Design, Synthesis and Anticancer Evaluation of Novel Quinazoline-Sulfonamide Hybrids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
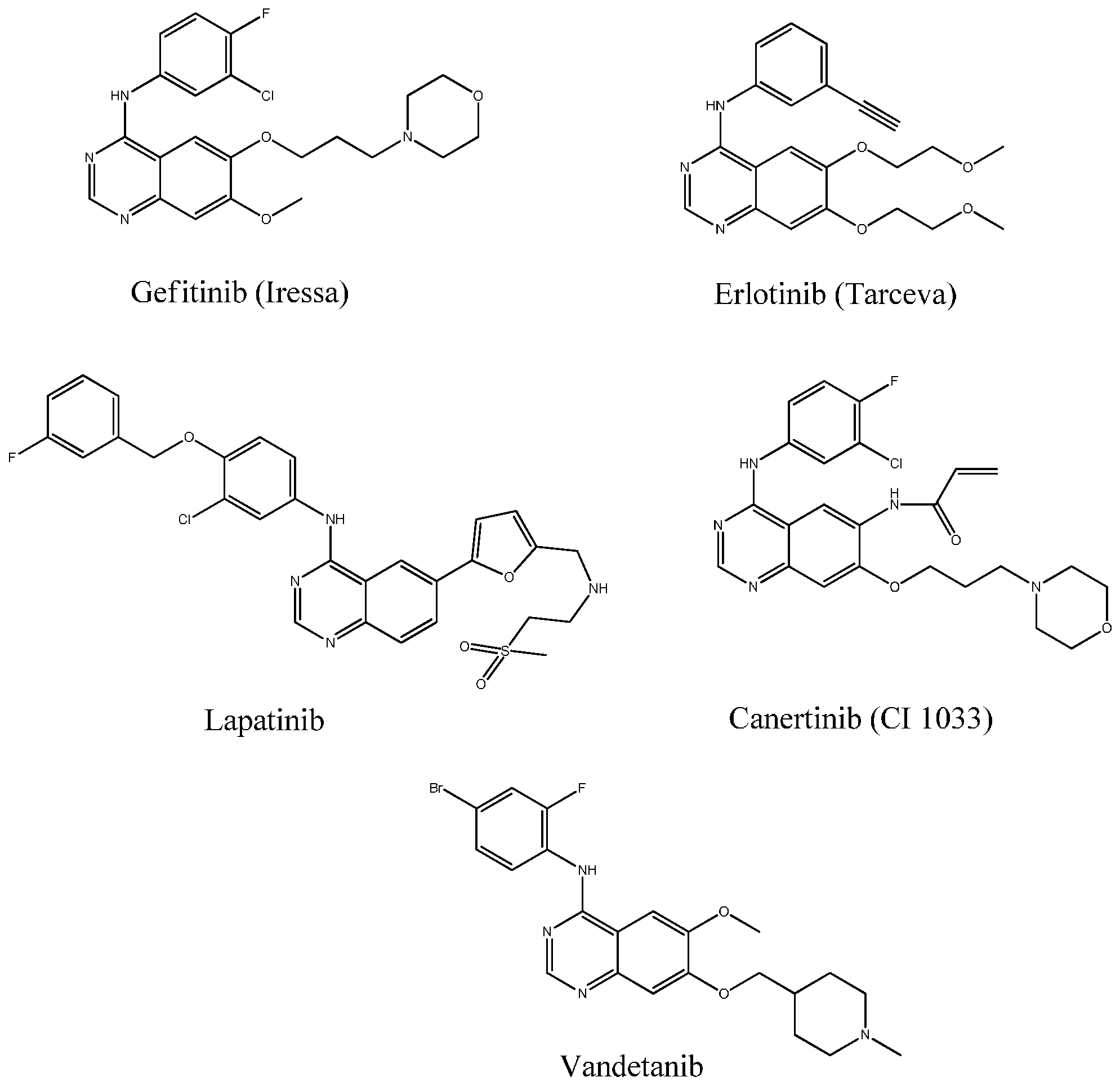
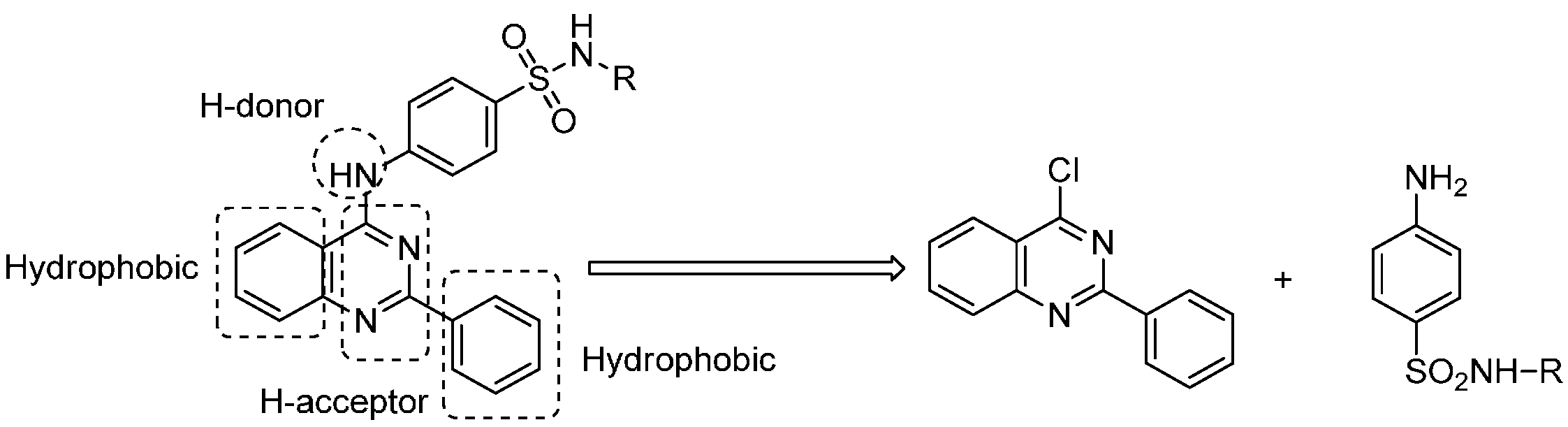
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
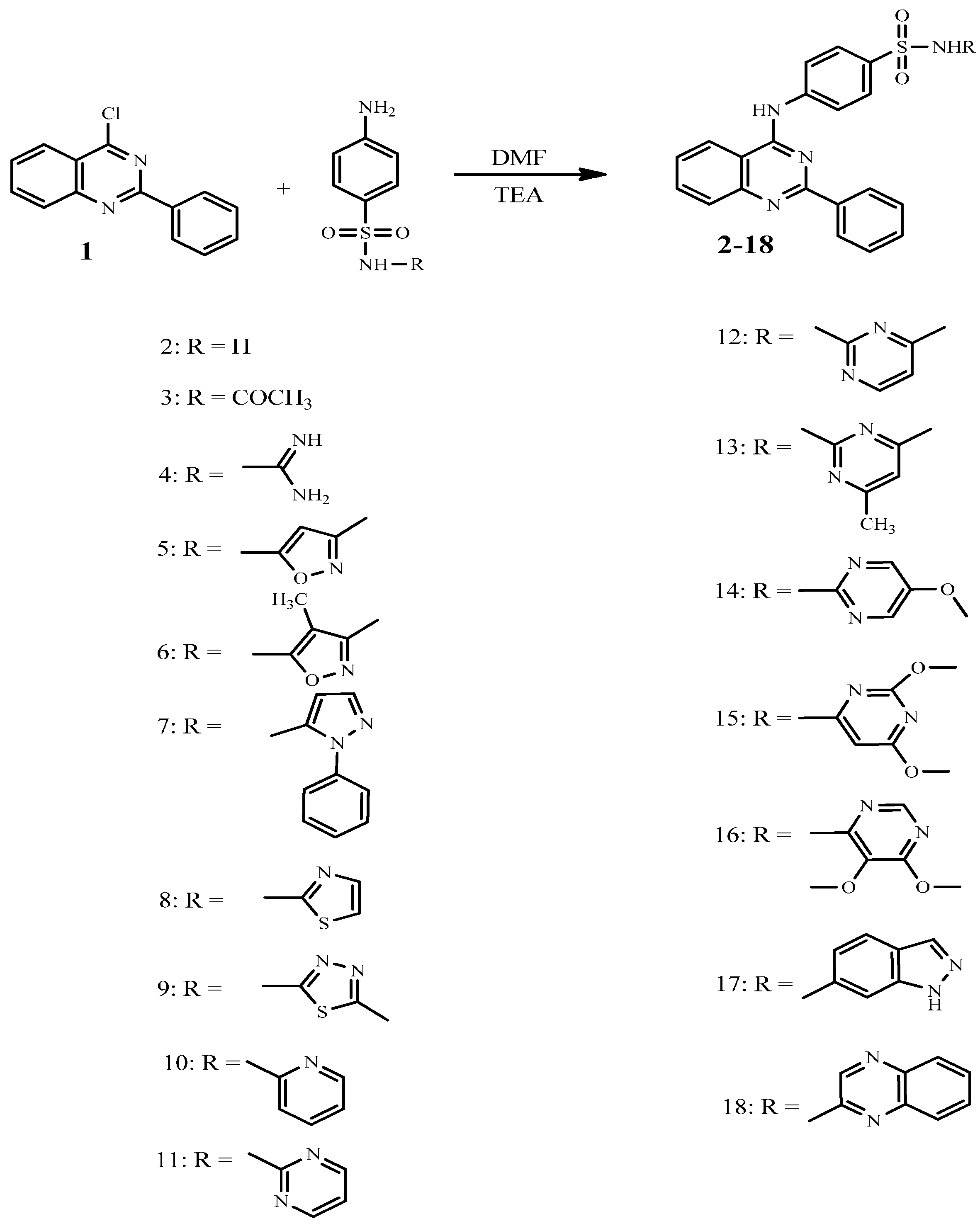
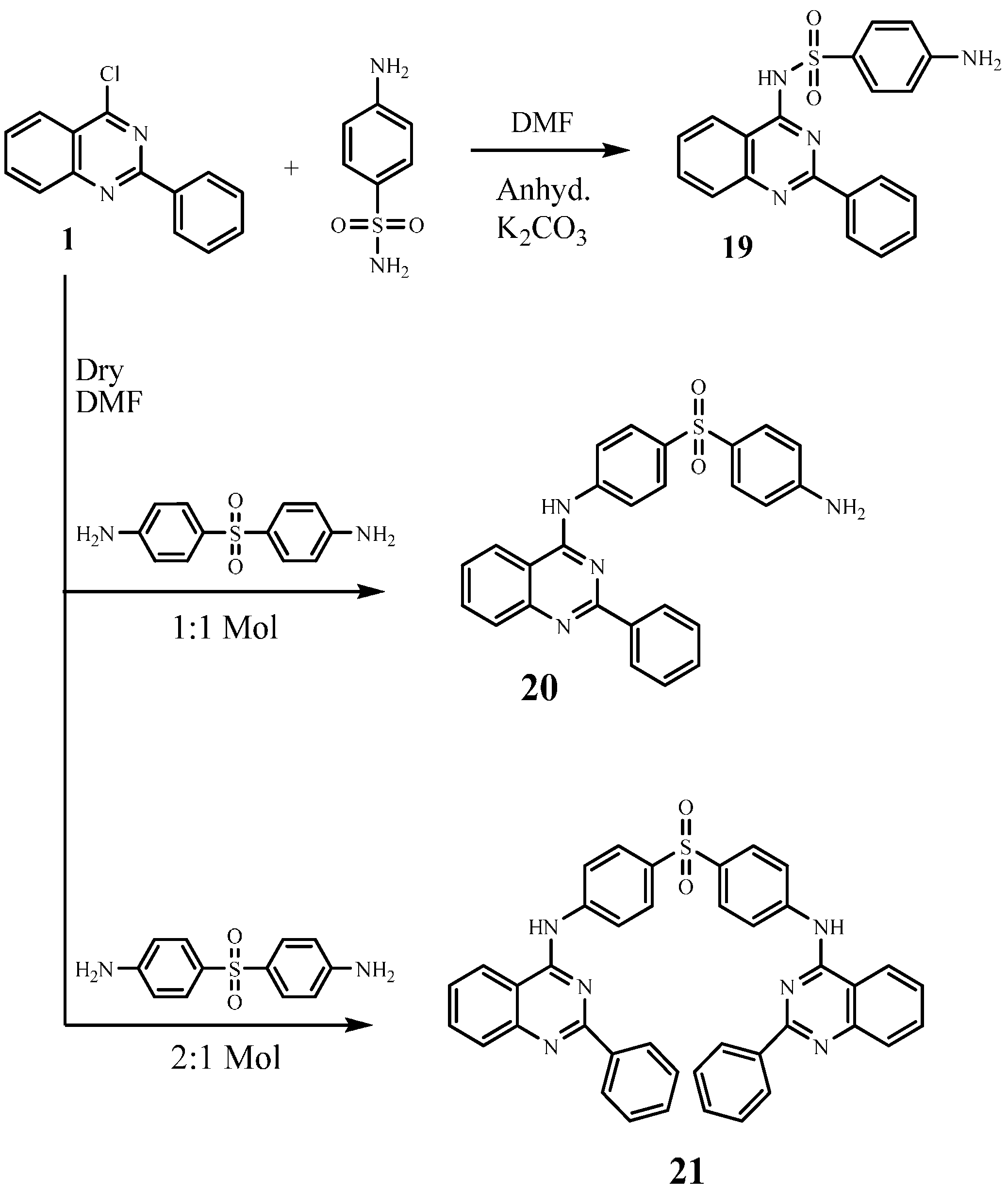
2.2. In-Vitro Anticancer Evaluation
| Cpd. No. | A549 (Lung Cancer Cells) | HeLa (Cervical) | LoVo (Colorectal Cancer Cells) | MDA-MB-231 (Breast Cancer Cells) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 134.9 ± 0.40 | NA | 94.9 ± 0.78 | 58.2 ± 1.76 |
| 3 | 113.5 ± 1.10 | 221.1 ± 1.22 | 80.5 ± 0.87 | 51.4 ± 1.32 |
| 4 | 129.4 ± 0.71 | 187.7 ± 1.10 | 61.7 ± 1.31 | 36.4 ± 0.34 |
| 5 | NA | NA | 212.8 ± 0.78 | NA |
| 6 | NA | NA | 217.0 ± 1.11 | NA |
| 7 | 77.8 ± 0.54 | 91.5 ± 0.41 | 96.5 ± 0.34 | 77.9 ± 0.36 |
| 8 | 130.4 ± 0.67 | 284.6 ± 1.03 | 160.1 ± 0.90 | 97.4 ± 1.40 |
| 9 | NA | NA | 182.5 ± 0.33 | NA |
| 10 | NA | NA | 125.4 ± 0.88 | 154.1 ± 1.12 |
| 11 | NA | NA | 54.2 ± 0.92 | NA |
| 12 | NA | NA | 58.6 ±0.50 | NA |
| 13 | NA | NA | 112.9 ± 0.35 | NA |
| 14 | NA | NA | 101.7 ± 0.67 | 93.9 ± 0.45 |
| 15 | NA | NA | 61.5 ± 0.01 | NA |
| 16 | NA | NA | 65.5 ± 1.65 | NA |
| 17 | 161.6 ± 0.78 | 87.6 ± 1.00 | 97.3 ± 0.23 | 42.8 ± 1.09 |
| 18 | NA | 276.0 ± 1.01 | 132.0 ± 1.04 | NA |
| 19 | NA | NA | 146.4 ± 1.34 | NA |
| 20 | NA | 251.6 ± 0.98 | 72.5 ± 0.26 | NA |
| 21 | NA | 189.8 ± 1.12 | 73.1 ± 1.54 | NA |
| Doxorubicin | 283.5 ± 0.01 | 120.7 ± 0.09 | 374.4 ± 1.00 | 26.5 ± 0.54 |
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Sulfonamide Derivatives 2–18
3.3. In-Vitro Anticancer Evaluation
3.3.1. Cell Culture
3.3.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Medina, J.C.; Roche, D.; Shan, B.; Learned, R.M.; Frankmoelle, W.P.; Clark, D.L.; Rosen, T.; Jaen, J.C. Novel halogenated sulfonamides inhibit the growth of multidrug resistant MCF-7/ADR cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 1843–1846. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.S.; Moon, E.Y.; Seong, S.K.; Choi, C.H.; Chung, C.H.; Jung, S.H.; Yoon, S.J. Characterization of the anticancer activity of DW2282, a new anticancer agent. Anticancer Res. 1999, 19, 5087–5093. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choo, H.Y.P.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.W.; Chung, S.W. Solid-phase combinatorial synthesis and cytotoxicity of 3-aryl-2,4-quinazolindiones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 517–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Antonello, A.; Tarozzi, A.; Morroni, F.; Cavalli, A.; Rosini, M.; Hrelia, P.; Bolognesi, M.L.; Melchiorre, C. Multitarget-directed drug design strategy: A novel molecule designed to block epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and to exert proapoptotic effects. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6642–6645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rachid, Z.; Brahimi, F.; Qiu, Q.; Williams, C.; Hartley, J.M.; Hartley, J.A.; Jean-Claude, B.J. Novel nitrogen mustard-armed combi-molecules for the selective targeting of epidermal growth factor receptor overexperessing solid tumors: Discovery of an unusual structure activity relationship. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 2605–2608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baselga, J.; Swain, S.M. Novel anticancer targets: Revisiting ERBB2 and discovering ERBB3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.H.J.; Lain, S.; Verma, C.H.S.; Fersht, A.R.; Lane, D.P. Awakening guardian angels: Drugging the p53 pathway. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lu, X.; Xing, M.; Yang, X.H.; Zhao, T.T.; Gong, H.B.; Zhu, H.L. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular docking studies of N,1,3-triphenyl-1H-pyrazole-4 carboxamide derivatives as anticancer agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3589–3593. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kidwai, M.; Venkataramanan, R.; Mohan, R.; Sapra, P. Chemotherapy and heterocyclic compounds. Curr. Med. Chem. 2002, 9, 1209–1228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salimon, J.; Salih, N.; Yousif, E.; Hameed, A.; Ibraheem, H. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of some new 1,3,4-oxadiazole and 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2010, 4, 2016–2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, H.A.; Lake, B.R.; Laing, T.; Phillips, R.M.; Willans, C.E. Synthesis and anticancer activity of silver(I)-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes derived from the natural xanthine products caffeine, theophylline and theobromine. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 7563–7569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Agarwal, S.K.; Mukherjee, R.; Burman, A.C. Synthesis of quinazolines as tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 246–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-López, O.; Conejo-García, A.; Núñez, M.C.; Kimatrai, M.; García-Rubiño, M.E.; Morales, F.; Gómez-Pérez, V.; Campos, J.M. Novel substituted quinazolines for potent EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 943–963. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, A.; Goossens, L.; Six, P.; Lemoine, A.; Ravez, S.; Farce, A.; Depreux, P. Impact of aryloxy-linked quinazolines: A novel series of selective VEGFR-2 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lüth, B.; Löwe, W. Syntheses of 4-(indole-3-yl)quinazolines: A new class of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Seo, S.H.; Yang, B.S.; Lee, J.Y. Synthesis and biological evaluation of bis(methoxy methyl)-7,8-dihydro-[1,4]dioxino[2,3-g]quinazolines as EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. 2005, 338, 502–505. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.; Cui, M.; Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, W.; Guo, H.; Zha, S. Galectin-3 knockdown increases gefitinib sensitivity to the inhibition of EGFR endocytosis in gefitinib insensitive esophageal squamous cancer cells. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 570–76. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, M.P.; Tan, E.; Saeui, C.T.; Bovonratwet, P.; Liu, L.; Bhattacharya, R.; Yarema, K.J. Metabolic glycoengineering sensitizes drug-resistant pancreatic cancer cells to tyrosine kinase inhibitors erlotinib and gefitinib. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellizzi, A.; Greco, M.R.; Rubino, R.; Paradiso, A.; Forciniti, S.; Zeeberg, K.; Cardone, R.A.; Reshkin, S.J. The scaffolding protein NHERF1 sensitizes EGFR-dependent tumor growth, motility and invadopodia function to gefitinib treatment in breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jackman, D.M.; Cioffredi, L.A.; Sharmeen, L.; Morse, L.K.; Lucca, J.; Plotkin, S.R.; Marcoux, P.J.; Rabin, M.S.; Lynch, T.J.; Johnson, B.E.; et al. A Phase I trial of high dose gefitinib for patients with leptomeningeal metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4527–4536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakao, M.; Muramatsu, H.; Sone, K.; Aoki, S.; Akiko, H.; Kagawa, Y.; Sato, H.; Kunieda, T. Epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors for non-small-cell lung cancer patients aged 80 years or older: A retrospective analysis. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, T.; Sasaki, S.; Sakamoto, A.; Kobayashi, T. Efficacy of erlotinib plus concurrent whole-brain radiation therapy for patients with brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2013, 2, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nolting, M.; Schneider-Merck, T.; Trepel, M. Lapatinib. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014, 201, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brassard, M.; Rondeau, G. Role of vandetanib in the management of medullary thyroid cancer. Biologics 2012, 6, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levitzki, A. Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, S11–S18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harakeh, S.; Assef, M.D.; El-Sabban, M.; Haddadin, M.; Muhatasib, H.G. Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis bt 2-benzoyl-3-phenyl-6,7-dichloroquinoxaline 1,4-dioxide in adults T-cell leukemia cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2004, 148, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levitzki, A. Protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors as noveltherapeutic agents. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 82, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Fairlie, D.P. A new paradigm for protein kinase inhibition: Blocking phosphorylation without directly targeting ATP binding. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drews, J. Drug discovery: A historical perspective. Science 2000, 287, 1960–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T.; Casini, A.; Mastrolorenzo, A.; Scozzafava, A. COX-2 selective inhibitors, carbonic anhydrase inhibition and anticancer properties of sulfonamides belonging to this class of pharmacological agents. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abbate, F.; Casini, A.; Owa, T.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: E7070, a sulfonamide anticancer agent, potently inhibits cytosolic isozymes I and II, and transmembrane, tumor-associated isozyme IX. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solomon, V.R.; Hu, C.; Lee, H. Hybrid pharmacophore design and synthesis of isatin-benzothiazole analogs for their anti-breast cancer activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 7585–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorab, M.M.; Ragab, F.A.; Heiba, H.I.; El-Gazzar, M.G.; Zahran, S.S. Synthesis, anticancer and radiosensitizing evaluation of some novel sulfonamide derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorab, M.M.; Alsaid, M.S.; Ceruso, M.; Nissan, Y.M.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Synthesis, molecular docking, cytotoxic and inhibition of the human carbonic anhydrase isoforms I, II, IX, XII with novel benzenesulfonamides incorporating pyrrole, pyrrolopyrimidine and fused pyrrolopyrimidine moieties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 3684–3695. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorab, M.M.; Ceruso, M.; Alsaid, M.S.; Nissan, Y.M.; Arafa, R.K.; Supuran, C.T. Novel sulfonamides bearing pyrrole and pyrrolopyrimidine moieties as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Synthesis, cytotoxic activity and molecular modeling. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 87, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghorab, M.M.; El-Gazzar, M.G.; Alsaid, M.S. Synthesis and Anti-Breast Cancer Evaluation of Novel N-(Guanidinyl)-benzenesulfonamides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5582–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorab, M.M.; El-Gazzar, M.G.; Alsaid, M.S. Synthesis, Characterization and Anti-Breast Cancer Activity of New 4-Aminoantipyrine-Based Heterocycles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 7539–7553. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Dosari, M.S.; Ghorab, M.M.; Alsaid, M.S.; Nissan, Y.M.; Ahmed, A.B. Synthesis and anticancer activity of some novel trifluoromethylquinolines carrying a biologically active benzenesulfonamide moiety. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 69, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorab, M.M.; Ragab, F.A.; Heiba, H.I.; El-Hazek, R.M. Anticancer and radio-sensitizing evaluation of some new thiazolopyrane and thiazolopyranopyrimidine derivatives bearing a sulfonamide moiety. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 5120–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Said, M.S.; Ghorab, M.M.; Al-Dosari, M.S.; Hamed, M.M. Synthesis and in vitro anticancer evaluation of some novel hexahydroquinoline derivatives having a benzenesulfonamide moiety. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghorab, M.M.; Ragab, F.A.; Heiba, H.I.; Youssef, H.A.; El-Gazzar, M.G. Synthesis of novel pyrrole and pyrrolo [2,3-d] pyrimidine derivatives bearing sulfonamide moiety for evaluation as anticancer and radiosensitizing agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6316–6320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Said, M.S.; Ghorab, M.M.; Al-Qasoumi, S.I.; El-Hossary, E.M.; Noaman, E. Synthesis and in vitro anticancer screening of some novel 4-[2-amino-3-cyano-4-substituted-5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-1-(4H)-yl]benzenesulfonamides. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 45, 3011–3018. [Google Scholar]
- Alqasoumi, S.I.; Al-Taweel, A.M.; Alafeefy, A.M.; Ghorab, M.M.; Noaman, E. Discovering some novel tetrahydroquinoline derivatives bearing the biologically active sulfonamide moiety as a new class of antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1849–1853. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alqasoumi, S.I.; Al-Taweel, A.M.; Alafeefy, A.M.; Noaman, E.; Ghorab, M.M. Novel quinolines and pyrimido[4,5-b]quinolines bearing biologically active sulfonamide moiety as a new class of antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghorab, M.M.; Ragab, F.A.; Hamed, M.M. Design, synthesis and anticancer evaluation of novel tetrahydroquinoline derivatives containing sulfonamide moiety. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 4211–4217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paul, K.; Sharma, A.; Luxami, V. Synthesis and in vitro antitumor evaluation of primary amine substituted quinazoline linked benzimidazole. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghorab, M.M.; Alsaid, M.S.; Al-Dosari, M.S.; El-Gazzar, M.G.; Parvez, M.K. Design, Synthesis and Anticancer Evaluation of Novel Quinazoline-Sulfonamide Hybrids. Molecules 2016, 21, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020189
Ghorab MM, Alsaid MS, Al-Dosari MS, El-Gazzar MG, Parvez MK. Design, Synthesis and Anticancer Evaluation of Novel Quinazoline-Sulfonamide Hybrids. Molecules. 2016; 21(2):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020189
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhorab, Mostafa M., Mansour S. Alsaid, Mohammed S. Al-Dosari, Marwa G. El-Gazzar, and Mohammad K. Parvez. 2016. "Design, Synthesis and Anticancer Evaluation of Novel Quinazoline-Sulfonamide Hybrids" Molecules 21, no. 2: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020189
APA StyleGhorab, M. M., Alsaid, M. S., Al-Dosari, M. S., El-Gazzar, M. G., & Parvez, M. K. (2016). Design, Synthesis and Anticancer Evaluation of Novel Quinazoline-Sulfonamide Hybrids. Molecules, 21(2), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020189






