| Isomers 3 | NHN | OHO |
|---|---|---|
| 1 BE(BLYP-D2) | −4.62 | −6.90 |
| 1 BE(BLYP) | −1.35 | −3.50 |
| 1 BE(disp) | −3.28 | −3.32 |
| 1 | −1.85 | −3.61 |
| 1 | −1.88 | −1.40 |
| 2 | −4.16 | −6.15 |
| 2 | −2.17 | −4.33 |
| 2 | −1.99 | −1.82 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, I.-S.; Li, J.-J.; Tsai, M.-K. Solvation Dynamics of CO2(g) by Monoethanolamine at the Gas–Liquid Interface: A Molecular Mechanics Approach. Molecules 2017, 22, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010008
Huang I-S, Li J-J, Tsai M-K. Solvation Dynamics of CO2(g) by Monoethanolamine at the Gas–Liquid Interface: A Molecular Mechanics Approach. Molecules. 2017; 22(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, I-Shou, Jia-Jen Li, and Ming-Kang Tsai. 2017. "Solvation Dynamics of CO2(g) by Monoethanolamine at the Gas–Liquid Interface: A Molecular Mechanics Approach" Molecules 22, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010008
APA StyleHuang, I.-S., Li, J.-J., & Tsai, M.-K. (2017). Solvation Dynamics of CO2(g) by Monoethanolamine at the Gas–Liquid Interface: A Molecular Mechanics Approach. Molecules, 22(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010008