Identification and Determination of the Polyhydroxylated Alkaloids Compounds with α-Glucosidase Inhibitor Activity in Mulberry Leaves of Different Origins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
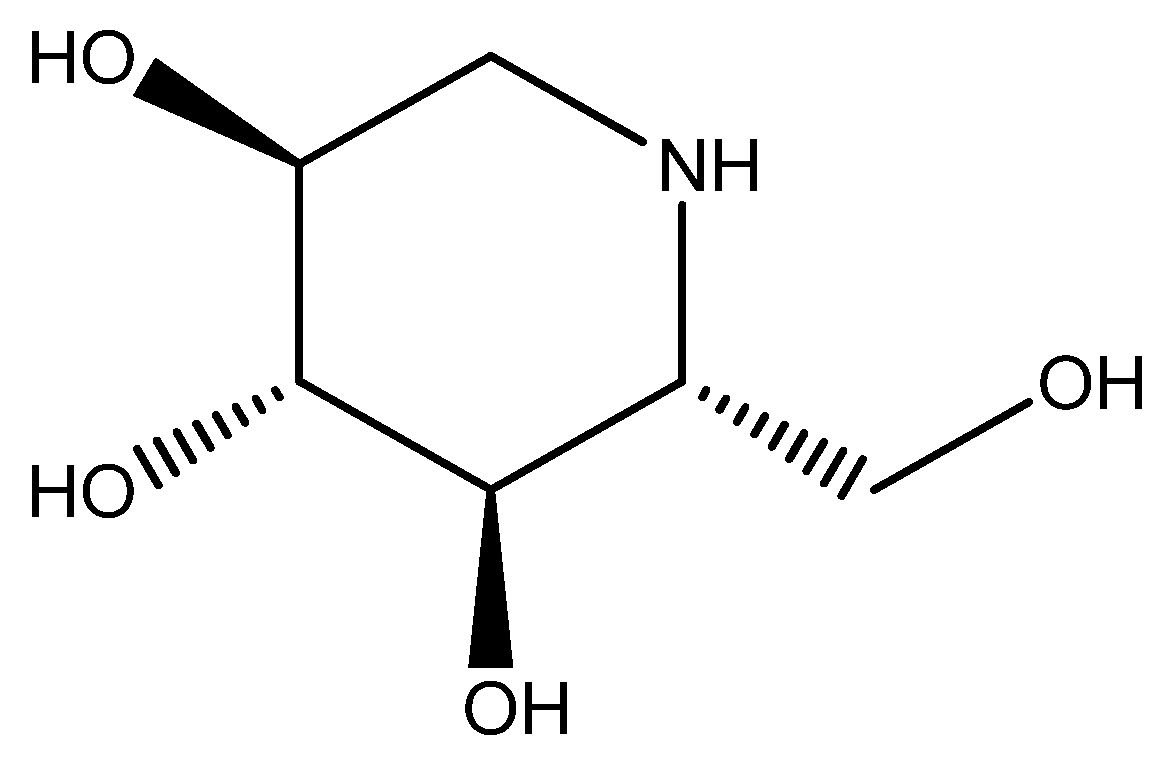
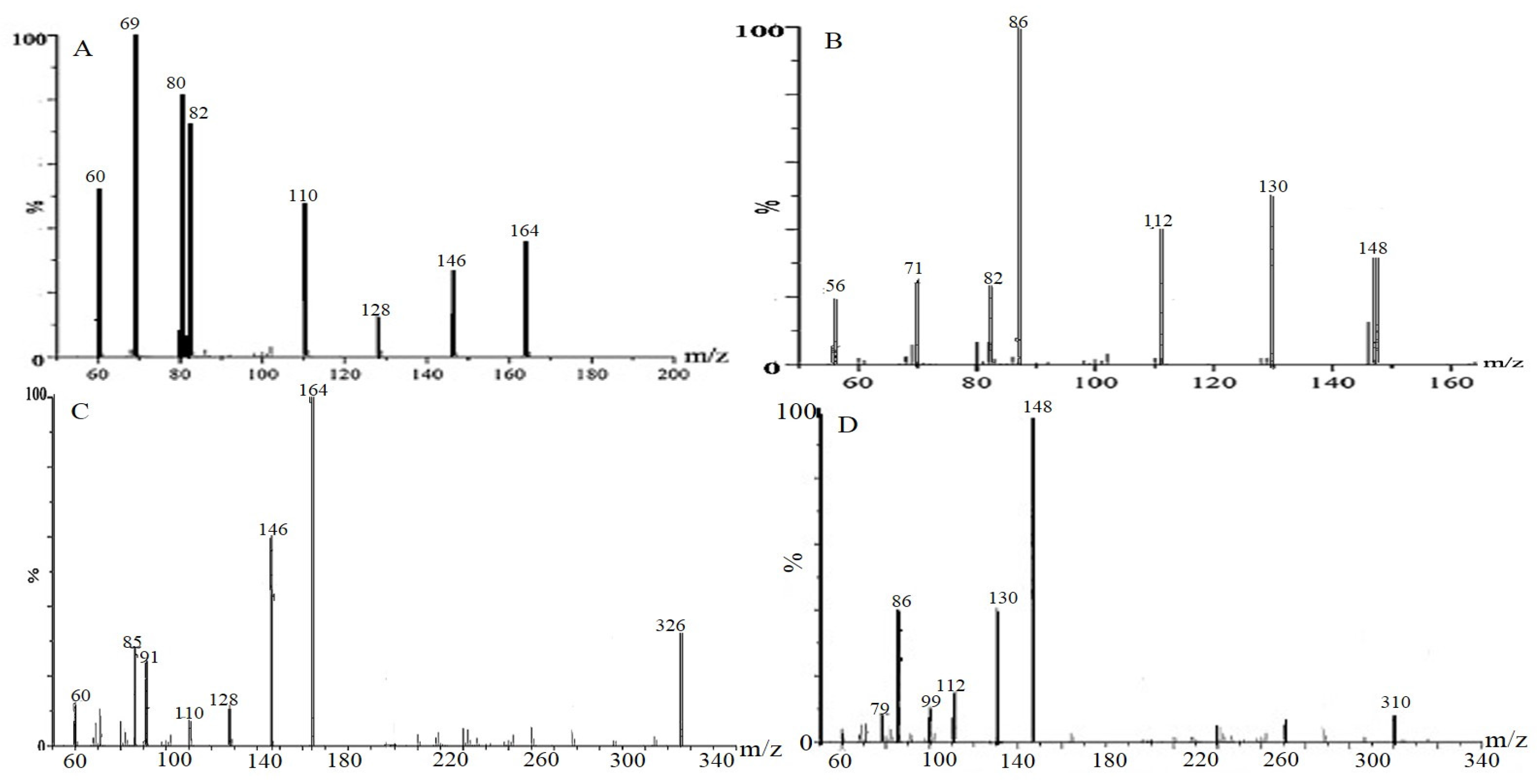
2.1. Identification of Polyhydroxylated Alkaloids in the Samples by UPLC-QTOF/MS
| No. | M (m/z) | Measured/[M + H]+ (m/z) | m/z (MS/MS) | Formula | Compound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 163.08 | 164.17 | 146, 110, 82 | C6H13NO4 | DNJ |
| 2 | 147.17 | 148.18 | 112, 86, 56 | C6H13NO3 | Fagomine |
| 3 | 147.17 | 148.18 | 112, 84, 56 | C6H13NO3 | Isofagomine |
| 4 | 325.24 | 326.31 | 164, 146, 110, 85 | C12H23NO9 | 2-O-α-d-Gal-DNJ |
| 5 | 309.33 | 310.32 | 148, 112, 86 | C12H23NO8 | 4-O-β-d-Glc-fagomine |
2.2. Optimization of the HPLC Separation
2.3. Optimization of ELSD Conditions

2.4. Analytical Method Validation
| No. | Item | DNJ |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Calibration curves | y = 1.394x + 11.54 |
| 2 | Linear range (mg/mL) | 0.025~1.015 |
| 3 | Correlation coefficient, r2 | 0.997 |
| 4 | Precision RSD, %, n = 6 | 1.1 |
| 5 | Repeatablity RSD, %, n = 6 | 1.8 |
| 6 | Stability RSD, %, n = 6 | 1.4 |
| 7 | Recovery, Mean, RSD% (n = 3) Low level (80%) Medium level (100%) High level (120%) | 94.78, 2.95 95.21, 3.01 94.96, 3.12 |
| 8 | Retention time, min | 5.8 |
| 9 | LOD (μg/mL) | 6.8 |
| 10 | LOQ (μg/mL) | 20.3 |
2.5. Quantification of DNJ in 29 Batches of Mulberry Leaves Samples
| Sample | Origin | Batch Number | Content (mg/g) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Xinjang | 130408 | 2.07 | 0.12 |
| S2 | Xinjang | 131102 | 0.78 | 0.11 |
| S3 | Xinjang | 131128 | 0.95 | 0.18 |
| S4 | Hangzhou, Zhejiang | 141106 | 1.72 | 0.11 |
| S5 | Hangzhou, Zhejiang | 141102 | 2.05 | 0.09 |
| S6 | Dabieshan, Anhui | 140901 | 1.38 | 0.07 |
| S7 | Dabieshan, Anhui | 141006 | 1.24 | 0.14 |
| S8 | Bozhou, Anhui | 130101 | 1.72 | 0.12 |
| S9 | Bozhou, Anhui | 140616 | 0.82 | 0.09 |
| S10 | Bozhou, Anhui | 140805 | 1.84 | 0.13 |
| S11 | Bozhou, Anhui | 140815 | 1.55 | 0.19 |
| S12 | Bozhou, Anhui | 140905 | 0.20 | 0.11 |
| S13 | Bozhou, Anhui | 141006 | 0.28 | 0.09 |
| S14 | Tongling, Anhui | 140301 | 1.02 | 0.14 |
| S15 | Hefei, Anhui | 130111 | 1.11 | 0.17 |
| S16 | Nanjing, Jiangsu | 141022 | 0.79 | 0.12 |
| S17 | Nanjing, Jiangsu | 141025 | 1.95 | 0.11 |
| S18 | Yixing, Jiangsu | 141015 | 1.11 | 0.15 |
| S19 | Wuxi, Jiangsu | 141015 | 1.43 | 0.14 |
| S20 | Zhenjiang, Jiangsu | 141120 | 3.15 | 0.11 |
| S21 | Y64, Zhenjiang | 121101 | 3.88 | 0.16 |
| S22 | Y66, Zhenjiang | 121101 | 3.01 | 0.14 |
| S23 | Nantong, Jiangsu | 140920 | 0.62 | 0.18 |
| S24 | Wuhan, Hubei | 140902 | 0.57 | 0.07 |
| S25 | Tongrentang, Nanjign | 120804 | 1.95 | 0.15 |
| S26 | Xuandetang, Nanjing | 120813 | 1.17 | 0.14 |
| S27 | Xiansheng, Nanjing | 130130 | 1.99 | 0.16 |
| S28 | Bailong, Nanjing | 130303 | 2.31 | 0.11 |
| S29 | Yifeng, Nanjing | 130211 | 1.35 | 0.13 |
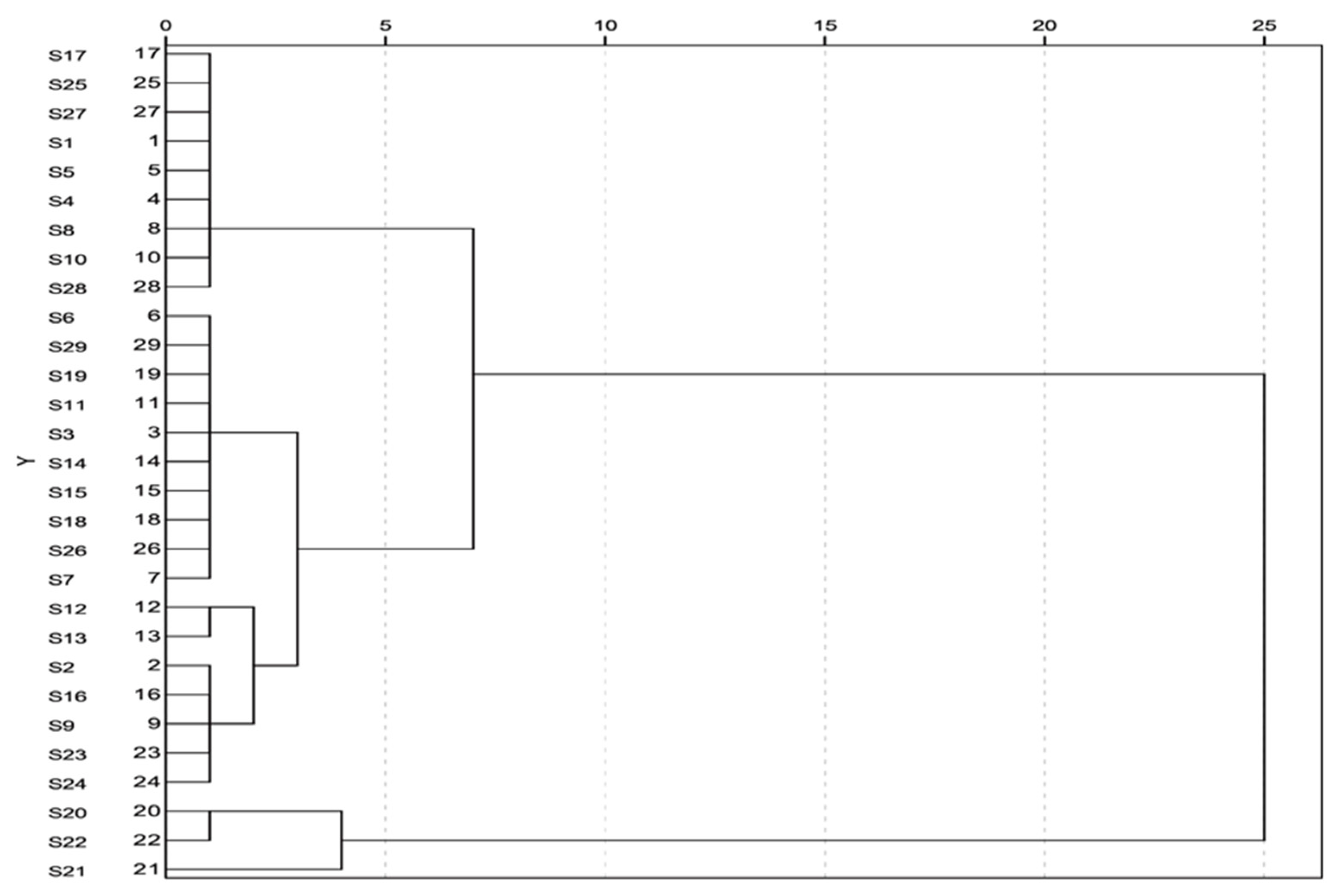
2.6. The Clustering Analysis of 29 Batches of Mulberry Leaves Samples
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Plant Materials
3.3. Preparation of Sample Solutions
3.4. UPLC-QTOF/MS Conditions for Identification Analyses
3.5. Preparation of Standard Solutions
3.6. Chromatographic Conditions and Instrument for Quantitative Analyses of DNJ
3.7. Validation of the Method
3.8. Cluster Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanabe, K.; Nakamura, S.; Omagari, K.; Oku, T. Repeated ingestion of the leaf extract from Morus alba reduces insulin resistance in KK-Ay mice. Nutr. Res. 2011, 31, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ji, D.; Zhong, S.; Lv, Z.; Lin, T.; Chen, S.; Hu, G. Hybrid of 1-deoxynojirimycin and polysaccharide from mulberry leaves treat diabetes mellitus by activating PDX-1/insulin-1 signaling pathway and regulating the expression of glucokinase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and glucose-6-phosphatase in alloxan-induced diabetic mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, C.; Lu, G.; Mu, Z.; Cui, W.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y. Anti-diabetic effect of mulberry leaf polysaccharide by inhibiting pancreatic islet cell apoptosis and ameliorating insulin secretory capacity in diabetic rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpato, G.T.; Calderon, I.M.P.; Sinzato, S.; Campos, K.E.; Rudge, M.V.C.; Damasceno, D.C. Effect of Morus nigra aqueous extract treatment on the maternal-fetal outcome, oxidative stress status and lipid profile of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, W. A polysaccharide extract of mulberry leaf ameliorates hepatic glucose metabolism and insulin signaling in rats with type 2 diabetes induced by high fat-diet and streptozotocin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.L.; Yang, L.; Zheng, H.Y. Hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects of mulberry (Morus alba L.) fruit in hyperlipidaemia rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2374–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Beshbishy, H.A.; Singab, A.N.; Sinkkonen, J.; Pihlaja, K. Hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects of Morus alba L. (Egyptian mulberry) root bark fractions supplementation in cholesterol-fed rats. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2724–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojima, H.; Kimura, I.; Chen, F.J.; Sugihara, Y.; Haruno, M.; Kato, A.; Asano, N. Antihyperglycemic effects of N-containing sugars from Xanthocercis zambesiaca, Morus bombycis, Aglaonema treubii, and Castanospermum australe in streptozotocin-diabetic mice. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naowaboot, J.; Pannangpetch, P.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Kongyingyoes, B.; Kukongviriyapan, U. Antihyperglycemic, antioxidant and antiglycation activities of mulberry leaf extract in streptozotocin-induced chronic diabetic rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2009, 64, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Flaczyk, E.; Jeszka, J.; Krejpcio, Z.; Król, E.; Buchowski, M.S. Mulberry leaf extract intake reduces hyperglycaemia in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats fed high-fat diet. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 8, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andallu, B.; Varadacharyulu, N. Antioxidant role of mulberry (Morus indica L. cv. Anantha) leaves in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 338, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, S.Z.; Kwon, T.O.; Jeong, S.I.; Jang, S.I. Antioxidant effect of astragalin isolated from the leaves of Morus alba L. against free radical-induced oxidative hemolysis of human red blood cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arfan, M.; Khan, R.; Rybarczyk, A.; Amarowicz, R. Antioxidant activity of mulberry fruit extracts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 2472–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Jhou, K.; Tseng, C. Antihypertensive effect of mulberry leaf aqueous extract containing γ-aminobutyric acid in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1796–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, J. Anti-inflammatory activity of mulberry leaf extract through inhibition of NF-κB. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, R. Anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic 2-arylbenzofurans from Morus wittiorum. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.C.; Yang, M.Y.; Lin, M.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Chang, W.C.; Wang, C.J. Mulberry leaf extract inhibits the development of atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits and in cultured aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Lai, D.; Lee, Y.; Chen, N.; Tseng, T. Antitumor progression potential of morusin suppressing STAT3 and NF-κB in human hepatoma SK-Hep1 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 232, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, G.; Dua, K.; Kazmi, I.; Anwar, F. Anticonvulsant activity of Morusin isolated from Morus alba: Modulation of GABA receptor. Biomed. Aging Pathol. 2014, 4, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniati, N.F.; Suryani, G.P.; Sigit, J.I. Vasodilator Effect of Ethanolic Extract of Mulberry Leaves (Morus alba L.) in Rat and Rabbit. Procedia Chem. 2014, 13, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabti, I.; Elfalleh, W.; Hannachi, H.; Ferchichi, A.; Campos, M.D.G.A. Identification and quantification of phenolic acids and flavonol glycosides in Tunisian Morus species by HPLC-DAD and HPLC-MS. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercisli, S.; Orhan, E. Chemical composition of white (Morus alba), red (Morus rubra) and black (Morus nigra) mulberry fruits. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Jing, Y.; Wang, G.C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.N.; Ye, W.C. Four new flavonoids from the leaves of Morus mongolica. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Khan, H.; Shah, M.; Khan, R.; Khan, F. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of certain Morus species. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2010, 11, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, N.; Yamashita, T.; Yasuda, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kizu, H.; Kameda, Y.; Kato, A.; Nash, R.J.; Lee, H.S.; Ryu, K.S. Polyhydroxylated alkaloids isolated from mulberry trees (Morus alba L.) and silkworms (Bombyx mori L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4208–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wan, Y.; Xu, J. Ultrasound extraction of polysaccharides from mulberry leaves and their effect on enhancing antioxidant activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Nie, W.J. Chemical properties in fruits of mulberry species from the Xinjiang province of China. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Salcedo, E.M.; Sendra, E.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Martínez, J.J.; Hernández, F. Fatty acids composition of Spanish black (Morus nigra L.) and white (Morus alba L.) mulberries. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.X.; Yang, H.J.; Bo, Y.K.; Ding, S.; Cao, B.H. Nutrient composition, polyphenolic contents, and in situ protein degradation kinetics of leaves from three mulberry species. Livest Sci. 2012, 146, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundogdu, M.; Muradoglu, F.; Sensoy, RIG.; Yilmaz, H. Determination of fruit chemical properties of Morus nigra L., Morus alba L. and Morus rubra L. by HPLC. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 132, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunami, K.; Saito, Y.; Fukuda, E. α-glucosidase inhibitory activity in leaves of some mulberry varieties. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2003, 9, 392–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xiang, W.; Yu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Huang, X.; Xu, L. Comparative analysis of 1-deoxynojirimycin contribution degree to α-glucosidase inhibitory activity and physiological distribution in Morus alba L. Ind. Crop Prod. 2015, 70, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuhisa, Y.; Masatoshi, K.; Satoshi, O. The relationship between 1-deoxynojirimyc in content and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity in leaves of 276 mulberry cultivars (Morus spp.) in Tokyo, Japan. J. Nat. Med. 2008, 62, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hansawasdi, C.; Kawabata, J. α-Glucosidase inhibitory effect of mulberry (Morus alba) leaves on Caco-2. Fitoterapia 2006, 77, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.L.; Bai, Y.L.; Shu, S.L.; Qian, D.W.; Ou-yang, Z.; Liu, L.; Duan, J.A. Simultaneous quantitation of nucleosides, nucleobases, amino acids, and alkaloids in mulberry leaf by ultra high performance liquid chromatography with triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuengchamnong, N.; Ingkaninan, K.; Kaewruang, W.; Wongareonwanakij, S.; Hongthongdaeng, B. Quantitative determination of 1-deoxynojirimycin in mulberry leaves using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2007, 44, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, D.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Liu, C.C.; Wu, G.H. Rapid determination of 1-deoxynojirimycin in Morus alba L. leaves by direct analysis in real time (DART) mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 114, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Wu, F.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J. Determination of 1-deoxynojirimycin in Morus alba L. leaves using reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography fluorescence detection with pre-column derivatization. Chromatography 2008, 26, 634–636. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.U.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, I.; Ahn, M.Y.; Ryu, K.S. Determination of 1-deoxynojirimycin in Morus alba L. leaves by derivatization with 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate followed by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1002, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, S.; Hernández-Hernández, O.; Ruiz-Matute, A.I.; Sanz, M.L. A derivatization procedure for the simultaneous analysis of iminosugars and other low molecular weight carbohydrates by GC-MS in mulberry (Morus sp.). Food Chem. 2011, 126, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Saito, Y.; Yamagishi, K.; Suzuki, M.; Yamaki, K.; Shinmoto, H.; Miyazawa, T. Determination of 1-deoxynojirimycin in mulberry leaves using hydrophilic interaction chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, N.; Tomioka, E.; Kizu, H.; Matsui, K. Sugars with nitrogen in the ring isolated from the leaves of Morus bombycis. Carbohydr. Res. 1994, 253, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, N.; Tomioka, E.; Kizu, H.; Matsui, K. N-containing sugars from Morus alba and their glycosidase inhibitory activities. Carbohydr. Res. 1994, 259, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, T.; Li, J.; Su, S.-L.; Zhu, Z.-H.; Guo, S.; Qian, D.-W.; Duan, J.-A. Identification and Determination of the Polyhydroxylated Alkaloids Compounds with α-Glucosidase Inhibitor Activity in Mulberry Leaves of Different Origins. Molecules 2016, 21, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020206
Ji T, Li J, Su S-L, Zhu Z-H, Guo S, Qian D-W, Duan J-A. Identification and Determination of the Polyhydroxylated Alkaloids Compounds with α-Glucosidase Inhibitor Activity in Mulberry Leaves of Different Origins. Molecules. 2016; 21(2):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020206
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Tao, Jun Li, Shu-Lan Su, Zhen-Hua Zhu, Sheng Guo, Da-Wei Qian, and Jin-Ao Duan. 2016. "Identification and Determination of the Polyhydroxylated Alkaloids Compounds with α-Glucosidase Inhibitor Activity in Mulberry Leaves of Different Origins" Molecules 21, no. 2: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020206
APA StyleJi, T., Li, J., Su, S.-L., Zhu, Z.-H., Guo, S., Qian, D.-W., & Duan, J.-A. (2016). Identification and Determination of the Polyhydroxylated Alkaloids Compounds with α-Glucosidase Inhibitor Activity in Mulberry Leaves of Different Origins. Molecules, 21(2), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020206