Abstract
The aim of this work was to synthesize selected thiophene-derived aminophosphonic systems and evaluate the phytotoxicity of newly obtained products according to the OECD 208 Guideline. Seven new thiophene-derived N-substituted dimethyl aminomethylphosphonic acid esters 2a–h were synthesized by the addition of an appropriate phosphite to azomethine bond of starting Schiff bases 1a–h, and NMR spectroscopic properties of aminophosphonates were investigated. These eight compounds were analyzed in regard to their phytotoxicity towards two plants, radish (Raphanus sativus) and oat (Avena sativa). On the basis of the obtained results, it was found that tested aminophosphonates 2a–h showed an ecotoxicological impact against selected plants, albeit to various degrees.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, since production of food in agricultural areas is in the phase of intensive growth, the use of herbicides is absolutely necessary to manipulate or control undesirable vegetation of plants. Herbicides are used in landscapes throughout all over the world and are generally accepted as a moderately safe compounds. However, widespread use or overdosage of herbicides over long periods of time can result in residues in crops, soil, and land waters and, as a consequence, may lead to health and environmental risks [1,2,3,4]. Permanent applications of a given herbicide can result in resistance of a weed to the agent. Consequently, the weeds, while becoming resistant will not respond to the herbicide’s active properties [5,6]. With this respect, there is a necessity of designing new compounds with potential herbicidal properties.
Sulfur-containing compounds, which have been developed as agrochemicals for plant protection, are currently being reviewed from the standpoint of their use and biological properties in each field of fungicides, insecticides, or herbicides [7,8,9].
Sulfur-containing herbicides are successfully and widely used as a foliar (applied to weed foliage) and a soil-applied herbicide absorbed by the root or shoot of emerging seedlings.
Biodegradability, photodegradation, persistence, soil mobility, and the accumulation in living organisms of sulfur-containing herbicides are currently in extensive research phases [10,11,12,13,14].
Designing new sulfur-containing compounds with potential herbicidal activity in soil, their persistence in soil must be taken into consideration. On the one side, herbicides, which are applied to the soil, typically affect seed emergence or the growth of weed seedlings and must remain in the soil to be effective. Unfortunately, on the other side, some herbicides like thifensulfuron-methyl can persist in the environment for a long time, becoming harmful agents for the surrounding environment. Therefore, planning the synthesis, it is difficult to strike a balance between the activity of a compound and its biodegradability in soil [15].
Biological properties of thiophene-deriving aminophosphonates have been largely studied [16,17,18,19,20]. Scientists found several of them to be promising plant protection agents [16] or to have rather strong antimicrobial [17], cytotoxic [18], antifungal [19,20], or even antiviral [20] properties. Therefore, working on new variations of methods for synthesis of aminophosphonic systems, chemists include derivatives bearing thiophene moiety as examples [17,21,22,23,24,25,26]. It is to stress that all those methodologies are mostly based on the Kabachnik–Fields reaction [27,28,29].
Working on our large project aimed at the search of a new class of herbicidal agents, we feel obliged to perform tests of phytotoxicity of newly synthesized compounds, especially when these compounds are aminophosphonic derivatives, which are known generally to have moderate-to-strong phytotoxic action on higher plants [30,31,32,33].
Our previous investigation provided results demonstrating that aminophosphonic acids bearing furfuryl moiety (derivatives of C-furfurylphosphonoglycine) are compounds of moderate phytotoxicity being able to kill both monocotyledonous oat (Avena sativa) and dicotyledonous radish (Raphanus sativus) with an amount of 100–200 mg in 1 kg of soil [34].
The presented research is concerned with a screening test of a synthesized series of variously N-substituted dimethyl amino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonates (2a–g) and dibenzyl N-furfurylamino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2h) with respect to their phytotoxic properties. Our assumption was that the potential hazard of thiophene-derived aminophosphonates is important enough in the light of their possible applications and therefore should be investigated.
Apart from that, we performed the preliminary evaluation of aminophosphonates 2a–h as potential soil-applied herbicides for agricultural/horticultural purposes. The potential effects of herbicides strongly results from their mechanism of action and the way they are applied. Since some types of herbicides are non-selective, which means the chemicals kill all classes of plants, not only unwanted weeds, for the proposed experiment, but also two types of plants (mono- and dicotyledonous) have been chosen as experimental objects.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
Schiff bases 1a–h were synthesized following the published and commonly known procedure of simple mixing thiophene-2-carboxaldehyde with appropriate amine in methanol and stirring them at room temperature for 24 h [35]. This procedure produced imines 1a–h, which were isolated and used for further conversions without any purification. 1H-NMR spectra were made only to verify the identity, based on the 1H-NMR diagnostic singlet of a proton of the azomethine group (–CH=N–) above 8 ppm [31,32].
Aminophosphonates 2a–h were synthesized basing on the aza-Pudovik reaction—a slightly modified procedure of a dimethyl or dibenzyl phosphite addition to the azomethine bond of corresponding Schiff bases 1a–h in boiling toluene for 5 h. After the workup described in Section 3, the resulting aminophosphonates 2a–h were obtained in 60%–70% yields (Scheme 1).
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of thiophene-derived aminophosphonates 2a–h.
2.2. Evaluation of Phytotoxicity of Aminophosphonates 2a–h
The rate of growth and development of plants as well as their quality, including increased number and size of leaves and stems, is strongly dependent (as commonly known) on the ground composition. Since plants have a high amount of water, its level depends on the contents of water in its environment, so taking dry mass as a measure of plant growth seems to be more credible.
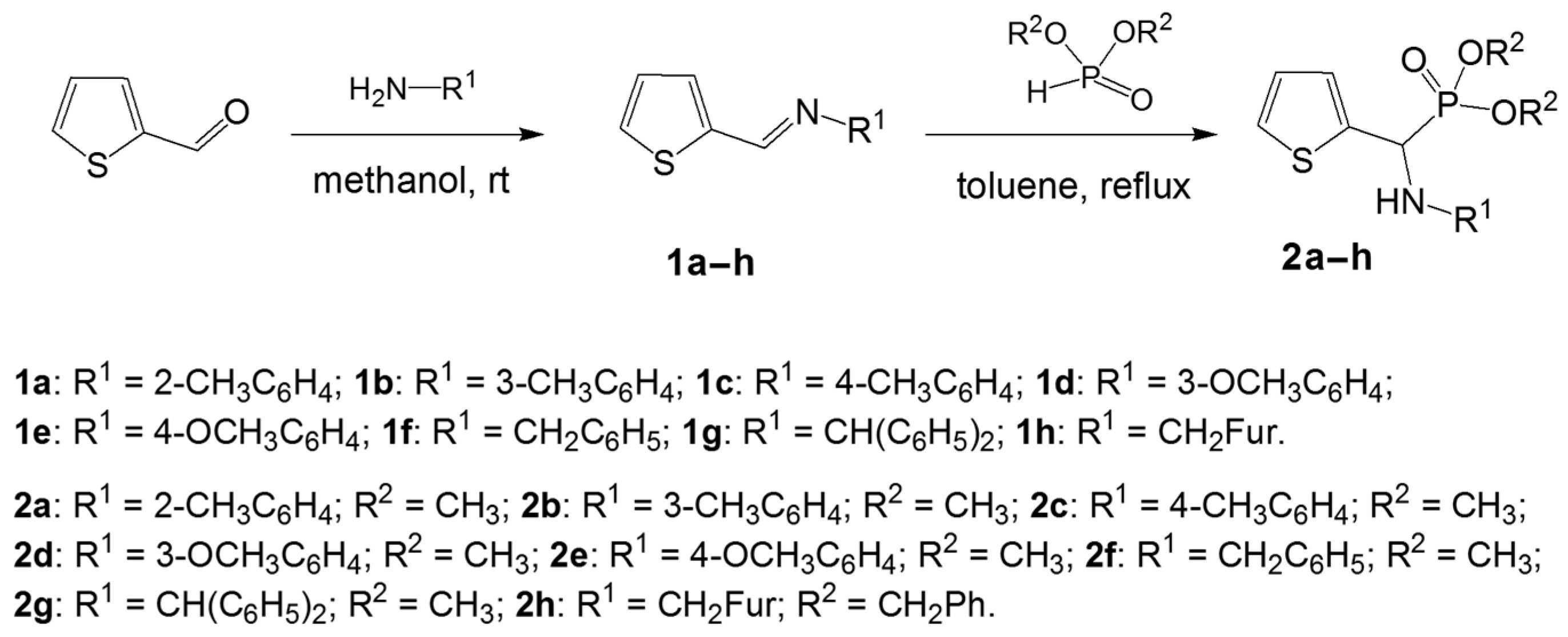
Water content is given as a percentage of the dry or fresh weight. To assess the phytotoxicity of the analyzed compounds, the emergence and weight (dry and green) of control plant seedlings, with the emergence and mass (dry and green) of plant seedlings growing on the soil with a given admixture of the examined substances 2a–h, were determined and compared. Dry weight changes of tested plants are shown in Figure 1. The visual assessment of any damage of tested plants concerns mainly the degree of plant growth inhibition, which is evaluated by visible or other signs of necrosis of chlorosis. Necrosis is the symptom of the death of plant tissues or organs caused by infection. Leaf and/or stem deformation may also be observed, while chlorosis is an inhibition of chlorophyll biosynthesis, resulting in yellowing of tissue.
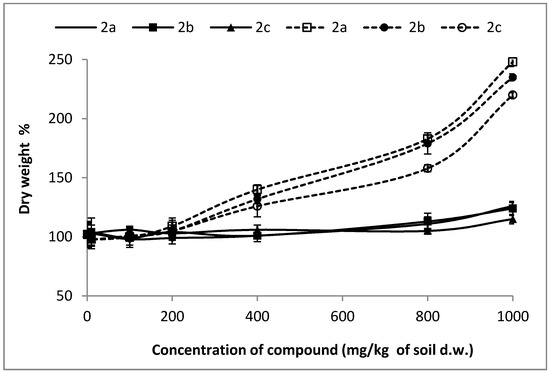
Figure 1.
Changes of dry weight of treated plants expressed as percent to the value in untreated plants (control plants = 100% of dry weight). Solid lines represent changes of oat dry weight. Dotted lines represent changes of radish dry weight.
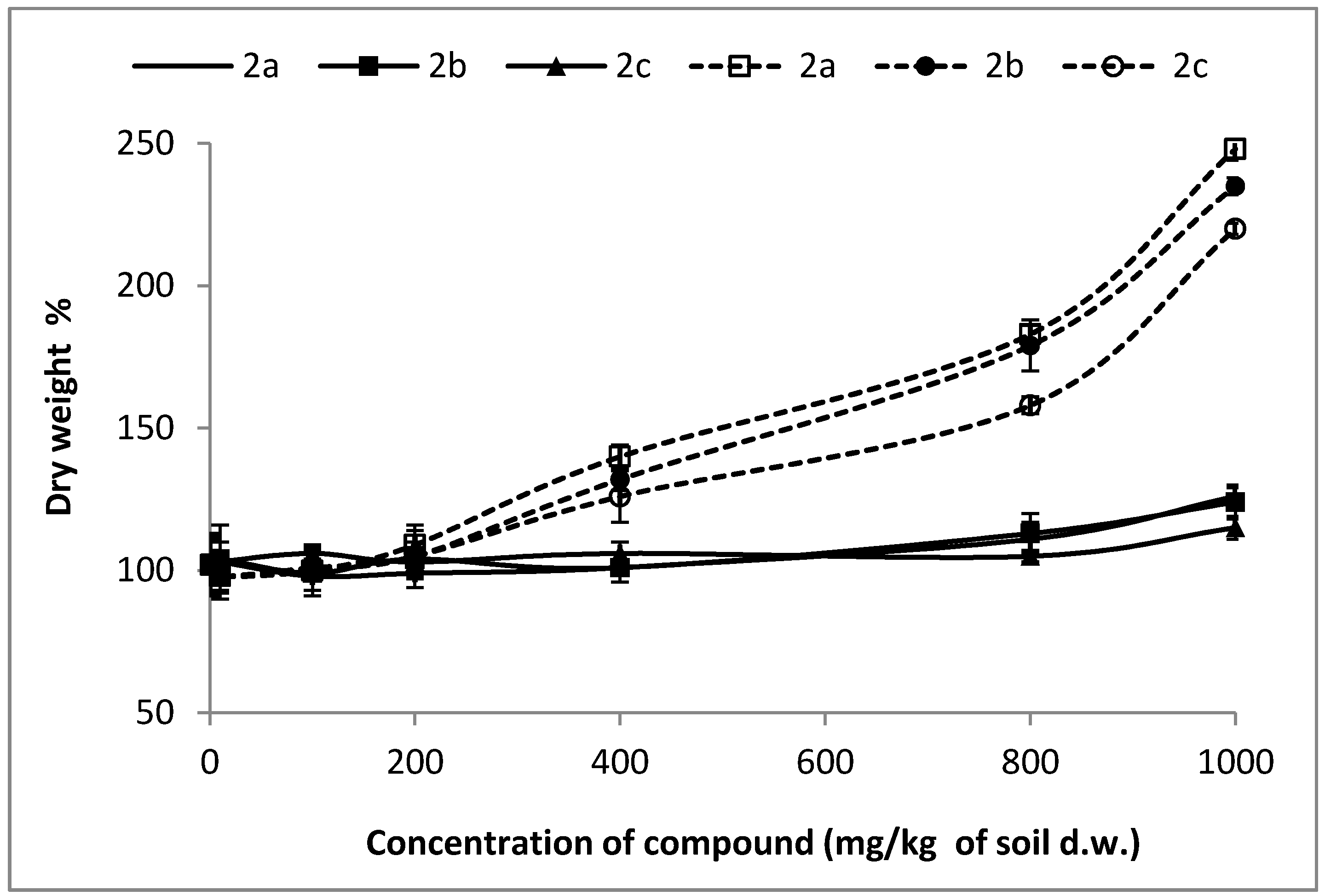
Preliminary tests for aminophosphonates 2a–c for both oat and radish have shown inhibitive effects for plants. The dicotyledonous radish was noticed as the more sensitive plant when compared to sprouts of oat. Comparing results of toxicity of aminophosphonates 2a–c for both types of tested plants, it was noticed that Compounds 2a and 2b are more toxic as compared with 2c (Table 1 and Table 2, Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4).

Table 1.
Average changes (mean of three replicates) in basic parameters of the plant growth test for oat (Avena sativa) treated with 2a–c. Least significant difference for samples (LSDS) and concentration (LSDC) is given for each tested parameter. %F.M. refers to plant biomass (fresh weight) expressed as percent of untreated control.

Table 2.
Average changes (mean of three replicates) in basic parameters of the plant growth test for radish (Raphanus sativus) treated with 2a–c.
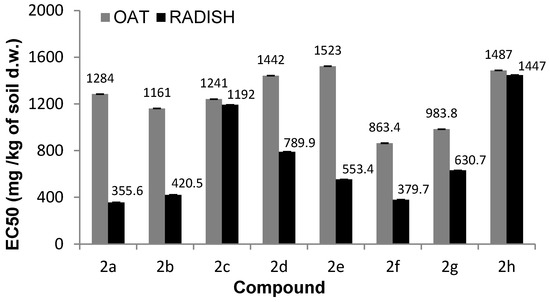
Figure 2.
The EC50 values of fresh weight inhibition following exposure to tested compounds.

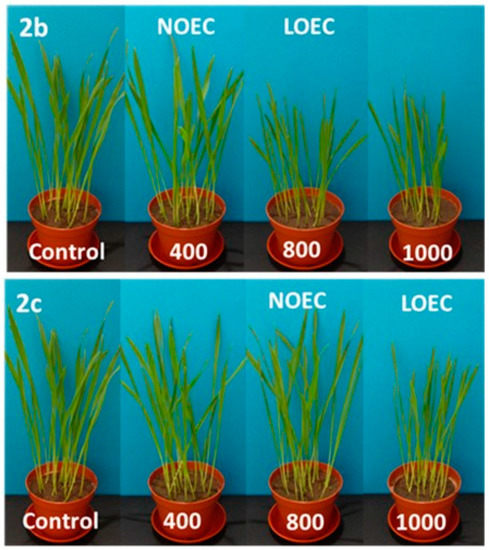
Figure 3.
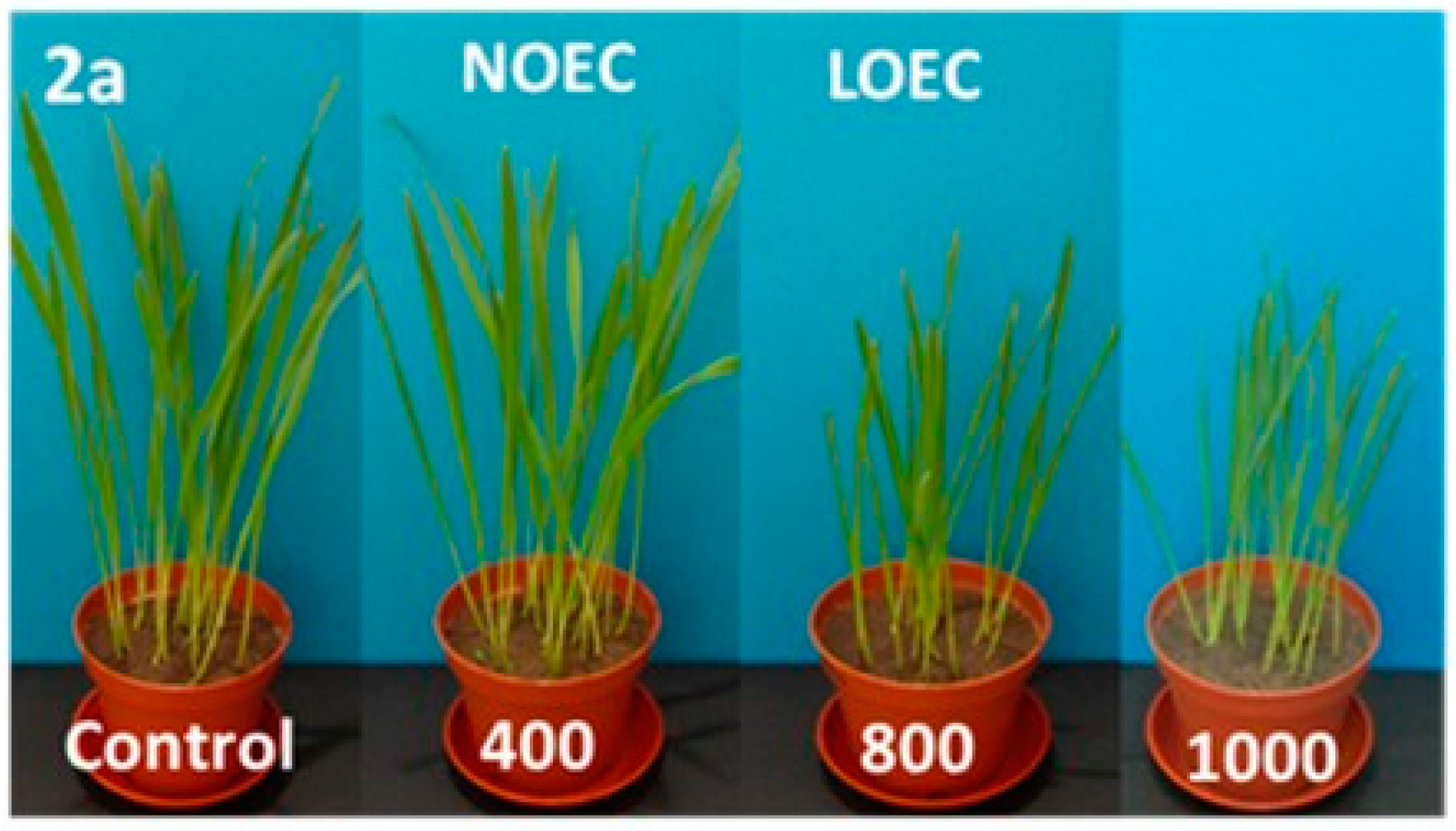
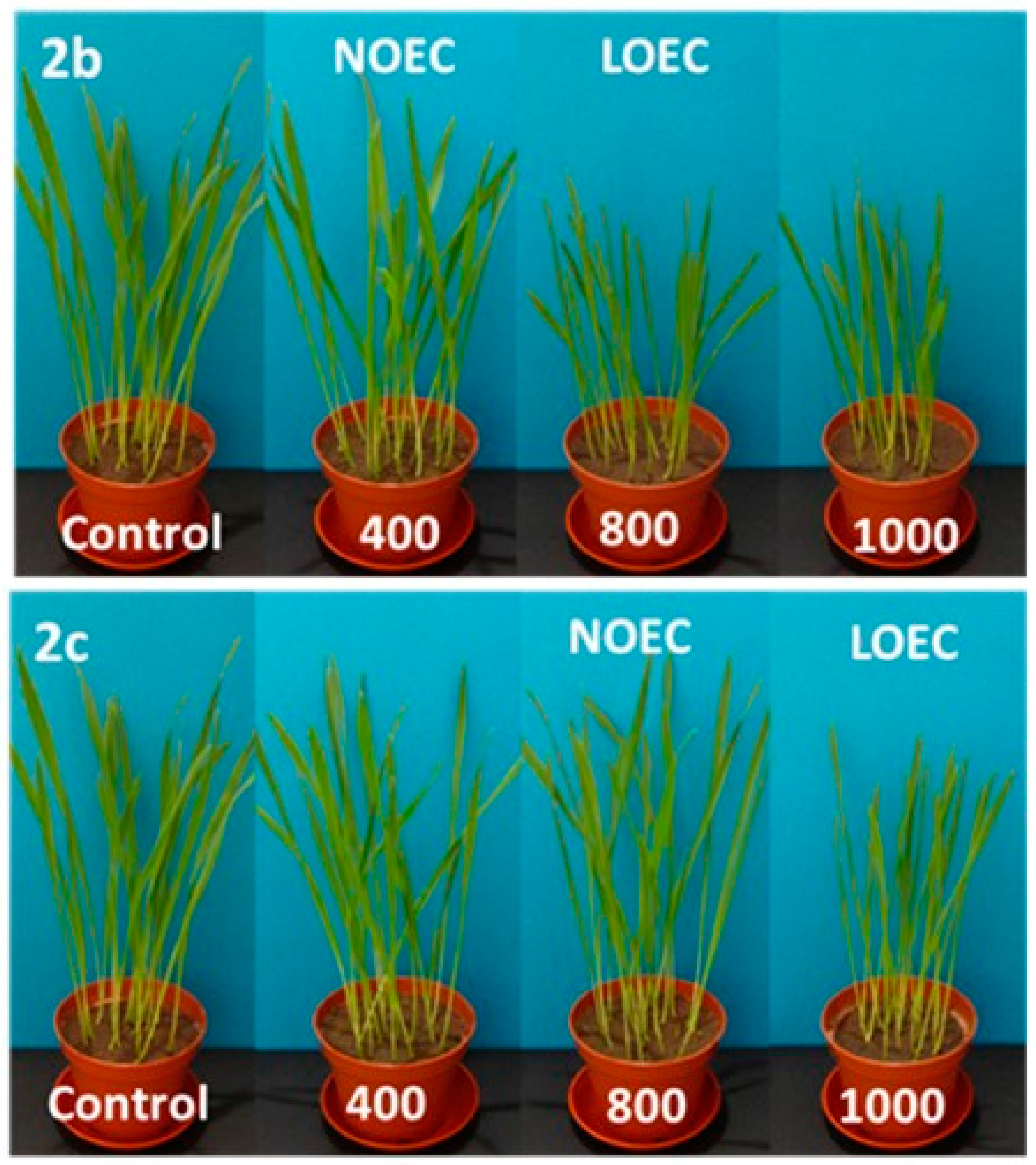
Digital photographs of oat treated with 2a–c (concentration in mg/kg of soil dry weight) on the 14th day of growth.
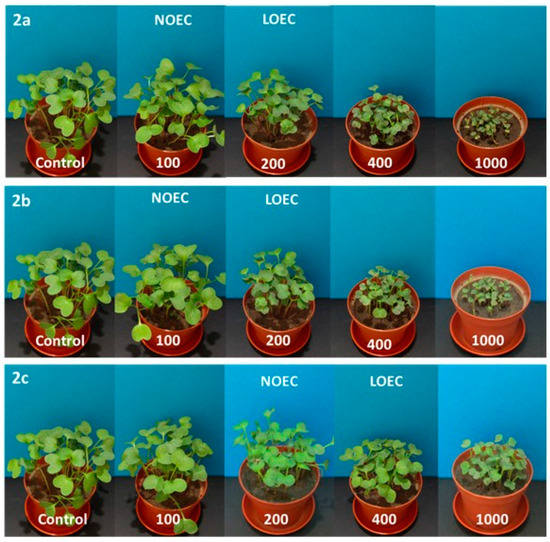

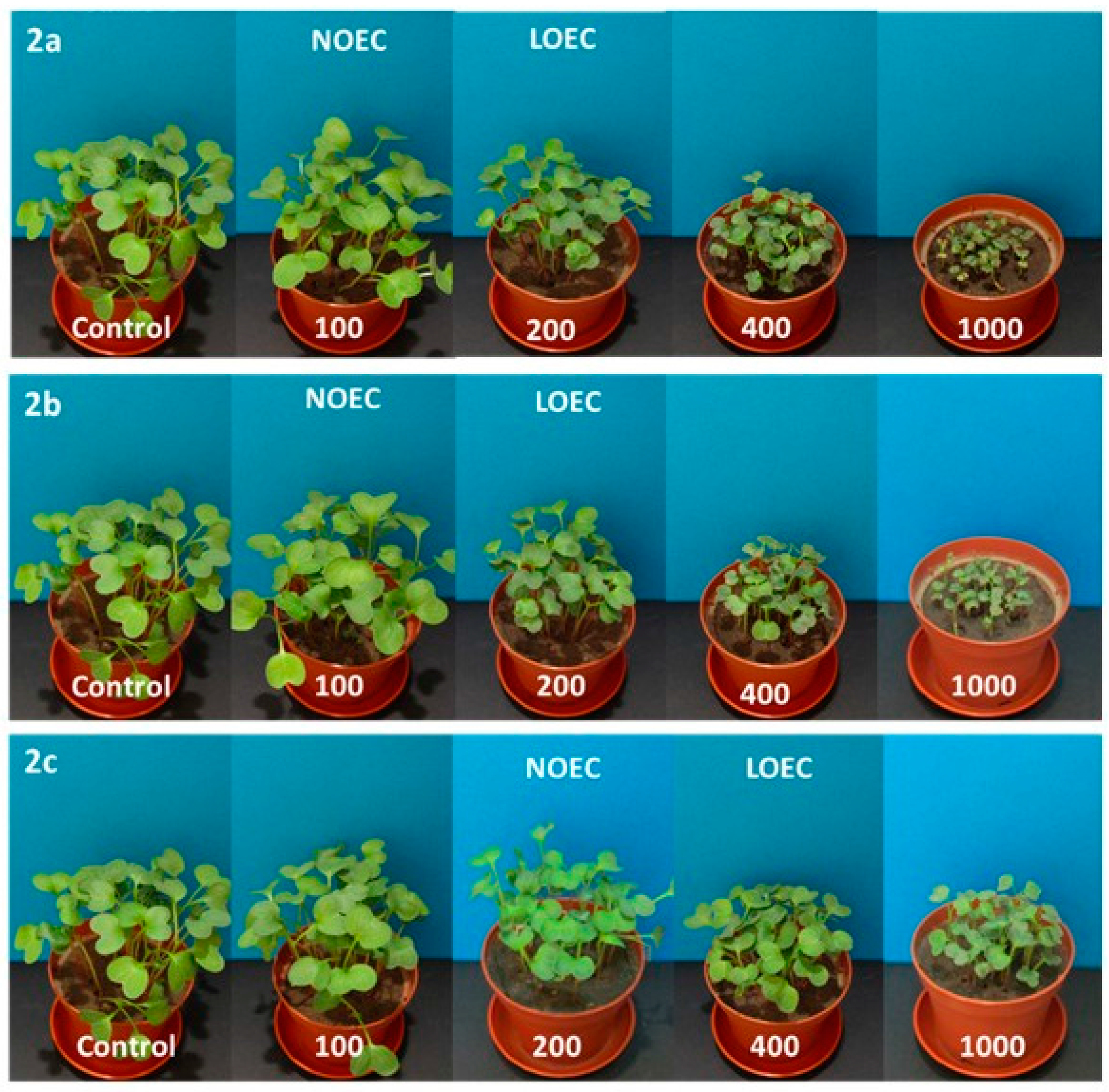
Figure 4.
Digital photographs of radish treated with 2a–c (concentration in mg/kg of soil dry weight) on the 14th day of growth.
N-methylphenyl aminophosphonates with ortho and meta substituted phenyl ring (2a, 2b) have a significantly stronger influence on the inhibition of plant growth as compared with N-para-methylphenyl aminophosphonate (2c). In a case of oat, the values of NOEC and LOEC for Compounds 2a and 2b were 400 and 800 mg/kg of soil dry weight, respectively. These values for Compound 2c were higher (NOEC and LOEC 800 and 1000 mg/kg d.w. of soil), indicating lower toxicity and subsequently higher tolerance of oat against this substance (Figure 3).
At the highest concentration (1000 mg), a ca. 40% decrease in fresh matter of oat sprouts for Compounds 2a and 2b when compared to control plants is observed (Table 1).
To make the description of the obtained results more readable and user-friendly, we only present selected tables and figures to the main text here (Table 1 and Table 2, Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4).
Tested substances were much more toxic for the seedlings of radish, resulting in a decrease in NOEC and LOEC values. The first observed negative symptoms of tested 2a–c compounds against radish were observed for the concentrations of 200 mg/kg of dry weight of soil (Samples 2a, 2b) and of 400 mg/kg of dry weight of soil for Compound 2c (Figure 4). A very high drop of fresh weight of radish seedling was noticed for all compounds (2a–c), but aminophosphonates 2a and 2b were more toxic. At the concentration of 1000 mg/kg of dry weight of soil, a decrease in radish fresh weight, resulting from the action of Compounds 2a–c, was 16%, 22%, and 55%, respectively. High values of dry matter at higher concentrations of the tested substances in pots correspond with a stronger inhibition of water uptake through the root system of plants (Figure 1). The increase in values of oat dry matter when compared to control plants is not as high as in the case of radish, which indicates better tolerance of oat roots against tested substances and moderately observed disturbances in the water uptake process.
The number of emerged seedlings at higher concentrations of tested compounds also decreased and was more visible for radish.
A plant growth test conducted for aminophosphonates bearing methoxy groups substituted in position meta (2d) and para (2e) in a phenyl ring have proved their toxic impact against both types of plants. Contrary to Compounds 2b–c substituted with meta-methyl and para-methylphenyl groups, respectively, the examined N-m-methoxyphenyl derivative 2d was less toxic for both radish and oat as compared with N-p-methoxyphenyl derivative 2e (Tables S1 and S2, Figures S1–S3). The NOEC and LOEC values in the oat growth test for Compounds 2d were much higher (800 and 1000 mg respectively) when compared to 2e (100 and 200 mg respectively). The same values of NOEC and LOEC of Sample 2e were revealed for radish. Again, as in the case of Compounds 2a–c, the much more sensitive plant was radish. In comparison, the yield of the fresh matter of oat at the highest concentration (1000 mg) of 2d and 2e was 19% and 31% (respectively) lower compared to non-treated plants. The yield of the fresh weight of radish at the highest concentration did not exceed 29% (for 2d) and 13% (for 2e) of fresh matter of control plants. The high increase in dry matter values point out the dysfunction of roots (Figure S1).
Comparing the phytotoxicity results of aminophosphonates 2f, 2g, and 2h, Compound 2h was the most toxic agent for both plants. NOEC and LOEC values of Compound 2h were the same for radish and oat—40 and 80 mg/kg of dry matter, respectively. Among Compounds 2f and 2g, the former had a higher negative impact on treated radish and oat. It was shown again that the more sensitive specimen of plant was radish. A very low yield of fresh matter for radish at the highest concentration (1000 mg) when compared to non-treated plants with simultaneously very high dry matter of plants indicates a strong inhibition of plant growth (both sprouts and roots) (Tables S3–S5, Figures S4–S8)
It is worth comparing the plant growth of Samples 2a–c with 2f, the non-aromatic amine derivative bearing the non-substituted phenyl ring. Sample 2f is much more toxic against oat when compared to 2a–c. In the case of radish, results are comparable to those obtained for Samples 2a,b (the same values of NOEC and LOEC). Samples 2a and 2b, as well as N-benzyl derivative 2f, in the highest applied concentration (1000 mg/kg), harmfully influenced radish seeds especially, while for oat, at the same concentration, Sample 2f (without substituted phenyl ring with methyl group) caused almost total inhibition of sprout germination. As a result, contrary to dimethyl N-benzylamino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2f), which kills both plants in a non-selective way, dimethyl N-(2-methylphenyl)amino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2a) and dimethyl N-(3-methylphenyl)amino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2b) were found to be selectively toxic towards radish, slightly harming oat.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
All solvents (POCh, Gliwice, Poland) were routinely distilled and dried prior to use. Amines, dimethyl and dibenzyl phosphites, as well as 2-thiophenecarboxaldehyde (Aldrich, Poznań, Poland) were used as received. Melting points were measured on a MelTemp II apparatus (Bibby Scientific Limited, Staffordshire, UK) and were not corrected. NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance III 600 MHz (Billerica, MA, USA) operating at 600 MHz (1H-NMR), 150 MHz (13C-NMR), and 243 MHz (31P-NMR). TMS was used as the internal standard for 1H- and 13C-NMR, and phosphoric acid was used as the external standard for 31P-NMR. The following abbreviations were used for listing NMR signals: s—singlet, d—doublet, dd—doublet of doublets, ddd—doublet of doublet of doublets, and m—multiplet. Elemental analyses were carried out at the Centre for Molecular and Macromolecular Science of the Polish Academy of Science in Łódź, Poland.
General Procedures of Preparaing Amino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonates 2a–h
2-Thiophenecarboxaldehyde (1.12 g, 10 mmol) was dissolved in methanol (15 mL), and a solution of an appropriate amine (10 mmol) in methanol (15 mL) was added. The obtained solution was stirred at room temperature for 24 h. Then, a small portion of anhydrous potassium carbonate was added, the mixture stirred for additional 15 min. Then, the inorganic salt was filtered off, and the filtrate was evaporated to achieve imines in quantitative yields, which were used for the further reaction without any purification.
Thus, the obtained imine (10 mmol) was dissolved in acetonitrile (15 mL), and an appropriate phosphite (10 mmol) in acetonitrile (15 mL) was added. The mixture was refluxed during the day and stirred at room temperature during the night. Total time of the reaction was 72 h. Then, the solvent was evaporated, and the crude product was isolated and purified using various procedures.
Dimethyl aminophosphonates 2a–g were isolated as follows: crude products were dissolved in DCM (30 mL), and the solution was washed 5 times with saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate. After the usual workup, DCM was evaporated, and the product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel using ethyl acetate-hexane in a 4:1 ratio.
Product 2h was chromatographed after evaporating acetonitrile, eluted using ethyl acetate—hexane in a 3:2 ratio.
Dimethyl N-(2-methylphenyl)amino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2a): Yield = 83% (2.58 g) yellow oil. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ 7.27–7.25 (m, H5thioph, 1H), 7.21–7.19 (m, H3thioph, 1H), 7.11 (d, 3JHH = 7.4 Hz, o-C6H4, 1H), 7.07 (ddd, 3J(1)HH = 3J(2)HH = 7.4 Hz and 4JHH = 1.7 Hz, o-C6H4, 1H), 7.01 (ddd, 3JHH = 5.0 and 4.2 Hz and 4JHH = 0.7 Hz, H4thioph, 1H), 6.74 (ddd, 3J(1)HH = 3J(2)HH = 7.4 Hz and 4JHH = 1.0 Hz, o-C6H4, 1H), 6.65 (d, 3JHH = 7.4 Hz, o-C6H4, 1H), 5.16 (d, 2JPH = 23.7 Hz, CHP, 1H), 3.82 (d, 3JPH = 10.6 Hz, POCH3, 3H), 3.67 (d, 3JPH = 10.6 Hz, POCH3, 3H), 2.28 (s, CH3, 3H). 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 150 MHz): δ 143.98 (d, 2JCP = 12.3 Hz, C2thioph), 139.81 (Carom), 130.41 (Carom), 127.19 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, Cthioph), 127.03 (Carom), 126.19 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, Cthioph), 125.43 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, Cthioph), 123.39 (Carom), 118.86 (Carom), 111.48 (Carom), 54.17 (d, 2JCP = 7.0 Hz, POC), 53.88 (d, 2JCP = 7.3 Hz, POC), 51.84 (d, 1JCP = 157.8 Hz, PC), 17.47 (ArC). 31P-NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ 23.33. Elem. Anal. Calcd. for C14H18NO3PS: C, 54.01, H, 5.83, N, 4.50. Found: C, 54.18, H, 5.97, N, 4.59.
Dimethyl N-(3-methylphenyl)amino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2b): Yield = 94% (2.92 g) yellow crystals, m.p.: 81–83 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ 7.26–7.25 (m, H5thioph, 1H), 7.21–7.20 (m, H3thioph, 1H), 7.07 (dd, 3JHH = 7.2 and 7.0 Hz, m-C6H4, 1H), 7.01 (m, H4thioph, 1H), 6.62 (d, 3JHH = 7.0 Hz, m-C6H4, 1H), 6.55 (s, m-C6H4, 1H), 6.52 (dd, 3JHH = 7.2 Hz and 4JHH = 1.9 Hz, m-C6H4, 1H), 5.11 (d, 2JPH = 24.4 Hz, CHP, 1H), 3.82 (d, 3JPH = 10.4 Hz, POCH3, 3H), 3.65 (d, 3JPH = 10.8 Hz, POCH3, 3H), 2.28 (s, CH3, 3H). 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 150 MHz): δ 145.94 (d, 2JCP = 13.1 Hz, C2thioph), 139.68 (Carom), 139.10 (Carom), 129.15 (Carom), 127.17 (d, J = 3.1 Hz, Cthioph), 126.25 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, Cthioph), 125.41 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, Cthioph), 120.09 (Carom), 114.94 (Carom), 111.01 (Carom), 54.13 (d, 2JCP = 6.7 Hz, POC), 53.83 (d, 2JCP = 7.4 Hz, POC), 51.73 (d, 1JCP = 158.4 Hz, PC), 21.54 (ArC). 31P-NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ 23.20. Elem. Anal. Calcd. for C14H18NO3PS: C, 54.01, H, 5.83, N, 4.50. Found: C, 54.17, H, 5.79, N, 4.51.
Dimethyl N-(4-methylphenyl)amino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2c): Yield = 54% (1.68 g) yellow crystals, m.p.: 98–100 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ 7.25–7.24 (m, H5thioph, 1H), 7.20–7.19 (m, H3thioph, 1H), 7.05–6.98 (m, H5thioph, p-C6H4, 3H), 6.64 (part of AA’XX’ system, 3JHH = 9.0 and 4JHH = 1.2 and 1.1 Hz, p-C6H4, 2H), 5.09 (d, 2JPH = 24.0 Hz, CHP, 1H), 3.82 (d, 3JPH = 10.8 Hz, POCH3, 3H), 3.65 (d, 3JPH = 10.8 Hz, POCH3, 3H), 2.24 (s, CH3, 3H). 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 150 MHz): δ 143.63 (d, 2JCP = 13.4 Hz, C2thioph), 139.77 (Carom), 129.79 (Carom), 128.40 (Carom), 127.15 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, Cthioph), 126.26 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, Cthioph), 125.41 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, Cthioph), 114.25 (Carom), 54.13 (d, 2JCP = 7.1 Hz, POC), 53.81 (d, 2JCP = 7.1 Hz, POC), 52.12 (d, 1JCP = 157.9 Hz, PC), 20.40 (ArC). 31P-NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ 23.27. Elem. Anal. Calcd. for C14H18NO3PS: C, 54.01, H, 5.83, N, 4.50. Found: C, 54.13, H, 5.88, N, 4.63.
Dimethyl N-(3-methoxyphenyl)amino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2d): Yield = 72% (2.35 g) yellow oil 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ 7.26–7.25 (m, H5thioph, 1H), 7.20–7.19 (m, H3thioph, 1H), 7.08 (dd, J1 = J2 = 7.8 Hz, m-C6H4, 1H), 7.01–6.99 (m, H4thioph, 1H), 6.35–6.34 (m, m-C6H4, 1H), 6.33–6.31 (m, m-C6H4, 1H), 6.28–6.26 (m, m-C6H4, 1H), 5.10 (d, 2JPH = 24.0 Hz, CHP, 1H), 3.81 (d, 3JPH = 10.8 Hz, POCH3, 3H), 3.74 (s, OCH3, 3H), 3.65 (d, 3JPH = 10.8 Hz, POCH3, 3H). 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 150 MHz): δ 160.77 (Carom), 147.34 (d, 2JCP = 13.5 Hz, C2thioph), 139.46 (Carom), 130.12 (Carom), 127.2 (d, J = 3.0 Hz, Cthioph), 126.3 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, Cthioph), 125.5 (d, J = 3.5 Hz, Cthioph), 106.91 (Carom), 104.38 (Carom), 100.23 (Carom), 55.08 (ArOC), 54.12 (d, 2JCP = 6.7 Hz, POC), 53.90 (d, 2JCP = 6.7 Hz, POC), 51.69 (d, 1JCP = 158.4 Hz, PC).31P-NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3: δ 23.06. Elem. Anal. Calcd. for C14H18NO4PS × 1/5 C6H14: C, 52.98, H, 6.08, N, 4.06. Found: C, 52.97, H, 5.96, N, 4.38.
Dimethyl N-(4-methoxyphenyl)amino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2e): Yield = 80% (2.62 g) yellow oil. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ 7.25–7.23 (m, H5thioph, 1H), 7.18–7.16 (m, H3thioph, 1H), 6.99–6.98 (m, H4thioph, 1H), 6.75 and 6.66 (AA’XX’ system, 3JHH = 9.0 and 4JHH = 1.2 and 1.1 Hz, p-C6H4, 4H), 4.94 (d, 2JPH = 23.4 Hz, CHP, 1H), 4.54 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, NH, 1H), 3.81 (d, 3JPH = 10.8 Hz, POCH3, 3H), 3.72 (s, OCH3, 3H), 3.64 (d, 3JPH = 10.8 Hz, POCH3, 3H). 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 150 MHz): δ 153.26 (Carom), 139.91 (d, 2JCP = 14.1 Hz, C2thioph), 139.73 (Carom), 127.1 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, Cthioph), 126.3 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, Cthioph), 125.4 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, Cthioph), 115.69 (Carom), 114.83 (Carom), 55.63 (ArOC), 54.13 (d, 2JCP = 6.7 Hz, POC), 53.81 (d, 2JCP = 6.7 Hz, POC), 52.85 (d, 1JCP = 158.4 Hz, PC). 31P-NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ 23.33. Elem. Anal. Calcd. for C14H18NO4PS × 1/6 C7H8: C, 53.16, H, 5.69, N, 4.09. Found: C, 53.21, H, 5.78, N, 4.26.
Dimethyl N-benzylamino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2f): Yield = 57% (1.77 g) yellow oil. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz): 7.26–7.20 (m, PhH, H5thioph, 5H), 7.18–7.15 (m, PhH, 1H), 7.02–7.01 (m, H3thioph, 1H), 6.93 (dd, 3JHH = 4.8 and 3.6 Hz, H4thioph, 1H), 4.24 (d, 2JPH = 23.8 Hz, CHP, 1H), 3.82 (d, 2JHH = 13.8 Hz, CH2Ph, 1H), 3.68 (d, 3JPH = 10.2 Hz, POCH3, 3H), 3.57 (d, 2JHH = 13.8 Hz, CH2Ph, 1H), 3.55 (d, 3JPH = 10.2 Hz, POCH3, 3H). 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 150 MHz): δ 139.30 (d, 2JCP = 4.3 Hz, C2thioph), 138.99 (Carom), 128.47 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, Cthioph), 128.38 (Carom), 128.23 (Carom), 127.28 (Carom), 126.97 (d, J = 3.5 Hz, Cthioph), 125.68 (d, J = 3.3 Hz, Cthioph), 54.74 (d, 1JCP = 159.7 Hz, PC), 53.94 (d, 2JCP = 6.8 Hz, POC), 53.63 (d, 2JCP = 6.8 Hz, POC), 51.24 (d, 3JCP = 15.6 Hz, PCC). 31P-NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ 23.98. Elem. Anal. Calcd. for C14H18NO3PS: C, 54.01, H, 5.83, N, 4.50. Found: C, 53.77, H, 5.67, N, 4.46.
Dimethyl N-benzhydrylamino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2g): Yield = 41% (1.59 g) yellow oil. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz): 7.44–7.34 (m, PhH, H5thioph, 6H), 7.32–7.22 (m, PhH, 5H), 7.07–7.06 (m, H3thioph, H4thioph, 2H), 4.91 (s, CH, 1H), 4.29 (d, 2JPH = 22.8 Hz, CHP, 1H), 3.91 (d, 3JPH = 10.8 Hz, POCH3, 3H), 3.64 (d, 3JPH = 10.8 Hz, POCH3, 3H), 2.57–2.48 (bs, NH, 1H). 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 150 MHz): δ 139.36 (d, 2JCP = 6.4 Hz, C2thioph), 139.73 (Carom), 128.75 (Carom), 128.56 (Carom), 127.89 (Carom), 127.17 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, Cthioph), 127.07 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, Cthioph), 125.72 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, Cthioph), 63.81 (d, 3JCP = 16.0 Hz, PCC), 54.12 (d, 2JCP = 6.7 Hz, POC), 53.53 (d, 2JCP = 6.7 Hz, POC), 53.19 (d, 1JCP = 161.5 Hz, PC). 31P-NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ 24.32. Elem. Anal. Calcd. for C20H22NO3PS × 1/5 C7H8: C, 63.33, H, 5.86, N, 3.45. Found: C, 63.54, H, 5.69, N, 3.75.
Dibenzyl N-furfurylamino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2h): Yield = 62% (2.81 g) yellow oil. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ 7.36–7.32 (m, PhH, 10H), 7.25–7.23 (m, H5thioph, H5fur, 1H), 7.11–7.09 (m, H3thioph, 1H), 7.03–7.02 (m, H4thioph, 1H), 6.33–6.31 (m, H3fur, 1H), 6.15–6.14 (m, H4fur, 1H), 5.10–5.02 (Part AB of ABX system, 3JPH = 7.5 and 8.8 Hz, 2JHH = 11.7 Hz, POCH2Ph, CHP, 2H), 5.00 (Part A of AMX system, 3JPH = 7.2 and 2JHH = 11.8 Hz, POCH2Ph, 1H), 4.90 (Part M of AMX system, 3JPH = 8.2 and 2JHH = 11.8 Hz, POCH2Ph, 1H), 4.43 (d, 2JPH = 19.3 Hz, CHP, 1H), 3.92 and 3.69 (2d, 2JHH = 14.6 Hz, CH2Fur, 3H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 152.60 (Carom), 142.12 (Carom), 138.67 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, Carom), 136.32 (d, 3JCP = 6.0 Hz, Carom), 136.19 (d, 3JCP = 6.3 Hz, Carom), 128.48 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, Carom), 128.34 (Carom), 128.28 (Carom), 128.00 (Carom), 127.84 (Carom), 127.36 (Carom), 127.30 (Carom), 126.92 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, Carom), 125.82 (d, J = 3.5 Hz, Carom), 110.14 (Carom), 107.92 (Carom), 68.58 and 68.18 (2d, 2JCP = 40.6 Hz, POC), 55.11 (d, 1JCP = 159.8 Hz, PC), 43.72 (d, 3JCP = 16.4 Hz, NC). 31P-NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ 22.19. Elem. Anal. Calcd. for C24H24NO4PS × 1/10 CH2Cl2: C, 62.66, H, 5.28, .N, 3.03. Found: C, 62.77, H, 5.03, N, 3.05.
3.2. Plant Growth Test of New Synthesized Compounds
The plant growth test of thiophene-derived aminophosphonates 2a–h was performed in laboratory conditions following the OECD 208 Guideline Terrestrial Plants Growth Test for oat (Avena sativa) as a monocotyledonous plant and radish (Raphanus sativus L. subvar. radicula Pers.), a dicotyledonous plant.
According to the mentioned OECD 208 standard, the plant growth test of Compounds 2a–h was carried out in sandy soil having the following parameters: granulometric composition of soil—77% sand, 14% dust and loam, organic carbon content of approx. 1.2%, pH (KCl) equal to 6.3.
Tests were carried out in polypropylene pots (diameter of 90 mm and capacity of 300 cm3), which were filled with the control soil or with the soil mixed with the tested Compounds 2a–h added at a specific concentration. Twenty identical seeds of each of the selected plant species were sown into the soil. Seeds originated from the same source. Plants were grown for 14 days under controlled conditions: a constant humidity content at the level required for the plants (70% field water capacity), light intensity (7000 lux), and temperature (20 ± 2 °C) were maintained. Then, seedlings were counted, and the dry as well as fresh weight of the plants was determined. The parts of plants above the soil surface were analyzed.
The performed plant growth was evaluated using a preliminary test; subsequently, the final test was conducted afterward based on the obtained screening results. Preliminary tests were performed to determine the range of concentrations of compounds affecting the soil quality; therefore, the used concentrations of Samples 2a–h were as follows: 0 mg (control), 1 mg, 10 mg, 100 mg, and 1000 mg/kg of soil dry weight.
As already mentioned, based on the obtained results from preliminary test, the final, more precise test to find values of the no observed effect concentration (NOEC) and the lowest observed effect concentration (LOEC) of the compounds under study 2a–h was performed.
The evaluation of phytotoxicity of the studied aminophosphonates 2a–h at applied concentrations was made by comparing the germination and (dry and fresh) weight of control plant sprouts (seedlings) with germination and of (dry and fresh) plants sprouts grown in the soil with an admixture of given amounts of the tested compounds.
The dry weights of tested plants were measured after drying at 75 °C until the constant weight.
The visual evaluation of phytotoxicity of aminophosphonates 2a–h at applied concentrations was performed by digital photography. Obtained pictures were analyzed in terms of any type of damage to tested plants, such as their growth inhibition, chlorosis, and necrosis. Tests were carried out three times for each sample.
The significance of the obtained results was evaluated using the analysis of variance (ANOVA). The least significant difference (LSD) values at a confidence level of 95% were computed using the Tukey test.
4. Conclusions
To conclude, the toxicity of N-methylphenyl aminophosphonates 2a–c was diagnosed to be promising as a potential soil-applied herbicide, especially for their selectivity—they are evidently toxic for dicotyledonous radish and not so harmful for monocotyledonous oat. Moreover, their herbicidal efficiency is stronger for the N-methylphenyl aminophosphonates substituted with methyl group at position ortho (2a) and meta (2b) in the phenyl ring.
Dimethyl N-benzylamino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2f) exhibited non-selective, harmful effects against both tested plants.
Among N-methoxyphenyl aminophosphonates 2d and 2e, the latter showed an inhibitive effect especially against dicotyldenous plants. Its impact, however, was significantly weaker than impact of 2a,b. This is to point out that the sole structural difference between N-methoxyphenyl aminophosphonates 2d,e and N-methylphenyl aminophosphonates 2a–c is the substituent of the phenyl moiety, i.e., the methoxy and methyl group, respectively, which indicates that the type and position of those groups in the phenyl ring play a key role in the toxicity effect against tested plants.
Among all tested samples, dibenzyl N-furfurylamino(2-thienyl)methylphosphonate (2h) was found to be the most toxic for radish and oat but without significant selectivity. The investigation of Compounds 2a,b, 2f, and 2h, such as their potential applications and mechanistic approaches, will be continued.
Some thiophene-derived aminophosphonic derivatives were found to have various biological properties (vide supra); therefore, important microbiological, herbicidal, and cytotoxic properties of the studied aminophosphonic systems bearing thiophene moiety 2a–h cannot be excluded. If so, the synthesis of such compounds for potential agrochemical or pharmacological application must be taken into consideration from the environmental protection point of view. Our results call attention to the necessity of further phytotoxicological investigation of any new synthesized aminophosphonic derivatives bearing thiophene moiety.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be accessed at: http://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/21/6/694/s1.
Acknowledgments
Studies were founded by the National Centre of Science of Polish State (NCN), grant no. 2014/13/B/NZ9/02418, where funds for publishing in open-access mode were scheduled. Special thanks are addressed to Paulina Tomczyk and Justyna Biernacka, former M.Sc. students at the University of Łódź, for their fruitful assistance in the preparation of the studied compounds.
Author Contributions
J.L. and P.R. conceived and designed the experiments; A.M., Z.M., M.M., and D.R. performed the experiments; J.L. and P.R. analyzed the data; J.L. and P.R. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Andersen, S.M.; Hertz, P.B.; Holst, T.; Bossi, R.; Jacobsen, C.S. Mineralisation studies of C14-labelled metsulfuron-methyl, tribenuron-methyl, chlorsulfuron and thifensulfuronmethyl in one Danish soil and groundwater sediment profile. Chemosphere 2001, 45, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polati, S.; Bottaro, M.; Frascarolo, P.; Gosetti, F.; Gianotti, V.; Gennaro, M.C. HPLC-UV and HPLC-MSn multiresidue determination of amidosulfuron, azimsulfuron, nicosulfuron, rimsulfuron, thifensulfuron methyl, tribenuron methyl and azoxystrobin in surface waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 579, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance thifensulfuron-methyl. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz, R.Y.; Baun, A.; Kusk, O. Growth inhibition and recoveryof Lemna gibba after pulse exposure to sulfonylurea herbicides. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 89, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckie, H.J.; Tardif, F.J. Herbicide cross resistance in weeds. Crop Prot. 2012, 35, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D. 2,4-D and Dicamba-Resistant Crops and Their Implications for Susceptible Non-Target Crops; Michigan State University Extension: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Filipe, O.M.S.; Santos, S.A.O.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Vidal, M.M.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Neto, C.P.; Santos, E.B.H. Photodegradation of the fungicide thiram in aqueous solutions. Kinetic studies and identification of the photodegradation products by HPLC-MS/MS. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchirico, R.; Pinto, G.; Pollio, A.; Cordella, M.; Cozzani, V. Thermal degradation of Fenitrothion: Identification and eco-toxicity of decomposition products. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 199, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghestani, M.A.; Zand, E.; Soufizadeh, S.; Jamali, M.; Mighany, F. Evaluation of sulfosulfuron for broadleaved and grass weed control in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in Iran. Crop Prot. 2007, 26, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xu, L.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zheng, M.; Pan, C.; Qiu, L. Biodegradation of thifensulfuron-methyl by Ochrobactrum sp. in liquid medium and soil. Biotechnol. Lett. 2015, 37, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cessna, A.J.; Donald, D.B.; Bailey, J.; Waiser, M. Persistence of the Sulfonylurea Herbicides Sulfosulfuron, Rimsulfuron, and Nicosulfuron in Farm Dugouts (Ponds). J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.A.; Cessna, A.J. Variability in the distribution and dissipation of the herbicide thifensulfuron-methyl in a prairie wetland. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 69, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.; Dumas, S.; el Azzouzi, M.; Sarakham, M.; Chovelon, J.-M. Photophysical and photochemical studies of thifensulfuron-methyl herbicide in aqueous solution. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2010, 209, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazartigues, A.; Thomas, M.; Banas, D.; Brun-Bellut, J.; Cren-Olivé, C.; Feidt, C. Accumulation and half-lives of 13 pesticides in muscle tissue of freshwater fishes through food exposure. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.M.; Joshi, M.M.; van Ailien, T.; Carski, T.H.; Dulka, J.J.; Patrick, M.C.; Reiser, R.W.; Livingston, R.S.; Doughty, J. Degradation of thifensulfuron methyl in soil: Role of microbial carboxyesterase activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boduszek, B. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Heterocyclic Amino-phosphonates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1999, 144, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janardhan Rao, A.; Visweswara Rao, P.; Koteswara Rao, V.; Mohan, C.; Naga Raju, C.; Suresh Reddy, C. Microwave Assisted One-pot Synthesis of Novel α-Amino-phosphonates and Their Biological Activity. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 1863–1868. [Google Scholar]
- Maheswara Rao, K.U.; Namkoong, S.; Yu, H.-C.; Park, J.; Chung, C.-M.; Oh, S.Y. Green Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of New Di-aminophosphonate Derivatives as Cytotoxic Agents. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2013, 346, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao Devineni, S.; Doddaga, S.; Donka, R.; Raju Chamarthi, N. CeCl3·7H2O-SiO2: Catalyst promoted microwave assisted neat synthesis, antifungal and antioxidant activities of α-diaminophosphonates. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2013, 24, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, S.; Venkataramana, K.; Chandrasekhar, K.; Fareeda, G.; Naga Raju, C. Ultrasound-Assisted Synthesis of Novel-Aminophosphonates and Their Biological Activity. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2012, 345, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banik, A.; Batta, S.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Banik, B.K. A Highly Efficient Bismuth Salts-Catalyzed Route for the Synthesis of α-Aminophosphonates. Molecules 2010, 15, 8205–8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boduszek, B. An efficient synthesis of 1-aminophosphonic acids and esters bearing heterocyclic moiety. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1995, 104, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, A.S.; Tanyeli, C.; Sesenoglu, O.; Demic, S. A Simple Synthesis of 1-Amino-phosphonic Acids from 1-Hydroxyiminophosphonates with NaBH4 in the Presence of Transition Metal Compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjula, A.; Vittal Rao, B.; Neelakantan, P. One-Pot Synthesis of α-aminophosphonates: An Inexpensive Approach. Synth. Commun. 2003, 33, 2963–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.-J.; Lei, M.-Y.; Zoua, J.-P.; Zhang, W. Microwave-assisted solvent-free and catalyst-free Kabachnik–Fields reactions for α-amino phosphonates. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 1125–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, B.; Egami, H.; Katsuki, T. Synthesis of an Optically Active Al(salalen) Complex and Its Application to Catalytic Hydrophosphonylation of Aldehydes and Aldimines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherkasov, R.A.; Galkin, V.I. The Kabachnik–Fields reaction: Synthetic potential and the problem of the mechanism. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1998, 67, 857–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keglevich, G.; Bálint, E. The Kabachnik–Fields reaction: Mechanism and synthetic use. Molecules 2012, 17, 12821–12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafarski, P.; Górniak, M.G.; Andrasiak, I. Kabachnik–Fields reaction under green conditions-A critical overview. Curr. Green Chem. 2015, 5, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafarski, P.; Lejczak, B. Biological Activity of Aminophosphonic Acids. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1991, 63, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlani, G.; Berlicki, Ł.; Duò, M.; Dziędzioła, G.; Giberti, S.; Bertazzini, M.; Kafarski, P. Synthesis and Evaluation of Effective Inhibitors of Plant δ1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylate Reductase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6792–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Occhipinti, A.; Berlicki, Ł.; Giberti, S.; Dziędzioła, G.; Kafarski, P.; Forlani, G. Effectiveness and mode of action of phosphonate inhibitors of plant glutamine synthetase. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giberti, S.; Bertazzini, M.; Liboni, M.; Berlicki, Ł.; Kafarski, P.; Forlani, G. Phytotoxicity of aminobisphosphonates targeting both δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase and glutamine synthetase. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matusiak, A.; Lewkowski, J.; Rychter, P.; Biczak, R. Phytotoxicity of New Furan-derived Aminophosphonic Acids, N-Aryl Furaldimines and 5-Nitrofuraldimine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7673–7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimczak, A.A.; Kuropatwa, A.; Lewkowski, J.; Szemraj, J. Synthesis of N-aryl, furan-derived aminophosponates and studies of their in vitro cytotoxicity against esophageal cancer cells. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 21, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 2a–h are available from the authors.
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).