Ambiphilic Frustrated Lewis Pair Exhibiting High Robustness and Reversible Water Activation: Towards the Metal-Free Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
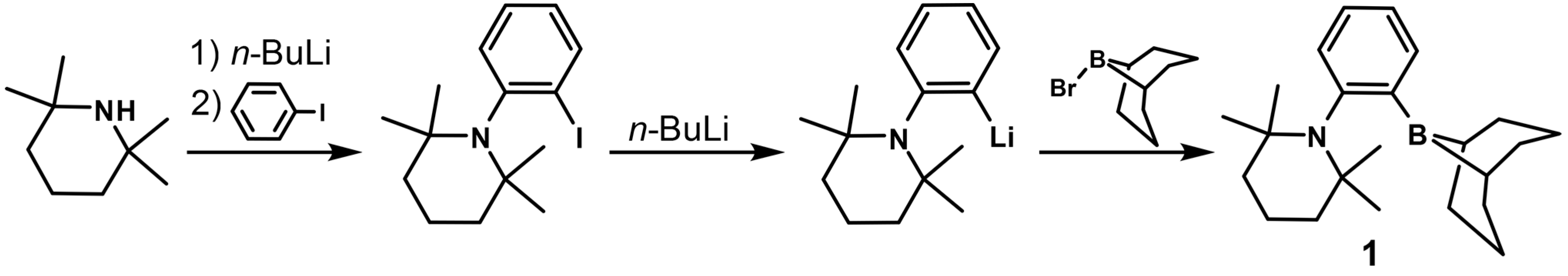
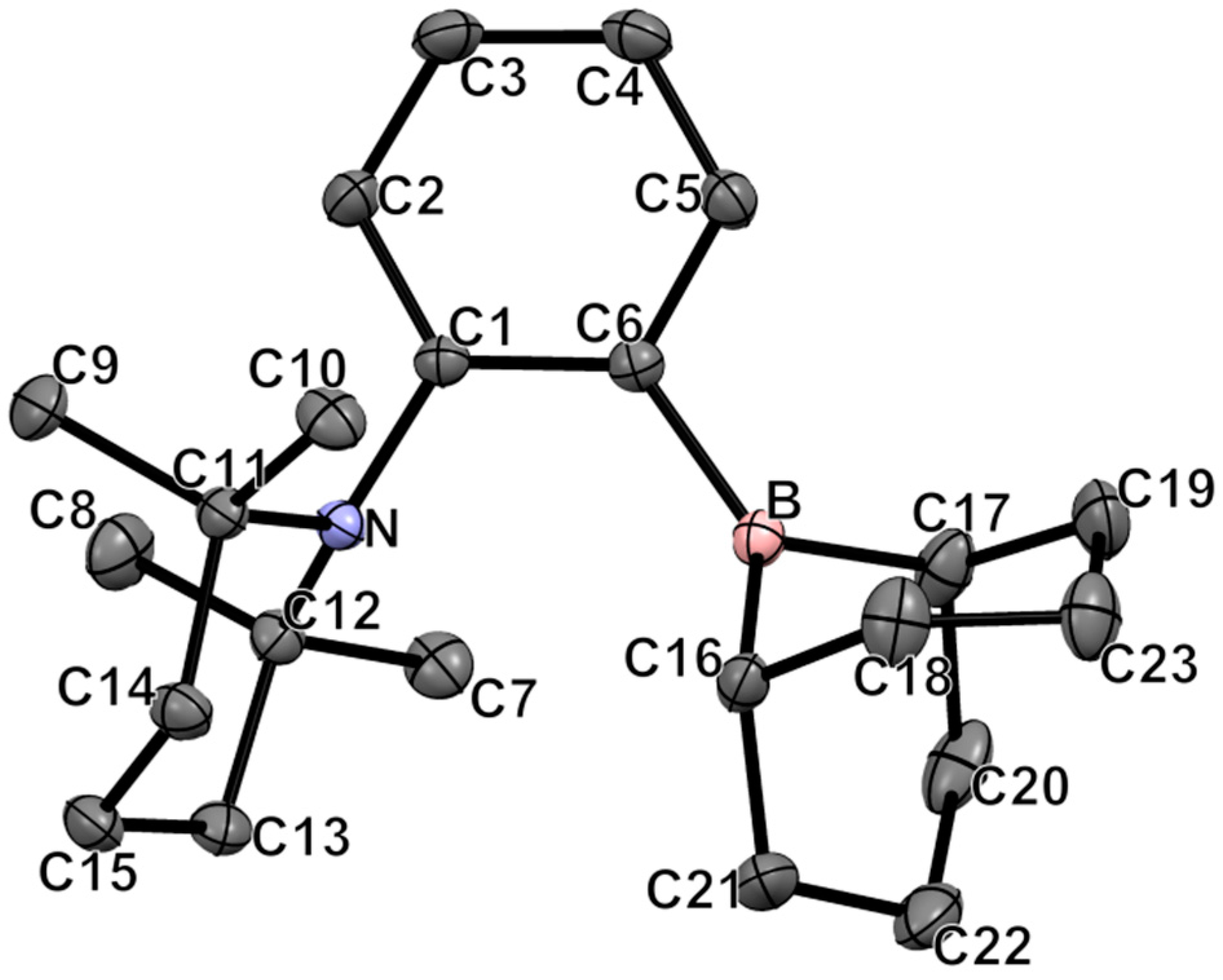
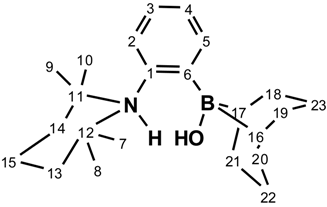
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of 1-(BBN)-2-(TMP)-C6H4
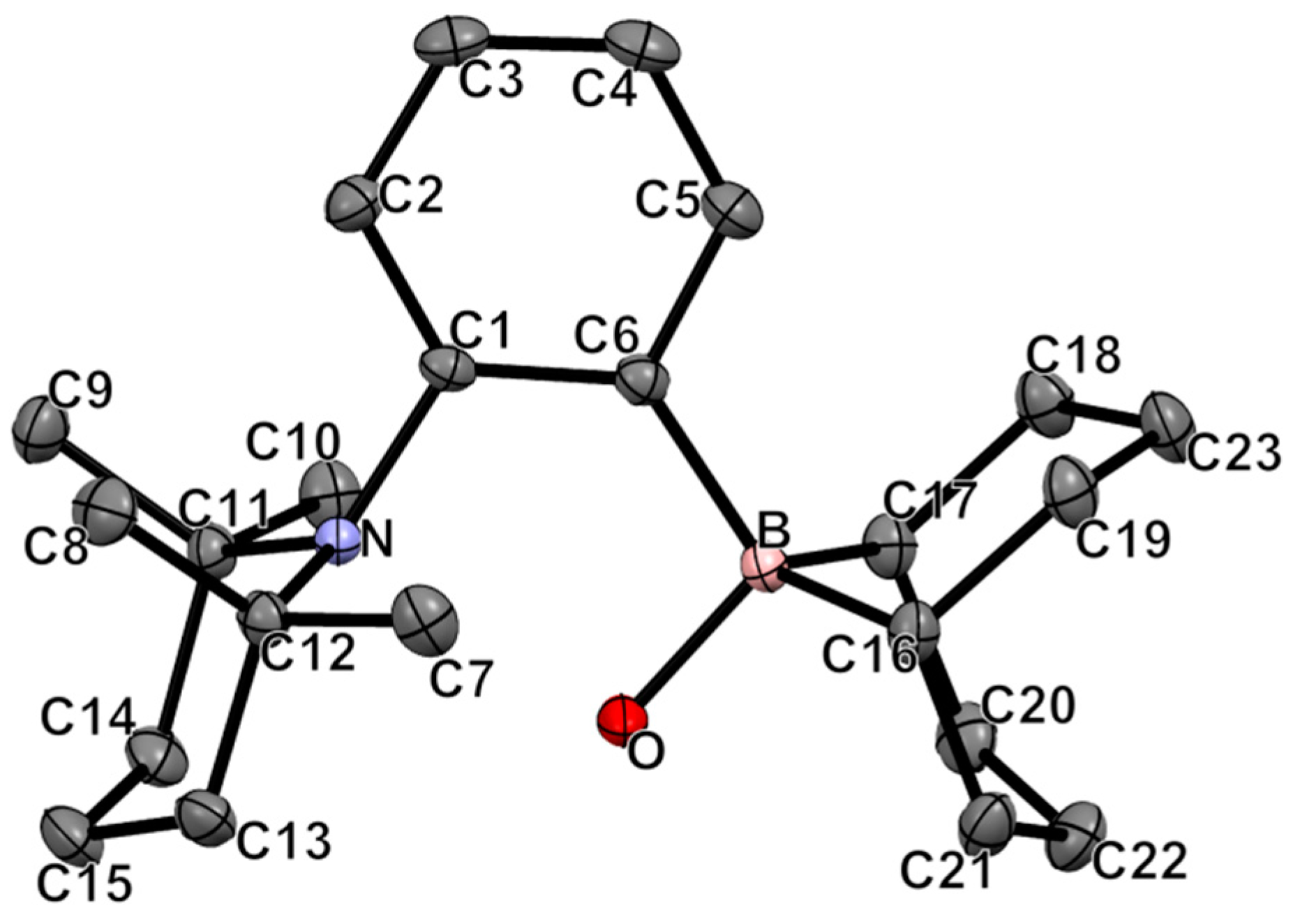
2.2. Reactivity of 1-(BBN)-2-(TMP)-C6H4 with Small Molecules
2.3. DFT Study of the Generated Adducts
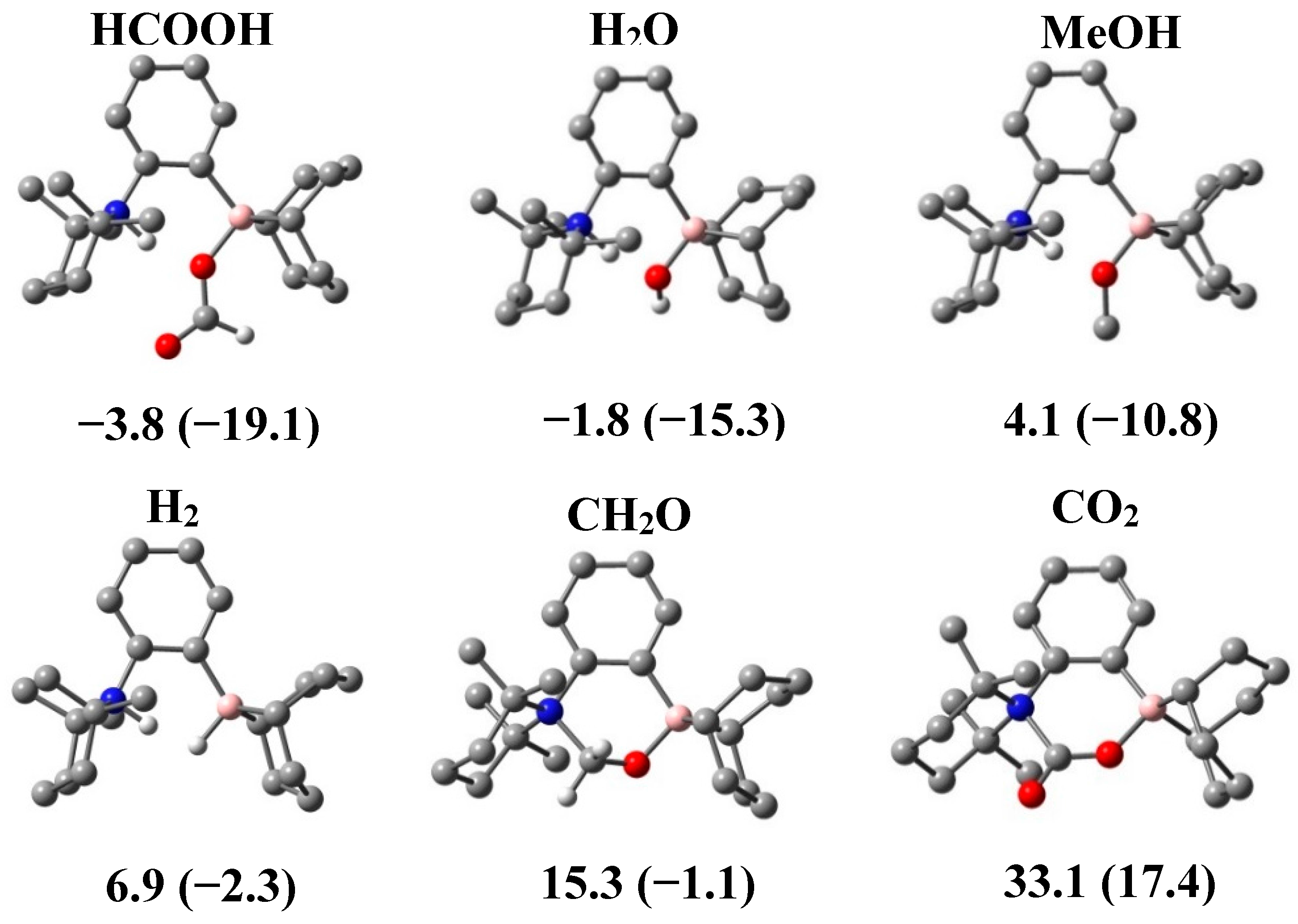
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Information
3.2. Synthesis


4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Welch, G.; Juan, R.S.; Masuda, J.; Stephan, D. Reversible, metal-free hydrogen activation. Science 2006, 314, 1124–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, P.A.; Welch, G.C.; Jurca, T.; Stephan, D.W. Metal-free catalytic hydrogenation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8050–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, P.; Schwendemann, S.; Lange, S.; Kehr, G.; Fröhlich, R.; Erker, G. metal-free catalytic hydrogenation of enamines, imines, and conjugated phosphinoalkenylboranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 7543–7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokob, T.A.; Hamza, A.; Papai, I. rationalizing the reactivity of frustrated Lewis pairs: thermodynamics of H2 activation and the role of acid-base properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10701–10710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, D.W.; Greenberg, S.; Graham, T.W.; Chase, P.; Hastie, J.J.; Geier, S.J.; Farrell, J.M.; Brown, C.C.; Heiden, Z.M.; Welch, G.C.; et al. Metal-free catalytic hydrogenation of polar substrates by frustrated lewis pairs. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 12338–12348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernichenko, K.; Madarász, A.; Pápai, I.; Nieger, M.; Leskelä, M.; Repo, T. A Frustrated-Lewis-pair approach to catalytic reduction of alkynes to cis-alkenes. Nature Chem. 2013, 5, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdi, T.; Stephan, D.W. Enabling catalytic ketone hydrogenation by frustrated lewis pairs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15809–15812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.J.; Fuchter, M.J.; Ashley, A.E. Nonmetal catalyzed hydrogenation of carbonyl compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15813–15816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindqvist, M.; Borre, K.; Axenov, K.; Kótai, B.; Nieger, M.; Leskela, M.; Pápai, I.; Repo, T. Chiral molecular tweezers: Synthesis and reactivity in asymmetric hydrogenation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4038–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otten, E.; Neu, R.; Stephan, D.W. Complexation of nitrous oxide by frustrated Lewis pairs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9918–9919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, R.C.; Otten, E.; Lough, A.; Stephan, D.W. The synthesis and exchange chemistry of frustrated lewis pair—Nitrous oxide complexes. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Klose, A.; Birkmann, B.; Liang, L.; Schirmer, B.; Wiegand, T.; Eckert, H.; Lough, A.J.; Fröhlich, R.; Daniliuc, C.G.; et al. Reactions of Phosphorus/boron Frustrated Lewis Pairs with SO2. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mömming, C.M.; Otten, E.; Kehr, G.; Fröhlich, R.; Grimme, S.; Stephan, D.W.; Erker, G. Reversible metal—Free carbon dioxide binding by frustrated Lewis pairs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6643–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelt, C.; Westenberg, H.; Bertini, F.; Ehlers, A.W.; Slootweg, J.C.; Lammertsma, K.; Uhl, W. Geminal phosphorus/Aluminum-based frustrated Lewis pairs: C-H versus C≡C activation and CO2 fixation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3925–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, J.; Courtemanche, M.A.; Fontaine, F.G. Reactivity of Lewis pairs (R2PCH2AlMe2)2 with carbon dioxide. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11131–11133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theuergarten, E.; Schlösser, J.; Schlüns, D.; Freytag, M.; Daniliuc, C.G.; Jones, P.G.; Tamm, M. Fixation of carbon dioxide and related small molecules by a bifunctional frustrated pyrazolylborane Lewis pair. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 9101–9110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, J.; Courtemanche, M.A.; Marx, V.M.; Burnell, D.J.; Fontaine, F.G. Ambiphilic molecules for trapping reactive intermediates: Interrupted Nazarov reaction of allenyl vinyl ketones with Me2PCH2AlMe2. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 11250–11252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moebs-Sanchez, S.; Bouhadir, G.; Saffon, N.; Maron, L.; Bourissou, D. Tracking reactive intermediates in phosphine-promoted reactions with ambiphilic phosphino-boranes. Chem. Commun. 2008, 44, 3435–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baslé, O.; Porcel, S.; Ladeira, S.; Bouhadir, G.; Bourissou, D. Phosphine-Boronates: Efficient bifunctional organocatalysts for michael addition. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4495–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, D.W.; Erker, G. Frustrated Lewis pairs: Metal-free hydrogen activation and more. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 46–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradies, J. Metal-free hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbons employing molecular hydrogen. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 3552–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontaine, F.G.; Courtemanche, M.A.; Légaré, M.A. Transition-metal-free catalytic reduction of carbon dioxide. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 2990–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, D.W. Frustrated Lewis pairs: From concept to catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyond Oil and Gas: The Methanol Economy; Olah, G.A.; Alain Goeppert, G.K.; Prakash, S. (Eds.) Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006.
- Das Neves Gomes, C.; Blondiaux, E.; Thuéry, P.; Cantat, T. Metal-free reduction of CO2 with hydroboranes: Two efficient pathways at play for the reduction of CO2 to methanol. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 7098–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, K.; Yasuda, S.; Mizuta, T. Reduction of CO2 to trimethoxyboroxine with BH3 in THF. Organometallics 2014, 6692–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.Y.F.; So, C.W.; Saffon-Merceron, N.; Mézailles, N. Formation of a zwitterionic boronium species from the reaction of a stable carbenoid with borane: CO2 reduction. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2107–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Légaré, M.A.; Courtemanche, M.A.; Fontaine, F.G. Lewis Base activation of borane-dimethysulfide into strongly reducing ion pairs for the transformation of carbon dioxide to methoxyboranes. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 11362–11365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Stephan, D.W. Phosphine catalyzed reduction of CO2 with boranes. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 7007–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riduan, S.N.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, J.Y. Conversion of carbon dioxide into methanol with silanes over N-heterocyclic carbene catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3322–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtemanche, M.A.; Légaré, M.A.; Rochette, É.; Fontaine, F.G. Phosphazenes: Efficient organocatalysts for the catalytic hydrosilylation of carbon dioxide. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6858–6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkefeld, A.; Piers, W.E.; Parvez, M. Tandem frustrated Lewis pair/tris (pentafluorophenyl) borane—Catalyzed deoxygenative hydrosilylation of carbon dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10660–10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ménard, G.; Stephan, D.W. Room temperature reduction of CO2 to methanol by al-based frustrated Lewis pairs and ammonia borane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1796–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ménard, G.; Gilbert, T.M.; Hatnean, J.A.; Kraft, A.; Krossing, I.; Stephan, D.W. Stoichiometric Reduction of CO2 to CO by Phosphine/AlX3-Based Frustrated Lewis Pairs. Organometallics 2013, 32, 4416–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtemanche, M.A.; Légaré, M.A.; Maron, L.; Fontaine, F.G. A highly active phosphine-borane organocatalyst for the reduction of CO2 to methanol using hydroboranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9326–9329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtemanche, M.A.; Légaré, M.A.; Maron, L.; Fontaine, F.G. Reducing CO2 to methanol using frustrated Lewis pairs: On the mechanism of phosphine-borane-mediated hydroboration of CO2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10708–10717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Declercq, R.; Bouhadir, G.; Bourissou, D.; Légaré, M.A.; Courtemanche, M.A.; Nahi, K.S.; Bouchard, N.; Fontaine, F.G.; Maron, L. Hydroboration of carbon dioxide using ambiphilic phosphine-borane catalysts: On the role of the formaldehyde adduct. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2513–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtemanche, M.A.; Larouche, J.; Légaré, M.A.; Bi, W.; Maron, L.; Fontaine, F.G. A Tris (triphenylphosphine) aluminum ambiphilic precatalyst for the reduction of carbon dioxide with catecholborane. Organometallics 2013, 32, 6804–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Stephan, D.W. Carbene-9-BBN ring expansions as a route to intramolecular frustrated Lewis Pairs for CO2 reduction. Chem. Eur J. 2014, 20, 3036–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, J.A.B.; Riddlestone, I.M.; Tirfoin, R.; Aldridge, S. Cooperative bond activation and catalytic reduction of carbon dioxide at a group 13 metal center. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Ma, R.; He, L.N.; Diao, Z.F. Homogeneous hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to methanol. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 1498–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, A.E.; Thompson, A.L.; O’Hare, D. Non-metal-mediated homogeneous hydrogenation of CO2 to CH3OH. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9839–9843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtemanche, M.A.; Pulis, A.P.; Rochette, É.; Légaré, M.A.; Stephan, D.W.; Fontaine, F.G. Intramolecular B/N frustrated Lewis pairs and the hydrogenation of carbon dioxide. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9797–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesler, R.; Piers, W.E.; Parvez, M. Synthesis, structural characterization and reactivity of the amino borane 1-(NPH2)-2-[B(C6F5)2]C6H4. J. Organomet. Chem. 2003, 680, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumerin, V.; Chernichenko, K.; Schulz, F.; Leskelä, M.; Rieger, B.; Repo, T. Amine-borane mediated metal—Free hydrogen activation and catalytic hydrogenation. In Frustrated Lewis Pairs I, 1st ed.; Erker, G., Stephan, D.W., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 111–156. [Google Scholar]
- Chemichenko, K.; Kótai, B.; Pápai, I.; Zhivonitko, V.; Nieger, M.; Leskela, M.; Repo, T. Intramolecular frustrated Lewis pair with the smallest boryl site: Reversible H2 Addition and kinetic analysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1749–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwendemann, S.; Fröhlich, R.; Kehr, G.; Erker, G. Intramolecular frustrated N/B Lewis pairs by enamine hydroboration. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1842–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; LeBlanc, R.; Durst, T. Formation of 2-substituted iodobenzenes from iodobenzene via benzyne and ate complex intermediates. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 1973–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernichenko, K.; Nieger, M.; Leskelä, M.; Repo, T. Hydrogen activation by 2-Boryl-N, N-dialkylanilines: A revision of piers’ ansa-aminoborane. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 9029–9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lalancette, R.A.; Jäkle, F. Chiral organoborane Lewis pairs derived from pyridylferrocene. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 9120–9129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rochette, É.; Courtemanche, M.-A.; Pulis, A.P.; Bi, W.; Fontaine, F.-G. Ambiphilic Frustrated Lewis Pair Exhibiting High Robustness and Reversible Water Activation: Towards the Metal-Free Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide. Molecules 2015, 20, 11902-11914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200711902
Rochette É, Courtemanche M-A, Pulis AP, Bi W, Fontaine F-G. Ambiphilic Frustrated Lewis Pair Exhibiting High Robustness and Reversible Water Activation: Towards the Metal-Free Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide. Molecules. 2015; 20(7):11902-11914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200711902
Chicago/Turabian StyleRochette, Étienne, Marc-André Courtemanche, Alexander P. Pulis, Wenhua Bi, and Frédéric-Georges Fontaine. 2015. "Ambiphilic Frustrated Lewis Pair Exhibiting High Robustness and Reversible Water Activation: Towards the Metal-Free Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide" Molecules 20, no. 7: 11902-11914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200711902
APA StyleRochette, É., Courtemanche, M.-A., Pulis, A. P., Bi, W., & Fontaine, F.-G. (2015). Ambiphilic Frustrated Lewis Pair Exhibiting High Robustness and Reversible Water Activation: Towards the Metal-Free Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide. Molecules, 20(7), 11902-11914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200711902




