Serum Interleukin-34 Levels Are Elevated in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Study Subjects
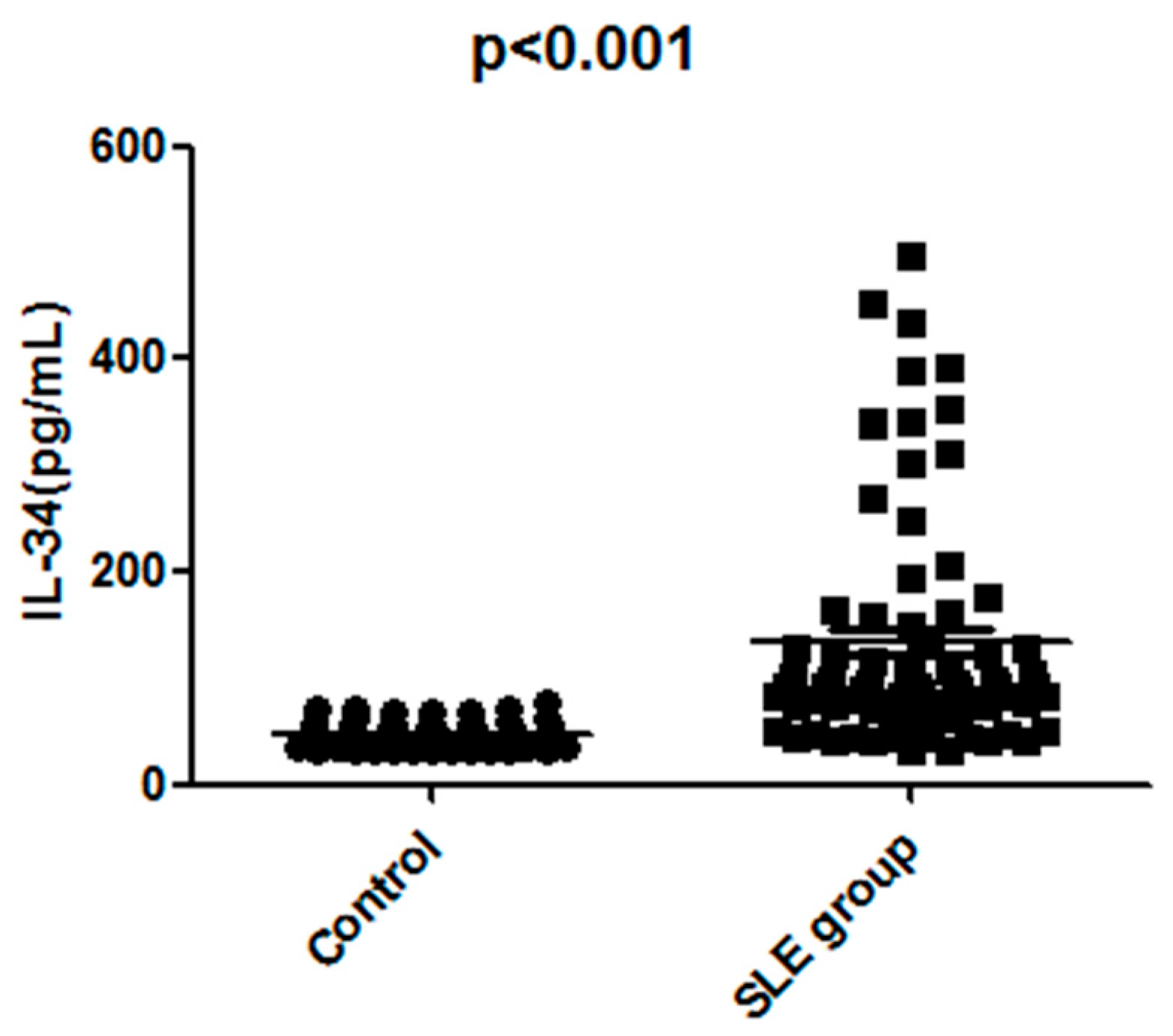
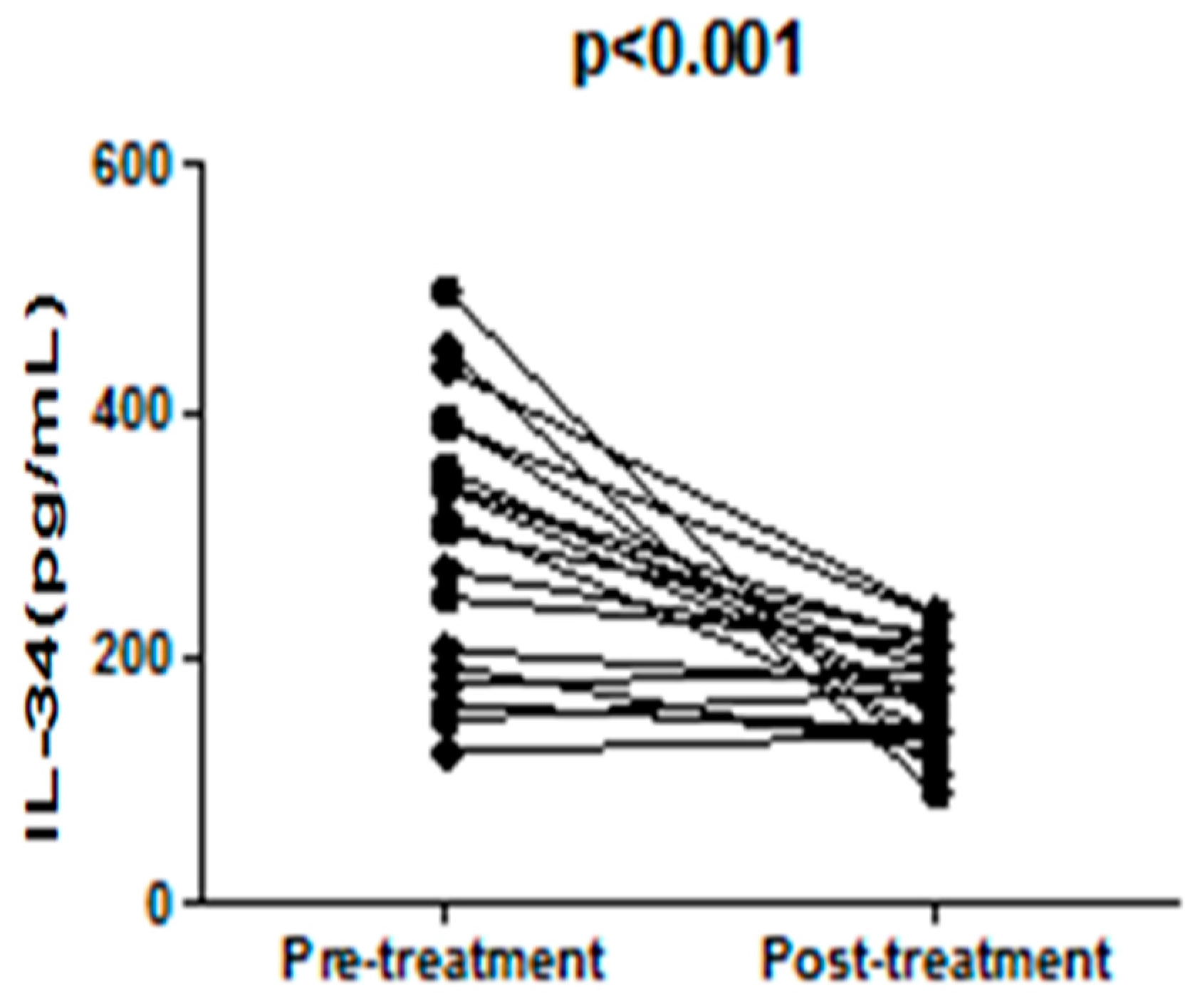
2.2. The Serum IL-34 Levels Were Elevated in Patients with SLE
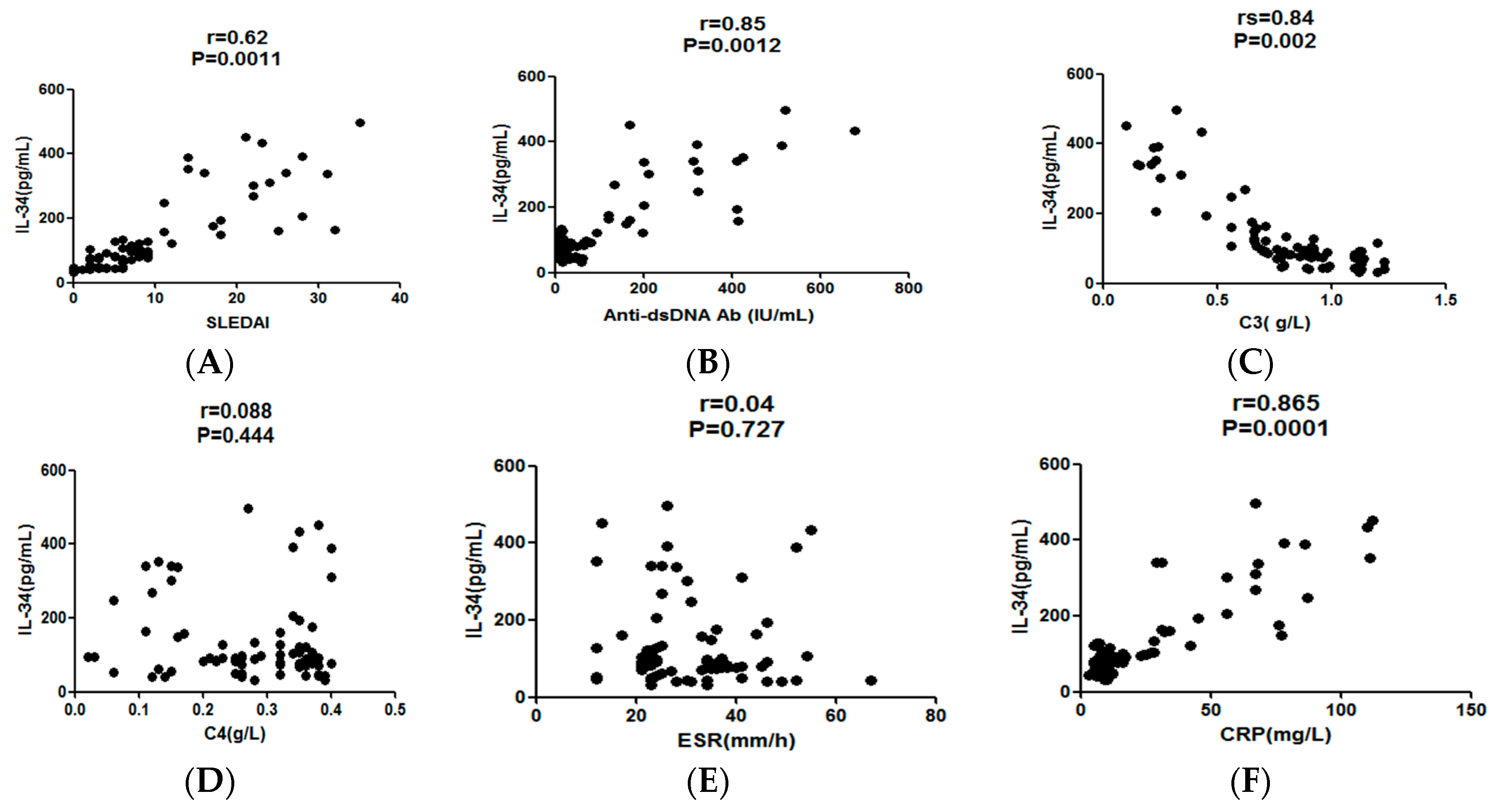
2.3. The Serum IL-34 Levels in SLE Patients Correlated with Disease Activities
2.4. The High Titers of Serum IL-34 Were Associated with the Accumulation of the Clinical Features of SLE
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Data Collection
4.3. Methods of Measurements
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakamichi, Y.; Udagawa, N.; Takahashi, N. IL-34 and CSF-1: Similarities and differences. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2013, 31, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzin, B.L. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell 1996, 85, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisnevskaia, L.; Murphy, G.; Isenberg, D. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 2014, 384, 1878–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihara, T.; Suzu, S.; Hassan, R.; Chutiwitoonchai, N.; Hiyoshi, M.; Motoyoshi, K.; Kimura, F.; Okada, S. IL-34 and M-CSF share the receptor Fms but are not identical in biological activity and signal activation. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Lee, E.; Hestir, K.; Leo, C.; Huang, M.; Bosch, E.; Halenbeck, R.; Wu, G.; Zhou, A.; Behrens, D.; et al. Discovery of a cytokine and its receptor by functional screening of the extracellular proteome. Science 2008, 320, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Buki, K.; Vaaraniemi, J.; Gu, G.; Vaananen, H.K. The critical role of IL-34 in osteoclastogenesis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.J.; Lee, S.K.; Song, Y.S.; Jang, Y.J.; Park, H.S.; Hong, J.P.; Ko, A.R.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; et al. IL-34 is associated with obesity, chronic inflammation, and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1263–E1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masteller, E.L.; Wong, B.R. Targeting IL-34 in chronic inflammation. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 1212–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.P.; Wu, X.S.; Xie, Y.Y.; Dai, B.B.; Hu, W.; Ge, J.F.; Chen, F.H. Functions of interleukin-34 and its emerging association with rheumatoid arthritis. Immunology 2016, 149, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bombardier, C.; Gladman, D.D.; Urowitz, M.B.; Caron, D.; Chang, C.H. Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1992, 35, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Leo, C.; Chen, X.; Wong, B.R.; Williams, L.T.; Lin, H.; He, X. The mechanism of shared but distinct CSF-1R signaling by the non-homologous cytokines IL-34 and CSF-1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1824, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, J.; Elegheert, J.; Gutsche, I.; Shkumatov, A.V.; Wen, Y.; Bracke, N.; Pannecoucke, E.; Vandenberghe, I.; Devreese, B.; Svergun, D.I.; et al. Human IL-34 and CSF-1 establish structurally similar extracellular assemblies with their common hematopoietic receptor. Structure 2013, 21, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Lin, W.Y.; Chen, Y.; Stawicki, S.; Mukhyala, K.; Wu, Y.; Martin, F.; Bazan, J.F.; Starovasnik, M.A. Structural basis for the dual recognition of helical cytokines IL-34 and CSF-1 by CSF-1R. Structure 2012, 20, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, S.; Cioce, M.; Yeung, Y.G.; Nieves, E.; Tesfa, L.; Lin, H.; Hsu, A.W.; Halenbeck, R.; Cheng, H.Y.; Gokhan, S.; et al. Receptor-type protein-tyrosine phosphatase zeta is a functional receptor for interleukin-34. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21972–21986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segaliny, A.I.; Brion, R.; Mortier, E.; Maillasson, M.; Cherel, M.; Jacques, Y.; Le Goff, B.; Heymann, D. Syndecan-1 regulates the biological activities of interleukin-34. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, J.A.; Tak, P.P. The dynamics of macrophage lineage populations in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1210–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eda, H.; Zhang, J.; Keith, R.H.; Michener, M.; Beidler, D.R.; Monahan, J.B. Macrophage-colony stimulating factor and interleukin-34 induce chemokines in human whole blood. Cytokine 2010, 52, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccia, F.; Alessandro, R.; Rodolico, V.; Guggino, G.; Raimondo, S.; Guarnotta, C.; Giardina, A.; Sireci, G.; Campisi, G.; de Leo, G.; et al. IL-34 is overexpressed in the inflamed salivary glands of patients with Sjogren’s syndrome and is associated with the local expansion of pro-inflammatory CD14(bright)CD16+ monocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2013, 52, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethunaickan, R.; Berthier, C.C.; Zhang, W.; Kretzler, M.; Davidson, A. Comparative transcriptional profiling of 3 murine models of SLE nephritis reveals both unique and shared regulatory networks. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, F.; Perricone, C.; Massaro, L.; Cipriano, E.; Alessandri, C.; Spinelli, F.R.; Valesini, G.; Conti, F. Assessment of disease activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Lights and shadows. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Av Wang, Y.; Szretter, K.J.; Vermi, W.; Gilfillan, S.; Rossini, C.; Cella, M.; Barrow, A.D.; Diamond, M.S.; Colonna, M. IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, M.C. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.

| Features | Healthy Controls (n = 53) Mean (95% Confidence Interval) | SLE Group (n = 78) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years (edian (IQ range)) | 57.6 (45.5–66.1) | 55.2 (48.1–66.7) |
| Male/female | 6/47 | 9/69 |
| Disease duration, years (median (IQ range)) | No | 7 (3.6–12.1) |
| Anti-dsDNA Ab, IU/mL (median (IQ range)) | 14 (9–22) | 30.1 (7.9–678) * |
| IL-34, pg/mL (median (IQ range)) | 41.2 (31.3–77) | 91.3 (32.1–498.4) * |
| ESR, mm/h (median (IQ range)) | 7 (5–15) | 26 (12.0–67.0) * |
| CRP, mg/L (median (IQ range)) | <9 | 11.0 (3.0–112.0) * |
| C3, g/L (median (IQ range)) | 1.21 (0.79–1.32) | 0.8 (0.1–1.23) * |
| C4, g/L (median (IQ range)) | 0.25 (0.21–0.38) | 0.32 (0.02–0.4) * |
| Clinical Features | Number | Median IL-34 (95% Confidence Interval) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 14 | 43 (30.1–50.3) * |
| 1–2 | 44 | 124.2 (50.5–202.4) * |
| 3–8 | 20 | 312.0 (193.5–498.4) * |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Cao, J.; Lai, X. Serum Interleukin-34 Levels Are Elevated in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Molecules 2017, 22, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010035
Wang H, Cao J, Lai X. Serum Interleukin-34 Levels Are Elevated in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Molecules. 2017; 22(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hongxu, Ju Cao, and Xiaofei Lai. 2017. "Serum Interleukin-34 Levels Are Elevated in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" Molecules 22, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010035
APA StyleWang, H., Cao, J., & Lai, X. (2017). Serum Interleukin-34 Levels Are Elevated in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Molecules, 22(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010035





