1-Deoxynojirimycin Alleviates Liver Injury and Improves Hepatic Glucose Metabolism in db/db Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Serum Levels of Triglyceride (TG), Total Cholesterol (TC), High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C)
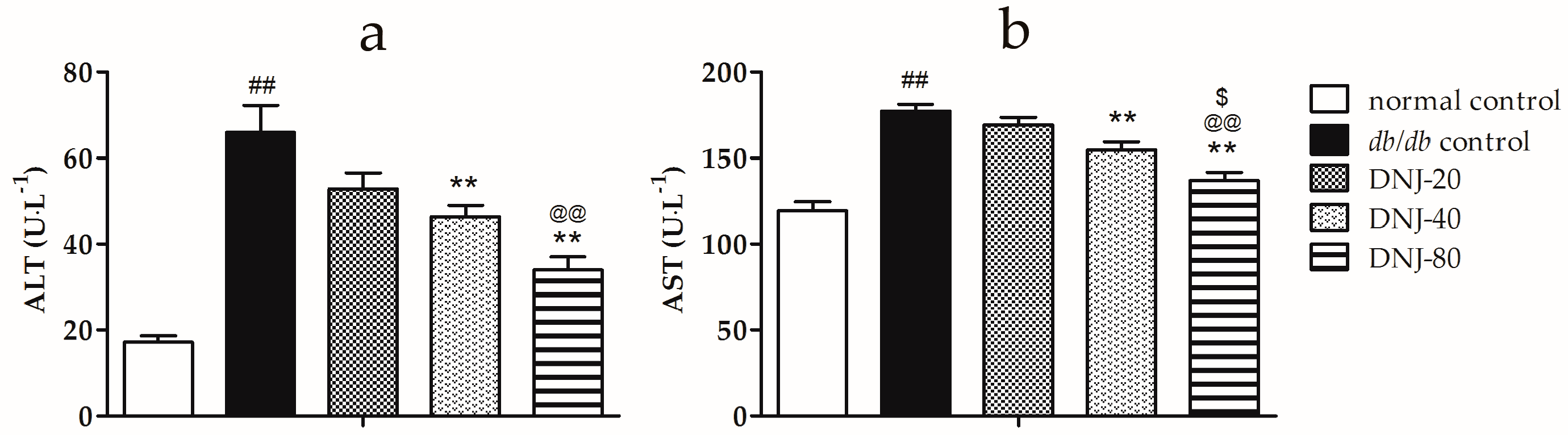
2.2. Effect of CGB on Activities of Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) and Aspartate Transaminase (AST)
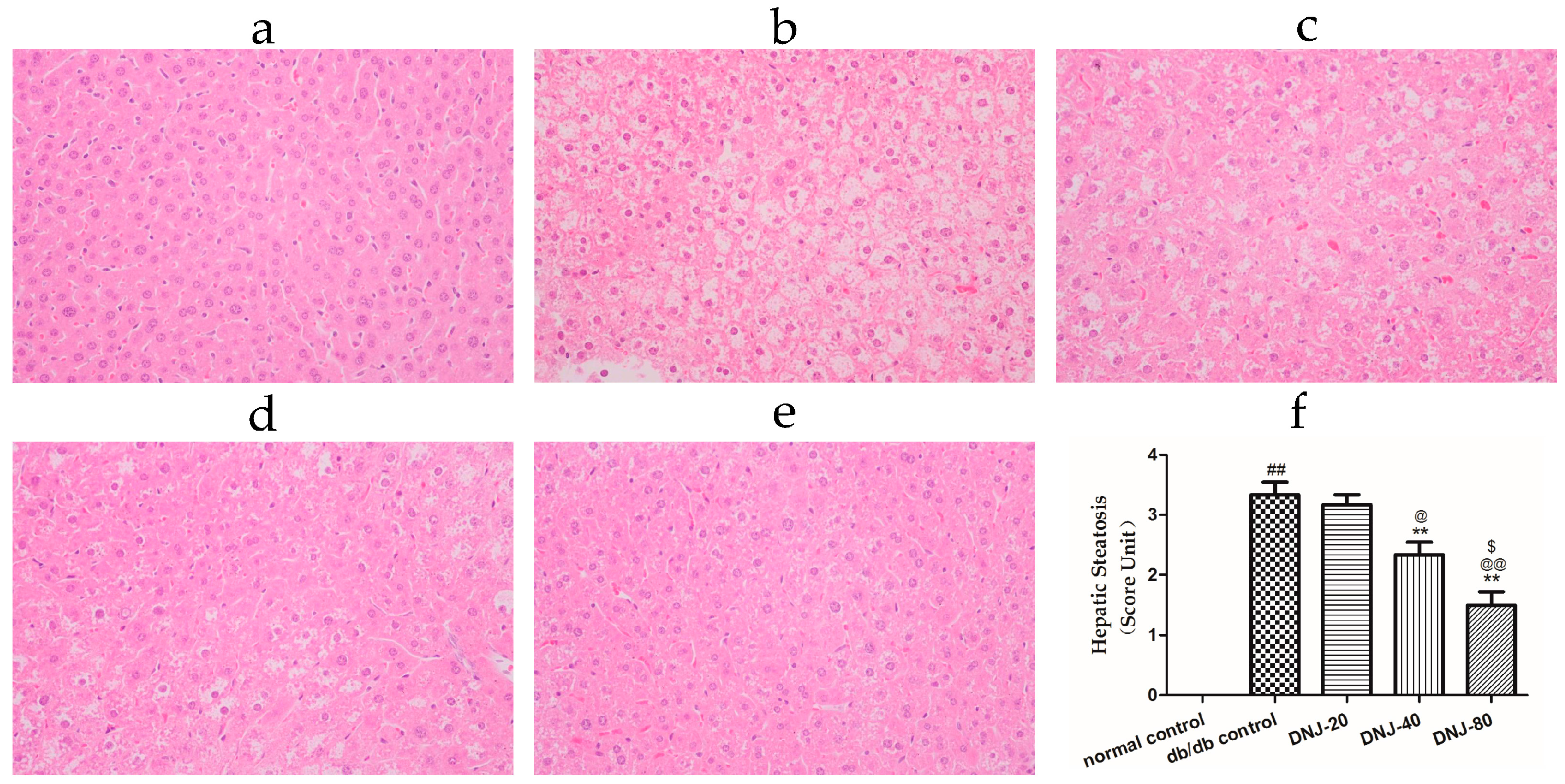
2.3. Effects of DNJ on Hepatic Pathological Changes
2.4. Effects of DNJ on Levels of Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNF-α), Interleukin-1 (IL-1) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6) in Liver Tissue
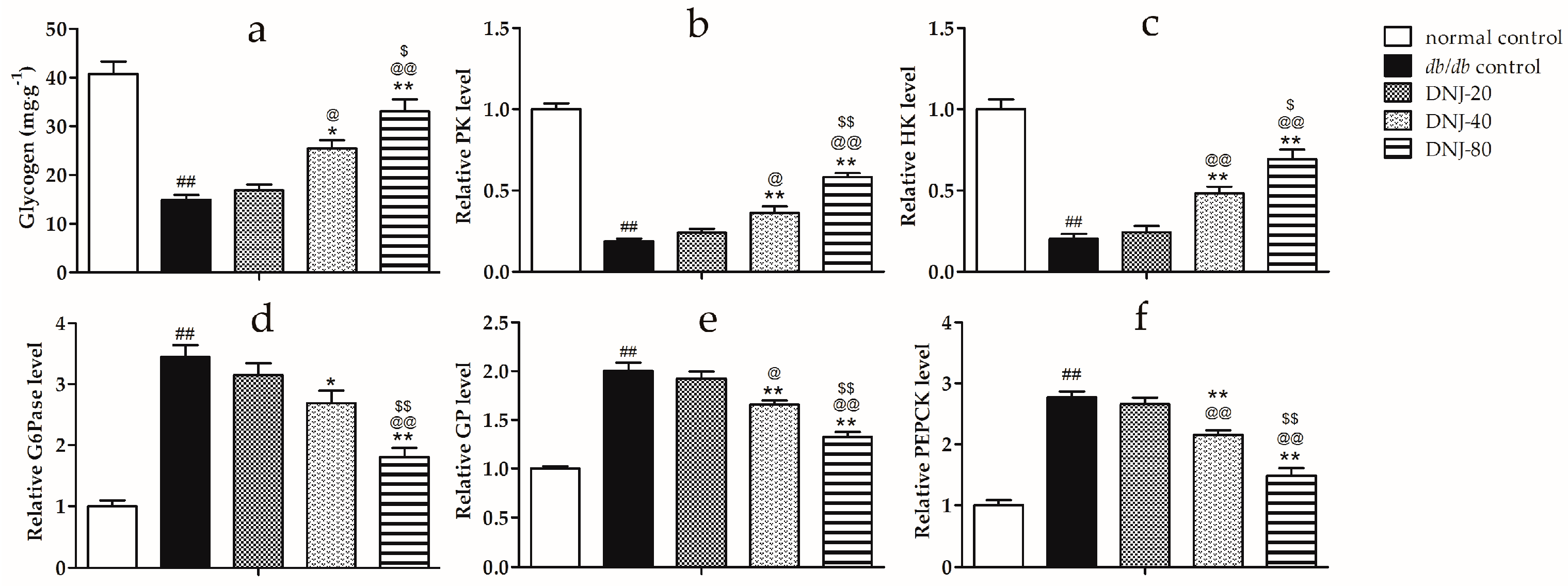
2.5. Effects of DNJ on Hepatic Glycogen Content, Activity Level of Hexokinase (HK), Pyruvate Kinase (PK), Glycogen Phosphorylase (GP) and Glucose-6-Phosphatase (G6Pase)
2.6. Effect of DNJ on Insulin PKB/GSK-3β Signal Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
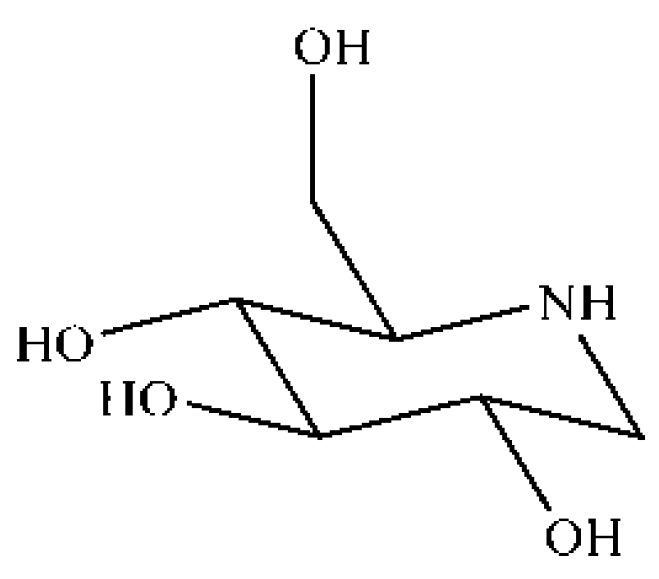
4.2. Preparation of DNJ
4.3. Animals
4.4. Experimental Design
4.5. Biochemical Estimations
4.6. Histological Examination
4.7. Determination of TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6 in Liver Tissues
4.8. Determination of Hepatic Glycogen and Enzymes of Glucose Metabolism in Liver Tissue
4.9. Western Blot
4.10. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zimmet, P.; Alberti, K.G.; Shaw, J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 2001, 414, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Abbas, A.K.; Fausto, N.; Robbins, S.L.; Cotran, R.S. The skin. In Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 7th ed.; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 1194–1195. [Google Scholar]
- DeBruyne, L.K.; Whitney, E.N.; Pinna, K. Nutrition and Diet Therapy, 7th ed.; Thomson Wadsworth: Belmont, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Min, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Han, J.S. Ishige okamurae ameliorates hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 93, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andallu, B.; Suryakantham, V.; Lakshmi Srikanthi, B.; Reddy, G.K. Effect of mulberry (Morus indica L.) therapy on plasma and erythrocyte membrane lipids in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2001, 314, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naowaboot, J.; Pannangpetch, P.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Kukongviriyapan, U.; Nakmareong, S.; Itharat, A. Mulberry leaf extract restores arterial pressure in streptozotocin-induced chronic diabetic rats. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuriyama, C.; Kamiyama, O.; Ikeda, K.; Sanae, F.; Kato, A.; Adachi, I.; Imahori, T.; Takahata, H.; Okamoto, T.; Asano, N. In vitro inhibition of glycogen-degrading enzymes and glycosidases by six-membered sugar mimics and their evaluation in cell cultures. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 7330–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, N.; Yamashita, T.; Yasuda, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kizu, H.; Kameda, Y.; Kato, A.; Nash, R.J.; Lee, H.S.; Ryu, K.S. Polyhydroxylated alkaloids isolated from mulberry trees (Morus alba L.) and silkworms (Bombyx mori L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4208–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, N. Glycosidase inhibitors: Update and perspectives on practical use. Glycobiology 2003, 13, 93R–104R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyahara, C.; Miyazawa, M.; Satoh, S.; Sakai, A.; Mizusaki, S. Inhibitory effects of mulberry leaf extract on postprandial hyperglycemia in normal rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2004, 50, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, N. Sugar-mimicking glycosidase inhibitors: Bioactivity and application. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1479–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, M.; Kouno, T.; Aoyagi, Y.; Murai, H. The structure of moranoline, a peperidine alkaloid from Morus species. Nippon Nogei Kagaku Kaishi 1976, 50, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, G. 1-Deoxynojirimycin Alleviates Insulin Resistance via Activation of Insulin Signaling PI3K/AKT Pathway in Skeletal Muscle of db/db Mice. Molecules 2015, 20, 21700–21714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizza, R.A. Pathogenesis of fasting and postprandial hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: Implications for therapy. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2697–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharabi, K.; Tavares, C.D.; Rines, A.K.; Puigserver, P. Molecular pathophysiology of hepatic glucose production. Mol. Aspects Med. 2015, 46, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.C.; Chang, W.C.; Chang, C.L. An extract from wax apple (Syzygium samarangense (Blume) Merrill and Perry) effects glycogenesis and glycolysis pathways in tumor necrosis factor-α-treated FL83B mouse hepatocytes. Nutrients 2013, 5, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhamed, F.; Denechaud, P.D.; Lemoine, M.; Robichon, C.; Moldes, M.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Ratziu, V.; Serfaty, L.; Housset, C.; Capeau, J.; et al. The lipogenic transcription factor chrebp dissociates hepatic steatosis from insulin resistance in mice and humans. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 2176–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrini, E.; Sullivan, S.; Klein, S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Biochemical, metabolic, and clinical implications. Hepatology 2010, 51, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferre, P.; Foufelle, F. Hepatic steatosis: A role for de novo lipogenesis and the transcription factor SREBP-1c. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2010, 12 (Suppl. 2), 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burra, P. Liver abnormalities and endocrine diseases. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Yang, X.; Wu, D.; Xing, S.; Bian, F.; Li, W.; Chi, J.; Bai, X.; Wu, G.; Chen, X.; et al. Salidroside ameliorates insulin resistance through activation of a mitochondria-associated AMPK/PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3284–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, K.; Kojima, T.; Fujimoto, Y. Mulberry leaf extract inhibits the oxidative modification of rabbit and human low density lipoprotein. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuduki, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Honma, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Kimura, T.; Ikeda, I.; Miyazawa, T. Intake of 1-deoxynojirimycin suppresses lipid accumulation through activation of the β-oxidation system in rat liver. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 11024–11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ann, J.Y.; Eo, H.; Lim, Y. Mulberry leaves (Morus alba L.) ameliorate obesity-induced hepatic lipogenesis, fibrosis, and oxidative stress in high-fat diet-fed mice. Genes Nutr. 2015, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altamirano, J.; Bataller, R. Alcoholic liver disease: Pathogenesis and new targets for therapy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floreani, N.A.; Rump, T.J.; Abdul Muneer, P.M.; Alikunju, S.; Morsey, B.M.; Brodie, M.R.; Persidsky, Y.; Haorah, J. Alcohol-induced interactive phosphorylation of Src and toll-like receptor regulates the secretion of inflammatory mediators by human astrocytes. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010, 5, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Day, C.P. Management strategies in alcoholic liver disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 4, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inzaugarat, M.E.; Ferreyra Solari, N.E.; Billordo, L.A.; Abecasis, R.; Gadano, A.C.; Chernavsky, A.C. Altered phenotype and functionality of circulating immune cells characterize adult patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, C.; Esposti, D.D.; Bouchet, A.; Brenner, C.; Lemoine, A. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: New insights from omics studies. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunersreuther, V.; Viviani, G.L.; Mach, F.; Montecucco, F. Role of cytokines and chemokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieckowska, A.; Papouchado, B.G.; Li, Z.; Lopez, R.; Zein, N.N.; Feldstein, A.E. Increased hepatic and circulating interleukin-6 levels in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.C.; Huang, H.P.; Lee, Y.J.; Tang, Y.H.; Wang, C.J. Hepatoprotective effect of mulberry water extracts on ethanol-induced liver injury via anti-inflammation and inhibition of lipogenesis in C57BL/6J mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnoni, L.J.; Vraskou, Y.; Palstra, A.P.; Planas, J.V. Amp-activated protein kinase plays an important evolutionary conserved role in the regulation of glucose metabolism in fish skeletal muscle cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agius, L. Role of glycogen phosphorylase in liver glycogen metabolism. Mol. Aspects Med. 2015, 46, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Basu, R.; Shah, P.; Vella, A.; Johnson, C.M.; Jensen, M.; Nair, K.S.; Schwenk, W.F.; Rizza, R.A. Type 2 diabetes impairs splanchnic uptake of glucose but does not alter intestinal glucose absorption during enteral glucose feeding: Additional evidence for a defect in hepatic glucokinase activity. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosterveer, M.H.; Mataki, C.; Yamamoto, H.; Harach, T.; Moullan, N.; van Dijk, T.H.; Ayuso, E.; Bosch, F.; Postic, C.; Groen, A.K.; et al. LRH-1-dependent glucose sensing determines intermediary metabolism in liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, S.; Garcia-Rocha, M.; Calbo, J.; Guinovart, J.J. Restoration of hepatic glycogen deposition reduces hyperglycaemia, hyperphagia and gluconeogenic enzymes in a streptozotocin-induced model of diabetes in rats. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2639–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Cha, B.Y.; Saito, K.; Yamakawa, H.; Choi, S.S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yonezawa, T.; Teruya, T.; Nagai, K.; Woo, J.T. Nobiletin improves hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in obese diabetic ob/ob mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Chang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from sea cucumber in combination with rosiglitazone improved glucose metabolism in the liver of the insulin-resistant mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 2263–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaresan, A.; Harini, R.; Pugalendi, K.V. Ursolic acid and rosiglitazone combination alleviates metabolic syndrome in high fat diet fed C57BL/6J mice. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2012, 31, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, S.; Weiss, J.N.; Ribalet, B. Subcellular localization of hexokinases I and II directs the metabolic fate of glucose. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Shukair, S.; Naik, T.J.; Moazed, F.; Ardehali, H. Glucose phosphorylation and mitochondrial binding are required for the protective effects of hexokinases I and II. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holyoak, T.; Zhang, B.; Deng, J.; Tang, Q.; Prasannan, C.B.; Fenton, A.W. Energetic coupling between an oxidizable cysteine and the phosphorylatable N-terminus of human liver pyruvate kinase. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Cros, M.; Hemmerlin, C.; Ferretti, S.; Zhang, J.; Gounarides, J.S.; Yin, H.; Muller, A.; Haberkorn, A.; Chene, P.; Sellers, W.R.; Hofmann, F. M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase is dispensable for tumor maintenance and growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouché, C.; Serdy, S.; Kahn, C.R.; Goldfine, A.B. The cellular fate of glucose and its relevance in type 2 diabetes. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 807–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, U.J.; Lee, M.K.; Jeong, K.S.; Choi, M.S. The hypoglycemic effects of hesperidin and naringin are partly mediated by hepatic glucose-regulating enzymes in C57BL/KSJ-db/db mice. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2499–2503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.G.; Ji, D.F.; Zhong, S.; Lv, Z.Q.; Lin, T.B.; Chen, S.; Hu, G.Y. Hybrid of 1-deoxynojirimycin and polysaccharide from mulberry leaves treat diabetes mellitus by activating PDX-1/insulin-1 signaling pathway and regulating the expression of glucokinase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and Glucose-6-phosphatase in alloxan-induced diabetic mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.E.; Sun, Y.; Ishizuka, T.; Farrell, C.J.; McCormack, S.E.; Herron, L.M.; Hakimi, P.; Lechner, P.; Yun, J.S. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene transcription and hyperglycemia are regulated by glucocorticoids in genetically obese db/db transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 31475–31481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltner-Law, M.E.; Wang, X.L.; Law, B.K.; Hall, R.K.; Nawano, M.; Granner, D.K. Epigallocatechin gallate, a constituent of green tea, represses hepatic glucose production. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 34933–34940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.G.; Ji, D.F.; Zhong, S.; Lin, T.B.; Lv, Z.Q.; Hu, G.Y.; Wang, X. 1-Deoxynojirimycin inhibits glucose absorption and accelerates glucose metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Fang, M.; Zhang, Y.Q. In vivo hypoglycaemic effect and inhibitory mechanism of the branch bark extract of the mulberry on STZ-induced diabetic mice. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 614265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollen, M.; Vandebroeck, A.; Stalmans, W. 1-Deoxynojirimycin and related compounds inhibit glycogenolysis in the liver without affecting the concentration of phosphorylase a. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1988, 37, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embi, N.; Rylatt, D.B.; Cohen, P. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Separation from cyclic-amp-dependent protein kinase and phosphorylase kinase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1980, 107, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, C.A.; Jope, R.S. The multifaceted roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3β in cellular signaling. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 65, 391–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plyte, S.E.; Hughes, K.; Nikolakaki, E.; Pulverer, B.J.; Woodgett, J.R. Glycogen synthase kinase-3: Functions in oncogenesis and development. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1114, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.E.; Erickson, R.L.; Hemati, N.; MacDougald, O.A. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 is an insulin-regulated C/EBPα kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 8433–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, E.J.; Sakamoto, K.; Armit, L.J.; Ronaldson, L.; Shpiro, N.; Marquez, R.; Alessi, D.R. Role that phosphorylation of gsk3 plays in insulin and wnt signalling defined by knockin analysis. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1571–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, P.; Frame, S. The renaissance of GSK3. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, S.; Saberi, M.; Olefsky, J.M. Insulin sensitivity: Modulation by nutrients and inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2992–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barillas, R.; Friehs, I.; Cao-Danh, H.; Martinez, J.F.; del Nido, P.J. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3β improves tolerance to ischemia in hypertrophied hearts. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 84, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Mihaylova, M.M.; Zheng, B.; Hou, X.; Jiang, B.; Park, O.; Luo, Z.; Lefai, E.; Shyy, J.Y.; et al. AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Ok, H.M.; Kwon, O. Protective effects of Korean red ginseng against alcohol-induced fatty liver in rats. Molecules 2015, 20, 11604–11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Sample of the 1-Deoxynojirimycin is available from the authors.



© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Peng, G. 1-Deoxynojirimycin Alleviates Liver Injury and Improves Hepatic Glucose Metabolism in db/db Mice. Molecules 2016, 21, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030279
Liu Q, Li X, Li C, Zheng Y, Wang F, Li H, Peng G. 1-Deoxynojirimycin Alleviates Liver Injury and Improves Hepatic Glucose Metabolism in db/db Mice. Molecules. 2016; 21(3):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030279
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qingpu, Xuan Li, Cunyu Li, Yunfeng Zheng, Fang Wang, Hongyang Li, and Guoping Peng. 2016. "1-Deoxynojirimycin Alleviates Liver Injury and Improves Hepatic Glucose Metabolism in db/db Mice" Molecules 21, no. 3: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030279
APA StyleLiu, Q., Li, X., Li, C., Zheng, Y., Wang, F., Li, H., & Peng, G. (2016). 1-Deoxynojirimycin Alleviates Liver Injury and Improves Hepatic Glucose Metabolism in db/db Mice. Molecules, 21(3), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030279




