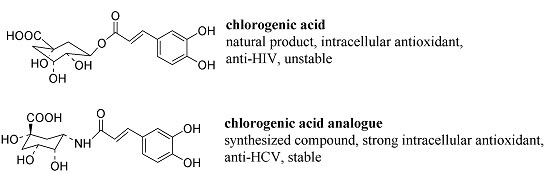
Synthesis, Anti-HCV, Antioxidant and Reduction of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Generation of a Chlorogenic Acid Analogue with an Amide Bond Replacing the Ester Bond †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
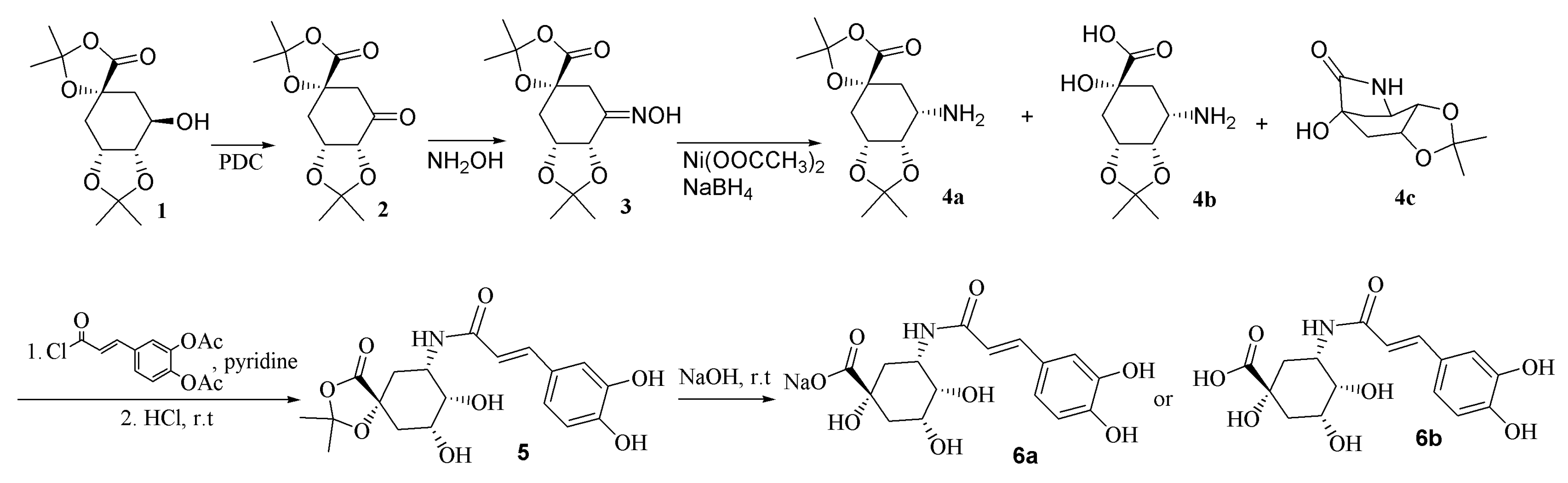
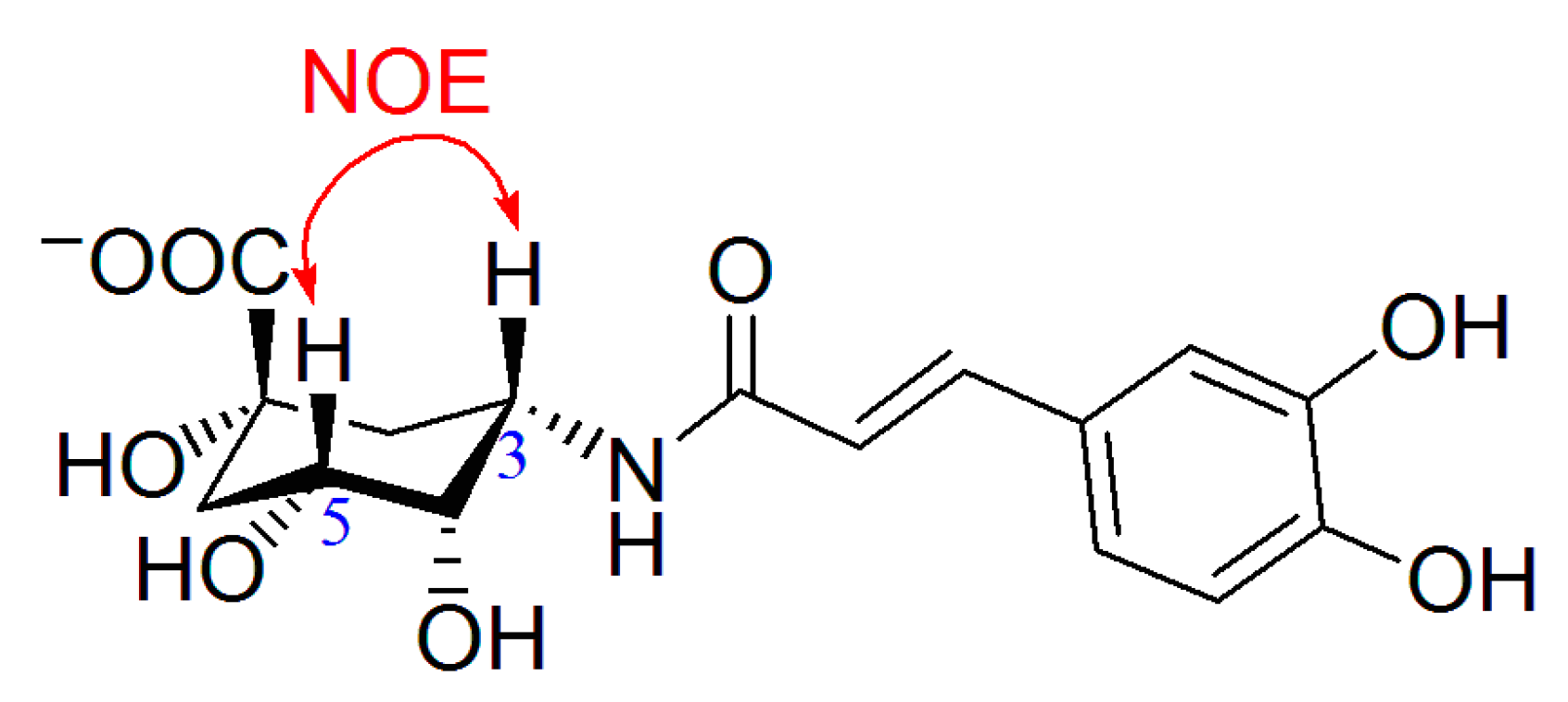
2.1. Synthesis of 5α-Caffeoylquinic Acid Amide
2.2. Antioxidant Activity
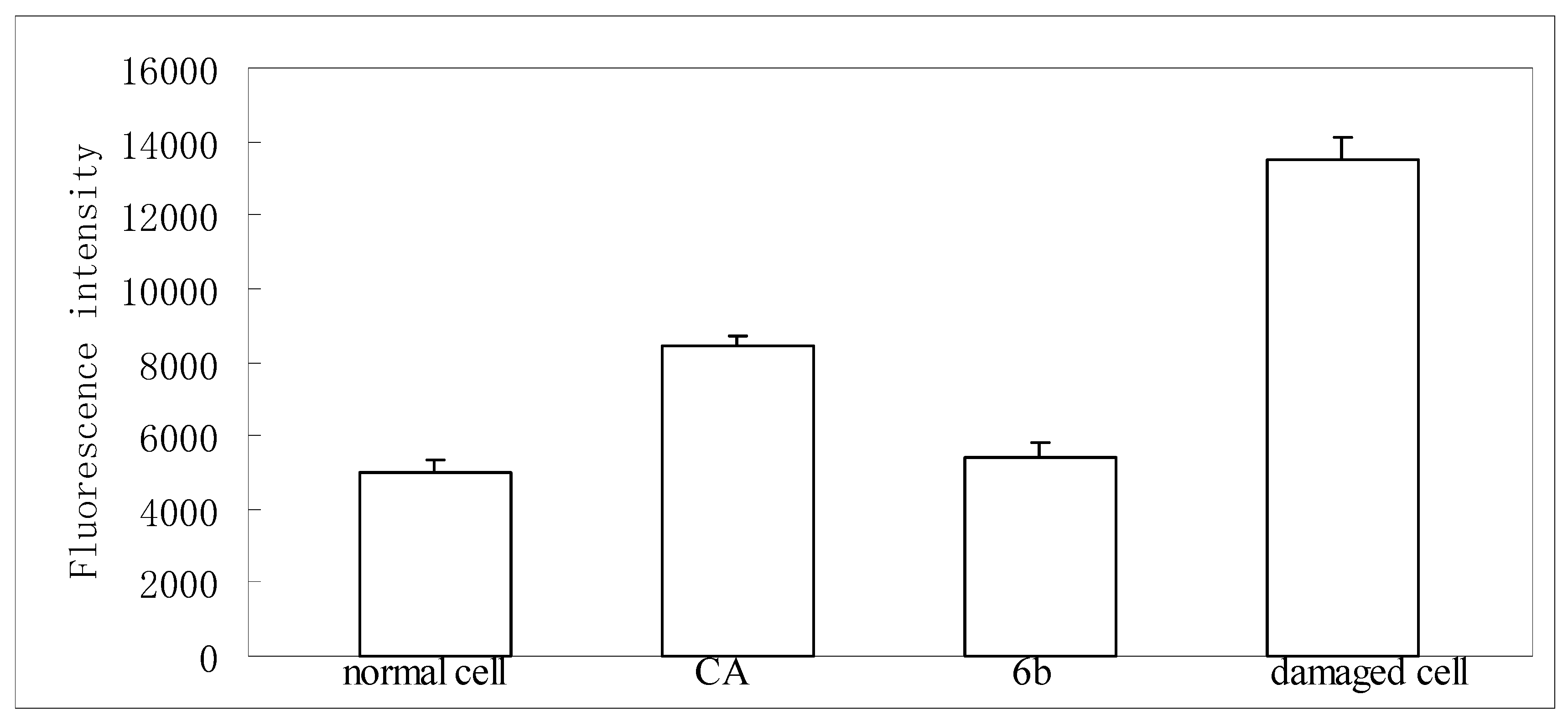
2.3. Protection on HepG2 against t-BuOOH Induced Oxidative Stress
2.4. Anti-HCV Activity
2.5. Toxicity on Brine Shrimps
2.6. Stability of Chlorogenic Acid and 5α-Caffeoylquinic Acid Amide
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Apparatus
3.2. Chemical Synthesis
3.3. Spectral Data
3.4. Measurement of Radical Scavenging Activity and Superoxide Dismutase (SOD)-Like Activity
3.5. Test for Anti-HCV Activity
3.6. Assay of the Toxicity on Brine Shrimps
3.7. Cell Culture and Cytotoxic Assay
3.8. Determination of ROS Formation in HepG2 Cells
3.9. Stability Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clifford, M.N. Chlorogenic acids and other cinnamates-nature, occurrence and dietary burden. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, K.L.; Clifford, M.N.; Morgan, L.M. Coffee acutely modifies gastrointestinal hormone secretion and glucose tolerance in humans: Glycemic effects of chlorogenic acid and caffeine. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 728–733. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, L.W.; Caccettah, R.A.-A.; Puddey, I.B.; Croft, K.D. Chemistry and biological effects of dietary phenolic compounds: Relevance to cardiovascular disease. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2000, 27, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jassim, S.A.A.; Naji, M.A. Novel antiviral agents: A medicinal plant perspective. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Wang, S.T.; Ren, J.; Camer, D.; Hua, Y.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Xue, D.L.; Zhang, X.F.; et al. Chlorogenic acid protects d-galactose-induced liver and kidney injury via antioxidation and anti-inflammation effects in mice. Pharm. Boil. 2016, 1, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, L.X.; Zhou, J.W.; Liu, Y.J.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, J.L.; Deng, J.G. Chlorogenic acid induces apoptosis to inhibit inflammatory proliferation of IL-6-induced fibroblast-like synoviocytes through modulating the activation of JAK/STAT and NF-kappa B signaling pathways. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 5, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.Q.; Wang, Y.T.; Wei, J.X.; Lu, X.M. Beneficial effects of Chlorogenic acid on alcohol-induced damage in PC12 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 4, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopia Committee. Chinese Pharmacopia; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 205–206. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, P.W.; Below, P.; Hemmerle, H.; Burger, H.-J.; Screedhara, S.; Arion, W.J.; Efendic, S.; Herling, A.W. Identification of two new inhibitors of hepatic glucose-6-phosphate translocase. Drug Dev. Res. 1998, 44, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmerle, H.; Burger, H.J.; Below, P.; Schubert, G.; Rippel, R.; Schindler, P.W.; Paulus, E.; Herling, A.W. Chlorogenic acid and synthetic chlorogenic acid derivatives: Novel inhibitors of hepatic glucose-6-phosphate translocase. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, D.; Herling, A.W.; Hemmerle, H.; Schubert, G.; Hagenbuch, B.; Burger, H.J. Hepatic uptake of synthetic chlorogenic acid derivatives by the organic anion transportproteins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 296, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.M.; Kully, M.; Khan, J.K.; Hattori, M.; Daneshtalab, M. Synthesis of chlorogenic acid derivatives with promising antifungal activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 6830–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.M.; Hattori, M.; Daneshtalab, M.; Wang, L. Chlorogenic acid derivatives with alkyl chains of different lengths and orientations: Potent α-glucosidase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 6188–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sefkow, M. First efficient synthesis of chlorogenic acid. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 6, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardini, M.; Cirillo, E.; Natella, F.; Scaccini, C. Absorption of phenolic acids in humans after coffee consumption. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2002, 50, 5735–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafay, S.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Manach, C.; Morand, C.; Besson, C.; Scalbert, A. Chlorogenic acid is absorbed in its intact form in the stomach of rats. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.M.; Abe, T.; Komiyama, T.; Wang, W.; Hattori, M.; Daneshtalab, M. Synthesis, anti-fungal and 1,3-β-d-glucan synthase inhibitory activities of caffeic and quinic acid derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 7009–7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.A. Foye’s Principles of Medicinal Chemistry; Lemke, T.L., Williams, D.A., Roche, V.F., Zito, S.W., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadephia, PA, USA, 2008; pp. 284–285. [Google Scholar]
- Kehrer, J.P. Free radicals as mediators of tissue injury anddisease. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1993, 23, 21–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyslop, P.A.; Hinshaw, D.B.; Halsey, W.A.; Schraufstatter, I.U.; Sauerheber, R.D.; Spragg, R.G.; Jackson, J.H.; Cochrane, C.G. Mechanisms of oxidant-mediated cell injury. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 1665–1675. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alía, M.; Ramos, S.; Mateos, R.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L. Response of the antioxidant defense system to t-Butyl hydroperoxide and hydrogen peroxide in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2). J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2005, 19, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.H.; Liu, M.M.; Zhong, D.W.; Zhu, Y.L.; Bosscher, M.; Zhou, L.; Ye, D.Y.; Yuan, Z.H. Tetrazole and triazole as bioisosteres of carboxylic acid: Discovery of diketotetrazoles and diketotriazoles as anti-HCV agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4528–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.M.; Zhou, L.; He, P.L.; Zhang, Y.N.; Zhou, J.Y.; Shen, Q.; Chen, X.W.; Zuo, J.P.; Li, W.; Ye, D.Y. Discovery of flavonoid derivatives as anti-HCV agents via pharmacophore search combining molecular docking strategy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 52, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.M.; Kawahata, T.; Hattori, M.; Otake, T.; Wang, L.; Daneshtalab, M. Synthesis, anti-HIV and anti-oxidant activities of caffeoyl 5,6-anhydroquinic acid derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.N.; Wang, S.L.; Zhang, K.; Wu, Z.G.; Hattori, M.; Chen, G.L.; Ma, C.M. Chemical components and antioxidant activity of the peels of commercial apple-shaped pear (fruit of Pyrus pyrifolia cv. pingguoli). J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C1097–C1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alía, M.; Ramos, S.; Mateos, R.; Granado-Serrano, A.B.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L. Quercetin protects human hepatoma HepG2 against oxidative stress induced by tert-butyl hydroperoxide. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 212, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of compounds 1, 2, 3, 6a and 6b are available from the authors.
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.-N.; Wang, W.; Hattori, M.; Daneshtalab, M.; Ma, C.-M. Synthesis, Anti-HCV, Antioxidant and Reduction of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Generation of a Chlorogenic Acid Analogue with an Amide Bond Replacing the Ester Bond. Molecules 2016, 21, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060737
Wang L-N, Wang W, Hattori M, Daneshtalab M, Ma C-M. Synthesis, Anti-HCV, Antioxidant and Reduction of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Generation of a Chlorogenic Acid Analogue with an Amide Bond Replacing the Ester Bond. Molecules. 2016; 21(6):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060737
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ling-Na, Wei Wang, Masao Hattori, Mohsen Daneshtalab, and Chao-Mei Ma. 2016. "Synthesis, Anti-HCV, Antioxidant and Reduction of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Generation of a Chlorogenic Acid Analogue with an Amide Bond Replacing the Ester Bond" Molecules 21, no. 6: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060737
APA StyleWang, L.-N., Wang, W., Hattori, M., Daneshtalab, M., & Ma, C.-M. (2016). Synthesis, Anti-HCV, Antioxidant and Reduction of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Generation of a Chlorogenic Acid Analogue with an Amide Bond Replacing the Ester Bond. Molecules, 21(6), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060737